Experimental Study on Diversion Dike to Mitigate Debris Flow Blocking River Disaster
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment Method
2.1. Case Prototype
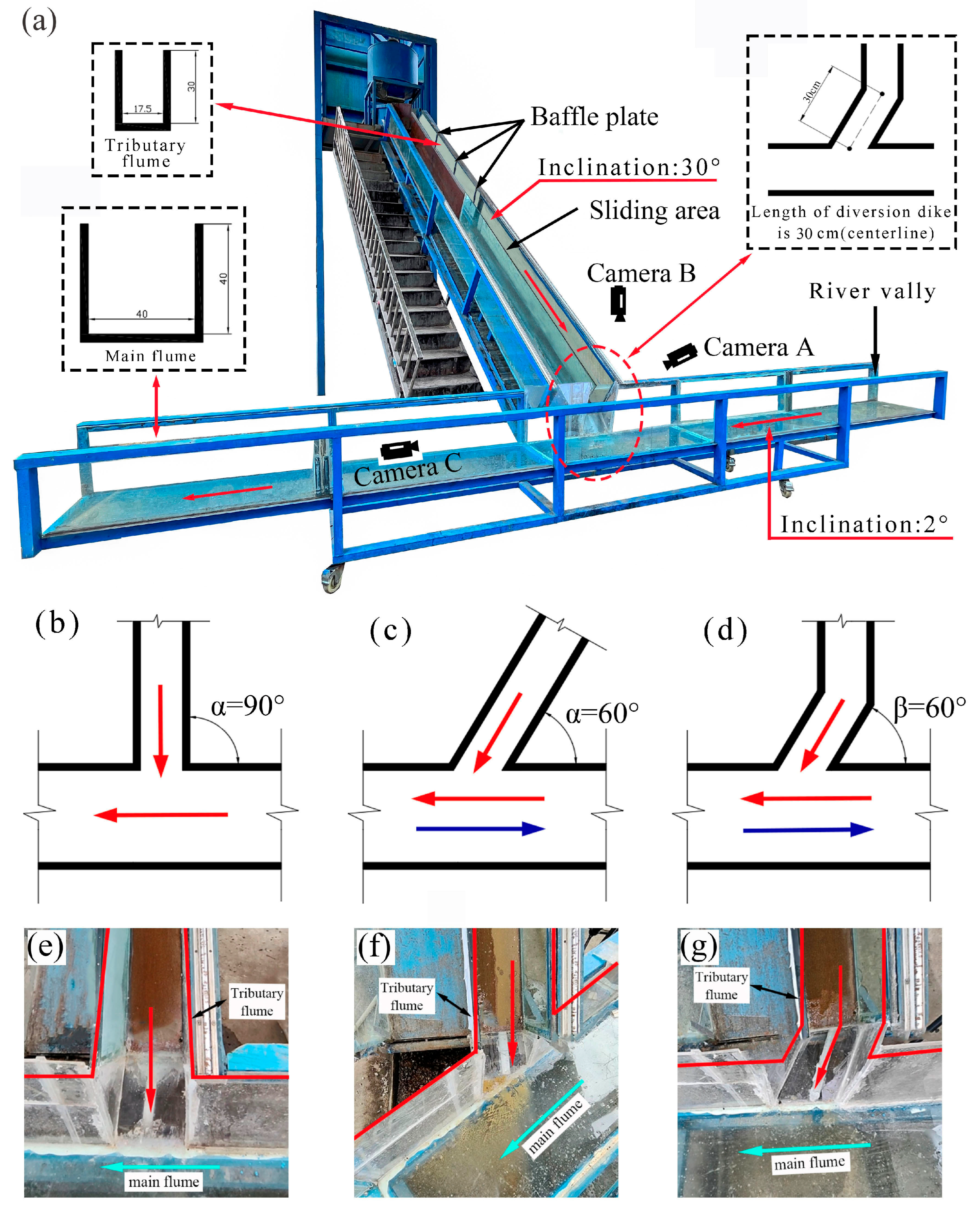
2.2. Experiment Setup
2.3. Test Procedure and Experimental Design
2.4. Data Acquisition
3. Experiment Results
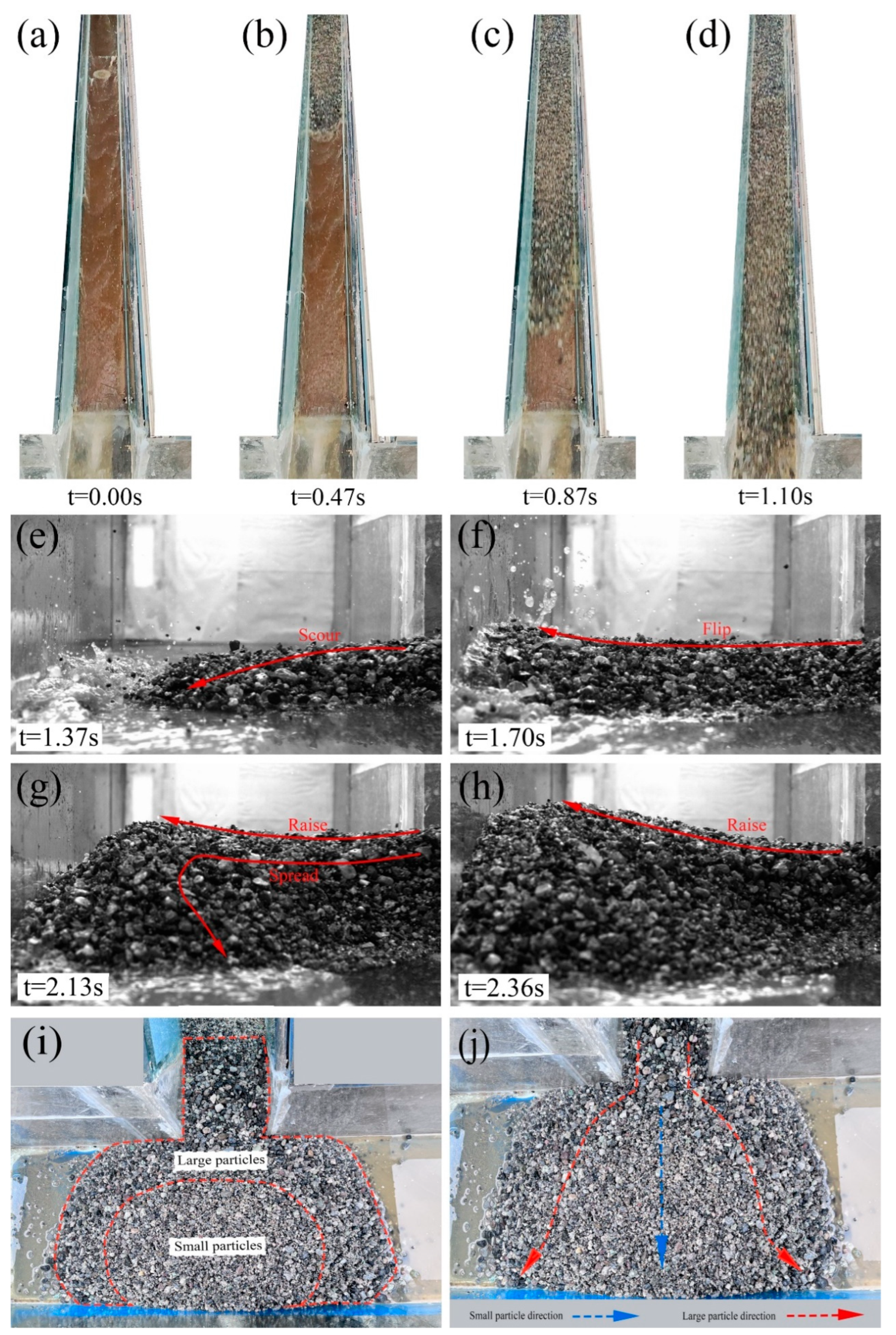
3.1. Debris Flow Movement and Deposition
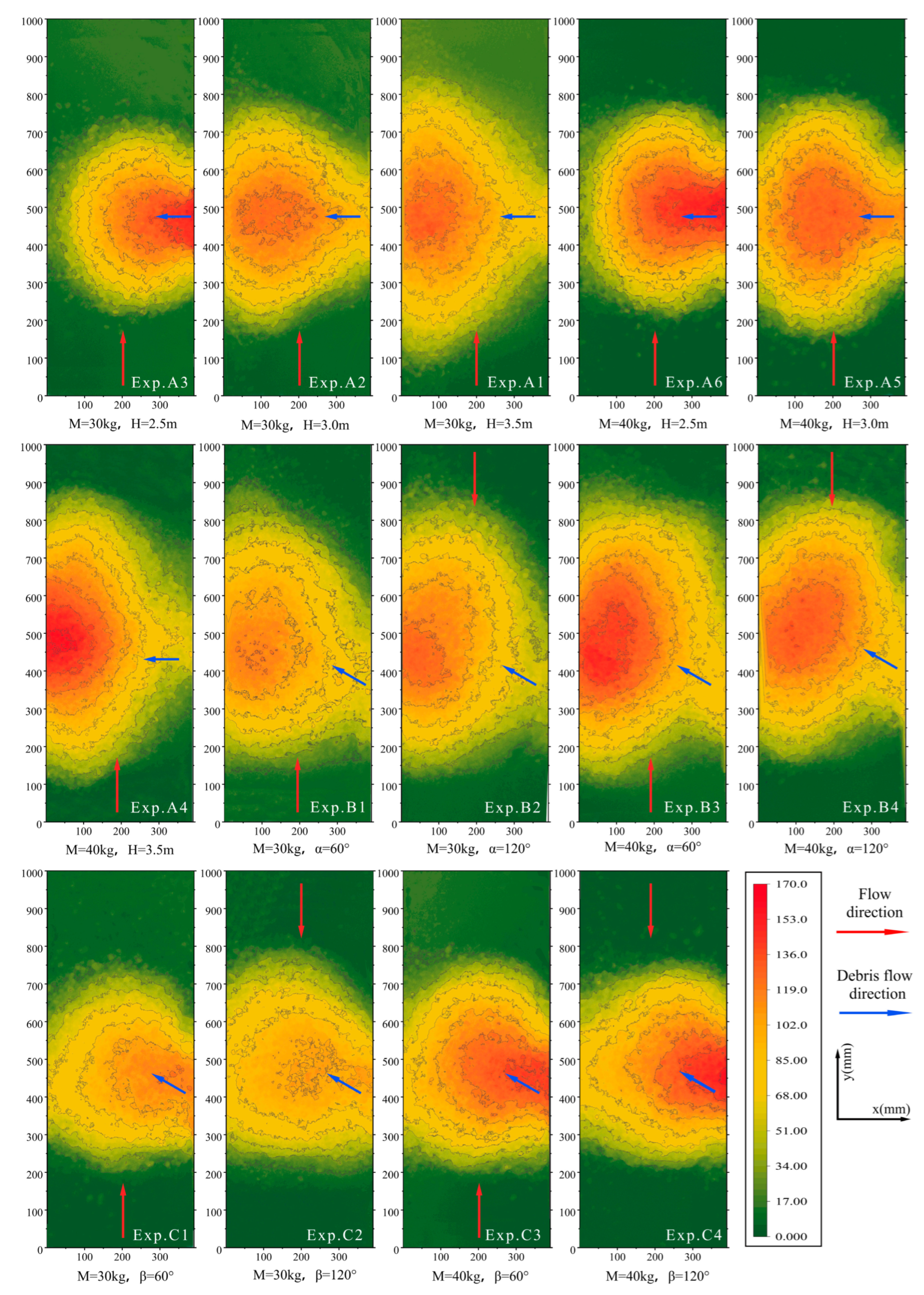
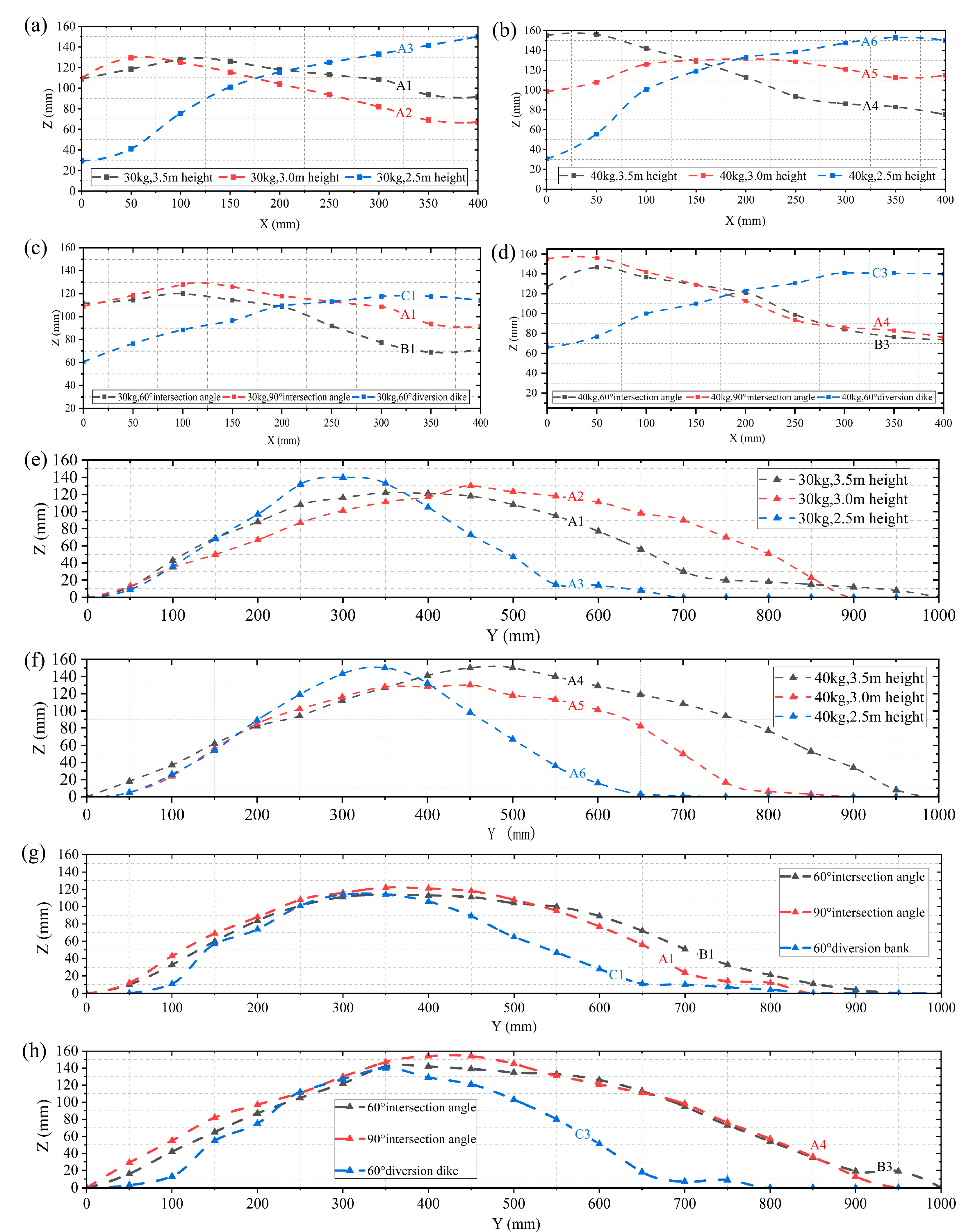
3.2. Debris Flow Deposit Morphology
3.3. Breaching Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Deposit Morphology
4.2. Breaching Morphological Characteristics
5. Conclusions
- Effectiveness of diversion dikes:
- 2.
- Influence on barrier lake breach dynamics:
- 3.
- Impact of entry angle on deposit morphology:
- 4.
- Role of mass and velocity of debris flow:
- 5.
- Application potential of diversion dikes:
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jakob, M.; Hungr, O. Debris-flow Hazards and Related Phenomena; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.E.; Schuster, R.L. The formation and failure of natural dams. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1988, 100, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Ermini, L.; Rosati, G. Determining grain size distribution of the material composing landslide dams in the Northern Apennines: Sampling and processing methods. Eng. Geol. 2003, 69, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Yu, M. Experimental study on the critical condition of river blockage by a viscous debris flow. In Catena: An Interdisciplinary; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Lv, D.; Peng, K.; Chen, Z.; Liao, H. Modeling experiment of river damming by debris landslide. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2023, 41, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.D.; Li, S.; Song, D.; Choi, C.E.; Chen, X. Depositional mechanisms and morphology of debris flow: Physical modelling. Landslides 2019, 16, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Zheng, W.; Xu, W. Catastrophic debris flows triggered by a 4 July 2013 rainfall in Shimian, SW China: Formation mechanism, disaster characteristics and the lessons learned. Landslides 2014, 11, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Chen, H.; Robin, N.; Li, H.; Ruan, H. Process of Debris Flow Dam Break Under Different Conditions. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 40, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.C.; Shi, C.B.; Jiang, Y.M.; Wang, S.H.; Hu, X.L.; Wang, J. Failure characteristics and formation mechanism of the shaziba landslide in Enshi. Resour. Environ. Eng. 2023, 37, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tie, Y.; Ning, Z.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, J. Characteristics and activity analysis of the catastrophic “6.26” debris flow in the Banzi catchment, Wenchuan County of Sichuan Province. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2023, 50, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Hu, X.; Liu, B.; Xi, C.; He, K. Analysis on the mechanism of debris fow in Meilong valley in Danba County on June 17, 2020. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2022, 33, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Tang, C.; Xiong, J.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X. Cause Analysis of ‘8.20′ Debris Flow and Forecast of River-blocking Range in Xiazhuang Gully of Wenchuan County, Sichuan Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 40, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Chen, G.; Meng, X.-M.; Yue, D.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, F.; Li, Y.; Zeng, R.; Zhao, Y.; Bian, S.; et al. Analysis of the transformation mechanism and prediction of a landslide-debris flow multi-hazards chain in an alpine canyon area: A case study in Zhouqu. J. Lanzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 58, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Chen, H.; Robin, N. Research progress on debris flow dams. Yangtze River 2020, 51, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, T.; Wu, H.; Chen, G.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D. Research progress on stability evaluation method and disaster chain effect of landslide dam. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2018, 37, 1796–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Fan, X. The landslide story. Nat. Geoence 2013, 6, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Fan, G.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, J. Study on the process of landslide blocking the river based on seismic signal analysis: A case study of the Baige landslide dammed lake. Yangtze River 2023, 54, 90–97+202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Tang, C.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Q.; Gong, L. Activity characteristics and enlightenment of the debris flow triggered by the rainstorm on 20 August 2019 in Wenchuan County, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 80, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walder Joseph, S. Tsunamis generated by subaerial mass flows. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lange, S.I.; Santa, N.; Pudasaini, S.P.; Kleinhans, M.G.; de Haas, T. Debris-flow generated tsunamis and their dependence on debris-flow dynamics. Coast. Eng. 2019, 157, 103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, X.Q.; Chen, J.G. Experimental study on the energy dissipation characteristics of debris flow deceleration baffles. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Liu, J.-F.; You, Y.; Liu, D.-C.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W.-B. The siltation of debris flow behind check dam in the midstream of Bailong River. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Ding, M.; Gao, Z.; Téllez, R.D. Check dam storage capacity calculation based on high-resolution topogrammetry: Case study of the Cutou Gully, Wenchuan County, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Qi, L.; Wang, X. A prototype experiment of debris flow control with energy dissipation structures. Nat. Hazards 2012, 60, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xu, Q.; Dong, X.; Yu, B.; Frost, J.; Li, H. Design and performance of a novel multi-function debris flow mitigation system in Wenjia Gully, Sichuan. Landslides 2017, 14, 2089–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugai, K.; Yagi, H.; Wakai, A. Earthquake-Induced Landslides; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.; Zhou, J.W.; Yang, X.G.; Zhou, H.-W. Effects of a flexible net barrier on the dynamic behaviours and interception of debris flows in mountainous areas. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 1903–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Fei, W.P.; Zhou, H.W.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.W.; Wang, J.M.; Wu, J.J. Experimental and numerical study on the load and deformation mechanism of a flexible net barrier under debris flow impact. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 2213–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hassan, M.A.; Saletti, M.; Yang, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, J. Experimental study on the mitigation effects of deflection walls on debris flow hazards at the confluence of tributary and main river. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.C.; Chen, N.S.; Hu, G.S.; Deng, M.F. Magnitude-frequency relationship of debris flows in the Jiangjia Gully, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Z. Causes and prevention measures of the debris flow diversion embankment breach in the lower reaches of Jiangjiagou. J. Catastrophology 2001, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Jang, B.; Wu, C. Damming process and characteristics of landslide-debris avalanches. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 121, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-G.; Yao, L.-K.; Yang, Q.-H. Experimental Research on Confluence between Debris Flow and Main River. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2004, 39, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, P.; Zeng, C.; Lei, Y. Experimental analysis on the impact force of viscous debris flow. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Cui, P. An empirical formula for suspended sediment delivery ratio of main river after confluence of debris flow. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.T.; Chen, X.Q.; Hu, G.S.; Kuo, Y.-S.; Huang, Y.-R.; Shieh, C.-L. Dimensionless Assessment Method of Landslide Dam Formation Caused by Tributary Debris Flow Events. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 7083058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-H.; Li, M.-H.; Gao, Y.-C. Prediction of Possibility of River Blocking by Debris Flow in Section of Yeniu Gully in Dadu River Watershed. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 34, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xie, Z.S.; Shi, S.W.; Yu, T. Characteristic and Countermeasures of River-bolcking Debris Flow of Haermu Gully in Wenchuan Area After Earthquake. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 35, 327–332+337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, J.; Yu, T. A new algorithm for the automatic extraction of valley floor width. Geomorphology 2019, 335, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Li, C. Problems and prospects of studying riverbed deposition dynamics of viscous debris inflow catchment areas. Chin. J. Geomech. 2020, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Hu, Y.X.; Fan, G.; Zhu, Q.-Y.; Liu, D.-R.; Zhou, J.-W. Exploring debris flow deposit morphology in river valleys: Insights from physical modeling experiments. Eng. Geol. 2024, 332, 107465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Xu, L.; Li, Y. Evaluation of vulnerability of diversion dike suffering from debris flow disasters. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2023, 45, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Shi, Z.; Peng, M.; Zhou, Y. Review and Prospect of the Formation Mechanism of Landslide Dams Caused by Landslide and Avalanche Debris. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2020, 52, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Numerical simulation of flow variation during overtopping and breach of a dam. Shuili Xuebao 2008, 39, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Zhang, L.M. Breaching parameters of landslide dams. Landslides 2012, 9, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, S.L.; Stefano, L.; Enrico, F. Mutual Interference of Two Debris Flow Deposits Delivered in a Downstream River Reach. J. Mt. Sci. 2014, 11, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T. Debris flow on prismatic open channel. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1980, 106, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. Experiments on Gravity-Free Dispersion of Large Solid Spheres in a Newtonian Fluid Under Shear. Proc. R. Soc. A 1954, 225, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Dang, C.; Liu, J.; Gong, Y. Experiments of Debris Flow Damming in Southeast Tibet. Earth Sci. Front. 2007, 14, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Nian, T.-K.; Chen, G.-Q.; Zhao, W.; Li, D.-Y. Laboratory-scale investigation of the 3-D geometry of landslide dams in a U-shaped valley. Eng. Geol. 2024, 265, 105428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, F.; Wang, Z.-F.; Li, S.-J. Numerical analysis of landslides based on coupling model of material point method and depth integral. Rock Soil Mech. 2024, 45, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, J.J. Depositional processes in large-scale debris-flow experiments. J. Geol. 1997, 105, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Shi, Z.; Hanley, K.J.; Peng, M.; Guan, S.; Feng, S.; Chen, K. Deposition characteristics of debris flows in a lateral flume considering upstream entrainment. Geomorphology 2021, 394, 107960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




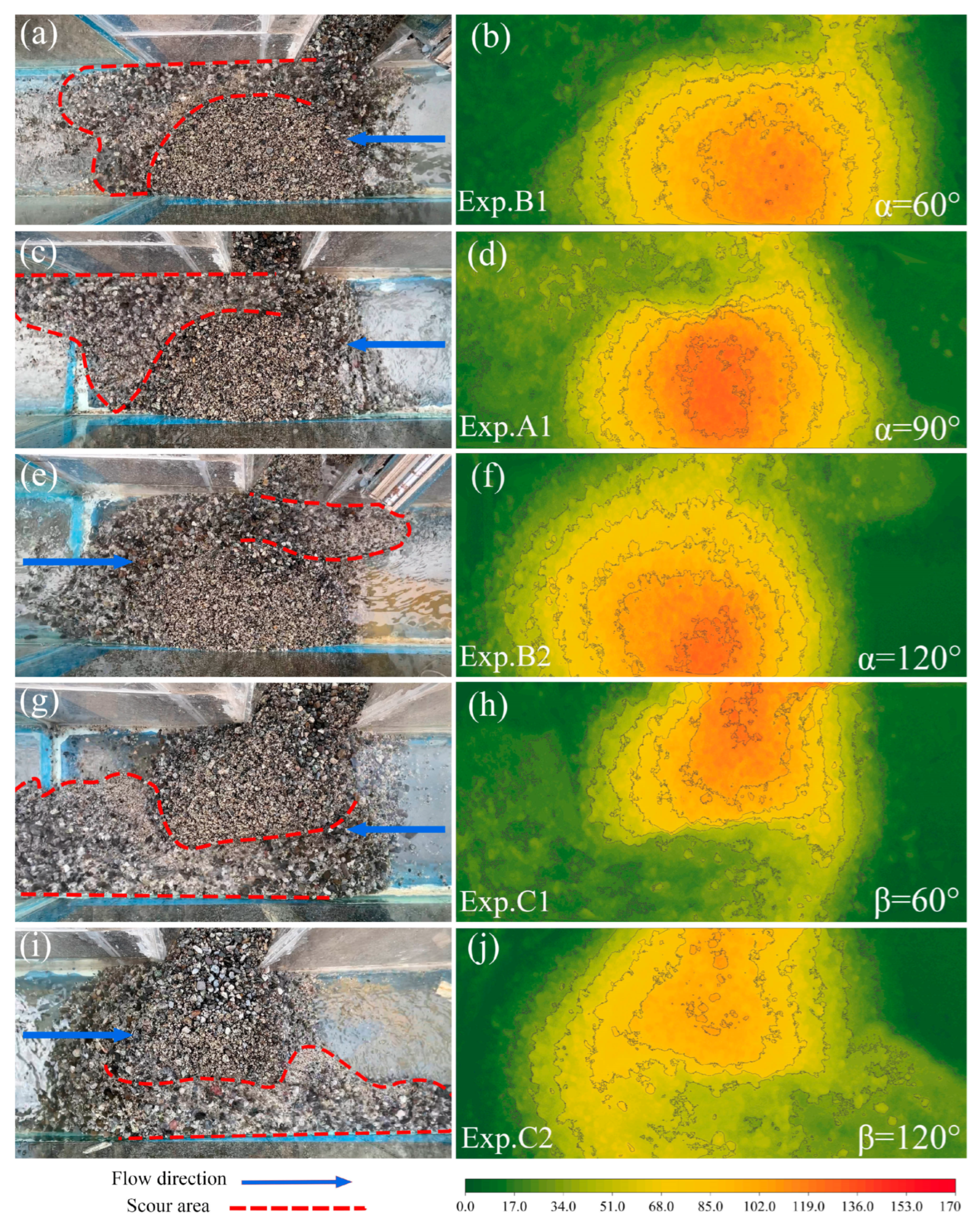
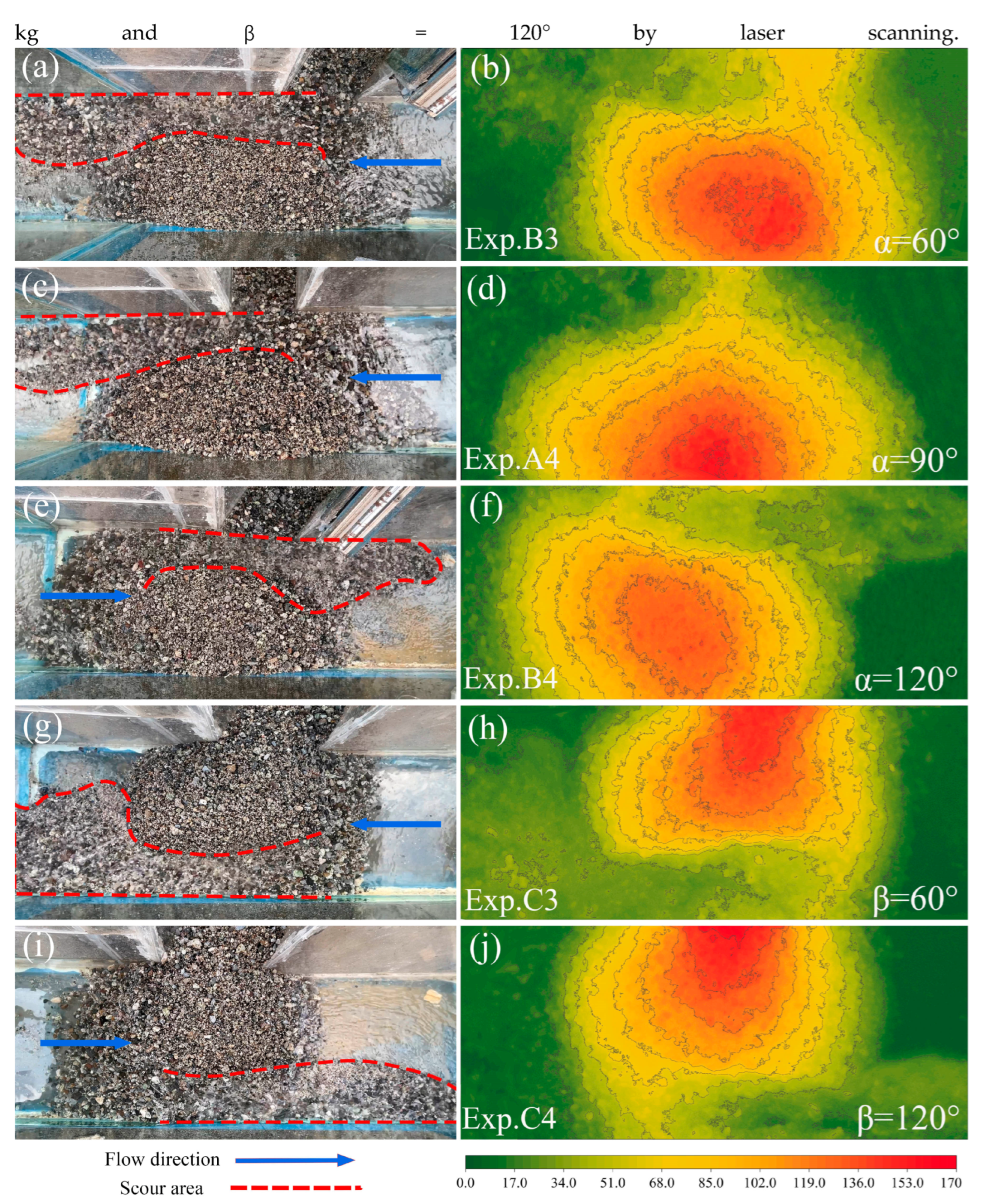

| Exp ID | M/kg | H/m | α/° | β/° | Exp ID | M/kg | H/m | α/° | β/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 30 | 3.5 | 90 | \ | B2 | 30 | 3.5 | 120 | \ |
| A2 | 30 | 3 | 90 | \ | B3 | 40 | 3.5 | 60 | \ |
| A3 | 30 | 2.5 | 90 | \ | B4 | 40 | 3.5 | 120 | \ |
| A4 | 40 | 3.5 | 90 | \ | C1 | 30 | 3.5 | \ | 60 |
| A5 | 40 | 3 | 90 | \ | C2 | 30 | 3.5 | \ | 120 |
| A6 | 40 | 2.5 | 90 | \ | C3 | 40 | 3.5 | \ | 60 |
| B1 | 30 | 3.5 | 60 | \ | C4 | 40 | 3.5 | \ | 120° |
| M = 30 kg | M = 40 kg | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp ID | Condition | Breach Duration | Exp ID | Condition | Breach Duration |
| A1 | α = 90° | 76.78 s | A4 | α = 90° | 114.10 s |
| B1 | α = 60° | 68.62 s | B3 | α = 60° | 87.82 s |
| B2 | α = 120° | 70.25 s | B4 | α = 120° | 84.12 s |
| C1 | β = 60° | 62.02 s | C3 | β = 60° | 75.28 s |
| C2 | β = 120° | 67.82 s | C4 | β = 120° | 78.78 s |
| Material Quality | Exp ID | Intersection Angle | Relative Change in Volume (%) | Relative Change in Height (%) | Relative Change in Length (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 kg | B1 | 60° | −2.10 | −12.32 | −9.48 |
| A1 | 90° | −56.26 | −34.75 | −2.33 | |
| 40 kg | B3 | 60° | −31.54 | −10.81 | −25.05 |
| A4 | 90° | −48.32 | −13.16 | −7.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Li, L.; Pan, L.; Yang, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Rao, P. Experimental Study on Diversion Dike to Mitigate Debris Flow Blocking River Disaster. Water 2025, 17, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121736
Gao X, Li L, Pan L, Yang X, Zhou H, Liu J, Wang M, Rao P. Experimental Study on Diversion Dike to Mitigate Debris Flow Blocking River Disaster. Water. 2025; 17(12):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121736
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xing, Liang Li, Longyang Pan, Xingguo Yang, Hongwei Zhou, Jian Liu, Mingyang Wang, and Peimin Rao. 2025. "Experimental Study on Diversion Dike to Mitigate Debris Flow Blocking River Disaster" Water 17, no. 12: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121736
APA StyleGao, X., Li, L., Pan, L., Yang, X., Zhou, H., Liu, J., Wang, M., & Rao, P. (2025). Experimental Study on Diversion Dike to Mitigate Debris Flow Blocking River Disaster. Water, 17(12), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121736





