Risk Assessment of Oil Spills along the Coastline of Jiaozhou Bay Using GIS Techniques and the MEDSLIK-II Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
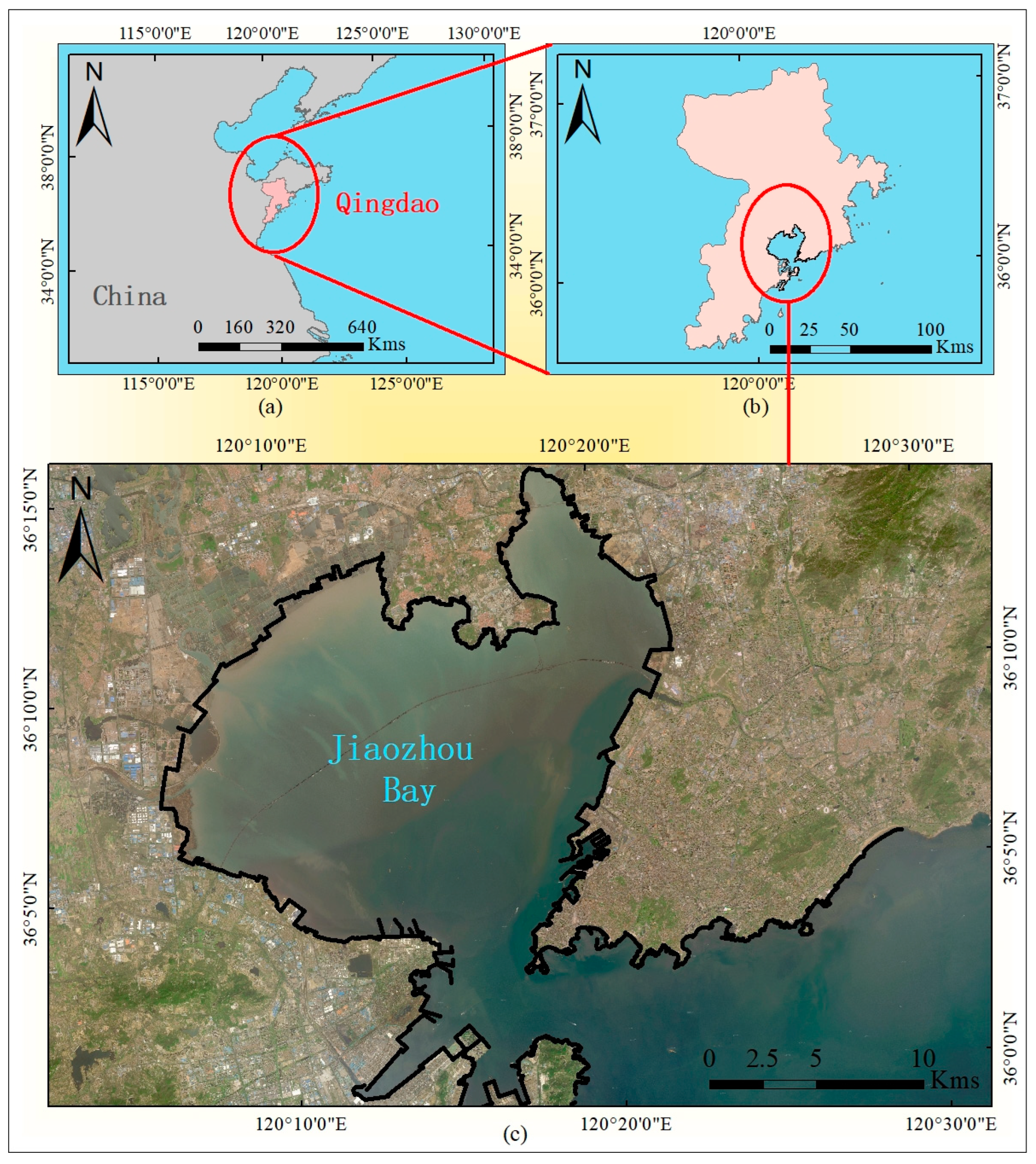
2.1. Study Area
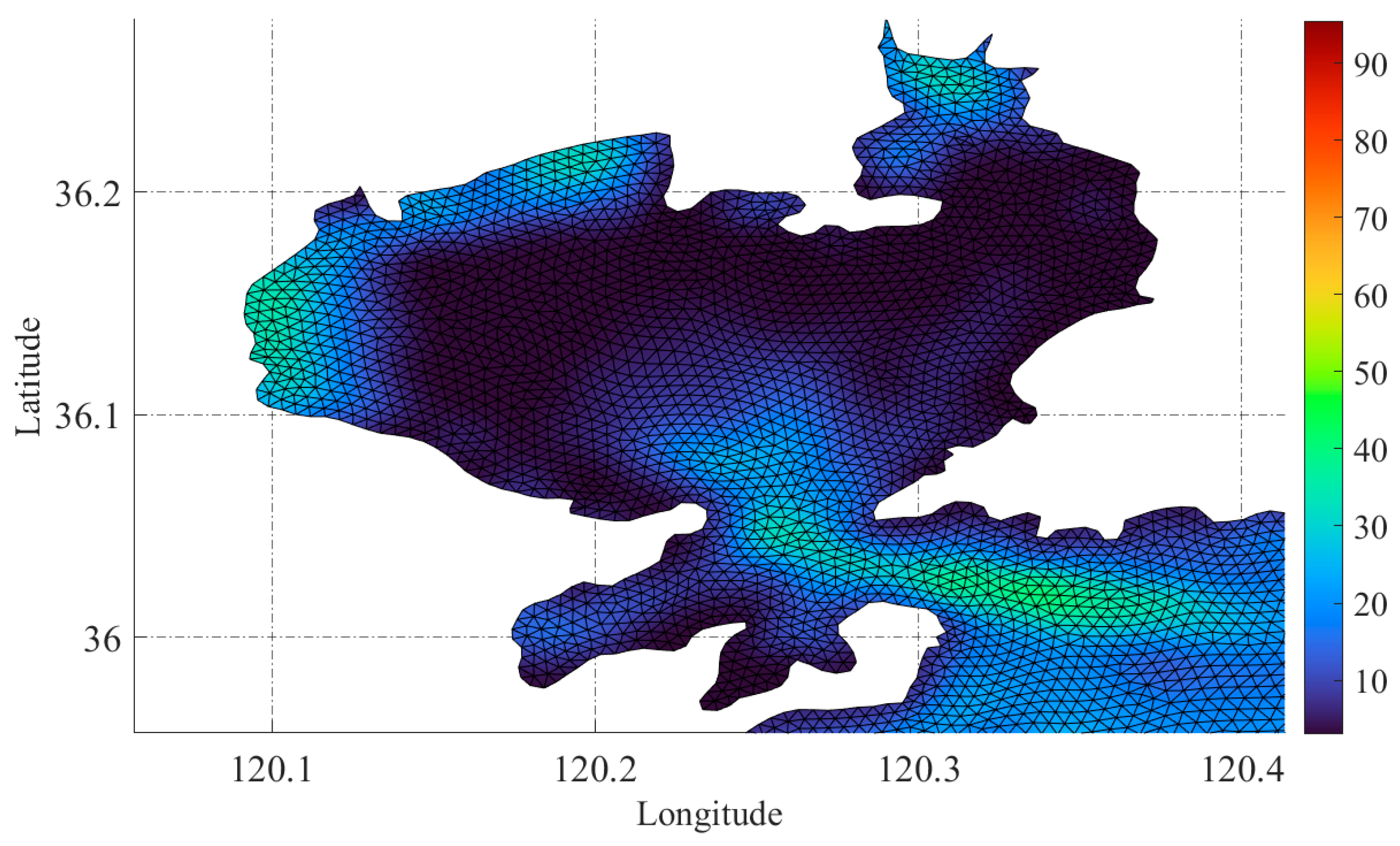
2.2. Datasets
3. Methodology
3.1. Step1: Establishment of Hypothetical Scenarios
3.2. Step 2: Simulation of Oil Spill Trajectory
3.3. Step 3: Shoreline Vulnerability Assessment
3.4. Step 4: Oil Spill Risk Assessment
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Validation of Models and Simulation of Oil Spill
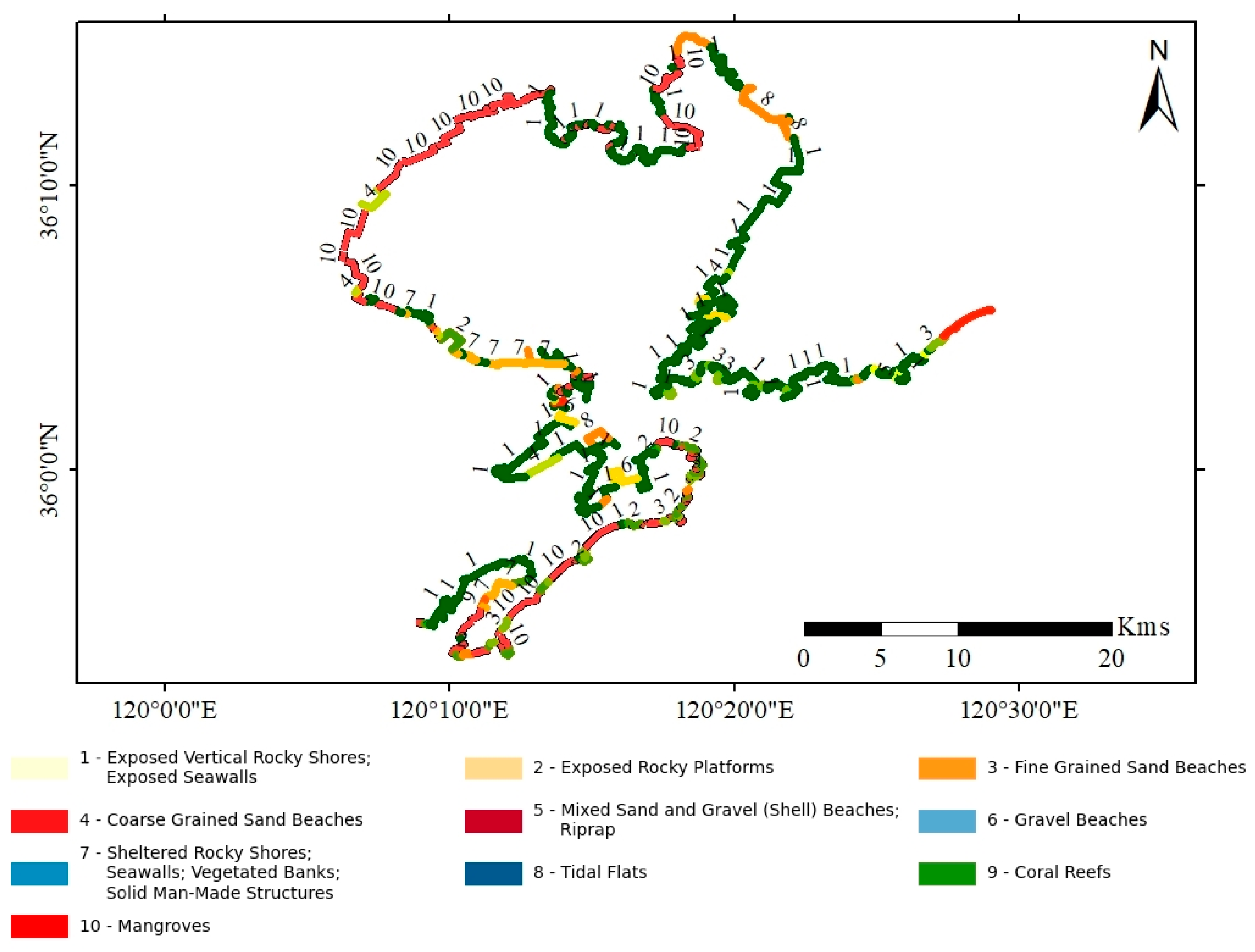
4.2. ESI Evaluation
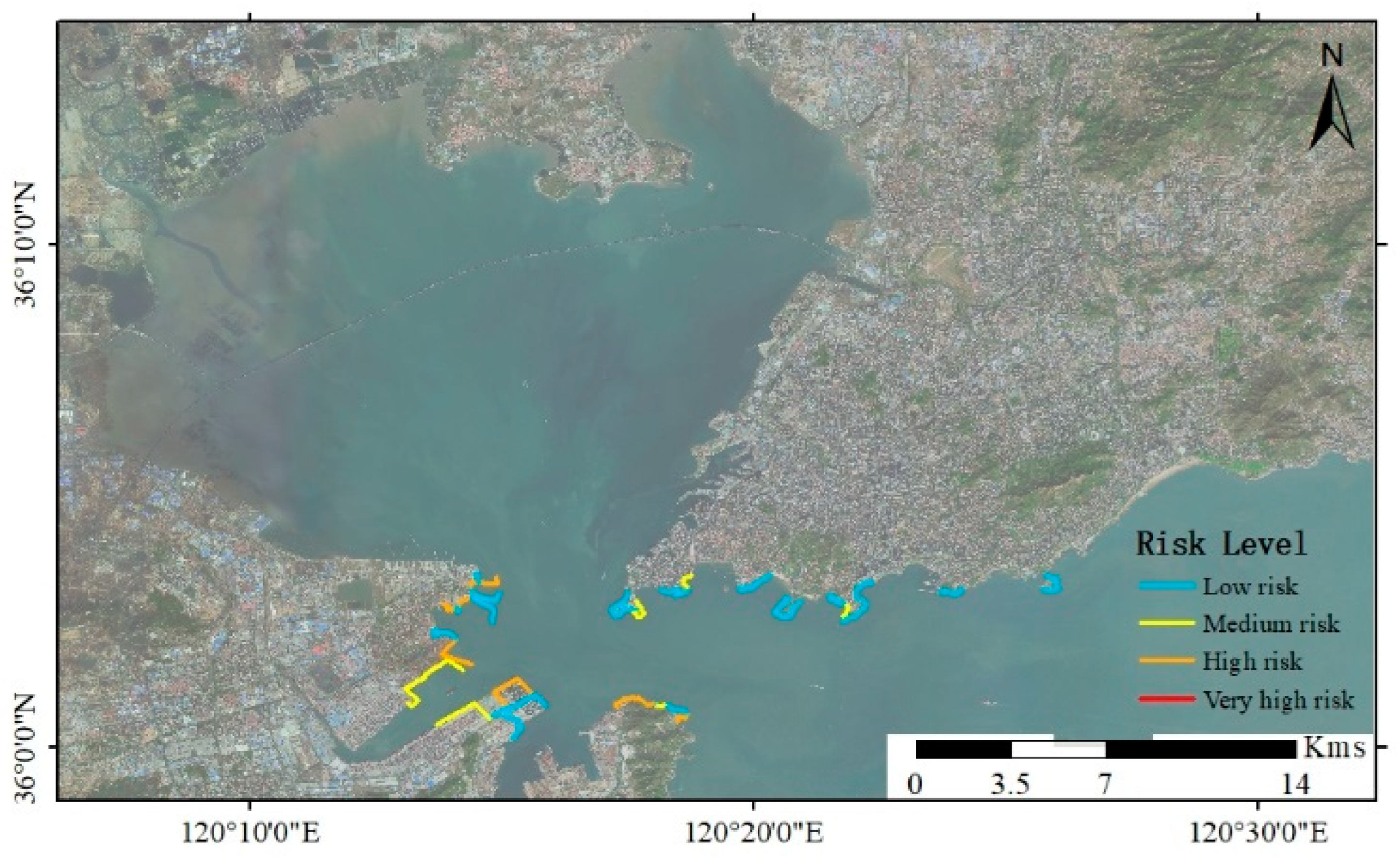
4.3. Risk Assessment of Oil Spill
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Date | Location | Ship Name | Cause of Accident | Spilled Oil (t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1974/9/1 | Zhongsha Reef | Daqing 31 | Grounding | 895.0 |
| 2 | 1975/3/1 | Huangdao Dock | Daqing 35 | Oil Tank Overflow | 4.0 |
| 3 | 1975/5/1 | Channel (Horseshoe Reef) | Daqing 30 | Grounding | 33.0 |
| 4 | 1975/9/1 | Huangdao Dock | Daqing 53 | Collision | 3.0 |
| 5 | 1975/9/1 | Dagang Dock | Nanping | Misoperation | 20.0 |
| 6 | 1975/10/1 | Anchorage | Daqing 15 | Oil Tank Overflow | 7.0 |
| 7 | 1975/10/1 | Dagang Dock | Daqing 36 | Oil Tank Overflow | 4.0 |
| 8 | 1975/12/1 | Huangdao Dock | Daqing 41 | Oil Tank Overflow | 2.0 |
| 9 | 1976/7/1 | Dagang Dock | Huangdao | Oil Pipe Detachment | 15.0 |
| 10 | 1977/11/1 | Huangdao Dock | Daqing 244 | Oil Tank Overflow | 30.0 |
| 11 | 1979/6/1 | Huangdao Dock | Daqing 240 | Misoperation | 10.0 |
| 12 | 1979/6/1 | Huangdao Dock | Sairus | Collision | 350.0 |
| 13 | 1980/8/1 | Zhongsha Reef | Daqing 256 | Grounding | 43.0 |
| 14 | 1983/11/1 | Zhongsha Reef | Eastern Ambassador | Grounding | 3343.0 |
| 15 | 1984/9/1 | Zhongsha Reef | Jiacui | Grounding | 757.0 |
| 16 | 1986/10/1 | Huangdao Dock | Daqing 245 | Explosion | 100.0 |
| 17 | 1987/9/1 | Huangdao Dock | Huahai 2 | Oil Pipe Breakage | 120.0 |
| 18 | 1994/7/1 | Qingdao Port Anchorage | Praba Cyprus | Collision | 100.0 |
| 19 | 2001/7/1 | Dagang Dock | Huahai 78 | Oil Tank Overflow | 3.0 |
| 20 | 2001/9/1 | Main Channel | Samitun Kuwait | Oil Pipe Detachment | 25.0 |
| 21 | 2002/10/1 | Huangdao Dock | Bao De 1136 | Misoperation | 1.0 |
| 22 | 2004/11/1 | Huangdao Dock | Zhele Oil 7 | Collision Leakage | 3.0 |
| 23 | 2005/7/1 | Qingdao Port | Titan Giant | Hull Damage and Oil Arm Break | 25.0 |
| 24 | 2006/2/1 | Qingdao Port | Fuhai | Hull Damage and Oil Leak | 64.0 |
| 25 | 2010/6/1 | Dagang Dock | Hehua | Oil Tank Crack | 1.0 |
| 26 | 2011/4/1 | Huangdao Dock | Youlan | Oil Arm Detachment | 2.0 |
| 27 | 2011/10/1 | Main Channel | Eastern Sunrise | Collision | 30.0 |
| 28 | 2013/11/1 | Huangdao Dock | None | Land Source | 2000.0 |
| 29 | 2014/4/1 | Main Channel | Huashun 88 | Collision | 30.0 |
| 30 | 2021/4/27 | Main Channel | SEA JUSTICE | Collision | 9400.0 |
| 31 | 2021/9/30 | Qianwan Dock | Xin *** | Air Pipe Overflow | 1.83 |
| 32 | 2022/3/21 | Huangdao Dock | ARZOYI | Cable Break during Unloading | 84.6 |
| 33 | 2022/4/21 | Qianwan Dock | Li *** | Air Pipe Overflow | 1.41 |
| 34 | 2022/6/17 | Qianwan Dock | Zhong **** | Air Pipe Overflow | 2.6 |
References
- International Tanker Owners Pollution Federation Limited. Fate of Oil Spills. 2022. Available online: https://www.itopf.org/knowledge-resources/documents-guides/fate-of-oil-spills/ (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Bousso, R. BP Deepwater Horizon Costs Balloon to $65 Billion. 2018. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSKBN1F50O5/ (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Michel, J.; Owens, E.H.; Zengel, S.; Graham, A.; Nixon, Z.; Allard, T.; Holton, W.; Reimer, P.D.; Lamarche, A.; White, M.; et al. Extent and degree of shoreline oiling: Deepwater Horizon oil spill, Gulf of Mexico, USA. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Di, Z.; Shi, J.; Shu, Y.; Wan, Z.; Song, L.; Zhang, W. Marine oil spill pollution causes and governance: A case study of Sanchi tanker collision and explosion. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, T.; Jin, D. Extent and frequency of vessel oil spills in US marine protected areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassler, B. Accidental versus operational oil spills from shipping in the Baltic Sea: Risk governance and management strategies. AMBIO 2011, 40, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.E.; Stone, J.; Demes, K.; Piscitelli, M. Consequences of oil spills: A review and framework for informing planning. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.R.; Grubesic, T.H. Oil spill modeling: Risk, spatial vulnerability, and impact assessment. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2020, 44, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepp Neves, A.A.; Pinardi, N.; Martins, F.; Janeiro, J.; Samaras, A.; Zodiatis, G.; De Dominicis, M. Towards a common oil spill risk assessment framework—Adapting ISO 31000 and addressing uncertainties. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 159, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, A.; Fortunato, A.B.; Epifânio, B.; den Boer, S.; Oliveira, E.R.; Alves, F.L.; Dias, J.M. An oil risk management system based on high-resolution hazard and vulnerability calculations. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2017, 136, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W. Development of a statistical oil spill model for risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.G.; Li, Z.; Johnson, W.; Auad, G. Progress of the oil spill risk analysis (OSRA) model and its Applications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenning, R.J.; Robinson, H.; Bock, M.; Rempel-Hester, M.A.; Gardiner, W. Current practices and knowledge supporting oil spill risk assessment in the Arctic. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 141, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valis, D.; Zak, L.; Walek, A. Selected mathematical functions used for operation data information. In Safety, Reliability and Risk Analysis: Beyond the Horizon; CRC Press-Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Abingdon, UK, 2014; pp. 1303–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Water, Resources, and Resilience: Insights from Diverse Environmental Studies. Water 2023, 15, 3965. [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, M.L. State of the art review and future directions in oil spill modeling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir-Heidari, P.; Raie, M. Response planning for accidental oil spills in Persian Gulf: A decision support system (DSS) based on consequence modeling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French-McCay, D.; Crowley, D.; Rowe, J.J.; Bock, M.; Robinson, H.; Wenning, R.; Parkerton, T. Comparative risk assessment of spill response options for a deepwater oil well blowout: Part 1. Oil spill modeling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Yin, J.; Zhang, X. Numerical simulation of oil spill trajectory and diffusion in the Bohai Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Samra, R.M.; Eissa, R.; El-Gammal, M. Applying the environmental sensitivity index for the assessment of prospective oil spills along the Nile Delta Coast, Egypt. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustandi, Y.; Damar, A.; Rakasiwi, G.; Afandy, A.; Hamdani, A.; Mulyana, D. Environmental sensitivity index mapping as a prevention strategy against oil spill pollution: A case study on the coastal area of South Sumatera Province in Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 414, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachite, D.; Domínguez, N.D.E.; El M’rini, A.; Anfuso, G. Environmental Sensitivity Index maps in a high maritime transit area: The Moroccan coast of the Gibraltar Strait study case. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 163, 103750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Guo, W.; Kong, S.; Xu, T. Estimating offshore exposure to oil spill impacts based on a statistical forecast model. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Rong, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Mu, L.; Lv, X. Modeling the long-term transport and fate of oil spilled from the 2021 A Symphony tanker collision in the Yellow Sea, China: Reliability of the stochastic simulation. Ocean. Model. 2023, 186, 102285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Bu, S. Trajectory and weathering of oil spill in Daya Bay, the South China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W. Annual Container Throughput of Qingdao Port in China from 2016 to 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1318460/container-throughput-port-of-qingdao/ (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Zhao, L. Analysis of Spilled Oil Pollution in Qingdao Port. World Maritime University Dissertations, 2017. Available online: https://commons.wmu.se/all_dissertations/1533/ (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- De Dominicis, M.; Pinardi, N.; Zodiatis, G.; Archetti, R. MEDSLIK-II, a Lagrangian marine surface oil spill model for short-term forecasting–Part 2: Numerical simulations and validations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1871–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dominicis, M.; Pinardi, N.; Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R. MEDSLIK-II, a Lagrangian marine surface oil spill model for short-term forecasting–Part 1: Theory. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1851–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Mu, L.; Ha, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, E. An innovative coupling technique for integrating oil spill prediction model with finite volume method-based ocean model. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Beardsley, R.C.; Cowles, G.; Qi, J.; Lai, Z.; Gao, G.; Stuebe, D.; Xu, Q.; Xue, P.; Ge, J.; et al. An Unstructured-Grid, Finite-Volume Community Ocean Model: FVCOM User Manual; Sea Grant College Program, Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- D’Affonseca, F.M.; Reis, F.A.G.V.; Corrêa, C.V.S.; Wieczorek, A.; Giordano, L.D.C.; Marques, M.L.; Rodrigues, F.H.; Costa, D.M.; Kolya, A.d.A.; Veiga, V.M.; et al. Environmental sensitivity index maps to manage oil spill risks: A review and perspectives. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2023, 239, 106590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundlach, E.R.; Hayes, M.O. Vulnerability of coastal environments to oil spill impacts. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 1978, 12, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Getter, C.D.; Thebeau, L.C.; Ballou, T. Mapping the distribution of protected and valuable, oil-sensitive coastal fish and wildlife. In Proceedings of the 1981 Oil Spill Conference, Atlanta, Georgia, 2–5 March 1981; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1981; pp. 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Tri, D.Q.; Don, N.C.; Ching, C.Y.; Mishra, P.K. Application of environmental sensitivity index (ESI) maps of shorelines to coastal oil spills: A case study of Cat Ba Island, Vietnam. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3433–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankara, R.S.; Arockiaraj, S.; Prabhu, K. Environmental sensitivity mapping and risk assessment for oil spill along the Chennai Coast in India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.F.; Abessa, D.M.S.; Fontes, R.F.C.; Silva, G.H. Integrated assessment for establishing an oil environmental vulnerability map: Case study for the Santos Basin region, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J. Environmental Sensitivity Index Guidelines: Version 4.0. 2019. Available online: https://response.restoration.noaa.gov/sites/default/files/ESI_Guidelines.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2024).




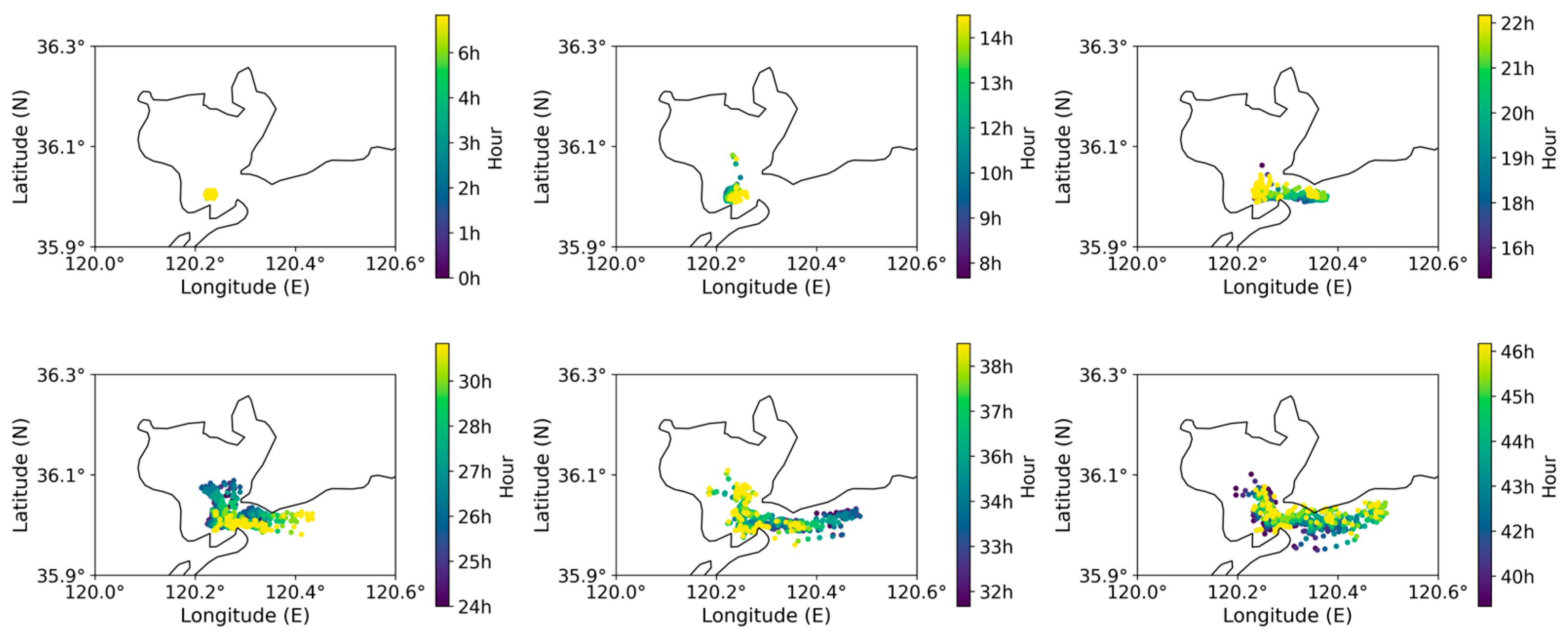


| Time | Oil Type | Spill Volume | Oil Spill Duration | Forecast Time | Temperature (°C) | Locations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27 April 2021–29 April 2021 | Crude oil | 400 t | 2 h | 48 h | 25 °C | Qianwan Port, Huangdao Oil Port, Dagang Port, Horseshoe Reef, and the channel entrance |
| ESI Rank | Estuarine Environment |
|---|---|
| 1A | Exposed, rocky shores |
| 1B | Exposed, solid, man-made structures |
| 1C | Exposed, rocky cliffs with boulder talus base |
| 2A | Exposed, wave-cut platforms in bedrock, mud, or clay |
| 2B | Exposed scarps and steep slopes in clay |
| 3A | Fine- to medium-grained sand beaches |
| 3B | Scarps and steep slopes in sand |
| 3C | Tundra cliffs |
| 4 | Coarse-grained sand beaches |
| 4 | Sand beaches |
| 5 | Mixed sand and gravel beaches |
| 6A | Gravel beaches |
| 6B | Riprap |
| 6D | Boulder rubble |
| 7 | Exposed tidal flats |
| 8A | Sheltered scarps in bedrock, mud, or clay; sheltered, impermeable, rocky shores |
| 8B | Sheltered, solid man-made structures; sheltered, permeable, rocky shores |
| 8C | Sheltered riprap |
| 8D | Sheltered, rocky rubble shores |
| 8E | Peat shorelines |
| 9A | Sheltered tidal flats |
| 9B | Vegetated low banks |
| 9C | Hyper-saline tidal flats |
| 10A | Salt and brackish water marshes |
| 10B | Freshwater marshes |
| 10C | Swamps |
| 10D | Scrub and shrub wetlands |
| 10E | Inundated low-lying |
| Location | Risk Level | Segments Count | Total Length | Avg. Length per Segment | ESI Range | Sensitive Areas Identified | Management Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qianwan Port | Low | 25 | 22,380.4 | 895.2 | 1–2 | Widespread Biodiversity | Low |
| Medium | 8 | 8278.7 | 1034.8 | 2–3 | Tidal Flats, Potential Habitat Significance | Moderate | |
| High | 10 | 8561.2 | 856.1 | 3–4 | Intertidal Zones, Cetacean Migration Routes | High | |
| Horseshoe Reef | Low | 2 | 2643.5 | 1321.8 | 2 | General Marine Area | Moderate |
| Medium | 4 | 1693.8 | 423.5 | 3 | Seagrass Meadows, Coral Reefs | High | |
| Huangdao Oil Port | Low | 5 | 5095.2 | 1019.0 | 2–3 | Coastal Buffer Zone | Low |
| Medium | 2 | 1431.8 | 715.9 | 3–4 | Community Use Areas | Moderate | |
| High | 1 | 2165.7 | 2165.7 | 4 | Mangrove Forests | High | |
| Very High | 2 | 1551.8 | 775.9 | 5 | Bird Nesting Areas, Fish Breeding Grounds | Urgent |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, J.; Wang, S.; Mu, L.; Wang, S. Risk Assessment of Oil Spills along the Coastline of Jiaozhou Bay Using GIS Techniques and the MEDSLIK-II Model. Water 2024, 16, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070996
Peng J, Wang S, Mu L, Wang S. Risk Assessment of Oil Spills along the Coastline of Jiaozhou Bay Using GIS Techniques and the MEDSLIK-II Model. Water. 2024; 16(7):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070996
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Jialong, Shaoqiang Wang, Lin Mu, and Si Wang. 2024. "Risk Assessment of Oil Spills along the Coastline of Jiaozhou Bay Using GIS Techniques and the MEDSLIK-II Model" Water 16, no. 7: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070996
APA StylePeng, J., Wang, S., Mu, L., & Wang, S. (2024). Risk Assessment of Oil Spills along the Coastline of Jiaozhou Bay Using GIS Techniques and the MEDSLIK-II Model. Water, 16(7), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070996







