Investigation of the Growth and Mortality of Bacteria and Synechococcus spp. in Unvegetated and Seagrass Habitats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Sampling Methods
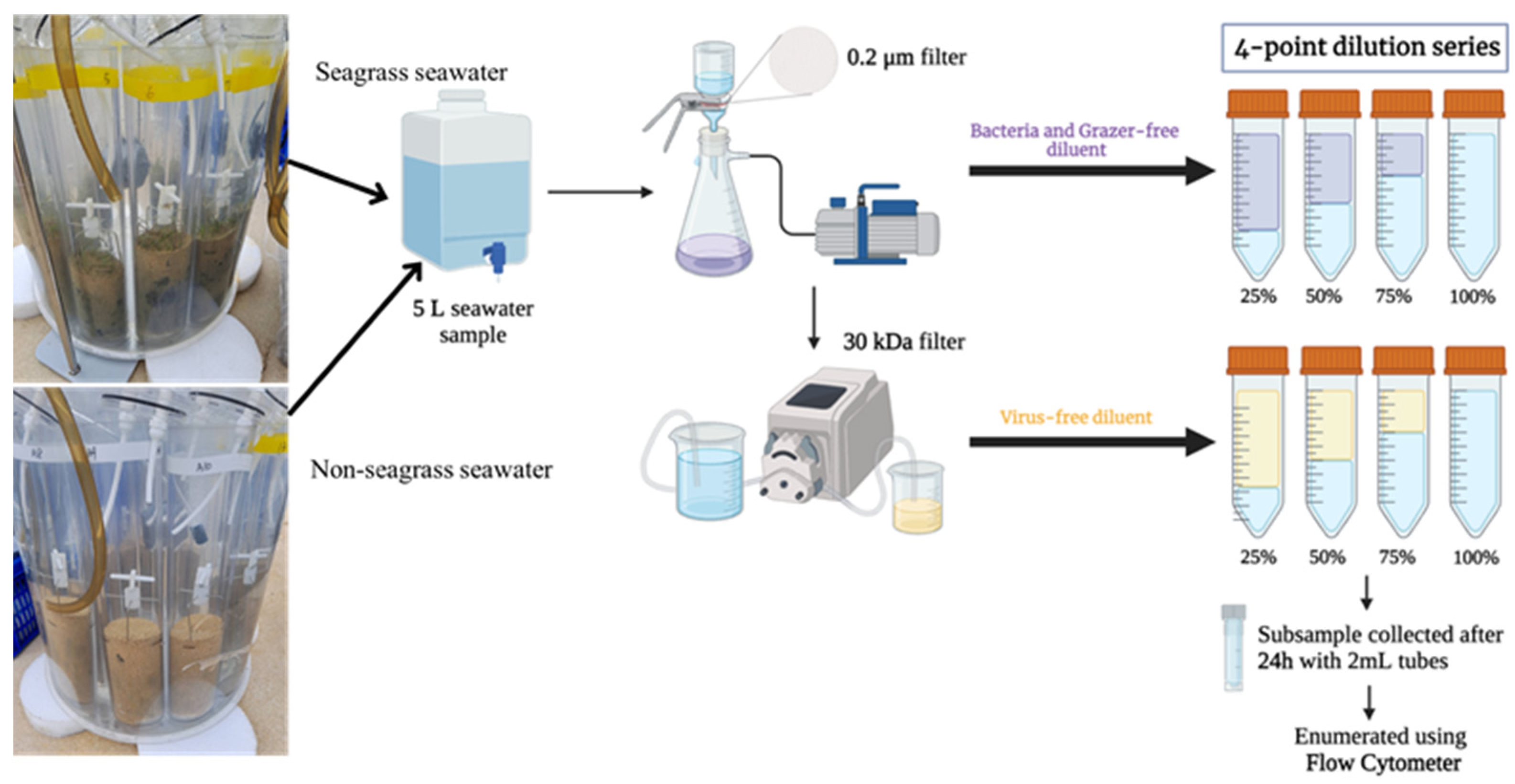
2.2. Modified Dilution Experiments
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
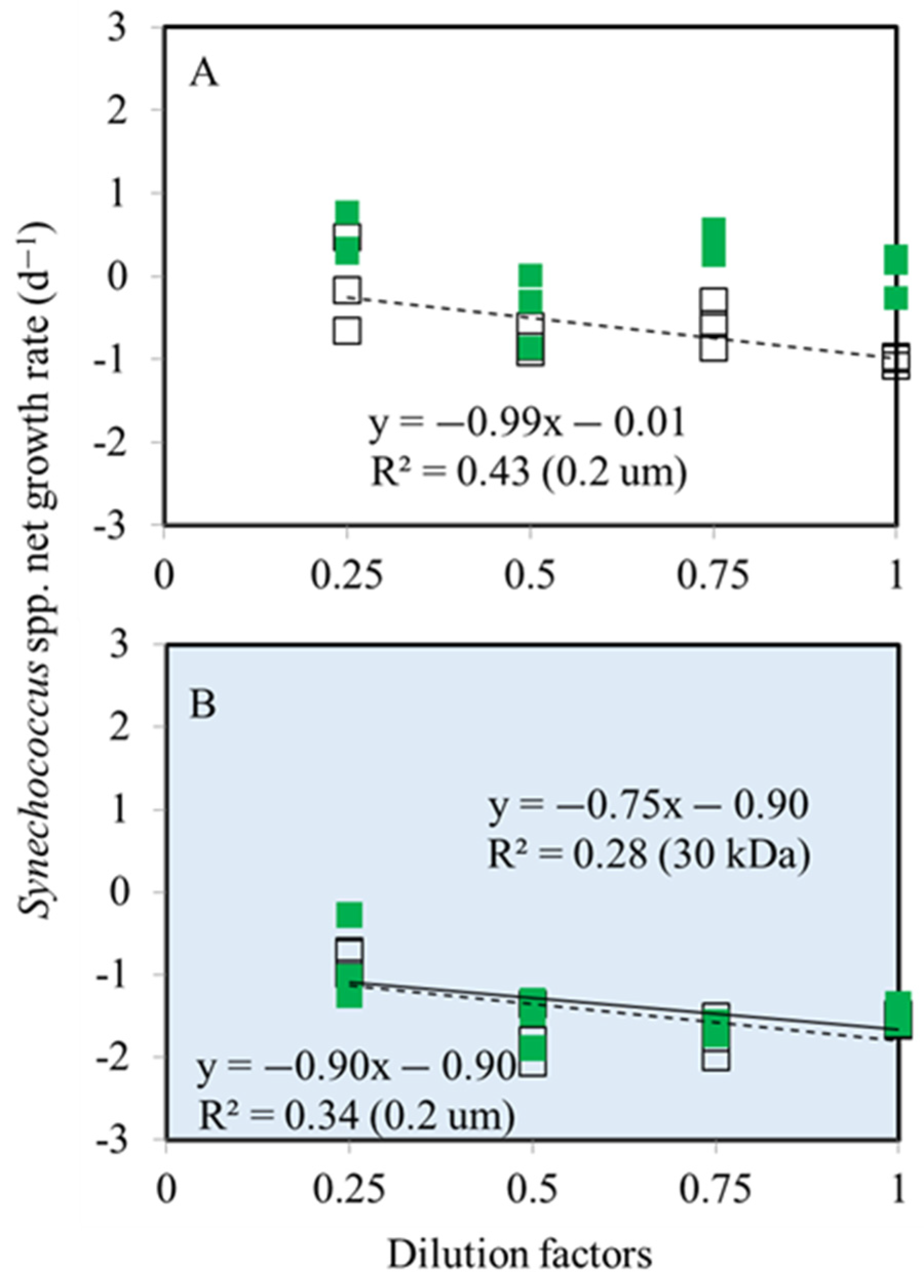
3.1. Bacterial and Synechococcus spp. Growth Rates
3.2. Bacterial and Synechococcus spp. Mortality
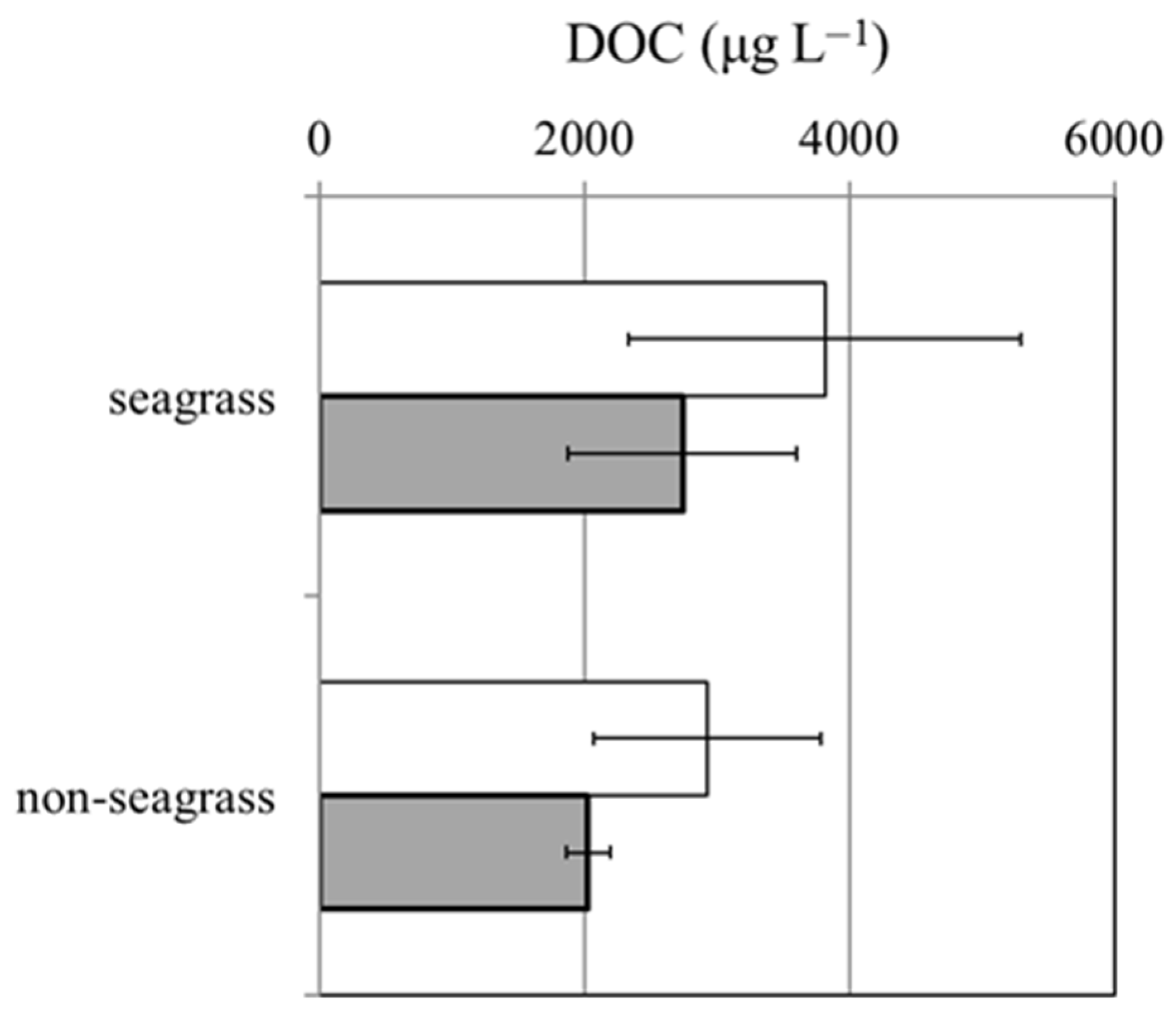
3.3. Dynamic Changes in DOC Concentration
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambo-Rappe, R. Differences in richness and abundance of species assemblages in tropical seagrass beds of different structural complexity. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, S.; Srinivasan, A.; Padmavathy, P.; Jawahar, P. Seasonal variation of phytoplankton diversity in seagrass ecosystem of Mandapam coast of Gulf of Mannar. J. Exp. Zool. India 2018, 21, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks, I.E.; Sintes, T.; Bouma, T.J.; Duarte, C.M. Experimental assessment and modeling evaluation of the effects of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica on flow and particle trapping. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 356, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; Nordlund, L.M.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C. Seagrass meadows support global fisheries production. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, P.C.; Moriarty, D.J.W. Organic carbon decomposition, primary and bacterial productivity, and sulphate reduction, in tropical seagrass beds of the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 69, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeboom, H.J.; Sandee, A.J.J. Production and consumption of tropical seagrass fields in eastern Indonesia measured with bell jars and microelectrodes. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1989, 23, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.A.; Romero, J. Detritus dynamics in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: Elements for an ecosystem carbon and nutrient budget. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 151, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrón, C.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Duarte, C.M. Dissolved organic carbon fluxes by seagrass meadows and macroalgal beds. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, B.C.; Gleeson, D.; Statton, J.; Siebers, A.R.; Grierson, P.; Ryan, M.H.; Kendrick, G.A. Low light availability alters root exudation and reduces putative beneficial microorganisms in seagrass roots. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lønborg, C.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Duggan, S.; Carreira, C. Organic matter bioavailability in tropical coastal waters: The Great Barrier Reef. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elovaara, S.; Eronen-Rasimus, E.; Asmala, E.; Tamelander, T.; Kaartokallio, H. Contrasting patterns of carbon cycling and dissolved organic matter processing in two phytoplankton–bacteria communities. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 6589–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigemann, F.; Rahav, E.; Grossart, H.P.; Aharonovich, D.; Voss, M.; Sher, D. Phytoplankton Producer Species and Transformation of Released Compounds over Time Define Bacterial Communities following Phytoplankton Dissolved Organic Matter Pulses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00539-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, E.; Bouillon, S.; Dittmar, T.; Marchand, C. Organic carbon dynamics in mangrove ecosystems: A review. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 89, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, J.K.; Giorgio, P.D. Organic substrate quality as the link between bacterioplankton carbon demand and growth efficiency in a temperate salt-marsh estuary. ISME J. 2007, 1, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delille, D.; Canon, C.; Windeshausen, F. Comparison of Planktonic and Benthic Bacterial Communities Associated with a Mediterranean Posidonia Seagrass System. Bot. Mar. 1996, 39, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Shan, X.; Liu, S. Bacterioplankton, Picoeukaryotes and Synechococcus Distribution Associated with Seagrass in South Coast of Hainan Island, China. Nat. Resour. 2014, 2014, 48438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Säwström, C.; Hyndes, G.A.; Eyre, B.D.; Huggett, M.J.; Fraser, M.W.; Lavery, P.S.; Thomson, P.G.; Tarquinio, F.; Steinberg, P.D.; Laverock, B. Coastal connectivity and spatial subsidy from a microbial perspective. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 6662–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, A.Y.; Gong, G.C.; Hung, J. Seasonal variations of virus- and nanoflagellate-mediated mortality of heterotrophic bacteria in the coastal ecosystem of subtropical western Pacific. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 3055–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, X.A.; Baltar, G.; Carreira, F.C.; Lønborg, C. Responses of physiological groups of tropical heterotrophic bacteria to temperature and DOM additions: Food matters more than warming. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1930–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, E.I.; Calleja, M.L.; Daffonchio, D.; Morán, X.A.G. Seasonality of top-down control of bacterioplankton at two central Red Sea sites with different trophic status. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 25, 2002–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.W.-Y.; Olivia, M.; Chou, W.-C.; Shiu, R.-F.; Mukhanov, V.; Tsai, A.-Y. Differences in Bacterial Growth and Mortality between Seagrass Meadows and Adjacent Unvegetated Areas. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llabrés, M.M.; Agustí, S. Picophytoplankton cell death induced by UV radiation: Evidence for oceanic Atlantic communities. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Y.; He, J.; Fang, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, S.; Huang, X. Interspecific differences in root exudation for three tropical seagrasses and sediment pore-water dissolved organic carbon beneath them. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wit, R.; Troussellier, M.; Courties, C.; Buffan-Dubau, E.; Lemaire, E. Short-Term Interactions between Phytoplankton and Intertidal Seagrass Vegetation in a Coastal Lagoon (Bassin d’Arcachon, SW France). Hydrobiologia 2012, 699, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agawin, N.S.; Duarte, C.M. Evidence of direct particle trapping by a tropical seagrass meadow. Estuaries 2002, 25, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, R.-F.; Vazquez, C.I.; Tsai, Y.-Y.; Torres, G.V.; Chen, C.-S.; Santschi, P.; Quigg, A.; Chin, W.-C. Nano-plastics induce aquatic particulate organic matter (microgels) formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.; Archer, S.D.; Jacquet, S.; Wilson, W.H. Direct estimates of the contribution of viral lysis and microzooplankton grazing to the decline of a Micromonas spp. population. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 30, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, F.; Egli, T. Cytometric methods for measuring bacteria in water: Advantages, pitfalls and applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.J.; Zettler, E.R.; Armbrust, E.V.; Chisholm, S.W. Pigment, size and distribution of Synechococcus in the North Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.R.; Hassett, R.P. Estimating the grazing impact of marine microzooplankton. Mar. Biol. 1982, 67, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbauer, M.G.; Christaki, U.; Nedoma, A.; Simek, K. Comparing the effects of resource enrichment and grazing on viral production in a meso-eutrophic reservoir. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 31, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmance, S.A.; Brussaard, C.P.D. Estimation of viralinduced phytoplankton mortality using the modified dilution method. In Manual of Aquatic Viral Ecology; Wilhelm, S., Weinbauer, M., Suttle, C., Eds.; American Society of Limnology and Oceanography: Waco, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Traving, S.J.; Clokie, M.R.J.; Middelboe, M. Increased acidification has a profound effect on the interactions between the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. WH7803 and its viruses. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, T.; Jacquet, S. Complex interactions in the microbial world: Underexplored key links between viruses, bacteria and protozoan grazers in aquatic environments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 51, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettarel, Y.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Bouvy, M.; Arfi, R.; Amblard, C. Low consumption of virus-sized particles by heterotrophic nanoflagellates in two lakes the French Massif Central. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 39, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Andersen, F.Ø.; Nielsen, S.L.; Boschker, H.T. The importance of mineralization based on sulphate reduction for nutrient regeneration in tropical seagrass sediments. Aquat. Bot. 2001, 71, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.J.; Boyer, J.N.; Jochem, F.J. Microbial activity and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus content in a subtropical seagrass estuary (Florida Bay): Evidence for limited bacterial use of seagrass production. Mar. Boil. 2009, 156, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deborde, J.; Abril, G.; Mouret, A.; Jézéquel, D.; Thouzeau, G.; Clavier, J.; Bachelet, G.; Anschutz, P. Effects of seasonal dynamics in a Zostera noltii meadow on phosphorus and iron cycles in a tidal mudflat (Arcachon Bay, France). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 355, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.W.; Udy, J.W.; Perry, C.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Lomstein, B.A. Effect of the seagrass Zostera capricorni on sediment microbial processes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 199, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, B.D.; Ferguson, A.J. Comparison of carbon production and decomposition, benthic nutrient fluxes and denitrification in seagrass, phytoplankton, benthic microalgae-and macroalgae-dominated warm-temperate Australian lagoons. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 229, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, W.M.; Lackey, G.J.; Christian, R.R. Significance of eutrophic, subtidal sediments to oxygen and nutrient cycling in a temperate estuary. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 86, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, S.P.; Roberts, D.E.; Ajani, P.; Underwood, A.J. Comparisons of assemblages of phytoplankton between open water and seagrass habitats in a shallow coastal lagoon. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2004, 55, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.W.-Y.; Annabel, C.N.; Olivia, M.; Chou, W.-C.; Chen, J.-J.; Shiu, R.-F.; Mukhanov, V.; Natividad, M.; Shen, Y.-L.; Tsai, A.-Y. Investigation of the Growth and Mortality of Bacteria and Synechococcus spp. in Unvegetated and Seagrass Habitats. Water 2024, 16, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070939
Chen PW-Y, Annabel CN, Olivia M, Chou W-C, Chen J-J, Shiu R-F, Mukhanov V, Natividad M, Shen Y-L, Tsai A-Y. Investigation of the Growth and Mortality of Bacteria and Synechococcus spp. in Unvegetated and Seagrass Habitats. Water. 2024; 16(7):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070939
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Patrichka Wei-Yi, Clara Natalie Annabel, Madeline Olivia, Wen-Chen Chou, Jian-Jhih Chen, Ruei-Feng Shiu, Vladimir Mukhanov, Mariche Natividad, Yi-Le Shen, and An-Yi Tsai. 2024. "Investigation of the Growth and Mortality of Bacteria and Synechococcus spp. in Unvegetated and Seagrass Habitats" Water 16, no. 7: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070939
APA StyleChen, P. W.-Y., Annabel, C. N., Olivia, M., Chou, W.-C., Chen, J.-J., Shiu, R.-F., Mukhanov, V., Natividad, M., Shen, Y.-L., & Tsai, A.-Y. (2024). Investigation of the Growth and Mortality of Bacteria and Synechococcus spp. in Unvegetated and Seagrass Habitats. Water, 16(7), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070939







