Treatment of Slaughterhouse Wastewater through a Series System: Upflow Anaerobic Reactor and Artificial Wetland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
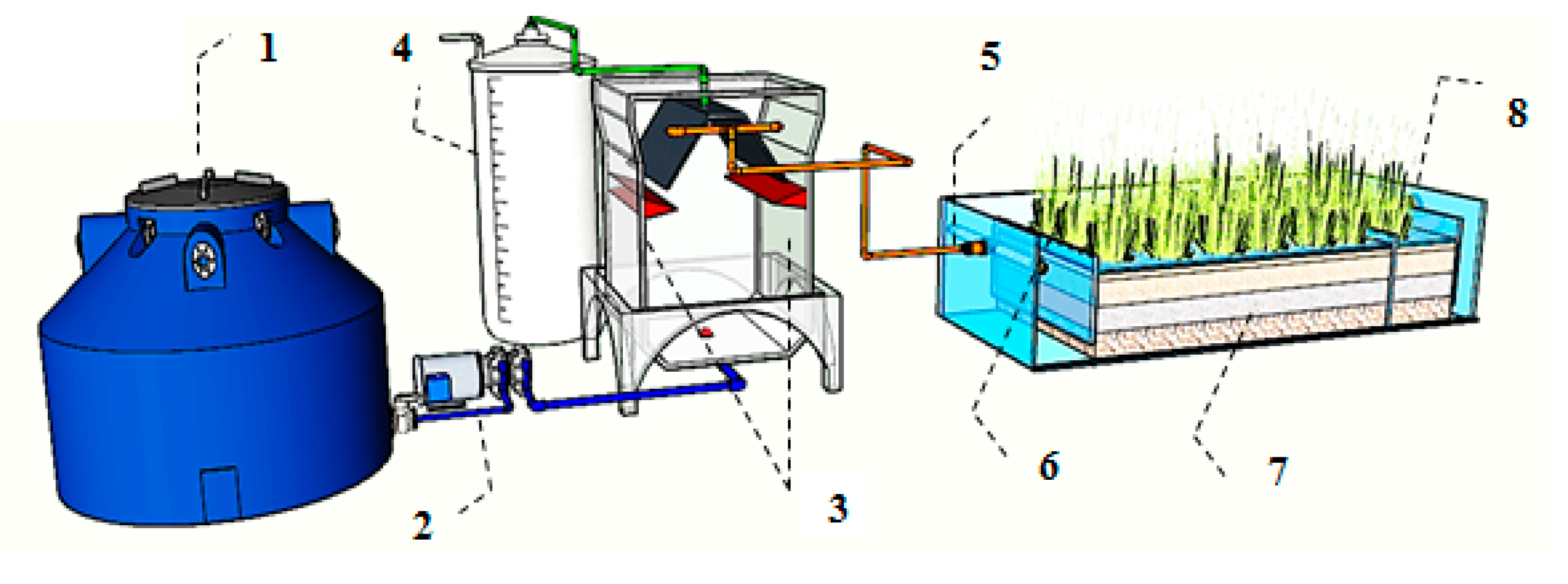
2.1. Design of the Experimental System
2.2. Operation of the Experimental System
2.2.1. UASB Inoculation
2.2.2. System Start-Up
2.2.3. Wetland Setup
2.2.4. System Operation
2.2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
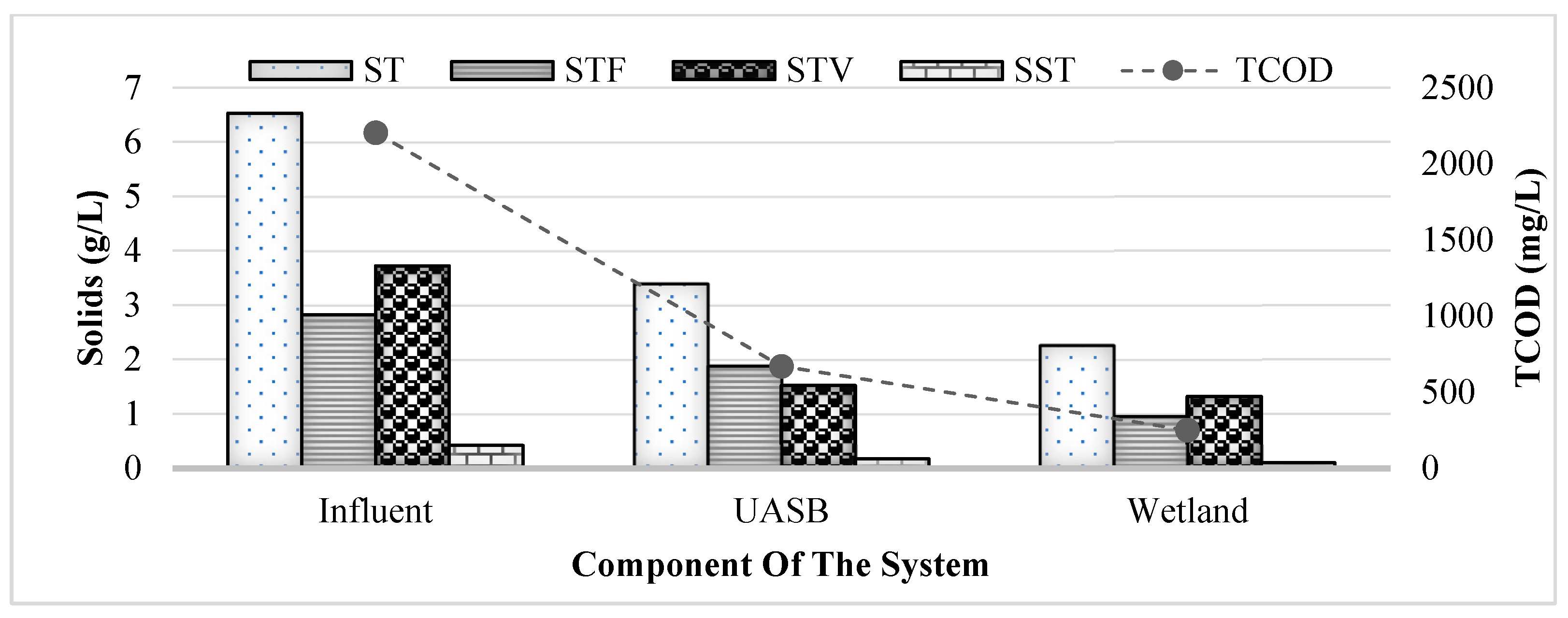
3.1. Sludge Characteristics
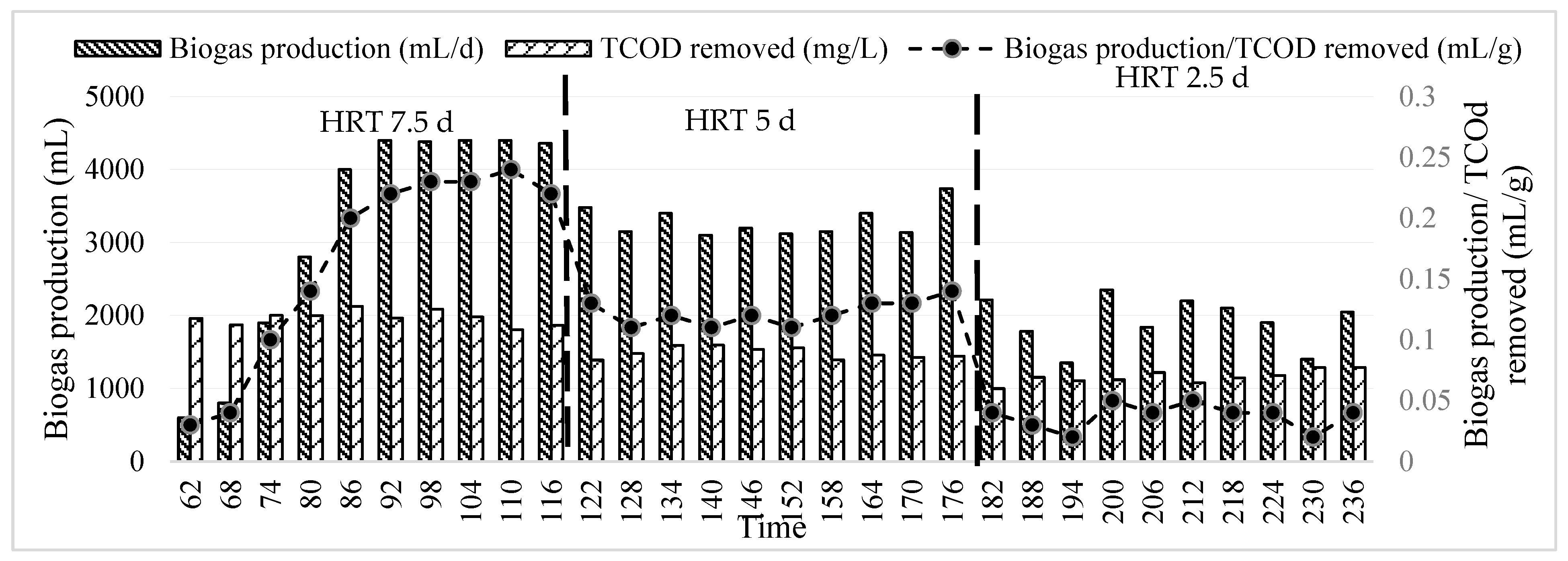
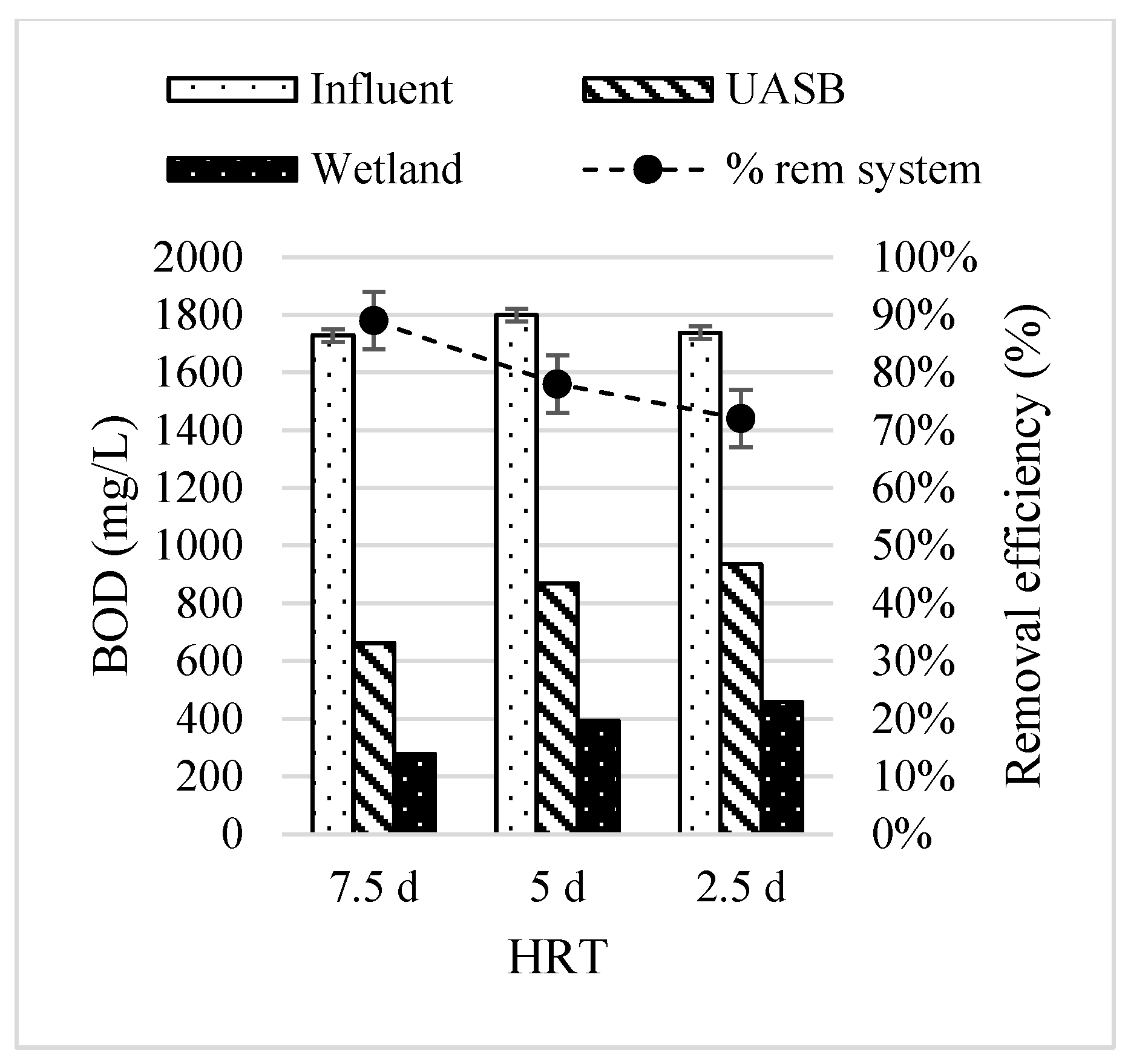
3.2. Operational Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saghir, A.; Hajjar, S. Biological treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater using Up Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB)—Anoxic-aerobic system. Sci. Afr. 2022, 16, e01236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahomi, A.; Razman, M.; Sohaili, J.; Nur, A.; Krishna, S. Performance of integrated anaerobic / aerobic sequencing batch reactor treating poultry slaughterhouse wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalantai, T.; Rhee, C.; Kim, D.W.; Yu, S.I.; Shin, J.; Triolo, J.M.; Shin, S.G. Complex network analysis of slaughterhouse waste anaerobic digestion: From failure to success of long-term operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldera, Y.; Gutiérrez, E.; Luengo, M.; Chávez, J.; Ruesga, L. Wastewater treatment system evaluation of a poultry industry. Rev. Científica 2010, 20, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Ratanatamskul, C.; Siritiewsri, T. A compact on-site UASB-EGSB system for organic and suspended solid digestion and biogas recovery from department store wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 2–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, A.; Vallejo-Rodriguez, R.; Méndez-Romero, D.C. Evaluation of a combined anaerobic and aerobic system for the treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Basheer, F.; Sengar, A.; Khan, S.U.; Farooqi, I.H. Biological wastewater treatment (anaerobic-aerobic) technologies for safe discharge of treated slaughterhouse and meat processing wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 681–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo-Lecompte, C.F.; Mehrvar, M. Slaughterhouse wastewater characteristics, treatment, and management in the meat processing industry: A review on trends and advances. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 161, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, C.; Xu, B.; Zhu, M. Enhanced alure-type biological system (E-ATBS) for carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus removal from slaughterhouse wastewater: A case study. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; Carvajal, A.; Huiliñir, C.; Salazar, R. Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment by a combined anaerobic digestion/solar photoelectro-Fenton process performed in semicontinuous operation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmann, B.E.; McCarty, P.L. Environmental Biotechnology: Principles and Applications; Tata McGraw: New Delhi, India, 2012; Available online: https://www.worldcat.org/title/environmental-biotechnology-principles-and-applications/oclc/847108341?referer=di&ht=edition#.YuKxITRoaJw.mendeley (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Moukazis, I.; Pellera, F.M.; Gidarakos, E. Slaughterhouse by-products treatment using anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loganath, R.; Mazumder, D. Performance study on organic carbon, total nitrogen, suspended solids removal and biogas production in hybrid UASB reactor treating real slaughterhouse wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3474–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakumar, R.; Meenambal, T.; Saravanan, P.M.; Ananthanarayanan, P. Treatment of poultry slaughterhouse wastewater in hybrid upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor packed with pleated poly vinyl chloride rings. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.T.; Ahammed, M.M. Water treatment sludge for phosphate removal from the effluent of UASB reactor treating municipal wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 94, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travieso, L.; Benítez, F.; Sánchez, E.; Borja, R.; León, M.; Raposo, F.; Rincón, B. Evaluation of UASB effluent post-treatment in pilot-scale by microalgae HRP and macrophytes pond for nutrient recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Silva, F.; Masceno, G.P.; Panicio, P.P.; Imoski, R.; Prola, L.D.T.; Vidal, C.B.; Xavier, C.R.; Ramsdorf, W.A.; Passig, F.H.; de Liz, M.V. Removal of micropollutants by UASB reactor and post-treatment by Fenton and photo-Fenton: Matrix effect and toxicity responses. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Gaur, R.Z.; Tyagi, V.K.; Khursheed, A.; Lew, B.; Mehrotra, I.; Kazmi, A.A. Sustainable options of post treatment of UASB effluent treating sewage: A. review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 1232–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Doherty, L.; Hu, Y.; Hao, X. A review of incorporation of constructed wetland with other treatment processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengers, E.E.; da Silva, J.B.; Paulo, P.L.; Janzen, J.G. Hydraulic performance of a modified constructed wetland system through a CFD-based approach. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2016, 12, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for treatment of industrial wastewaters: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 724–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khateeb, M.A.; Al-Herrawy, A.Z.; Kamel, M.M.; El-Gohary, F.A. Use of wetlands as post-treatment of anaerobically treated effluent. Desalination 2009, 245, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzadi, M.; Afzal, M.; Khan, M.U.; Islam, E.; Mobin, A.; Anwar, S.; Khan, Q.M. Enhanced degradation of textile effluent in constructed wetland system using Typha domingensis and textile effluent-degrading endophytic bacteria. Water Res. 2014, 58, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lissner, J.; Mendelssohn, I.A.; Brix, H.; Lorenzen, B.; McKee, K.L.; Miao, S. Nutrient and growth responses of cattail (Typha domingensis) to redox intensity and phosphate availability. Ann. Bot. 2010, 105, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Luca, G.A.; Mufarrege, M.M.M.; Hadad, H.R.; Maine, M.A. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal and Typha domingensis tolerance in a floating treatment wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinícius, M.; Gomes, T.; Rodrigues, R.; Souza, D.; Silva, V.; Araújo, É. Chemosphere Phytoremediation of water contaminated with mercury using Typha domingensis in constructed wetland. Chemosphere 2014, 103, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Ziyang, L.; Tajuddin, R.M.; Farraji, H.; Alifar, N. Co-treatment of landfill leachate and municipal wastewater using the ZELIAC/zeolite constructed wetland system. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alufasi, R.; Gere, J.; Chakauya, E.; Lebea, P.; Chingwaru, W. Mechanisms of pathogen removal by macrophytes in constructed wetlands. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2017, 2515, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wei, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Sun, S. Effect of the supernatant reflux position and ratio on the nitrogen removal performance of anaerobic-aerobic slaughterhouse wastewater treatment process. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyar, H.; Younesi, H.; Bahramifar, N.; Zinatizadeh, A.A. Biological CNP removal from meat-processing wastewater in an innovative high rate up-flow A2O bioreactor. Chemosphere 2018, 213, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghangrekar, M.M.; Asolekar, S.R.; Joshi, S.G. Characteristics of sludge developed under different loading conditions during UASB reactor start-up and granulation. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, J.; Qian, G.; Liu, J. Effective anaerobic biodegradation of municipal solid waste fresh leachate using a novel pilot-scale reactor: Comparison under different seeding granular sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 165, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohdziewicza, J.; Kwarciakb, A. The application of hybrid system UASB reactor-RO in landfill leachate treatment. Desalination 2009, 248, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Ye, J.; Zhang, P.; Xu, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Fang, W.; Wang, B.; Zeng, G. Bioresource Technology Hydrogen sulfide formation control and microbial competition in batch anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse wastewater sludge: Effect of initial sludge pH. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apha. APHA (2012) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, American Journal of Public Health and the Nations Health: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Available online: http://www.sciepub.com/reference/226577 (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Sanchez Sanchez, A. Combining Submerged Membrane Technology with Anaerobic and Aerobic Wastewater Treatment. 2013. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/tesis?codigo=113296&info=resumen&idioma=ENG (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, W.; Chen, H. Enhancing the hydrolysis and acidification of steam-exploded cornstalks by intermittent pH adjustment with an enriched microbial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, B.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Shen, M.; Lu, J.; Duan, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z. Science of the Total Environment Inhibitors degradation and microbial response during continuous anaerobic conversion of hydrothermal liquefaction wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandera, L. Treatment of Wastewater from the Municipal Slaughterhouse of Riohacha using a Pilot Scale UASB Reactor; Research project; Faculty of Engineering, University of La Guajira and University of Zulia: La Guajira, Colombia, 2016; 171p. [Google Scholar]
- Sarioglu, M.; Begüm, Ö. Investigation of the treatability of molasses and industrial oily wastewater mixture by an anaerobic membrane hybrid system. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Zeeman, G.; Rijnaarts, H.; Liu, Y. Improving the energy efficiency of a pilot-scale UASB-digester for low temperature domestic wastewater treatment. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 135, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, I.; Díaz, M.A.; Crujeiras, B.; García, J.; Soto, M. Solids hydrolysis and accumulation in a hybrid anaerobic digester-constructed wetlands system. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Mehrvar, M. Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment by combined anaerobic baffled reactor and UV/H2O2 processes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Mccabe, B.K.; Harris, P.W.; Lee, S. Bioresource Technology Effect of trace element addition and increasing organic loading rates on the anaerobic digestion of cattle slaughterhouse wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Varga, D.; Díaz, M.A.; Ruiz, I.; Soto, M. Heavy metal removal in an UASB-CW system treating municipal wastewater. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasquero Ferrer, S.J.; Marquina Gelvez, D.C.; Soto López, J.G.; Viloria Rincón, S.; Pire Sierra, M.C.P.; Diaz Montiel, A.R.D. Nutrient removal in wastewater from a beef slaughterhouse using a sequential biological reactor. Cienc. Ing. Neogranadina 2015, 25, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, D. Simultaneous COD and Ammonium Nitrogen Removal from a High-strength Wastewater in a Shaft-type Aerobic Hybrid Bioreactor. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2010, 1, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, B. Nutrient removal in constructed microcosm wetlands for treating polluted river water in northern China. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 4, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, D.Q.; Dong, J.W.; Tan, S.K. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in cold climate—A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo-Lecompte, C.F.; Mehrvar, M. Treatment of actual slaughterhouse wastewater by combined anaerobic-aerobic processes for biogas generation and removal of organics and nutrients: An optimization study towards a cleaner production in the meat processing industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

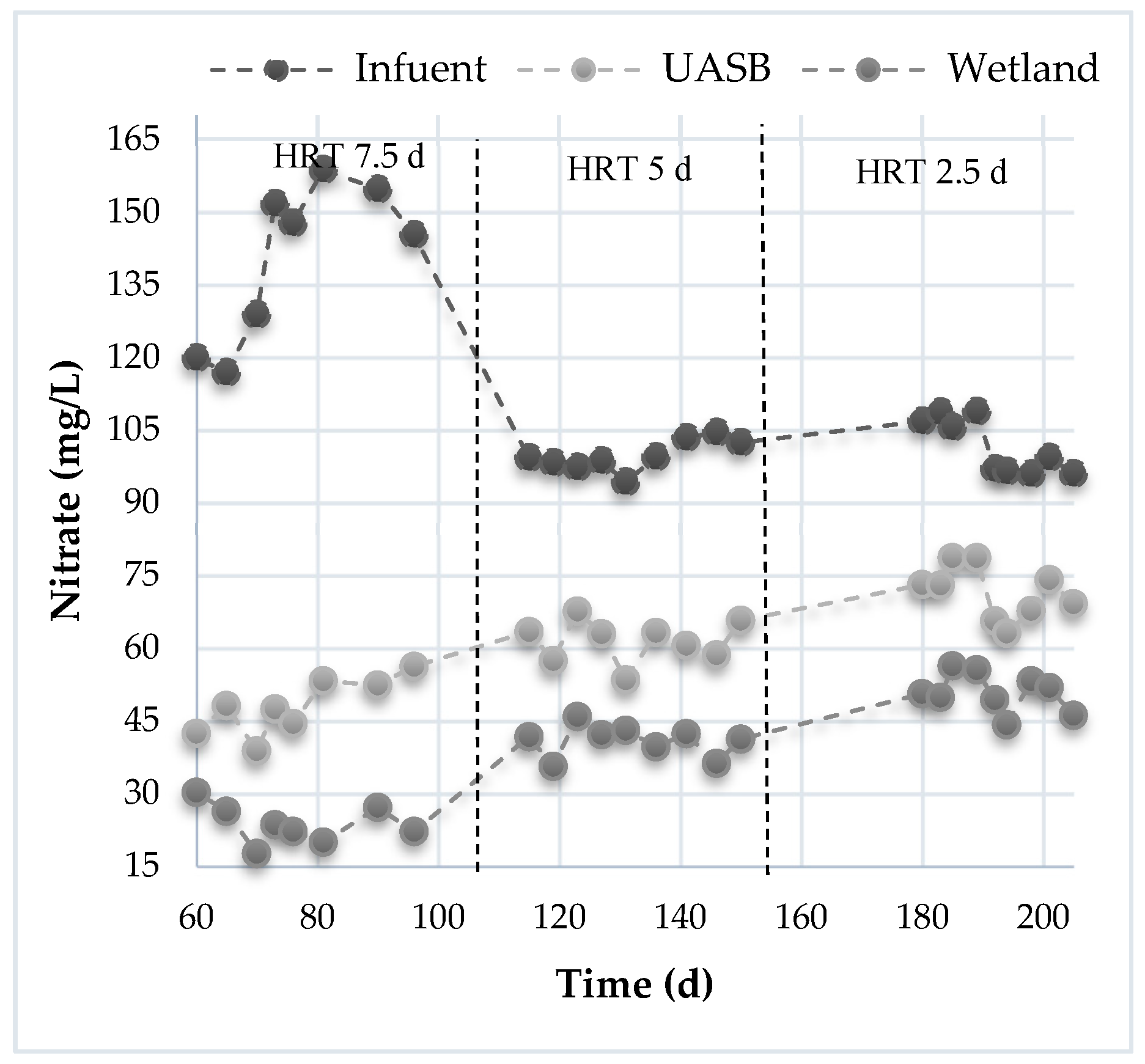


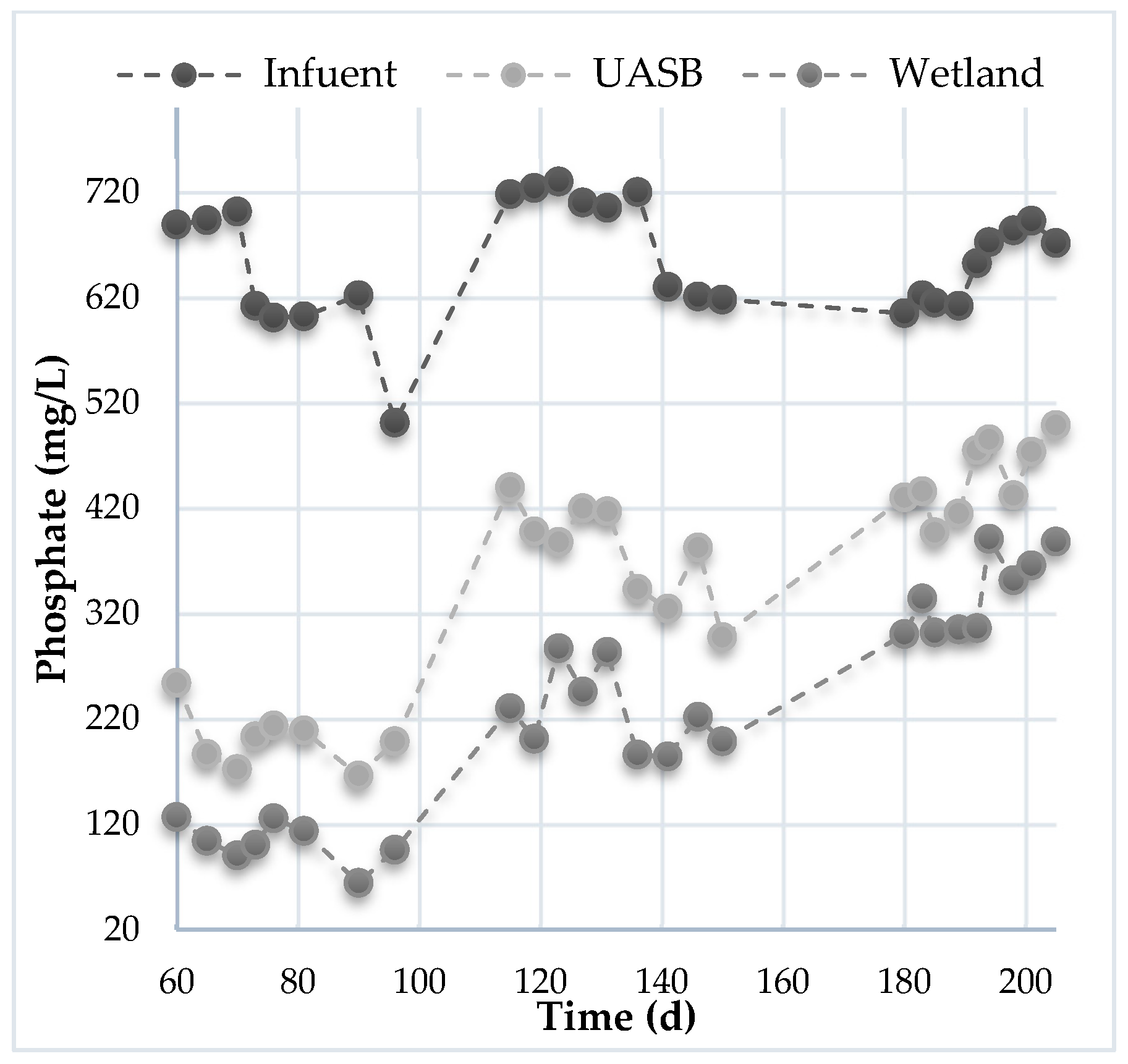
| Hydraulic Retention Time: 7.5 Days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRT (h) 36 | Component | (°C) ± σ | pH ± σ | Alk P (mg/L) ± σ | Alk T (mg/L) ± σ |
| Influent | 28.1 ± 2 | 8.54 ± 0.22 | 347 ± 144 | 520 ± 203 | |
| Effluent UASB | 31.1 ± 1.36 | 7.43 ± 0.88 | 766 ± 492 | 933 ± 499 | |
| Hydraulic Retention Time: 5.0 days | |||||
| HRT (h) | Component | T (°C) ± σ | pH ± σ | Alk P (mg/L) ± σ | Alk T (mg/L) ± σ |
| 24 | Influent | 28.8 ± 1.31 | 8.49 ± 0.36 | 557 ± 154 | 799 ± 157 |
| Effluent UASB | 30.5 ± 0.96 | 7.79 ± 0.22 | 1700 ± 319 | 2006 ± 346 | |
| Hydraulic Retention Time: 2.5 days | |||||
| HRT (h) | Component | T (°C) ± σ | pH ± σ | Alk P (mg/L) ± σ | Alk T (mg/L) ± σ |
| 12 | Influent | 27.9 ± 1.57 | 8.65 ± 0.20 | 538 ± 190 | 756 ± 226 |
| Effluent UASB | 31.1 ± 0.87 | 8.01 ± 0.17 | 1462 ± 430 | 1736 ± 448 | |
| Parameter | EPA, USA | EU | India | China | Canada | Australia | Colombia | UASB–Wetland HRT 7.5 d, Riohacha | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | ||||||||
| pH | 6–9 | - | 6.5–8.5 | 6–9 | 6–9 | 5–9 | 6.00–9.00 | 5.00–9.00 | 7.23–8.38 |
| COD (mg/l) | - | 125 | 250 | 100–300 | - | 40 | 900 | 1350 | 340 |
| BOD (mg/l) | 16–26 | 25 | 30 | 20–100 | 5–30 | 5–20 | 450 | 675 | 375 |
| NT (mg/l) | 4–8 | 10–15 | - | 15–20 | 1.25 | 10–20 | - | - | 0.4 |
| PT (mg/l) | - | 1–2 | - | 0.1–1 | 1 | 2 | - | - | 0.23 |
| F&O (mg/L) | - | - | 10 | - | - | - | 50 | 75 | 50 |
| TSSs (mg/L) | 20–30 | 35–60 | 50 | 20–30 | 5–30 | 5–20 | 200 | 300 | 75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galindo Montero, A.A.; Berrio Arrieta, Y.M.; Pimienta Serrano, E.V. Treatment of Slaughterhouse Wastewater through a Series System: Upflow Anaerobic Reactor and Artificial Wetland. Water 2024, 16, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050700
Galindo Montero AA, Berrio Arrieta YM, Pimienta Serrano EV. Treatment of Slaughterhouse Wastewater through a Series System: Upflow Anaerobic Reactor and Artificial Wetland. Water. 2024; 16(5):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050700
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalindo Montero, Andrés A., Yeison M. Berrio Arrieta, and Estefany V. Pimienta Serrano. 2024. "Treatment of Slaughterhouse Wastewater through a Series System: Upflow Anaerobic Reactor and Artificial Wetland" Water 16, no. 5: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050700
APA StyleGalindo Montero, A. A., Berrio Arrieta, Y. M., & Pimienta Serrano, E. V. (2024). Treatment of Slaughterhouse Wastewater through a Series System: Upflow Anaerobic Reactor and Artificial Wetland. Water, 16(5), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050700






