Process Waters from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Waste Biomasses like Sewage Sludge: Challenges, Legal Aspects, and Opportunities in EU and Germany
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Process Water Characterization and Influences on the Composition
3.1. Overview
3.2. Influences on Process Water Composition
4. Possible Utilization Pathways
4.1. Reuse of Process Water/Recirculation
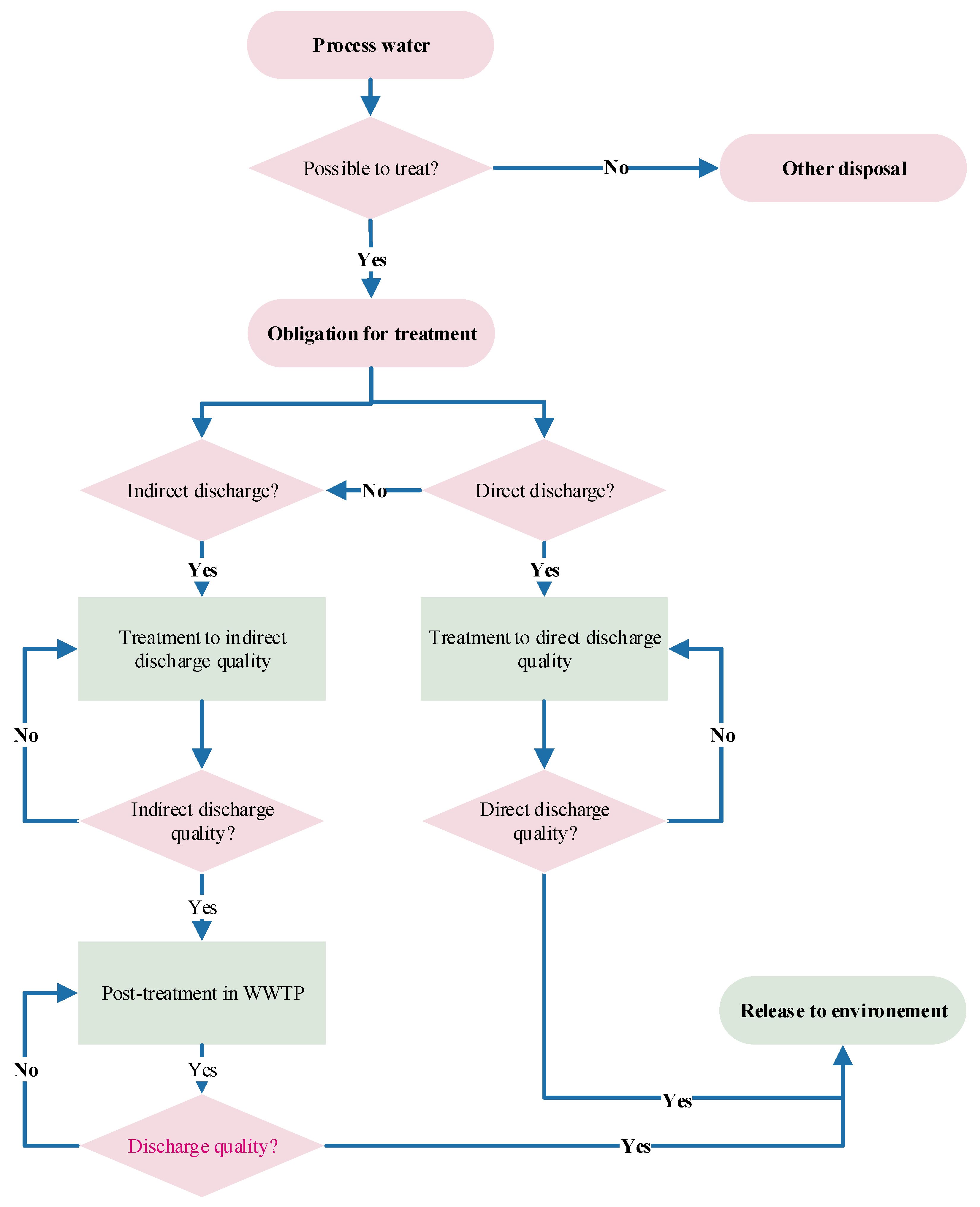
4.2. Treatment Concepts
4.3. Anaerobic Treatment
4.4. Co-Digestion of PW
4.5. Wet Oxidation
4.6. Nutrient Recovery
4.7. Use as a Nutrient Source for Plant and Fungi Growth
5. Challenges and Opportunities
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Xu, C.; Champagne, P. Overview of recent advances in thermo-chemical conversion of biomass. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.; Funke, A.; Titirici, M.-M. Hydrothermal conversion of biomass to fuels and energetic materials. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón-Briceño, C.I.; Pozarlik, A.K.; Bramer, E.A.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Brem, G. Hydrothermal carbonization of wet biomass from nitrogen and phosphorus approach: A review. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.C.; Wüst, D.; Köhler, H.; Lautenbach, A.; Kruse, A. Novel approach of phosphate-reclamation as struvite from sewage sludge by utilising hydrothermal carbonization. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Federation of National Associations of Water Services, EurEau an Overview of the European Drinking Water and Waste Water Sectors. 2021. Available online: https://www.eureau.org/resources/publications/eureau-publications/5824-europe-s-water-in-figures-2021/file (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Klärschlammverordnung (AbfKlärV) vom 27. September 2017 (BGBl. I S. 3465), die Zuletzt Durch Artikel 137 der Verordnung vom 19. Juni 2020 (BGBl. I S. 1328) geändert worden ist. Available online: https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/abfkl_rv_2017/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Statistisches Bundesamat, DESTATIS Klärschlammentsorgung Nach Bundesländern. 2024. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Gesellschaft-Umwelt/Umwelt/Wasserwirtschaft/Tabellen/liste-klaerschlammverwertungsart.html (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Domini, M.; Bertanza, G.; Vahidzadeh, R.; Pedrazzani, R. Sewage Sludge Quality and Management for Circular Economy Opportunities in Lombardy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montag, D.; Adam, C.; Baumann, P.; Frank, D.; Kabbe, C.; Klein, D.; Meyer, C.; Mocker, M.; Morf, L.; Pinnekamp, J.; et al. Rechtliche Vorgaben der Klärschlammverordnung und deren Auswirkungen auf die Phosphor-Rückgewinnung. KA Korresp. Abwasser Abfall 2022, 69, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mix-Spagl, K. Die neue Klärschlammverordnung—Was müssen Betreiber beachten? Wwt-Online De-Spec. Klärschlamm-Recht Gesetz 2017, 10, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chang, Y.; Li, A. Hydrothermal carbonization for energy-efficient processing of sewage sludge: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 108, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergius, F. Die Anwendung Hoher Drucke bei Chemischen Vorgängen und eine Nachbildung des Entstehungsprozesses der Steinkohle; W. Knapp.: Jamestown, NY, USA, 1913. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Distribution and transformation behaviors of heavy metals and phosphorus during hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 17109–17122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Wirth, B.; Lüder, U.; Werner, M. Behavior of selected hydrolyzed and dehydrated products during hydrothermal carbonization of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, A.; Ziegler, F. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Biomass: A Summary and Discussion of Chemical Mechanisms for Process Engineering. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2010, 4, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-X.; Ma, X.-Q.; Zhou, D.; Duan, P.-G.; Zhou, W.-Y.; Ahmad, A.; Luque, R. The influence of key reactions during hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge on aqueous phase properties: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 167, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djandja, O.S.; Yin, L.; Wang, Z.-C.; Duan, P.-G. From wastewater treatment to resources recovery through hydrothermal treatments of municipal sewage sludge: A critical review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 151, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, S.A.; Au, H.; Modugno, P.; Luo, H.i.; Szego, A.E.; Qiao, M.; Li, L.; Yin, W.; Heeres, H.; Berge, N.; et al. Recent advances in hydrothermal carbonization: From tailored carbon materials and biochemicals to applications and bioenergy. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4747–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Liu, Q.; He, X.; Wang, G.; Chen, N.; Peng, J.; Ma, L. Molecular Structure and Formation Mechanism of Hydrochar from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Carbohydrates. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 9904–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, M. Thermo Chemical Conversion of Biomass to Liquid Fuels and Chemicals; Royal Society of Chemistry Publishing: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetea, P.; Tippayawong, N. Recovery of Value-Added Products from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2013, 268947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huezo, L.; Vasco-Correa, J.; Shah, A. Hydrothermal carbonization of anaerobically digested sewage sludge for hydrochar production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, T.; Engelhart, M. Optimizing the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge—Response Surface Methodology and the Effect of Volatile Solids. Water 2020, 13, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, S.; Peng, H.; Yuan, X.; Huang, H. Valorization of the aqueous phase produced from wet and dry thermochemical processing biomass A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woriescheck, T. Charakterisierung, Aufreinigung und Wertstoffgewinnung von Prozesswasser der Hydrothermalen Carbonisierung. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Oldenburg, Oldenburg, Germany, 2019. Available online: https://plus.orbis-oldenburg.de/primo-explore/fulldisplay?docid=49GBVUOB_ALMA51338789630003501&context=L&vid=UB_V1&lang=de_DE&search_scope=UB_all&adaptor=Local%20Search%20Engine&tab=default_tab&query=any,contains,49GBVUOB_ALMA51338789630003501 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Blöhse, D. Hydrothermale Karbonisierung—Nutzen dieser Konversionstechnik für die Optimierte Entsorgung Feuchter Massenreststoffe. Ph.D. Dissertation, University Essen, Duisburg-Essen, Germany, 2017. Available online: https://duepublico2.uni-due.de/receive/duepublico_mods_00044976 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Reißmann, D.; Thrän, D.; Blöhse, D.; Bezama, A. Hydrothermal carbonization for sludge disposal in Germany: A comparative assessment for industrial-scale scenarios in 2030. J. Ind. Ecol. 2020, 25, 720–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency Industrial Waste Water Treatment–Pressures on Europe’s Environment. Publications Office of the European Union. 2019. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2800/496223 (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- DWA, Deutsche Vereinigung für Wasserwirtschaft, Abwasser und Abfall e.V. DWA-Positionen, Revision der Europäischen Kommunalabwasserrichtlinie. 2021. Available online: https://de.dwa.de/files/_media/content/01_DIE_DWA/Politikinformationen/Positionspapiere/Revision_Europaeische_Kommunalabwasserrichtlinie_2021_Netz.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Wasserhaushaltsgesetz (WHG) vom 31. Juli 2009 (BGBl. I S. 2585), das zuletzt durch Artikel 12 des Gesetzes vom 20. Juli 2022 (BGBl. I S. 1237) geändert worden ist. Available online: https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/whg_2009/ (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Abwasserverordnung (AbwV) in der Fassung der Bekanntmachung vom 17. Juni 2004 (BGBl. I S. 1108, 2625), die zuletzt durch Artikel 1 der Verordnung vom 20. Januar 2022 (BGBl. I S. 87) geändert worden ist. Available online: https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/abwv/AbwV.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Londong, J.; Rosenwinkel, K.H. Industrieabwasserbehandlung. Dritte Auflage; Verlag der Bauhaus-Universität Weimar: Weimar, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schnell, M.; Horst, T.; Quicker, P. Thermal treatment of sewage sludge in Germany: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quicker, P.; Weber, K. Biokohle—Herstellung, Eigenschaften und Verwendung von Biomassekarbonisaten; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, E. Treatment of urban sludge by hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettig, J.; Austermann-Haun, U.; Liebe, H.; Meier, J.F.; Wichern, M. Ein Konzept zur Behandlung von Prozesswässern aus der Hydrothermalen Carbonisierung. Korresp. Abwasser Abfall 2015, 62, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiefel, R. Abwasserrecycling: Technologien und Prozesswassermanagement; Springer-Fachmedien: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, B.; Mumme, J. Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Water from HTC of Corn Silage. Appl. Bioenergy 2013, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, K.; Ren, S.; Clark, J.H.; Fan, J.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S. Characterization and utilization of aqueous products from hydrothermal conversion of biomass for bio-oil and hydro-char production: A review. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1553–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambo, H.S.; Minaret, J.; Dutta, A. Process Water from the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Biomass: A Waste or a Valuable Product? Waste Biomass Valor 2018, 9, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso-Boateng, E.; Sharma, G.; Wheatly, A.D.; Martin, S.J.; Holdich, R.G. Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge: Effect of process conditions on product characteristics and methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekman, S.K.; Broch, A.; Robbins, C.; Zielinska, B.; Felix, L. Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of selected woody and herbaceous biomass feedstocks. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2013, 3, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.; Dorgerloh, U.; Paulke, E.; Mumme, J.; Nehls, I. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Biomass: Major Organic Components of the Aqueous Phase. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpo, U.; Ross, A.B.; Camargo-Valero, M.A.; Fletcher, L.A. Influence of pH on hydrothermal treatment of swine manure: Impact on extraction of nitrogen and phosphorus in process water. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, B.; Reza, M.T.; Mumme, J. Influence of digestion temperature and organic loading rate on the continuous anaerobic treatment of process liquor from hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón-Briceño, C.I.; Ross, A.B.; Camargo-Valero, M.A. Evaluation and comparison of product yields and bio-methane potential in sewage digestate following hydrothermal treatment. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, N.D.; Ro, K.S.; Mao, J.; Flora, J.R.V.; Chappell, M.A.; Bae, S. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Municipal Waste Streams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5696–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, K.J.; Stuart, B.; Kumar, S. Investigation of Anaerobic Digestion of the Aqueous Phase from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Mixed Municipal Solid Waste. Biomass 2021, 1, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Freitas, A.; Yang, X.; Hiibel, S.; Lin, H.; Coronella, C.J. Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of cow manure: Carbon and nitrogen distributions in HTC products. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2016, 35, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, V.; Quance, J.; Posmanik, R.; Gross, A. Phases’ characteristics of poultry litter hydrothermal carbonization under a range of process parameters. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Batista, J.D.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodríguez, J.J.; de la Rubia, M.A. Energy and phosphorous recovery through hydrothermal carbonization of digested sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskosch, A.; Heidecke, P.; Bannick, C.; Brandt, S.; Bernicke, M.; Dienemann, C.; Gast, M.; Hofmeier, M.; Kabbe, C.; Schwirn, K.; et al. Klärschlammentsorgung in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland [Sewage Sludge Disposal in Germany]; Umweltbundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann, S.M.; Molde, J.S.; Timler, J.G.; Wood, B.M.; Mikula, A.L.; Vozhdayev, G.V.; Colosky, E.C.; Spokas, K.A.; Valentas, K.J. Phosphorus reclamation through hydrothermal carbonization of animal manures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10323–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.; Koch, F.; Stelzl, K.; Wüst, D.; Zeller, M. Fate of Nitrogen during Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 8037–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Rao, Y.; Cao, L.; Shi, Y.; Hao, S.; Lou, G.; Zhang, S. Hydrothermal conversion of sewage sludge: Focusing on the characterization of liquid products and their methane yields. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettigondahalli, E.V.; Narra, S.; Ender, T.; Antwi, E.; Nelles, M. Influence of Post- and Pre-Acid Treatment during Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge on P-Transformation and the Characteristics of Hydrochar. Processes 2022, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Falyouna, O.; Malloum, A.; Othmani, A.; Bornman, C.; Bedair, H.; Onyeaka, H.; Al-Sharify, Z.T.; Oluwaseun Jacob, A.; Miri, T.; et al. A general review on the use of advance oxidation and adsorption processes for the removal of furfural from industrial effluents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 331, 111638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, L.G.C.; Mashhadi, N.; Chen, M.; Mukherjee, D.; Taylor, K.E.; Biswas, N. A Short Review of Techniques for Phenol Removal from Wastewater. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, B.; Krebs, M.; Andert, J. Anaerobic degradation of increased phenol concentrations in batch assays. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19048–19059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdogan, E.; Atila, B.; Mumme, J.; Reza, M.T.; Toptas, A.; Elibol, M.; Yanik, J. Characterization of products from hydrothermal carbonization of orange pomace including anaerobic digestibility of process liquor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Ji, W.; Chen, Y.; Gui, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, C. Effect of Temperature on the Properties of Liquid Product from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Animal Manure and Function as a Heavy Metal Leaching Agent in Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekman, S.K.; Broch, A.; Robbins, C. Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC) of Lignocellulosic Biomass. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arauzo, P.J.; Olszewski, M.P.; Wang, X.; Pfersich, J.; Sebastian, V.; Manyà, J.; Hedin, N.; Kruse, A. Assessment of the effects of process water recirculation on the surface chemistry and morphology of hydrochar. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köchermann, J.; Görsch, K.; Wirth, B.; Mühlenberg, J.; Klemm, M. Hydrothermal carbonization: Temperature influence on hydrochar and aqueous phase composition during process water recirculation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Q.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T. Thermal behavior of hydrochar from co-hydrothermal carbonization of swine manure and sawdust: Effect of process water recirculation. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 2329–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, A.; Volpe, M.; Messineo, A. Process Water Recirculation during Hydrothermal Carbonization of Waste Biomass Current Knowledge and Challenges. Energies 2021, 14, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemann, J.; Putschew, A.; Ziegler, F. Hydrothermal carbonization_Process water characterization and effects. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutaieb, M.; Román, S.; Ledesma, B.; Sabio, E.; Guiza, M.; Ouederni, A. Towards a more efficient Hydrothermal Carbonization Processing water recirculation under different conditions. Waste Manag. 2021, 132, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, B.; Poerschmann, J.; Wedwitschka, H.; Koehler, R.; Kopinke, F.-D. Influence of Process Water Reuse on the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Paper. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2165–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüst, D.; Arauzo, P.; Habicht, S.; Cazaña, F.; Fiori, L.; Kruse, A. Process Water Recirculation during Hydrothermal Carbonization as a Promising Process Step Towards the Production of Nitrogen-Doped Carbonaceous Materials. Waste Biomass Valor 2022, 13, 2349–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Salaudeen, S.; Dutta, A.; Acharya, B. Effects of Process Water Recycling and Particle Sizes on Hydrothermal Carbonization of Biomass. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 11576–11586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, V.; Neumann, J.; Wehrli, B.; Gross, A. Nutrient Behavior in Hydrothermal Carbonization Aqueous Phase Following Recirculation and Reuse. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10426–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenwinkel, K.-H.; Hinken, L.; Borchmann, A.; Kipp, S.; Lorey, C. Die Zukunft der industriellen Abwasserreinigung. KA Korresp. Abwasser Abfall 2011, 58, 920–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, T.; Lechevallier, P.; Engelhart, M. Effect of temperature during the hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge on the aerobic treatment of the produced process waters. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettig, J.; Austermann-Haun, U.; Liebe, H.; Meier, J.F.; Busch, A.; Gilbert, E. Möglichkeiten und Grenzen der Behandlung von Prozesswässern aus der Hydrothermalen Carbonisierung. gwf-Wasser + Abwasser 2018, 159, 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kläusli, T. AVA-CO2 Firmen Präsentation. 2014. Available online: http://www.bv-htc.de/stuff/downloads/ifta2014/6_AVA-CO2.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2024).
- Wittmann, T. Verfahren zur Aufbereitung von Prozesswasser aus einer Anlage zur hydrothermalen Karbonisierung nachwachsender Rohstoffe und organischer Reststoffe. WO2012100954, 28 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moosbrugger, R. Praxisorientierte Simulation für die anaerobe Abwasserbehandlung. KA Korresp. Abwasser Abfall 2012, 59, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Massé, D.I.; Singh, G. A critical review on inhibition of anaerobic digestion process by excess ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austermann-Haun, U.; Fischer, P.; Jörderning, H.-J.; Kroiss, H.; Meyer, H.; Müller, G.; Pascik, I.; Rosenwinkel, K.-H.; Seyfried, C.F.; Svardal, K.; et al. Anaerobe Reaktoren und ihre Einsatzbereiche. KA Korresp. Abwasser Abfall 2009, 56, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil, J.A.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodríguez, J.J.; de la Rubia, M.A. Valorisation of the liquid fraction from hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge by anaerobic digestion. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil, J.A.; Mohedano, A.F.; San Martín, J.; Rodríguez, J.J.; de la Rubia, M.A. Anaerobic co-digestion of the process water from waste activated sludge hydrothermally treated with primary sewage sludge. A new approach for sewage sludge management. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenwinkel, K.-H.; Kroiss, H.; Dichtl, N.; Seyfried, C.-F.; Weiland, P. Anaerobtechnik. Dritte, neu bearbeitete Auflage; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Yi, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, Y. Anaerobic co-digestion of corn stover and wastewater from hydrothermal carbonation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Rubia, M.A.; Villamil, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Borja, R.; Mohedano, A.F. Mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste with the liquid fraction from hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil, J.A.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Borja, R.; de la Rubia, M.A. Anaerobic Co-digestion of the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste and the Liquid Fraction From the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Industrial Sewage Sludge under Thermophilic Conditions. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.K.; Tardio, J.; Prasad, J.; Föger, K.; Akolekar, D.A.; Grocott, S.C. Wet Oxidation and Catalytic Wet Oxidation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 1221–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, B.; Breulmann, M.; Wedwitschka, H.; Fühner, C.; Kopinke, F.-D. Wet oxidation of process waters from the hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2018, 90, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Application and Improvement of Wet Oxidation Technology. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 514, 052042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levec, J.; Pintar, A. Catalytic wet-air oxidation processes: A review. Catal. Today 2007, 124, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Freitas, A.; Yang, X.; Coronella, C.J. Wet Air Oxidation of Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC) Process Liquid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3250–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzenstein, P.; Weiner, B.; Köhler, R.; Pfeifer, C.; Kopinke, F.-D. Wet oxidation of process water from hydrothermal carbonization of biomass with nitrate as oxidant. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, F. Wet air oxidation: Past, present and future. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, F. A review of industrial catalytic wet air oxidation processes. Catal. Today 1996, 27, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettigondahalli, E.V.; Narra, S.; Sprafke, J.; Nelles, M. Influence of Acids and Alkali as Additives on Hydrothermally Treating Sewage Sludge: Effect on Phosphorus Recovery, Yield, and Energy Value of Hydrochar. Processes 2021, 9, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, L.B.S.; Anastasakis, K.; Biller, P. Wet oxidation of aqueous phase from hydrothermal liquefaction of sewage sludge. Water Res. 2022, 209, 117863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Q. Fate and distribution of nutrients and heavy metals during hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge with implication to land application. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhan, H.; Yin, X.; Wu, C. The transformation pathways of nitrogen in sewage sludge during hydrothermal treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245 Pt A, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorick, D.; Macura, B.; Ahlström, M.; Grimvall, A.; Harder, R. Effectiveness of struvite precipitation and ammonia stripping for recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from anaerobic digestate: A systematic review. Environ. Evid. 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celletti, S.; Lanz, M.; Bergamo, A.; Benedetti, V.; Basso, D.; Baratieri, M.; Cesco, S.; Mimmo, T. Evaluating the Aqueous Phase from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Cow Manure Digestate as Possible Fertilizer Solution for Plant Growth. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 687434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsarpali, M.; Arora, N.; Kuhn, J.K.; Philippidis, G.P. Beneficial use of the aqueous phase generated during hydrothermal carbonization of algae as nutrient source for algae cultivation. Algal Res. 2021, 60, 102485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ding, L.; Liu, R.; Xu, S.; Li, L.; Gao, L.; Wei, L.; Leng, S.; Li, J.; Li, J.; et al. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Microalgae-Fungal Pellets: Removal of Nutrients from the Aqueous Phase Fungi and Microalgae Cultivation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16823–16832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerner, G.; Meyer, L.; Wanner, R.; Keller, T.; Krebs, R. Sewage Sludge Treatment by Hydrothermal Carbonization: Feasibility Study for Sustainable Nutrient Recovery and Fuel Production. Energies 2021, 14, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Input Material | HTC Reaction Parameters | HTC Process Water | Source | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature [°C] | Retention Time [min] | pH-Value | Chemical Oxygen Demand [mg L−1] | Total Organic Carbon [mg L−1] | Dissolved Organic Carbon [mg L−1] | Volatile Fatty Acids [mg L−1] | Ammonium-Nitrogen [mg L−1] | Total Phosphorus [mg L−1] | ||
| Mixed municipal solid waste | 250 | 10 | 20,500.00 | 6700.00 | [48] | |||||
| 250 | 60 | 22,500.00 | 7100.00 | |||||||
| 250 | 360 | 21,000.00 | 6100.00 | |||||||
| 280 | 10 | 25,500.00 | 8160.00 | |||||||
| 280 | 60 | 24,000.00 | 7800.00 | |||||||
| 280 | 360 | 30,500.00 | 6200.00 | |||||||
| 310 | 10 | 25,000.00 | 7700.00 | |||||||
| 310 | 60 | 23,500.00 | 6750.00 | |||||||
| Sewage sludge as raw sludge | 220 | 135 | 8510.00 | 975.00 | [23] 1 | |||||
| 190 | 30 | 9160.00 | 575.00 | |||||||
| 190 | 240 | 9395.00 | 730.00 | |||||||
| 250 | 30 | 8055.00 | 980.00 | |||||||
| 250 | 240 | 7640.00 | 1223.00 | |||||||
| 220 | 30 | 9160.00 | 783.00 | |||||||
| 220 | 240 | 8520.00 | 1045.00 | |||||||
| 220 | 30 | 8650.00 | 858.00 | |||||||
| 220 | 240 | 8335.00 | 995.00 | |||||||
| Anaerobic digested sewage sludge | 160 | 30 | 9.15 | 12,642.00 | 4686.77 | 191.10 | 1258.00 | 94.03 | [46] | |
| 220 | 30 | 7.14 | 12,992.00 | 4583.71 | 406.00 | 1704.00 | 72.60 | |||
| 250 | 30 | 8.08 | 12,164.00 | 4879.33 | 715.00 | 1685.00 | 103.83 | |||
| Cow manure | 180 | 5 | 6.4 ± 0.1 | 4400.00 | 0 | [49] | ||||
| 220 | 5 | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 10,000.00 | 100 | ||||||
| 260 | 5 | 5.1 ± 0.1 | 9200.00 | 100 | ||||||
| 180 | 30 | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 4600.00 | 100 | ||||||
| 220 | 30 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 6100.00 | 100 | ||||||
| 260 | 30 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 7100.00 | 100 | ||||||
| Poultry litter | 180 | 60 | 5.1 ± 0.01 | 25,151.00 ± 1064 | 2301.00 ± 23 | [50] | ||||
| 200 | 60 | 5.5 ± 0.02 | 19,352.00 ± 516 | 1896.00 ± 36 | ||||||
| 220 | 60 | 5.7 ± 0.03 | 19,242.00 ± 492 | 1303.00 ± 46 | ||||||
| 250 | 60 | 5.3 ± 0.05 | 19,999.00 ± 916 | 856.00 ± 29 | ||||||
| Anaerobic digested sewage sludge (addition of citric acid to HTC process) | 200 | 360 | 4.7 | 34,300.00 | 13,400.00 | [45] | ||||
| Paper | 250 | 1200 | 5 | 76,000.00 | 27,000.00 | [47] | ||||
| Food waste | 250 | 1200 | 5.3 | 52,000.00 | 18,000.00 | |||||
| Mixed municipal solid waste | 250 | 1200 | 4.8 | 62,000.00 | 19,000.00 | |||||
| Anaerobic digested waste (dried) | 250 | 1200 | 8 | 10,000.00 | 4000.00 | |||||
| Provider | Treatment Concept | Source |
|---|---|---|
| AVA-CO2 Schweiz AG | nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, recirculation of concentrate into HTC process | [76] |
| CS Carbon Solutions GmbH | nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, discharge of permeate into wastewater treatment plant | [75] |
| Grenol GmbH | aerobic treatment in a constructed wetland | [75] |
| SunCoal Industries GmbH | thermal processing by evaporation and condensation | [77] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ender, T.; Ekanthalu, V.S.; Jalalipour, H.; Sprafke, J.; Nelles, M. Process Waters from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Waste Biomasses like Sewage Sludge: Challenges, Legal Aspects, and Opportunities in EU and Germany. Water 2024, 16, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071003
Ender T, Ekanthalu VS, Jalalipour H, Sprafke J, Nelles M. Process Waters from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Waste Biomasses like Sewage Sludge: Challenges, Legal Aspects, and Opportunities in EU and Germany. Water. 2024; 16(7):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071003
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnder, Tommy, Vicky Shettigondahalli Ekanthalu, Haniyeh Jalalipour, Jan Sprafke, and Michael Nelles. 2024. "Process Waters from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Waste Biomasses like Sewage Sludge: Challenges, Legal Aspects, and Opportunities in EU and Germany" Water 16, no. 7: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071003
APA StyleEnder, T., Ekanthalu, V. S., Jalalipour, H., Sprafke, J., & Nelles, M. (2024). Process Waters from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Waste Biomasses like Sewage Sludge: Challenges, Legal Aspects, and Opportunities in EU and Germany. Water, 16(7), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071003










