Review of the Occurrence of Herbicides in Environmental Waters of Taihu Lake Basin and Its Potential Impact on Submerged Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Succession of Submerged Plants in the Taihu Lake
2.1. Species
2.2. Spatiotemporal Distribution
2.2.1. Interannual Distribution
2.2.2. Seasonal Distribution
3. Environmental Source and Occurrence of Herbicides in Taihu Lake
3.1. Classification of Herbicides
3.2. Targets of Herbicides
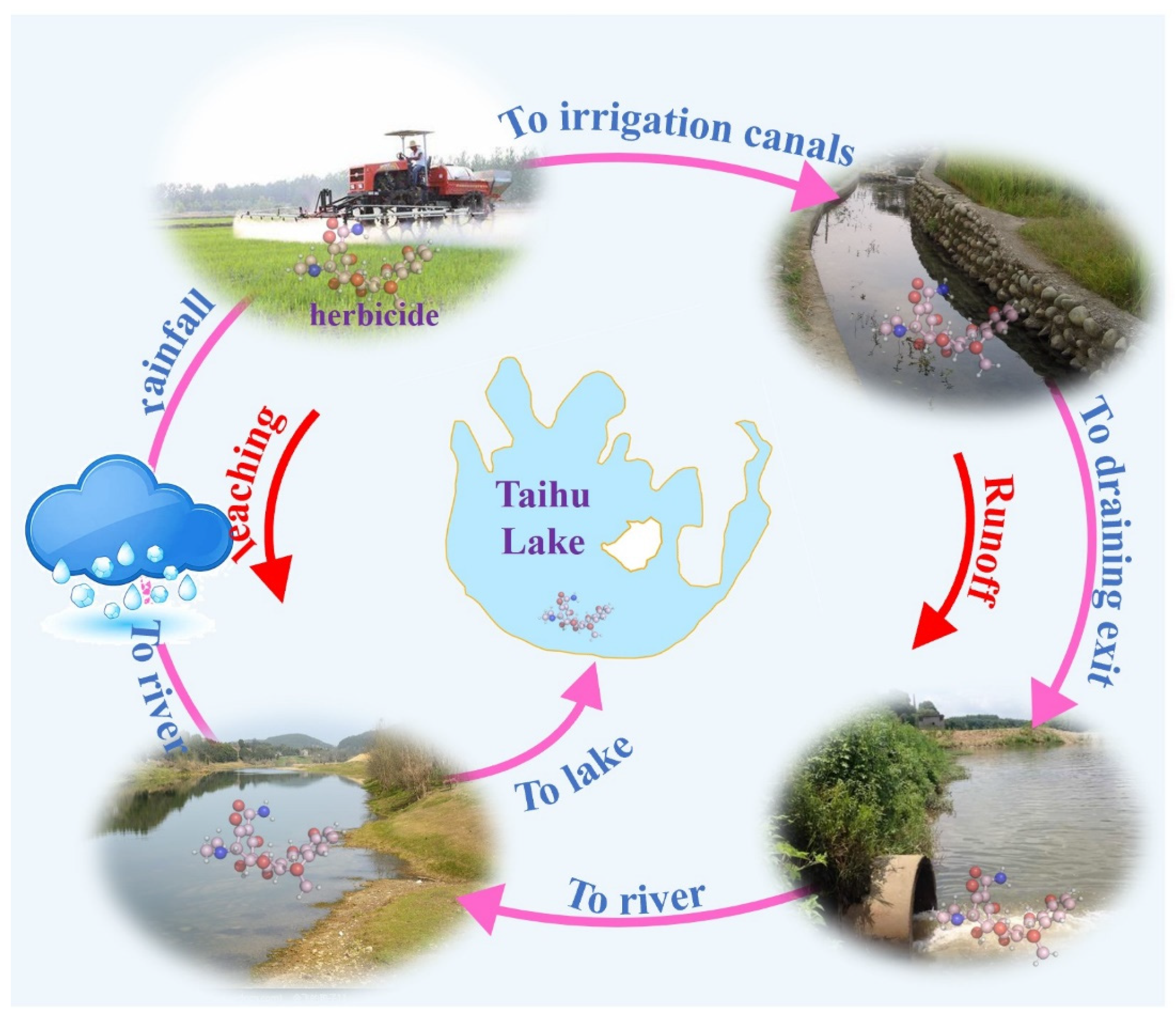
3.3. Environmental Occurrence of Herbicides
4. Impact of Herbicides on Submerged Plants
4.1. Apparent Growth Status
4.2. Physiological and Ecological Indicators
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, Q.; Ruan, L.; Deng, X.; Wang, L.; Rao, X.; Liu, J.; Xia, W.; Xu, P.; Shen, H.; Chen, J.; et al. Stoichiometric and Physiological Mechanisms that Link Hub Traits of Submerged Macrophytes with Ecosystem Structure and Functioning. Water Res. 2022, 202, 117392–117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Deng, J.; Zhou, Y. Aquatic Vegetation in Response to Increased Eutrophication and Degraded Light Climate in Eastern Lake Taihu: Implications for Lake Ecological Restoration. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23867–23878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Gaüzère, P.; Molinos, J.G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Niu, Y.; Yu, H.; Brown, L.E.; Xu, J. Mitigation of Urbanization Effects on Aquatic Ecosystems by Synchronous Ecological Restoration. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117587–117599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortajada, S.; David, V.; Brahmia, A.; Dupuy, C.; Laniesse, T.; Parinet, B.; Pouget, F.; Rousseau, F.; Simon-Bouhet, B.; Robin, F.X. Variability of Fresh- and Salt-water Marshes Characteristics on the West Coast of France: A Spatio-temporal Assessment. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4152–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, H. Numerical Investigation of the Effects of Aquatic Plants on Wind-induced Currents in Taihu Lake in China. J. Hydrodynam. B 2018, 31, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A Drinking Water Crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to Climatic Variability and Lake Management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Environmental Issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Que, X.; Zheng, R.; Pang, Z.; Li, C.; Xiao, B. Phytotoxicity Assessment of Atrazine on Growth and Physiology of Three Emergent Plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 9646–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.; McGlathery, K.; Wiberg, P. Stability and bistability of seagrass ecosystems in shallow coastal lagoons: Role of Feedbacks with Sediment Resuspension and Light Attenuation. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2010, 115, 108636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Liu, Z. Nitrogen, Macrophytes, Shallow Lakes and Nutrient Limitation: Resolution of a Current Controversy? Hydrobiologia 2012, 710, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, M.; Qin, B. Wind and Submerged Aquatic Vegetation Influence Bio-optical Properties in Large Shallow Lake Taihu, China. J. Geophys. 2013, 118, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Hua, Z. The Effect of Vegetation on Sediment Resuspension and Phosphorus Release under Hydrodynamic Disturbance in Shallow Lakes. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 69, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y. Profound Changes in the Physical Environment of Lake Taihu From 25 Years of Long-Term Observations: Implications for Algal Bloom Outbreaks and Aquatic Macrophyte Loss. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 4319–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, W. Responses of Propagule Germination and Sexual Reproduction of Submerged Macrophytes Exposed to Cadmium. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Gao, K. Photosynthetic Acclimation to Different Light Levels in the Brown Marine Macroalga, Hizikia fusiformis (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 22, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugdale, T.M.; Islam, M.S.; Hunt, T.D.; Liu, Z.; Butler, K.L.; Clements, D.; Netherland, M.D. Hydrodynamic Exposure and Time Since Application Influence Endothall Amine Potency Against Submersed Aquatic Plants. Aquat. Bot. 2019, 155, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, K.; Papastergiadou, E. Influence of Hydrophyte Abundance on the Spatial Distribution of Zooplankton in Selected Lakes in Greece. Hydrobiologia 2010, 656, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M.; Walery, M. Aquatic Macrophyte Biomass Periodically Harvested Form Shipping Routes and Drainage Systems in a Selected Region of Poland as a Substrate for Biogas Production. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4184–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soana, E.; Naldi, M.; Bartoli, M. Effects of Increasing Organic Matter Loads on Pore Water Features of Vegetated (Vallisneria spiralis L.) and Plant-free Sediments. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 47, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vormeier, P.; Liebmann, L.; Weisner, O.; Liess, M. Width of Vegetated Buffer Strips to Protect Aquatic Life from Pesticide Effects. Water Res. 2023, 231, 119627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.H.; Hou, K.K.; Liu, J.C. Sorption and Desorption of Selected Phenyl Urea Herbicides in Laboratory Water-sediment Systems. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 191, 012021–012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeport, E.; Tournebize, J.; Chaumont, C.; Guenne, A.; Coquet, Y. Pesticide Contamination Interception Strategy and Removal Efficiency in Forest Buffer and Artificial Wetland in a Tile-drained Agricultural Watershed. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Li, Q. Pesticides in Surface Waters of Tropical River Basins Draining Areas with Rice-vegetable Rotations in Hainan, China: Occurrence, relation to environmental factors, and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117100–117109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystrom, B.; Hans, B. Effects of the Sulfonylurea Herbicide Metsulfuron Methyl on Growth and Macromolecular Synthesis in the Green Alga Selenastrum capricornutum. Aquat. Toxicol. 1998, 43, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauert, S.; Singer, H.; Hollender, J.; Knauer, K. Phytotoxicity of Atrazine, Isoproturon, and Diuron to Submersed Macrophytes in Outdoor Mesocosms. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, J.C.; Conley, D.J.; Owens, M.; Stevenson, J.C. The Decline of Submerged Vascular Plants in Upper Chesapeake Bay—Summary of Results Concerning Possible Causes. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 1983, 17, 78–89. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wu, X.; Leng, X.; An, S. Variations of Food Web Structure and Energy Availability of Shallow Lake with Long-Term Eutrophication: A Case Study from Lake Taihu, China. Clean–Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y. Three-dimensional Eutrophication Model and Application to Taihu Lake, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Fang, Q. Exploring the Spatial-Seasonal Dynamics of Water Quality, Submerged Aquatic Plants and Their Influencing Factors in Different Areas of a Lake. Water 2017, 9, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gan, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Wu, S.; Du, L. Research Status on Remediation of Eutrophic Water by Submerged Macrophytes: A Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 169, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, X. Modelling the Role of Epiphyton and Water Level for Submerged Macrophyte Development with a Modified Submerged Aquatic Vegetation Model in a Shallow Reservoir in China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Zuniga, R.; Morrison, D. Environmental and Economic Costs of Nonindigenous Species in the United States. BioScience 2000, 50, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.; You, K.; Song, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, J. Identification for the Species of Aquatic Higher Plants in the Taihu Lake Basin Based on Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 905–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Lv, M.; Jiang, H.; Cai, Y.; Xu, D.; An, S. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Aquatic Vegetation in Taihu Lake over the Past 30 Years. Tem. Var. Aquatic Veg. 2013, 8, 66365–66371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhai, S.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Y. Long-term and Inter-monthly Dynamics of Aquatic Vegetation and its Relation with Environmental Factors in Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, E.; Lin, Q.; Cheng, L.; Liu, L.; Jeppesen, E. Aquatic Macrophyte Fluctuations Since the 1900s in the Third Largest Chinese Freshwater Lake (Lake Taihu): Evidences, Drivers and Management Implications. Catena 2022, 213, 106153–106164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; Xu, J.; Yin, Y. Long-Term Study of the Relationship between Precipitation and Aquatic Vegetation Succession in East Taihu Lake, China. Scientifica 2017, 2017, 6345138–6345145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Guan, B.; Liu, S.; Xie, H.; Li, Q.; Li, K. Transformation of Aquatic Plant Diversity in an Environmentally Sensitive Area, the Lake Taihu Drainage Basin. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 513788–513797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. Changes of Aquatic Vegetation in Lake Taihu since 1960s. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Jiang, H.; Cai, Y.; An, S. Artificial Regulation of Water Level and its Effect on Aquatic Macrophyte Distribution in Taihu Lake. Water Level Aqu. Macro. 2012, 7, 44836–44845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, X.; Huang, W. Applying Remote Sensing Techniques to Monitoring Seasonal and Interannual Changes of Aquatic Vegetation in Taihu Lake, China. Ecol. Res. 2016, 60, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Man, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, X. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Three Chloroamide Herbicides in Water and Soil Environment in Northeastern, Eastern and Southern China. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115104–115111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Huang, H.; Li, N.; Li, F.; Wang, D.; Luo, Q. Occurrence and Ecological Risk of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) and Pesticides in Typical Surface Watersheds, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 175, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Granger, C.; Dong, H.; Mao, Y.; Duan, S.; Li, J.; Qiang, Z. Occurrences of 29 Pesticides in the Huangpu River, China: Highest Ecological Risk Identified in Shanghai Metropolitan Area. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126411–126421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A.; Newman, J.C.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Robinson, D.; Poisson, D.; Hall, L.M. Sulfonylurea Herbicide Resistance in Sonchus Asper Biotypes in Alberta, Canada. Weed Res. 2003, 43, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensen, J.J.S. Molecular Mechanisms of Herbicide Action Near Photosystem II. Physiol. Plant. 1982, 54, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chu, M.; Zhao, L.; Liu, K.; Liu, W. Enantiomeric Impacts of Two Amide Chiral Herbicides on Echinochloa Crus-galli Physiology and Gene Transcription. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, K. Auxin Herbicides: Current Status of Mechanism and Mode of Action. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J. Research Progress of Pyridine Pesticides. Agrochemicals 2022, 61, 705–712. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Phosphorus Interception in Floodwater of Paddy Field During the Rice-growing Season in TaiHu Lake Basin. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Cai, G.; Huang, W.; Hao, F. Temporal-spatial Loss of Diffuse Pesticide and Potential Risks for Water Quality in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, P.; Sheng, J.; Zheng, J. Methane and Nitrous Oxide Emission under Different Paddy-upland Crop Rotation Systems during Rice Growth Seasons in Taihu Lake Region. Chin. J. Eco-Agricul. 2013, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Chen, S.; Ouyang, W.; Shan, Y.; Qi, S. Temporal Rainfall Patterns with Water Partitioning Impacts on Maize Yield in a Freeze—Thaw Zone. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Wang, G.; Su, W.; Gao, Q. Selecting Low-carbon Technologies and Measures for High Agricultural Carbon Productivity in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 49913–49920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graef, F. Agro-environmental Effects Due to Altered Cultivation Practices with Genetically Modified Herbicide-tolerant Oilseed Rape and ImpliCations for Monitoring. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Miao, S.; Jin, S.; Yang, H. A Newly Developed Molecularly Imprinted Polymer on the Surface of TiO2 for Selective Extraction of Triazine Herbicides Residues in Maize, Water, and Soil. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8803–8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, H.; Cui, H.; Chen, J.; Li, X. High Antioxidant Ability Confer Resistance to Atrazine in Commelina communis L. Plants 2021, 10, 2685–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Cai, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Dong, L. Toxicity and Selective Mechanism of Imazamox by Weedy Rice and Imidazolinone—Resistant Rice in China. Weed Res. 2022, 63, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, R. Relationships Among Socioeconomic Factors, Rice Planting Method and Pesticide Use. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 7358–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yu, J.; Pan, L.; Song, G.; Zhang, H. Dissipation and Residues of Dichlorprop-P and Bentazone in Wheat–Field Ecosystem. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Study on Resistance of Alopecurus japonicus Steud. Populations to Haloxyfop-R-methyl in Oilseed Rape Fields. Sci. Agri. Sinica. 2007, 40, 2759–2765. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Wu, L.; Li, R.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Q. Nannan Field Control Efficacy of Different Herbicide Dosages and Their Effects on Maize Safety. J. Zhejiang Agri. Sci. 2023, 64, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Key Techniques and Suggestions of Weed Control in Soybean and Maize Strip Compound Planting Field. Modern Agr. 2023, 22, 46–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H. Analysis of the Recommended Dosage of Herbicides Registered in the Fields of Four Staple Food Crops in China. J. Plant Prot. 2020, 47, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mubashir, A.; He, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, R.; Guo, S. Identification of Target Traits and Genetic Stability of Transgenic Cotton GGK2. Sci. Agri. Sinica 2023, 56, 3251–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Deng, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y. Control Effect of Two Soil Treatment Herbicides on Sugarcane Fields Weeds and Theirs Safety Evaluation. Agrochemicals 2022, 61, 622–624. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Efficacy Test of Different Herbicides to Control Weeds in Cherry Orchard. J. Fruit Tree Res. 2021, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Miroslav, J.; Michaela, K.; Josef, K. Effect of Weather Conditions on Efficacy of Different Herbicides Used in Bromus Sterilis Control. Weed Res. 2023, 63, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Maruya, K.A.; Snyder, S.A.; Zeng, E.Y. China’s Water Pollution by Persistent Organic Pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhu, L.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y. Distribution of Organochlorine Pesticides in Surface Water and Sediments from Qiantang River, East China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwick, L.M.; Fouss, J.L.; Kornecki, T.S. Atrazine and Metolachlor in Surface Runoff under Typical Rainfall Conditions in Southern Louisiana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5355–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, T.; Fan, L.; Liu, S.; Wu, N.; Xu, A.; Qian, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, M.; et al. Construction and Comparison of Synthetic Microbial Consortium System (SMCs) by Non-living or Living Materials Immobilization and Application in Acetochlor Degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129460–129471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.S.; Koskinen, W.C.; Graff, C.D.; Anderson, J.L.; Mulla, D.J.; Nater, E.A.; Alonso, D.G. Acetochlor Persistence in Surface and Subsurface Soil Samples. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H. Assessment of Photodegradation of Herbicide Prometryn in Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Liu, G.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Yan, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhu, D. Fate of Atrazine and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in Distinctly Different Lake Sediments Associated with Hydrophytes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113371–113379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cessna, A.; Knight, J.; Dean, N.; Wolf, T. Effect of Temperature on the Dissipation of Seven Herbicides in a Biobed Matrix. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 97, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, N.; Zhou, F.; Gao, Z.; Zhong, M.; Sun, C. The Status of Pesticide Residues in the Drinking Water Sources in Meiliangwan Bay, Taihu Lake of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 123, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Song, H.; Wang, Z. Residue Characteristics and Ecological risk Assessment of Twenty-nin Pesticides in Surface Water of Major River-Basin in China. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2016, 11, 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y. Screening Hundreds of Emerging Organic Pollutants (EOPs) in Surface Water from the Yangtze River Delta (YRD): Occurrence, Distribution, Ecological risk. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xian, Q. Contamination Status of Four Herbicides in Jiuli River from the West Bank of Wangyu River. Environ. Monit. Forew. 2019, 11, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Guo, R.; Liang, X.; Yao, B.; Yan, S.; Guo, Y.; Han, Y.; Cui, J. Pollution Characteristics of 13 Sulfonylurea Herbicides in Taihu Lake Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhong, M.; Lu, M.; Xu, D.; Xue, Y.; Huang, J.; Lee, B.; Yu, G. Occurrence, Spatiotemporal Distribution, and Risk Assessment of Current-use Pesticides in Surface Water: A Case Study Near Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146826–146838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, Z.; Yu, D.; Yang, L. Toxicity of the Herbicide Flurochloridone to the Aquatic Plants Ceratophyllum Demersum and Lemna Minor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 3923–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anja, C.; Jochen, K.; Monika, H.; Tido, S. Application of In-situ Bioassays with Macrophytes in Aquatic Mesocosm Studies. Ecotoxicology 2006, 15, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgers, J.D.M.; Lieverloo, R.J.V.; Leo, J.T.; Brink, P.J.V. Effects of the Herbicide 2,4-D on the Growth of Nine Aquatic Macrophytes. Aquatic Bot. 2007, 86, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Gao, S. Phytotoxicity of Four Herbicides on Ceratophyllum demersum, Vallisneria natans and Elodea nuttallii. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolaki, P.; Mouridsen, M.B.; Nielsen, E.; Olesen, A.; Jensen, S.M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Sorrell, B.K.; Riis, T. A Comparison of Nutrient Uptake Efficiency and Growth Rate Between Different Macrophyte Growth Forms. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 111181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedergreen, N.; Streibig, J.C.; Spliid, N.H. Sensitivity of Aquatic Plants to the Herbicide Metsulfuron-methyl. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Honegger, J.L.; Tencalla, F.G.; Meregalli, G.; Brain, P.; Newman, J.R.; Pitchford, H.F. Herbicide Risk Assessment for Non-target Aquatic Plants: Sulfosulfuron—A cAse Study. Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netherland, M.D.; Richardson, R.J. Evaluating Sensitivity of Five Aquatic Plants to a Novel Arylpicolinate Herbicide Utilizing an Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development Protocol. Weed Sci. 2017, 64, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.J. Response of Seven Aquatic Plants to a New Arylpicolinate Herbicide. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2016, 54, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Graymore, M.; Stagnitti, F.; Allinson, G. Impacts of Atrazine in Aquatic Ecosystems. Environ. Int. 2001, 26, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, R.; Solomon, D.B.B.; Richards, R.P.; Dixon, K.R.; Klaine, S.J.; La, T.W.; Kendall, R.J.; Weisskopf, C.P.; Giddings, J.M.; Giesy, J.P.; et al. Ecological Risk Assessment of Atrazine in North American Surface Waters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 31–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.R.J.; Greer, C.D.; Manning, G.; Wooding, K.; Beckett, K.J.; Brain, R.A.; Marshall, G. A Weight-of-Evidence Approach for Deriving a Level of Concern for Atrazine That Is Protective of Aquatic Plant Communities. Integr. Environ. Assess Manag. 2017, 13, 686–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.; Wersal, J.D.M.; Woolf, T.E.; Eckberg, N. Assessment of Herbicide Efficacy on Eurasian Watermilfoil and Impacts to the Native Submersed Plant Community in Hayden Lake, Idaho, USA. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2010, 48, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Susan, V.C.; Kimon, T.B. The Effects of Herbicides on Development of Myriophyllum spicatum L. Cultured In Vitro. J. Environ. Qual. 1992, 21, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.W.; Cope, W.G.; LePrevost, C.E.; Tom, A.; Annette, M.; Shea, D. A Retrospective Analysis of Agricultural Herbicides in Surface Water Reveals Risk Plausibility for Declines in Submerged Aquatic Vegetation. Toxics 2017, 5, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Ma, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, R. Toxicity of 40 Herbicides to the Green Alga Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotoxicol Environ. Saf. 2002, 51, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dominant Species | Families | Frequency | Years |
| Potamogeton malaianus | Potamogetonaceae | High | 1960–2014 |
| Vallisneria natans | Hydrocharitaceae | High | 1960, 1988, 2002, 2009–2010 |
| Hydrilla verticillata | Hydrocharitaceae | Low | 2002 |
| Myriophyllum spicatum | Halorrhagidaceae | Medium | 1988, 2009–2010 |
| Potamogeton maackianus | Potamogetonaceae | Low | 2014 |
| Elodea muttalli | Hydrocharitaceae | Medium | 1996, 2009–2010 |
| Nymphoides peltata | Menyanthaceae | Low | 2009–2010 |
| No. | Type of Herbicide | Representative Compounds |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Triketones | Mesotrione, mesotrione, etc. |
| 2 | Pyrazoles | Cypyrafluone, bipyrazone, tripyrasulfone, fenpyrazone, etc. |
| 3 | Pyridines | Fluroxypyr, halauxifen-methyl, etc. |
| 4 | Sulfonylureas | Tribenuron, bensulfuron-methyl, nicosulfuron, pyrazosulfuron-ethyl, mesosulfuron-methyl, etc. |
| 5 | Sulfonamides | Florasulam, penoxsulam, pyroxsulam, flumetsulam, etc. |
| 6 | Pyrimidylsalicylates | Isopropyl ether, pyribenzoxim, bispyribac-sodium, pyrithiobac-sodium, pyriftalid, etc. |
| 7 | Imidazolinones | Imazethapyr, imazamox, etc. |
| 8 | Aryloxyphenoxypropionates | Fenoxaprop-p-ethyl, quizalofop-p-ethyl, clodinafop-propargyl, cyhalofop-butyl, metamifop, etc. |
| 9 | Phenoxyalkanoic acids | 2,4-D, 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid, clodinafop-propargyl, clopyralid, fluazifop-p-butyl, haloxyfop-P-methyl, fenoxaprop-p-ethyl, etc. |
| 10 | Triazines | Atrazine, desmetryn, prometryne, terbuthylazine, etc. |
| 11 | Amides | Pretilachlor, acetochlor, metolachlor, butachlor, etc. |
| 12 | Dinitroanilines | Trifluralin, pendimethalin, butralin, etc. |
| 13 | Cyclohexanediones | Sethoxydim, clethodim, etc. |
| 14 | Ureas | Isoproturon, chlortoluron, diuron, etc. |
| 15 | Diphenylethers | Fomesafen, fluoroglycofen-ethyl, oxyfluorfen, etc. |
| 16 | Cyclic imines | Oxadiazon, flumiclorac-pentyl, etc. |
| 17 | Carbamates | Thiobencarb, phenmedipham, molinate, etc. |
| 18 | Organophosphates | Glyphosate, glufosinate ammonium, etc. |
| 19 | Bipyridines | Paraquat, diquat dibromide, etc. |
| 20 | Heterocycles/Others | Bentazone, etc. |
| Crop | Growth Period | Types of Applied Herbicides |
|---|---|---|
| Rice | May–October | Chlorimuron-ethyl, pyrazosulfuron-ethyl, bensulfuron-methyl, penoxsulam, bispyribac-sodium, cyhalofop-butyl, 2,4-D, 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid, prometryne, butachlor, pretilachlor, pendimethalin, oxadiazon, bentazone, quinclorac |
| Winter wheat | Early October–early June of the next year | Carfentrazone-ethyl, fluroxypyr, thifensulfuron-methyl, mesosulfuron-methyl, flucarbazone-sodium, florasulam, pyroxsulam, clodinafop-propargyl, fenoxaprop-p-ethyl, isoproturon, 2,4-D butyl ester, pinoxaden |
| Oil-seed rape | September to November-May of the next year | Acetochlor, butralin, trifluralin, clopyralid, fluazifop-p-butyl, haloxyfop-p-methyl, benzoic acid, quizalofop-p-ethyl, fenoxaprop-p-ethyl, benazolin |
| Corn | June–October | Acetochlor, metolachlor, nicosulfuron, atrazine, mesotrione, 2,4-D, diquat dibromide, glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium |
| Soybean | Mid-June–late September | Quizalofop-p-ethyl, haloxyfop-p-methyl, 2,4-D butyl ester, thifensulfuron-methyl, clethodim, fluoroglycofen-ethyl, fomesafen, butralin, acetochlor, prometryne, quizalofop-p-ethyl, bentazone |
| Type | Species | Frequency | Potential Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenoxy carboxylic acid | 2,4-D | High | Rice, wheat |
| Triazines | Atrazine | High | Maize |
| Ureas | Isoproturon | Medium | Rice, orchard |
| Sonylurea | Tribenuron-methyl, sulfonylurea nicosulfuron | High | Rice |
| Amides | Metolachlor, pretilachlor | High | Rice, wheat |
| Others | Bentazone | Medium | Rice, wheat |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, A. Review of the Occurrence of Herbicides in Environmental Waters of Taihu Lake Basin and Its Potential Impact on Submerged Plants. Water 2024, 16, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050726
Zhang Y, Hu M, Li A. Review of the Occurrence of Herbicides in Environmental Waters of Taihu Lake Basin and Its Potential Impact on Submerged Plants. Water. 2024; 16(5):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050726
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yangyang, Min Hu, and Aimin Li. 2024. "Review of the Occurrence of Herbicides in Environmental Waters of Taihu Lake Basin and Its Potential Impact on Submerged Plants" Water 16, no. 5: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050726
APA StyleZhang, Y., Hu, M., & Li, A. (2024). Review of the Occurrence of Herbicides in Environmental Waters of Taihu Lake Basin and Its Potential Impact on Submerged Plants. Water, 16(5), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050726





