Abstract
Sulfidation has gained increasing attention due to its merits to improve the structural-activity of nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) and thus enhance its reactivity toward contaminants. Few studies have been conducted to elucidate the correlation between the structural-activity and reactivity of nZVI, which is important for up-scaling such a decontamination strategy. Taking chromate (Cr(VI)) as the targeted contaminant, this study found that sulfidation enhanced the reactivity of nZVI toward Cr(VI) to varying extents, which was closely related to the degree and order of sulfidation. Particularly, the optimal rate constants of S-nZVI for Cr(VI) removal were 9.79 and 1.48 times higher than that of nZVI in the batch and column systems, respectively. In addition, this study suggested that sulfidation enhanced the electrical conductivity of nZVI by forming conductive iron sulfides (FeSx), while simultaneously reducing the particle aggregation and thus attenuating the settling rate of nZVI in water. More importantly, the reactivity of S-nZVI toward Cr(VI) exhibited negative correlations with its sedimentation activity and electrical conductivity. These relationships can be potentially used to predict the decontamination reactivity of S-nZVI if its sedimentation or conductivity activity was known in advance. Finally, this study clarified the sulfidation-induced improvement in reactivity of nZVI toward Cr(VI), which should be primarily associated with the improved reactive site of S-nZVI due to excellent dispersion and excellent conductivity due to FeSx introduction, ultimately facilitating the reduction of Cr(VI) by nZVI.
1. Introduction
Chromium (Cr) contamination persists as a critical environmental issue, particularly in soils and aquatic systems impacted by anthropogenic activities such as mining, metallurgy, electroplating, and pigment production [1,2]. Among the different valence states of Cr, hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) poses greater environmental risk due to its higher solubility, mobility, and carcinogenic potency than Cr in a low valence state, such as trivalent chromium (Cr(III)) [3,4,5]. Consequently, the reductive transformation of mobile Cr(VI) to immobile Cr(III) species has become a key strategy for the remediation of Cr(VI) contamination [6,7]. In recent years, nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) has emerged as a promising reducing agent owing to its high electron donor capacity and environmental compatibility [8,9,10]. However, the practical application of nZVI technology still faces two major challenges [11]. Firstly, nZVI particles tend to agglomerate due to their high surface energy and magnetic interactions, significantly reducing their mobility in groundwater environments [12,13]. Secondly, nZVI is prone to corrosion with water and oxygen, which not only inhibits its reactivity, but also diminishes reduction capacity toward Cr(VI) [14,15,16].
So far, researchers have developed various modification methods to address the issues of reactivity decreasing and/or particle agglomeration in the practical application of nZVI [17,18,19]. For instance, bimetallic doping (e.g., Pd, Ni) could accelerate the electron transfer of nZVI through the formation of a galvanic cell effect, thereby enhancing the reactivity of nZVI [20,21]. In terms of improving the dispersion of nZVI, surface dispersants such as chitosan and cellulose could effectively inhibit the agglomeration of the iron nanoparticles, thus increasing their mobility in groundwater environments [22,23]. Notably, the modification of nZVI by sulfidation could form an FeSx layer on the surface of nZVI, which not only significantly sustained the reactivity of nZVI, but also improved the electron conductivity of nZVI toward Cr(VI) [24,25,26,27]. Particularly, the sulfidation of nZVI (S-nZVI) also significantly enhanced its dispersion and stability [28,29], providing a promising modification approach for groundwater remediation by nZVI technology.
Generally, the synthesis of S-nZVI via one-step (S-nZVIone) facilitated the uniform distribution of FeSx in the iron nanoparticles through concurrent Fe(II)/Fe(III) reduction and S(−II) incorporation [30,31]. The synthesis of S-nZVI via two-step (S-nZVItwo) enabled the distribution of FeSx on the surface of nZVI through post-sulfidation [32]. The spatial distribution heterogeneity of FeSx derived from different sulfidation methods (one-step vs. two-step) endowed nZVI with different electrical conductivity and particle dispersion properties, which ultimately affected the reactivity and reducing efficiency of nZVI for Cr(VI) removal. Apart from the order of sulfidation, the S/Fe molar ratio (i.e., sulfidation degree) had a significant impact on the structural-activity and reactivity of nZVI [33,34]. For example, when the S/Fe molar ratio was below 0.1, the formed FeSx layer was thin, which could improve the conductivity and reactivity but limited the dispersion of nZVI [35]. However, when the S/Fe molar ratio exceeded 0.2, even if the dispersion of nZVI was improved, too much FeSx might cover the reactive sites [36]. As such, the structural-activity of S-nZVI and its reactivity toward contaminants should be closely related to their synthesis methods. Nevertheless, the influences of sulfidation with different orders and degrees on the structural-activity of S-nZVI and its reactivity are not yet fully understood. Moreover, the correlation between the reactivity and structural-activity of S-nZVI needs to be illustrated.
Accordingly, the objectives of this study are to: synthesize and characterize the S-nZVI with different orders and degrees of sulfidation; investigate the influence of sulfidation on the reactivity, sedimentation activity, and electrical conductivity of nZVI; establish correlation analysis to explore the relationship between the decontamination reactivity and structural-activity by S-nZVI; and elucidate the interfacial redox reaction of S-nZVI with Cr(VI). In general, the findings of this study will provide important theoretical foundations and methodological guidance for groundwater remediation by nZVI-based technology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials Synthesis
All chemical reagents, including ferric chloride (FeCl3), sodium borohydride (NaBH4), and sodium sulfide nonahydrate (Na2S·9H2O), were of analytical grade and purchased from Aladdin Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Ultrapure water (18.2 MΩ·cm) from a Milli-Q Advantage A10 system (Merck Millipore, Nanjing, China) was used for solution preparation. The synthesis procedures for the preparation of nZVI and S-nZVI were carried out according to previously established protocols as documented in the literature [37,38]. Particularly, the S-nZVI was synthesized via one-step and two-step protocols, often referred to as S-nZVIone-X and S-nZVItwo-X, respectively, where X is the S/Fe molar ratio. After synthesis, the iron nanoparticles were subjected to a purification process involving three cycles of ethanol washing via centrifugation. The purified nanoparticles were then stored in an ethanol medium to prevent oxidation, thereby maintaining their reactivity and structural integrity for subsequent applications.
2.2. Experimental Sections
To investigate the decontamination reactivity in a batch system, 0.05 g of iron nanoparticles were dried by the vacuum dryer and then added to 0.5 L of reaction solution containing 8.0 mg Cr(VI). The initial pH (pHini) of the reaction solutions was adjusted to 5.0 with NaOH and H2SO4 without buffers. All decontamination experiments were mixed by a mechanical stirrer (HD, 2004 W, Shanghai Silo Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) at 400 rpm. The temperature of the reaction solution was controlled at 25.0 °C using a water bath (HH-1, Jiaxing Junshi Electronics Co., Jiaxing, China). Unless stated otherwise, 0.2 mM Na2SO4 was employed as the background ion in the batch systems. To test the sedimentation activity, 5.00 mg of iron nanoparticles was added to a 50 mL volumetric flask, followed by sonication (CR-020S, Shenzhen Chunlin Cleaning Equipment Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Then, 4 mL of the suspension was added to a cuvette and the absorbance at 508 nm was recorded using a UV spectrophotometer (UV-9600, Beijing Ruili Analytical Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). To test the performance of iron nanoparticles for Cr(VI) removal in a column system, the material used as the reactive layer in the column was nZVI or S-nZVItwo-0.32. A column with an inner diameter of 2 cm and a height of 30 cm was packed with 30–50 mesh quartz sand. Before the column test, the column was pre-saturated with 0.2 g/L iron nanoparticles and 0.2 mM Na2SO4 solution (pH 5.0). Then, Cr(VI) solution (10.0 mg/L) was introduced at a constant flow rate of 0.5 mL/min, yielding a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 60 min. All kinetic assays were repeated at least twice, the data points in the graphs are mean values, and the error bars indicate standard deviations.
2.3. Chemical Analysis and Characterizations
For the analysis of Cr(VI) in water, 5 mL of reaction solution was collected from the decontamination test at given time intervals. Then, it was filtered through a 0.22 µm membrane filter. Subsequently, the sample was acidified and analyzed by diphenylcarbazide colorimetry with a UV–visible spectrophotometer at 540 nm wavelength. For the structural features of iron nanoparticles, they were investigated using transmission electron microscopy (TEM, FEI Tecnai F20, Hillsboro, OR, USA) coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) for elemental mapping. In addition, the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Thermo Scientific K-Alpha, Shanghai, China) with argon ion sputtering capability was employed to analyze elemental oxidation states and their depth-dependent chemical profiles. For the electrical conductivity of iron nanoparticles, they were calculated by electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) using a CHI660D electrochemical workstation (CH Instruments, Shanghai, China) in a three-electrode configuration, which was equipped with a clamping electrode (working electrode), a platinum wire counter electrode, and a Ag/AgCl reference electrode. Prior to testing, 5 mg of iron nanoparticles (nZVI or S-nZVI) was uniformly deposited on the pretreated nickel foam (1 cm × 1 cm) through the drop-casting method, followed by 1 h vacuum drying to ensure material adhesion. The electrolyte composition contained 0.2 Mm Na2SO4 and the pHini was adjusted to 5.0 with NaOH and H2SO4 without the buffers. The EIS test was carried out at an amplitude of 0.005 V in the frequency range of 12,000 Hz to 0.01 Hz. As for the calculation of the interfacial charge transfer resistances of iron nanoparticles, they were fitted via an equivalent circuit (EC) model using the method previously developed [39,40] and implemented in the workstation software. The results (R or Rct, ohm) derived from this EC model to the EIS data were considered as the charge-transfer resistance for reaction at the interface of nZVI-based materials.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations of nZVI and S-nZVI
Figure 1a clearly reveals that the spherical iron nanoparticles aggregate into irregular chains due to the combined effects of magnetic and electrostatic forces. This chain aggregation can significantly influence the mobility of the iron nanoparticles in aqueous environments, thereby impacting their decontamination reactivity. In addition, Figure 1b demonstrates a distinct contrast between the core and the periphery of the nanoparticles, with the core region appearing brighter and the surrounding area darker. This contrast suggests a notable difference in elemental composition and distribution between the core and the shell, confirming the presence of a typical ‘core-shell’ structure. Elemental mappings in Figure 1c–e further support that the nanoparticles exhibit an ‘Fe0 core–Fe (hydr)oxide shell’ configuration. This structure arises from the spontaneous oxidation of Fe0 in environmental conditions, leading to the formation of an iron oxide layer encapsulating the Fe0 core [10,34]. The ‘core-shell’ structure not only alters the availability of active sites on the surface of nZVI, but also impedes electron transfer capabilities, ultimately diminishing the reactivity of nZVI toward Cr(VI).
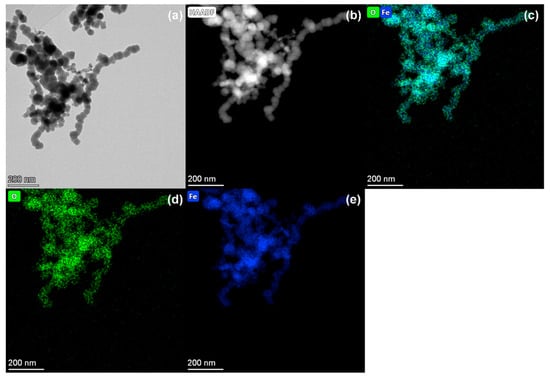
Figure 1.
TEM image (a), HAADF image (b), and EDS mappings (c–e) of nZVI: Fe + O color overlay (c), O mapping (d), and Fe mapping (e).
Figure 2 highlights the distinct morphological contrasts between S-nZVIone and S-nZVItwo. As shown in Figure 2a, the S-nZVIone exhibits fragmented nanoparticles with localized lamellar edge structures, aligning with prior studies on surface restructuring caused by one-step sulfidation [10,30]. In contrast, while the S-nZVItwo partially retains the chain-like arrangement of pristine nZVI, its intrinsic chain structure is notably disrupted by two-step sulfidation (Figure 2f). This structural divergence underscores the critical influence of sulfidation orders (one-step vs. two-step) on nanoparticle organization. The elemental mappings in Figure 2 further reveal homogeneous S distribution within both S-nZVIone and S-nZVItwo, confirming the successful formation of FeSx layers during sulfidation. As FeSx exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to iron (hydr)oxides [29], this phase likely enhances electron transfer from the Fe0 core of S-nZVI to its shell, thereby amplifying the redox reactivity toward Cr(VI). It should be emphasized that the surface O signal of S-nZVItwo (Figure 2i) is significantly stronger than that of S-nZVIone (Figure 2d). This surface iron (hydr)oxide likely weakens electron transfer of S-nZVItwo, suggesting that the S-nZVIone with optimized conductivity may be beneficial for the reductive removal of Cr(VI). Together, these findings suggest that the sulfidation orders (one-step versus two-step) affect the structural-activity of nZVI and thus the reactivity towards Cr(VI). Therefore, the following section will systematically investigate the effect of sulfidation on the structural-activity of nZVI and its reactivity toward Cr(VI) in water.
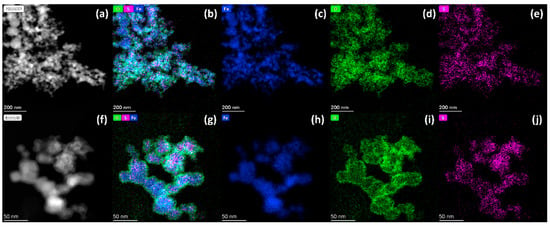
Figure 2.
TEM−EDS elemental mappings of S-nZVIone (a–e) and S-nZVItwo (f–j) with S/Fe molar ratio of 0.16: HAADF images (a,f), Fe + O + S color overlays (b,g), Fe mappings (c,h), O mappings (d,i), and S mappings (e,j).
3.2. Effect of Sulfidation on the Reactivity and Structural-Activity of nZVI
Figure 3a,b demonstrates that both sulfidation methods and sulfidation degrees significantly improved the Cr(VI) removal by nZVI. Notably, the pristine nZVI exhibits limited removal capacity, achieving only 13.2% Cr(VI) elimination after 90 min of reaction. In contrast, approximately 45.0–59.9% and 33.3–39.0% of Cr(VI) can be removed by S-nZVIone and S-nZVItwo, respectively. Furthermore, the S/Fe molar ratio exhibits distinct impacts on the reactivity of nZVI. For S-nZVIone, a monotonic increase in Cr(VI) removal efficiency is observed as the S/Fe molar ratio escalated from 0.08 to 0.32. On the contrary, as shown in Figure 3b, S-nZVItwo illustrates an eruptive trend. The reactivity of S-nZVItwo toward Cr(VI) is firstly increased and then decreased with increasing the S/Fe molar ratio from 0 to 0.32. Even so, the minimum removal efficiency of Cr(VI) by S-nZVItwo at the S/Fe molar ratio of 0.32 (33%) is still significantly higher than that of nZVI (13.2%). Interestingly, the superior performance of one-step sulfidation over the two-step sulfidation in Cr(VI) removal in the comparative analysis should be emphasized. In addition, the degree of sulfidation via two-step has a minor effect on nZVI reactivity compared to one-step. These differential responses further highlight the critical influence of sulfidation methods on the reactivity of iron nanoparticles.
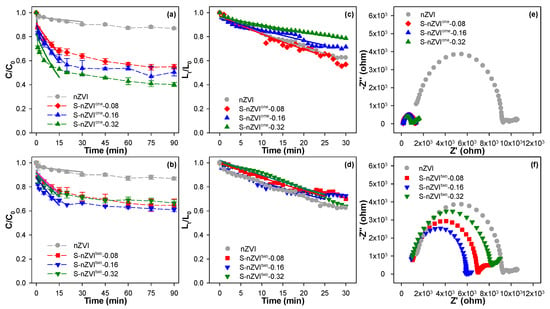
Figure 3.
The kinetics of Cr(VI) removal (a,b) and sedimentation (c,d) by nZVI and S-nZVI, as well as their electrochemical impedance spectra (e,f). Reaction conditions: [nZVI or S-nZVI] = 0.1 g/L, [Cr(VI)]0 = 8.0 mg/L (without in Figure (c–f)), [Na2SO4] = 0.2 mM, pHini = 5.0, T = 25 °C.
A low settling of iron nanoparticle facilitates their migration to the target contaminated area and thus reaction with contaminants in practical groundwater applications. As such, this study further investigated the colloidal stability through sedimentation kinetic monitoring, as illustrated in Figure 3c,d. The experimental results reveal that both sulfidation approaches significantly influence the settling behavior of nZVI. Notably, the two-step sulfidation approach exhibited minimal impact on nZVI sedimentation, whereas the one-step sulfidation method demonstrated remarkable suppression of nanoparticle settling rates. Furthermore, increasing the S/Fe molar ratio from 0.08 to 0.32 in S-nZVIone reduced its aqueous sedimentation efficiency from 43.0% to 21.3%. The superior colloidal dispersion of one-step sulfidated nanoparticles primarily stems from the elimination of chain-like aggregation structures in S-nZVI (Figure 2). This phenomenon should be attributed to the enhanced interparticle electrostatic repulsion induced by FeSx coatings on the surface of S-nZVIone, thus ultimately improving the dispersion of S-nZVIone.
Furthermore, sulfidation treatment can effectively enhance the charge transfer capability of nZVI through the incorporation of FeSx phases, which exhibit superior electrical conductivity compared to iron (hydr)oxides. As illustrated in Figure 3e,f, S-nZVIone demonstrates significantly enhanced conductivity relative to S-nZVItwo. Specifically, with increasing S/Fe molar ratios from 0.08 to 0.32, the interfacial charge transfer resistance of S-nZVIone shows a progressive decline from 1026.0 Ω to 688.7 Ω. In contrast, S-nZVItwo exhibits a nonlinear variation in interfacial resistance, initially decreasing from 6146.0 Ω to 5257.0 Ω before rising markedly to 7173.0 Ω within the same S/Fe ratio range. This divergent conductive behavior can be primarily attributed to distinct spatial distribution patterns of FeSx phases within the S-nZVI. In contrast to the one-step sulfidation, the two-step protocol does not significantly affect the chain structure and sedimentation behavior of nZVI, but improves the electrical conductivity of nZVI to a large extent. This conductivity enhancement should be attributed to the establishment of electron-conducting pathways between Fe0 cores and FeSx shells, which facilitated the interfacial electron flux to Cr(VI). Consequently, the higher reactivity of S-nZVItwo compared to that of nZVI predominantly stems from the augmented electron transfer rather than structural or colloidal modifications. It should be additionally noted that the positive effect of the sulfidation via one-step also involves the modulation of the nZVI sedimentation characteristics to some extent. This further promotes the positive contact between nZVI and Cr(VI) in water, thus facilitating the removal of Cr(VI) by S-nZVIone-step.
3.3. Correlation Analysis of the Reactivity and Structural-Activity of S-nZVI
To facilitate comparative analysis of the decontamination reactivity and structural-activity of iron nanoparticles, the reaction data in Figure 2a–d were modeled using pseudo-first-order kinetic equations (Equations (1) and (2)).
where C0 (mg·L−1) is the concentration of Cr(VI) in solution at time t, L is the solution absorbance at time t, and kobs-Cr (min−1) and kobs-Sed. (min−1) represent the apparent rate constants for Cr(VI) removal and nanoparticle settling in aqueous solution, respectively. In addition, to better elucidate the reaction kinetics, this work also used some other kinetic models including zero-order and second-order kinetic models to estimate the kinetic behaviors of nZVI-based materials. Unfortunately, their fitting results are not satisfactory. The first-order kinetic model was statistically validated by achieving a high-fitting R2 and low standard errors, as shown in Table S1 of SI. Figure 4a summarizes the reactivity, sedimentation rate, and electrochemical impedance values of iron-based nanoparticles. In terms of reactivity, S-nZVI demonstrated significantly enhanced performance, exhibiting 3.69 to 9.79 times higher reactivity than that of nZVI. Conversely, regarding sedimentation activity, nZVI showed 0.9 to 2.1 times greater than its sulfidated counterpart. Notably, S-nZVIone-0.32 demonstrates the most superior comprehensive performance, exhibiting the slowest sedimentation rate constant (0.0072 min−1), the lowest impedance value (688.7 Ω), and concurrently the fastest Cr(VI) removal rate constant (0.0382 min−1). Interestingly, a significant inverse correlation can be additionally found between the kinetic parameters, particularly between the reactivity (kobs-Cr) and the electrochemical impedance (R) of the iron nanoparticles.
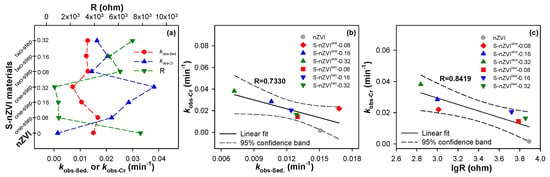
Figure 4.
Summary of the activities of S-nZVI samples (a) and their relationships of the rates for Cr(VI) removal by S-nZVI with their sedimentation rates (b) and resistance values (c).
To further elucidate the relationships between the activity parameters of iron-based nanoparticles, we conducted comprehensive correlation analyses between the Cr(VI) removal rate constant and the sedimentation rate constant, as well as between the Cr(VI) removal rate constant and the electrochemical impedance. The results revealed a negative correlation (R = 0.7330) between the kobs-Cr and the kobs-Sed., as observed in Figure 4b. This correlation can be attributed to the increase in surface-active sites of the iron nanoparticles due to dispersion modification, which enhances the mass transfer of Cr(VI) toward the nanoparticles. In contrast, as shown in Figure 4c, the negative correlation between the kobs-Cr and the lgR of the iron nanoparticles was more pronounced (R = 0.8419). This is primarily due to the excellent electron-mediating capability of FeSx, which facilitates electron transfer from the iron nanoparticles to the Cr(VI), ultimately promoting the reductive removal of Cr(VI). In summary, sulfidation not only modulates the sedimentation of nZVI, but also improves its electrical conductivity, ultimately significantly improving the reactivity of nZVI toward target pollutants. As documented Table S2, these two validated relationships can be potentially used to predict the decontamination reactivity of S-nZVI if its sedimentation or conductivity activity is known in advance.
3.4. Enhanced Redox Reaction of nZVI with Cr(VI) by Sulfidation
To manifest the impact of sulfidation on the mass transfer behavior between nZVI and Cr(VI), we employed TEM–EDS elemental mapping to characterize the Cr(VI) immobilization by iron nanoparticles after 90 min in a batch reaction system. As illustrated in Figure S1, the Cr signal intensity in S-nZVI was more significant than that in nZVI. Moreover, to illustrate the effect of sulfidation on the interfacial electron transfer between nZVI and Cr(VI), we conducted an XPS analysis of Cr speciation and content in nZVI and S-nZVI. It can be found in Figure 5a–c that, at 5 nm below the nanoparticle surface, the Cr(III) fractions were 71.21% and 75.04% for nZVI and S-nZVI, respectively, while at 20 nm depth, these values increased to 78.79% and 84.69%, respectively. The Cr(III) content in the S-nZVI system is consistently higher, especially at deeper depths. This suggests that the introduction of FeSx significantly enhances the electrical conductivity of nZVI, thus facilitating a more efficient reduction of Cr(VI). Furthermore, XPS analysis of sulfur speciation in S-nZVI before and after the reaction provided additional mechanistic insights (Figure 5d–f). The pre-reaction S-nZVI predominantly contained S2− species (72.72% at 5 nm depth and 92.81% at 20 nm depth). Post-reaction analysis showed a substantial decrease in S2− content to 36.53% and 50.84% at 5 nm and 20 nm depths, respectively.
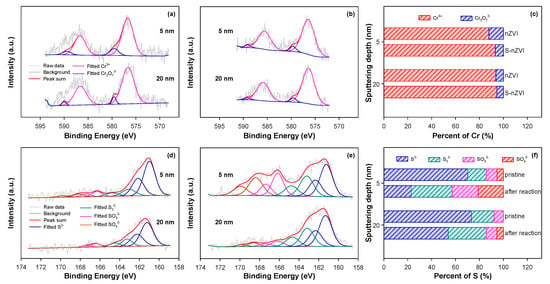
Figure 5.
Cr 2p XPS depth profiling spectra of nZVI (a), S-nZVIone-0.32 (b), and their relative contents of Cr species in subshells at 5 nm and 20 nm (c), along with the S 2p XPS depth profiling spectra of S-nZVIone-0.32 before (d) and after (e) reaction with Cr(VI), as well as the relative contents of S species in the subshell of S-nZVIone at 5 nm and 20 nm (f). Reaction conditions: [nZVI or S-nZVI] = 0.1 g/L, S/Fe molar ratio = 0.32, [Cr(VI)]0 = 8.0 mg/L, [Na2SO4] = 0.2 mM, pHini = 5.0, reaction time = 90 min, T = 25 °C.
Accordingly, the improved reactivity of S-nZVI toward Cr(VI) can be attributed to six primary mechanisms: (1) sulfidation effectively improved the dispersion of iron nanoparticles, thereby facilitating interfacial reactions between nZVI and Cr(VI); (2) sulfidation favored the electron transfer of nZVI toward Cr(VI) and thus enhanced the reduction of Cr(VI) into Cr(III); (3) the redox reactions of S2−/S22− with Cr(VI) can be additionally beneficial for the reduction removal of Cr(VI) by S-nZVI in water [10,29]. In general, the findings in this work corroborated the correlations between the structural-activity of sulfidated iron nanoparticles and their reactivity toward Cr(VI), providing experimental evidence for understanding the gap between the performances in laboratory and field-scale scenarios.
Moreover, a column experiment in Figure 6 further demonstrated that S-nZVI achieved a migration distance of 0.96 m in porous media, representing a 48% enhancement (1.48-fold) compared to pristine nZVI. This should be mainly attributed to the sulfur modification-induced suppression of particle agglomeration and improvement of surface charge stability. Meanwhile, the Fe retention capacity in the S-nZVI system exhibited a 32% increase with penetration depth progression (Figure 6b), indicating superior media permeability. In addition, as shown in Figure S2, the dispersion of S-nZVI in porous media was also more significant than that of nZVI in porous media. Correspondingly, a 1.40-fold improvement in Cr(VI) removal capacity for S-nZVI compared to nZVI was found in Figure 6c. Obviously, the migration- or dispersion-activity of nZVI and S-nZVI are also related to their reactivity toward Cr(VI) in the column-scale experiment.
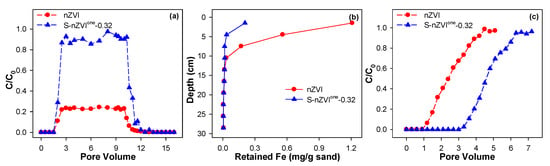
Figure 6.
Effect of sulfidation on the breakthrough curve (a) of nZVI and its retention profile (b), along with the removal kinetics (c) of Cr(VI) by nZVI and S-nZVIone-0.32 in porous media water. Reaction conditions: [nZVI or S-nZVI]Input = 0.2 g/L, [Cr(VI)]0 = 10.0 mg/L, Quartz sand mesh = 30–50 mesh, [Na2SO4] = 0.2 mM, pHini = 5.0, T = 25 °C.
4. Conclusions
A comprehensive understanding of the structural-activity of nZVI is crucial for predicting its reactivity and developing an effective strategy. This study systematically compared and optimized the reactivity of S-nZVI through controlled sulfidation orders and degrees. Among the synthesized materials, S-nZVIone-0.32 demonstrated exceptional reactivity toward Cr(VI), exhibiting 9.79- and 1.48-fold higher reactivity than that of pristine nZVI in batch and column systems, respectively. Through TEM–EDS elemental mapping and XPS analysis, the fundamental mechanisms by which sulfidation enhances mass and electron transfer processes between nZVI and Cr(VI) were elucidated. This work further revealed significant negative correlations between the Cr(VI) removal rate and both the sedimentation activity and electrical conductivity. Building upon these findings, this work developed a novel evaluation framework based on the structural-activity and reactivity of S-nZVI. In general, the results of this study not only validate the effectiveness of sulfidation as a performance enhancement strategy, but also provide insight for the practical implementation of S-nZVI in environmental remediation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17121737/s1, Figure S1: TEM−EDS elemental mappings of nZVI and S-nZVIone-0.32 after their reaction with Cr(VI) in the batch systems. Figure S2: SEM images of nZVI and S-nZVIone-0.32 after their reaction with Cr(VI) in the column systems. Table S1: Parameters of zero-order and first-order models for fitting the removal kinetics of Cr(VI) by nZVI-based materials. Table S2: Parameters for the correlation analysis of the reactivity and structural-activity of S-nZVI.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.; methodology, W.W.; software, Z.F. and Z.B.; validation, J.L.; formal analysis, M.Z.; investigation, M.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.L.; visualization, M.Z.; supervision, M.Z.; funding acquisition, M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Special Funding for Scientific Research of Suzhou Polytechnic Institute of Agriculture Ph.D. Enhancement Program (No. BS [2022]24) and the Special Funding for Suzhou Polytechnic Institute of Agriculture Innovative Research Team (CXTD202407).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to institutional policies regarding sensitive information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Parakh, S.K.; Tong, Y.W. Health hazards of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) and its microbial reduction. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4923–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukhurebor, K.E.; Aigbe, U.O.; Onyancha, R.B.; Nwankwo, W.; Osibote, O.A.; Paumo, H.K.; Ama, O.M.; Adetunji, C.O.; Siloko, I.U. Effect of hexavalent chromium on the environment and removal techniques: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orooji, Y.; Nezafat, Z.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Kamali, T.A. Polysaccharide-based (nano)materials for Cr(VI) removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 950–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Yang, Q. Interaction characteristics and mechanism of Cr(VI)/Cr(III) with microplastics: Influence factor experiment and DFT calculation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yu, D.; Yang, J.; Zhao, T.; Yu, D.; Li, L.; Wang, D. A novel sequential extraction method for the measurement of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) species distribution in soil: New insights into the chromium speciation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamoun, I.; Falyouna, O.; Eljamal, R.; Idham, M.F.; Tanaka, K.; Eljamal, O. Bench-scale injection of magnesium hydroxide encapsulated iron nanoparticles (nFe0@Mg(OH)2) into porous media for Cr(VI) removal from groundwater. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Ma, S.; Liu, T.; Deng, X. Green synthesis of nano zero-valent iron/Cu by green tea to remove hexavalent chromium from groundwater. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Qiao, J. Enhanced immobilization of chromium(VI) in soil using sulfidated zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Qin, H.; Li, J. Relationships of ternary activities for the enhanced Cr(VI) removal by coupling nanoscale zerovalent iron with sulfidation and carboxymethyl cellulose. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, J. Kinetic insights into the relationships between anaerobic corrosion and decontamination of nanoscale zerovalent iron improved by sulfidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 501, 157638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Gu, K.; Li, J. Sulfidation of zerovalent iron for improving the selectivity toward Cr(VI) in oxic water: Involvements of FeSx. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, X.; Luo, J.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J. Mediating the reactivity and selectivity of nanoscale zerovalent iron toward nitrobenzene under porous carbon confinement. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amrani, W.A.; Onaizi, S.A. Adsorptive removal of heavy metals from wastewater using emerging nanostructured materials: A state-of-the-art review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 343, 127018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Collins, R.N.; Waite, T.D.; Hanna, K. Advances in surface passivation of nanoscale zerovalent iron: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12010–12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.-X. Wet milling of zerovalent iron in sulfide solution: Preserving and securing the metallic iron. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Liu, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, W.-X. Evolution of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in water: Microscopic and spectroscopic evidence on the formation of nano- and micro-structured iron oxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhao, Z.; He, L.; Yang, Y.; Jia, B.; Wang, W.; Liu, S. Modified zero-valent iron nanoparticles enhanced remediation of PCBs-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 940, 173349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Sun, A.; Tong, S.; Su, G.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; et al. Enhanced nitrobenzene reduction by modified biochar supported sulfidated nano zerovalent iron: Comparison of surface modification methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, G.; Wang, D.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles supported by functionalized waste rock wool for efficient removal of hexavalent chromium. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhuang, M.; Shan, L.; Wu, J.; Quan, G.; Cui, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J. Bimetallic FeNi nanoparticles immobilized by biomass-derived hierarchically porous carbon for efficient removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Herzing, A.A.; Li, X.-Q.; Kiely, C.J.; Zhang, W.-X. Structural Evolution of Pd-Doped Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) in Aqueous Media and Implications for Particle Aging and Reactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4288–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Ren, H.; Ma, X.; Zhou, S.; Huang, J.; Jiao, W.; Qi, G.; Liu, Y. High-gravity continuous preparation of chitosan-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron towards Cr(VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wu, Z.; Shi, S.; Cai, S.; Yang, D.; Yang, L.; He, F.; Liang, L.; Wang, Z. Dual role of soil in dechlorination of soil-sorbed trichloroethene by CMC stabilized and sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xia, C.; He, F.; Wang, Z.; Liang, L. Sulfidation of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron by Sulfide: The Dynamic Process, Mechanism, and Role of Ferrous Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 17147–17156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Lan, Y.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Johnson, R.L.; Filip, J.; O’Carroll, D.M.; Nunez Garcia, A.; Agrawal, A. Sulfidation of Iron-Based Materials: A Review of Processes and Implications for Water Treatment and Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13070–13085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Gao, F.; Zhang, C.; Ahmad, S.; Tang, J. Sulfidation of zero-valent iron for enhanced reduction of chlorinated contaminants: A review on the reactivity, selectivity, and interference resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Sun, Y.; Guan, X. Simultaneous Sequestration of Humic Acid-Complexed Pb(II), Zn(II), Cd(II), and As(V) by Sulfidated Zero-Valent Iron: Performance and Stability of Sequestration Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Qian, J.; Shen, J.; Guan, X. Partial aging can counter-intuitively couple with sulfidation to improve the reactive durability of zerovalent iron. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Guan, X. Enhanced Reactivity and Electron Selectivity of Sulfidated Zerovalent Iron toward Chromate under Aerobic Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2988–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Weng, C.; Bai, W.; Jiao, Y.; Kaegi, R.; Lowry, G.V. Reactivity, Selectivity, and Long-Term Performance of Sulfidized Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron with Different Properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5936–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, X. Properties and reactivity of sulfidized nanoscale zero-valent iron prepared with different borohydride amounts. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Shi, S.; Qi, J.; Cai, S.; Yu, Y.; O’Carroll, D.M.; He, F. Carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized and sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron: Characterization and trichloroethene dechlorination. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 262, 118303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Huang, J.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, T.; Long, J.; Peng, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. High sulfur-to-iron ratios enhance thallium(I) sequestration by sulfidated zero-valent iron. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 190, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Lowry, G.V. Sulfur Dose and Sulfidation Time Affect Reactivity and Selectivity of Post-Sulfidized Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13344–13352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, K.; Lou, Z.; Lou, L.; Xu, X. Mechanism and influence factors of chromium(VI) removal by sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Lin, Z.; Su, X.; Liu, B. The removal of heavy metal cations by sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-nZVI): The reaction mechanisms and the role of sulfur. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-B.; Zhang, W.-X. Synthesizing nanoscale iron particles for rapid and complete dechlorination of TCE and PCBs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2154–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liang, L.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X. Advances in Sulfidation of Zerovalent Iron for Water Decontamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13533–13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.A. A nonlinear least squares fit procedure for analysis of immittance data of electrochemical systems. Solid State Ion. 1986, 20, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcio-Ortega, D.; Fan, D.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Kim, E.; Chang, Y.S. Reactivity of Fe/FeS Nanoparticles: Electrolyte Composition Effects on Corrosion Electrochemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12484–12492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).