Abstract
The Pearl River is one of China’s large rivers, the second-largest river and the fourth-longest river in China. Its unique geography, landform, and climate conditions create unique fluvial geomorphological processes. Affected by human activities and climate change, the fluvial geomorphological processes in the Pearl River Basin have undergone significant changes in recent decades, seriously affecting the river’s sustainable development. This paper critically reviews changes in fluvial geomorphological processes and analyzes influencing factors in the Pearl River Basin with a focus on possibilities for policy overhaul and strategic adjustments.
1. Introduction
Due to the increasingly dramatic impacts of global climate change and human activities, the ecological balance characterized by the material and energy cycles via fluvial geomorphological processes has received widespread attention in recent decades [1,2,3]. Rivers are a primary component in fluvial geomorphological cycles; they serve as important sources of water resources and critical functions for terrestrial ecosystems [4,5]. Understanding the new status in fluvial geomorphological processes is valuable in mitigating natural hazards such as floods and droughts, as well as assessing the anthropogenic impact on natural ecosystems [6]. Asia is one of the most densely populated regions on the Earth. The influence of human activities on fluvial geomorphological processes is particularly pronounced in Asia, with China’s large rivers being the most representative [7].
The Pearl River is one of the large rivers in China, composed of the West (Xijiang) River, North (Beijing) River, East (Dongjiang) River, and the Pearl River Delta (PRD). It spans six provinces in China, namely Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi, Guangdong, Hunan, and Jiangxi provinces, as well as the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macao and an extremely small northeastern part in Vietnam [5,8]. The total area of the Pearl River Basin (PRB) is 45.37 × 104 km2, with 44.21 × 104 km2 in China [9]. The Pearl River ranks as the second-largest river and the fourth-longest river in China [10]. The main stem of the Pearl River is the West River, originating from the eastern foothills of the Wumeng Mountains in the Qujing Prefecture of Yunnan province. Flowing from west to east, it traverses Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi, and Guangdong provinces, with a total length of 2075 km and a drainage area of 35.31 × 104 km2 (Figure 1). Major tributaries include the Beipan River, Liu River, Yu River, Gui River, and He River. Another major tributary, the North River, originates from the Xiaomao Mountain in Xinfeng County, Jiangxi Province. It flows through the provinces of Hunan, Jiangxi, and Guangdong, with a total length of 468 km and a drainage area of 4.67 × 104 km2. Major tributaries include the Wushui River, Lian River, and Sui River. The West River and North River converge at Sanshui District in Foshan (Figure 1b), Guangdong Province. The third major tributary, the East River, originates from the Yajiboshan Mountain in Xunwu County, Jiangxi Province, and flows southward into Guangdong Province. It has a total length of 520 km and a drainage area of 2.70 × 104 km2. Major tributaries include the Xinfeng River and Xizhi River. The PRD, situated in the downstream area, exhibits a dense network of waterways and intricate channels, covering a drainage area of 2.68 × 104 km2. With nearly 100 small creeks, it forms a typical subtropical river delta [11,12].
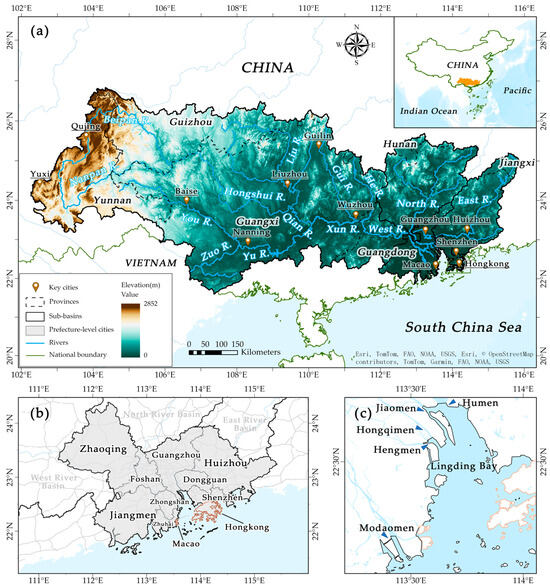
Figure 1.
(a) Geographical configuration of the Pearl River Basin, (b) nine cities and two special administrative regions in the Pearl River Delta, and (c) main outlets in the Pearl River Estuary. The PRD, serving as an individual study unit, encompasses 11 cities, as depicted in (b). It constitutes the study area for numerous research endeavors mentioned in this paper. Its delineation is primarily driven by economic considerations rather than geographical considerations, as will be discussed in Section 3.1.1. In this study, the term “PRD” refers to the region depicted in (b).
The increase in extreme precipitation events can lead to changes in fluvial geomorphological processes, which are particularly pronounced in tropical and subtropical regions. The PRB is situated in a subtropical zone with a mild and monsoon climate. The average annual temperature ranges from 14 to 22 °C, with average annual precipitation from 1200 to 2200 mm [13]. From 1954 to 2022, the annual average water discharge in the PRB reached over 290 billion m3, with an annual average sediment load of over 66 million tons [14]. The temporal distribution of water discharge and sediment load is uneven, with high observations in the wet season, typically from April to September, contributing approximately 80% of the annual water discharge [15,16] and 91% to 95% of the sediment load. Because of the uneven distribution, the PRB often experiences frequent water and drought disasters [17,18]. Issues such as soil erosion and karst rocky desertification are prominent, leading to a decline in water quality and degradation of the basin ecosystem. Severe soil erosion, covering an area of 79,928 km2 [19], is mainly in the middle and upper reaches. The substantial soil erosion and karst rocky desertification have created various issues in ecological security, food security, flood control, and human settlement safety in the basin. Consequently, governance, development, and protection remain quite challenging tasks [20,21].
In addition, there is an extreme imbalance in economic development within the basin. Provinces in the upstream regions, such as Yunnan, Guizhou, and Guangxi, experienced relatively slow economic growth. In contrast, the downstream PRD region saw a fast economic development and stands as one of China’s three major megaregions benefiting from the national policy of Reform and Opening Up. It is also recognized as a world-class center for advanced manufacturing and modern service industries. However, rapid economic development has also brought various challenges, including the deterioration of the river environment and human settlement environment [22].
The PRB, with a total population of 118 million, is one of China’s densely populated areas, which needs substantial natural resources and thus may exert a highly complex influence on the river environment. Activities related to basin governance and development, such as the construction of reservoirs, river channelization, embankment construction, and sand mining, can also alter the basin’s runoff and hydrological processes. Moreover, the basin is experiencing an increased frequency of floods, droughts, and other natural hazards due to climate change, posing higher challenges in flood control and drought prevention and thus hindering the pursuit of rapid and sustainable socio-economic development [23].
In the past few decades, significant changes in fluvial geomorphological processes have occurred in the PRB. Understanding these changes is crucial for promoting the sustainable development of the Pearl River. Currently, the new status of hydrogeomorphic processes in the PRB under the dramatic impacts of global climate change and human activities is still not clear. It is necessary to provide a comprehensive review of such processes and identify the issues to propose possible policy adjustments in river management. This information is pivotal in promoting flood protection and hazard mitigation, ensuring water security, protecting water resources, restoring ecological balance, and achieving integrated basin management in the PRB.
2. Changes over Recent Decades
The wet season in the PRB spans from April to September, while the dry season extends from October to March of the following year. The seasonal distribution of precipitation significantly influences the water discharge and water levels of rivers throughout the entire basin. Based on long-term monitoring data from hydrological stations, previous studies have found that over the past few decades, there has been a reduction in the difference in water discharge between the wet and dry seasons in the PRB. Specifically, there has been a slight decrease in water discharge during the wet season, concurrent with a significant increase during dry seasons [24,25,26,27]. However, no statistically significant changes in interannual water discharge have been identified [28,29,30,31], except for a declining trend observed in the northern part of the West River Basin (WRB) in the Liu River and the southwestern Nanpan River [32].
The Pearl River is characterized by a relatively low sediment load among China’s seven large rivers. Sediment concentration tends to be higher in the west than in the east and the northwest than in the southeast. Tributaries with high sediment concentration, such as the Nanpan River, Beipan River, Hongshui River, and Yu River, are all located in the WRB. Unlike the relatively consistent stability in water discharge, sediment load displays notable variations over different periods. From the 1950s to the mid-1980s, visible increases in sediment load were observed in the estuarine zones of the West River and North River, notably between the late 1970s and the mid-1980s [23,24]. However, since the mid-1980s, there has been a distinct decline in sediment concentration [16,33,34,35] and a faster reduction from the 1990s to the early 21st century [31,34,36]. The East River Basin (ERB) has also experienced an overall decrease in sediment load since the 1960s [29,37]. Several studies conducted in the Pearl River Estuary (PRE) have reported a consistent decline in suspended sediment concentrations (SSC) in recent decades [38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. This decline significantly increases estuarine erosion and alters the coastal geomorphology of the PRE. The variations in both water discharge and sediment load across the entire basin are influenced by multiple factors, broadly categorized as anthropogenic and natural ones. This section aims to provide a detailed analysis of these impacts.
2.1. Human-Induced Changes
2.1.1. Land-Use Change
Previous studies on land-use/cover change (LUCC) across the PRB have identified a common trend over recent decades. With the development of urbanization, a large amount of cropland has been reclaimed for build-ups. The total area of grassland and forestland initially decreased, followed by an increase after 2000, but overall, both have reported a net decrease. Unused land remained decreasing. Previous studies also revealed [45] that the decrease in grassland mainly happened in the northwestern part, but the decrease in cropland was mainly observed in the central part as well as in the coastal and delta areas. The increase in build-ups was concentrated in the PRD (Figure 2). To be specific:
In the WRB, cropland and forestland in Guangxi Province (Figure 1) accounted for about 88% of the province’s total area [46], which decreased substantially during 2005–2015. Build-up land increased rapidly, which was the fastest change in land use during this period, and it was mainly transferred from cropland. The total area of waterbody, grassland, and barren land also increased. In the past 20–30 years, studies on LUCC in Yunnan Province (mainly distributed in the Nanpan River basin) and Guizhou Province [47,48,49] found that cropland and forestland accounted for the largest proportion in land uses, but their areas tended to decrease. On the contrary, the build-up area has increased rapidly, with a significantly higher growth rate from 2010 to 2020. Other land uses have undergone relatively minor changes.
In the ERB, forestland is still the most important land-use type, accounting for a constant share of over 58% from the 1970s to the beginning of the 21st century [50]. As changes in the WRB, there has been a continuous decline in cropland in recent years. Build-up land area has steadily increased [51,52] and experienced the fastest growth among all land-use types, which primarily came from forestland, cropland, and unused land [51].
Likewise, in the North River Basin (NRB), forestland is also the predominant land-use type, encompassing over 63% of the basin’s total area, while cropland makes up approximately 20% [53]. From 2000 to 2015, both cropland and forestland witnessed a decline, with a total reduction of 3.5% in forestland and approximately 4.45% in cropland. Changes in grassland and water bodies were relatively inconspicuous. Similarly, built-up land has expanded significantly during the same period. In 2000, built-up land accounted for approximately 3.96% of the North River Basin, while in 2015, the proportion reached 7.23%, marking an increase of 82.93%.
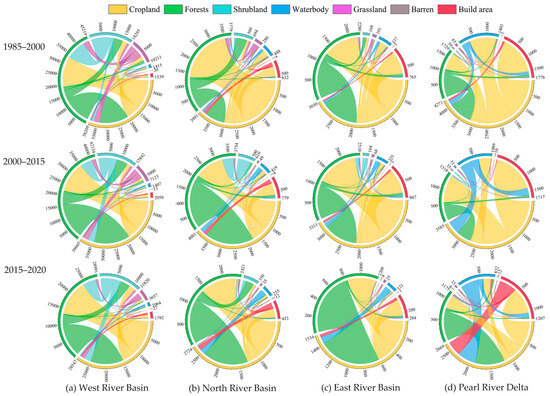
Figure 2.
Land-use type transformation network in (a) WRB, (b) NRB, (c) ERB, and (d) PRD. (data from Ref. [54]).
Owing to the consistent economic importance, cities in the PRD exhibited a similar trend in land-use change. From the late 20th century to the first two decades of the 21st century, LUCC in PRD cities has shown a significant expansion in build-up land accompanied by rapid decreases in cropland and forestland [55,56,57]. The proportion of build-up land increased from 5.47% in 1990 to 14.56% in 2020 [57], with a loss of 31.74% of cropland from 1990 to 2006. Forestland remains the dominant land use in the PRD, constituting over 53% of the total area, but the majority of forestland is located in the outer PRD (Zhaoqing, Huizhou, and northern Guangzhou areas) instead of the central PRD [58]. The areas of waterbody and grassland fluctuated, with a decreasing trend similar to unused land. The changes in build-up land and cropland are statistically negatively correlated [59]. During the period from 2010 to 2015, the rate of expansion of build-up land slowed down, but during this period, there was also an increase in urbanization based on unused land.
Changes in land use can alter hydrological processes, consequently impacting soil erosion, especially in the areas with the reduction in forestland [60,61]. Over the past few decades, forestland has undergone an initial decrease followed by an increase in the PRB. Previous studies [62] indicate that during the period from 1990 to 2020, soil erosion in the PRB exhibited a decreasing trend, with an annual reduction rate of 13.44 (±1.53) t/(km2·a). Soil erosion primarily occurs in the western tributaries of the West River, especially in the areas with slopes greater than 15°, low vegetation cover, and inadequate forest management.
2.1.2. River Channel Alterations
The PRB has numerous tributaries, and over the years, the river channels have undergone varying degrees of modifications. Since the mid-1980s, dramatic channel downcutting has occurred in the lower reaches of the West River and North River [11,16,63,64,65,66]. The average channel downcutting depths are 0.59 to 1.73 m and 0.34 to 4.43 m, respectively [11]. The West River and North River converge at Sanshui District, Guangdong Province. The downcutting in the North River is greater than in the West River, leading to a significant increase in the diversion ratio at the confluence of the three rivers at Sanshui District—this results in water supply initially from the North River as a provider to the West River shifting to water acquisition from the West River as a provider to the North River [65]. Since the 1990s, substantial downcutting also occurred in the lower reaches of the East River, with an average depth ranging from 1.77 to 6.0 m, surpassing that of the West River and North River [11]. Despite the unclear trend in water discharge changes in Pearl River’s three major tributaries, the downcutting of river channels has significantly lowered water levels downstream in the three major tributaries [24,63,67,68,69]. Additionally, fluctuations in sediment load and water discharge contribute to sedimentation and erosion along different sections of each tributary, with erosion being a common phenomenon in the lower reaches. For example, the middle and lower reaches of the East River experienced siltation under previous natural conditions. The annual accumulated sediment transport volume reaches 280.66 million m3 per year. However, from 2003 to 2009, the riverbed underwent significant downcutting with an average erosion depth of 1.9 m [70]. In the middle reaches of the North River, the area of sandbars increased 19.75 km2 from 1975 to 1984. However, after 1988, the area decreased rapidly, and some sandbars at the lower end were eroded, resulting in a widening of the river channel [71,72]. Changes in siltation and erosion have led to channel shifts and water flow alterations, primarily occurring in sections adjacent to urban areas, such as the lower reaches of the North River and the Huizhou section of the East River (Figure 3).
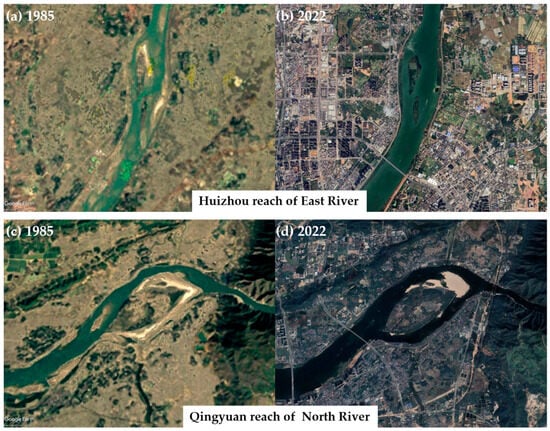
Figure 3.
Satellite images of parts of the East River and North River obtained from Google Earth.
The PRD is characterized by a highly branched, tree-like river network with frequent bifurcations and mergers [12]. The temporal variation in water discharge and sediment load within the delta is primarily influenced by the redistribution of upstream water and sediment [64], exacerbating changes in the PRD river network. Since the mid-1980s, there has been an overall uneven downcutting in the river channels of the PRD [73], with cross-section narrowing and deepening [74,75,76]. The downcutting became more evident from the 1990s to the early 21st century, leading to a dramatic decrease in water levels [11]. Due to human activities such as land reclamation and the construction of embankments and sluice gates, the coastline of the PRE has continued to extend seaward [77]. Between 1976 and 2006, the average annual extension was approximately 20 m [78]. This extension is manifested near the estuary as the narrowing and elongation of river channels, with typical areas near Modaomen and the northern part of Lingding Bay (Figure 1c) [79,80,81].
2.1.3. Reservoir and Dike Construction
Since the 1950s, over 9000 reservoirs have been constructed in the PRB, collectively holding approximately 21% of the basin’s annual runoff [82]. Among these, 72 are large reservoirs (storage capacity ≥ 100 million m3), with 36 located in the WRB. The two largest reservoirs in the WRB, Tianshengqiao Reservoir (completed in 1997) and Longtan Reservoir (completed in 2006), have capacities of 10.8 billion m3 and 27.3 billion m3, respectively. In the NRB, the total storage capacity of large reservoirs has exceeded 5 billion m3, with Nanshui Reservoir (constructed in 1971) and Feilaixia Reservoir (completed in 1999) having capacities of 1.243 billion m3 and 1.95 billion m3, respectively. Additionally, the ERB possesses three major regulating reservoirs—Xinfengjiang, Fengshuba, and Baipenzhu—constructed in 1962, 1973, and 1985, respectively, with storage capacities of 13.896 billion m3, 1.94 billion m3, and 1.22 billion m3, respectively [37,83] (Figure 4).
Most of the dikes in the middle and upper reaches of the PRB were constructed between the mid-1950s and the 1970s, primarily consisting of small-scale dikes. In the absence of effective flood storage reservoirs, dike construction served as the principal defense infrastructure against frequent floods. Key dike constructions included the Zhanyi, Qujing, and Donghedi projects along the Nanpan River in the upper reaches, while the middle reaches featured the Yongjiang dike project along the Yu River and the Sidan dike project along the Xun River. Downstream in the PRD, major dike construction includes the Beijiang, Zhongshun, and Jiangxinlian dike projects (Figure 4). Given the intricate river network and proximity to the South China Sea, large-scale construction projects on dikes and sluices were crucial in mitigating floods. Between 1949 and 1976, more than 10,000 low-rise riverine and coastal dikes in the PRD were connected, forming 494 sections [84]. This enables water drainage downstream within the dikes, facilitating separate flood prevention and drainage irrigation. It concentrates the flow regulation, carrying sediment to the estuary while also bolstering defenses against coastal saltwater erosion.
The construction of dikes and reservoirs on rivers has direct implications, leading to nonlinear alterations in river runoff and sediment load dynamics [43]. These alterations often display a long time lag before the impacts are evident. Reservoir construction causes a decrease in maximum annual water discharge while significantly increasing the minimum water discharge. Interannual changes in water discharge are predominantly influenced by precipitation, without apparent impacts from reservoir construction [16,40,63,64]. However, alterations in sediment load in the mainstreams primarily result from large reservoirs or dams, while tributaries’ sediment changes mainly from extreme climatic events and soil conservation measures [85]. Post-1990s, the effects of reservoir construction and soil conservation practices have surpassed the impacts of deforestation, significantly reducing sediment load in lower reaches [29]. For instance, after the closure of the Yantan Dam on the Hongshui River in 1992, the annual sediment load at the downstream Qianjiang station decreased by 27.6 Mt/a (58.7%) from 1992 to 2002 compared to the previous period of 1989–1991 [40]. Since the closure of the Longtan and Baise reservoirs in 2006, sediment load in the Pearl River has decreased by 70% compared to the 1950s to the 1980s [30]. Overall, subsequent to the completion of numerous large reservoirs on the mainstem and major tributaries, sediment load in the 2000s and 2010s decreased to less than half and one third of that in the 1950s, respectively [31]. This may exacerbate channel downcutting and erosion in downstream floodplains.
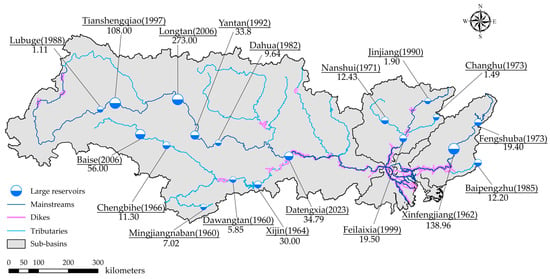
Figure 4.
Major large reservoirs in the PRB (modified from Refs. [31,33,86]). Dam locations are denoted by circles with the dam name, year of closure, and storage capacity of the corresponding reservoir (unit in 100 million m3) under each dam name.
2.2. Natural Climate Variations
Temperature and precipitation are two crucial climatic factors regulating fluvial geomorphological processes. Variations in temperature can affect processes such as water body evaporation, vegetation transpiration, and soil evaporation, therefore influencing runoff generation and resultant fluvial geomorphological processes. The intensity, frequency, and spatial-temporal distribution of precipitation can directly regulate river water discharge.
2.2.1. Temperature
Since 1954, the annual average temperature in the PRB has shown a significant upward trend [87,88,89,90,91,92], generally increasing from west to east PRB [90,91]. The seasonal average temperature in the PRB has experienced varying degrees of increase [89,90]. As seen in Figure 5, the warming rate in winter is higher than in summer [91], and the temperature increase during the monsoon season is lower than during the non-monsoon season [92]. Additionally, most months have shown an upward trend in temperatures [87,88,92]. In terms of spatial distribution, the monthly average temperature has increased at a faster rate in coastal areas [93], and there has been an increase in May, July, August, and September in almost all regions [94]. Overall, the average temperature in most areas of the PRB is increasing, with the most significant warming in the PRD and ERB [87,88,90].
The PRB generally shows an increase in extremely high-temperature events and a decrease in extremely low-temperature events [95]. The monthly extreme minimum temperature TNn, the monthly minimum temperature maximum TNx, the monthly extreme maximum temperature TXx, and the monthly maximum temperature minimum TXn have all shown an upward trend [95,96,97,98,99]. Spatially, there are notable spatial differences in the trend of extremely high temperature [98], with an increasing trend from west to east, particularly in the eastern part [100]. The number of warm days increases and cold days decreases, which is significant and consistent in most areas in the PRB, especially in the Yu River, Zuo River, You River basins, and the PRD [95]. Furthermore, the daily maximum temperature shows a significant upward trend, with a significant shift occurring around 2002 [100]. Generally, extreme temperature has a high correlation with average temperature, and their spatiotemporal trends are relatively similar [98].
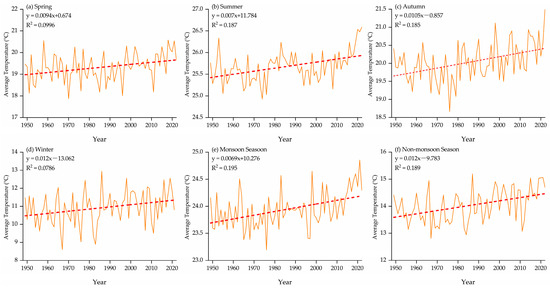
Figure 5.
Temporal variations in average temperature in (a) Spring, (b) Summer, (c) Autumn, (d) Winter, (e) Monsoon Season, and (f) Non-Monsoon Season from 1949 to 2022 (Data from Ref. [101]).
2.2.2. Precipitation
Unlike the variation in temperature, precipitation in the PRB is characterized by small interannual variability and uneven spatiotemporal distribution, which affects the effective use of water resources.
The annual precipitation in the PRB shows non-significant changes [92,102,103,104,105,106]. In terms of spatial distribution, the eastern PRB has higher annual average precipitation but fewer rainy days, while the western areas have lower precipitation and more rainy days. The number of rainy days is decreasing in almost the entire basin [67,102,107]. There is a non-significant temporal trend in annual precipitation, and the number of rainy days is decreasing, leading to an increase in precipitation intensity in the eastern PRB [105]. In seasonal precipitation (Figure 6), there is a slight upward trend in summer and winter [102,108], a steady downward trend in spring and autumn [109], and a significant decrease in the number of rainy days in autumn [105]. Additionally, it was found that there is an insignificant decrease in precipitation during the monsoon season, while the non-monsoon season shows an insignificant increasing trend [108].
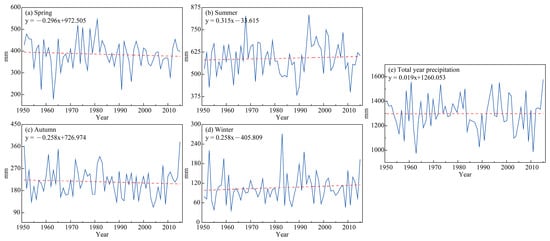
Figure 6.
Temporal variations in precipitation in (a) Spring, (b) Summer, (c) Autumn, (d) Winter, and (e) Total year (modified from Ref. [109]).
For extreme precipitation, the extreme precipitation index gradually decreases from east to west in the PRB [110]. The threshold of extreme precipitation is higher in the east and lower in the west, and there was a significant change in the entire basin in the late 1960s and 1980s [111] (Figure 7). The upper reaches show a significant increasing trend in extreme precipitation in both volume and frequency [67,112] and are more prone to extreme events compared to the lower reaches [104]. The number of days of extreme events in the entire basin shows a non-significant decreasing trend, while the duration of consecutive non-rainy days exhibits a significant increasing trend [106].
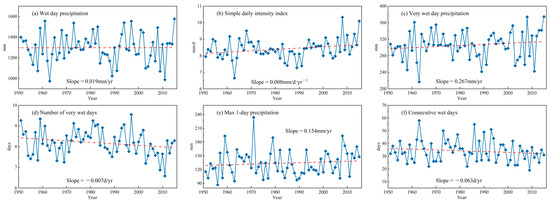
Figure 7.
Interannual variation of extreme precipitation magnitude in the PRB during 1951–2015 (modified from Ref. [109]).
3. Analysis of Influencing Factors
3.1. Impacts of Anthropogenic Factors on Basin Changes
3.1.1. Socio-Economic Development
The changes in the ecological environment of the river basin are closely linked to the socio-economic development within the PRB. Since the establishment of the People’s Republic of China, the economic policies have profoundly influenced the ecological environment of the PRB, which can be roughly divided into the following stages:
Early years of the establishment of the People’s Republic of China (1949–1978): During this period, the PRB was in a state of destruction after World War II. The economy of the PRB was mainly focused on agriculture and the handicraft industry. The urbanization process was thus slow. To quickly change the country’s poor situation, the government proposed the “Great Leap Forward” policy at the end of the 1950s to promote industrial development. Large-scale deforestation took place for steel production, leading to substantial deforestation [113]. Water environment problems also emerged due to large-scale cropland improvement, land reclamation, and reservoir construction [114]. However, due to the relatively low technology in hydraulic engineering, only small tributary reservoirs were built, with a relatively small impact on the variation of river runoff and sediment [115].
From 1978 to 2008, China began implementing its Reform and Opening-Up policy, which provided new opportunities for economic development in the PRB: The government increased investment in rural water conservancy infrastructure and expanded the irrigation area for cropland. In the 1980s, the Chinese government implemented the Forest Contract Responsibility System [113]. This system transfers the ownership of forests from the government to individual farmers under contract. Some farmers began to harvest forests for immediate profits, particularly in the WRB. During this period, there was a significant decrease in forestland and a substantial increase in cropland in the WRB, which exacerbated the soil erosion issue [116]. In the late 20th century, the government began to implement measures such as returning cropland to forestland and water and soil conservation in the WRB. These measures had a significant effect on vegetation recovery and soil erosion regulation in the WRB from 2002 to 2014 [117].
After 1995, with the support of the central government, the Guangdong provincial government formally proposed the establishment of the Pearl River Delta Economic Zone. As industry and labor force continued to expand, the urbanization process in the PRD region advanced rapidly. From 2008 to the present, guided by the active direction of the Reform and Opening-Up policy, urbanization construction in the PRD region has been basically completed. The size of cities also nearly doubled from 1995 to 2015 [55]. Urbanization has led to adjustments and optimizations in land use, but it has also exerted certain pressures on the ecological environment of the PRB. For example, urban development can cause changes in regional surface water processes, therefore affecting the entire river system’s ecosystem.
3.1.2. Water Resources Management Policies Development
The Pearl River is renowned for its numerous tributaries and dense waterways, with abundant water resources and strong potential for hydropower utilization, which have significant applications in agriculture, forestry, hydroelectric power generation, and transportation. However, due to uneven spatiotemporal distribution in river runoff, the lower reaches face dramatic flood protection pressures in the monsoon season, while the upper reaches, such as the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau and the northwest mountains of Guangxi, often suffer from severe droughts during the dry season. Basin policymakers have tried various measures to cope with the uneven spatiotemporal distribution of water resources.
In the early stages of the establishment of the People’s Republic of China, flood-control reservoirs were mostly constructed with high dams, underestimating the role of dikes in flood control. After the 1960s, cascade development plans with runoff-type power stations became popular. Due to technological glitches, the constructed reservoirs often failed to run with full storage capacity, except for a few hydropower stations that showed satisfactory benefits [118]. During this period, flood control and water infrastructure in the PRB remained weak, with only a few large cities having piped water supply facilities and small-scale self-built water conservancy projects being the main reliance for agricultural irrigation by farmers.
In the 1970s, the construction of embankments moved to another extreme. The constructed reservoirs were relatively small and could not meet the storage capacity required for flood control. In addition to insufficient storage capacity, the existing reservoirs also suffered from varying degrees of siltation, with some reservoirs even becoming fully silted and abandoned. This led to a significant loss of effective storage capacity and even dam collapses. For example, the Baidonghe Reservoir, built in 1958 in the Baise prefecture, had accumulated sediment of 11.81 million m3 by 1982, equivalent to 32% of its effective storage capacity. Likewise, the Xiangshuiba Reservoir in Yunnan impounded sediment of 71.2 million m3 within 20 years of its completion, resulting in a loss of 36% of its effective storage capacity [119].
In the 1980s, flood-control planning in the PRB proposed the principle of “balancing upstream and downstream, giving priority to flood water release with a combination of flood regulation” [120]. The role of existing dikes received comprehensive attention. Key dikes were strengthened, and several problematic and poorly constructed reservoirs underwent reinforcement. At the same time, it was proposed that key mainstem reservoirs in the upper and middle reaches be constructed to reduce peak flood flow, therefore increasing the flood-control capacity in the middle and lower reaches.
Since the early 1990s, more large-scale dams and dikes have been constructed in the PRB, with a sharp increase in total reservoir capacity on both mainstem and tributaries. Compared to the reservoirs constructed in the 1980s and earlier, the total reservoir capacity in the PRB in the 1990s almost doubled [31]. For instance, The Tianshengqiao Reservoir in the XRB was completed in 1997, with a total storage capacity of 10.8 billion m3, greater than the combined capacity of all the larger reservoirs (storage capacity > 10 million m3) previously built in the PRB.
It also should be highlighted that from the mid-1980s to the early 21st century, driven by profits from urban expansion, large-scale sand mining activities became increasingly frequent in the PRB. Previous studies suggested that from the 1950s to the 1980s, the increase in sediment discharge in the three major tributaries was mainly attributed to intensified deforestation and resultant soil erosion [28,29,30,31,32,33,64]. The small-scale reservoirs have been constructed on tributaries and had a relatively weak impact on sediment trapping. However, after the mid-1980s, the sediment trapping by large reservoirs significantly increased, coupled with large-scale sand mining activities, resulting in a drastic reduction in sediment load in the delta region [11,16,33,34,40,65] (Figure 8). In addition, large-scale river dredging also occurred since the 1990s to guarantee maritime shipping [63]. All these factors have caused significant riverbed incisions in the downstream channels. Although climate change also played an important role in river flow change, anthropogenic impacts contributed more than 80% of the changes [30,82].
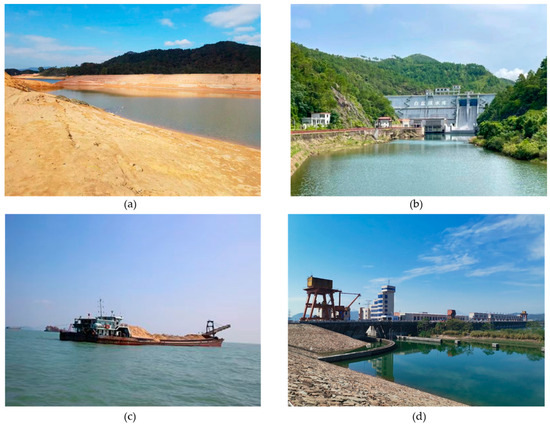

Figure 8.
(a) Water level decreased in December in the segment of the North River; (b) The Baipenzhu Reservoir; (c) Sand mining vessel in the PRD; (d) Feilaixia water conservancy hub. All the photos were taken by the authors of this article.
At the beginning of the 21st century, the rapid economic and social development, as well as the impact of climate factors, have caused a series of ecological issues and natural hazards in the river basin. As a result, the water resources development and utilization shifted towards an overall consideration of development, protection, and regulation, which was the major feature of water resources planning during this period.
Several factors have contributed to this shift. First, changes in runoff have dramatically affected the self-purification capacity of rivers. Since the release of the policy of Reform and Opening Up in 1978, economic development and population growth have led to an increase in domestic and industrial water consumption, as well as an increase in sewage discharge. The Nanpan and Beipan river basins in the upper reaches, serving as an industrial and energy base for Yunnan and Guizhou provinces, have large sewage discharge and lack effective governance measures. During dry seasons, the low runoff and poor self-purification capacity in these areas have exacerbated river pollution. In the middle reaches of the Pearl River, pollution in some small and medium-sized rivers in Guangxi is also prominent. In the 1990s, during dry seasons, the water in the Gui River in the middle and lower reaches turned black, leading to a complete halt in the water supply for local residents [121].
Second, the problem of annual imbalance in water discharge has become more prominent. Despite the construction of large-scale dams and embankments, the basin has experienced several regional flood events since the 1990s. In the PRD region, three consecutive years of low water levels from 2003 to 2005 resulted in saltwater intrusion into the estuary, severely affecting the water supply of 15 million local residents in Zhuhai, Zhongshan, and Macao [122]. This situation caused an urgent water dispatch from upstream reservoirs.
In addition, intensive human activities such as hydropower projects, navigation, and sewage treatment have had a significant impact on the river ecosystems [123]. For example, the West River’s largest tributary, the Yu River, has been blocked by the Xijin hydropower dam, disrupting the migration routes of some fish species and damaging the spawning grounds of fish both upstream and downstream, resulting in reduced fish populations. Although some fish species that can live in shallow waters or pass through sluices have increased their yields due to expanded habitats, overall, the negative impacts of dam construction on fish survival have outweighed the corresponding benefits, especially for rare and endangered fish species that require long-distance migration [124].
In 2003, the Chinese government proposed the concept of “scientific development” as the national policy guideline. “Maintaining river health and building a sustainable Pearl River” became the guideline for water management in the new century. In October 2007, the Pearl River Water Resources Commission (PRWRC) organized the signature of the “Trans-province River Water Affairs Convention in the Pearl River Basin”, which regulated trans-province water activities through a contractual framework [125]. Disorderly sand mining activities in the PRD region were completely prohibited in 2008. Overall, with the implementation of scientific, systematic, and sustainable development concepts, basin governance has emphasized the coordinated management among provinces, cities, and river sections. Outdated notions of water resource exploitation have been gradually abandoned. Various state-of-the-art perspectives, such as river ecology, upstream–downstream interactions, and adaptation to climate change, have been incorporated into river management.
After 2010, the concept of scientific and sustainable development has become a consensus across society and the entire basin, emphasizing the harmony between humans and nature as a top priority in river management. Within the legal framework, various administrative departments are performing their duties and carrying out administrative law enforcement activities in an orderly manner, gradually forming an administrative law enforcement system and a scientific water resources management system. At the end of June 2018, the “River-Director System” policy was established nationwide, with the heads of local governments serving as “River Directors” responsible for organizing and leading the management and protection of corresponding rivers and lakes [126]. This further clarified the regulatory and accountability issues in the management of rivers in the PRB. Overall, the concept of scientific and sustainable development has provided valuable guidelines for river management in the PRB.
3.2. Impacts of Atmospheric Oscillations on Climate Variability
Under global warming and enhanced human activities, climate change in different regions is significantly influenced by amplified changes in global and regional-scale water cycles. Therefore, many studies [15,127,128,129,130,131] have attempted to investigate its large-scale patterns, which are characterized by the fluctuations in sea surface temperature. The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a fluctuation between warm El Niño and cold La Niña events in the ocean. During El Niño, annual precipitation increased in southeastern China and decreased in southwestern China, while the trend reversed during La Niña events [130]. The impact of ENSO on precipitation varies significantly with seasons and months. In the lower reaches of the Pearl River, winter precipitation is relatively lower in summer and autumn during El Niño events than in La Niña events [132].
Previous studies investigated the influences of ENSO, North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), and Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) on climate change across the PRB. It has been found that ENSOs are positively correlated with autumn and winter precipitation and have a strong impact on the occurrence of drought events [133], especially during El Niño events [134]; NAO has a significant negative correlation with summer precipitation and a positive correlation with winter precipitation [135] and serves as the dominant climatic indicator affecting droughts in the WRB [131]. PDO has a significant positive correlation with annual precipitation in the Beipan and Hongshui tributary basins [136]. The average winter precipitation showed an upward trend when IOD was observed [137]. In ERB, NRB, and the southwestern WRB, the average annual runoff and maximum daily runoff were found to be very sensitive to IOD events [138]. Generally, ENSO and IOD are two large-scale climate indicators that have a strong impact on climate change in the PRB. Both of them play crucial roles in rainfall and drought events [139]. It is worth noting that these climate events do not happen independently but often interact simultaneously [137,140,141], which may contribute to the differences observed in various studies.
Due to global climate change, the spatial and temporal changes in precipitation are becoming more uncertain. Therefore, studying the impacts of climate change is of great significance for water resources management in the PRB [8,15]. Previous studies on atmospheric circulation [127,142,143] have shown that the Western Pacific Subtropical High and the Eurasian High have a significant impact on the regulation of the East Asian monsoon by ENSO. The variation of monsoon affects the changes in water vapor transport, leading to changes in rainfall patterns in coastal areas of China [144]. In southeastern China, water vapor primarily originates from the Indian Ocean and the tropical Pacific [145]. The southwest monsoon and southeast monsoon transport water vapor from the Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean to the Chinese monsoon regions, respectively [146]. Sea surface temperature changes in the central tropical Pacific are crucial to East Asian summer monsoon precipitation [147]. For example, the northwest Pacific subtropical high and the East Asian summer monsoon were weak during El Niño events, resulting in insufficient water vapor transport to the PRB, triggering the occurrence of drought events [134]. However, when the Northwestern Pacific subtropical high moves westward or enhances, the East winds in the equatorial convergence zone will intensify, leading to a continuous weak East Asian southwest monsoon. As a result, water vapor transported by the southwest monsoon from the Indian Ocean is unable to reach North China, and a large amount of water vapor is retained in South China [148]. Moreover, the wind direction in the eastern PRB shifted to the east, facilitating the convergence and uplift of water vapor, increasing the amount and frequency of precipitation, and causing floods in the coastal areas of the PRB [139,149].
4. Major Issues Faced by the Pearl River Basin
4.1. Increased Extreme Precipitation Events
Since 1980, the frequency of extreme flood events in the PRB has significantly increased [150]. In comparison to the period from 1951 to 1980, the occurrence of extreme flood events in the NRB and the northern WRB showed an increasing trend from 1981 to 2010, while a decreasing trend was observed in the ERB. Larger-scale floods may occur in the northeastern part of the WRB and the NRB [83,151,152,153]. Zhang et al. reported a significant increase in peak flow and flood magnification in the WRB and the NRB [21]. Over the past century, there has been an increasing trend in flood risk in the middle and lower reaches of the PRB. Following the frequent occurrence of large floods in the mid-1990s, an unprecedented surge in dike construction projects took place across the region, altering the natural hydrological conditions. Additionally, due to uneven regional development, flood-control facilities (such as embankments) are more sparse in remote areas, potentially exposing farmers in these remote regions to greater flood threats [86].
4.2. Desertification and Soil Loss
The PRB is a region with the most concentrated distribution and the most severe degree of karst rocky desertification in China. The presence of karst rocky desertification and soil erosion directly impacts the safety of water resources and hydropower facilities, as well as the aquatic ecological security in the PRB, therefore influencing the overall sustainable development of the entire basin [154]. The karst geomorphology is widely distributed in the WRB, where frequent droughts and severe rocky desertification are influenced by climatic factors [155]. Anthropogenic activities, such as indiscriminate logging, steep slope cultivation, excessive grazing, as well as unreasonable agricultural production, mining, and road construction, all contribute to the exacerbation of rocky desertification [33]. Since the 1990s, the WRB has undergone multiple rounds of measures, including reforestation and grassland restoration, in response to such issues as karst rocky desertification and urban expansion [154]. The forestland initially decreased and then increased, while the grassland gradually expanded [156]. Despite a decreasing trend in soil erosion in the PRB over the past 30 years [62], the Nanpan and Beipan River Basin and the northern NRB still face severe rocky desertification.
4.3. Water-Level Reduction and Saltwater Intrusion at Estuaries
Since the mid-1980s, the river channels in the PRD have shown an overall uneven trend of downcutting [73]. The cross-sections of riverbeds have been narrowing and deepening [74,75,76], with this trend intensifying from the 1990s to the early 21st century. Consequently, the water levels in the PRD rivers have noticeably decreased compared to the 1980s. For example, in 2005, the water level at the Sanshui station dropped by 2.45 m under similar runoff conditions compared to 1989 [11]. The issue of saltwater intrusion in the estuarine areas has gradually become a significant factor hindering economic development and threatening residents’ livelihoods. Since 2009, saltwater intrusion has become a continuous phenomenon throughout the entire delta region during the dry season. In 2011–2012, the annual average extent of saltwater intrusion reached 36.3 km, twice that of 2001–2002. The duration of salinity exceeding thresholds has become longer, and the seasonality has happened earlier, indicating a deterioration of saltwater intrusion over the past decade. Specifically, between 2011 and 2012, the duration of salinity exceeding thresholds exceeded 700 h, whereas in 2003, it was less than 250 h. From 2005 to 2009, the intrusion of seawater occurred one month earlier than in previous years, from November to February, whereas previously, it occurred from December to March [157]. The decrease in water levels in upstream rivers is the primary cause of exacerbated saltwater intrusion in the estuary. In the delta region, there is a noticeable downward trend in water levels in the lower reaches of the West River and the North River, weakening the ability of the estuarine areas to resist seawater intrusion.
Modaomen and Lingding Bay (Figure 1c) are the two areas facing the most severe threats from saltwater intrusion in the PRE, and they are also regions with a higher prevalence of land reclamation and embankment projects. Between 1980 and 2018, the total reclaimed area in the PRE reached 769.2 km2 [158]. Sand mining, dredging, and reclamation projects can narrow water channels and reduce water exchange capacity, not only hindering river runoff dispersion but also diminishing the effective wave height in the estuary, ultimately exacerbating seawater intrusion [159,160,161]. Another significant factor to consider is the rise in sea level. From 1959 to 2011, there was a noticeable upward trend in sea levels in the PRD, with a linear trend of 4.08 mm/yr [162]. The rising sea level enhances tidal range and ocean currents, causing tidal currents to arrive earlier and increasing the distance of saltwater intrusion. Moreover, the intrusion distance of seawater increases with the rising sea level and reduced river runoff. Previous studies indicate that during the dry season, with a sea level rise of 0.8 m, the intrusion distance of saltwater in Lingding Bay will increase approximately by 10 km, while in Modaomen, it will increase approximately by 3.7 km [163]. The saltwater intrusion in the PRE is highly sensitive to sea level rise [164]. Multiple factors contribute to the intrusion of seawater in the PRD region, and effective measures are urgently needed to counteract the upstream intrusion of saltwater in the estuarine areas.
4.4. Climate Change and Increased Drought Events in the Upper and Middle Reaches
The drought situation in the PRB has become more severe. Between 1960 and 2005, noticeable drought trends were observed in November, December, and January in the PRB [165]. The western and northeastern regions of the basin have lower drought risks, while the PRD faces higher drought risks [20], with longer average durations of droughts, especially during extreme drought conditions [166]. However, in the western regions of the basin, particularly in the Nanpan and Beipan Basin, the probability of drought occurrence is relatively higher. During the period from 1997 to 2010, short-term extreme hot and dry weather events in the PRB intensified, primarily occurring in the northeastern and western regions of the basin, with a significant increasing trend observed in the central-western and southeastern areas [167]. Since the 21st century, the number of events of moderate droughts and severe droughts and the duration and intensity of droughts have significantly increased in the PRB [168]. The most notable changes are seen in autumn droughts, with a trend of hydrological droughts shifting from summer to autumn [169].
5. Sustaining the Pearl River: Policy Overhaul and Strategic Adjustments
5.1. Basin Governance Framework
The establishment of a comprehensive management institution for the entire PRB has undergone a complex process [170]. Since its re-establishment in August 1979, the Pearl River Water Resources Commission (PRWRC) has played a crucial role in the integrated management of the PRB for over 40 years. However, China’s Water Law, enacted in 2002, states that, “the central government implements a combined water resources management from river commissions and provincial governments”. This provision has significantly limited the functions of the PRWRC as a basin management institution [171], and this limitation has persisted to the present day (Figure 9).
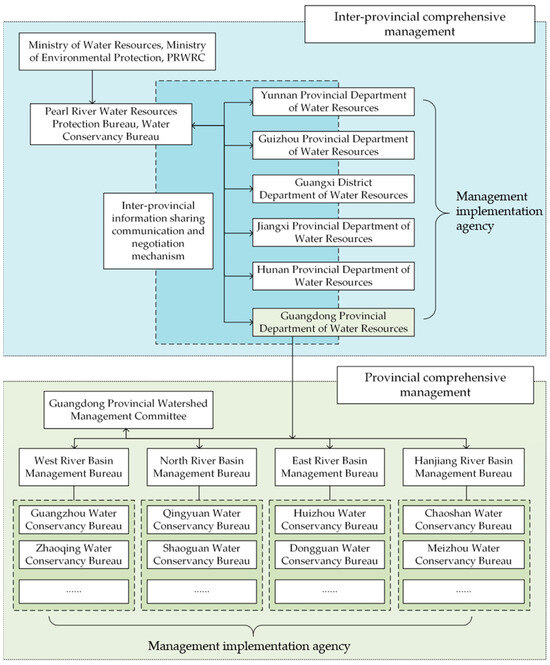
Figure 9.
Framework of PRB Management Institutional (modified from Ref. [172]).
PRWRC is a branch organization established by the Ministry of Water Resources, responsible for the development, planning, and management of water resources in the PRB. However, functions such as the jurisdiction of hydropower, navigation, and water pollution control are under other departments subordinate to the State Council. Under these structures, although PRWRC can handle tasks like regional water project planning, water resource supervision, and administrative law enforcement [18], the actual control over the development and utilization of water energy resources are regulated by the electricity department; waterway management is overseen by the State Council’s transportation department, and pollution prevention and control are led by the State Council’s ecological environment department. This management divides responsibilities based on the functions of water resources, which significantly has undermined integrated water resources management. Each department prioritizes its own interests, neglecting the overall interests of the PRB [172,173,174].
Therefore, it is recommended that the responsibilities and jurisdiction of PRWRC be legislated and clearly defined. This would establish a more comprehensive water resource management system, breaking away from the existing administrative fragmentation. The goal is to transform basin management into a model led by a single institution with collaboration from multiple departments [173,174,175,176]. This approach aims to strengthen unified basin management [177], fully leveraging the role of PRWRC as a comprehensive basin management institution and a mediator for trans-province water affairs negotiations.
5.2. Adapting to Future Climate Change
Compared to northern China, the PRB is an area abundant in precipitation, making it prone to flood hazards during the monsoon season. However, drought events also occur frequently during dry seasons. Both floods and droughts are significantly influenced by climate change, causing severe disruptions to local residents. Therefore, there is an urgent need to explore adaptive strategies for climate change. Currently, research on the impact factors of climate change in the PRB primarily focuses on the correlation between large-scale climate indices and climatic indicators such as rainfall and drought. However, there are limited studies on adaptation strategies, preparation efforts, and adaptive training for local residents. The natural ecosystems in the PRB exhibit relatively weak adaptive capacities to climate change. To address extreme climate events such as floods and droughts, decision-makers should optimize the layout of hydrological monitoring stations and enhance monitoring capabilities for key tributaries, small and medium-sized rivers, and small to medium-sized reservoirs. This includes improving monitoring capabilities for river and ecological flows and soil conservation. The use of new monitoring methods should be promoted, expanding the scope of real-time online monitoring and enhancing the capabilities of intelligent water security monitoring.
5.3. Estuary and Coastal Zone Development
With rising sea levels, the reduction in sediment load to the sea has significantly weakened the coastal resistance to erosion; this, in turn, has led to severe land loss in the delta region [178]. The decrease in sediment load has a serious impact on the morphological changes in estuarine and coastal areas. Not just the decrease in SSC but also the extensive reclamation of intertidal resources in estuarine areas for urbanization and industrialization has also widely occurred. From 1985 to 2015, the net loss of mangrove forests in the PRD region was approximately 11.73 km2 [179]. Additionally, due to human activities such as sea reclamation, the coastline in the PRE has extended seaward in recent years [77,78,79]. Between 1976 and 2006, the average annual net extension was approximately 19.3 m, implying an elongation of river channels at the estuary. This extension was often achieved by blocking lateral channels that connect with deep water passages [180]. This will prevent floodwaters from being discharged into the sea in a short time, putting the estuary area at greater risk of flooding.
The significant reduction in sediment load is largely attributed to the sediment trapping in dams. Some studies have suggested taking into account sediment release measures during water impoundment and considering the creation of designated sediment bypass channels [119]. In estuarine areas, it is recommended to establish ecological reserves to prevent the fast degradation in wetlands, coupled with the implementation of ecological protection red lines in estuarine regions, use of policy regulation, ecological transformation and restoration of artificial shorelines, controlling such activities as sea reclamation and pollution discharge, aiming to maintain the ecological balance of in estuary regions [181,182,183].
5.4. Sustaining Water Resouces
The PRB experiences significant disparities in precipitation between the wet and dry seasons, with approximately 80% of the annual precipitation occurring during the wet season. This difference significantly affects the annual distribution of river flow, hindering the balanced allocation of water resources throughout the year and posing challenges to economic development and normal domestic activities.
The persistent issue of winter saltwater intrusion in the PRD region poses a serious threat to regional water security. PRWRC has addressed this by organizing water dispatches from key dams and sluicegates on various tributaries during the dry season. By releasing water from upstream reservoirs, water levels can be increased to cope with saltwater intrusion. By 2021, this practice has been implemented continuously for 16 rounds [184]. Water dispatch not only helps maintain a stable water supply downstream but also plays a crucial role in the ecological health of fish populations, agricultural irrigation, and shipping traffic in different river sections upstream and midstream. However, the legal and regulatory framework for water dispatches in the PRB is insufficient, especially concerning large-scale water transfers to ensure winter water supply to Macao and Zhuhai. Early initiatives heavily relied on administrative orders [173]. This situation has led to numerous conflicts and contradictions in the coordination of water dispatches, with economically disadvantaged upstream regions making sacrifices to ensure water stability for the developed downstream areas.
The “Regulations on Pearl River Water Dispatch” is a legal document addressing the allocation of water resources in the basin. It has been submitted for approval by the State Council multiple times over recent decades. However, formal and comprehensive legal provisions have not yet been released. To strengthen the legitimacy of basin water dispatches, it is advisable to expedite the promulgation and improvement of the “Regulations” [173]. Furthermore, enhancing information exchange between different departments and establishing an intelligent and informative platform for collaborative reservoir dispatch between upstream and downstream [185,186] can improve the efficiency of river flow dispatch. Introducing market mechanisms into river management, compensating upstream regions through water pricing to alleviate conflicts and contradictions in water dispatches [174,187], and using price leverage to promote water conservation and efficiency [176] can all facilitate the rational allocation and utilization of river water resources.
5.5. River Ecosystem Conservation
From the perspective of river biota and fish species, the biodiversity of the PRB exceeds that of the Yangtze River, securing its position as the top river system among the seven major rivers in China. The period from the 1960s to the 1980s witnessed a severe decline in fishery resources in the Pearl River system. The natural fish yield in Guangdong Province plummeted by 52% from 1966 to 1973, and in Guangxi Province, it dropped by 66.5% from 1962 to 1979. Several precious fish species, especially those inhabiting rivers and estuaries, were endangered [124]. Before the establishment of the People’s Republic of China, large-scale water conservancy projects were not yet constructed in the PRB, and water quality pollution was scarce. However, with the massive construction of reservoirs starting in the 1960s, the ecological integrity of fish populations came under serious threat. In recent decades, improvements in water quality in the PRB have been achieved through measures such as controlling the discharge of pollutants from industrial and domestic wastewater, enhancing forest environmental protection, and improving solid waste management [9]. Nevertheless, the discharge of industrial and domestic wastewater has led to nutrient and heavy metal pollution in rivers [188], highlighting the persistent pollution issues in the PRB. Therefore, it is recommended to follow the example of the first basin-wide protection regulation implemented in 2021, the “Yangtze River Protection Law”, and enact comprehensive regulations for the protection and utilization of water resources in the PRB [189]. This would strengthen and standardize ecological protection efforts across the entire basin.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.O. and X.Y.; data curation, S.C. and W.F.; writing—original draft preparation, H.O.; writing—review and editing, S.C., W.F., J.Q., X.M., T.Z., X.Y. and L.P.; supervision, X.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No.: 2021YFE0117300) and Major Project of High-Resolution Earth Observation System (Grant No.: 30-Y60B01-9003-22/23).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article..
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to scholars for their research on the Pearl River Basin. They also thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their professional and pertinent comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Kettner, A.J.; Green, P. Impact of Humans on the Flux of Terrestrial Sediment to the Global Coastal Ocean. Science 2005, 308, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whipple, K.X. The Influence of Climate on the Tectonic Evolution of Mountain Belts. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, S.D.; McCoy, S.W.; Beeson, H.W. Transience of the North American High Plains Landscape and Its Impact on Surface Water. Nature 2018, 561, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, L.; Lu, X.; Fang, N.; Yang, X. Effective Soil Erosion Control Represents a Significant Net Carbon Sequestration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, S.-P.; He, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Yue, Y.; Zeng, H.; Xu, N. Assessing Water Quality in the Pearl River for the Last Decade Based on Clustering: Characteristic, Evolution and Policy Implications. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, R.I.; Lewin, J.; Hardy, R.J. Fluvial Processes and Landforms. Geol. Soc. Lond. Mem. 2022, 58, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Ran, L. Sustaining China’s Large Rivers: River Development Policy, Impacts, Institutional Issues and Strategies for Future Improvement. Geoforum 2016, 69, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Chen, T.; Yang, N.; Qu, L.; Li, M.; Chen, D. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Rainfall and Drought Characteristics across the Pearl River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Brookes, J.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, S.; Qin, B. Water Quality Improvement and Existing Challenges in the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Chen, X. Covariates for Nonstationary Modeling of Extreme Precipitation in the Pearl River Basin, China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 229, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-L.; Zeng, E.Y.; Ji, R.-Y.; Wang, C.-P. Effects of In-Channel Sand Excavation on the Hydrology of the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 343, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.K.S.; Yang, L.E.; Scheffran, J.; Mitchell, G.; Adekola, O.; Griffiths, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Lu, X.; Qi, Y.; et al. Urban Flood Risks and Emerging Challenges in a Chinese Delta: The Case of the Pearl River Delta. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 122, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Bai, W. Spatio-Temporal Variation in Rainfall Erosivity during 1960–2012 in the Pearl River Basin, China. CATENA 2016, 137, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl River Water Resources Commission. Pearl River Sediment Bulletin, Guangzhou, China, 2022. Available online: http://www.pearlwater.gov.cn/zwgkcs/lygb/nsgb/202311/P020231110315588395900.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Liu, L. Transitional Properties of Droughts and Related Impacts of Climate Indices in the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.D.; Jiang, J. Abrupt Behaviors of the Streamflow of the Pearl River Basin and Implications for Hydrological Alterations across the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Chen, J.; Sivakumar, B. Teleconnection Analysis of Runoff and Soil Moisture over the Pearl River Basin in Southern China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1475–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.P.; Wu, Y.D. An Overview of Water Resources Management of the Pearl River. Water Supply 2007, 7, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl River Water Resources Commission. Pearl River Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, Guangzhou, China, 2020. Available online: http://www.pearlwater.gov.cn/zwgkcs/lygb/stbc/202109/P020210914335796341337.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Singh, V.P.; Li, J. Regionalization and Spatial Changing Properties of Droughts across the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472–473, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gu, X.; Singh, V.P.; Shi, P.; Sun, P. More Frequent Flooding? Changes in Flood Frequency in the Pearl River Basin, China, since 1951 and over the Past 1000 Years. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2637–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y. Mapping Watershed-Level Ecosystem Service Bundles in the Pearl River Delta, China. Ecolog. Econ. 2018, 152, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Shao, Q.; Hao, Z.-C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.-Y.; Sun, L. Regional Frequency Analysis and Spatio-Temporal Pattern Characterization of Rainfall Extremes in the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2010, 380, 386–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Yang, T.; Xu, C.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Hao, Z.-C. Hydrologic Alteration along the Middle and Upper East River (Dongjiang) Basin, South China: A Visually Enhanced Mining on the Results of RVA Method. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2010, 24, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Multiscale Streamflow Variations of the Pearl River Basin and Possible Implications for the Water Resource Management within the Pearl River Delta, China. Quat. Int. 2010, 226, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, P. Multiscale Variability of Streamflow Changes in the Pearl River Basin, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2012, 26, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, F. Spatiotemporal variation of discharge and its influencing factors in the Pearl River Delta network area. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2022, 52, 97–106. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.X.; Higgitt, D.L.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Han, J.; Sun, H. Recent Changes of Water Discharge and Sediment Load in the Zhujiang (Pearl River) Basin, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 60, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, Q.; Chen, S.; Luo, Z.; Yuan, F.; Wang, R. Temporal and Spatial Variability of Sediment Flux into the Sea from the Three Largest Rivers in China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 87, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Yang, S.L.; Lei, Y. Quantifying the Anthropogenic and Climatic Impacts on Water Discharge and Sediment Load in the Pearl River (Zhujiang), China (1954–2009). J. Hydrol. 2012, 452–453, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Cai, S.; Ni, P.; Zhan, W. Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on the Water Discharge and Sediment Load of the Pearl River, Southern China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Duan, K.; Hao, L. Analysis on changes in water level-flow of the Pearl River Basin in recent years and its causes. Pearl River. 2021, 42, 1–7+28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.B.; Yang, S.L.; Cai, A.M. Impacts of Dams on the Sediment Flux of the Pearl River, Southern China. CATENA 2008, 76, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, X.; Jinhai, Z.; Yuliang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Estimating Suspended Sediment Loads in the Pearl River Delta Region Using Sediment Rating Curves. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 38, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, S.; Liu, F.; Yang, Q. Characteristics of interannual and intra-annual variation of sediment discharge in the Pearl River Basin over the past 60 years. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 155–162. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hu, S.; Guo, X.; Luo, X.; Cai, H.; Yang, Q. Recent Changes in the Sediment Regime of the Pearl River (South China): Causes and Implications for the Pearl River Delta. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Huang, C.; Wu, H.; Cai, S.; Liu, F. Abnormal changes diagnosis and its control factors of water and sediment discharge in the lower reaches of Pearl River Basin from 1960 to 2019. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 21–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, W.; Xie, X.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.; Li, H. Retrieval of Suspended Sediment Concentrations in the Pearl River Estuary Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ma, C.; Bin, A.; Xu, X.; Huang, W.; Zhao, J. Assessing the Effects of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge on the Total Suspended Solids in the Pearl River Estuary Based on Landsat Time Series. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2020, 125, e2020JC016202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Huang, B.; Liu, K.; Chen, H.; Liu, F.; Qiu, J.; Yang, J. Using the Wavelet Transform to Detect Temporal Variations in Hydrological Processes in the Pearl River, China. Quat. Int. 2017, 440, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. The Spatial and Temporal Variation of Total Suspended Solid Concentration in Pearl River Estuary during 1987–2015 Based on Remote Sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Wu, J.; Wei, X.; Tang, S.; Zhan, H. Spatio-Temporal Variation of the Suspended Sediment Concentration in the Pearl River Estuary Observed by MODIS during 2003–2015. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 172, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, A.P.; Masago, Y.; Boulange, J.; Hijioka, Y. Natural and Anthropogenic Forces on Suspended Sediment Dynamics in Asian Estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Gao, G.; Huang, A.; Li, D.; Ran, L.; Nawaz, M.; Xu, Y.J.; Fu, B. Streamflow and Sediment Load Changes from China’s Large Rivers: Quantitative Contributions of Climate and Human Activity Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Fu, J.; Zang, C. Spatiotemporal variability characteristics and driving forces of land use in the Pan-Pearl River Basin, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 573–580. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, H.; Hu, B. Eco-environmental Effects of Land Use Change in the Xijiang River Basin of Guangxi. J. Nanning Norm. Univ. 2020, 37, 104–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Jin, T.; Wang, J. LUCC spatial simulation of urban agglomeration in central Yunnan. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2022, 38, 1318–1329. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Land Use Change and Its Eco-Environmental Effects of Urban Agglomeration in Central Yunnan. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2021. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD202202&filename=1021111261.nh&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Li, M. Study on Land Use Landscape Pattern Change and Ecosystem Service Value Accounting in Guizhou Province. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2019. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD202001&filename=1020802391.nh&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Shi, W. Research on Conversion Trend and Spatial Pattern of Land-Use/Cover Change in Dongjiang Region Based on Geographic Information System. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2012. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD2012&filename=1012376046.nh&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Deng, X.; Chen, Y. Land use change and its driving mechanism in Dongjiang River Basin from 1990 to 2018. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 40, 236–242+258+331. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Gu, C.; Liu, Z.; Lin, W.; Zhou, P. Impact of land use change during 1989-2009 on eco-capacity in Dongjiang watershed. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 38, 675–686. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Z.; Huo, Z.; Tian, Z.; Huo, G. Effect of LUCC on hydrological response in Beijiang basin. Yangtze River 2020, 51, 89–94+129. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. 30 m Annual Land Cover and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019; Earth System Science Data, 2021. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-2021-7 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Hu, M.M.; Xia, B.C. Land-Use Variations in Regions with Rapid Economic Development—A Case Study in the Pearl River Delta. J. Environ. Inform. Lett. 2020, 3, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Feng, Y. Ecological risk assessment for Pearl River Delta based on land use change. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 224–232+294. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Xie, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, B.; Jia, Q.; Huang, Y.; et al. Prediction and Valuation of Ecosystem Service Based on Land Use/Land Cover Change: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 179, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Lin, M.; Gong, J.; Wu, Z. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity and Influencing Mechanism of Ecosystem Services in the Pearl River Delta from the Perspective of LUCC. J. Geog. Sci. 2019, 29, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, M.; Huang, B.; Liang, C. Land use change and its response to urbanization in the Pearl River Delta. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2020, 29, 303–310. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of Land Use Changes on Soil Erosion in a Fast Developing Area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Pang, G. Assessment of soil erosion intensity in Pearl River Basin based on CSLE model. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 19, 86–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Qiu, J.; Cao, B.; Cai, S.; Niu, K.; Yang, X. Mapping Soil Erosion Dynamics (1990–2020) in the Pearl River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Yang, T.; Chen, X.; Jiang, T. Change-Point Alterations of Extreme Water Levels and Underlying Causes in the Pearl River Delta, China. River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yuan, L.; Yang, Q.; Ou, S.; Xie, L.; Cui, X. Hydrological Responses to the Combined Influence of Diverse Human Activities in the Pearl River Delta, China. CATENA 2014, 113, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.X.; Zhang, S.R.; Xie, S.P.; Ma, P.K. Rapid Channel Incision of the Lower Pearl River (China) since the 1990s as a Consequence of Sediment Depletion. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Tian, T.; Cheng, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. River evolution and reason analysis of the Beiiang River main stream in recent ten years. Port Waterw. Eng. 2022, 1, 131–135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Peng, J.; Chen, Y.D.; Li, J. Spatial–Temporal Changes of Precipitation Structure across the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 440–441, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, K.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, X.; Li, J. Changes in Stage–Flow Relation of the East River, the Pearl River Basin: Causes and Implications. Hydrol. Res. 2013, 44, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Huang, B.S.; Yang, Q.S.; Qiu, J. Hydrodynamic Characteristics Change of the Pearl River Delta Channel Network in the Recent 50 Years. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 573–574, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C. The recent evolution and future trend of middle and lower reaches of Dongiiang River. Guangdong Water Resour. Hydropower 2022, 12, 37–42. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2023&filename=GDSD202212007&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Liu, W.; Zhong, K.; Liu, K. An analysis on the evolution of the river course at lower reaches of the Beiiang by remote sensing technique. Trop. Geogr. 2006, 2, 123–128. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2006&filename=RDDD200602005&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Zhong, K.; Liu, W.; Huang, J. A riverway evolution analysis based on remote sensing technique: A case study of the lower reaches of the Beijiang River. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2006, 3, 69–73. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2006&filename=GTYG200603017&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Yuan, F.; He, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, B. Fluvial processes in the Pearl River Delta in recent decades. J. Sediment Res. 2018, 43, 40–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, G. Research of the Human Activity Impact on Hydrodynamic Environment in Pearl River Delta. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2005. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CDFD&dbname=CDFD9908&filename=2006035294.nh&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Qian, Y. Impacts and management measures of disordered sand mining in the Pearl River Delta rivers. Pearl River 2004, 2, 44–46+58. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2004&filename=RMZJ200402016&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Liu, B.; Peng, S.; Liao, Y.; Long, W. The Causes and Impacts of Water Resources Crises in the Pearl River Delta. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Z.; Zhang, H.-G.; Fu, B.; Shi, A. Analysis on the Coastline Change and Erosion-Accretion Evolution of the Pearl River Estuary, China, Based on Remote-Sensing Images and Nautical Charts. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 073519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoitink, A.J.F.; Sassi, M.G.; Zheng, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C. Morphological Change in the Pearl River Delta, China. Mar. Geol. 2015, 363, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Damen, M.C.J. Coastline Change Detection with Satellite Remote Sensing for Environmental Management of the Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 82, S54–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D. Morphological Evolution of the Pearl River Delta in the Past 165 Years and Its Response to Human Activities. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2017. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CDFD&dbname=CDFDLAST2018&filename=1018000274.nh&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Wang, B.; Zhu, J.; Wu, H.; Yu, F.; Song, X. Dynamics of Saltwater Intrusion in the Modaomen Waterway of the Pearl River Estuary. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1901–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ji, C.; Shi, B.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Mu, J. The Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities on Streamflow and Sediment Load in the Pearl River Basin. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2019, 34, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z. Evaluation on stationarity assumption of annual maximum peak flows during 1951-2010 in the Pearl River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 824–835. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X. Achievements in flood control in the Pearl River Basin. Pearl River. 1990, 5, 2–6. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD9093&filename=RMZJ199005000&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, P.; Yang, L.; Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Wang, B.; Du, P.; Gao, P.; Sun, W. Relationship between Sediment Load and Climate Extremes in the Major Chinese Rivers. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Cao, B.; Park, E.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Tarolli, P. Flood Monitoring in Rural Areas of the Pearl River Basin (China) Using Sentinel-1 SAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, G. Spatio-temporal change characteristics of mean temperature in the Pearl River Basin during 1961–2000. Trop. Geogr. 2007, 4, 289–293+322. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X. Change trend of average temperature in the Pearl River Basin and its spatial distribution characteristics. Pearl River 2007, 5, 4–6+12. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2007&filename=RMZJ200705002&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Liu, L.; Jiang, T.; Yuan, F. Observed (1961–2007) and projected (2011–2060) climate change in the Pearl River Basin. Clim. Chang. Res. 2009, 5, 209–214. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2009&filename=QHBH200904008&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Luo, S. Spatio-temporal variation of average temperature over the Pearl River basin during 1959–2013. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2016, 55, 30–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Prange, M.; Merkel, U. Precipitation and Temperature Changes in the Major Chinese River Basins during 1957–2013 and Links to Sea Surface Temperature. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Gemmer, M.; Lüliu, L.; Buda, S. Temperature and Precipitation Trends and Dryness/Wetness Pattern in the Zhujiang River Basin, South China, 1961–2007. Quat. Int. 2011, 244, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Gemmer, M.; Liu, L.; Su, B. Trends in Monthly Temperature and Precipitation Extremes in the Zhujiang River Basin, South China (1961–2007). Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2010, 1, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lei, X.; Jiang, Y.; Bai, J. Analysis on character of temperature variation in upstream of Pearl River basin during 55 years. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2012, 23, 20–25. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2012&filename=XBSZ201202006&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Huang, Q.; Chen, Z. Regional study on the trends of extreme temperature and precipitation events in the Pearl River Basin. Adv. Earth Sci. 2014, 29, 956–967. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, B. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of extreme temperature in the Pearl River Basin during 1960-2012. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1356–1366. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J. Analysis on spatial and temporal variation characteristics of extreme climate events in the Pear River Basin within Yunnan Province from 1964 to 2013. Pearl River 2019, 40, 95–102+109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Gong, Q. Spatio-temporal variability in extreme temperature from 1960 to 2018 in the Pearl River Basin, China. Mt. Res. 2022, 40, 343–354. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, Z.; Zeng, G. Change of extreme temperatures in China during 1955–2005. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 1, 123–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Wu, X.; Zhu, T.; Lai, C. Research on spatial-temporal variation characteristics and influencing factors of annual maximum daily temperature in the Pearl River Basin under the background of global warming. Pearl River 2020, 41, 1–6+61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. 1-Km Monthly Mean Temperature Dataset for China (1901–2022). National Tibetan Plateau Data Center 2020. Available online: https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/data/71ab4677-b66c-4fd1-a004-b2a541c4d5bf/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Lu, W.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Variation trend of precipitation in the pear river basin in recent 50 years. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 80–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Wu, L. Characteristics of precipitation period in Pear River Basin. J. China Hydrol. 2013, 33, 82–86. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2013&filename=SWZZ201302019&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Peng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C. Changing properties of precipitation regimes over the Pearl River Basin. Pearl River 2012, 33, 13–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Lu, W.; Chen, X.; Lian, Y. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Precipitation Changes in the Pearl River Basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 123, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zou, X.; Cao, L.; Xu, X. Changes in Precipitation Extremes over the Pearl River Basin, Southern China, during 1960–2012. Quat. Int. 2014, 333, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Observed Changes of Drought/Wetness Episodes in the Pearl River Basin, China, Using the Standardized Precipitation Index and Aridity Index. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 98, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal change characteristics of precipitation in the Pearl River Basin in recent 40 years. J. China Hydrol. 2006, 6, 71–75. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2006&filename=SWZZ200606021&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Cai, S.; Niu, K.; Mu, X.; Yang, X.; Pirotti, F. Spatiotemporal Changes in Extreme Precipitation in China’s Pearl River Basin during 1951–2015. Water 2023, 15, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lai, C. Spatiotemporal variations and the causes of non-stationary extreme precipitation in the Pearl River basin. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 46, 1055–1063. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, X. Multi-scale spatio-temporal characteristics and influence of precipitation variation in Zhujiang River Basin during the last 50 years. Sci. Geogr. Sinica. 2015, 35, 476–482. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Becker, S.; Zhang, Z.X.; Chen, Y.D.; Coulibaly, M. Trends and Abrupt Changes of Precipitation Maxima in the Pearl River Basin, China. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2009, 10, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. A discussion on ecological problems in Guangxi. Acad. Forum. 2001, 2, 80–83+1. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y. A review of the development history of water pollution prevention and control in China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2012, 1, 63–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Fan, J. Overview of the Pearl River Basin and opinions on development and governance. Pearl River 1980, 1, 16–38. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD7984&filename=RMZJ198001005&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Liu, G.; Jin, Q.; Li, J.; Li, L.; He, C.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y. Policy Factors Impact Analysis Based on Remote Sensing Data and the CLUE-S Model in the Lijiang River Basin, China. CATENA 2017, 158, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, H. Drought and Intensified Agriculture Enhanced Vegetation Growth in the Central Pearl River Basin of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Luo, C.; Wang, Y. Review and prospect of water conservancy planning in the Pearl River Basin. Pearl River 2009, 30, 10–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zeng, Z. A brief discussion on the sediment problem in reservoirs in the Pearl River Basin. Pearl River 1997, 5, 26–28. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD9697&filename=RMZJ199705008&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Fan, J. Discussion on major comprehensive planning issues in the Pearl River Basin. Pearl River 2001, 4, 1–4. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2001&filename=RMZJ200104000&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Li, Z. Review and prospect of water resources protection work in the Pearl River Basin. Pearl River 1999, 5, 12–14. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD9899&filename=RMZJ199905006&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Cai, S.; Lu, S. Some thoughts on comprehensively implementing the “Water Law” and promoting legal water management in the Pearl River. Pearl River 2013, 34, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Song, L.; Shu, Y.; Li, B.; Peijnenburg, W.; Zheng, C. Evaluating the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Emerging Contaminants in the Pearl River Basin for Regulating Purposes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, J. A tentative discussion on river ecological problems and countermeasures in the Pearl River system. Water Resour. Dev. Res. 2005, 9, 7–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z. Strengthen comprehensive management of river basins, improve water management and management capabilities, and promote the construction of a green Pearl River. China Water Resour. 2014, 24, 73–74. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2015&filename=SLZG201424022&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Shen, K.; Jin, G. The policy effects of local governments’ environmental governance in China-A study based on the evolution of the “River-Director” system. Soc. Sci. China 2018, 5, 92–115+206. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=6e6DrGrvy4NjC2LY_x-hlq9dwxO0-_s-J1ugbcaHxHydxzWjEn805HsWBkq3l_gsbnC7xaShVTezDl4qFm_rTAh0eSJDEMx1e1geIsXczRYqBftzr3kcOsq3i6g757Vp&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=gb (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Gu, X.; Kong, D.; Xiao, M. Impacts of ENSO and ENSO Modoki+A Regimes on Seasonal Precipitation Variations and Possible Underlying Causes in the Huai River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Menzel, L.; Dong, C.; Fang, R. Temporal Dynamics and Spatial Patterns of Drought and the Relation to ENSO: A Case Study in Northwest China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2886–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Aguilar, E.; Martínez, R.; Martín-Hernández, N.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Kenawy, A.E.; Tomás-Burguera, M.; Moran-Tejeda, E.; López-Moreno, J.I.; et al. The Complex Influence of ENSO on Droughts in Ecuador. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, R.; Liu, W.; Fu, G.; Liu, C.; Hu, L.; Wang, H. Linkages between ENSO/PDO Signals and Precipitation, Streamflow in China during the Last 100 Years. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3651–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Droughts in the Xijiang River Basin, China and Its Responses to Global Climatic Events. Water 2017, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Singh, V.P.; Xu, C.-Y.; Deng, J. Influence of ENSO on Precipitation in the East River Basin, South China: ENSO and Precipitation in South China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Gu, X.; Shi, P. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Dryness/Wetness across the Pearl River Basin, China, and Relation to Climate Indices: Dryness/Wetness across the Pearl River Basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Fang, W.; Zhang, Y. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Drought Structure across China Using an Integrated Drought Index. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 218, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M. Influences of ENSO, NAO, IOD and PDO on precipitation regimes in the Pearl River basin. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni. 2016, 55, 134–142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Xiao, M. Spatio-temporal variations of dryness/wetness and influence from climate factors in Pearl River Basin. J. China Hydrol. 2017, 37, 12–20+59. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2017&filename=SWZZ201705003&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Heng, C.; Yoon, S.-K.; Kim, J.-S.; Xiong, L. Inter-Seasonal Precipitation Variability over Southern China Associated with Commingling Effect of Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño. Water 2019, 11, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Shi, P. Hydrological Response to Large-Scale Climate Variability across the Pearl River Basin, China: Spatiotemporal Patterns and Sensitivity. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 149, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Chen, X.; An, J.; Yao, C.; Su, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, Y. Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics of Droughts and Their Connection to Climate Variability and Human Activity in the Pearl River Basin, South China. Water 2023, 15, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, M. Numerical simulation of the Indian ocean dipole influence on climate variations over east Asian monsoon region during equator East Pacific SSTA. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2004, 4, 375–382. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.L. PDO, ENSO and the Early Summer Monsoon Rainfall over South China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L08810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L. Discussion of Relationship between Tropical Pacific Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly and Winter Rainfall over South China. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2013. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201401&filename=1013340651.nh&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Zou, X.; Zhang, C.; AghaKouchak, A.; Kong, F. Changes in Precipitation Extremes in the Beijing Metropolitan Area during 1960–2012. Atmos. Res. 2019, 222, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hou, X.; Zhao, Y. Changes in Consecutive Dry/Wet Days and Their Relationships with Local and Remote Climate Drivers in the Coastal Area of China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H. Climate Control for Southeastern China Moisture and Precipitation: Indian or East Asian Monsoon?: Climate Control for Moisture in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M. Circulation Effect: Response of Precipitation δ18O to the ENSO Cycle in Monsoon Regions of China. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Yang, N.; Li, M.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, X. Rainfall Seasonality Changes and Its Possible Teleconnections with Global Climate Events in China. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 3529–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhou, S. The effect of Indian Ocean SST anomaly on Indian monsoon and summer precipitation over Tibetan Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2003, S1, 132–137. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2003&filename=GYQX2003S1017&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Luo, L.; Jiang, T.; Sun, H.; Jing, C.; Su, B. Variation of droughts and floods and their connection with atmospheric circulation in the Pearl River Basin. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2017, 31, 142–147. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-Y.; Lu, G.-H.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Xiao, H. Trends of Extreme Flood Events in the Pearl River Basin during 1951–2010. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2013, 4, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gu, X.; Singh, V.P.; Xiao, M.; Xu, C.-Y. Flood Frequency under the Influence of Trends in the Pearl River Basin, China: Changing Patterns, Causes and Implications: Flood Frequency under Influences of Trends. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Q. Non-stationary flood risk analysis in Pearl River Basin, considering the impact of hydrological trends. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 1680–1693. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gu, X.; Singh, V.P.; Xiao, M.; Xu, C.-Y. Stationarity of Annual Flood Peaks during 1951–2010 in the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 3263–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, W.; Ning, X.; Song, J.; Wu, Z.; Dan, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, L. Dynamic change of land rocky desertification and river sediment content in Pearl River Basin. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 41, 22–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kang, Q.; Yang, D. Current status of soil erosion and rocky desertification in the upper reaches of the Pearl River, their causes and prevention strategies. Subtrop. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 26, 38–41. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2014&filename=FJSB201403012&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Dou, X.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W.; Yi, Q.; Li, M. Impacts of LUCC and climate change on runoff in the Nanpan River Basin based on Scenario analysis. J. Catastrophology 2020, 35, 84–89. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Peng, S.; Liao, Y.; Wang, H. The Characteristics and Causes of Increasingly Severe Saltwater Intrusion in Pearl River Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 220, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, F.; Su, F. Changes in Coastline and Coastal Reclamation in the Three Most Developed Areas of China, 1980–2018. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 204, 105542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J. Hydrodynamics and Water Quality Impacts of Large-Scale Reclamation Projects in the Pearl River Estuary. Ocean Eng. 2022, 257, 111432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hoitink, A.J.F. Impact of Trends in River Discharge and Ocean Tides on Water Level Dynamics in the Pearl River Delta. Coast. Eng. 2020, 157, 103634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-X.; Shen, Y.-M.; Tang, J. Wave and Storm Surge Evolutions in the Pearl River Estuary with Large-Scale Land Reclamation Impacts. Ocean Eng. 2023, 273, 113977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Li, G.; Li, K.; Shu, Y. Estimation of Regional Sea Level Change in the Pearl River Delta from Tide Gauge and Satellite Altimetry Data. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 141, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zou, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, K. Responses of Estuarine Salinity and Transport Processes to Sea Level Rise in the Zhujiang (Pearl River) Estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Xu, S.; Huang, W.; Xie, Y. Effects of Sea Level Rise and Typhoon Intensity on Storm Surge and Waves in Pearl River Estuary. Ocean Eng. 2017, 136, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, X. Copula-Based Risk Evaluation of Droughts across the Pearl River Basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 111, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, D.; Zhang, Z. Research on drought behaviors in the Pearl River Basin based on markov chain. J. N. China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 37, 15–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Hu, B.X. Recent Intensification of Short-term Concurrent Hot and Dry Extremes over the Pearl River Basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 4924–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Empirical diagnostic analysis on spatial and temporal variations of droughts in the Pearl River basin, China. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni. 2020, 59, 33–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bai, B.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, H. Temporal and spatial characteristics of hydrological drought in the Pearl River Basin from 1981 to 2020. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2023, 51, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Review of the establishment of the Pearl River Water Resources Commission of the Ministry. Pearl River 1999, 5, 4–5. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD9899&filename=RMZJ199905002&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Shen, D. The 2002 Water Law: Its Impacts on River Basin Management in China. Water Policy 2004, 6, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L. Study on the Resources Management System in Pearl River Basin. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2009. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD2011&filename=2010048300.nh&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Zhang, J. Study and comparison on reforming models in China’s major river-basin management-system. J. Chongqing Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 20, 18–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H. Thoughts on the water resources management system and mechanism of the Pearl River Basin. Pearl River 2008, 1, 3–6. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2008&filename=RMZJ200801006&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Chen, Q. Study on the Rule of Law in the Cooperative Governance of the Pearl River Basin. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong University of Foreign Studies, Guangzhou, China, 2021. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD202201&filename=1021763253.nh&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Q. Discussing countermeasures and measures for water resources management in the Pearl River based on foreign experience. Water Resour. Plan. Design. 2006, 3, 32–35. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2006&filename=SLGH200603009&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Qian, Y. The Water Supply and Its Development in the Pearl River. Master’s Thesis, Hohai University, Nanjing, China, 2005. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD0506&filename=2006013253.nh&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Edmonds, D.A.; Toby, S.C.; Siverd, C.G.; Twilley, R.; Bentley, S.J.; Hagen, S.; Xu, K. Land Loss Due to Human-Altered Sediment Budget in the Mississippi River Delta. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, B.; Ma, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, R. The Impact of Rapid Urban Expansion on Coastal Mangroves: A Case Study in Guangdong Province, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 14, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. A Historical Perspective of River Basin Management in the Pearl River Delta of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Liu, P.; Chen, J. Thoughts on the regulation and protection for the Pearl River estuary. China Water Resour. 2020, 20, 36–39. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2020&filename=SLZG202020025&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Cui, S. Discussion on the urban water sources in the Pearl River estuary regions: Problems and solution. China Water Resour. 2010, 1, 32–35. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2010&filename=SLZG201001015&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
- Dominicis, M.D.; Wolf, J.; Hespen, R.V.; Zheng, P.; Hu, Z. Mangrove Forests Can Be an Effective Coastal Defence in the Pearl River Delta, China. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, C. Practice and reflection of Pearl River water dispatching in dry season. China Flood Drought Manag. 2021, 31, 68–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, L.; Cao, P. A brief discussion on the construction ideas of water management remote sensing monitoring system in the Pearl River Basin. Pearl River 2013, 34, 3–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Wu, H. Study on the construction of the digital twin Pearl River Basin. China Flood Drought Manag. 2022, 32, 36–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H. Research on The legal mechanism of valley water resources administration. Law Sci. Mag. 2007, 3, 103–105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hao, R.J. Environmental Pollution in Pearl River Delta, China: Status and Potential Effects. J. Environ. Inform. Lett. 2020, 3, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Construction of water culture and water policy and regulation in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. China Water Resour. 2023, 2, 62–66. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDAUTO&filename=SLZG202302016&v= (accessed on 1 February 2024). (In Chinese).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).