Experimental Study of Water Vapor Adsorption on Bare Soil and Gravel Surfaces in an Arid Region of Ningxia, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Lysimeter Data
2.3. Adsorption Identification Process
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
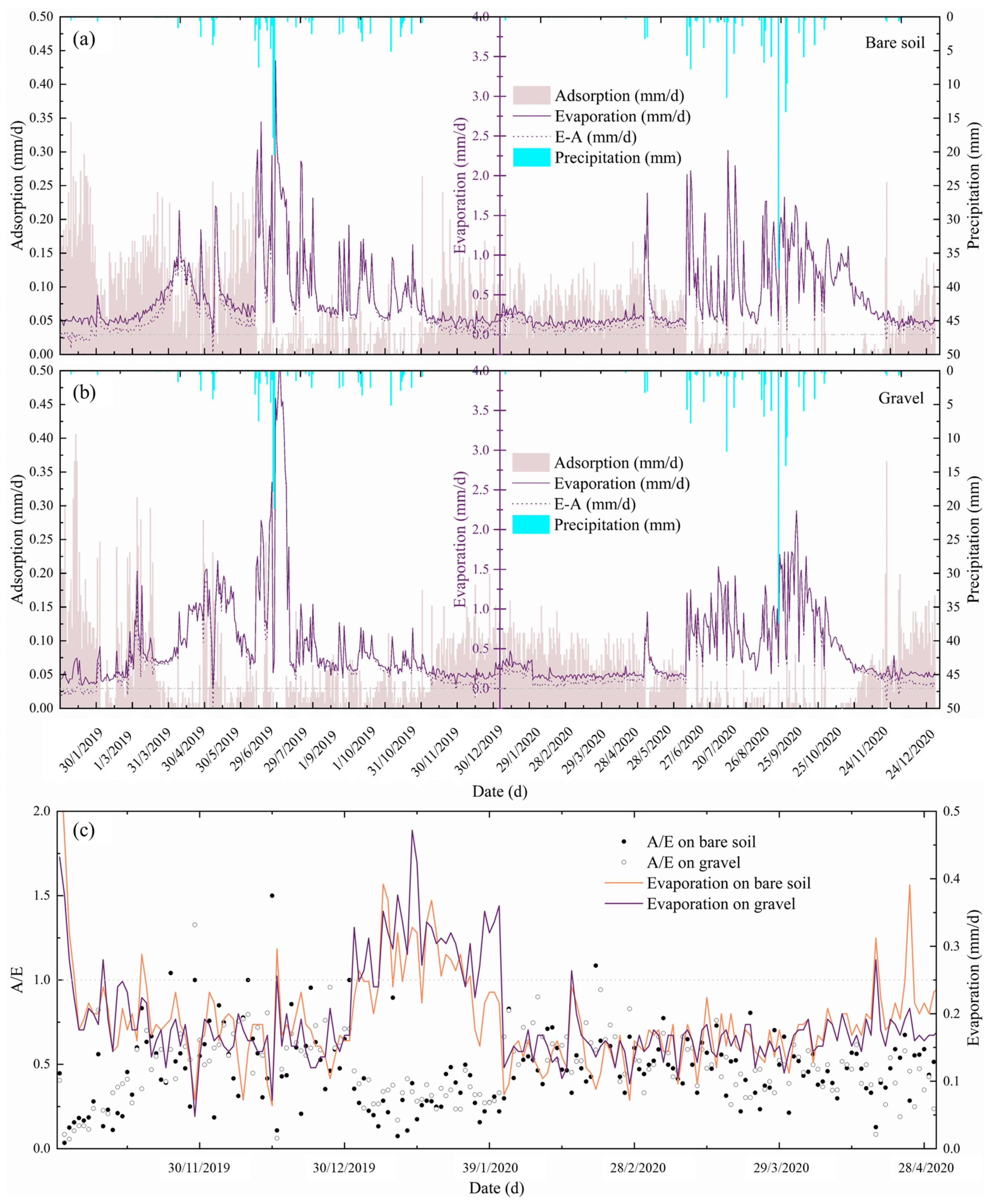
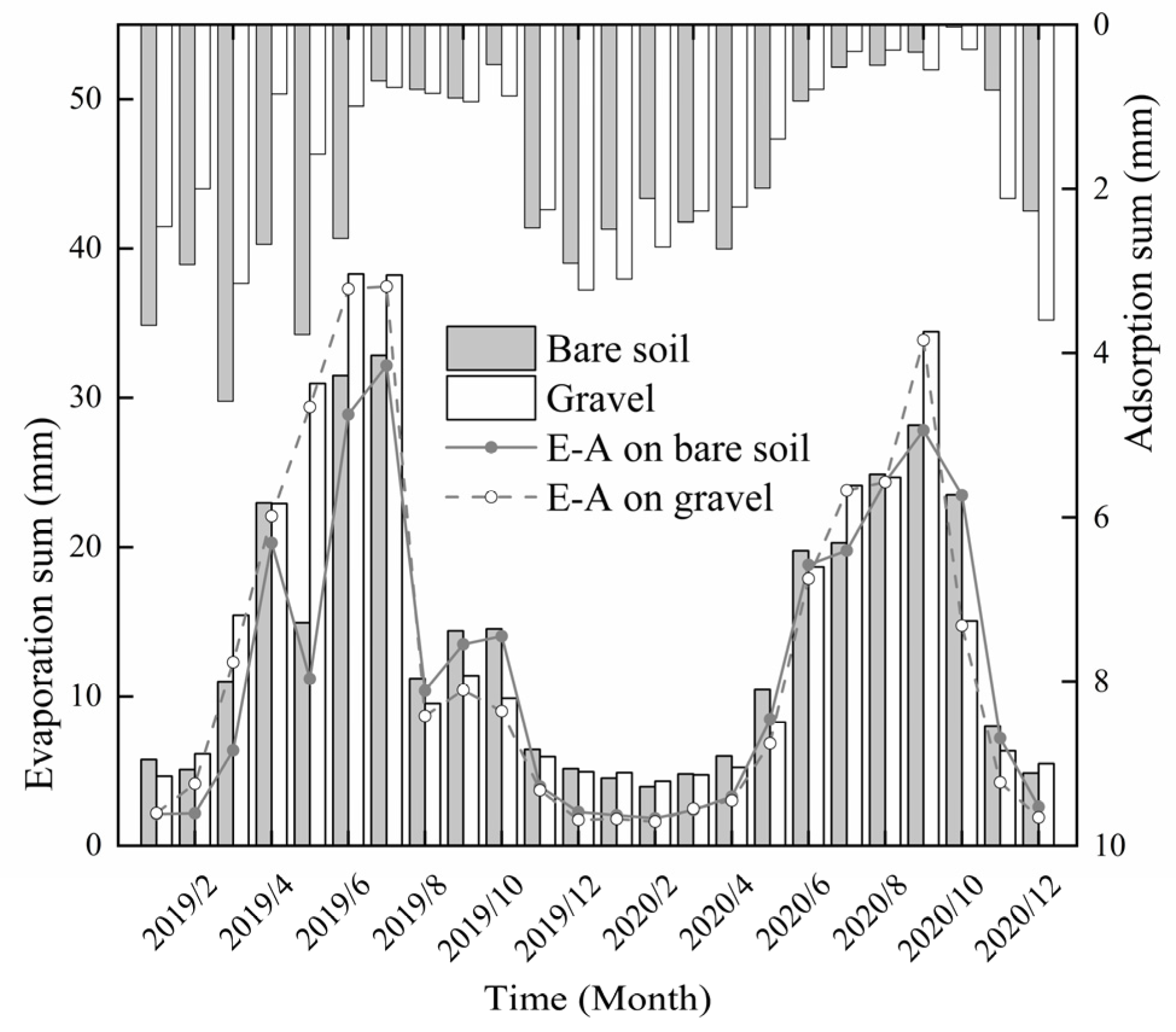
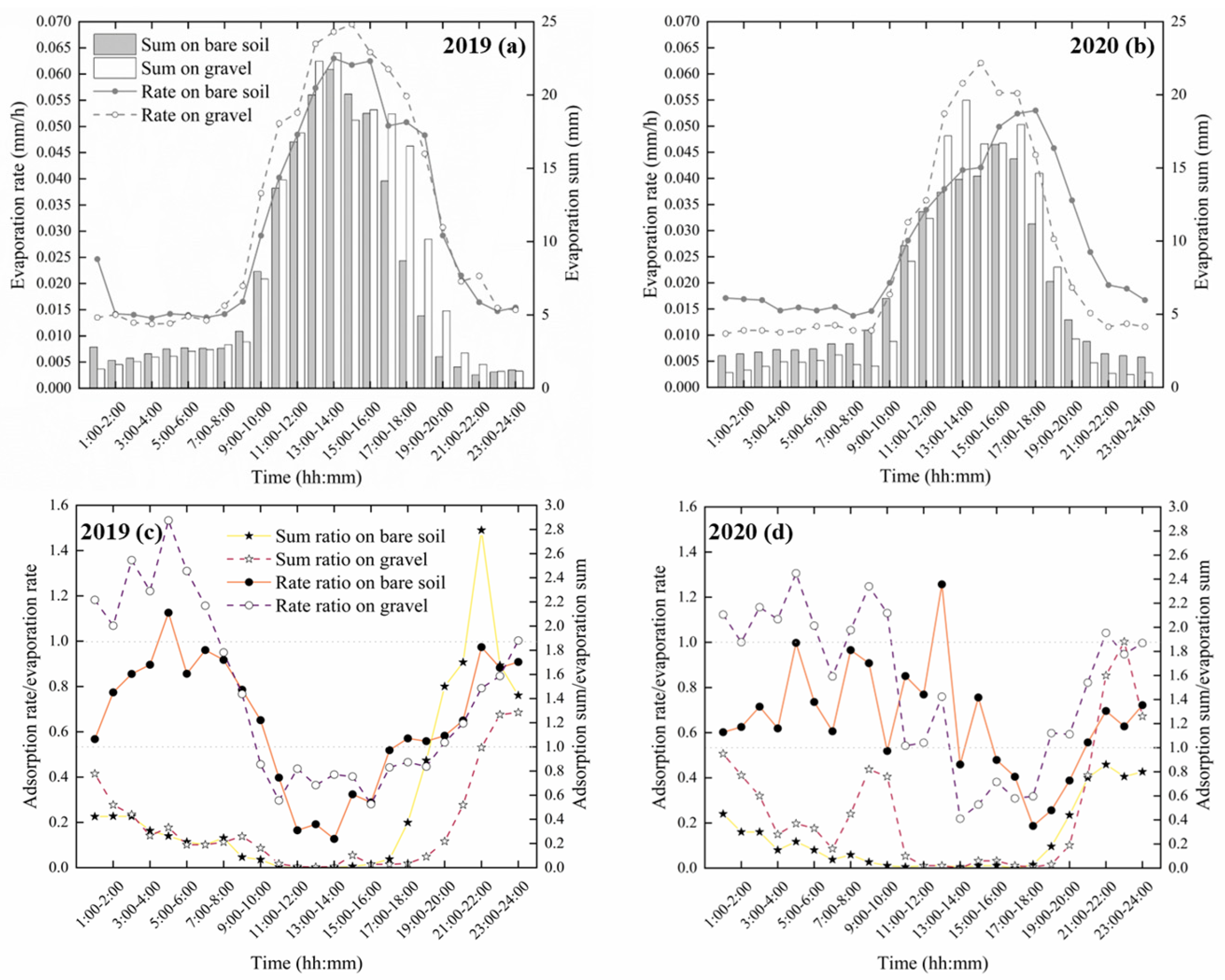
3.1. Water Vapor Adsorption Statistics
3.2. Combined Analysis of Evaporation and Adsorption
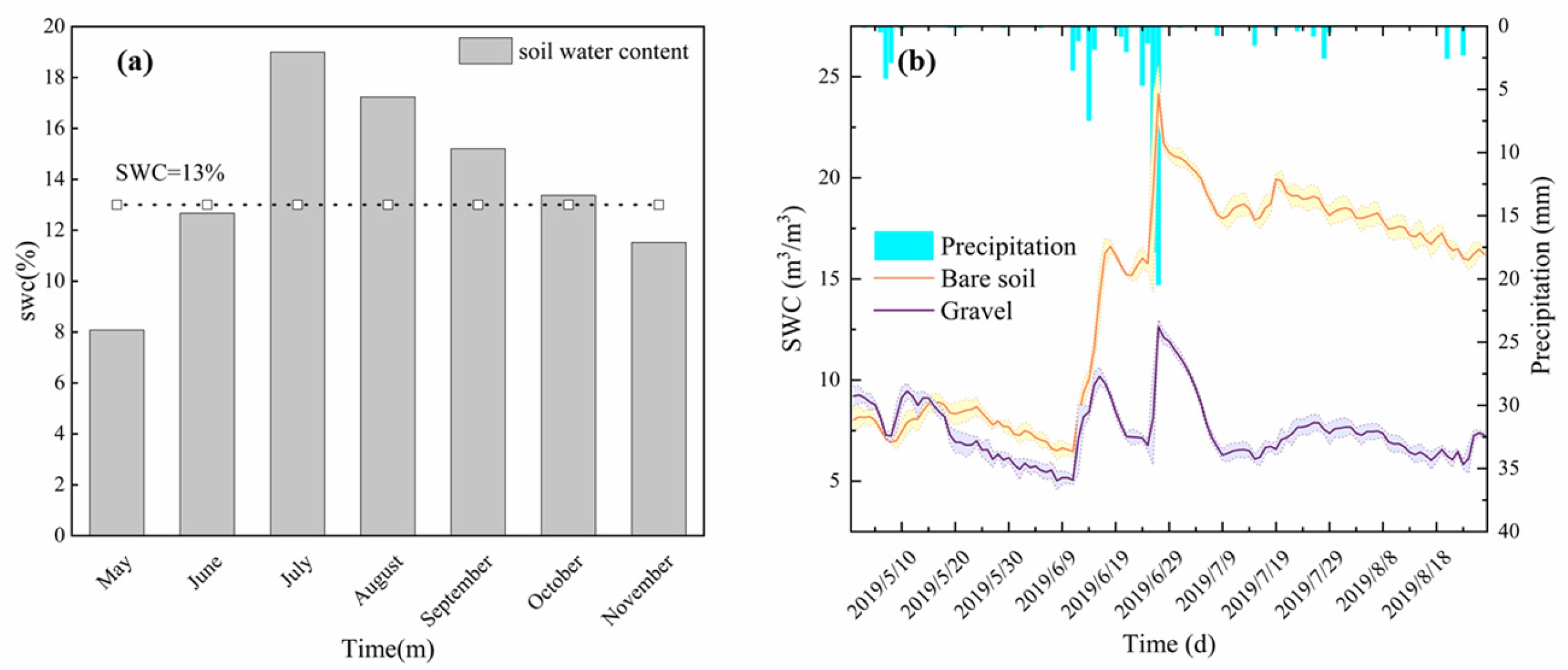
3.3. Soil Water Content and Soil Temperature
3.3.1. Soil Water Content
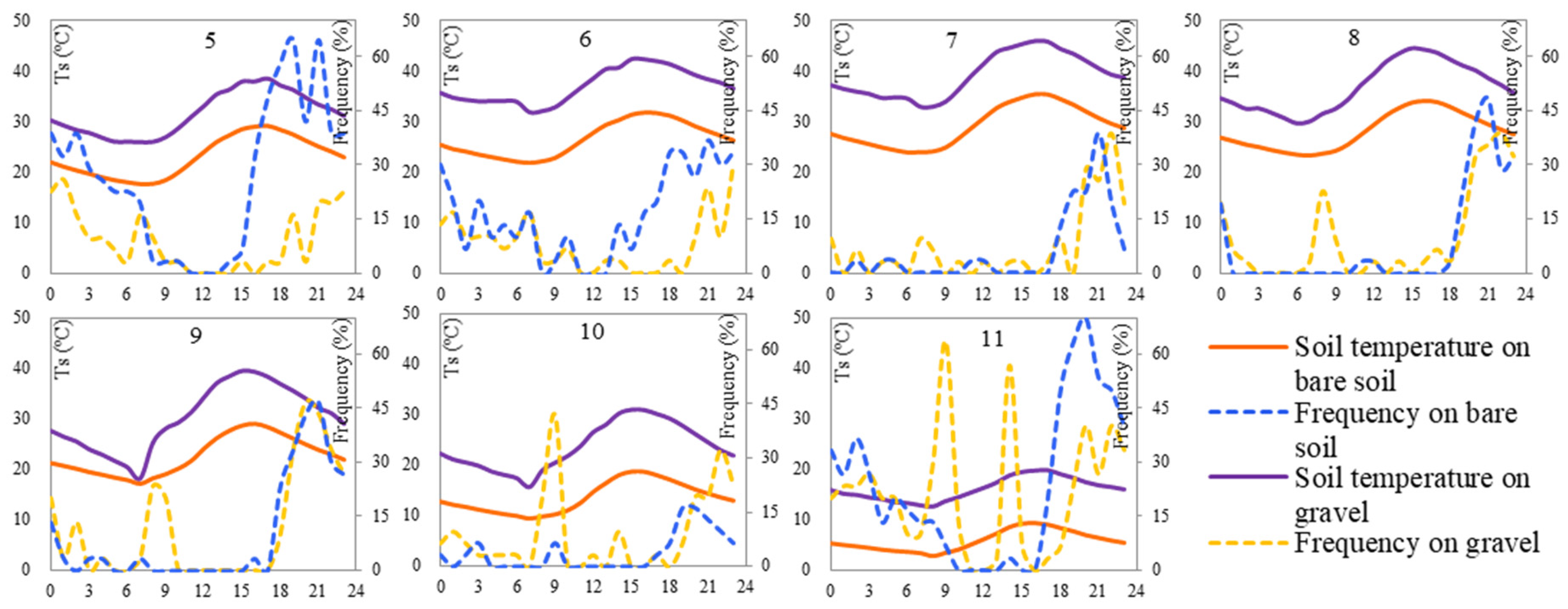
3.3.2. Soil Temperature
3.3.3. Gravel Cover
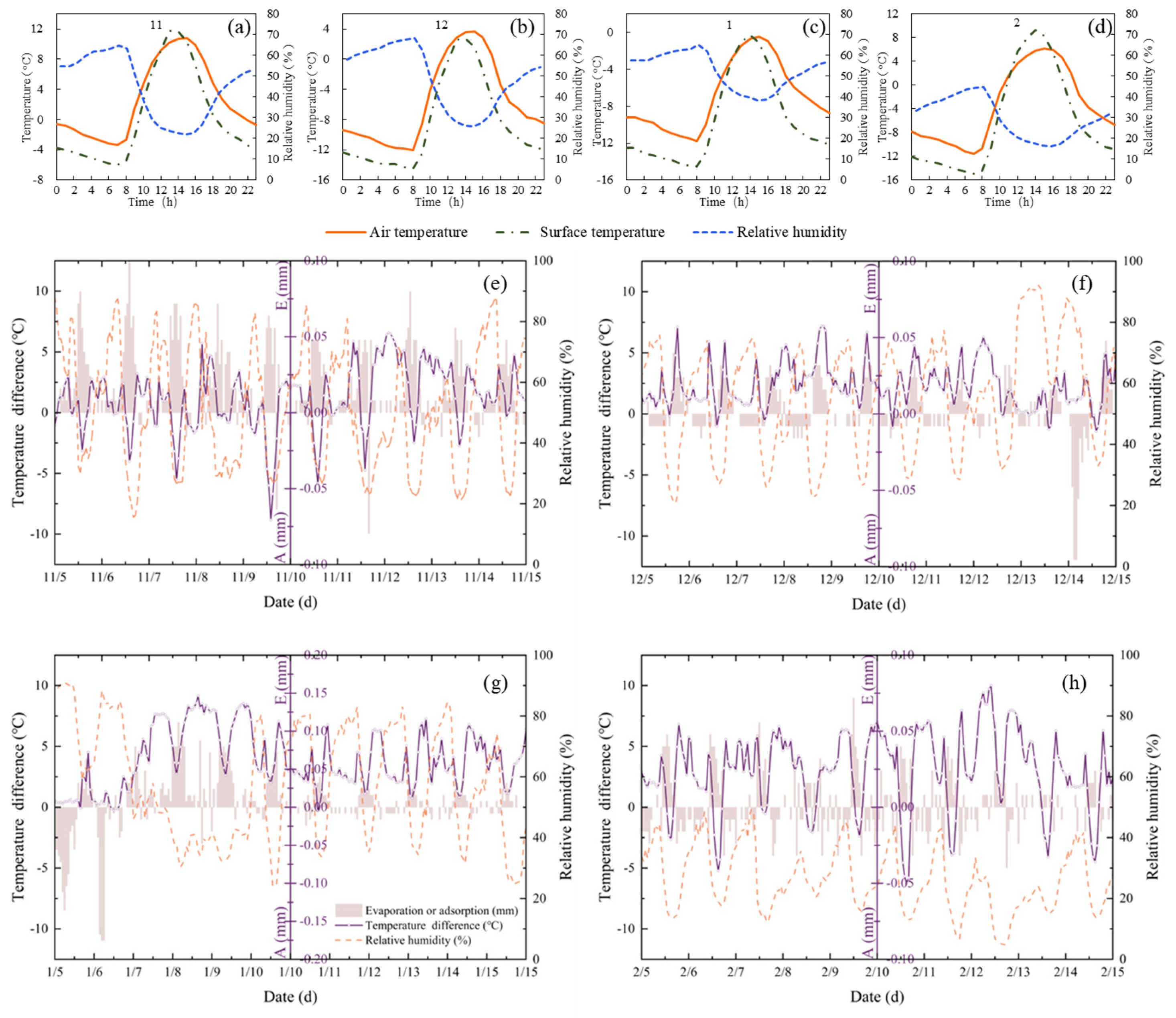
3.4. Hydrothermal and Meteorological Analysis
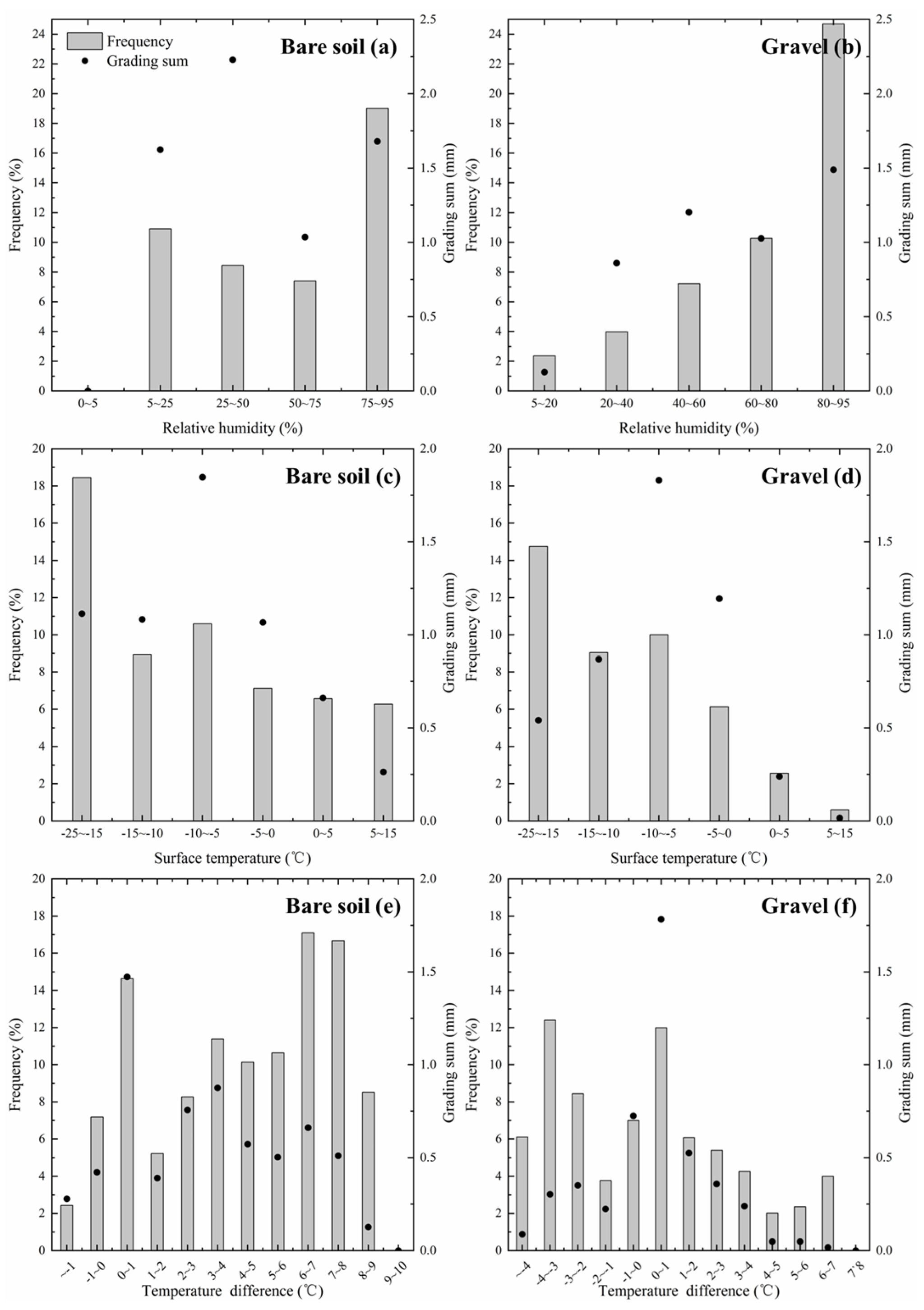
3.4.1. Adsorption Occurrence Conditions
3.4.2. Meteorological Drivers of Adsorption
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobs, A.F.G.; Heusinkveld, B.G.; Berkowicz, S.M. Dew deposition and drying in a desert system: A simple simulation model. J. Arid Environ. 1999, 42, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agam, N.; Berliner, P.R. Dew formation and water vapor adsorption in semi-arid environments–A review. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 65, 572–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Li, C.; Guo, B.; Ma, J.; Ayup, M.; Chen, Z. Dew formation and its long-term trend in a desert riparian forest ecosystem on the eastern edge of the Taklimakan Desert in China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Prado, R.; Sancho, L.G. Dew as a key factor for the distribution pattern of the lichen species Teloschistes lacunosus in the Tabernas Desert (Spain). Flora 2007, 202, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, T.A.; Morrissey, E.M.; Reed, S.C.; Hungate, B.A.; Schwartz, E. Water from air: An overlooked source of moisture in arid and semiarid regions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.K. Non-rainfall water contributions to dryland jujube plantation evapotranspiration in the Hilly Loess Region of China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseke, K.F.; Mills, A.J.; Brown, R.; Esler, K.J.; Henschel, J.R.; Seely, M.K. A method for direct assessment of the “Non-Rainfall” atmospheric water cycle: Input and evaporation from the soil. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2012, 169, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucles, O.; Villagarcia, L.; Canton, Y.; Domingo, F. Partitioning of non-rainfall water input regulated by soil cover type. Catena 2016, 139, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidron, G.J. Analysis of dew precipitation in three habitats within a small arid drainage basin, Negev Highlands, Israel. Atmos. Res. 2000, 55, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agam, N.; Berliner, P.R.; Zangvil, A.; Ben-Dor, E. Soil water evaporation during the dry season in an arid zone. J. Geophys. Res-Atmos. 2004, 109, D16103. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef, A.; Diaz-Espejo, A.; Knight, J.R.; Villagarcia, L.; Fernandez, J.E. Adsorption of water vapor by bare soil in an olive grove in southern Spain. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, D.; Agra, E.; Drabkin, A.; Duncan, A.; Fendinat, P.P.; Leduc, S.; Lupovitch, G.; Nambwandja, A.N.; Ndilenga, N.S.; Nguyễn Thị, T.; et al. The overlooked non-rainfall water input sibling of fog and dew: Daily water vapor adsorption on a! Nara hummock in the Namib Sand Sea. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarani, M.R.; Bookhagen, B.; Schmidt, T.; Wickert, J.; de la Torre, A.; Hierro, R. Using convective available potential energy (CAPE) and dew-point temperature to characterize rainfall-extreme events in the South-Central Andes. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldauf, S.; Porada, P.; Raggio, J.; Maestre, F.T.; Tietjen, B. Relative humidity predominantly determines long-term biocrust-forming lichen cover in drylands under climate change. J. Hydrol. 2021, 109, 1370–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohfahl, C.; Saaltink, M.W.; Ruiz Bermudo, F. Vapor flow control in dune sediments under dry bare soil conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmas, C.; Marathianou, M.; Gerontidis, S.; Detsis, V.; Tsara, M.; Poesen, J. Parameters affecting water vapor adsorption by the soil under semi-arid climatic conditions. Agr. Water Manag. 2001, 48, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, G.; Beysens, D.; Milimouk-Melnytchouk, I. A study of dew water yields on Galvanized iron roofs in Kothara (North-West India). J. Arid Environ. 2007, 69, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Mills, A.J.; Jack, C. Non-rainfall moisture inputs in the Knersvlakte: Methodology and preliminary findings. Water SA 2008, 34, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.W.; Moldrup, P.; Jacobsen, O.H.; Rolston, D.E. Relations between specific surface area and soil physical and chemical properties. Soil Sci. 1996, 161, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y. Effects of gravel and sand mulches on dew deposition in the semiarid region of China. J. Hydrol. 2002, 260, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, S.; Duan, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. Effects of microbiotic crusts on dew deposition in the restored vegetation area at Shapotou, northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphangwa, K.W.; Musil, C.F.; Raitt, L.; Zedda, L. Differential interception and evaporation of fog, dew and water vapour and elemental accumulation by lichens explain their relative abundance in a coastal desert. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 82, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.; Danalatos, N.G.; Poesen, J.; Van Wesemael, B. The effect of water vapour adsorption on soil moisture content under Mediterranean climatic conditions. Agr. Water Manag. 1998, 36, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.T.; Ma, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.C.; He, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Water vapour adsorption under rice-straw and gravel mulch in lysimeters. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2012, 10, 949–955. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Shang, K.; Bi, J. Soil moisture characteristics and analysis on its moving mechanism in central Gansu, a part of the semi-arid Loess Plateau. J. Desert Res. 2014, 34, 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kharitonova, G.V.; Vityazev, V.G.; Lapekina, S.I. A mathematical model for the adsorption of water vapor by soils. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2010, 43, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danalatos, N.G.; Kosmas, C.S.; Moustakas, N.C.; Yassoglou, N. Rock fragments: II. Their impact on soil physical properties and biomass production under Mediterranean conditions. Soil Use Manag. 1995, 11, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Downing, A.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, X.B.; Zhang, B. The influence of biological soil crusts on dew deposition in Gurbantunggut Desert, Northwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, X. Influence factors and variation characteristics of water vapor absorption by soil in semi-arid region. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 2240–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidron, G.J. The effect of substrate properties, size, position, sheltering and shading on dew: An experimental approach in the Negev Desert. Atmos Res. 2010, 98, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.X.; Ding, Y.M.; Sun, Z.Y.; Zhu, L. Numerical simulation of spring wheat growth and yield in arid areas based on SWAP-IES. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 66–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R. Relationship between Soil Quality with Grape Growth and Composition at the Eastern Foot of Helan Mountain Wine Production Regions. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A& F University, Xianyang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hannes, M.; Wollschlaeger, U.; Schrader, F.; Durner, W.; Gebler, S.; Puetz, T.; Fank, J.; von Unold, G.; Vogel, H.J. A comprehensive filtering scheme for high-resolution estimation of the water balance components from high-precision lysimeters. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3405–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puetz, T.; Kiese, R.; Wollschlaeger, U.; Groh, J.; Rupp, H.; Zacharias, S.; Priesack, E.; Gerke, H.H.; Gasche, R.; Bens, O.; et al. TERENO-SOILCan: A lysimeter-network in Germany observing soil processes and plant diversity influenced by climate change. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabela, E.D.; Hornbuckle, B.K.; Cosh, M.H.; Anderson, M.C.; Gleason, M.L. Dew frequency, duration, amount, and distribution in corn and soybean during SMEX05. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 2009, 149, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Yue, P.; Wang, R. A measurement, quantitative identification and estimation method (QINRW) of non-rainfall water component by lysimeter. MethodsX 2019, 6, 2873–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Han, S. Experimental study on the condensate water in arid areas of northwest China. Adv. Water Sci. 2002, 13, 623–628. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Comparison of moisture absorption and condensed water amount of three underlying soils in Mu Us sandy Land. J. Arid Land Res. Environ. 2009, 23, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R. Analysis on the source characteristics of condensed water vapor in the surface soil of the Gurbantunggut Desert. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 985–989. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Malhi, S.S.; Vera, C.L.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Particle-size effects on soil temperature, evaporation, water use efficiency and watermelon yield in fields mulched with gravel and sand in semi-arid Loess Plateau of northwest China. Agr. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zha, T.; Jia, X.; Wu, B.; Feng, W.; Xie, J.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Peltola, H. Dynamics of dew in a cold desert-shrub ecosystem and its abiotic controls. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Ding, Y. Relationship between condensation water of sandy soil and micrometeorological factors in arid desert area. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar]
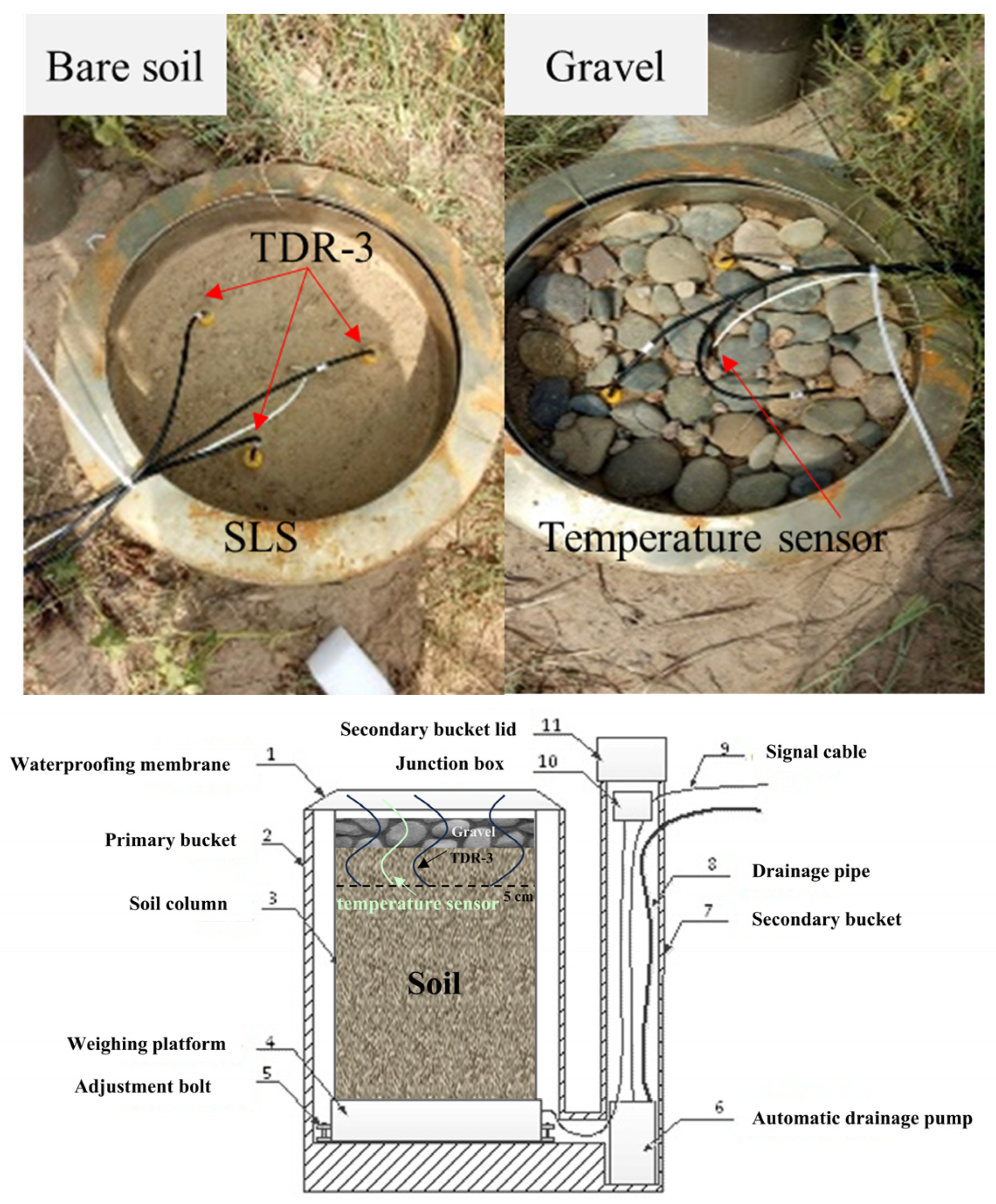
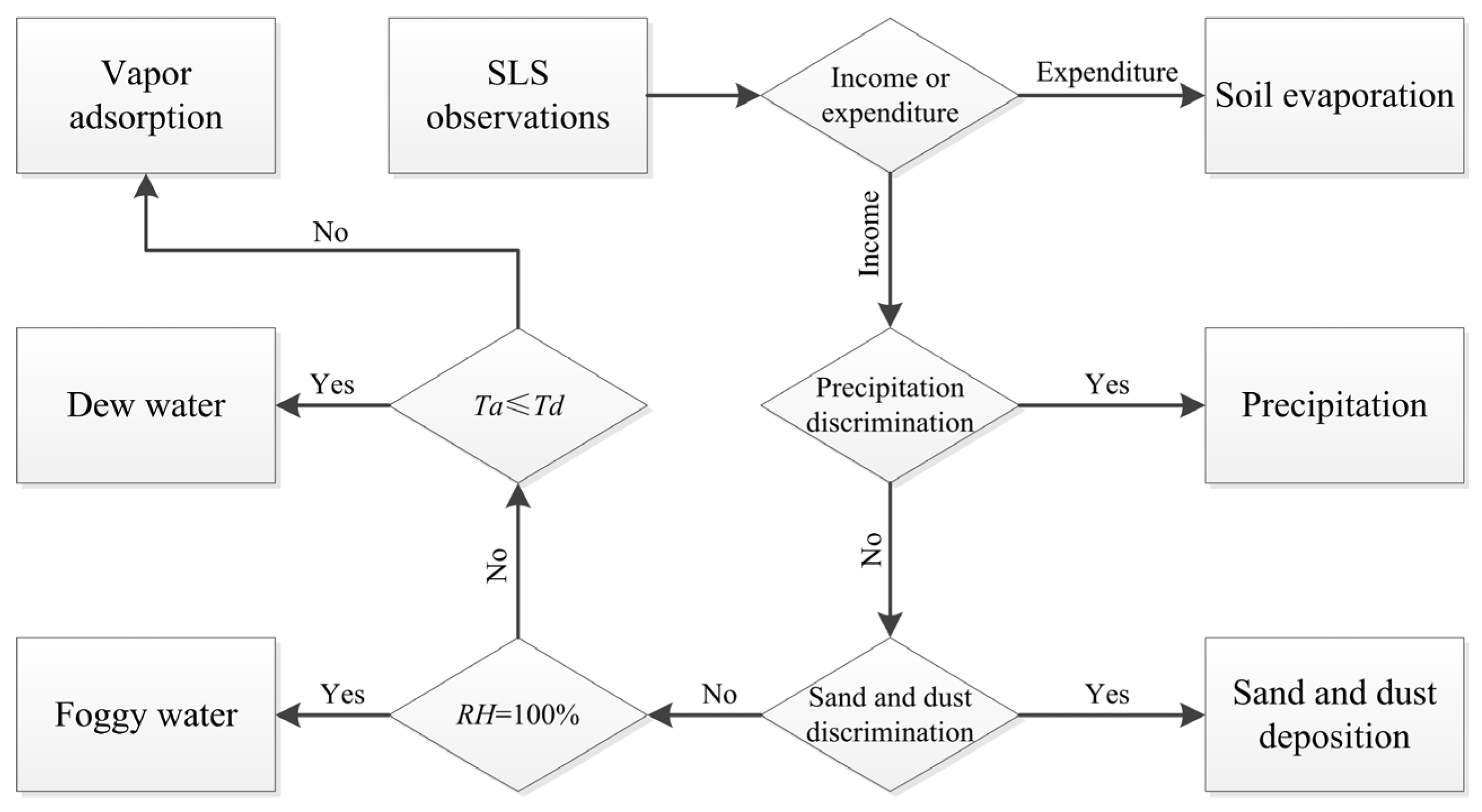
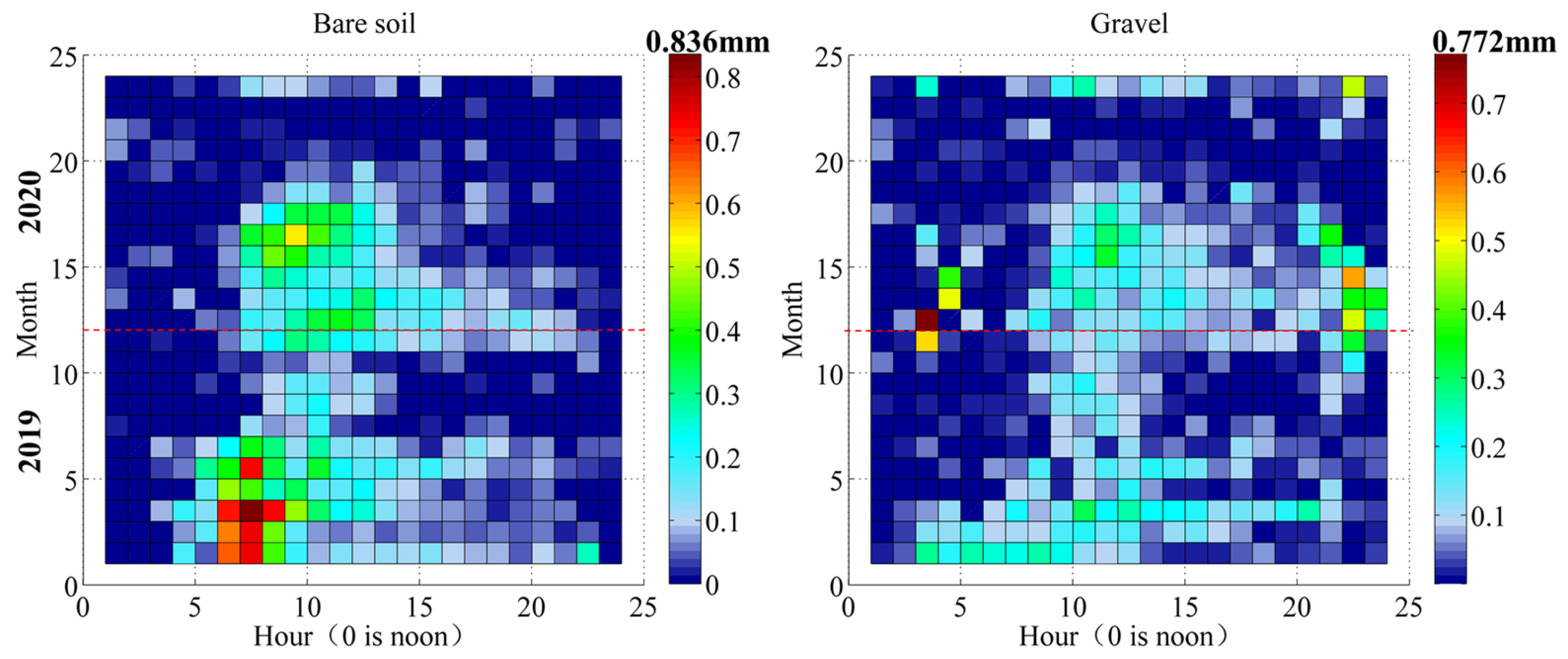
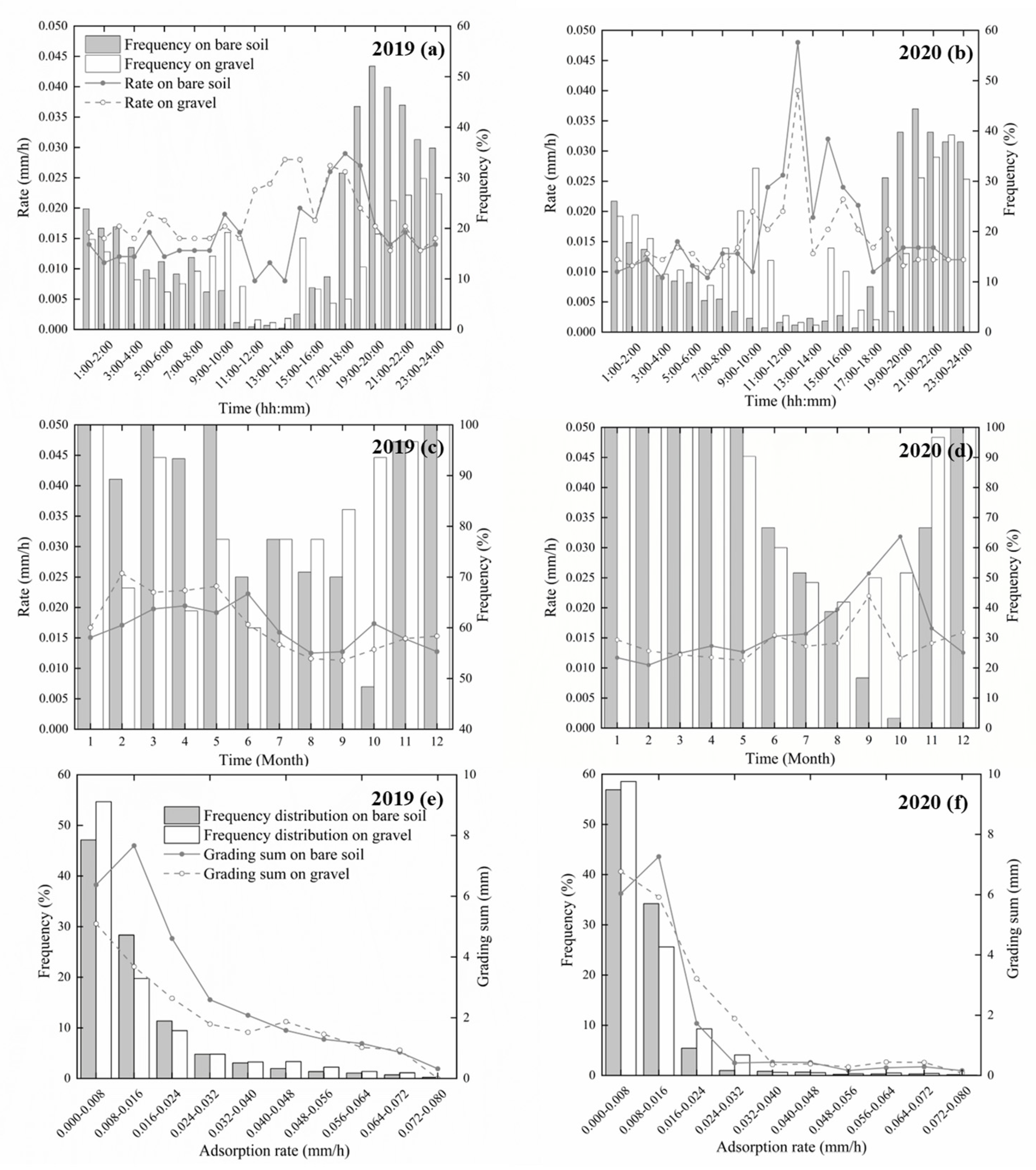
| Year | Precipitation (P, mm) | Surface | Adsorption (A, mm) | Evaporation (E, mm) | E-A (mm) | A/E | Occurrences of A | Days of A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 124.83 | Bare soil | 28.39 | 177.48 | 149.09 | 0.16 | 1904 | 320 |
| Gravel | 19.79 | 198.89 | 179.10 | 0.10 | 1376 | 313 | ||
| 2020 | 150.98 | Bare soil | 17.11 | 163.54 | 146.43 | 0.10 | 1327 | 256 |
| Gravel | 19.68 | 161.48 | 141.80 | 0.12 | 1445 | 286 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Chen, T.; Guan, S. Experimental Study of Water Vapor Adsorption on Bare Soil and Gravel Surfaces in an Arid Region of Ningxia, China. Water 2024, 16, 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070984
Zhang Q, Wang H, Wang Z, Xie H, Chen T, Guan S. Experimental Study of Water Vapor Adsorption on Bare Soil and Gravel Surfaces in an Arid Region of Ningxia, China. Water. 2024; 16(7):984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070984
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qingtao, Heng Wang, Zhiqiang Wang, Haoxuan Xie, Tuo Chen, and Shuai Guan. 2024. "Experimental Study of Water Vapor Adsorption on Bare Soil and Gravel Surfaces in an Arid Region of Ningxia, China" Water 16, no. 7: 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070984
APA StyleZhang, Q., Wang, H., Wang, Z., Xie, H., Chen, T., & Guan, S. (2024). Experimental Study of Water Vapor Adsorption on Bare Soil and Gravel Surfaces in an Arid Region of Ningxia, China. Water, 16(7), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070984






