Contaminant Trends in Urban Groundwater: Case Study from Ljubljana (Central Slovenia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
Background and Perspective
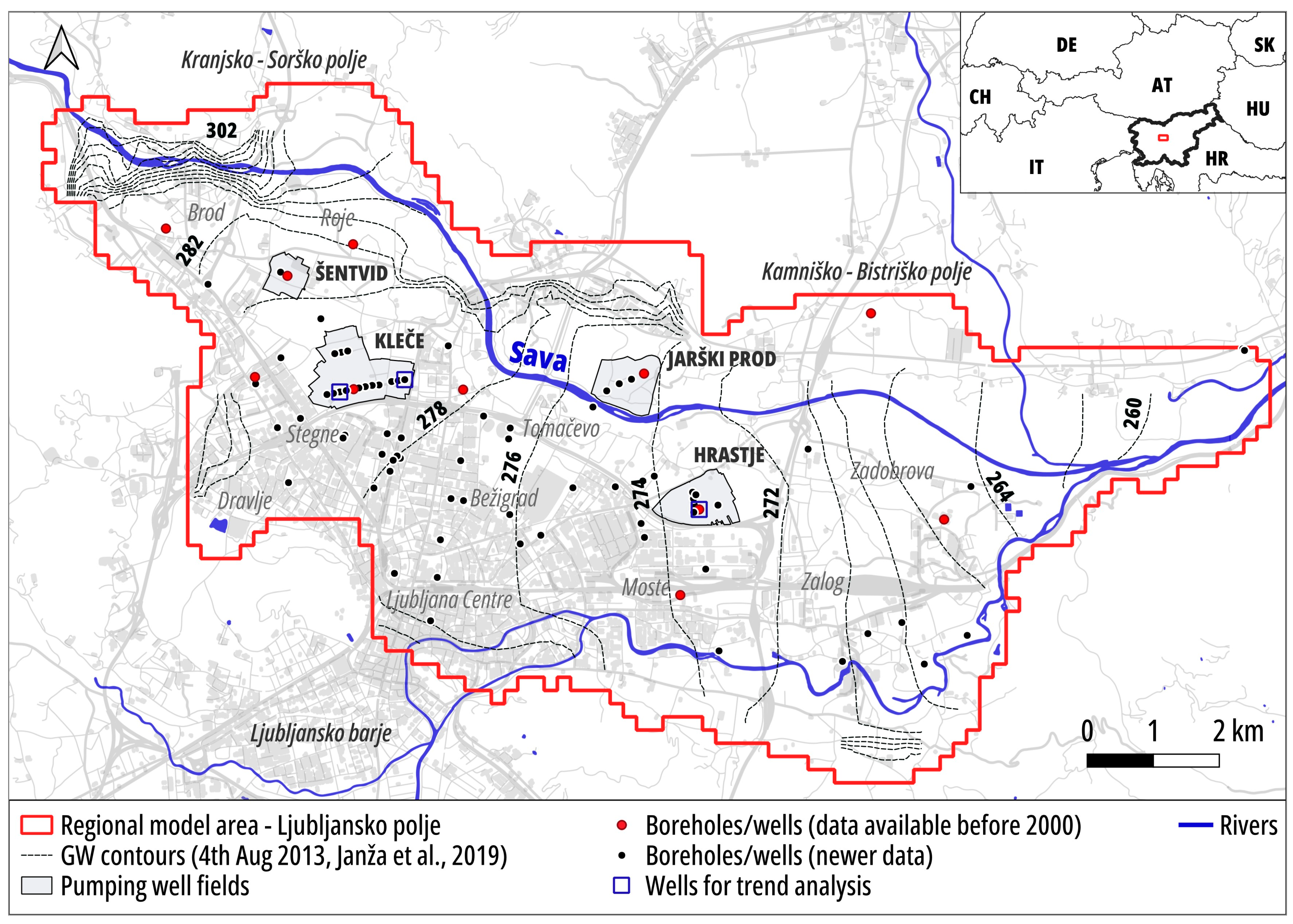
2. Site-Specific Conditions
3. Methodology
4. Results
4.1. Inorganic Contaminants
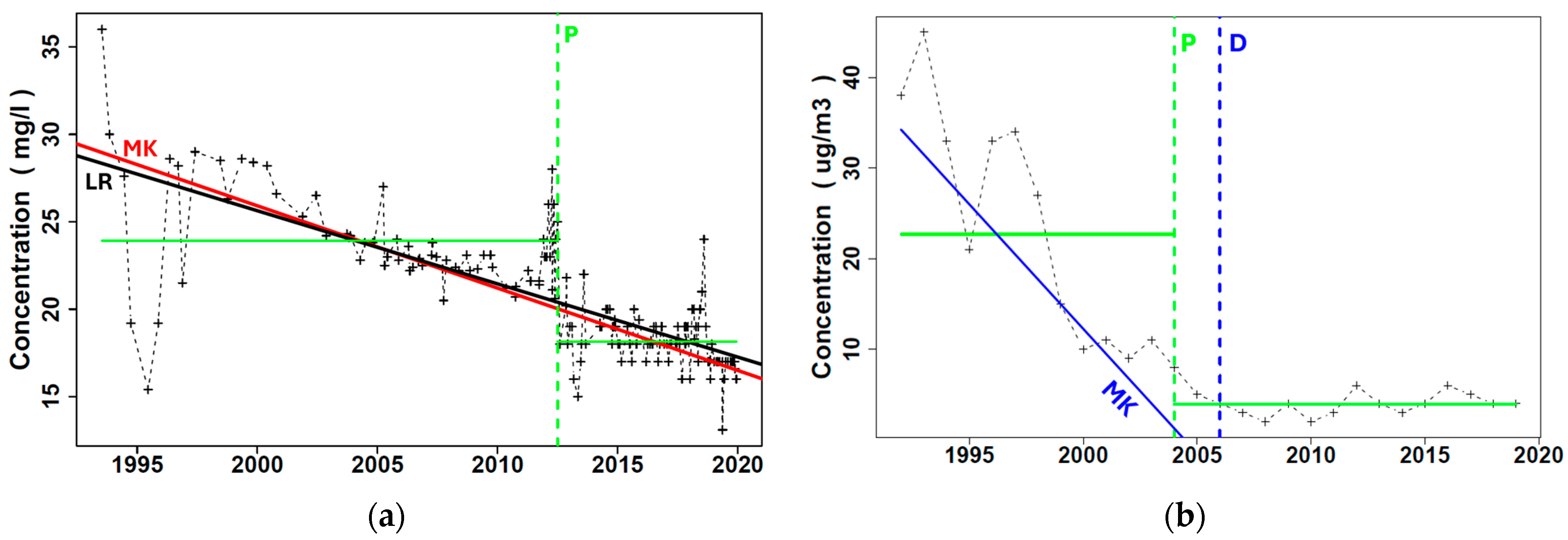
4.1.1. Nitrate
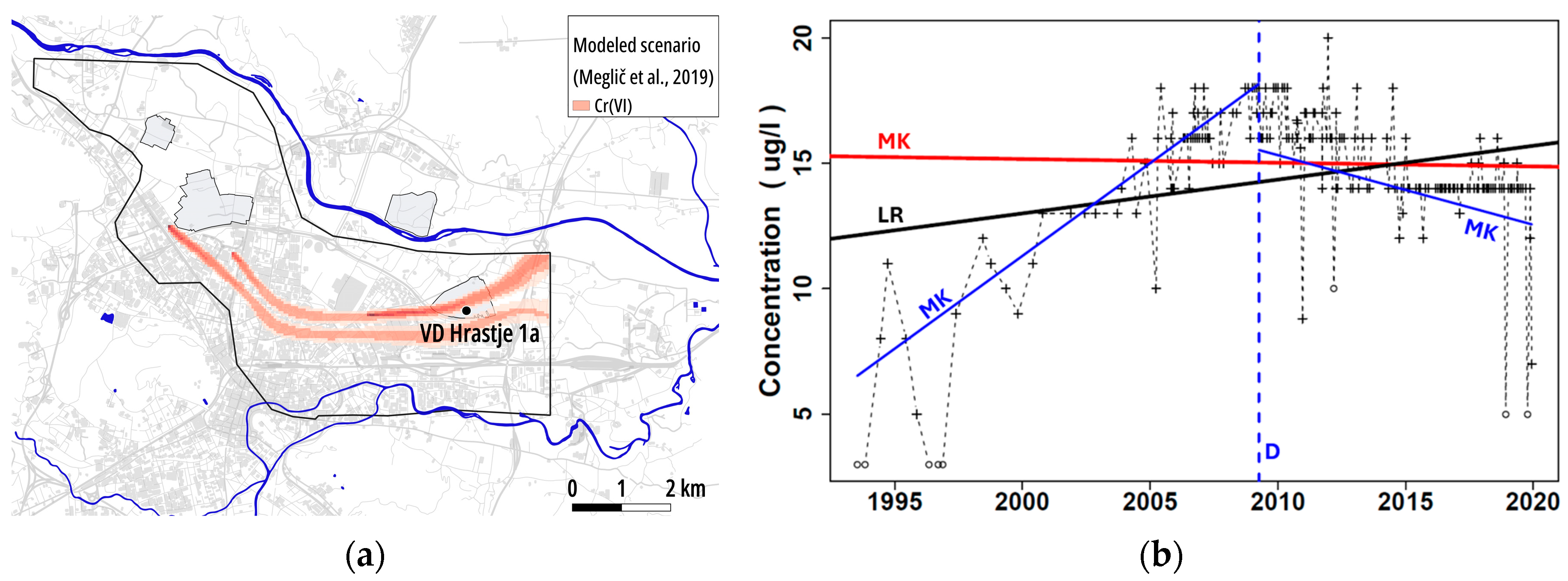
4.1.2. Hexavalent Chromium
4.1.3. Other Inorganic Contaminants
4.2. Organic Contaminants
4.2.1. Pesticides
4.2.2. Volatile Halogenated Hydrocarbons
4.2.3. Pharmaceutical Residues and Other Synthetic Organic Pollutants
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krajnc, M.; Gacin, M.; Krsnik, P.; Sodja, E.; Kolenc, A. Groundwater Quality in Slovenia Assessed upon the Results of National Groundwater Monitoring. Eur. Water 2007, 19, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Janža, M. A Decision Support System for Emergency Response to Groundwater Resource Pollution in an Urban Area (Ljubljana, Slovenia). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3763–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auersperger, P.; Lah, K.; Kus, J.; Marsel, J. High Precision Procedure for Determination of Selected Herbicides and Their Degradation Products in Drinking Water by Solid-Phase Extraction and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1088, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janža, M.; Prestor, J.; Pestotnik, S.; Jamnik, B. Nitrogen Mass Balance and Pressure Impact Model Applied to an Urban Aquifer. Water 2020, 12, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrinc, N.; Tamše, S.; Zavadlav, S.; Vrzel, J.; Jin, L. Evaluation of Geochemical Processes and Nitrate Pollution Sources at the Ljubljansko Polje Aquifer (Slovenia): A Stable Isotope Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1588–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamnik, B.; Auersperger, P.; Urbanc, J.; Lah, K.; Prestor, J. Pharmaceuticals as Indicators of Anthropogenic Influence on the Groundwater of Ljubljansko Polje and Ljubljansko Barje Aquifers. Geologija 2009, 52, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Prestor, J.; Cerar, S.; Svetina, J.; Meglič, P. Analysis of the Occurence of New Emerging Pollutants in the Groundwater of Ljubljansko Polje; Geological Survey of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2020. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Cerar, S.; Prestor, J.; Meglič, P.; Svetina, J.D. T2.2.5—Presentations of Statistical and Environmental Trends and Long-Term Forecasts, Version 2: Part 2; Project AMIIGA, Interreg Central Europe: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2007 Revision; Population Division of the Department of Economic and Soicial Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Burri, N.M.; Weatherl, R.; Moeck, C.; Schirmer, M. A Review of Threats to Groundwater Quality in the Anthropocene. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Suñé, E.; Sánchez-Vila, X.; Carrera, J. Introductory Review of Specific Factors Influencing Urban Groundwater, an Emerging Branch of Hydrogeology, with Reference to Barcelona, Spain. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Vigna, F. Review: Urban Groundwater Issues and Resource Management, and Their Roles in the Resilience of Cities. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 30, 1657–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Leschik, S.; Musolff, A. Current Research in Urban Hydrogeology—A Review. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, D.N. Identifying and Quantifying Urban Recharge: A Review. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Barberio, M.D.; Banzato, F.; Billi, A.; Boschetti, T.; Franchini, S.; Gori, F.; Petitta, M. Climate Change and Its Effect on Groundwater Quality. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 45, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earman, S.; Dettinger, M. Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Groundwater Resources—A Global Review. J. Water Clim. Change 2011, 2, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigter, T.Y.; Miller, J.; Chen, J.; Re, V. Groundwater and Climate Change: Threats and Opportunities. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 31, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kløve, B.; Ala-Aho, P.; Bertrand, G.; Gurdak, J.J.; Kupfersberger, H.; Kværner, J.; Muotka, T.; Mykrä, H.; Preda, E.; Rossi, P.; et al. Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater and Dependent Ecosystems. J. Hydrol. 2014, 518, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanambu, A.C.; Obarein, O.A.; Mossa, J.; Li, L.; Ayeni, S.S.; Balogun, O.; Oyebamiji, A.; Ochege, F.U. Groundwater System and Climate Change: Present Status and Future Considerations. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grischek, T.; Nestler, W. Urban Groundwater in Dresen, Germany. Hydrogeol. J. 1996, 4, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.; Peters, N.E. Effects of Urbanization on Streamflow in the Atlanta Area (Georgia, USA): A Comparative Hydrological Approach. Hydrol. Process 2001, 15, 1441–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, O.V.; Donn, M.J.; Barr, A.D. Urbanisation and Shallow Groundwater: Predicting Changes in Catchment Hydrological Responses. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarello, M.C.; Sharp, J.M.; Pierce, S.A. Estimating Urban-Induced Artificial Recharge: A Case Study for Austin, TX. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2012, 18, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnig, M.; Moeck, C.; Radny, D.; Schirmer, M. Impact of Urbanization on Groundwater Recharge Rates in Dübendorf, Switzerland. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molle, F.; López-Gunn, E.; van Steenbergen, F. The Local and National Politics of Groundwater Overexploitation. Water Altern. 2018, 11, 445–457. [Google Scholar]
- Bierkens, M.F.P.; Wada, Y. Non-Renewable Groundwater Use and Groundwater Depletion: A Review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jago-on, K.A.B.; Kaneko, S.; Fujikura, R.; Fujiwara, A.; Imai, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Zhang, J.; Tanikawa, H.; Tanaka, K.; Lee, B.; et al. Urbanization and Subsurface Environmental Issues: An Attempt at DPSIR Model Application in Asian Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3089–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEA. Europe’s Groundwater—A Key Resource under Pressure; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- EEA. European Waters—Assessment of Status and Pressures 2018; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.J.; Green, A.; Lewis, K.A. A Broad-Scale Spatial Analysis of the Environmental Benefits of Fertiliser Closed Periods Implemented under the Nitrates Directive in Europe. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mititelu-Ionuș, O.; Simulescu, D.; Popescu, S.M. Environmental Assessment of Agricultural Activities and Groundwater Nitrate Pollution Susceptibility: A Regional Case Study (Southwestern Romania). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velthof, G.L.; Lesschen, J.P.; Webb, J.; Pietrzak, S.; Miatkowski, Z.; Pinto, M.; Kros, J.; Oenema, O. The Impact of the Nitrates Directive on Nitrogen Emissions from Agriculture in the EU-27 during 2000–2008. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, G.; Honecker, U.; Kubiniok, J. Nitrate Dynamics in Springs and Headwater Streams with Agricultural Catchments in Southwestern Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oenema, O.; Witzke, H.P.; Klimont, Z.; Lesschen, J.P.; Velthof, G.L. Integrated Assessment of Promising Measures to Decrease Nitrogen Losses from Agriculture in EU-27. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 133, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducci, D.; della Morte, R.; Mottola, A.; Onorati, G.; Pugliano, G. Nitrate Trends in Groundwater of the Campania Region (Southern Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 2120–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakida, F.T.; Lerner, D.N. Non-Agricultural Sources of Groundwater Nitrate: A Review and Case Study. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyńska, A.; Jarnuszewski, G.; Nowakowska, M.; Wexler, S.K.; Wiśniowski, Z.; Burczyk, P.; Durkowski, T.; Woźnicka, M. Identifying Causes of Poor Water Quality in a Polish Agricultural Catchment for Designing Effective and Targeted Mitigation Measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjerps, R.M.A.; Kooij, P.J.F.; van Loon, A.; van Wezel, A.P. Occurrence of Pesticides in Dutch Drinking Water Sources. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suciu, N.; Farolfi, C.; Zambito Marsala, R.; Russo, E.; de Crema, M.; Peroncini, E.; Tomei, F.; Antolini, G.; Marcaccio, M.; Marletto, V.; et al. Evaluation of Groundwater Contamination Sources by Plant Protection Products in Hilly Vineyards of Northern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Lorenzo, T.; Cifoni, M.; Fiasca, B.; di Cioccio, A.; Galassi, D.M.P. Ecological Risk Assessment of Pesticide Mixtures in the Alluvial Aquifers of Central Italy: Toward More Realistic Scenarios for Risk Mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakoun, V.; Orban, P.; Dassargues, A.; Brouyère, S. Factors Controlling Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Multiple Pesticide Compounds in Groundwater (Hesbaye Chalk Aquifer, Belgium). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, E.; Renau-Pruñonosa, A.; Ibáñez, M.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Estrela, T.; Jiménez, S.; Pérez-Martín, M.Á.; González, F.; Hernández, F.; Morell, I. Investigation of Pesticides and Their Transformation Products in the Júcar River Hydrographical Basin (Spain) by Wide-Scope High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Screening. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenner, K.; Canonica, S.; Wackett, L.P.; Elsner, M. Evaluating Pesticide Degradation in the Environment: Blind Spots and Emerging Opportunities. Science 2013, 341, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K. Recent Advances in Environmental Risk Assessment of Transformation Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3835–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Forcada, E.; Bencini, A.; Pranzini, G. Hydrogeochemical Considerations about the Origin of Groundwater Salinization in Some Coastal Plains of Elba Island (Tuscany, Italy). Environ. Geochem. Health 2010, 32, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delsman, J.R.; van Baaren, E.S.; Siemon, B.; Dabekaussen, W.; Karaoulis, M.C.; Pauw, P.S.; Vermaas, T.; Bootsma, H.; de Louw, P.G.B.; Gunnink, J.L.; et al. Large-Scale, Probabilistic Salinity Mapping Using Airborne Electromagnetics for Groundwater Management in Zeeland, the Netherlands. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 084011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corniello, A.; Ducci, D. Hydrogeochemical Characterization of the Urban Coastal Aquifers of Napoli (Southern Italy): An Overview. Acque Sotter. Ital. J. Groundw. 2019, 8, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czinnerova, M.; Nguyen, N.H.A.; Nemecek, J.; Mackenzie, K.; Boothman, C.; Lloyd, J.; Laszlo, T.; Spanek, R.; Cernik, M.; Sevcu, A. In Situ Pilot Application of NZVI Embedded in Activated Carbon for Remediation of Chlorinated Ethene-Contaminated Groundwater: Effect on Microbial Communities. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, A.; Ghirardi, M.; Emiliani, R. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Evaluate the Effectiveness of Natural Attenuation at a Contaminated Site. Hydrology 2021, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulatović, S.; Ilić, M.; Šolević Knudsen, T.; Milić, J.; Pucarević, M.; Jovančićević, B.; Vrvić, M.M. Evaluation of Potential Human Health Risks from Exposure to Volatile Organic Compounds in Contaminated Urban Groundwater in the Sava River Aquifer, Belgrade, Serbia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 3451–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niculae, A.; Vasile, G.G.; Ene, C.; Cruceru, L.V. The Study of Groundwater Contamination with Volatile Organic Micropollutants (Trichloroethylene) in Northern Bucharest. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, L.; Colombo, L.; Formentin, G. Null-Space Monte Carlo Particle Tracking to Assess Groundwater PCE (Tetrachloroethene) Diffuse Pollution in North-Eastern Milan Functional Urban Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åhlgren, K.; Sjöberg, V.; Allard, B.; Bäckström, M. Groundwater Chemistry Affected by Trace Elements (As, Mo, Ni, U and V) from a Burning Alum Shale Waste Deposit, Kvarntorp, Sweden. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30219–30241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokou, Z.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Karatzas, G.P. Assessing Groundwater Quality in Greece Based on Spatial and Temporal Analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, E.; Bergamini, M.; Lazzari, E.; Musacchio, A.; Mor, J.R.; Pugliaro, E. Natural Background Levels of Potentially Toxic Elements in Groundwater from a Former Asbestos Mine in Serpentinite (Balangero, North Italy). Water 2021, 13, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, A.; la Torre, G.L.; Mangano, V.; Casale, K.E.; Bartolomeo, G.; Santini, A.; Granata, T.; Dugo, G. Toxic Inorganic Pollutants in Foods from Agricultural Producing Areas of Southern Italy: Level and Risk Assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Luqueño, F.; López-Valdez, F.; Gamero, P.; Luna, S. Heavy Metal Pollution in Drinking Water-a Global Risk for Human Health: A Review. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 567–584. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; van Liedekerke, M.; Yigini, Y.; Montanarella, L. Contaminated Sites in Europe: Review of the Current Situation Based on Data Collected through a European Network. J. Environ. Public. Health 2013, 2013, 158764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroša, A.; Brenčič, M.; Mali, N. Estimating the Transport Parameters of Propyphenazone, Caffeine and Carbamazepine by Means of a Tracer Experiment in a Coarse-Gravel Unsaturated Zone. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.; Lapworth, D.; Crane, E.; Hart, A. Review of Risk from Potential Emerging Contaminants in UK Groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczyńska, A. Presence of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Groundwater with Respect to Land Use in the Vicinity of Sampling Sites. Geologos 2019, 25, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Lopez, B.; Laabs, V.; Kozel, R.; Wolter, R.; Ward, R.; Vargas Amelin, E.; Besien, T.; Claessens, J.; Delloye, F.; et al. Developing a Groundwater Watch List for Substances of Emerging Concern: A European Perspective. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, S.Y.; Lapworth, D.J.; Crane, E.J.; Grima-Olmedo, J.; Koroša, A.; Kuczyńska, A.; Mali, N.; Rosenqvist, L.; van Vliet, M.E.; Togola, A.; et al. Emerging Organic Compounds in European Groundwater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 115945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.C.; de Souza, A.O.; Bernardes, M.F.F.; Pazin, M.; Tasso, M.J.; Pereira, P.H.; Dorta, D.J. A Perspective on the Potential Risks of Emerging Contaminants to Human and Environmental Health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13800–13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; He, Y.; Jekel, M.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y.H. Emerging Contaminants of Public Health Significance as Water Quality Indicator Compounds in the Urban Water Cycle. Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaroli, S.; Lancia, M.; Re, V. Microplastics Contamination of Groundwater: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeck, C.; Davies, G.; Krause, S.; Schneidewind, U. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Agriculture—A Potential Source of Soil and Groundwater Contamination? Grundwasser 2023, 28, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, E.; Ducci, L.; Sutti, A.; Robottom, S.; Sutti, S.; Celico, F. River–Groundwater Interaction and Recharge Effects on Microplastics Contamination of Groundwater in Confined Alluvial Aquifers. Water 2022, 14, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, A.H.; Carre, F.; Quiot, F. State of Knowledge and Future Research Needs on Microplastics in Groundwater. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 1479–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koreimann, C.; Grath, J.; Winkler, G.; Nagy, W.; Vogel, W.R. Groundwater Monitoring in Europe; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, H.-J.; Jenn, F.; Nitsche, C. European Strategies of Groundwater Monitoring for Different Aims. Baltica 2008, 21, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva, F.; Vegas, E.; Civit, S.; Garrido, T.; Fraile, J.; Munné, A. Trend Assessment for Groundwater Pollutants: A Brief Review and Some Remarks. In Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 43, pp. 25–62. [Google Scholar]
- Frollini, E.; Preziosi, E.; Calace, N.; Guerra, M.; Guyennon, N.; Marcaccio, M.; Menichetti, S.; Romano, E.; Ghergo, S. Groundwater Quality Trend and Trend Reversal Assessment in the European Water Framework Directive Context: An Example with Nitrates in Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22092–22104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, B.; Baran, N.; Bourgine, B. An Innovative Procedure to Assess Multi-Scale Temporal Trends in Groundwater Quality: Example of the Nitrate in the Seine-Normandy Basin, France. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlin, K.; Grimvall, A. Uncertainty in Water Quality Data and Its Implications for Trend Detection: Lessons from Swedish Environmental Data. Environ. Sci. Policy 2008, 11, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balderacchi, M.; Benoit, P.; Cambier, P.; Eklo, O.M.; Gargini, A.; Gemitzi, A.; Gurel, M.; Kløve, B.; Nakic, Z.; Predaa, E.; et al. Groundwater Pollution and Quality Monitoring Approaches at the European Level. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 323–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevauviller, P. Science-Policy Interfacing in the Context of the WFD Implementation. J. Soils Sediments 2006, 6, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasin, S.; Gzyl, G.; Bellotti, M.; Colombo, L.; Ghirardi, M.; Gjetvaj, G.; Kohout, P.; Prestor, J.; Rollwagen, S. Developing Groundwater Contaminant Remediation Strategies for Seven Regional Aquifers. Proc. Inst. Civil. Eng. Water Manag. 2022, 176, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talabi, A.O.; Kayode, T.J. Groundwater Pollution and Remediation. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2019, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premru, U. Tectonics and Tectogenesis of Slovenia; Geological Survey of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2005. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Kolar-Jurkovšek, T.; Jurkovšek, B. Late Carboniferous Flora of Castle Hill in Ljubljana (Slovenia). Geologija 2007, 50, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premru, U. Basic Geological Map of SFRY. Interpreter for List Ljubljana: L 33-66; Zvezni Geološki Zavod Beograd: Beograd, Serbia, 1983. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Žlebnik, L. Pleistocene Deposits of the Kranj, Sora and Ljubljana Fields. Geologija 1971, 14, 5–51. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Bračič Železnik, B.; Pintar, M.; Urbanc, J. Natural Conditions of the Aquifer. In Groundwater of Ljubljansko Polje = Podtalnica Ljubljanskega Polja; Perko, D., Ed.; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2005; 258p. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Vizintin, G.; Souvent, P.; Veselič, M.; Cencur Curk, B. Determination of Urban Groundwater Pollution in Alluvial Aquifer Using Linked Process Models Considering Urban Water Cycle. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šram, D.; Brenčič, M.; Lapanje, A.; Janža, M. Perched Aquifers Spatial Model: A Case Study for Ljubljansko Polje (Central Slovenia). Geologija 2012, 55, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janža, M.; Meglič, P.; Prestor, J.; Jamnik, B.; Pestotnik, S.D. T2.2.3—Report on the Improved Transport and Surface-Groundwater Interactions Model, Version 2; Project AMIIGA, Interreg Central Europe: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Janža, M.; Meglič, P.; Šram, D. Numerical Hydrological Modeling; Project INCOME Action Report; Geological Survey of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vrzel, J.; Solomon, D.K.; Blažeka, Ž.; Ogrinc, N. The Study of the Interactions between Groundwater and Sava River Water in the Ljubljansko Polje Aquifer System (Slovenia). J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hribernik, K.; Šinigoj, J.; Krivic, M.; Podboj, M. Establishment and Maintenance of Database System; Project INCOME Report; Geological Survey of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Croiset, N.; Lopez, B. HYPE: Tool for the Statistical Analysis of Time Series of Groundwater Quality—User Manual; BRGM: Orléans, France, 2013. Available online: https://www.brgm.fr/en/software/hype-tool-characterising-evaluating-trends-temporal-evolution-groundwater-quality (accessed on 1 March 2024). (In French)
- Darken, P.F. Testing for Changes in Trend in Water Quality Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pettitt, A.N. A Non-Parametric Approach to the Change-Point Problem. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOP. Rules on Groundwater Status Monitoring; Official Gazette RS, no. 13/21 in 44/22—ZVO-2; MOP: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament; the Council of the European Union. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020.
- MOP. Rules on Drinking Water; Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, no. 19/04, 35/04, 26/06, 92/06, 25/09, 74/15, 51/17 and 61/23; MOP: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Directorate-General for Environment (DG ENV). Proposal for a Directive Amending the Water Framework Directive, the Groundwater Directive and the Environmental Quality Standards Directive; DG ENV: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brilly, M.; Jamnik, B.; Drobne, D. Chromium Contamination of the Ljubljansko Polje Aquifer. RMZ—Mater. Geoenviron. 2003, 50, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Jamnik, B.; Janža, M.; Smrekar, A.; Breg Valjavec, M.; Cerar, S.; Cosma, C.; Hribernik, K.; Krivic, M.; Meglič, P.; Pestotnik, S.; et al. Care for Drinking Water = Skrb Za Pitno Vodo; Kladnik, D., Topole, M., Eds.; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2014. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Meglič, P.; Janža, M.; Prestor, J.; Pestotnik, S.; Jamnik, B.D. T2.2.7—Report on the Results of the Most Probable Scenarios Threatening Groundwater, Version 2; Project AMIIGA, Interreg Central Europe: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ARSO Air Quality Annual Reports. Available online: http://www.arso.gov.si/zrak/kakovost%20zraka/poro%c4%8dila%20in%20publikacije/kakovost_letna.html (accessed on 14 February 2024). (In Slovene)
- Auersperger, P.; Jamnik, B.; Krajnc, M. Groundwater Load = Obremenjenost Podzemne Vode. In Groundwater of Ljubljansko Polje = Podtalnica Ljubljanskega Polja; Perko, D., Ed.; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2005; 258p. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- Tasca, A.L.; Puccini, M.; Fletcher, A. Terbuthylazine and Desethylterbuthylazine: Recent Occurrence, Mobility and Removal Techniques. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Republic of Slovenia List of Phytopharmaceuticals That Are Prohibited for Use in the Inner Water Protection Zones. Available online: https://spletni2.furs.gov.si/FFS/REGSR/FFS_RegSeznVVO.asp?top=1 (accessed on 6 February 2024). (In Slovene)
- Schüth, C.; Piepenbrink, M.; Cosma, C.; Janža, M. Contaminant Fingerprinting Using Stable Isotopes and Multilevel Sampling with Passive Samplers = Prstni Odtisi Onesnaževal z Uporabo Stabilnih Izotopov in Večnivojskim Vzorčenjem s Pasivnimi Vzorčevalniki. In Care for Drinking Water = Skrb za Pitno Vodo; Kladnik, D., Topole, M., Eds.; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2014; pp. 54–59. (In Slovene) [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11843-2:2000; Capability of Detection, Part 2: Methodology in the Linear Calibration Case. ISO: Geneve, Switzerland, 2000.
- Gourcy, L.; Lopez, B. Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive and the Floods Directive: Technical Report. on Groundwater Quality Trend and Trend Reversal Assessment. 2019. Available online: https://circabc.europa.eu/sd/a/7a9bdbc8-5b2c-4c16-8832-404b31bd0735/GW_Trend_technical_report_final.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Urresti-Estala, B.; Gavilán, P.J.; Pérez, I.V.; Cantos, F.C. Assessment of Hydrochemical Trends in the Highly Anthropised Guadalhorce River Basin (Southern Spain) in Terms of Compliance with the European Groundwater Directive for 2015. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15990–16005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gr | SubGr | Np | Np > LOQ | Na | Na > LOQ | Na < LOD | MA | MD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IP | MacE | 19 | 11 | 15,982 | 12,813 | 1253 | K | K |
| MicE | 58 | 50 | 9468 | 3412 | 1127 | Cr(VI) | Cr(T) | |
| OP | VHH | 32 | 12 | 14,552 | 1697 | 9047 | 1,1,1-TCA | PCE |
| Pest | 131 | 29 | 53,571 | 4113 | 38,896 | MTC | DAT | |
| PCBs | 1 | - | 12 | - | - | - | - | |
| PAHs | 14 | 1 | 152 | 1 | 45 | PAH | Benzene | |
| PhR | 51 | 13 | 6369 | 237 | 4138 | CBZ | CAFF-PROP | |
| OthOC | 23 | 11 | 1782 | 124 | 1392 | 2M-2H-BTA | 2M-2H-BTA | |
| OthOC Sum | 3 | 2 | 976 | 404 | 377 | AOX | AOX |
| Parameter | Unit | Concentration Range in the Study Area (2010–2019) | Occurrence Rate above Quality Standard 1 | Human Consumption (EU) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nitrate | mg/L | 2–75 | 0.1% | 50 |
| sulphate | mg/L | 5–55 | 250 | |
| chloride | mg/L | 2–114 | 250 | |
| hexavalent chromium | µg/L | <3–54 | ||
| total chromium | µg/L | <3–54 | 5.3% * | 25 * |
| atrazine | µg/L | <0.002–0.15 | 1.3% | 0.1 ** |
| desethylatrazine | µg/L | <0.002–0.18 | 1.4% | 0.1 |
| terbuthylazine | µg/L | <0.001–0.023 | 0.1 ** | |
| desethylterbutylazine | µg/L | <0.001–0.017 | 0.1 | |
| sum of pesticides | µg/L | <0.002–0.507 | 0.2% | 0.5 |
| tetrachloroethene | µg/L | <0.05–5.9 | 10 *** | |
| trichloroethene | µg/L | <0.05–1.0 | 10 *** | |
| carbamazepine | µg/L | <0.008–0.1 | 0.25 **** | |
| 2-methyl-2H-benzotriazole | µg/L | <0.001–0.047 |
| Parameter (2010–2019) | Na > LOQ | Na | Nmp > LOQ | Nmp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| desethylatrazine | 1381 | 1573 | 73 | 76 |
| atrazine | 1152 | 1382 | 71 | 75 |
| metazachlor | 259 | 1594 | 17 | 73 |
| desethylterbutylazine | 39 | 1016 | 22 | 68 |
| metolachlor | 82 | 1693 | 28 | 76 |
| bentazone | 74 | 555 | 19 | 29 |
| terbuthylazine | 33 | 1136 | 17 | 74 |
| isoproturon | 4 | 555 | 4 | 29 |
| dimethenamid | 5 | 1379 | 2 | 76 |
| metalaxyl | 7 | 596 | 5 | 29 |
| desisopropylatrazine | 1 | 1161 | 1 | 74 |
| Concentration Value Level | Original Value [µg/L] | Numerical Value [µg/L] |
|---|---|---|
| Conc. > LOQ | 0.078 (>LOQ = 0.033) | 0.078 |
| LOQ > Conc. > LOD | <LOQ = 0.033 & >LOD = 0.010 (0.0215) | 0.0215 |
| Conc. < LOQ | <LOQ = 0.033 (0.017) | 0.017 |
| Conc. < LOD | <LOD = 0.0100 (0.00758) | 0.00758 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svetina, J.; Prestor, J.; Jamnik, B.; Auersperger, P.; Brenčič, M. Contaminant Trends in Urban Groundwater: Case Study from Ljubljana (Central Slovenia). Water 2024, 16, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060890
Svetina J, Prestor J, Jamnik B, Auersperger P, Brenčič M. Contaminant Trends in Urban Groundwater: Case Study from Ljubljana (Central Slovenia). Water. 2024; 16(6):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060890
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvetina, Janja, Joerg Prestor, Brigita Jamnik, Primož Auersperger, and Mihael Brenčič. 2024. "Contaminant Trends in Urban Groundwater: Case Study from Ljubljana (Central Slovenia)" Water 16, no. 6: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060890
APA StyleSvetina, J., Prestor, J., Jamnik, B., Auersperger, P., & Brenčič, M. (2024). Contaminant Trends in Urban Groundwater: Case Study from Ljubljana (Central Slovenia). Water, 16(6), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060890






