Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Optimization of Reservoir Operations Under Climate Variability in the Chao Phraya River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Reservoir Operations
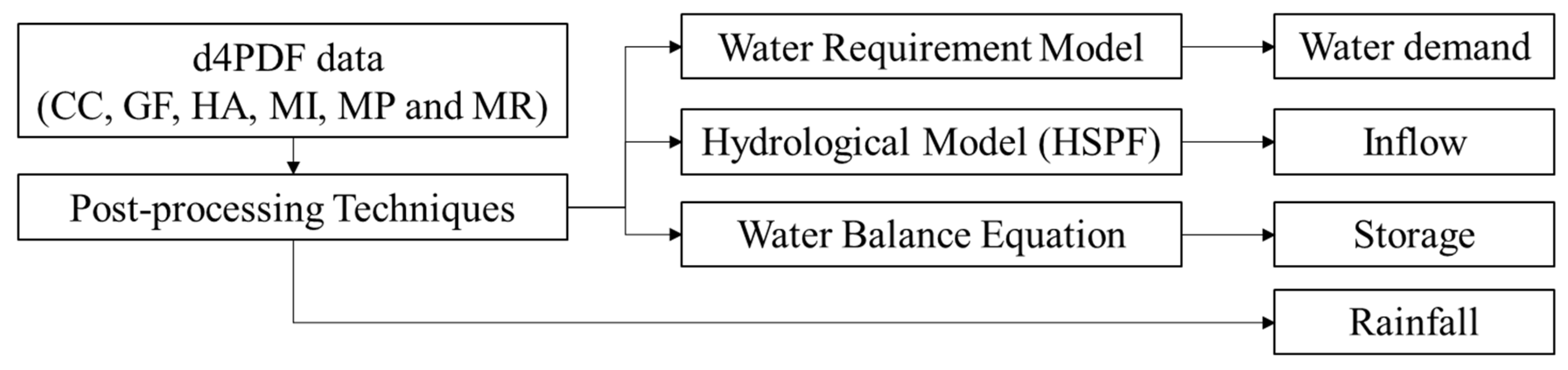
2.3. Data
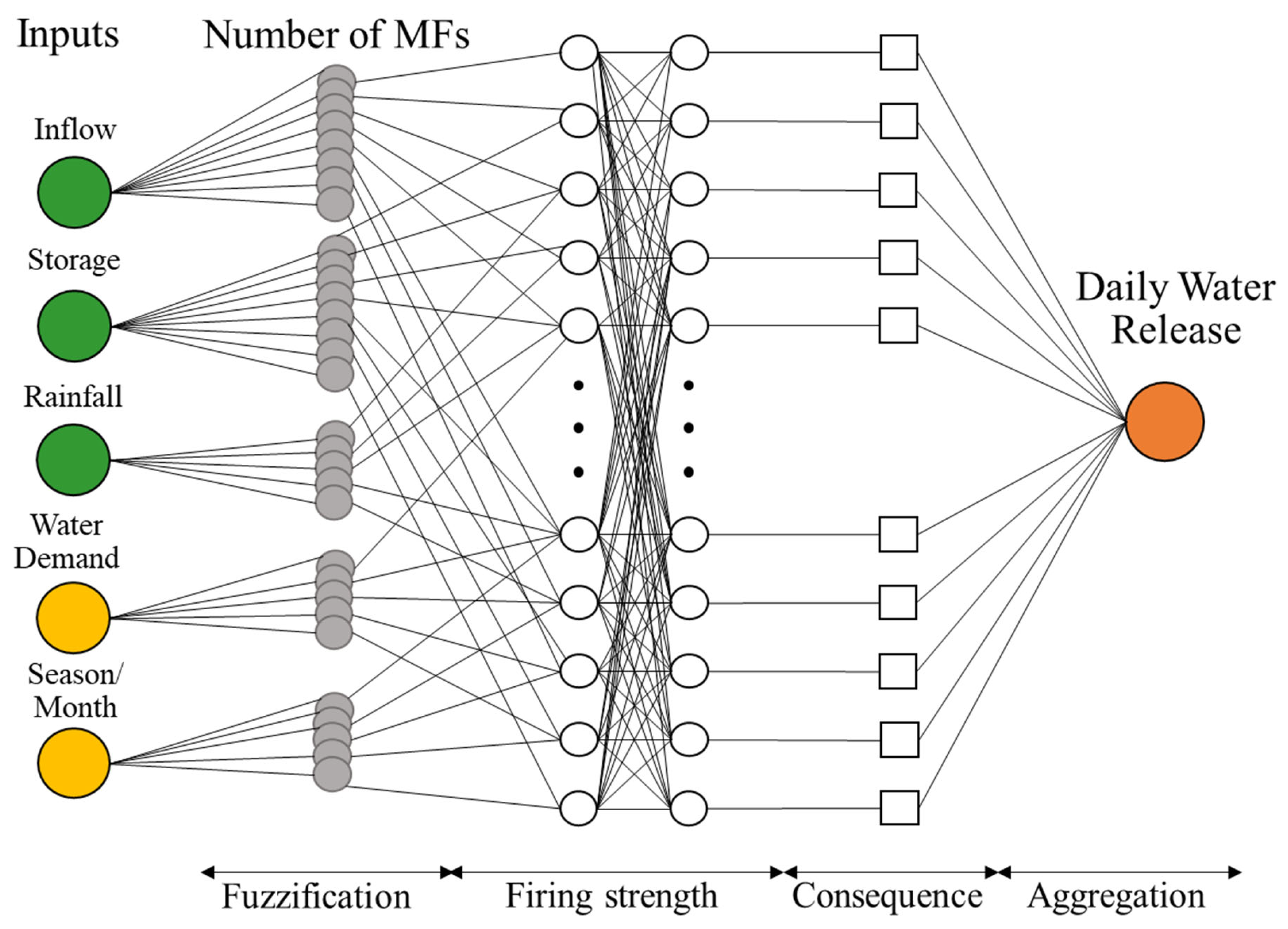
2.4. ANFIS Model Developments
2.4.1. ANFIS Model Construction
2.4.2. Dam Operation Policy
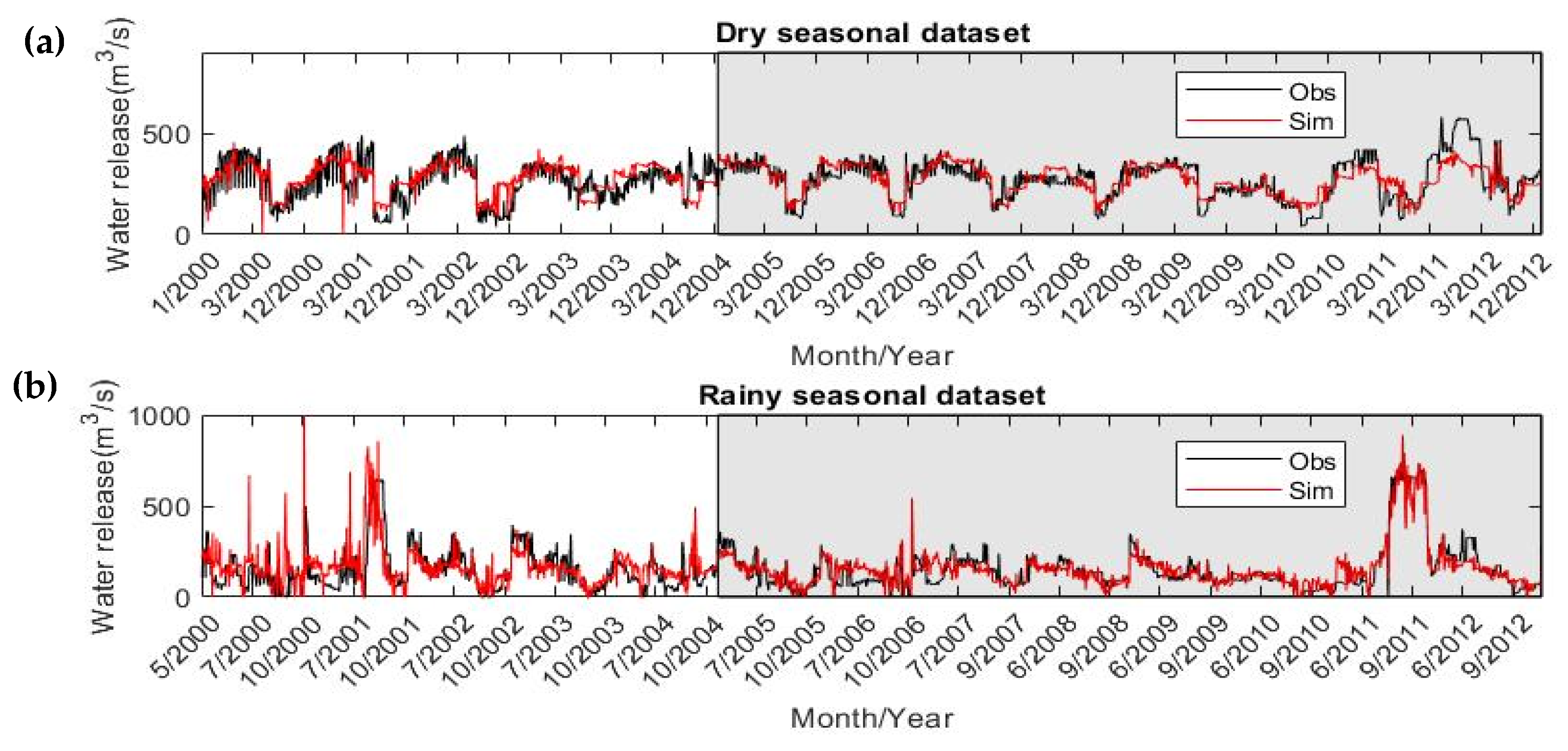
2.4.3. Model Performance
2.4.4. Additional Reservoir Operation for Flood and Drought Protections
3. Results and Discussion
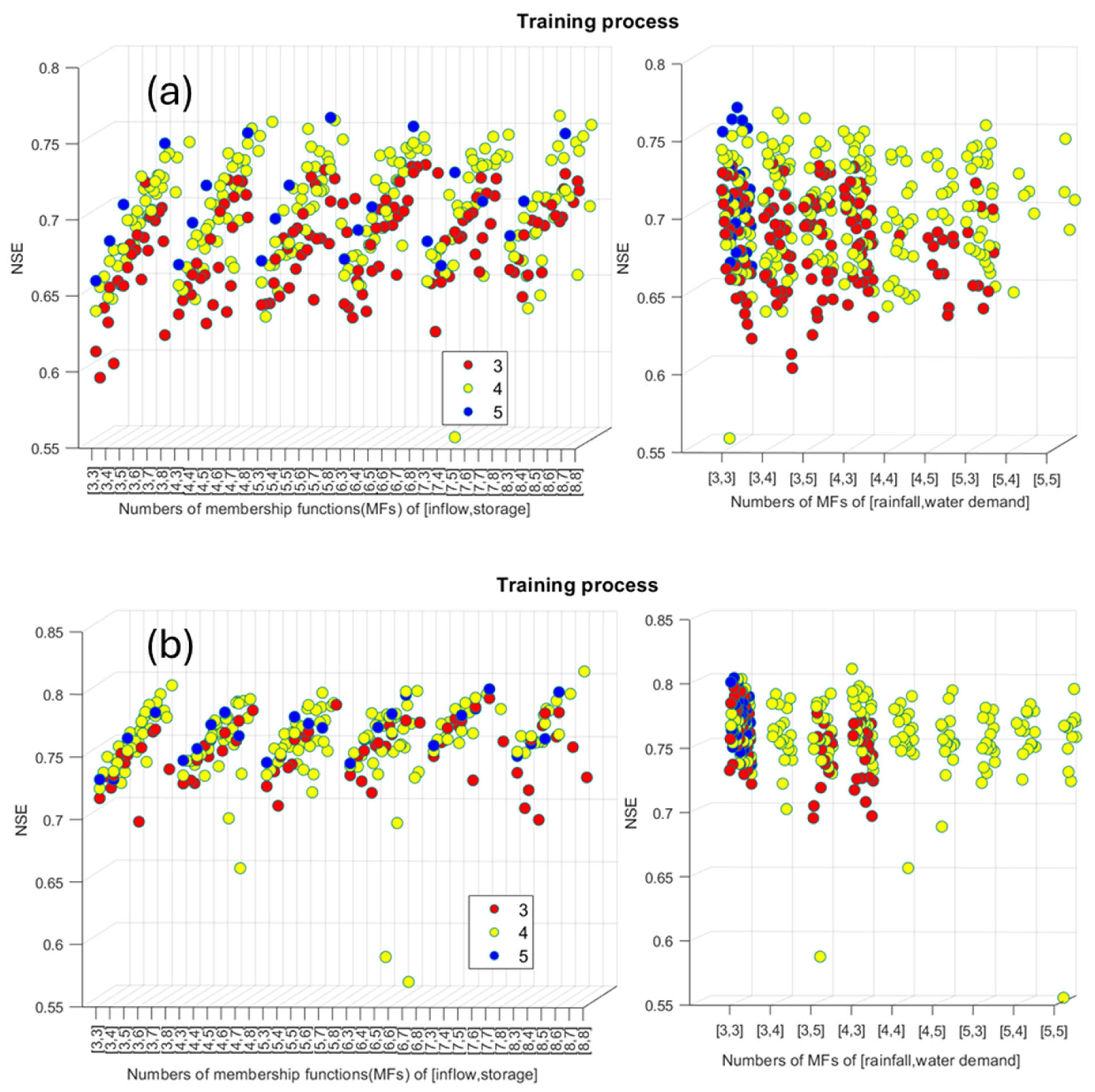
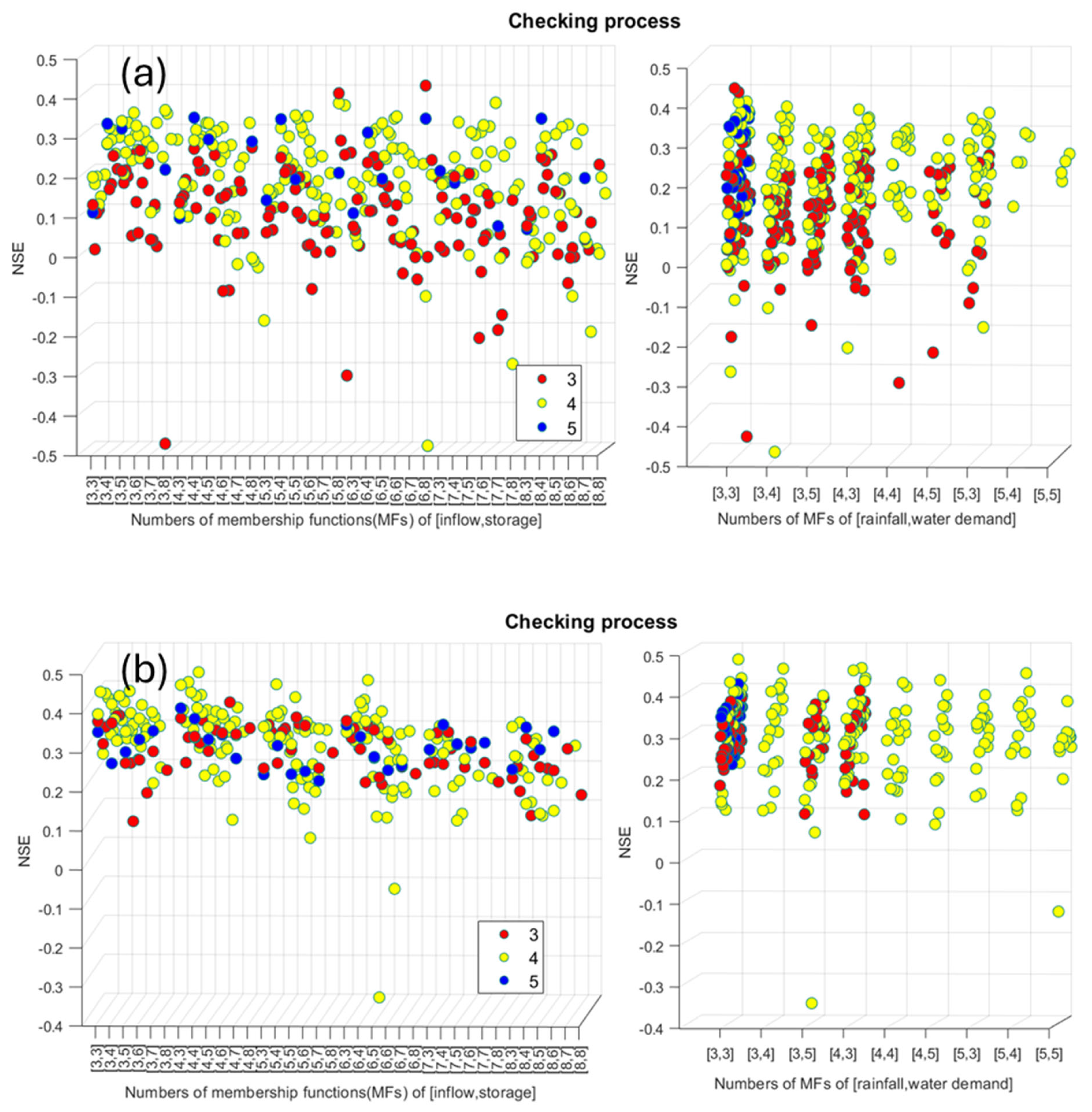
3.1. ANFIS Model Development
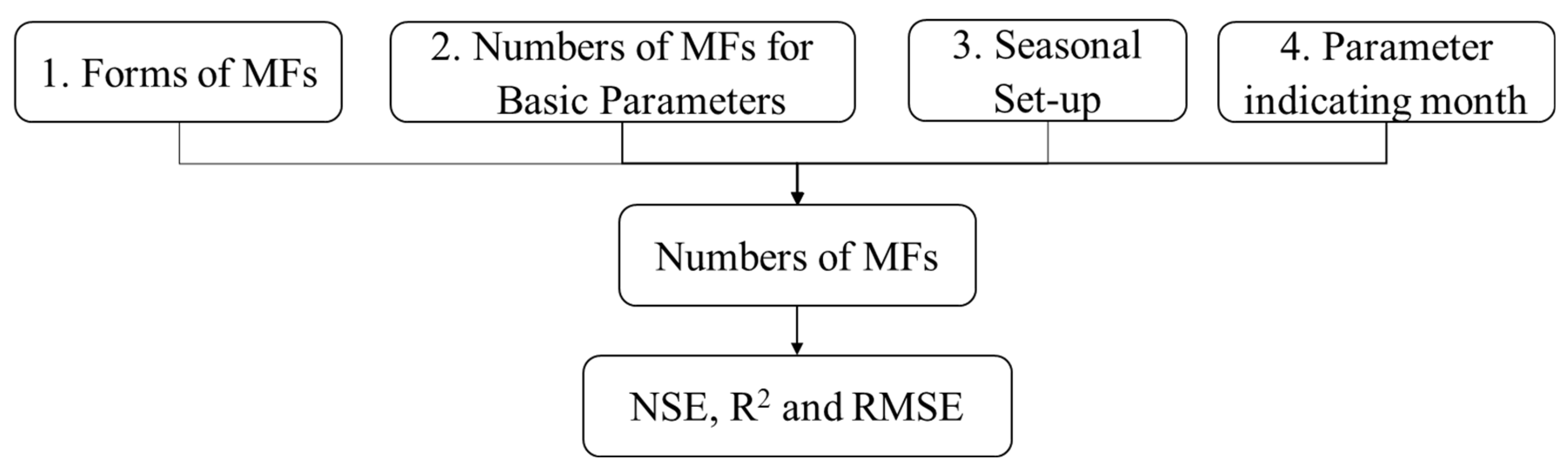
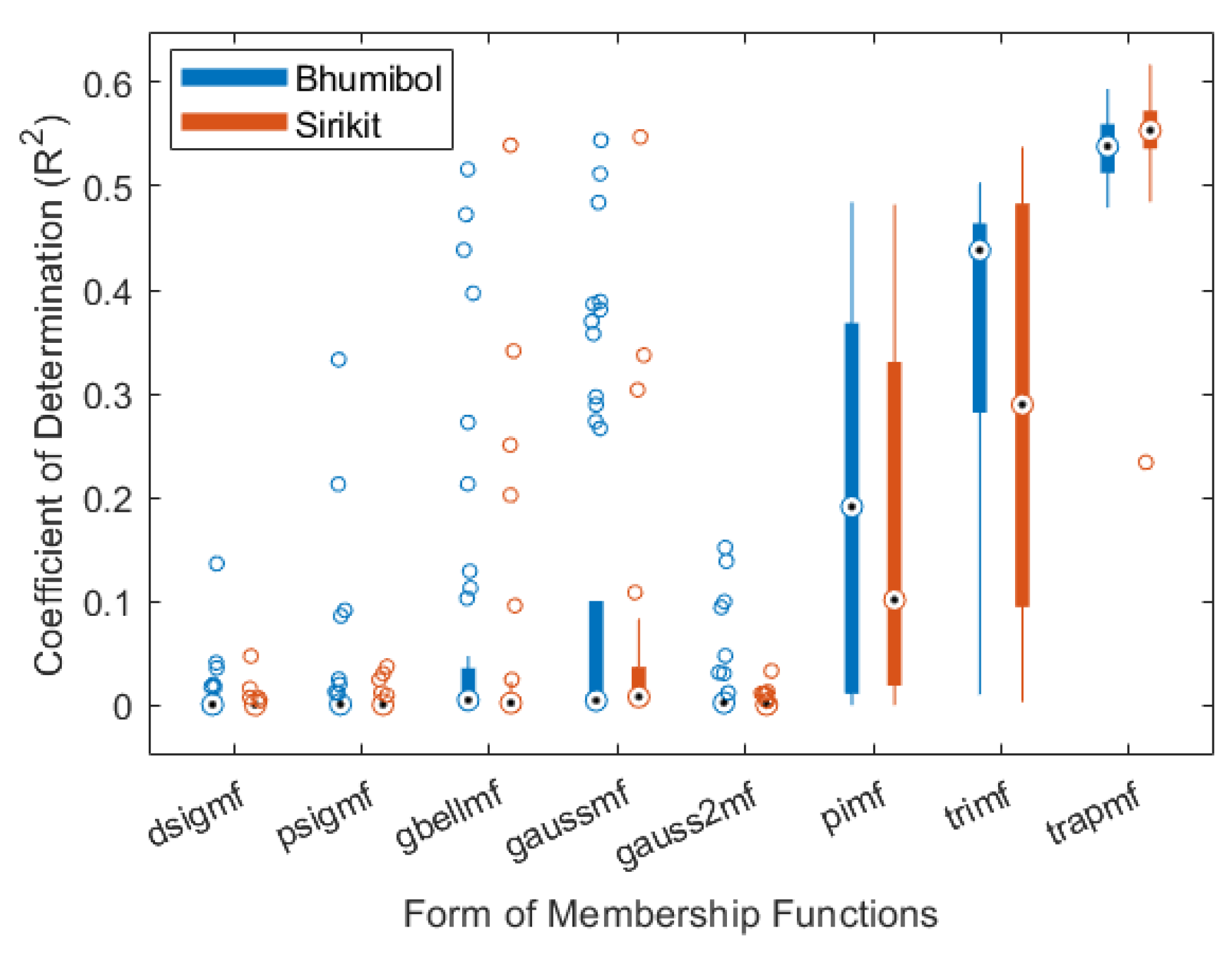
3.1.1. Selecting a Form of Membership Functions (MFs)
3.1.2. Impacts of Input Variables
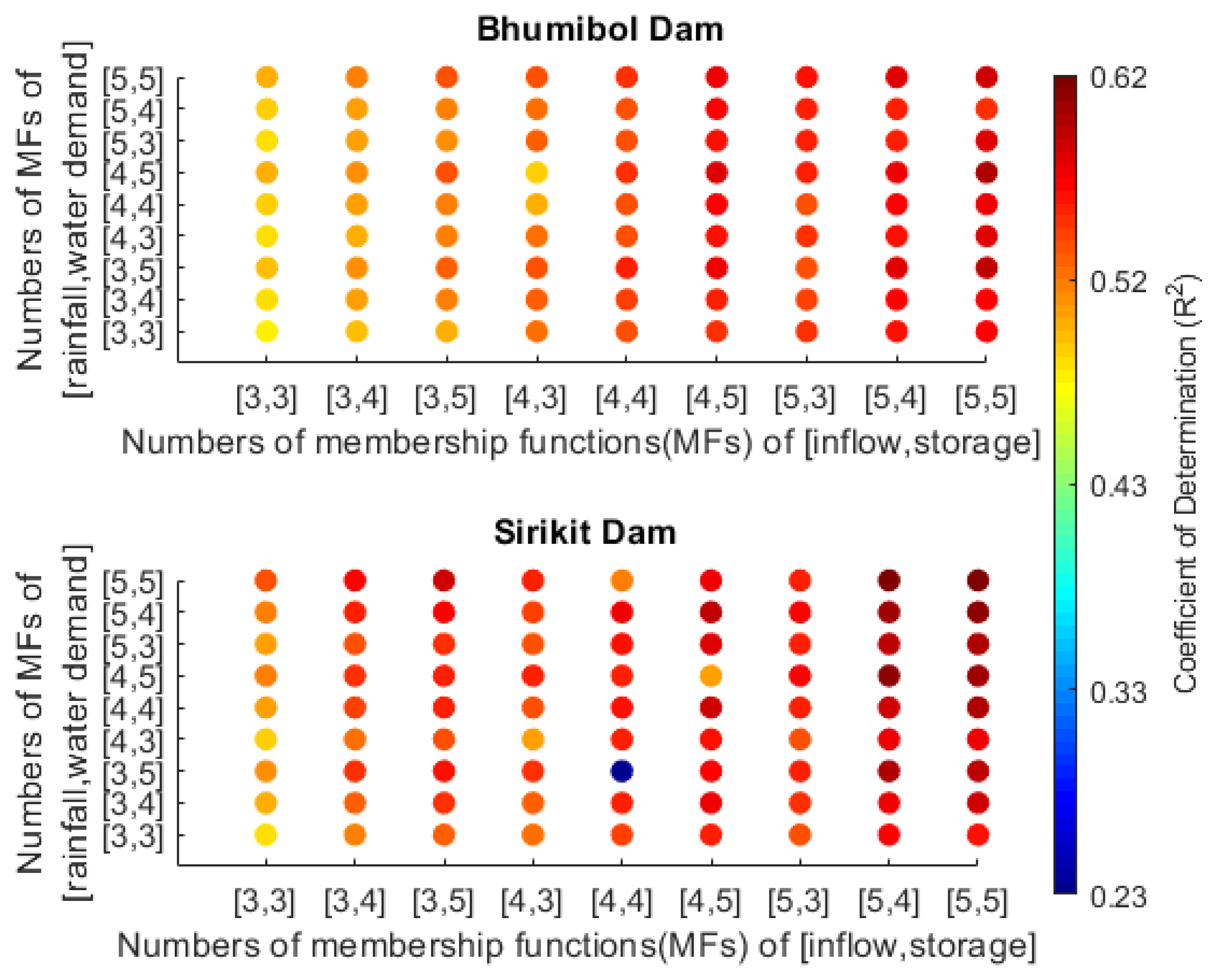
3.1.3. Impacts of Numbers of Membership Functions (MFs)
- Bhumibol Dam
- b.
- Sirikit Dam
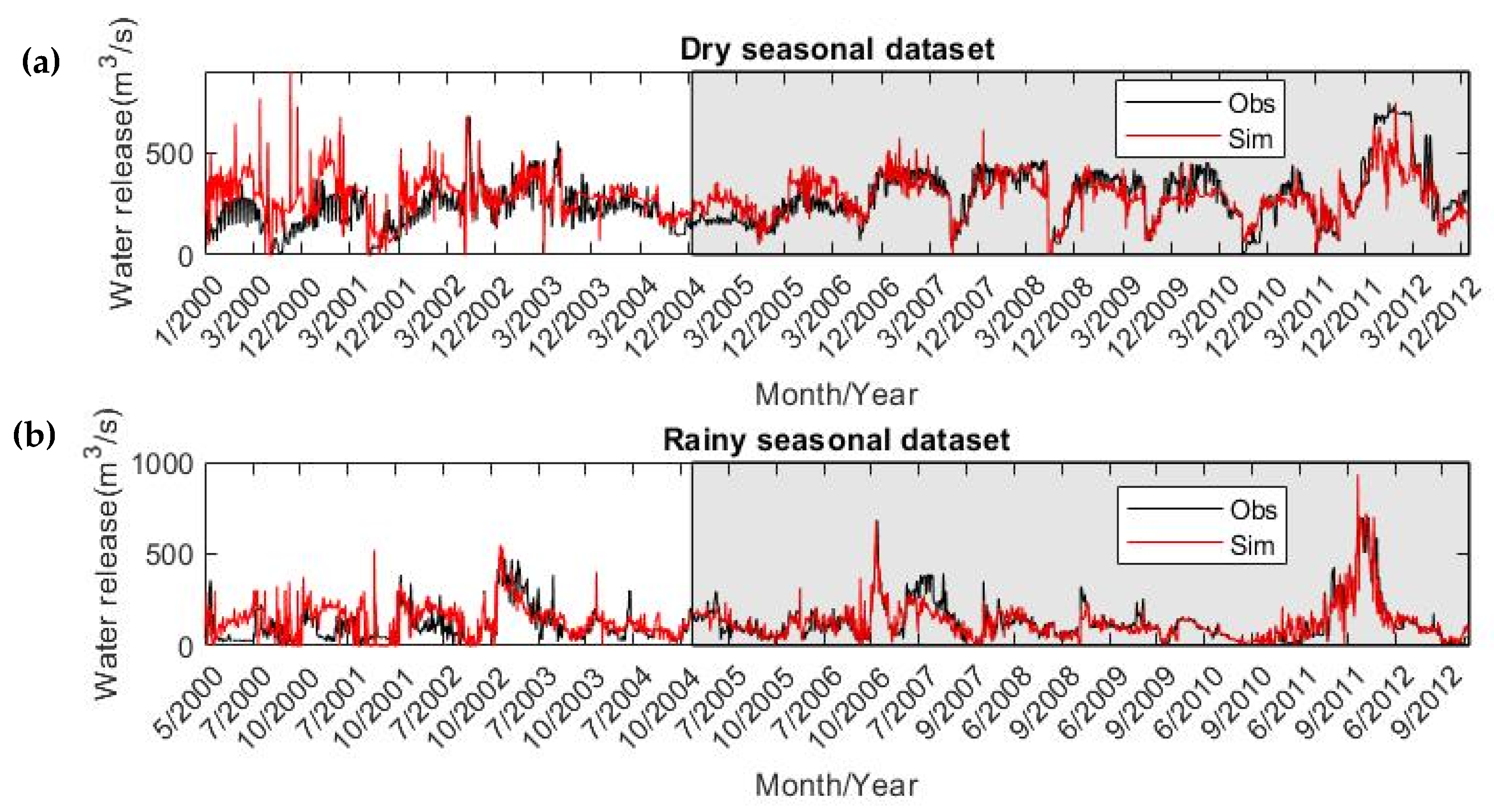
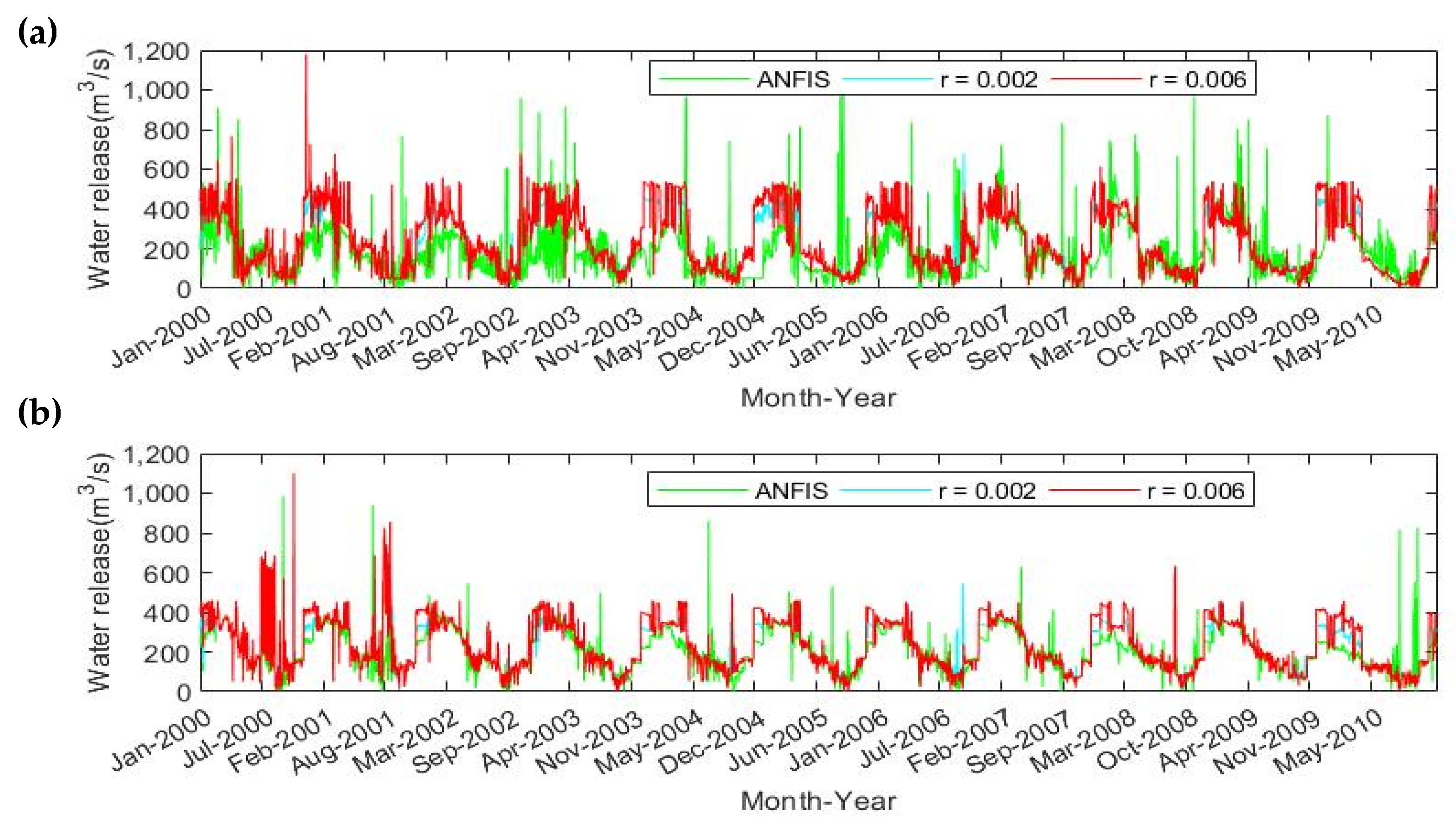
3.2. Additional Dam Operation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Promchote, P.; Wang, S.-Y.S.; Johnson, P.G. The 2011 great flood in Thailand: Climate diagnostics and implications from climate change. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kure, S.; Tebakari, T. Hydrological impact of regional climate change in the Chao Phraya River Basin, Thailand. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2012, 6, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Jain, S.K. Optimal operation of a multi-purpose reservoir using neuro-fuzzy technique. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothiprakash, V.; Magar, R.B. Multi-time-step ahead daily and hourly intermittent reservoir inflow prediction by artificial intelligent techniques using lumped and distributed data. J. Hydrol. 2012, 450, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.S. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullér, R. Introduction to Neuro-Fuzzy Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, F.J.; Chang, Y.T. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for prediction of water level in reservoir. Adv. Water Resour. 2006, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanasaki, N.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T. A reservoir operation scheme for global river routing models. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coerver, H.M.; Rutten, M.M.; Van De Giesen, N.C. Deduction of reservoir operating rules for application in global hydrological models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 831–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, D.P.; Van Beek, E. Water Resource Systems Planning and Management: An Introduction to Methods, Models, and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alquraish, M.M.; Abuhasel, K.A.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Khadr, M. A comparative analysis of Hidden Markov Model, hybrid Support Vector Machines, and hybrid Artificial Neural Fuzzy Inference System in reservoir inflow forecasting: Case study of the King Fahd Dam, Saudi Arabia. Water 2021, 13, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.; Cheng, L.; Li, G. The prediction of concrete dam displacement using Copula-PSO-ANFIS hybrid model. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 4335–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.A.; Zhouri, L.; Zerouali, B.; Wong, Y.J. Reducing uncertainty in future projections of potential evapotranspiration using a regional climate model and observational datasets: A case study of Egypt. J. Bulg. Geogr. Soc. 2024, 51, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneechot, L.; Wong, Y.J.; Try, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Bharambe, K.P.; Hanittinan, P.; Ram-Indra, T.; Usman, M. Evaluating the necessity of post-processing techniques on d4PDF data for extreme climate assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 102531–102546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, J.L.; Mailhot, A.; Brissette, F.; Caya, D. Role of natural climate variability in the detection of anthropogenic climate change signal for mean and extreme precipitation at local and regional scales. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4241–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Arumugasamy, S.K.; Chung, C.H.; Selvarajoo, A.; Sethu, V. Comparative study of artificial neural network (ANN), adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and multiple linear regression (MLR) for modeling of Cu (II) adsorption from aqueous solution using biochar derived from rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum) peel. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.J.; Shimizu, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Maneechot, L.; Bharambe, K.P.; Fong, C.S.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M. Application of artificial intelligence methods for monsoonal river classification in Selangor river basin, Malaysia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.L.; Jie, W.Y.; Arumugasamy, S.K. Dynamic simulation of airborne pollutant concentrations associated with the effect of climate change in Batu Muda region, Malaysia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, D.R. Handbook of Hydrology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chaowiwat, W. Adaptation of Reservoir Operation to Climate Change Conditions; Chulalongkorn University: Sirikit Dam, Thailand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rom Phy, S.; Try, S.; Wong, Y.J.; Ly, S.; Uk, S.; Sok, T.; Oeurng, C. Understanding climate change, dam impact, and flood management in the Mekong River Basin. In The Mekong Delta Environmental Research Guidebook; Park, E., Loc, H.H., Tran, D.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; Volume 2, pp. 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ndehedehe, C.E.; Farah, H.; Ahmad, B.; Wong, Y.; Adeyeri, O.E. Application of a Conceptual Hydrological Model for Streamflow Prediction Using Multi-Source Precipitation Products in a Semi-Arid River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Description | Unit | Bhumibol Dam | Sirikit Dam |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | - | 17°14′31″ N | 17°46′05″ N |
| Longitude | - | 98°58′31″ E | 100°33′15″ E |
| Drainage Area | km2 | 26,386 | 13,130 |
| Storage at Maximum High-water Level | million cubic meters (MCM) | 13,462 | 10,508 |
| Maximum High-water Level | m | 260 | 166 |
| Normal High-water Level | m | 260 | 162 |
| Minimum Water Level | m | 213 | 128 |
| Average Annual Inflow | million cubic meters (MCM) | 5704 (1965–2010) | 5638 (1974–2010) |
| Date of Completion of Construction Works | - | June 1964 | July 1974 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maneechot, L.; Chang, J.H.-W.; He, K.; Hu, M.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ilham, Z.; García Castro, C.; Wong, Y.J. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Optimization of Reservoir Operations Under Climate Variability in the Chao Phraya River Basin. Water 2025, 17, 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121740
Maneechot L, Chang JH-W, He K, Hu M, Wan-Mohtar WAAQI, Ilham Z, García Castro C, Wong YJ. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Optimization of Reservoir Operations Under Climate Variability in the Chao Phraya River Basin. Water. 2025; 17(12):1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121740
Chicago/Turabian StyleManeechot, Luksanaree, Jackson Hian-Wui Chang, Kai He, Maochuan Hu, Wan Abd Al Qadr Imad Wan-Mohtar, Zul Ilham, Carlos García Castro, and Yong Jie Wong. 2025. "Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Optimization of Reservoir Operations Under Climate Variability in the Chao Phraya River Basin" Water 17, no. 12: 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121740
APA StyleManeechot, L., Chang, J. H.-W., He, K., Hu, M., Wan-Mohtar, W. A. A. Q. I., Ilham, Z., García Castro, C., & Wong, Y. J. (2025). Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Optimization of Reservoir Operations Under Climate Variability in the Chao Phraya River Basin. Water, 17(12), 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121740










