Oxygenates Removal from Water by Hydrophobic Pervaporation with Polyalkylmethylsiloxane Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
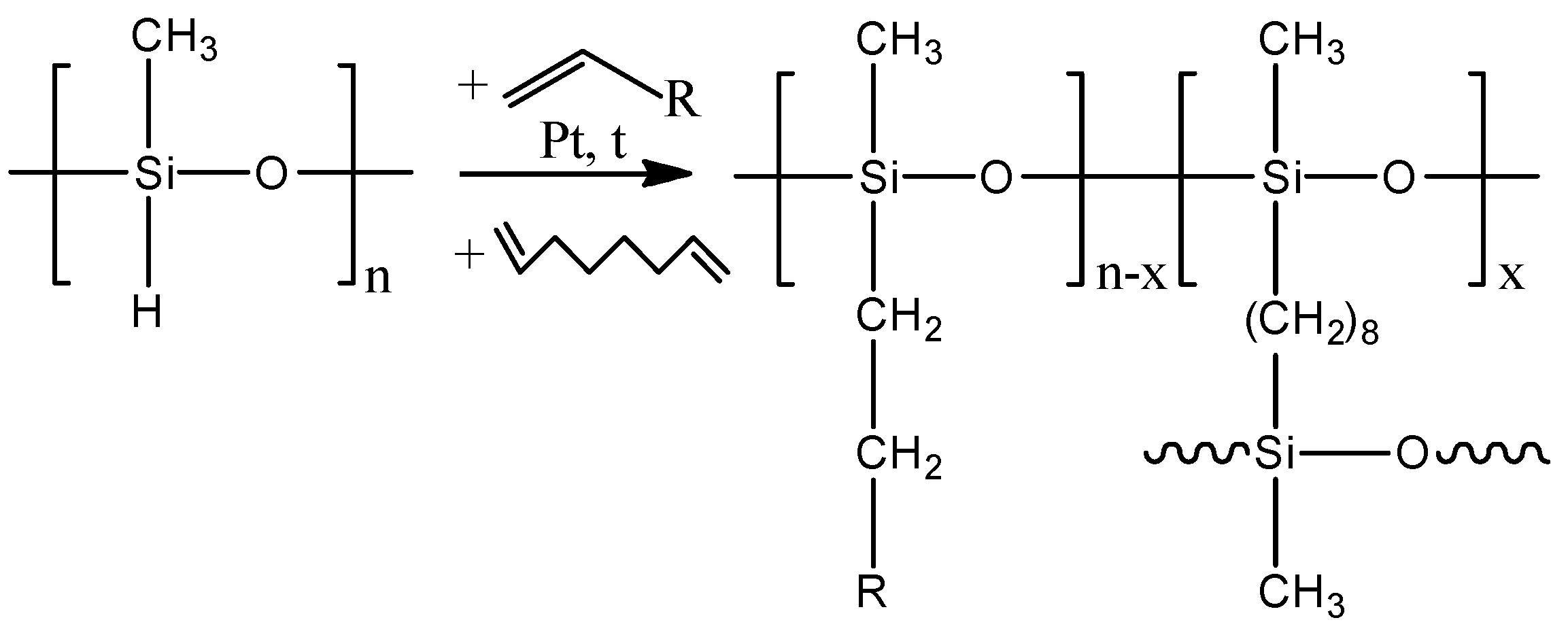
2.2. Composite Membrane
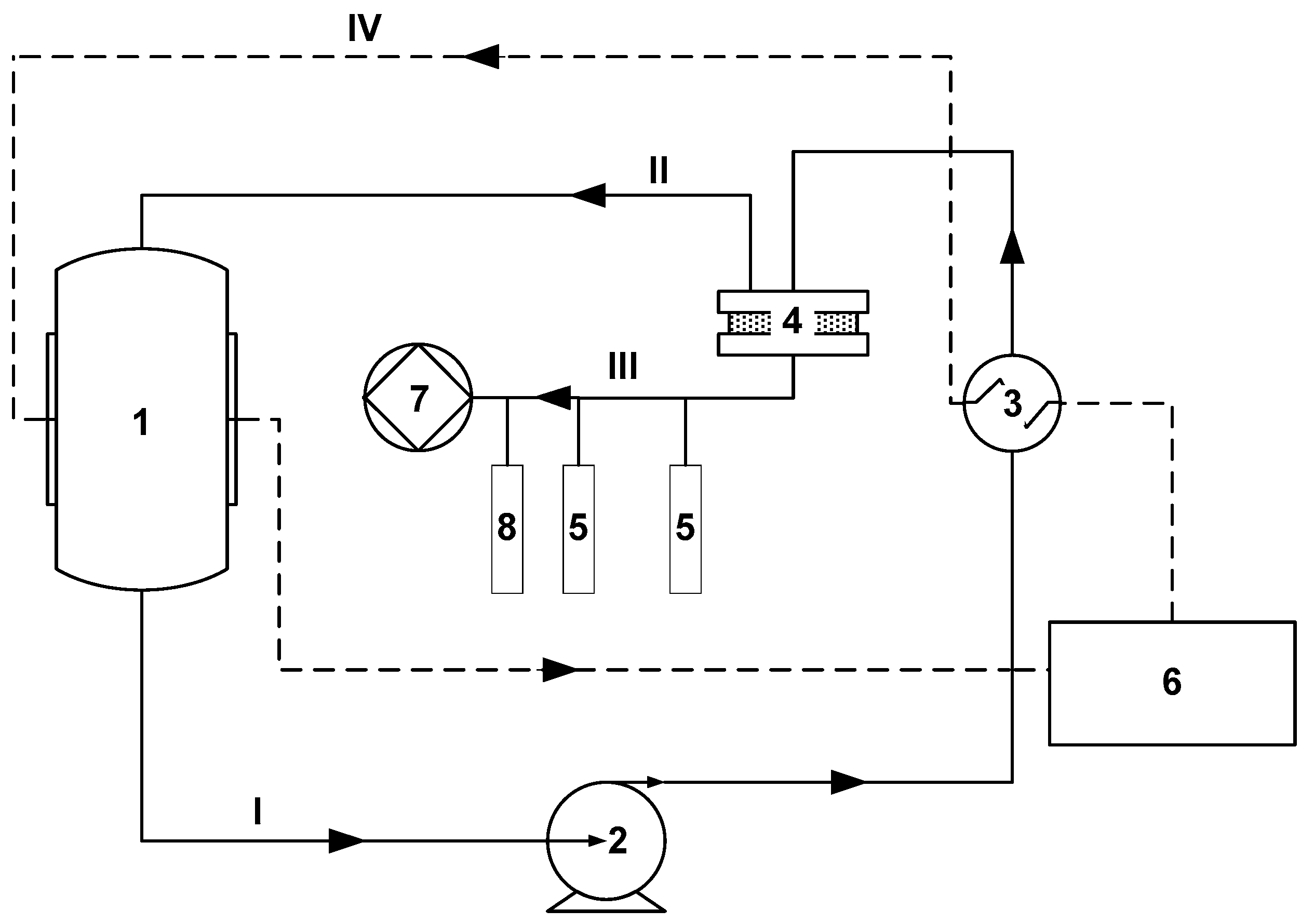
2.3. Vacuum Pervaporation
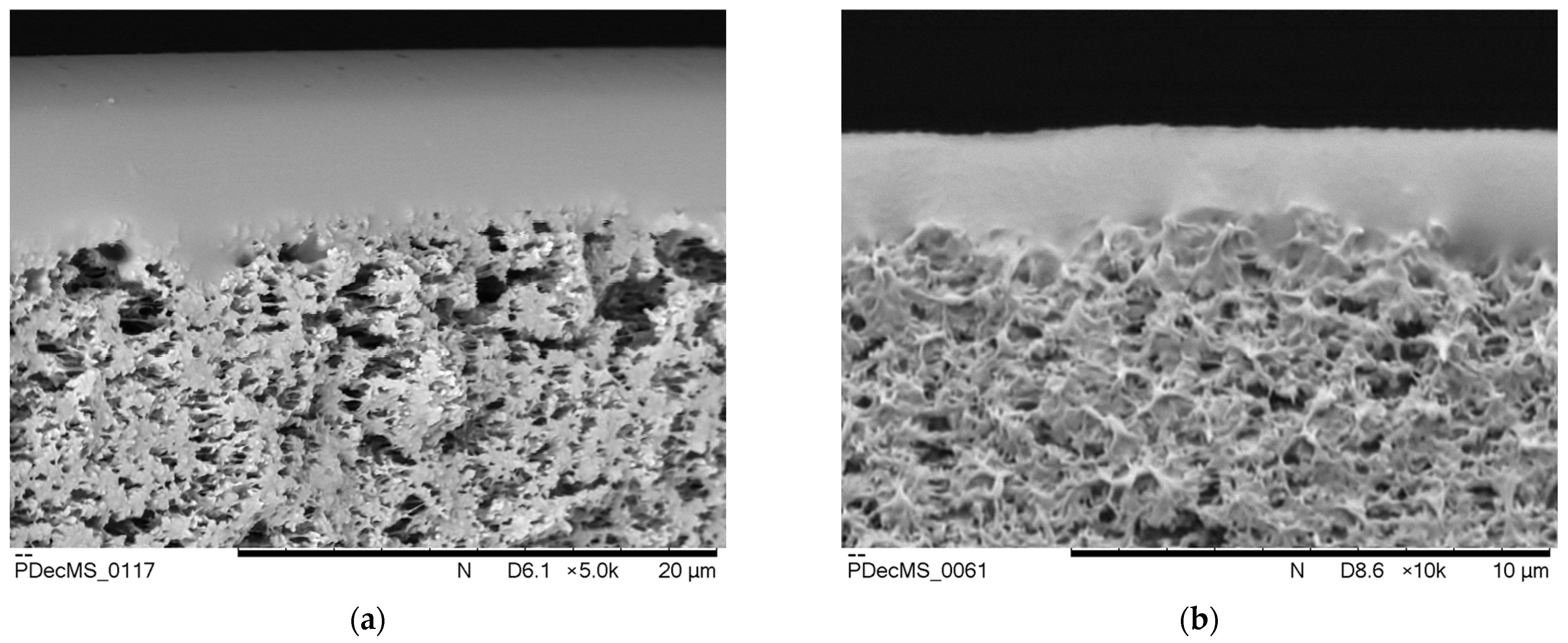
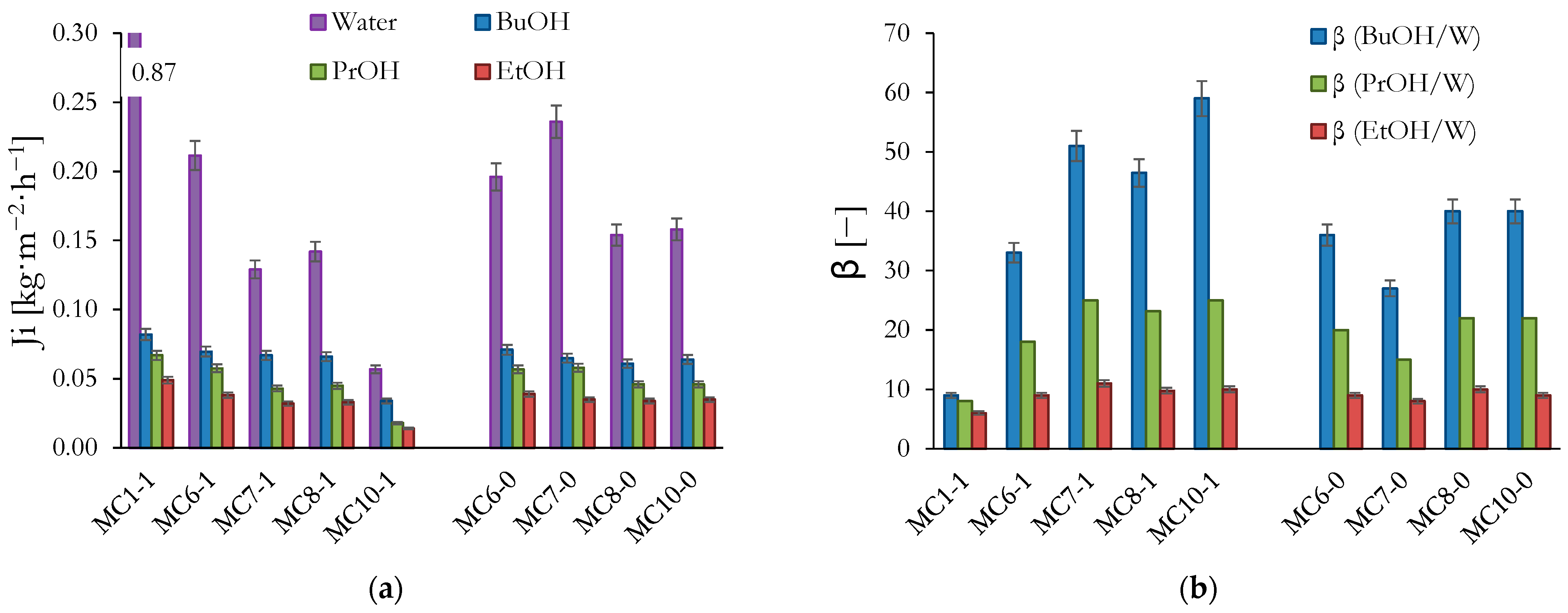
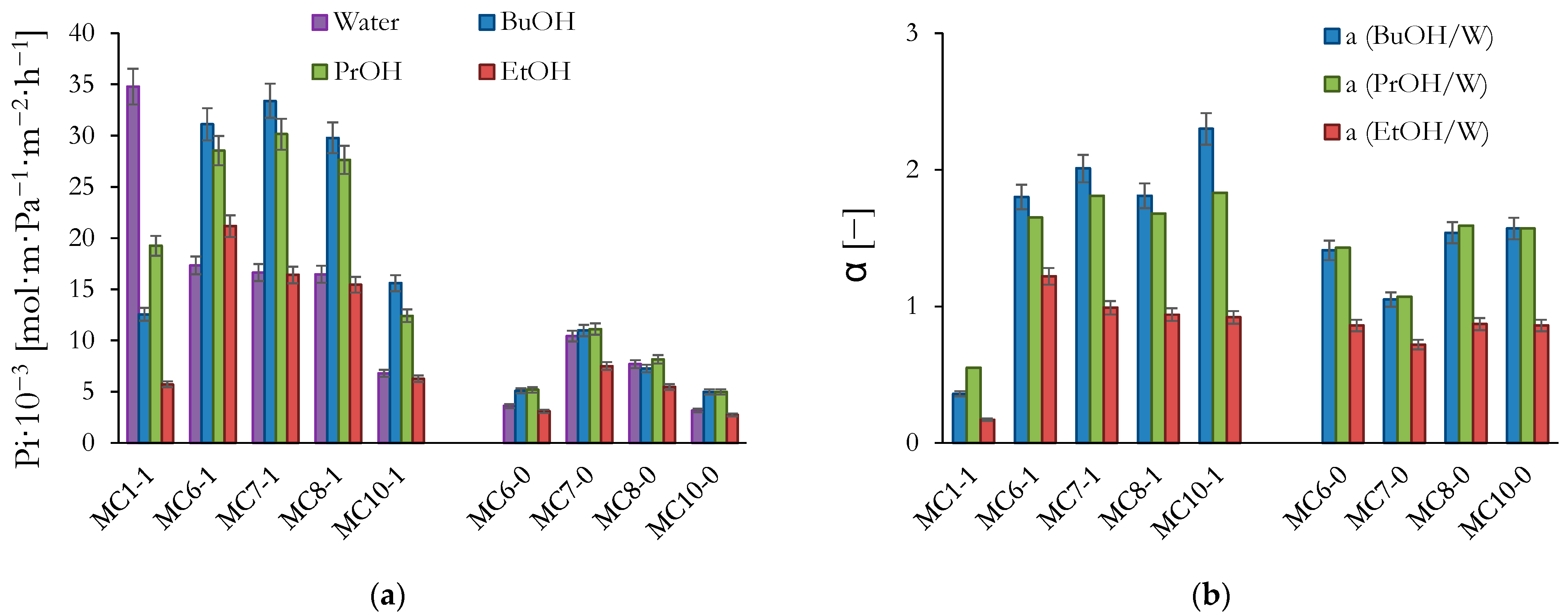
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eryılmaz, C.; Genç, A. Review of Treatment Technologies for the Removal of Phenol from Wastewaters. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2021, 43, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surkatti, R.; El-Naas, M.H.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Benamor, A.; Al-Naemi, F.; Onwusogh, U. Biotechnology for Gas-to-Liquid (GTL) Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Water 2020, 12, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ekama, G.A.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Brdjanovic, D. Biological Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rosal, R.; Rodríguez, A.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Petre, A.; García-Calvo, E.; Gómez, M.J.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Occurrence of Emerging Pollutants in Urban Wastewater and Their Removal through Biological Treatment Followed by Ozonation. Water Res. 2010, 44, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tijani, J.O.; Fatoba, O.O.; Madzivire, G.; Petrik, L.F. A Review of Combined Advanced Oxidation Technologies for the Removal of Organic Pollutants from Water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, A.; Bibi, S.; Abu-Dieyeh, M.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Towards Sustainable Physiochemical and Biological Techniques for the Remediation of Phenol from Wastewater: A Review on Current Applications and Removal Mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 137810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabidi, Z.B.; El-Naas, M.H.; Zhang, Z. Immobilization of Microbial Cells for the Biotreatment of Wastewater: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majone, M.; Aulenta, F.; Dionisi, D.; D’Addario, E.N.; Sbardellati, R.; Bolzonella, D.; Beccari, M. High-Rate Anaerobic Treatment of Fischer–Tropsch Wastewater in a Packed-Bed Biofilm Reactor. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2745–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhara, S.; Zakaria, Y.; McKay, G. Potential of GTL Biosolids in a Circular Economy: Investigating Blending, Pyrolysis, Activation, and Characterisation. Environ. Technol. 2024, 45, 4017–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Klerk, A. Fischer-Tropsch Refining; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Krylova, A.Y.; Kryazhev, Y.G.; Kulikova, M.V.; Kurkin, V.I.; Lyadov, A.S.; Sagitov, S.A. Synthesis of Alcohols from CO and H2 on Iron Catalysts Containing Carbon Fiber. Solid Fuel Chem. 2011, 45, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylova, A.Y.; Kurkin, V.I.; Kulikova, M.V.; Lyadov, A.S.; Sagitov, S.A. Synthesis of Monohydric Alcohols from CO and H2 on Fe/Sibunit Catalysts. Solid Fuel Chem. 2011, 45, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölbel, H.; Ralek, M. The Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis in the Liquid Phase. Catal. Rev. 1980, 21, 225–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Surkatti, R.; Ba-Abbad, M.M.; El-Naas, M.H. Optimization of the Biotreatment of GTL Process Water Using Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Immobilized in PVA Hydrogel. Processes 2022, 10, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, N.M.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Alsalhy, Q.F. Modeling and Simulation of Pervaporation (PV) Separation for Alcohol Dehydration. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeji, T.C.; Qureshi, N.; Blaschek, H.P. Butanol Fermentation Research: Upstream and Downstream Manipulations. Chem. Rec. 2004, 4, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachipudi, P.S.; Kittur, A.A.; Sajjan, A.M.; Kamble, R.R.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Solving the Trade-off Phenomenon in Separation of Water–Dioxan Mixtures by Pervaporation through Crosslinked Sodium–Alginate Membranes with Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid-Co-Maleic Acid. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 94, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjan, A.M.; Premakshi, H.G.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyelectrolyte Complex Membranes for the Pervaporation Separation of Water–Isopropanol Mixtures Using Sodium Alginate and Gelatin. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wei, W.; Jin, W. Pervaporation Membranes for Biobutanol Production. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemoto, M.; Negishi, H.; Sakaki, K.; Ikegami, T.; Chohnan, S.; Nitta, Y.; Kurusu, Y.; Ohta, H. Efficient Butanol Recovery from Acetone–Butanol–Ethanol Fermentation Cultures Grown on Sweet Sorghum Juice by Pervaporation Using Silicalite-1 Membrane. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Jang, K.-S.; Galebach, P.; Gilbert, C.; Tompsett, G.; Conner, W.C.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Seeded Growth, Silylation, and Organic/Water Separation Properties of MCM-48 Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.L.; Malakhov, A.O.; Khotimsky, V.S.; Litvinova, E.G.; Finkelshtein, E.S.; Ushakov, N.V.; Volkov, V.V. Novel PTMSP-Based Membranes Containing Elastomeric Fillers: Enhanced 1-Butanol/Water Pervaporation Selectivity and Permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žák, M.; Klepic, M.; Štastná, L.Č.; Sedláková, Z.; Vychodilová, H.; Hovorka, Š.; Friess, K.; Randová, A.; Brožová, L.; Jansen, J.C.; et al. Selective Removal of Butanol from Aqueous Solution by Pervaporation with a PIM-1 Membrane and Membrane Aging. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, A.; Friedl, A. Investigation of Pervaporation Performance of POMS Membrane during Separation of Butanol from Water and the Effect of Added Acetone and Ethanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozicka, A.; Niemistö, J.; Keiski, R.L.; Kujawski, W. Apparent and Intrinsic Properties of Commercial PDMS Based Membranes in Pervaporative Removal of Acetone, Butanol and Ethanol from Binary Aqueous Mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, T.; Yanagishita, H.; Kitamoto, D.; Haraya, K.; Nakane, T.; Matsuda, H.; Koura, N.; Sano, T. Production of Highly Concentrated Ethanol in a Coupled Fermentation/Pervaporation Process Using Silicalite Membranes. Biotechnol. Tech. 1997, 11, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Ge, R.; Gao, Z.; Gao, T.; Wang, L.; Li, J. PVA-Based MMMs for Ethanol Dehydration via Pervaporation: A Comparison Study between Graphene and Graphene Oxide. Separations 2022, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Atta, R.; Zolotarev, A.; Kuzminova, A.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Development of Novel Membranes Based on Polyvinyl Alcohol Modified by Pluronic F127 for Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, W.N.; Saeed, W.S.; Alwarthan, A.A.; Badjah-Hadj-Ahmed, A.Y.; Aouak, T. Extraction of Organic Volatile Pollutants in Over-Saturated Water by Pervaporation Technique Using a Poly (Dimethylsiloxane)-Based Sealer as a Membrane. Water 2021, 13, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamelian, F.S.; Naeimpoor, F.; Mohammadi, T. Using a Novel Pervaporative Sequential-Co-Immobilized Two-Sectional Bioreactor with an Ultralow Fouling–Biofouling Superhydrophobic Silicallite-1/PDMS Membrane to Enhance Bioethanol Production. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 3133–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, N.; Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Q. Enhancing Pervaporation Performance for Alcohol Recovery from Aqueous Solutions with Silicalite-1/Polydimethyldiethoxysilane (PDMDES) Nanocomposite Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Xue, T.; Yang, S.; Cai, D.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; et al. Epoxide-Based PDMS Membranes with an Ultrashort and Controllable Membrane-Forming Process for 1-Butanol/Water Pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushevenko, E.A.; Borisov, I.L.; Volkov, A.V. High-Selectivity Polysiloxane Membranes for Gases and Liquids Separation (A Review). Pet. Chem. 2021, 61, 959–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubev, G.S.; Volkov, V.V.; Borisov, I.L.; Volkov, A. V High Free Volume Polymers for Pervaporation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022, 36, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Martínez, J.; Mohsenpour, S.; Ameen, A.W.; Budd, P.M.; García-Payo, C.; Khayet, M.; Gorgojo, P. High-Flux Thin Film Composite PIM-1 Membranes for Butanol Recovery: Experimental Study and Process Simulations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 42635–42649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talluri, V.P.; Tleuova, A.; Hosseini, S.; Vopicka, O. Selective Separation of 1-Butanol from Aqueous Solution through Pervaporation Using PTSMP-Silica Nano Hybrid Membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Hou, R.; Konstas, K.; Akram, A.; Lau, C.H.; Hill, M.R. Control of physical aging in super-glassy polymer mixed matrix membranes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. Recent Progress in Separation Membranes and Their Fermentation Coupled Processes for Biobutanol Recovery. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 11962–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, V.; Borisov, I.; Golubev, G.; Vasilevsky, V.; Matveev, D.; Bondarenko, G.; Volkov, A. Sorption-assisted Thermopervaporation Method for Organics Recovery from ABE Fermentation Broth. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, M.F.S.; Vandezande, P.; Van Hecke, W.H.S.; Porto-Carrero, W.J.; Dotremont, C.T.E. Study on Ageing/Fouling Phenomena and the Effect of Upstream Nanofiltration on in-Situ Product Recovery of n-Butanol through Poly [1-(Trimethylsilyl)-1-Propyne] Pervaporation Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 447, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, A.; Knozowska, K.; Kujawa, J.; Li, G.; Kujawski, W. Fabrication of PDMS Based Membranes with Improved Separation Efficiency in Hydrophobic Pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, L.; Xu, Z.; Meng, Q. Preparation of Stable Multilayer PDMS Composite Pervaporation Membrane Incorporated with In-Situ Transformed Metal Organic Frameworks for Enhanced Butanol Recovery. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 700, 122727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Fan, L. Enhanced Pervaporation of the Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) Mixed Matrix Membrane Based on the Self-Assembly of Multidimensional Carbon Nanomaterials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, N.; Wang, N.; Yi, S.; An, Q.-F. A Review on the Design and Fabrication of Polydimethylsiloxane Thin-Film Composite Membranes (TFCMs) for Alcohol Permselective Pervaporation. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Goethem, C.; Naik, P.V.; Van de Velde, M.; Van Durme, J.; Verplaetse, A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Stability of Filled PDMS Pervaporation Membranes in Bio-Ethanol Recovery from a Real Fermentation Broth. Membranes 2023, 13, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Wang, T.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, J. Fabrication and Characterization of Superhydrophobic PDMS Composite Membranes for Efficient Ethanol Recovery via Pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushevenko, E.A.; Podtynnikov, I.A.; Borisov, I.L. High-Selectivity Pervaporation Membranes for 1-Butanol Removal from Wastewater. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2019, 92, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, A.; Knozowska, K.; Kujawa, J.; Kujawski, W. Influence of Downstream Pressure on Pervaporation Properties of PDMS and POMS Based Membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 159, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadav, G.L.; Aswal, V.K.; Bhatt, H.; Chaudhari, J.C.; Singh, P.S. Influence of Film Thickness on the Structure and Properties of PDMS Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.H. High performance and thermally stable PDMS pervaporation membranes prepared using a phenyl-containing tri-functional crosslinker for n-butanol recovery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, A.V.; Shalygin, M.G.; Matson, S.M.; Khotimskiy, V.S.; Teplyakov, V.V. Separation of Diluted Butanol–Water Solutions via Vapor Phase by Organophilic Membranes Based on High Permeable Polyacetylenes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, B.J.A.; Cren, É.C.; Windmöller, D.; Figueiredo, K.C. de S. Activated Carbon-Loaded Polydimethylsiloxane Membranes for the Pervaporation of 1-Butanol from Aqueous Solutions. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20180573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Estager, J.; Monbaliu, J.M.; Debecker, D.P.; Luis, P. Separation of Bio-based Chemicals Using Pervaporation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2311–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, C.; Capilla, M.; Valles, A.; San-Valero, P.; Gabaldón, C.; Javier Álvarez-Hornos, F. Developing a High-Rate ABE Fermentation System for Rice Straw: CSTR with Immobilization on Granular-Activated Carbon with Ex Situ Pervaporation. Fuel 2024, 360, 130538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Wu, H.; Qin, P.; Van der Bruggen, B. Polydimethylsiloxane Based Membranes for Biofuels Pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-P.; Shareef, U.; Xu, Z.-L.; Taymazov, D.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Xu, Y.-S. Epoxide-Based PDMS TFC Membrane Fabricated via the T-FLO Technique for the Phenol Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.; Brisdon, B.J.; England, R.; Field, R.W. Performance of PDMS and Organofunctionalised PDMS Membranes for the Pervaporative Recovery of Organics from Aqueous Streams. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 137, 63–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hecke, W.; De Wever, H. High-Flux POMS Organophilic Pervaporation for ABE Recovery Applied in Fed-Batch and Continuous Set-Ups. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börjesson, J.; Karlsson, H.O.E.; Trägårdh, G. Pervaporation of a Model Apple Juice Aroma Solution: Comparison of Membrane Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 119, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.L.; Grushevenko, E.A.; Anokhina, T.S.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Levin, I.S.; Bondarenko, G.N.; Volkov, V.V.; Volkov, A.V. Influence of Side Chains Assembly on the Structure and Transport Properties of Comb-like Polysiloxanes in Hydrocarbon Separation. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 22, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiao, Z.; Tan, S.; Pu, L.; Zhang, Z. Composite PDMS membrane with high flux for the separation of organics from water by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.; Podtynnikov, I.; Grushevenko, E.; Scharova, O.; Anokhina, T.; Makaev, S.; Volkov, A.; Volkov, V. High Selective Composite Polyalkylmethylsiloxane Membranes for Pervaporative Removal of MTBE from Water: Effect of Polymer Side-Chain. Polymers 2020, 12, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushevenko, E.A.; Borisov, I.L.; Knyazeva, A.A.; Volkov, V.V.; Volkov, A.V. Polyalkylmethylsiloxanes Composite Membranes for Hydrocarbon/Methane Separation: Eight Component Mixed-Gas Permeation Properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.L.; Volkov, V.V. Thermopervaporation Concept for Biobutanol Recovery: The Effect of Process Parameters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 146, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Hao, P. Influence of the Porous Support on Diffusion in Composite Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 494, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipnizki, F.; Hausmanns, S.; Field, R.W. Influence of Impermeable Components on the Permeation of Aqueous 1-Propanol Mixtures in Hydrophobic Pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 228, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Symbol | Polymer of the Selective Layer | Porous Support |
|---|---|---|
| MC1-1 | poly(dimethylsiloxane) | MFFK-1 |
| MC6-1 | poly(hexylmethylsiloxane) | MFFK-1 |
| MC7-1 | poly(heptylmethylsiloxane) | MFFK-1 |
| MC8-1 | poly(octylmethylsiloxane) | MFFK-1 |
| MC10-1 | poly(decylmethylsiloxane) | MFFK-1 |
| MC6-0 | poly(hexylmethylsiloxane) | UFFK |
| MC7-0 | poly(heptylmethylsiloxane) | UFFK |
| MC8-0 | poly(octylmethylsiloxane) | UFFK |
| MC10-0 | poly(decylmethylsiloxane) | UFFK |
| Membrane. | Solution | Temperature, °C | Permeability [mol·m–2·h–1·Pa–1] | Selectivity (X/H2O) | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BuOH | PrOH | EtOH | BuOH | PrOH | EtOH | ||||
| MC6-1 | 1% BuOH, 1% PrOH, 3% EtOH in water | 30 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 0.9 | - |
| MC7-1 | 1% BuOH, 1% PrOH, 3% EtOH in water | 30 | 3.5 | 3.1 | 1.7 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.0 | - |
| MC8-1 | 1% BuOH, 1% PrOH, 3% EtOH in water | 30 | 3.4 | 3.2 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 0.9 | - |
| MC10-1 | 1% BuOH, 1% PrOH, 3% EtOH in water | 30 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 0.9 | - |
| MDK-3 | 1% BuOH in water | 30 | 6.4 | - | - | 0.9 | - | - | [47] |
| Pervap 4060 | 1% BuOH in water | 30 | 5.6 | - | - | 0.9 | - | - | [47] |
| PolyAn | 1% BuOH in water | 30 | 7.5 | - | - | 0.4 | - | - | [47] |
| Pervatech BV | 1% BuOH in water | 30 | 5.1 | - | - | 0.5 | - | - | [47] |
| Pervatech PDMS | 4% BuOH in water | 30 | 5.5 | - | - | 0.5 | - | - | [48] |
| Pervatech PDMS | 4% BuOH in water | 30 | 0.9 | - | - | 0.4 | - | - | [48] |
| Pervap 1060 | 4% PrOH in water | 80 | - | 1.3 | - | - | 0.6 | - | [66] |
| Pervap 1070 | 4% PrOH in water | 80 | - | 0.7 | - | - | 1.0 | - | [66] |
| Pervap 4060 | 5% BuOH in water | 25 | 9.4 | - | - | 1.6 | - | - | [25] |
| Pervatech BV | 3.5% BuOH in water | 42 | 8.2 | - | - | 0.9 | - | - | [25] |
| Pervatech BV | 5% BuOH in water | 25 | 4.6 | - | - | 0.4 | - | - | [25] |
| PolyAn | 5% BuOH in water | 25 | 7.9 | - | - | 0.4 | - | - | [25] |
| Pervap 4060 | 5% EtOH in water | 25 | - | - | 4.5 | - | - | 0.6 | [25] |
| Pervatech BV | 5% EtOH in water | 25 | - | - | 6.0 | - | - | 0.5 | [25] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grushevenko, E.; Rokhmanka, T.; Chechenov, I.; Safronov, P.; Anokhina, T.; Bazhenov, S.; Borisov, I. Oxygenates Removal from Water by Hydrophobic Pervaporation with Polyalkylmethylsiloxane Membranes. Water 2025, 17, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010060
Grushevenko E, Rokhmanka T, Chechenov I, Safronov P, Anokhina T, Bazhenov S, Borisov I. Oxygenates Removal from Water by Hydrophobic Pervaporation with Polyalkylmethylsiloxane Membranes. Water. 2025; 17(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrushevenko, Evgenia, Tatyana Rokhmanka, Islam Chechenov, Petr Safronov, Tatyana Anokhina, Stepan Bazhenov, and Ilya Borisov. 2025. "Oxygenates Removal from Water by Hydrophobic Pervaporation with Polyalkylmethylsiloxane Membranes" Water 17, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010060
APA StyleGrushevenko, E., Rokhmanka, T., Chechenov, I., Safronov, P., Anokhina, T., Bazhenov, S., & Borisov, I. (2025). Oxygenates Removal from Water by Hydrophobic Pervaporation with Polyalkylmethylsiloxane Membranes. Water, 17(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010060











