Geochemical Assessment of the Evolution of Groundwater under the Impact of Seawater Intrusion in the Mannar District of Sri Lanka
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
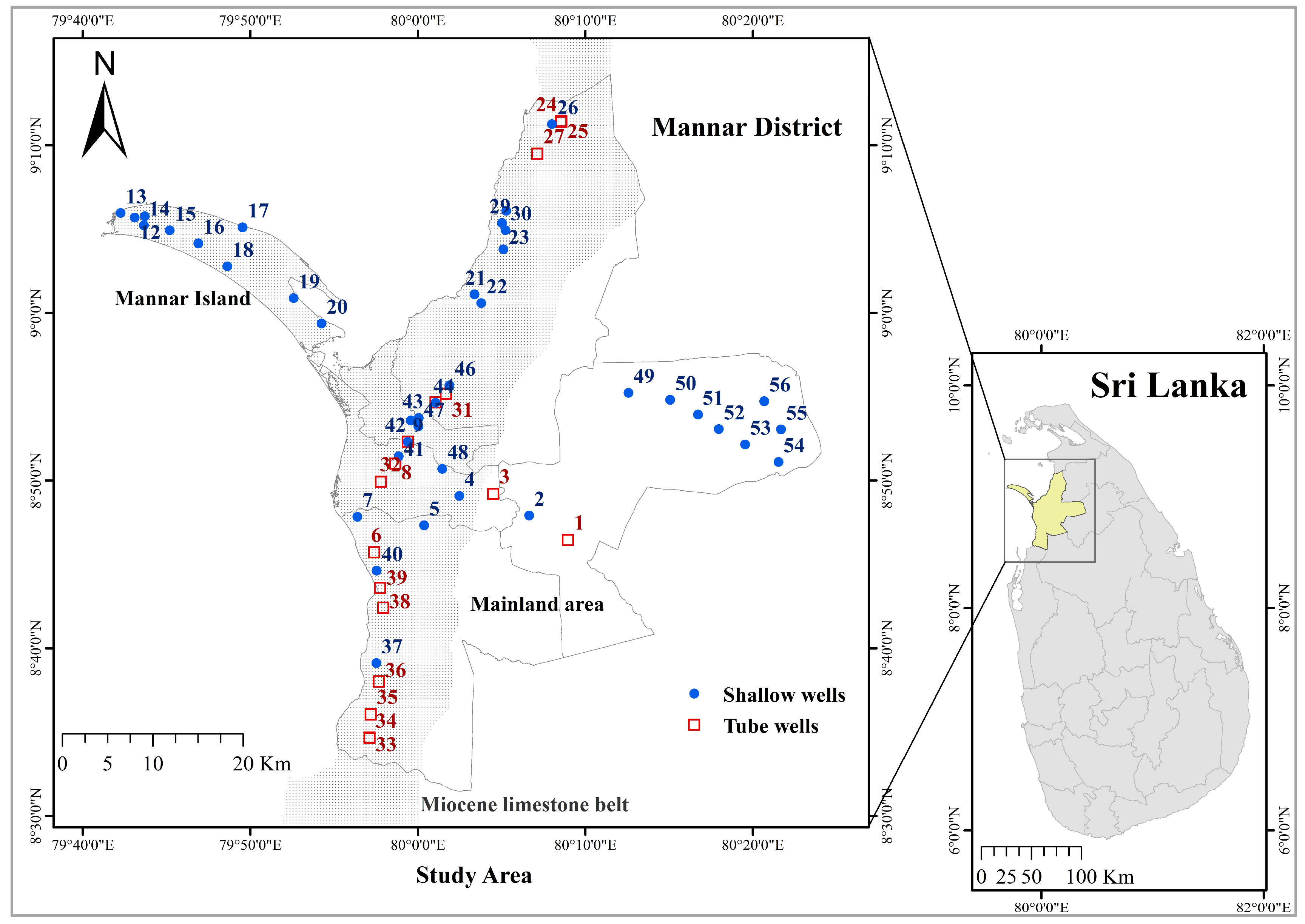
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. Sample Collections and Measurements
2.3. Water Quality Index (WQI) and Seawater Mixing Index (SMI) Calculations
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Evolution Mechanisms of Groundwater
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Groundwater Geochemical Characteristics
3.2. WQI and SMI
3.3. Groundwater Evolution Process and Mechanism
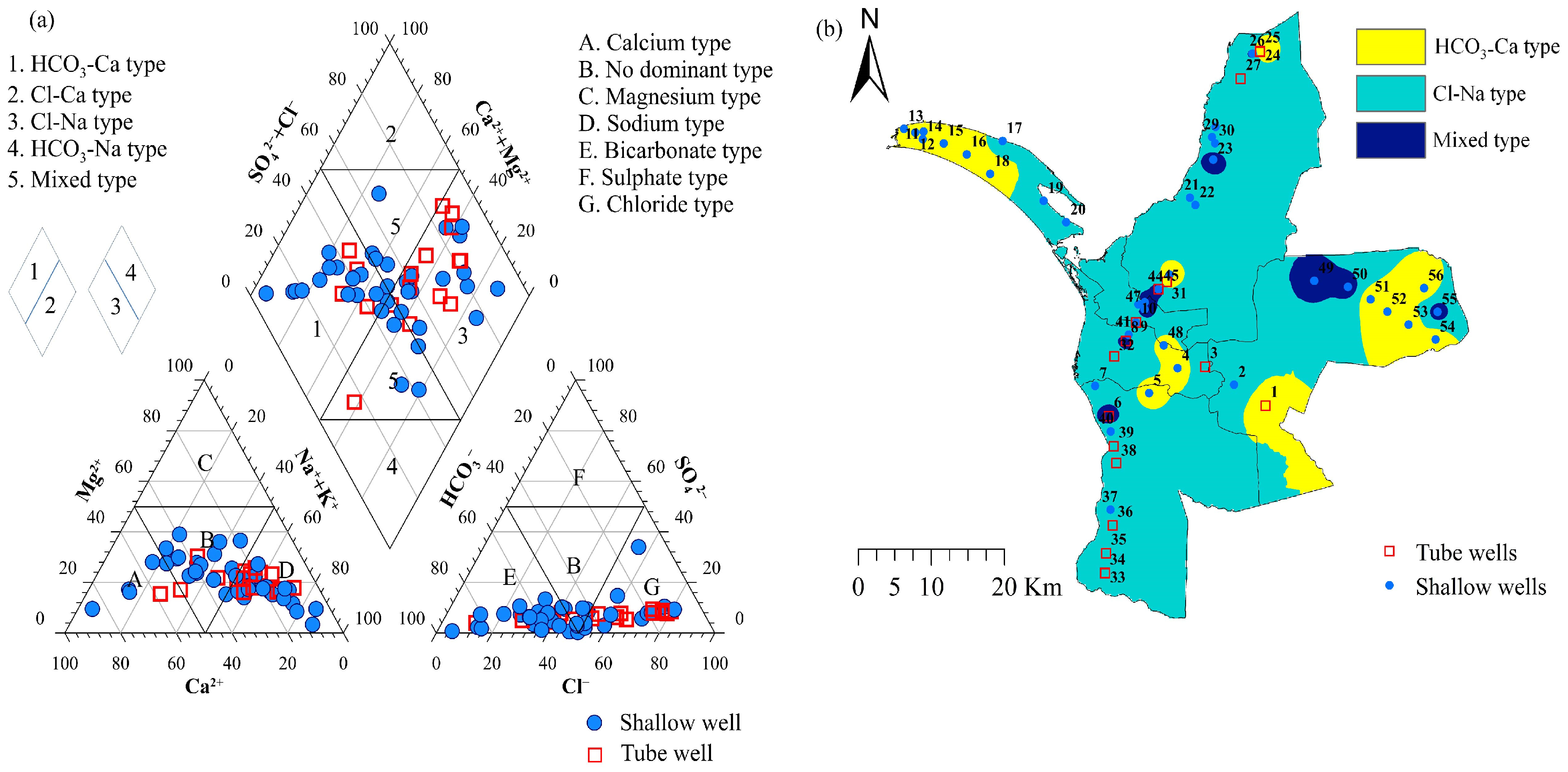
3.4. Hydrochemical Types in Groundwater
3.5. Chemical Evolution of Groundwater
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.; Biswas, A.; Banerjee, S. Spatio-temporal variability of seawater mixing in the coastal aquifers based on hydrogeochemical fingerprinting and statistical modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 346, 118937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntoriero, M.L.; Cirelli, A.F.; Volpedo, A.V. Geochemical mechanisms controlling the chemical composition of groundwater and surface water in the southwest of the Pampean plain (Argentina). J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 150, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, S.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of the groundwater quality with WQI (Water Quality Index) and multivariate analysis: A case study of the Tefenni plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1725–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghesquière, O.; Walter, J.; Chesnaux, R.; Rouleau, A. Scenarios of groundwater chemical evolution in a region of the Canadian Shield based on multivariate statistical analysis. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 246–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Prakash, R.; Saravanan, K.; Karunanidhi, D. Hydrogeochemistry of Groundwater From Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry Coastal Aquifers, South India: Implication for Chemical Characteristics and Sea Water Intrusion. In GIS and Geostatistical Techniques for Groundwater Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastén-Zapata, E.; Ledesma-Ruiz, R.; Harter, T.; Ramírez, A.I.; Mahlknecht, J. Assessment of sources and fate of nitrate in shallow groundwater of an agricultural area by using a multi-tracer approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurl, J.; Imaz-Lamadrid, M.A.; Mendez-Rodriguez, L.C.; Hernández-Morales, P. Hydrochemical Indicator Analysis of Seawater Intrusion into Coastal Aquifers of Semiarid Areas. Resources 2023, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Mahlknecht, J. Tracking nitrate and sulfate sources in groundwater of an urbanized valley using a multi-tracer approach combined with a Bayesian isotope mixing model. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carol, E.; Kruse, E.; Mas-Pla, J. Hydrochemical and isotopical evidence of ground water salinization processes on the coastal plain of Samborombón Bay, Argentina Eleonora. J. Hydrol. 2009, 365, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, L.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Bertrand, G.; Kloppmann, W.; Aquilina, L.; Martins, V.; Hirata, R.; Montenegro, S.; Pauwels, H.; Chatton, E.; et al. Origins and processes of groundwater salinization in the urban coastal aquifers of Recife (Pernambuco, Brazil): A multi-isotope approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530–531, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaska, M.; La Salle, C.L.G.; Lancelot, J.; Mohamad, A.; Verdoux, P.; Noret, A.; Simler, R.; ASTER Team. Origin of groundwater salinity (current seawater vs. saline deep water) in a coastal karst aquifer based on Sr and Cl isotopes. Case study of the La Clape massif (southern France). Appl. Geochem. 2013, 37, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, F.; Vallejos, A.; Daniele, L.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Identification of a Holocene aquifer-lagoon system using hydrogeochemical data. Quat. Res. 2014, 82, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, P.M.; Reichard, E.G. L’intrusion d’eau salée dans les régions côtières d’Amérique du Nord. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, G.; Monni, S.; Oggiano, G.; Paternoster, M.; Sinisi, R. Tracing groundwater salinization processes in coastal aquifers: A hydrogeochemical and isotopic approach in the Na-Cl brackish waters of northwestern Sardinia, Italy. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2917–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Galván, C.; Prol-Ledesma, R.M.; Torres-Vera, M.A. Geothermal prospects in the Baja California Peninsula. Geothermics 2015, 55, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabchi, H.; Mahmoodzadeh, D.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T. Sea-level rise impacts on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Review and integration. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, J.; Allen, D.M. Assessing the risk of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.V.S.G.; Rao, G.T.; Surinaidu, L.; Mahesh, J.; Rao, S.T.M.; Rao, B.M. Assessment of geochemical processes occurring in groundwaters in the coastal alluvial aquifer. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8259–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Rao, V.V.S.G. Hydrogeochemical, seawater intrusion and oxygen isotope studies on a coastal region in the Puri District of Odisha, India. Catena 2019, 172, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Chaturangani, D.; Abeykoon, S.; Barth, J.A.; van Geldern, R.; Edirisinghe, E.A.N.V.; Dissanayake, C.B. Quantification of groundwater–seawater interaction in a coastal sandy aquifer system: A study from Panama, Sri Lanka. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S.; Joye, S.B. Saltwater Intrusion and Submarine Groundwater Discharge: Acceleration of Biogeochemical Reactions in Changing Coastal Aquifers. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 600710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holding, S.; Allen, D.M. From days to decades: Numerical modelling of freshwater lens response to climate change stressors on small low-lying islands. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, G.; Sun, S.; Hagan DF, T.; Chen, T.; Dolman, H.; Liu, Y. Long-term changes in evapotranspiration over China and attribution to climatic drivers during 1980–2010. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 126037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Bandara, U.G.C.; Diyabalanage, S.; Senaratne, S.; Barth, J.A.C. Application of Water Quality Index as a vulnerability indicator to determine seawater intrusion in unconsolidated sedimentary aquifers in a tropical coastal region of Sri Lanka. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 19, 100831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Diyabalanage, S.; Premathilake, K.M.; Hanke, C.; Van Geldern, R.; Barth, J.A.C. Science of the Total Environment Controls of evaporative irrigation return fl ows in comparison to seawater intrusion in coastal karstic aquifers in northern Sri Lanka: Evidence from solutes and stable isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Mata, L.J.; Arnell, N.W.; Döll, P.; Jimenez, B.; Miller, K.; Oki, T.; Şen, Z.; Shiklomanov, I. The implications of projected climate change for freshwater resources and their management. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Döll, P. Will groundwater ease freshwater stress under climate change? Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.L. Handbook of Climate Change Adaptation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, U.G.C.; Diyabalanage, S.; Hanke, C.; van Geldern, R.; Barth, J.A.C.; Chandrajith, R. Arsenic-rich shallow groundwater in sandy aquifer systems buffered by rising carbonate waters: A geochemical case study from Mannar Island, Sri Lanka. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathunga, K.; Diyabalanage, S.; Frank, A.H.; Chandrajith, R.; Barth, J.A.C. Influences of seawater intrusion and anthropogenic activities on shallow coastal aquifers in Sri Lanka: Evidence from hydrogeochemical and stable isotope data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23002–23014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, P.G. An Introduction to the Geology of Sri Lanka (Ceylon), 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendram, D.K. An Assessment of Drought in Mannar District, Sri Lanka. Int. J. Humanit. Appl. Soc. Sci. 2019, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekara, S.S.K.; Pathmarajah, S.; Obeysekera, J.; Vithanage, M. Water Scarcity—A Concealed Phenomenon in Sri Lanka: A Mini Review. ACS ES&T Water 2023, 3, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Chandrapala, L. Water balance variability across Sri Lanka for assessing agricultural and environmental water use. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 58, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Selvarathnam, R. The Groundwater Resources of the Murunkan Area; North-West Land Water Resources Development Project Sri Lanka; Water Resources Board, Groundwater Division: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Panabokke, C.R.; Perera, A.P.G.R.L. Groundwater Resources of Sri Lanka; Water Resources Board: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Alexakis, D.E. Linking dpsir model and water quality indices to achieve sustainable development goals in groundwater resources. Hydrology 2021, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaidy, A.H.M.J.; Abid, H.S.; Maulood, B.K. Application of Water Quality Index for Assessment of Dokan Lake Ecosystem, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2010, 2, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 398–403. [Google Scholar]
- Aladejana, J.A.; Kalin, R.M.; Sentenac, P.; Hassan, I. Groundwater quality index as a hydrochemical tool for monitoring saltwater intrusion into coastal freshwater aquifer of Eastern Dahomey Basin, Southwestern Nigeria. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 13, 100568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, G.; Elango, L.; Sridhar, S.G.D.; Gowrisankar, G. Hydrogeochemical processes and influence of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8989–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Yun, S.T.; Chae, G.T.; Yoo, I.S.; Shin, K.S.; Heo, C.H.; Lee, S.K. Regional hydrochemical study on salinization of coastal aquifers, western coastal area of South Korea. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indika, S.; Hu, D.; Wei, Y.; Yapabandara, I.; Cooray, T.; Makehelwala, M.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Weragoda, S.K.; Weerasooriya, R.; Pang, Z. Spatiotemporal Variation of Groundwater Quality in North Central Province, Sri Lanka. ACS ES&T Water 2023, 3, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistr. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 2012, 170, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar]
- Giménez-Forcada, E. Space/time development of seawater intrusion: A study case in Vinaroz coastal plain (Eastern Spain) using HFE-Diagram, and spatial distribution of hydrochemical facies. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-forcada, E. Dynamic of Seawater Interface using Hydrochemical Facies Evolution Diagram (HFE-D). Groundwater 2010, 48, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahir, M.; Ouazar, D.; Ouhamdouch, S.; Zouari, K. Groundwater for Sustainable Development Assessment of groundwater mineralization of alluvial coastal aquifer of essaouira basin (Morocco) using the hydrochemical facies evolution diagram (HFE-Diagram). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Forcada, E. Use of the Hydrochemical Facies Diagram (HFE-D) for the evaluation of salinization by seawater intrusion in the coastal Oropesa Plain: Comparative analysis with the coastal Vinaroz Plain, Spain. HydroResearch 2019, 2, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Geirnaert, W. Processes accompanying the intrusion of salt water. Geol. Appl. Idrogeol. 1983, 18, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, S.; Sarma, K. Qualitative assessment, geochemical characterization and corrosion-scaling potential of groundwater resources in Ghaziabad district of Uttar Pradesh, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costall, A.R.; Harris, B.D.; Teo, B.; Schaa, R.; Wagner, F.M.; Pigois, J.P. Groundwater Throughflow and Seawater Intrusion in High Quality Coastal Aquifers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, C.N. Chemistry for Sanitary Engineers; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Nebbioso, A.; Piccolo, A. Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM): A critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Indika, S.; Makehelwala, M.; Titus, C.O.O.R.A.Y.; Zhu, L.; Pang, Z.; Zhong, H.; Weragoda, S.K.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Weerasooriya, R.; et al. Chemical characteristics and water stability evaluation of groundwater in the CKDu Zone of Sri Lanka. J. Environ. Sci. 2023; 1001-0742, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xie, R.; Lv, Z. Chemical characteristics of groundwater and source identification in a coastal city. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, J.; He, S. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in terms of health risks in Luohe aquifer in Wuqi County of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupre, B.; Louvat, P.; Allegre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugulothu, S.; Subbarao, N.; Das, R.; Dhakate, R. Geochemical evaluation of groundwater and suitability of groundwater quality for irrigation purpose in an agricultural region of South India. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; Jing, L.; Yu, P. Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in and around a mountainous tourist town of China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H. Hydrogeochemistry and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the southern part of the yellow river alluvial plain (Zhongwei section), Northwest China. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2015, 18, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Biswas, A.; Banerjee, S.; Rathore, S.; Rana, V.; Ram, K.; Acharya, T. Integrating magnetic susceptibility, hydrogeochemical, and isotopic data to assess the seawater invasion in coastal aquifers of Digha, West Bengal, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 23474–23503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Parameters | Unit | Shallow Well | Tube Well | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean ± SD | CV | Range | Mean ± SD | CV | ||
| pH | 5.92–7.97 | 6.97 ± 0.55 | 0.08 | 5.89–7.15 | 6.48 ± 0.40 | 0.06 | |
| Temperature | °C | 27.30–28.20 | 27.63 ± 0.18 | 0.01 | 27.50–28.10 | 27.68 ± 0.16 | 0.01 |
| EC | µS/cm | 384.00–5910.00 | 1548.23 ± 1249.07 | 0.81 | 847.00–5310.00 | 2336.24 ± 1360.39 | 0.58 |
| TDS | mg/L | 192.00–2950.00 | 773.79 ± 624.13 | 0.81 | 424.00–2650.00 | 1168.35 ± 680.17 | 0.58 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 4.77–797.00 | 162.20 ± 178.90 | 1.10 | 57.62–482.60 | 234.12 ± 156.83 | 0.67 |
| K+ | mg/L | 0.29–68.01 | 16.21 ± 16.95 | 1.05 | 0.95–39.71 | 13.02 ± 11.58 | 0.89 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 4.85–111.55 | 31.20 ± 20.60 | 0.66 | 14.43–100.37 | 43.95 ± 21.98 | 0.50 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 17.54–187.83 | 65.09 ± 33.81 | 0.52 | 27.57–215.23 | 83.63 ± 48.07 | 0.57 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 190.32–980.88 | 405.48 ± 160.65 | 0.40 | 190.32–790.56 | 492.59 ± 121.01 | 0.25 |
| F− | mg/L | 0.14–2.48 | 0.64 ± 0.44 | 0.68 | 0.29–1.73 | 0.79 ± 0.43 | 0.54 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 7.38–1530.96 | 301.77 ± 368.19 | 1.22 | 35.80–1494.38 | 505.24 ± 430.86 | 0.85 |
| Br− | mg/L | 0–5.16 | 0.93 ± 1.11 | 1.20 | 0.15–5.50 | 1.75 ± 1.57 | 0.90 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 0–85.60 | 4.92 ± 14.23 | 2.89 | 0–61.02 | 10.56 ± 16.64 | 1.58 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 0.99–906.70 | 70.91 ± 148.15 | 2.09 | 15.74–200.20 | 78.43 ± 61.52 | 0.78 |
| TH | mg/L | 84.81–928.36 | 291.00 ± 155.46 | 0.53 | 128.27–950.75 | 389.81 ± 192.97 | 0.50 |
| DOC | mg/L | 0.59–15.16 | 6.64 ± 3.19 | 0.48 | 1.26–9.15 | 3.93 ± 2.55 | 0.65 |
| WQI | 29.01–306.54 | 100.12 ± 61.89 | 0.62 | 69.98–278.38 | 127.03 ± 61.91 | 0.49 | |
| SMI | 0.05–7.91 | 1.67 ± 1.95 | 1.17 | 0.51–6.82 | 2.60 ± 2.02 | 0.78 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Athauda, S.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Indika, S.; Yapabandara, I.; Weragoda, S.K.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y. Geochemical Assessment of the Evolution of Groundwater under the Impact of Seawater Intrusion in the Mannar District of Sri Lanka. Water 2024, 16, 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081137
Athauda S, Wang Y, Hao Z, Indika S, Yapabandara I, Weragoda SK, Liu J, Wei Y. Geochemical Assessment of the Evolution of Groundwater under the Impact of Seawater Intrusion in the Mannar District of Sri Lanka. Water. 2024; 16(8):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081137
Chicago/Turabian StyleAthauda, Samadhi, Yunwen Wang, Zhineng Hao, Suresh Indika, Isuru Yapabandara, Sujithra K. Weragoda, Jingfu Liu, and Yuansong Wei. 2024. "Geochemical Assessment of the Evolution of Groundwater under the Impact of Seawater Intrusion in the Mannar District of Sri Lanka" Water 16, no. 8: 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081137
APA StyleAthauda, S., Wang, Y., Hao, Z., Indika, S., Yapabandara, I., Weragoda, S. K., Liu, J., & Wei, Y. (2024). Geochemical Assessment of the Evolution of Groundwater under the Impact of Seawater Intrusion in the Mannar District of Sri Lanka. Water, 16(8), 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081137







