Stability Enhancement of Microalgae–Fungal Pellets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material
2.1.1. MFPs
2.1.2. Crosslinking Agents
2.1.3. Wastewater
2.2. Preparation of MFPs Strengthened with Crosslinking Agents
2.3. Analytical Method
2.3.1. Structural Stability Analysis of MFPs
2.3.2. Water Quality Determination
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Impact of Crosslinking Agents on the Structural Stability of MFPs
3.1.1. The Impact of Crosslinking Agents on the Mechanical Hardness of Microalgal–Fungal Pellets
3.1.2. The Impact of Crosslinking Agents on the Zeta Potential of MFP
3.1.3. The Impact of Crosslinking Agents on the 3D Fluorescence of the Extracellular Polymeric Substances in MFPs
3.1.4. The Impact of Crosslinking Agents on the Protein and Polysaccharide Contents of EPSs in Various MFPs on Day 1 and Day 9
3.2. The Impact of Crosslinking Agents on the Microstructure of MFPs
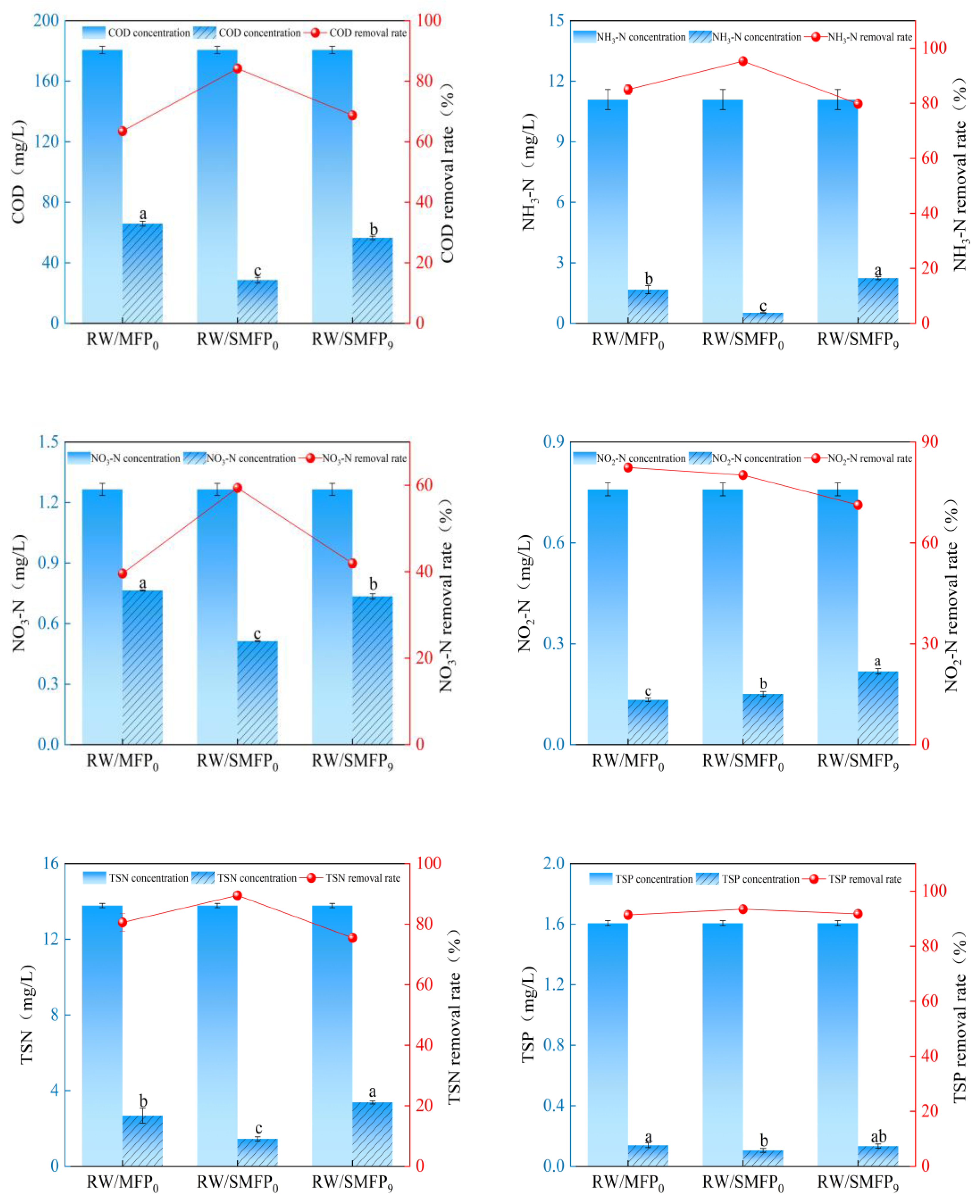
3.3. Treatment Efficiency of SA-Crosslinked MFPs for High-Density Aquaculture Wastewater
3.4. Economic Benefits and Operational Parameter Analysis of SA-Crosslinked MFP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, Y.; Zhan, W.; Wu, R.; Han, Y.; Yang, S.; Ding, J.; Ren, N. Insight into the roles of microalgae on simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in microalgal-bacterial sequencing batch reactors: Nitrogen removal, extracellular polymeric substances, and microbial communities. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 379, 129038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Yousif Abdellah, Y.A.; Wang, L.; Elsheikh, E.A.E.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, G. NaCl as an excellent trigger-induced biodiesel production and phenol-containing wastewater treatment in a novel salt-tolerant microalgae Ankistrodesmus sp. ACC. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 429, 132515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewuyi, S.; Babatunde, T.; Mmuoegbulam, A.; Abimbade, S.; Abiodun, O.; Klink, M.J.; Nelana, S.; Malomo, D.; Ayanda, O. Toxicity and health implications of pesticides and the need to remediate pesticide-contaminated wastewater through the advanced oxidation processes. Water Conserv. Manag. WCM 2024, 8, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.G.; Cheng, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Lin, X.Y.; Ruan, R. Novel Fungal Pelletization-Assisted Technology for Algae Harvesting and Wastewater Treatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Jiang, L.; He, R. Uncovering anaerobic oxidation of methane and active microorganisms in landfills by using stable isotope probing. Environ. Res. 2025, 271, 121139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, D.; Wu, T.; Ge, Z.; Ying, Z.; Sun, S.; Huang, D.; Zhang, J. The coupling effect promotes superoxide radical production in the microalgal-fungal symbiosis systems: Production, mechanisms and implication for Hg(II) reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muradov, N.; Taha, M.; Miranda, A.F.; Wrede, D.; Kadali, K.; Gujar, A.; Stevenson, T.; Ball, A.S.; Mouradov, A. Fungal-assisted algal flocculation: Application in wastewater treatment and biofuel production. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.M.; Li, H.K.; Wang, Q. A novel one-step method for oil-rich biomass production and harvesting by co-cultivating microalgae with filamentous fungi in molasses wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Qian, J.; Fan, L.; Toda, T.; Li, H.; Sekine, M.; Song, P.; Takayama, Y.; Koga, S.; Li, J.; et al. Enhancing biomass yield, nutrient removal, and decolorization from soy sauce wastewater using an algae-fungus consortium. Algal Res. 2022, 68, 102878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-K.; Yang, K.-X.; Zhu, Y.-R.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Nie, D.-F.; Jiao, N.; Angelidaki, I. One-step co-cultivation and flocculation of microalgae with filamentous fungi to valorize starch wastewater into high-value biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Y.T.; Liu, L.; Li, P.; Yan, Y.; Chen, T.; Zheng, T.L.; Wang, H.L. Flocculation mechanism of Aspergillus niger on harvesting of Chlorella vulgaris biomass. Algal Res.-Biomass Biofuels Bioprod. 2017, 25, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.S.; Xi, L.M.; Liu, D.F.; Huang, W.W.; Lei, Z.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Huang, W.L. Effects of light intensity on oxygen distribution, lipid production and biological community of algal-bacterial granules in photo-sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, D.; Huang, W.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z. Achieving partial nitrification and high lipid production in an algal-bacterial granule system when treating low COD/NH4–N wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fan, H.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, C.X.; Huang, X. Development of algae-bacteria granular consortia in photo-sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.W.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.J.; Lei, Z.F.; Shimizu, K.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Adachi, Y. Stability and performance of algal-bacterial granular sludge in shaking photo-sequencing batch reactors with special focus on phosphorus accumulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.J.; Chen, R.F.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Song, J.Y. Natural sunlight induced rapid formation of water-born algal-bacterial granules in an aerobic bacterial granular photo-sequencing batch reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Tay, J.-H. Cultivation of aerobic granules in a bubble column and an airlift reactor with divided draft tubes at low aeration rate. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, B.Y.P.; Tay, J.H.; Toh, S.K.; Liu, Y.; Tay, S.T.L. High organic loading influences the physical characteristics of aerobic sludge granules. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 34, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liang, D.T.; Tay, J.H. Structure and stability of aerobic granules cultivated under different shear force in sequencing batch reactors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lens, P.N.L.; Shi, W.X.; Zhang, R.J.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Guo, Y.; Bao, X.; Cui, F.Y. Enhancement of aerobic granulation and nutrient removal by an algal-bacterial consortium in a lab-scale photobioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Liu, Z. Effect of different forms and components of EPS on sludge aggregation during granulation process of aerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, F.; Xu, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. Optimization and regeneration of chitosan-alginate hybrid adsorbent embedding iron-manganese sludge for arsenic removal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 607, 125500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, J. Immobilization of activated sludge in PVA matrix using innovative methods. Huanjing Kexue Xuebao/Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 33, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- HJ 535-2009; Water Quality―Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen―Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese)
- GB 7493-87; Water Quality-Determination of Nitrogen (Nitrite)-Spectrophotometric Method. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1987. (In Chinese)
- HJ/T 346-2007; Water Quality—Determination of Nitrate-Nitrogen—Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- HJ 636-2012; Water Quality-Determination of Total Nitrogen-Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- GB 11893-89; Water Quality-Determination of Total Phosphorus-Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1989. (In Chinese)
- GB 11914-89; Water Quality-Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand-Dichromate Method. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1989. (In Chinese)
- Lai, Z.; Cui, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J. The Hardness of Sodium Alginate-Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel. Mater. Rep. 2010, 24, 32–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Garrido, I. Microalgae immobilization: Current techniques and uses. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3949–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, F.R.; Wall, J.S. Polysaccharide Interactions with Wheat Proteins and Flour Doughs. Cereal Chem. 1979, 56, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, R.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Torres Sáez, R.; Fernández-Lafuente, R. Modifying enzyme activity and selectivity by immobilization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 42, 6290–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Du, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, J.; Fan, L.; Feng, T. Preparation of alginate/soy protein isolate blend fibers through a novel coagulating bath. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bao, K.; Cao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.W. Screening of microalgae for integral biogas slurry nutrient removal and biogas upgrading by different microalgae cultivation technology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Klemeš, J.J.; Tian, K.; Ma, T.; Sunden, B. A review on nanofluid stability: Preparation and application. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 188, 113854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekalska, M.; Sosnowska, K.; Czajkowska-Kośnik, A.; Winnicka, K. Calcium Chloride Modified Alginate Microparticles Formulated by the Spray Drying Process: A Strategy to Prolong the Release of Freely Soluble Drugs. Materials 2018, 11, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Curtis, T.; Dolfing, J.; Wu, Y.; Rittmann, B.E. N-acyl-homoserine-lactones signaling as a critical control point for phosphorus entrapment by multi-species microbial aggregates. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Rene, E.R.; Wu, D.; Sun, D.; Qiu, B. Stimulation of anaerobic biofilm development in the presence of low concentrations of toxic aromatic pollutants. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, J.; Shi, W.; Guo, Y.; Lens, P.N.L.; Zhang, B. Effect of different inocula on the granulation process, reactor performance and biodiesel production of algal-bacterial granular sludge (ABGS) under low aeration conditions. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, D.; Nafisi, S.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.-A. Encapsulation of Milk β-Lactoglobulin by Chitosan Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 6403–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daza, J.; Ramirez, M.; Henquín, E.; Rintoul, I. Modelling of swelling of PVA hydrogels considering non-ideal mixing behaviour of PVA and water. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4049–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Qu, Z.; Yu, J.; Ma, H.; Li, B.; Sun, D.; Ge, Y. Asymmetric 5-sulfosalicylic acid-PVA catalytic pervaporation membranes for the process intensification in the synthesis of ethyl acetate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Marin, A.; Mendoza-Espinosa, L.G.; Stephenson, T. Growth and nutrient removal in free and immobilized green algae in batch and semi-continuous cultures treating real wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.-J. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from aerobic granule with compact interior structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shah, F.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q. High-moisture extrusion of peanut protein-/carrageenan/sodium alginate/wheat starch mixtures: Effect of different exogenous polysaccharides on the process forming a fibrous structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Guo, C.; Hao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Long, H.; Li, M. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by sodium alginate based adsorbent-a review and new perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4423–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, M.; Aziz, A.; Kim, K. Biosorption and Binding Mechanisms of Ni2+ and Cd2+ with Aerobic Granules Cultivated in Different Synthetic Media. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2017, 40, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. High moisture extrusion cooking on soy proteins: Importance influence of gums on promoting the fiber formation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ociński, D.; Jacukowicz-Sobala, I.; Kociołek-Balawejder, E. Alginate beads containing water treatment residuals for arsenic removal from water—Formation and adsorption studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24527–24539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Egg-box model-based gelation of alginate and pectin: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Yan, G.; Dong, W.; Chu, Z.; Wang, H.; Chang, Y.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, Y. Initial carbon release characteristics, mechanisms and denitrification performance of a novel slow release carbon source. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 118, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Gong, T.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y. Interpenetrating network gels with tunable physical properties: Glucono-δ-lactone induced gelation of mixed Alg/gellan sol systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Thakur, M.K. Recent Advances in Graft Copolymerization and Applications of Chitosan: A Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2637–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Thakur, S.; Mamba, G.; Prateek; Gupta, R.K.; Thakur, P.; Thakur, V.K. Graphite modified sodium alginate hydrogel composite for efficient removal of malachite green dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Fang, F.; Guo, J. Insight into the role of exopolysaccharide in determining the structural stability of aerobic granular sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Zhao, F.; Rho, J.Y.; Goodrich, S.L.; Sumerlin, B.S.; He, Z. Use of polymeric nanoparticles to improve seed germination and plant growth under copper stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.; Müller, J.; Skoupi, M.; Niemeyer, C. Cascades in Compartments: EnRoute to Machine-Assisted Biotechnology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13574–13589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, L.; Banta, S.; Wheeldon, I. Engineering enzyme microenvironments for enhanced biocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5177–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetlove, L.J.; Fernie, A.R. The role of dynamic enzyme assemblies and substrate channelling in metabolic regulation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F. Microbial Control of Oceanic Carbon Flux: The Plot Thickens. Science 1998, 280, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalnina, K.; Louie, K.B.; Hao, Z.; Mansoori, N.; da Rocha, U.N.; Shi, S.; Cho, H.; Karaoz, U.; Loqué, D.; Bowen, B.P.; et al. Dynamic root exudate chemistry and microbial substrate preferences drive patterns in rhizosphere microbial community assembly. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doornbos, R.F.; van Loon, L.C.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Impact of root exudates and plant defense signaling on bacterial communities in the rhizosphere. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, Z.; Maqbool, T.; Shin, K.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Hur, J. Using stable isotope probing and fluorescence spectroscopy to examine the roles of substrate and soluble microbial products in extracellular polymeric substance formation in activated sludge process. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.; Babu, R.P.; McDonagh, C.; Jaiswal, S.; Tiwari, B.K.; Kerry, J.P.; Pathania, S. Pectin/sodium alginate-based active film integrated with microcrystalline cellulose and geraniol for food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothard, D.; Smith, E.; Kanczler, J.; Black, C.; Wells, J.; Roberts, C.; White, L.; Qutachi, O.; Peto, H.; Rashidi, H.; et al. In Vivo Assessment of Bone Regeneration in Alginate/Bone ECM Hydrogels with Incorporated Skeletal Stem Cells and Single Growth Factors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinsen, A.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Smidsrød, O. Alginate as immobilization material: I. Correlation between chemical and physical properties of alginate gel beads. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1989, 33, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, C.; Agnol, W.D.; Dallé, D.; Serpa, V.G.; Maciel, M.J.; Lehn, D.N.; Volken de Souza, C.F. Development of alginate-pectin microparticles with dairy whey using vibration technology: Effects of matrix composition on the protection of Lactobacillus spp. from adverse conditions. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DB42/2330-2024; Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Aquaculture Tailwater in Hubei Province. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2024. (In Chinese)
- Lu, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Qiu, R. Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar. Water Res. 2012, 46, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Peng, F. Ammonium removal potential and its conversion pathways by free and immobilized Scenedesmus obliquus from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 283, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Han, L.; Ma, R.; Phillips, G.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. All-Natural Food-Grade Hydrophilic-Hydrophobic Core-Shell Microparticles: Facile Fabrication Based on Gel-Network-Restricted Antisolvent Method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11936–11946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Thavamani, P.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Lee, Y.B.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Remediation approaches for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminated soils: Technological constraints, emerging trends and future directions. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 944–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orive, G.; Carcaboso, A.; Hernandez, R.; Gascón, A.; Pedraz, J. Biocompatibility Evaluation of Different Alginates and Alginate-Based Microcapsules. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, U.; Klöck, G.; Federlin, K.; Hannig, K.; Kowalski, M.; Bretzel, R.G.; Horcher, A.; Entenmann, H.; Sieber, U.; Zekorn, T. Production of mitogen-contamination free alginates with variable ratios of mannuronic acid to guluronic acid by free flow electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 1992, 13, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, S.; Heils, R.; Trieu, H.K.; Smirnova, I.; Yesil-Celiktas, O. An injectable alginate-based hydrogel for microfluidic applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 161, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.Q.; Zhao, S.K.; Cai, B.; He, R.X.; Rao, L.; Wu, Y.; Guo, S.S.; Liu, Q.Y.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.Z. Biocompatible fabrication of cell-laden calcium alginate microbeads using microfluidic double flow-focusing device. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 279, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Lian, C.-A.; Yang, L.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Qiu, Z.; Qiao, X.; Xiong, Z.; Dong, N.; Hu, J.; Luo, X.; et al. Self-adaptation of tolerant microalgae-bacterial consortia in landfill leachate: Simultaneous achievement of efficient nitrogen removal and value-added utilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 158912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
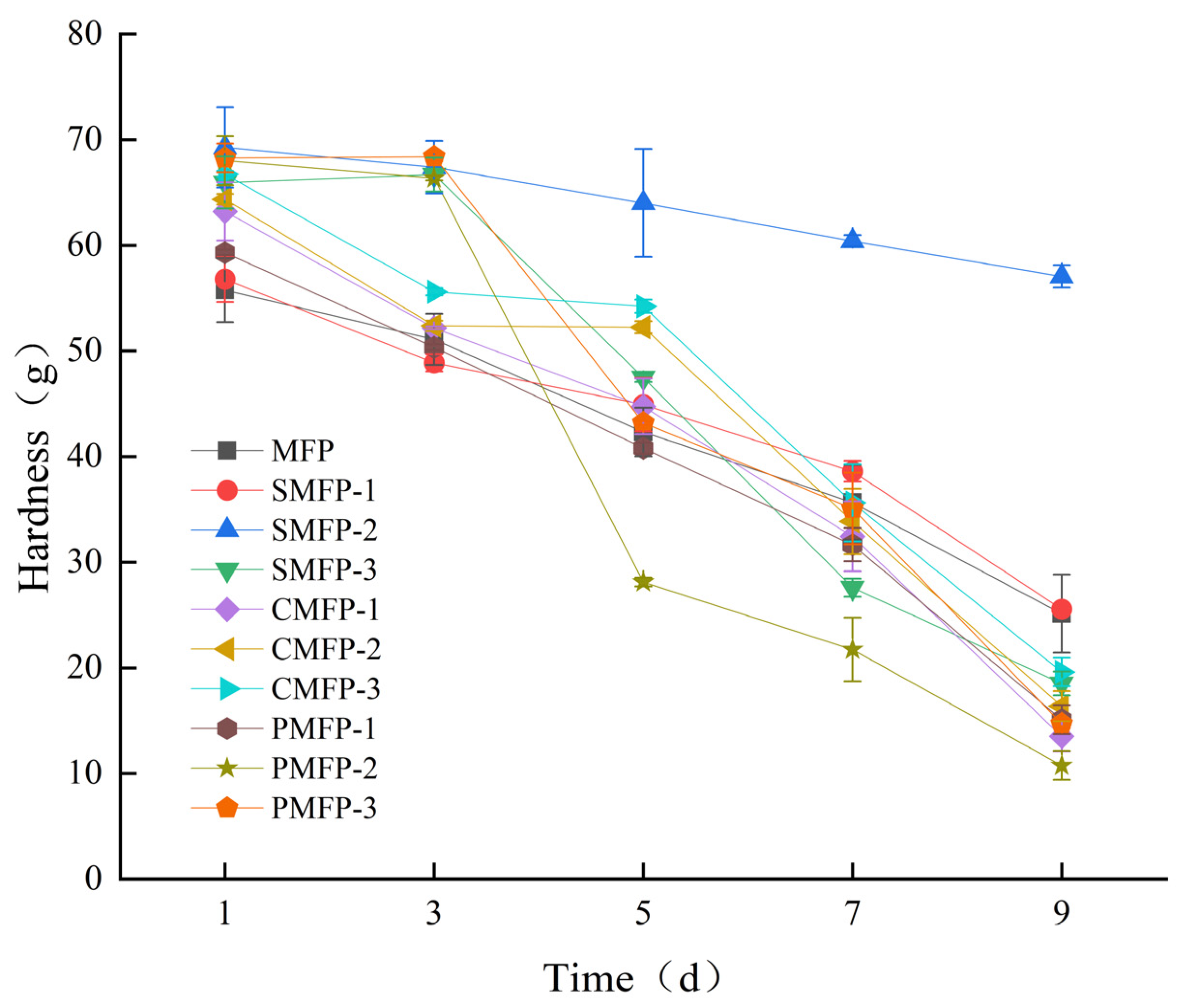
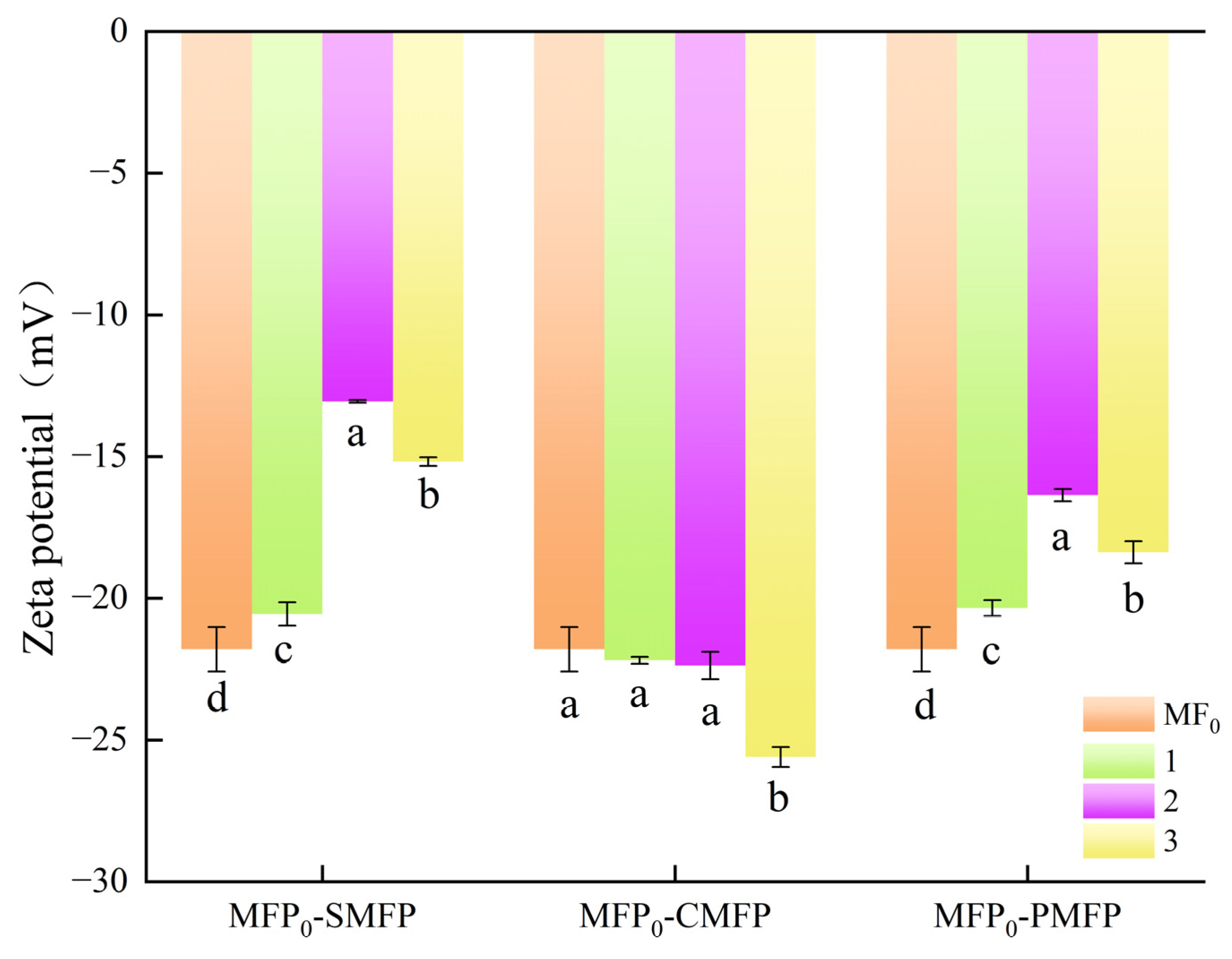

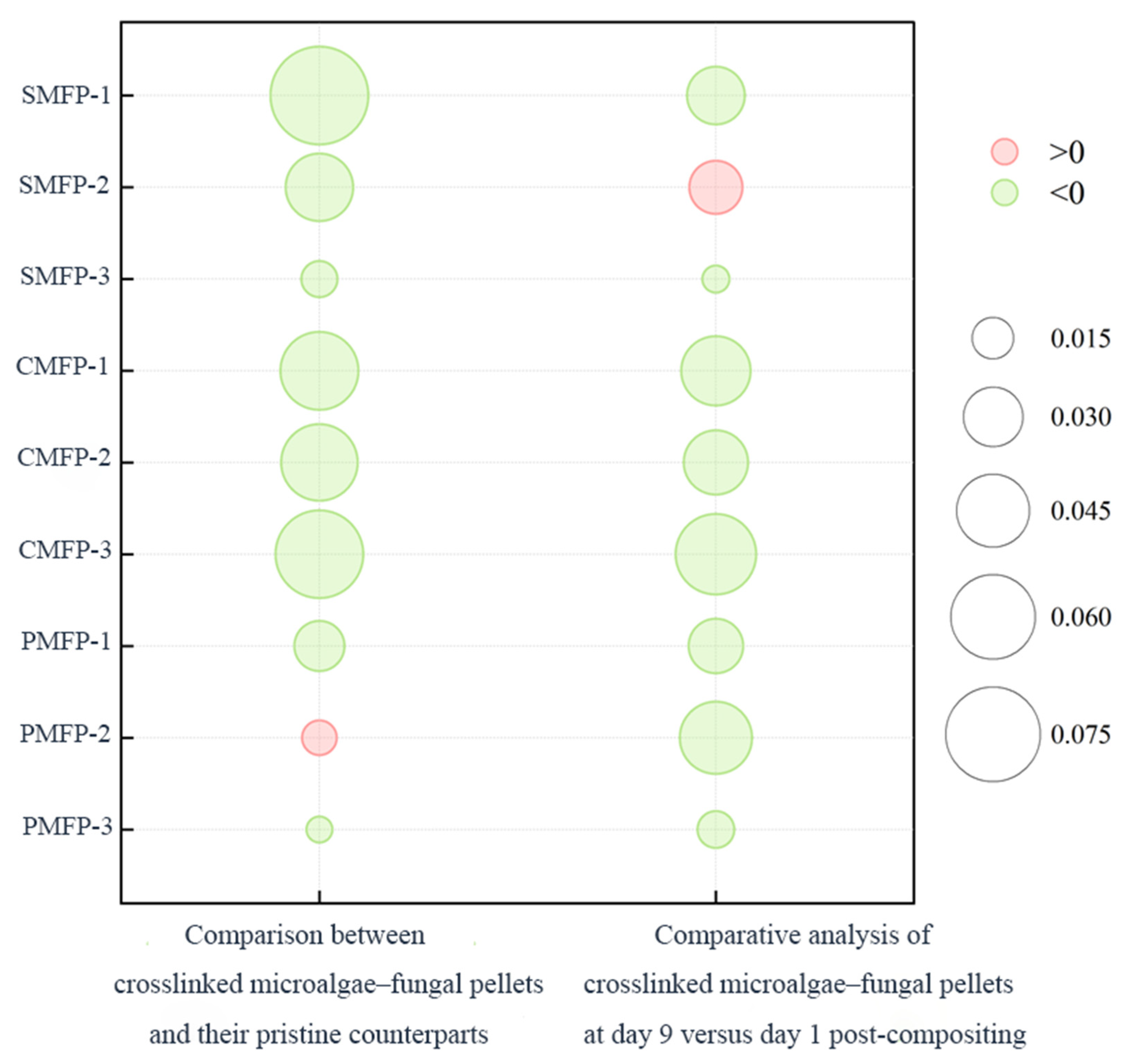

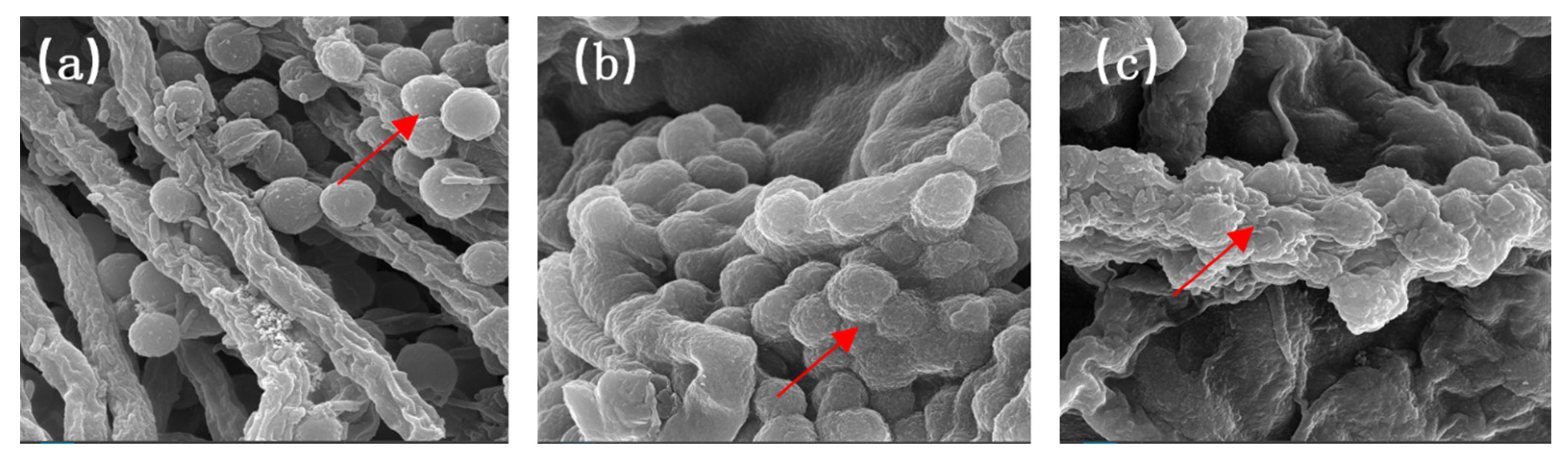
| Sample | 1st-Day Hardness (g) | 9th-Day Hardness (g) |
|---|---|---|
| MFP | 55.76 ± 3.03 d | 25.13 ± 3.69 b |
| SMFP-1 | 56.80 ± 2.17 d | 25.55 ± 0.41 b |
| SMFP-2 | 69.28 ± 3.80 a | 57.05 ± 1.05 a |
| SMFP-3 | 65.94 ± 2.47 abc | 18.51 ± 1.13 cd |
| CMFP-1 | 63.21 ± 2.76 c | 13.52 ± 1.43 e |
| CMFP-2 | 64.36 ± 0.50 bc | 16.38 ± 1.41 de |
| CMFP-3 | 66.74 ± 0.28 abc | 19.60 ± 1.30 c |
| PMFP-1 | 59.32 ± 0.26 abc | 15.09 ± 1.37 e |
| PMFP-2 | 68.02 ± 2.33 ab | 10.76 ± 1.36 f |
| PMFP-3 | 68.27 ± 1.37 ab | 14.71 ± 0.41 e |
| Performance Metric | MFP0 | SMFP0 | SMFP9 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (g) | 55.76 ± 3.03 b | 69.28 ± 3.80 a | 57.05 ± 1.05 b |
| PN (mg/L) | 54.75 ± 3.38 c | 75.62 ± 2.48 a | 64.22 ± 3.05 b |
| PS (mg/L) | 21.40 ± 1.95 b | 52.97 ± 2.67 a | 56.99 ± 2.54 a |
| COD removal rate (%) | 63.52 ± 0.87 c | 84.19 ± 1.03 a | 68.76 ± 0.62 b |
| NH3-N removal rate (%) | 84.98 ± 1.80 b | 95.29 ± 0.09 a | 79.82 ± 0.66 c |
| NO3-N removal rate (%) | 39.58 ± 0.16 c | 59.42 ± 0.16 a | 41.94 ± 1.05 b |
| NO2-N removal rate (%) | 82.42 ± 0.65 a | 80.17 ± 0.98 b | 71.30 ± 1.06 c |
| TSN removal rate (%) | 80.58 ± 2.88 b | 89.50 ± 0.78 a | 75.48 ± 0.60 c |
| TSP removal rate (%) | 91.38 ± 0.95 b | 93.46 ± 0.80 a | 91.73 ± 0.87 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Cheng, K.; Mei, H. Stability Enhancement of Microalgae–Fungal Pellets. Water 2025, 17, 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121766
Zhang G, Cheng K, Mei H. Stability Enhancement of Microalgae–Fungal Pellets. Water. 2025; 17(12):1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121766
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guang, Kai Cheng, and Hong Mei. 2025. "Stability Enhancement of Microalgae–Fungal Pellets" Water 17, no. 12: 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121766
APA StyleZhang, G., Cheng, K., & Mei, H. (2025). Stability Enhancement of Microalgae–Fungal Pellets. Water, 17(12), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121766





