Effective Treatment of High Arsenic Smelting Wastewater Synergetic Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Scorodite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Scorodite Precursors
2.3. Synthesis of Scorodite
2.4. Analysis and Detection
3. Results and Discussion
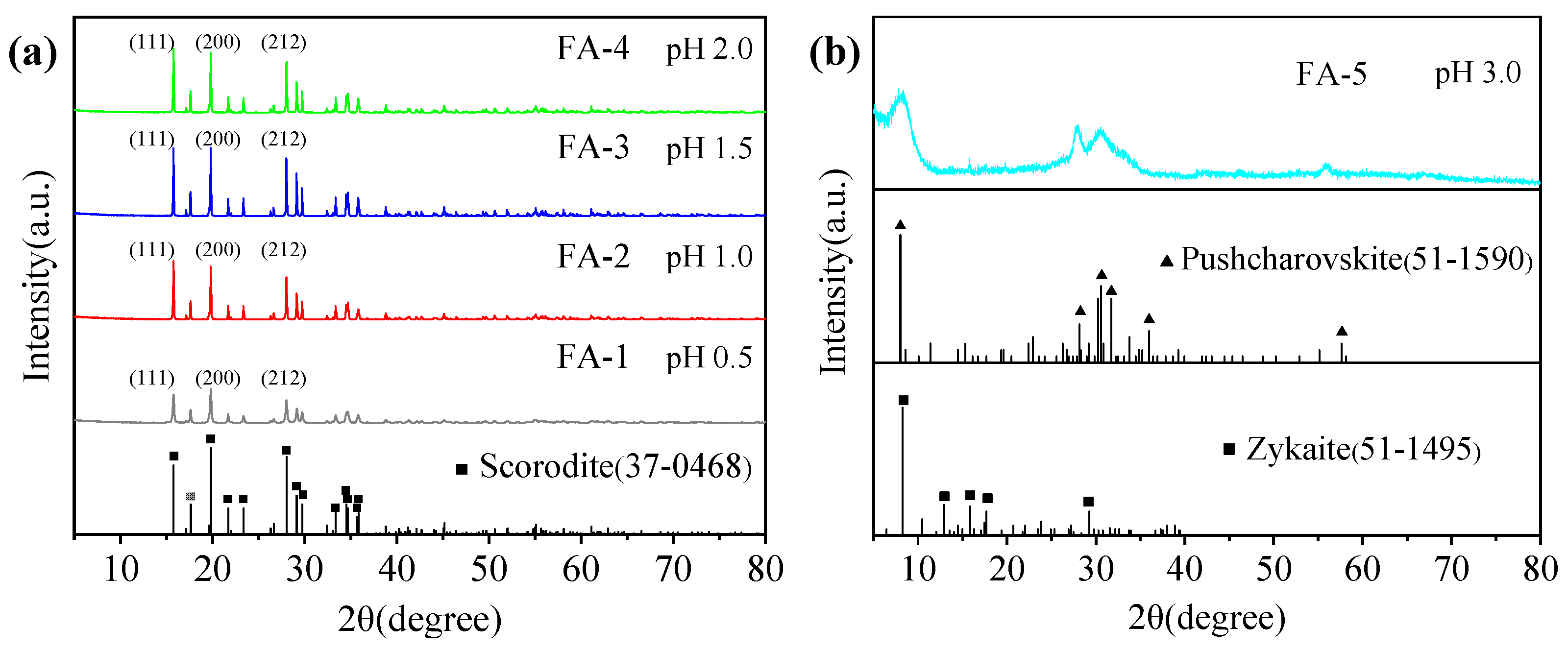
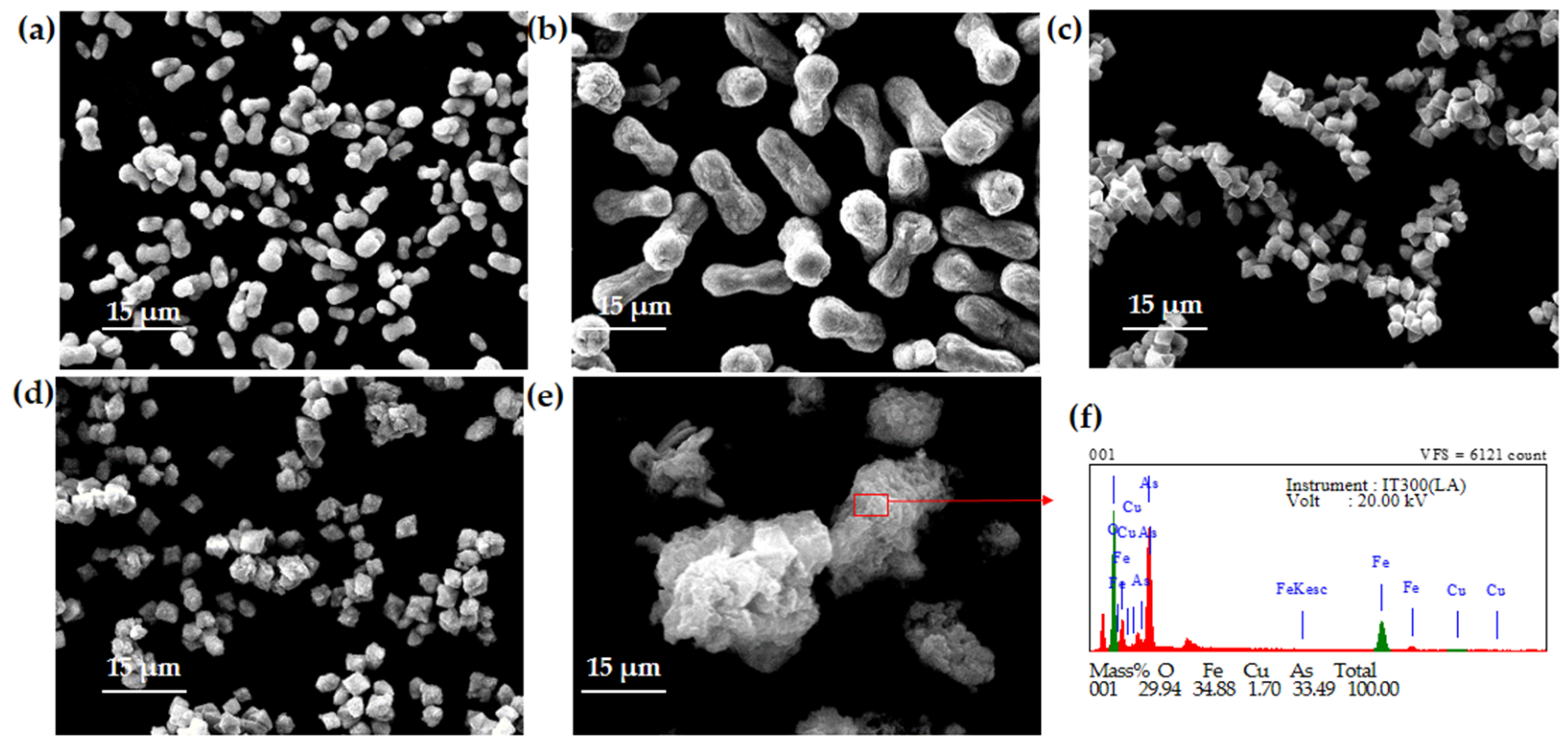
3.1. Effect of the Initial pH
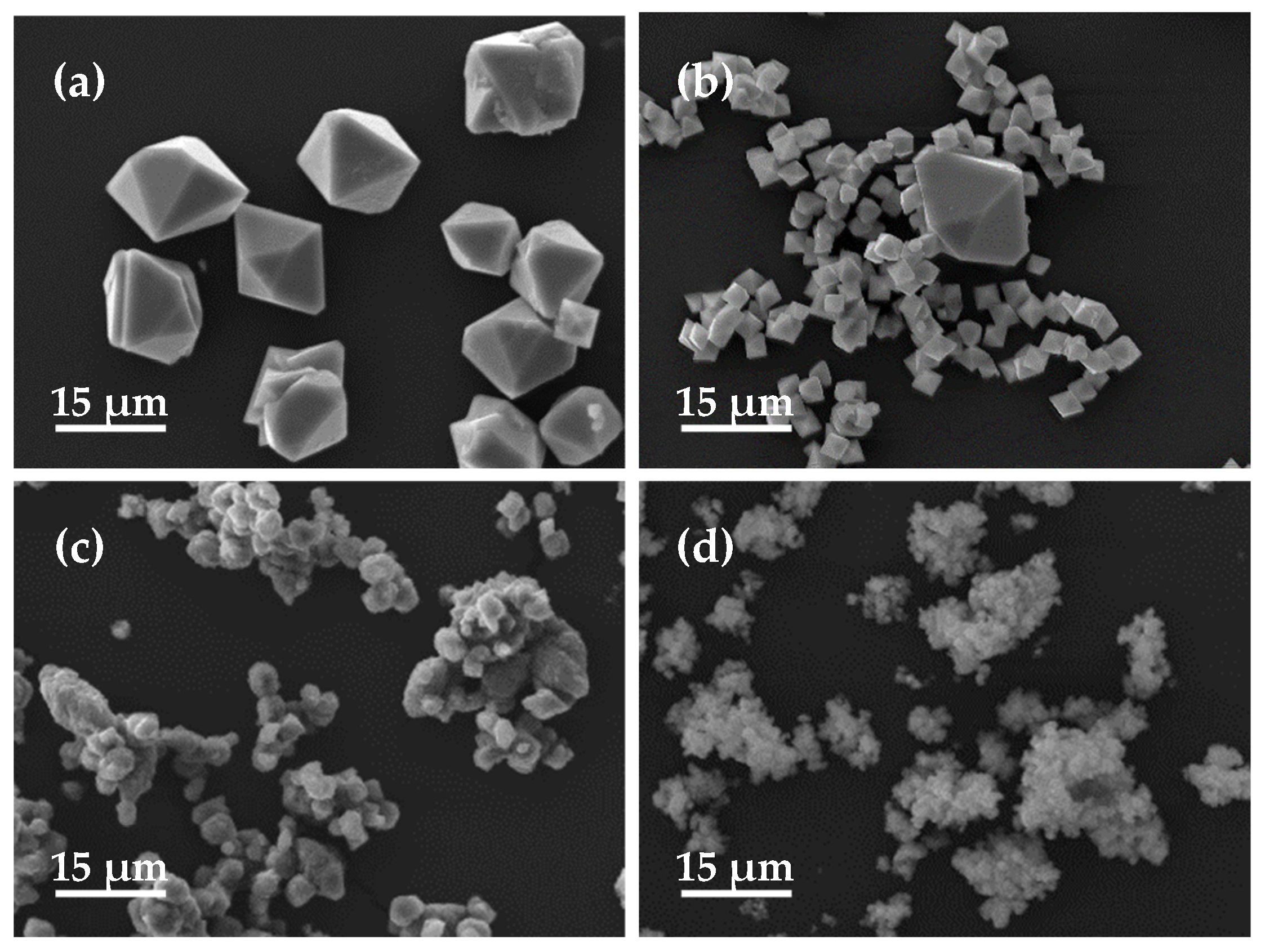
3.2. Effect of the Initial Fe/As Molar Ratio
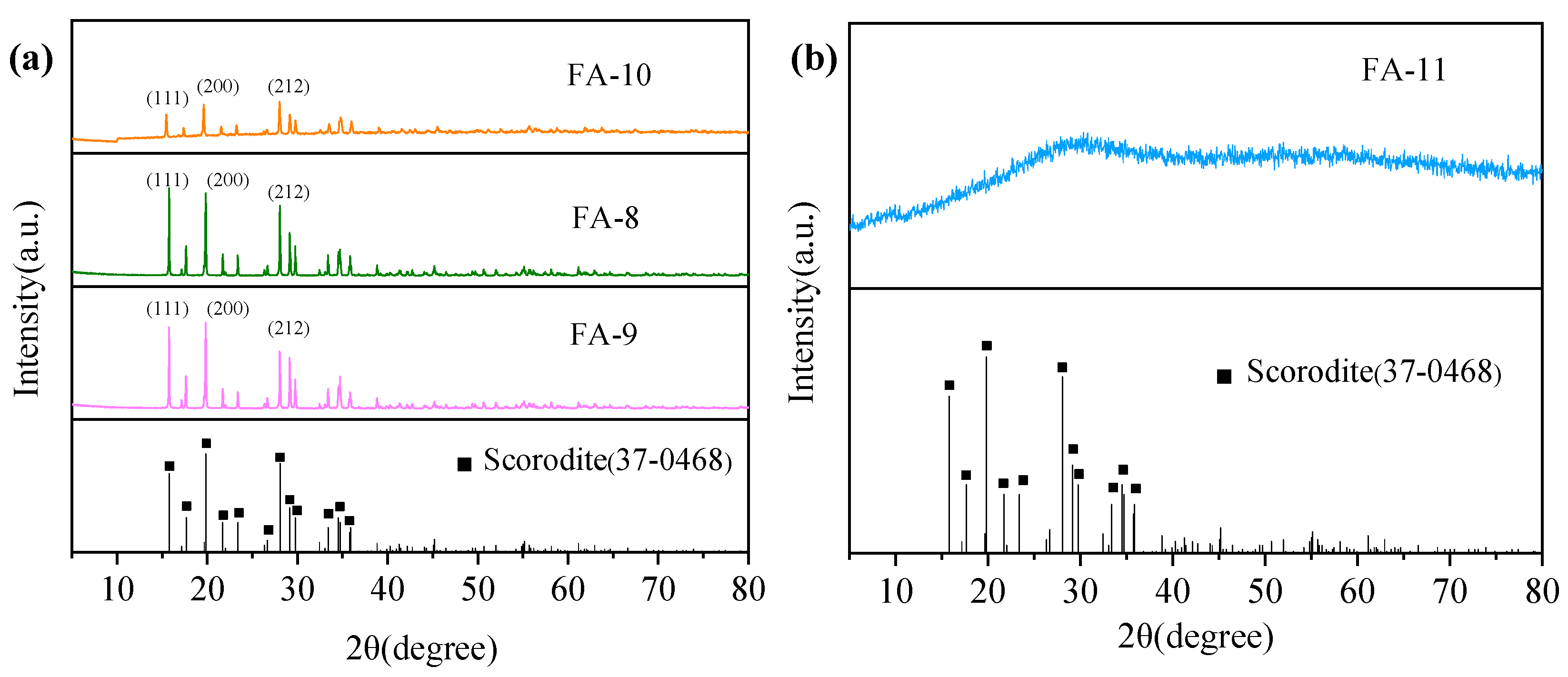
3.3. Effect of the Initial ORP
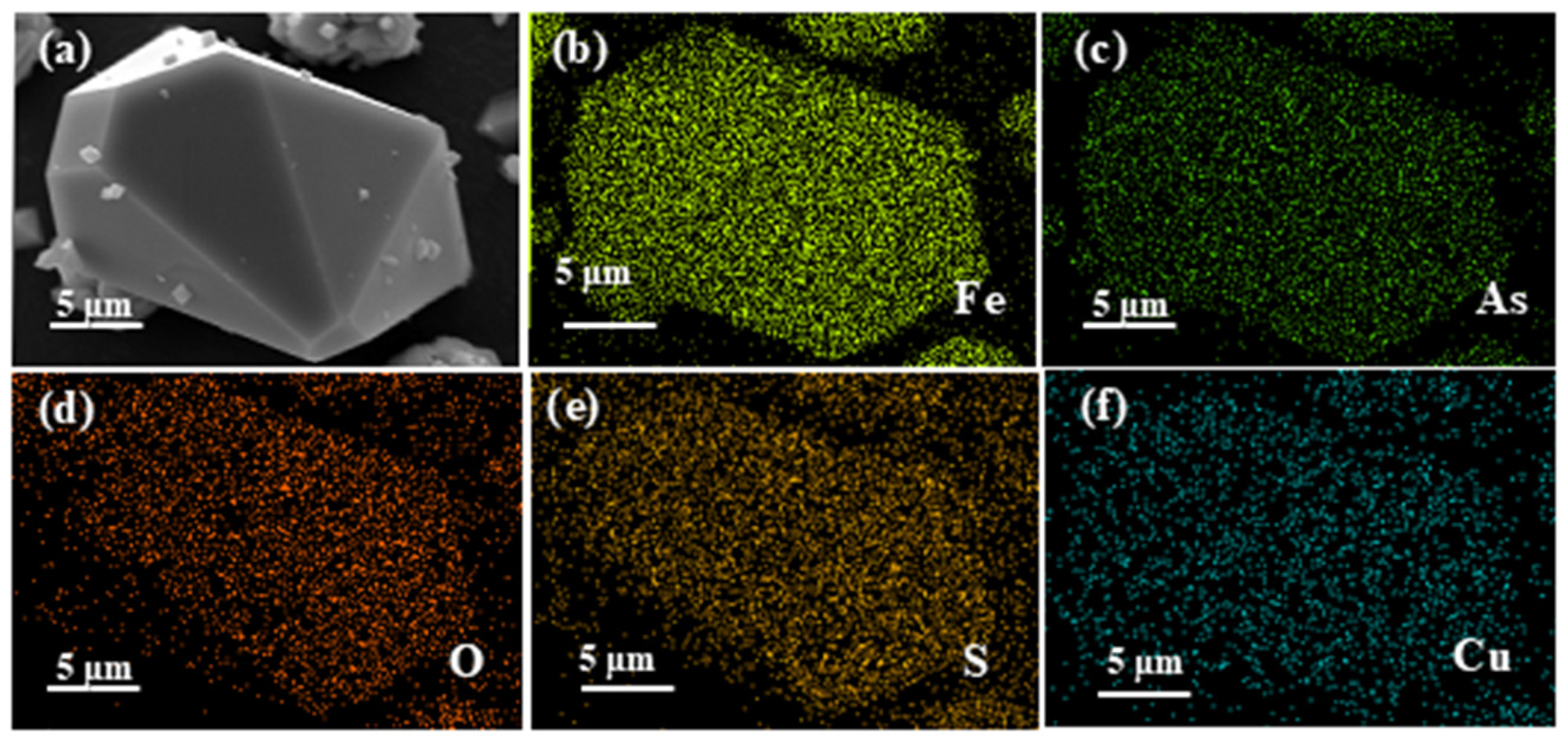
3.4. EDS Analysis
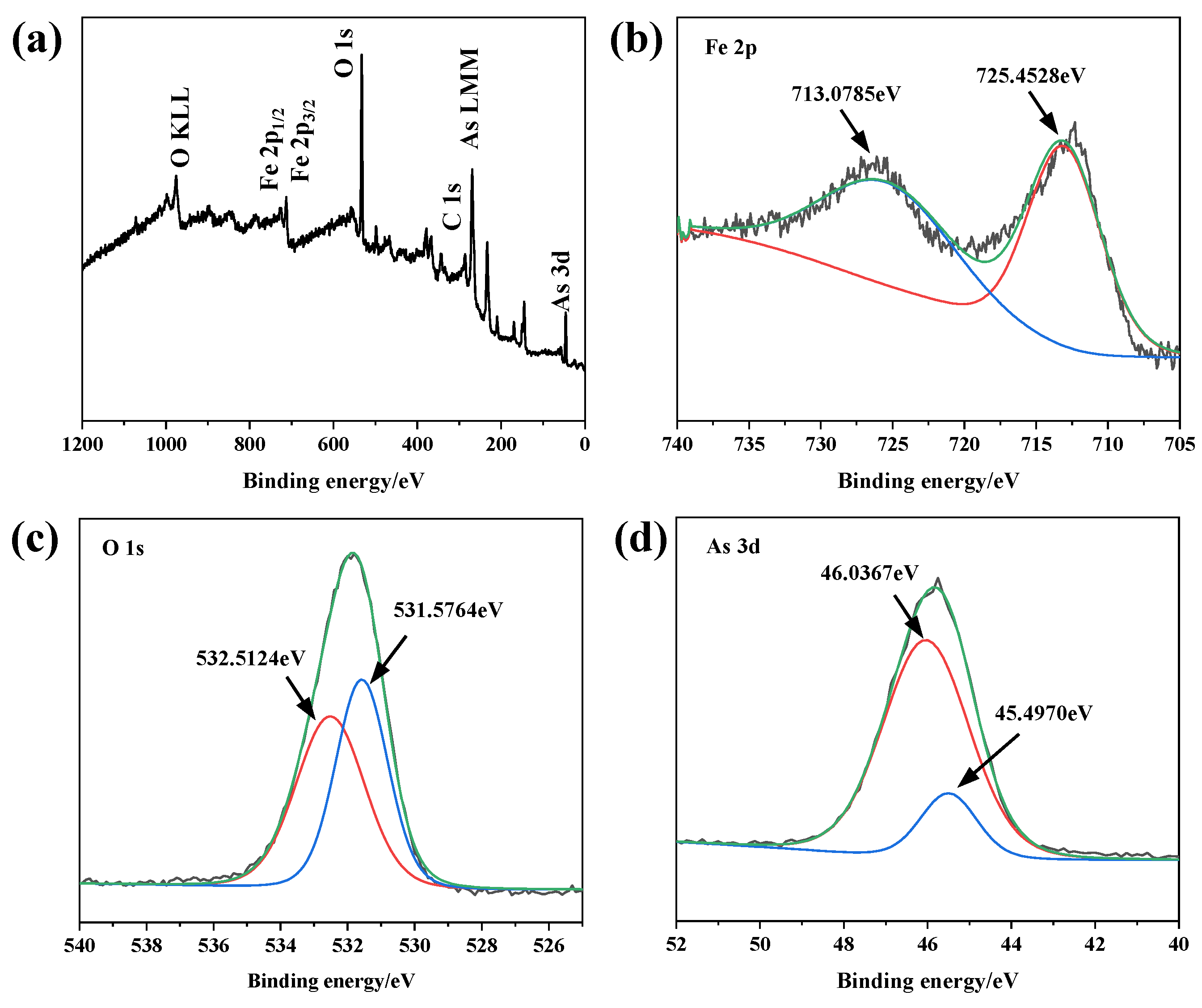
3.5. XPS Analysis
3.6. Leaching Stability of Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Yan, G.; Shi, J. Effective treatment of high-arsenic smelting wastewater—Immobilization arsenic and synthesis well-crystallized scorodite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 129, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Duan, X.; Qi, X.; Li, G.; Yan, G.; Wang, H. Removal of arsenic from copper smelting wastewater using zinc slag to synthesize scorodite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paktunc, D.; Dutrizac, J.; Gertsman, V. Synthesis and phase transformations involving scorodite, ferric arsenate and arsenical ferrihydrite: Implications for arsenic mobility. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 2649–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z. Arsenic removal from acid extraction solutions of copper smelting flue dust. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.H. V.—Note on the occurrence of scorodite, pharmacosiderite and olivenite in Greenstone at Terras Mine, St. Stephens. Mineral. Mag. J. Mineral. Soc. 1876, 1, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hague, A. Notes on the deposition of scorodite from arsenical waters in the Yellowstone National Park. Am. J. Sci. 1887, s3–s34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.G. Pegmatites and aplites: Their genetic and applied ore geology. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 69, 417–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzlan, J.; Drahota, P.; Filippi, M.; Grevel, K.-D.; Kahl, W.-A.; Plášil, J.; Boerio-Goates, J.; Woodfield, B.F. Thermodynamic properties of scorodite and parascorodite (FeAsO4·2H2O), kaňkite (FeAsO4·3.5H2O), and FeAsO4. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 117–118, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J.E.; Jambor, J.L. The synthesis of crystalline scorodite, FeAsO4·2H2O. Hydrometallurgy 1988, 19, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demopoulos, G.P.; Droppert, D.J.; Van Weert, G. Precipitation of crystalline scorodite (FeAsO4·2H2O) from chloride solutions. Hydrometallurgy 1995, 38, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.S.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Deng, G.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, X. Hydrothermal mineralized arsenic precipitation in H3AsO4-FeSO4-K2SO4-H2O system. Min. Metall. 2023, 32, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Yuan, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, C.; Han, H.; Sun, W. The application and mechanism of iron sulfides in arsenic removal from water and wastewater: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, G.; Wang, H. Efficient removal of arsenic from copper smelting wastewater via a synergy of steel-making slag and KMnO4. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Yang, X.F.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, Q.-H. Effects of Synthesis Methods for Scorodite on Its Leaching Stability. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2015, 15, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Fang, Z.W.; Long, H.; Zheng, Y.-J.; Zhang, S.-C. Stabilization of Arsenic from Arsenic Alkali Residue by Forming Crystalline Scorodite. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2020, 30, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Taguchi, R.; Abumiya, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Shibata, E.; Nakamura, T. Effects of zinc, copper and sodium ions on ferric arsenate precipitation in a novel atmospheric scorodite process. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 93, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Taguchi, R.; Abumiya, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Shibata, E.; Nakamura, T. Novel atmospheric scorodite synthesis by oxidation of ferrous sulfate solution. Part I. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 90, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Taguchi, R.; Abumiya, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Shibata, E.; Nakamura, T. Novel atmospheric scorodite synthesis by oxidation of ferrous sulfate solution. Part II. Effect of temperature and air. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 90, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Li, M.T.; Wei, C.; Li, X.B.; Deng, Z.G.; Liu, H.Y.; Lei, F.G. Effect of Supersaturation on Morphology and Stability of Atmospheric Pressure Scorodite Under As(V)-Fe(II) System. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2020, 30, 896–905, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Min, X.-B.; Liao, Y.-P.; Chai, L.-Y.; Yang, Z.-H.; Xiong, S.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.-Z. Removal and stabilization of arsenic from anode slime by forming crystal scorodite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, F.; Song, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wang, W. Mechanistic insights into ultrafast degradation of electron-rich emerging pollutants by waste cyanobacteria resource utilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 155918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z. Oxidation of As(III) by pressurized oxygen and the simultaneous precipitation of As(V) as scorodite in acidic sulfate solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 447, 137395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Okawa, H.; Kato, T.; Sugawara, K. Effect of ultrasound intensity on the size and morphology of synthesized scorodite particles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otgon, N.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, K.; Yang, C. Removal and fixation of arsenic by forming a complex precipitate containing scorodite and ferrihydrite. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.H.; Tang, X.C.; Wu, L.P.; Chen, X.; Dang, W.; Wang, Y. A novel method to synthesize scorodite using ferrihydrite and its role in removal and immobilization of arsenic. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 5848–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Ma, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Jia, Y. The effect of iron reduction on the long-term stability of scorodite in the presence of enolic hydroxyl groups and mineral transformation. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 122, 104730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.A.; Becze, L.; Celikin, M.; Demopoulos, G.P. The effect of copper on the precipitation of scorodite (FeAsO4·2H2O) under hydrothermal conditions: Evidence for a hydrated copper containing ferric arsenate sulfate-short lived intermediate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Cheng, Z.; Mao, L. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Effect of Cu2+ on the Arsenic Precipitation Process of Hydrothermal Scorodite. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2025, 56, 2821–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Niu, C.; Cai, T.; Wang, Z. Exposed redox-active iron enables electrochemically highly selective capture and conversion of arsenic from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Su, R.; Gao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, X.; Qi, B. Resource and stabilization cotreatment of metallurgical arsenic-alkali slag and siderite via scorodite formation. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 315, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ng, W.S.; Chen, M. Thermodynamic analysis of the immobilisation of arsenic during the pressure oxidation and curing processes. Miner. Eng. 2022, 185, 107681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 299-2007; Solid Waste-Extraction Procedure for Leaching Toxicity-Sulphuric Acid & Nitric Acid Method. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Wang, Y.; Rong, Z.; Tang, X.; Cao, S.; Chen, X.; Dang, W.; Wu, L. Mechanism analysis of the synthesis and growth process of large spindle-shaped scorodite as arsenic immobilization materials. Mater. Lett. 2019, 254, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhong, L.; Tang, L.; Fan, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Dong, H.; Zhou, C.; Rensing, C.; Zhou, S.; et al. Lysogenic bacteriophages encoding arsenic resistance determinants promote bacterial community adaptation to arsenic toxicity. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 5085.3-2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes-Identification for Extraction Toxicity. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.

| Index | Ion Concentration (mg/L) | ORP/mV | pH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Fe | Cu | Zn | Ni | |||
| Arsenic-containing solution | 25,000 | 10.2 | 15.3 | 8.9 | 2.3 | 340 | 0.89 |
| Number | Fe/As Molar Ratio | Initial pH | Initial ORP/mV | Final pH | Final ORP/mV | Product Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 425 | 0.36 | 406 | FA-1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1.0 | 425 | 0.84 | 407 | FA-2 |
| 3 | 1 | 1.5 | 425 | 1.28 | 409 | FA-3 |
| 4 | 1 | 2.0 | 425 | 1.82 | 408 | FA-4 |
| 5 | 1 | 3.0 | 425 | 2.98 | 410 | FA-5 |
| 6 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 425 | 0.33 | 404 | FA-6 |
| 7 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 425 | 0.86 | 408 | FA-7 |
| 8 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 425 | 1.41 | 413 | FA-8 |
| 9 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 385 | 1.43 | 383 | FA-9 |
| 10 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 485 | 1.38 | 474 | FA-10 |
| 11 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 585 | 1.36 | 570 | FA-11 |
| Detection Method | Element | Atomic % | Weight % | Fe/As Molar Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDS | O | / | / | 1.534 |
| Fe | 60.54 | 53.39 | ||
| As | 39.46 | 46.61 | ||
| XPS | C 1s | 32.25 | 16.30 | 1.566 |
| O 1s | 50.17 | 33.77 | ||
| Fe 2p | 10.73 | 30.47 | ||
| As 3d | 6.85 | 19.45 | ||
| ICP-AES | Fe | 50.30 | 43.04 | 1.012 |
| As | 49.70 | 56.96 |
| Number | Product Name | Topography | Size | Phase | Arsenic Leaching Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FA-1 | Bone-shaped | 5 μm | Scorodite | 1.56 |
| 2 | FA-2 | Bone-shaped | 15 μm | Scorodite | 0.74 |
| 3 | FA-3 | Bipyramidal polyhedral-shaped | 2.5 μm | Scorodite | 0.49 |
| 4 | FA-4 | Biconical polyhedral-shaped (with shell) | 2.5 μm | Scorodite | 0.66 |
| 5 | FA-5 | Agglomerate-shaped | No specific size | Amorphous ferric arsenate compounds | 11.71 |
| 6 | FA-6 | Bone-shaped | 10 μm | Scorodite | 1.32 |
| 7 | FA-7 | Bone-shaped + rice grain-shaped | 15–20 μm | Scorodite | 0.28 |
| 8 | FA-8 | Bipyramidal polyhedral-shaped | 2.5 μm | Scorodite | 0.19 |
| 9 | FA-9 | Bipyramidal polyhedral-shaped | 15–30 μm | Scorodite | 0.08 |
| 10 | FA-10 | Agglomerate-shaped | 2.5–10 μm | Scorodite + amorphous ferric arsenate compounds | 2.35 |
| 11 | FA-11 | Agglomerate-shaped | 1 μm | Amorphous ferric arsenate compounds | 5.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C.; Liang, Y.; Yan, G. Effective Treatment of High Arsenic Smelting Wastewater Synergetic Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Scorodite. Water 2025, 17, 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111599
Liao Y, Wu J, Zhou C, Liang Y, Yan G. Effective Treatment of High Arsenic Smelting Wastewater Synergetic Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Scorodite. Water. 2025; 17(11):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111599
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Yuanhang, Jianhui Wu, Chengyun Zhou, Yanjie Liang, and Guomeng Yan. 2025. "Effective Treatment of High Arsenic Smelting Wastewater Synergetic Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Scorodite" Water 17, no. 11: 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111599
APA StyleLiao, Y., Wu, J., Zhou, C., Liang, Y., & Yan, G. (2025). Effective Treatment of High Arsenic Smelting Wastewater Synergetic Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Scorodite. Water, 17(11), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111599






