Behavioral Responses of Galaxias platei to Salmo trutta: Experimental Evidence of Competition and Predation Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Fish Maintenance in the Laboratory
2.2. Microhabitat Preference Experiments
2.3. Competitive and Predator–Prey Interactions Experiments
2.4. Swimming Performance Experiments
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Galaxias platei Microhabitat Preferences
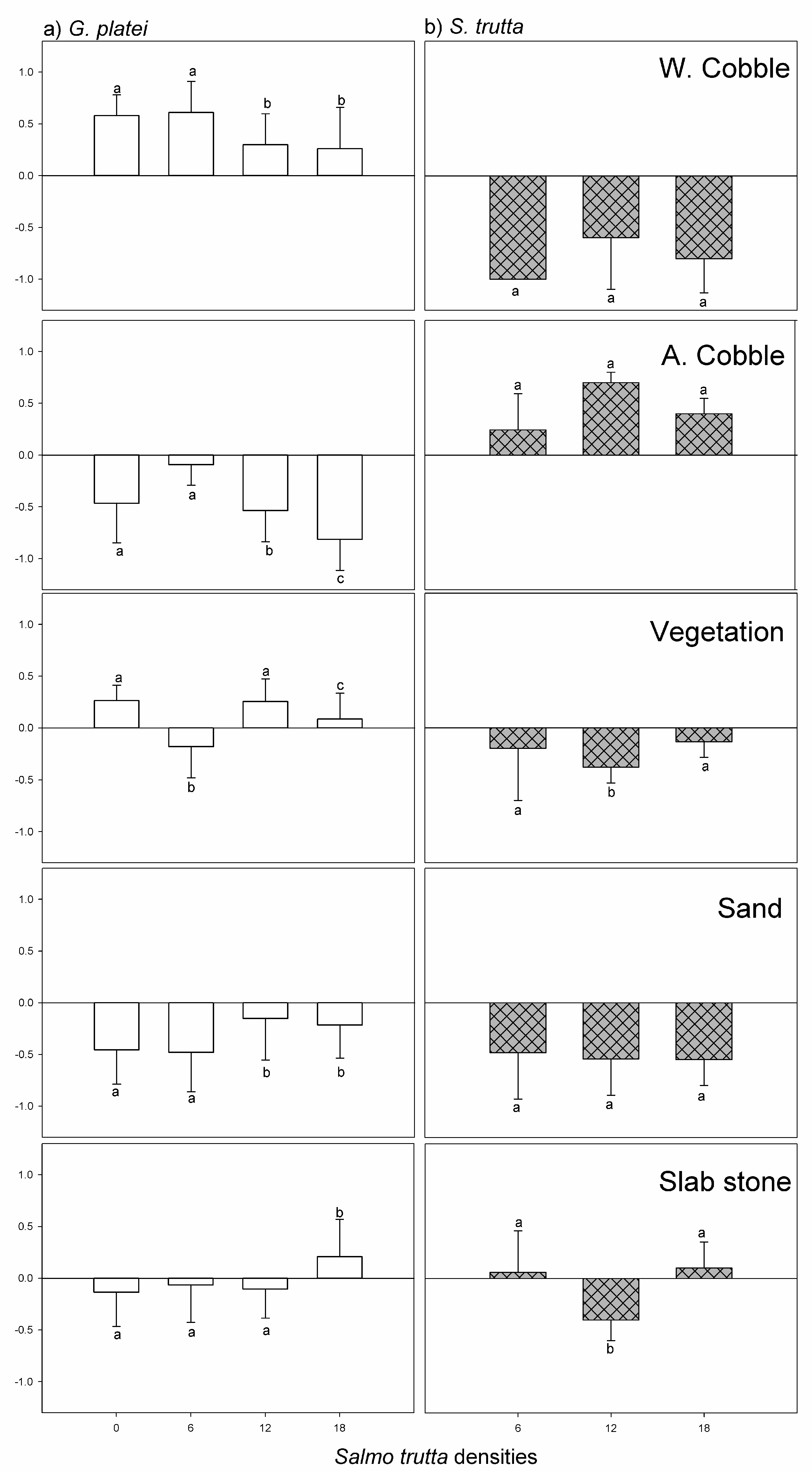
3.2. Experiment with Five Microhabitats (E3)
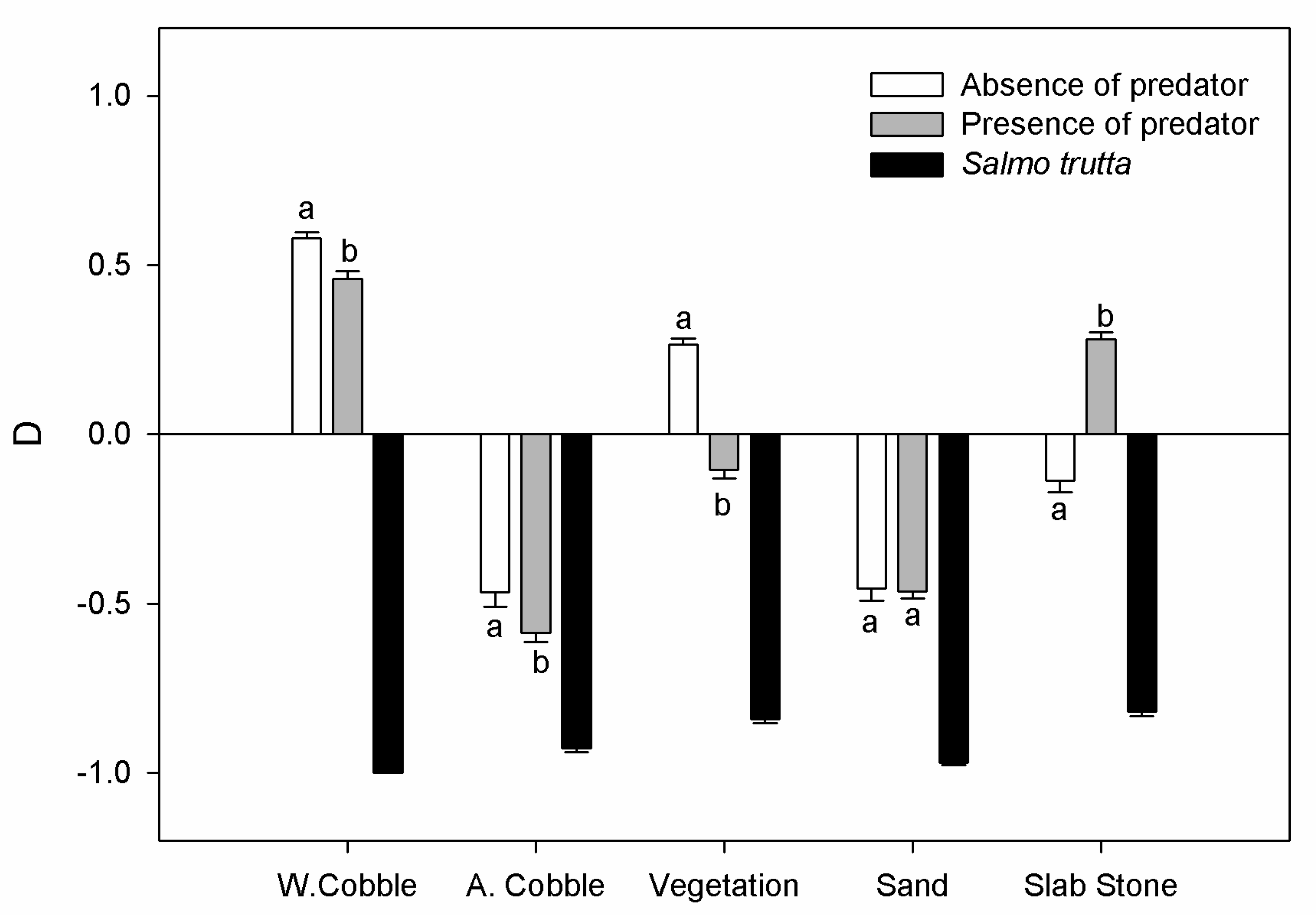
3.3. Microhabitat Preferences in Presence of a Predator (E4)
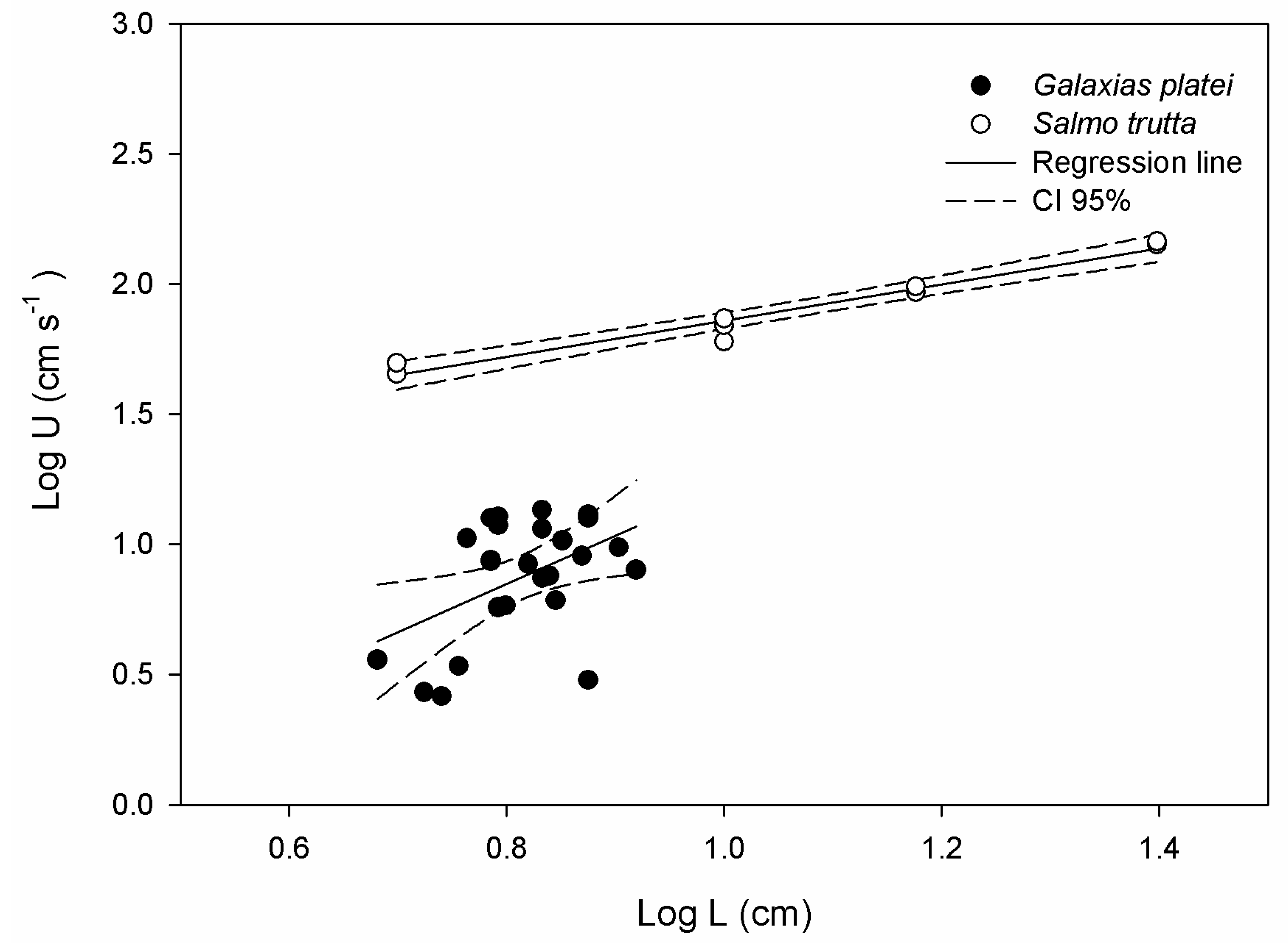
3.4. Swimming Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Do Galaxias platei Avoid Potential Competition of Juvenile Brown Trout?
4.2. How Does Galaxias platei Respond to Predation Risk Posed by Brown Trout?
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leprieur, F.; Beauchard, O.; Blanchet, S.; Oberdorff, T.; Brosse, S. Fish invasions in the world river systems: When natural processes are blurred by human activities. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 404–410. [Google Scholar]
- Su, G.; Logez, M.; Xu, J.; Tao, S.; Villéger, S.; Brosse, S. Human impacts on global freshwater fish biodiversity. Science 2021, 371, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowl, T.A.; Townsend, C.R.; McIntosh, A.R. The impact of introduced brown and rainbow trout on native fish: The case of Australasia. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1992, 3, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsed, C.R.; Crowl, T.A. Fragmented population structure in a native New Zealand fish: An effect of introduced brown trout? Oikos 1991, 61, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D. Multiple threats imperil freshwater biodiversity in the Anthropocene. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R960–R967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernery, C.; Bellard, C.; Courchamp, F.; Brosse, S.; Gozlan, R.; Jarić, I.; Teletchea, F.; Leroy, B. Freshwater Fish Invasions: A Comprehensive Review. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2022, 53, 427–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, N.J.; Reid, B.; Correa, C.; Madriz, R.I.; Neff, B.D.; Reynolds, J.D. Emergent trophic interactions following the Chinook salmon invasion of Patagonia. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, C.; Bravo, A.P.; Hendry, A.P. Reciprocal trophic niche shifts in native and invasive fish: Salmonids and galaxiids in Patagonian lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habit, E.; González, J.; Ruzzante, D.E.; Walde, S.J. Native and introduced fish species richness in Chilean Patagonian lakes: Inferences on invasion mechanisms using salmonid-free lakes. Divers. Distrib. 2012, 18, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arismendi, I.; Soto, D.; Penaluna, B.; Jara, C.; Leal, C.; León, J. Aquaculture, non-native salmonid invasions and associated declines of native fishes in Northern Patagonian lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriga, J.P.; Battini, M.A.; Macchi, P.J.; Milano, D.; Cussac, V.E. Spatial and temporal distribution of landlocked Galaxias maculatus and Galaxias platei (Pisces: Galaxiidae) in a lake in the South American Andes. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 36, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowall, R.M. Crying wolf, crying foul, or crying shame: Alien salmonids and a biodiversity crisis in the southern cool-temperate galaxioid fishes? Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2006, 16, 233–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García de Leaniz, C.; Gajardo, G.; Consuegra, S. From Best to Pest: Changing perspectives on the impact of exotic salmonids in the southern hemisphere. Syst. Biodivers. 2010, 8, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.A.; Dunham, J.B.; Stephenson, J.F.; Terreau, A.; Thailly, A.F.; Gajardo, G.; García de Leaniz, C. A trial of two trouts: Comparing the impacts of rainbow and brown trout on a native galaxiid. Anim. Conserv. 2010, 13, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penaluna, B.E.; Arismendi, I.; Soto, D. Evidence of interactive segregation between introduced trout and native fishes in Northern Patagonian rivers, Chile. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2009, 138, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Escalona, I.; Delgado, M.L.; Habit, E.; Ruzzante, D.E. Historical and contemporary diversity of galaxiids in South America: Biogeographic and phylogenetic perspectives. Diversity 2020, 12, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussac, V.; Ortubay, S.; Iglesias, G.; Milano, D.; Lattuca, M.E.; Barriga, J.P.; Battini, M.; Gross, M. The distribution of South American galaxiid fishes: The role of biological traits and post-glacial history. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussac, V.E.; Barrantes, M.E.; Boy, C.C.; Górski, K.; Habit, E.; Lattuca, M.E.; Rojo, J.H. New insights into the distribution, physiology and life histories of South American galaxiid fishes, and potential threats to this unique fauna. Diversity 2020, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprieur, F.; Hickey, M.A.; Arbuckle, C.J.; Closs, G.P.; Brosse, S.; Townsend, C.R. Hydrological disturbance benefits a native fish at the expense of an exotic fish. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzante, D.E.; Walde, S.J.; Gosse, J.C.; Cussac, V.E.; Habit, E.; Zemlak, T.S.; Adams, E.D.M. Climate control on ancestral population dynamics: Insight from Patagonian fish phylogeography. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 2234–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemlak, T.S.; Habit, E.; Walde, S.J.; Battini, M.A.; Adams, E.D.M.; Ruzzante, D.E. Across the southern Andes on fin: Glacial refugia, drainage reversals and a secondary contact zone revealed by the phylogeographical signal of Galaxias platei in Patagonia. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 5049–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, C.; Hendry, A.P. Invasive salmonids and lake order interact in the decline of puye grande Galaxias platei in western Patagonia lakes. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 828–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, D.; Vigliano, P.H. Nuevos registros de Galaxias platei Steindachner, 1898, en lagos andinos-patagónicos (Teleostei: Osmeriformes: Galaxiidade). Neotropica 1997, 43, 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Milano, D.; Cussac, V.E.; Macchi, P.; Ruzzante, D.E.; Alonso, M.; Vigliano, P.; Denegri, M. Predator associated morphology in Galaxias platei in Patagonian lakes. J. Fish. Biol. 2002, 61, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoebitz, K.; Rodríguez, E.L.; Campos, H. Complex mitochondria in the retinal cones of the Teleost Galaxias platei. J. Microsc. 1973, 18, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Milano, D.; Barriga, J. Reproductive aspects of Galaxias platei (Pisces, Galaxiidae) in a deep lake in North Patagonia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, P.; Cussac, V.; Alonso, M.; Denegri, M. Predation relationship between introduced salmonids and the native fish fauna in lakes and reservoirs in northern Patagonia. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 1999, 8, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, D.; Ruzzante, D.E.; Cussac, V.E.; Macchi, P.J.; Ferriz, R.A.; Barriga, J.P.; Aigo, J.C.; Lattuca, M.E.; Walde, S.J. Latitudinal and ecological correlates of morphological variation in Galaxias platei (Pisces, Galaxiidae) in Patagonia. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 87, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigliano, P.H.; Beauchamp, D.A.; Milano, D.; Macchi, P.J.; Alonso, M.F.; Asorey, M.I.G.; Denegri, M.A.; Ciancio, J.E.; Lippolt, G.; Rechencq, M.; et al. Quantifying predation on galaxiids and other native organisms by introduced rainbow trout in an ultraoligotrophic lake in northern Patagonia, Argentina: A bioenergetics modelling approach. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2009, 138, 1405–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belk, M.C.; Habit, E.; Ortiz-Sandoval, J.J.; Sobenes, C.; Combs, E.A. Ecology of Galaxias platei in a depauperate lake. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2014, 23, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechencq, M.; Sosnovsky, A.; Macchi, P.; Alvear, P.; Vigliano, P. Extensive diel fish migrations in a deep ultraoligotrophic lake of Patagonia Argentina. Hydrobiologia 2011, 658, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobenes, C.; Link, O.; Habit, E. Selección denso—Dependiente de microhábitat en Galaxias platei: Un estudio experimental. Gayana 2013, 77, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa-Muñoz, G.; Arismendi, I.; Parraguez, J.Z.; Isler, I.V. Unveiling growth and reproduction of a giant Patagonian galaxiid: An experimental rearing study. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 13, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggenes, J.; Krog, O.; Lindås, O.; Dokk, J. Homeostatic behavioural responses in a changing environment: Brown trout (Salmo trutta) become nocturnal during winter. J. Anim. Ecol. 1993, 6, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Sandoval, J.J.; Górski, K.; Sobenes, C.; Gonzalez, J.; Manosalva, A.; Elgueta, A.; Habit, E. Invasive trout affect trophic ecology of Galaxias platei in Patagonian lakes. Hydrobiologia 2017, 790, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, T.; Pyšek, P.; Bacher, S.; Carlton, J.; Duncan, R.; Jarošik, V.; Wilson, J.; Richardson, D. A proposed unified framework for biological invasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc, A.O.H.C.; Blondel, P.; Bernatchez, L. Behavioral plasticity and competition between native and invasive fish species. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 99, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Bøhn, T.; Amundsen, P.A.; Sparrow, A. Metabolic constraints in fish competition: How do native species cope with invasive salmonids? Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2020, 29, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, M.C.O.; Wisenden, B.D.; Chivers, D.P. Evolutionary history and the ability of prey to recognize novel predators. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Sobenes, C.; García, A.; Habit, E.; Link, O. Mantención de peces nativos dulceacuícolas en Chile en cautiverio: Un aporte a su conservación ex situ. Bol. Biodivers. 2012, 7, 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, H.; Kiljunen, M.; Amundsen, P.A. Dietary ontogeny and niche shift to piscivory in lacustrine brown trout Salmo trutta revealed by stomach content and stable isotope analyses. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 2448–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J. Quantitative measurement of food selection: A modification of the forage ratio and Ivlev’s lectivity index. Oecologia 1974, 14, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazka, P.; Volf, M.; Celepa, M. A new type of respirometer for determination of the metabolism of fish in an active state. Physiol. Bohemoslov. 1960, 9, 553–558. [Google Scholar]
- Brett, J.R. The respiratory metabolism and swimming performance of Young sockeye salmon. J. Fish. Res. Can. 1964, 21, 1183–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudorache, C.; Viaene, P.; Blust, R.; Vereecken, H.; De Boeck, G. A comparison of swimming capacity and energy use in seven European freshwater fish species. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2008, 17, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, S.J. Swimming Performance and Behaviour of Fish Species Endemic to Newfoundland and Labrador: A Literature Review for the Purpose of Establishing Design and Water Velocity Criteria for Fishways and Culverts; Canadian Manuscript Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences; Fisheries and Oceans Canada: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2008; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Ley N° 20.800. Septiembre 11, 2009, Sobre Protección de Animales. Ministerio de Salud; Subsecretaría de Salud Pública, Chile. Available online: https://bcn.cl/28eda (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- McArdle, B.H.; Anderson, M.J. Fitting multivariate models to community data: A comment on distance-based redundancy analysis. Ecology 2001, 82, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; Grossman, G.D. Utility of direct observational methods for assessing competitive interactions between non-native and native freshwater fishes. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2012, 19, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigo, J.; Cussac, V.; Peris, S.; Ortubay, S.; Gómez, S.; López, H.; Gross, M.; Barriga, J.; Battini, M. Distribution of introduced and native fish in Patagonia (Argentina): Patterns and changes in fish assemblages. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2008, 18, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, R.S.; McIntosh, A.; Lai, H.R.; Stouffer, D.B.; Boddy, N.; Zammit, C.; Tonkin, J. Introduced trout hinder the recovery of native fish following an extreme flood disturbance. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving Bioscience Research Reporting: The ARRIVE Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espmark, A.M.; Kolarevic, J.; Asgard, T.; Terjesen, B.F. Tank size and fish management history matters in experimental design. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 2876–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Boisclair, D. Influence of the Size of Enclosures on the Swimming Characteristics of Juvenile Brook Trout (Salvelinus-Fontinalis). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 1786–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.D.; Readman, G.D.; Owen, S.F. Key issues concerning environmental enrichment for laboratory-held fish species. Lab. Anim. 2009, 43, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naslund, J.; Johnsson, J.I. Environmental enrichment for fish in captive environments: Effects of physical structures and substrates. Fish Fish. 2016, 17, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbert, S. Pseudoreplication and the Design of Ecological Field Experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1984, 54, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER. Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Luccon-Xicatto, T.; Bisazza, A. Individual differences in cognition among teleost fishes. Behav. Process. 2017, 141, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.E.; Gilliam, J.F. The ontogenetic niche and species interactions in size-structured populations. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1984, 15, 393–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnett, M.; McIntosh, R. The influence of juvenile brown trout (Salmo trutta) on habitat use of inganga (Galaxias maculatus) in a stream simulator. J. R. Soc. N. Z. 2004, 34, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelbach, G.G.; Persson, L. The ontogeny of piscivory and its ecological consequences. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arismendi, I.; González, J.; Soto, D.; Penaluna, B. Piscivory and diet overlap between two non-native fishes in southern Chilean streams. Austral Ecol. 2012, 37, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.M. The food of brown and rainbow trout (Salmo trutta and S. gairdneri) in relation to the abundance of drifting invertebrates in a mountain stream. Oecologia 1973, 13, 29–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachman, R.A. Foraging behavior of free-ranging wild and hatchery brown trout in a stream. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1984, 113, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, F.; Barbeee, N.C.; Swearer, S.E. Avoidance of native versus non-native predator odours by migrating whitebait and juvenile of the common galaxiid, Galaxias maculatus. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2007, 41, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde, P.A.; Chiang, G.; Mancillas, G.; Contador, T.; Quezada-Romegialli, C.; Munkittirck, K.; Harrod, C. Ecological variation in invasive brown trout (Salmo trutta) within a remote coastal river catchment in Northern Patagonia complicates estimates of invasion impact. J. Fish Biol. 2023, 104, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivers, D.P.; Brown, G.E.; Smith, R.J.F. The evolution of chemical alarm signals: Attracting predators benefits alarm signal senders. Am. Nat. 1996, 148, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kats, L.B.; Dill, L.M. The scent of death: Chemosensory assessment of predation risk by prey animals. Ecoscience 1998, 5, 361–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réale, D.; Garant, D.; Humphries, M.M.; Bergeron, P.; Careau, V.; Montiglio, P.O. Personality and the emergence of the pace-of-life syndrome concept at the population level. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 4051–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, P.W. Form and function in fish swimming. Sci. Am. 1984, 251, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, P.; Blake, R.W. Fish fast-start kinematics and performance. J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 200, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, C.A. Fast-start swimming performance and reduction in lateral plate number in threespine stickleback. Can. J. Zool. 2002, 80, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaut, I. Critical swimming speed: Its ecological relevance. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001, 131, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Experiment | Galaxias platei | Salmo trutta | Microhabitats | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Length (cm) | Weight (g) | n | Length (cm) | Weight (g) | ||
| E1 | 4 | 7.0 ± 0.8 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 0 | Vegetation, Cobble, Slab Stone and Sand. | ||
| 8 | 6.7 ± 0.8 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 0 | ||||
| 12 | 7.2 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 0 | ||||
| 16 | 6.8 ± 0.7 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 0 | ||||
| 27 | 6.8 ± 1.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0 | ||||
| E2 | 12 | 6.5 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 6 | 8.1 ± 0.62 | 4.9 ± 0.96 | Vegetation, Cobble, Slab Stone and Sand. |
| 12 | 12 | 7.9 ± 0.56 | 4.7 ± 0.94 | ||||
| 12 | 18 | 8.4 ± 1.15 | 5.6 ± 0.53 | ||||
| 12 | 24 | 8.3 ± 0.50 | 5.3 ± 0.80 | ||||
| E3 | 12 | 6.1 ± 0.17 | 1.3 ± 0.14 | 0 | Vegetation, Above-Cobbles, Within-Cobbles, Slab Stone and Sand. | ||
| 12 | 6 | ||||||
| 12 | 12 | ||||||
| 12 | 18 | ||||||
| E4 | 12 | 6.7 ± 0.7 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 0 | - | - | Vegetation, Above-Cobbles, Within-Cobbles, Slab Stone and Sand. |
| 12 | 1 | 19.10 | 62.20 | ||||
| 12 | 1 | 22.00 | 97.10 | ||||
| 12 | 1 | 25.10 | 132.10 | ||||
| Lenght (cm) | Swimming Velocity (cm·s−1) |
|---|---|
| 5 | 45.0–49.6 |
| 10 | 59.8–73.6 |
| 15 | 93.0–97.6 |
| 25 | 141.0–145.6 |
| Galaxias platei | Salmo trutta | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Source | df | SS | Pseudo-F | p | df | SS | Pseudo-F | p |
| Cobbles | Density | 8 | 69.721 | 74.491 | <0.001 | 3 | 17.58 | 89.491 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 696 | 81.428 | 348 | 22.788 | |||||
| Vegetation | Density | 8 | 48.115 | 46.687 | <0.001 | 3 | 9.4241 | 29.553 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 696 | 89.661 | 348 | 36.991 | |||||
| Slab stone | Density | 8 | 118.62 | 125.56 | <0.001 | 3 | 20.51 | 100.75 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 696 | 82.191 | 348 | 23.614 | |||||
| Sand | Density | 8 | 27.114 | 22.457 | <0.001 | 3 | 1.2499 | 3.6703 | <0.05 |
| Residual | 696 | 105.04 | 348 | 39.503 | |||||
| Galaxias platei | Salmo trutta | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Source | df | SS | Pseudo-F | p | df | SS | Pseudo-F | p |
| Above cobbles | Density of S. trutta | 3 | 23.426 | 64.976 | <0.001 | 2 | 9.4972 | 61.043 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 348 | 41.822 | 261 | 20.304 | |||||
| Within cobbles | Density of S. trutta | 3 | 8.8845 | 24.263 | <0.001 | 2 | 7.1472 | 19.16 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 348 | 42.476 | 261 | 48.679 | |||||
| Vegetation | Density of S. trutta | 3 | 11.443 | 62.324 | <0.001 | 2 | 2.859 | 10.421 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 348 | 21.299 | 261 | 35.804 | |||||
| Slab stone | Density of S. trutta | 3 | 6.6223 | 19.45 | <0.001 | 2 | 13.74 | 79.971 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 348 | 39.495 | 261 | 22.421 | |||||
| Sand | Density of S. trutta | 3 | 7.2657 | 19.721 | <0.001 | 2 | 0.25175 | 0.91453 | NS |
| Residual | 348 | 42.737 | 261 | 35.923 | |||||
| Galaxias platei | Salmo trutta | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Source | df | SS | Pseudo-F | p | df | SS | Pseudo-F | p |
| Above cobbles | Presence of predator (S. trutta) | 3 | 13.461 | 30.552 | <0.001 | 2 | 1.9653 | 37.286 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 348 | 51.109 | 261 | 6.8784 | |||||
| Within cobbles | Presence of predator (S. trutta) | 3 | 1.4965 | 5.3644 | <0.001 | _ | _ | _ | _ |
| Residual | 348 | 32.36 | _ | _ | |||||
| Vegetation | Presence of predator (S. trutta) | 3 | 17.272 | 53.53 | <0.001 | 2 | 8.7008 | 433.82 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 348 | 37.428 | 261 | 2.6173 | |||||
| Slab stone | Presence of predator (S. trutta) | 3 | 21.166 | 77.375 | <0.001 | 2 | 7.1299 | 198.57 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 348 | 31.732 | 261 | 4.6858 | |||||
| Sand | Presence of predator (S. trutta) | 3 | 1.2004 | 3.6105 | <0.05 | 2 | 0.50232 | 23.957 | <0.001 |
| Residual | 348 | 38.567 | 261 | 2.7363 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobenes, C.; Habit, E.; Górski, K.; Link, O. Behavioral Responses of Galaxias platei to Salmo trutta: Experimental Evidence of Competition and Predation Risk. Water 2025, 17, 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121774
Sobenes C, Habit E, Górski K, Link O. Behavioral Responses of Galaxias platei to Salmo trutta: Experimental Evidence of Competition and Predation Risk. Water. 2025; 17(12):1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121774
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobenes, Catterina, Evelyn Habit, Konrad Górski, and Oscar Link. 2025. "Behavioral Responses of Galaxias platei to Salmo trutta: Experimental Evidence of Competition and Predation Risk" Water 17, no. 12: 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121774
APA StyleSobenes, C., Habit, E., Górski, K., & Link, O. (2025). Behavioral Responses of Galaxias platei to Salmo trutta: Experimental Evidence of Competition and Predation Risk. Water, 17(12), 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121774









