Effects of Norflurazon and UV Radiation on Symbiotic and Free-Living Hydra
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Organisms and Treatments
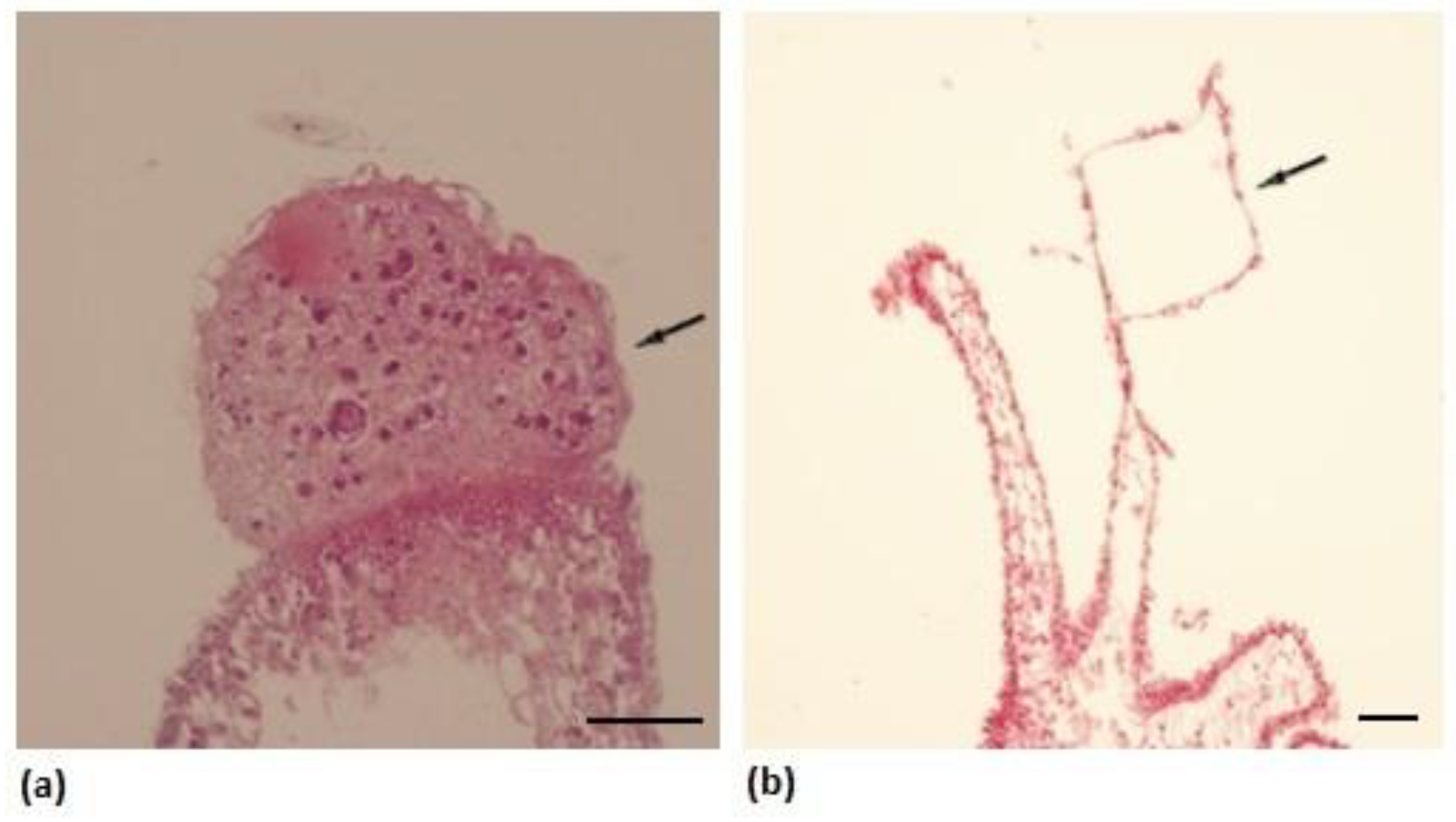
2.2. Histological Changes
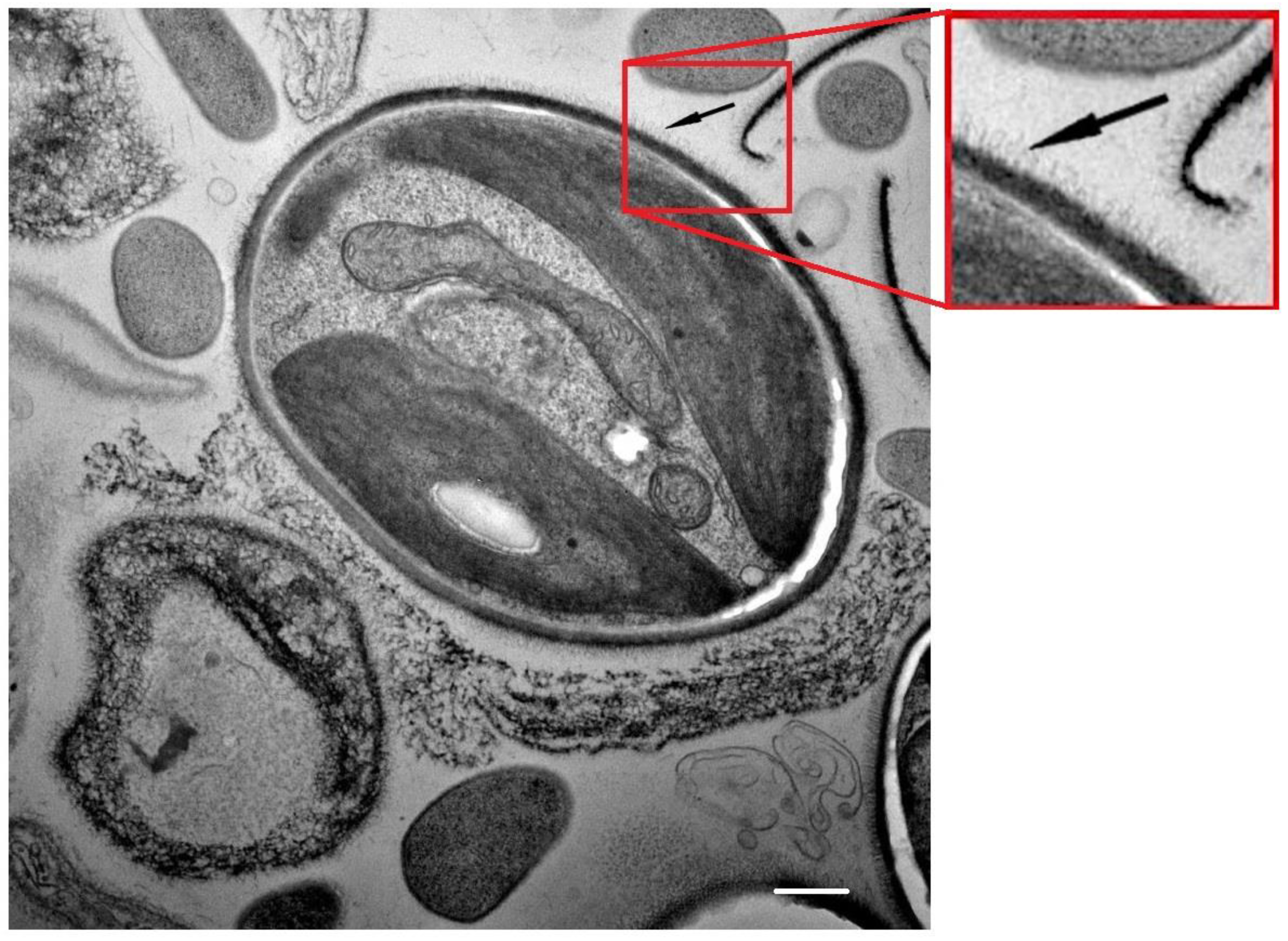
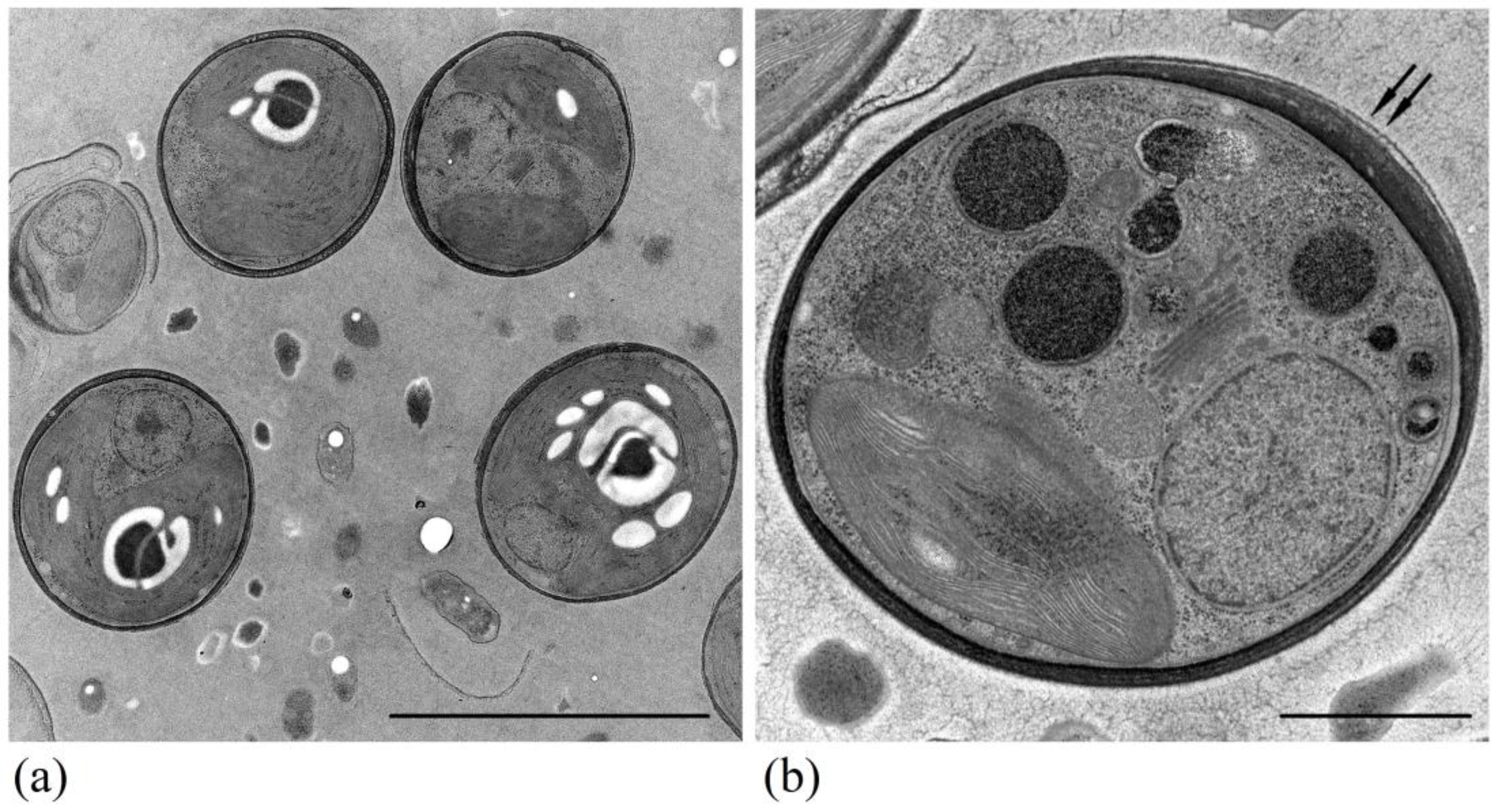
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
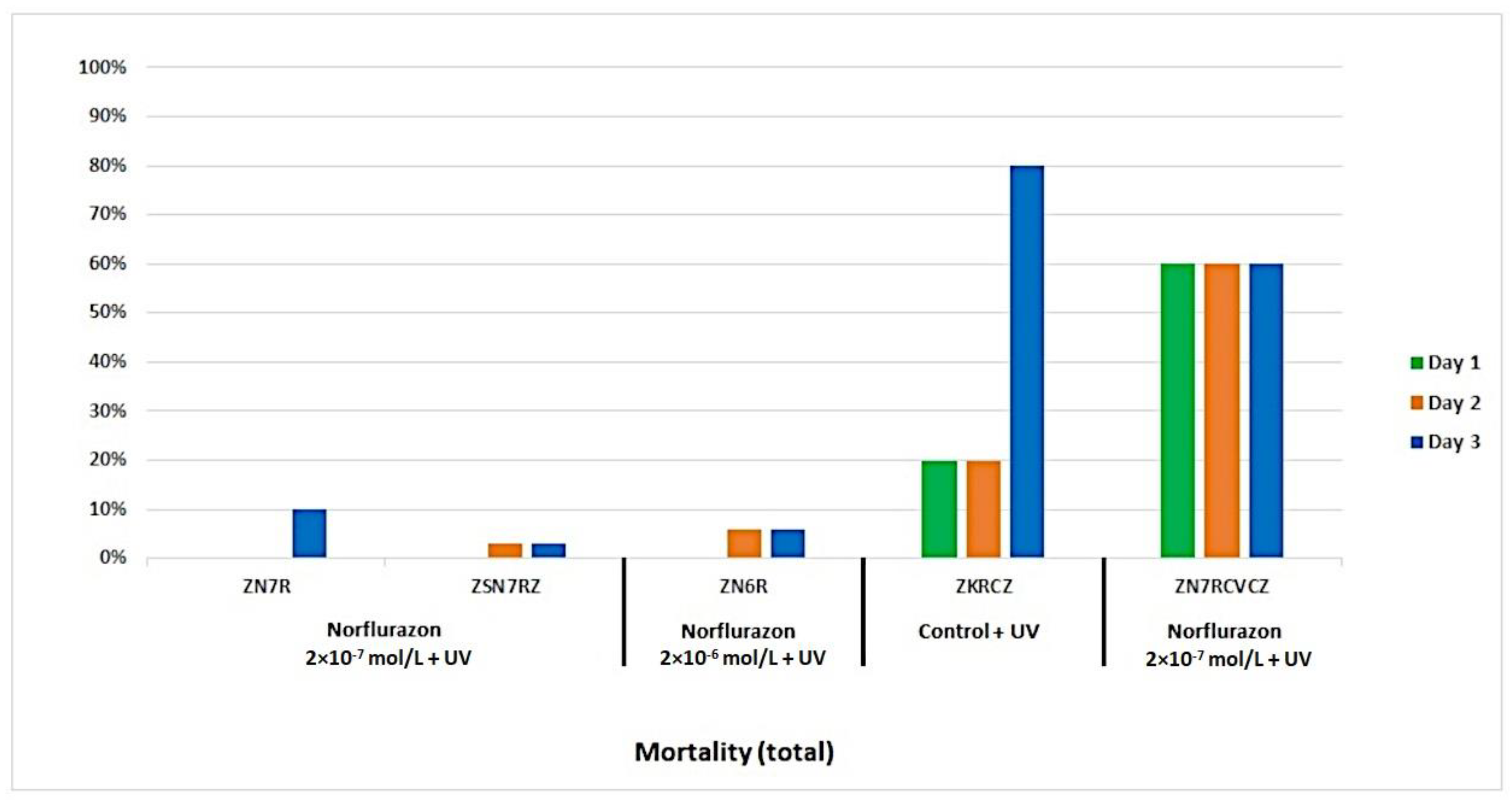
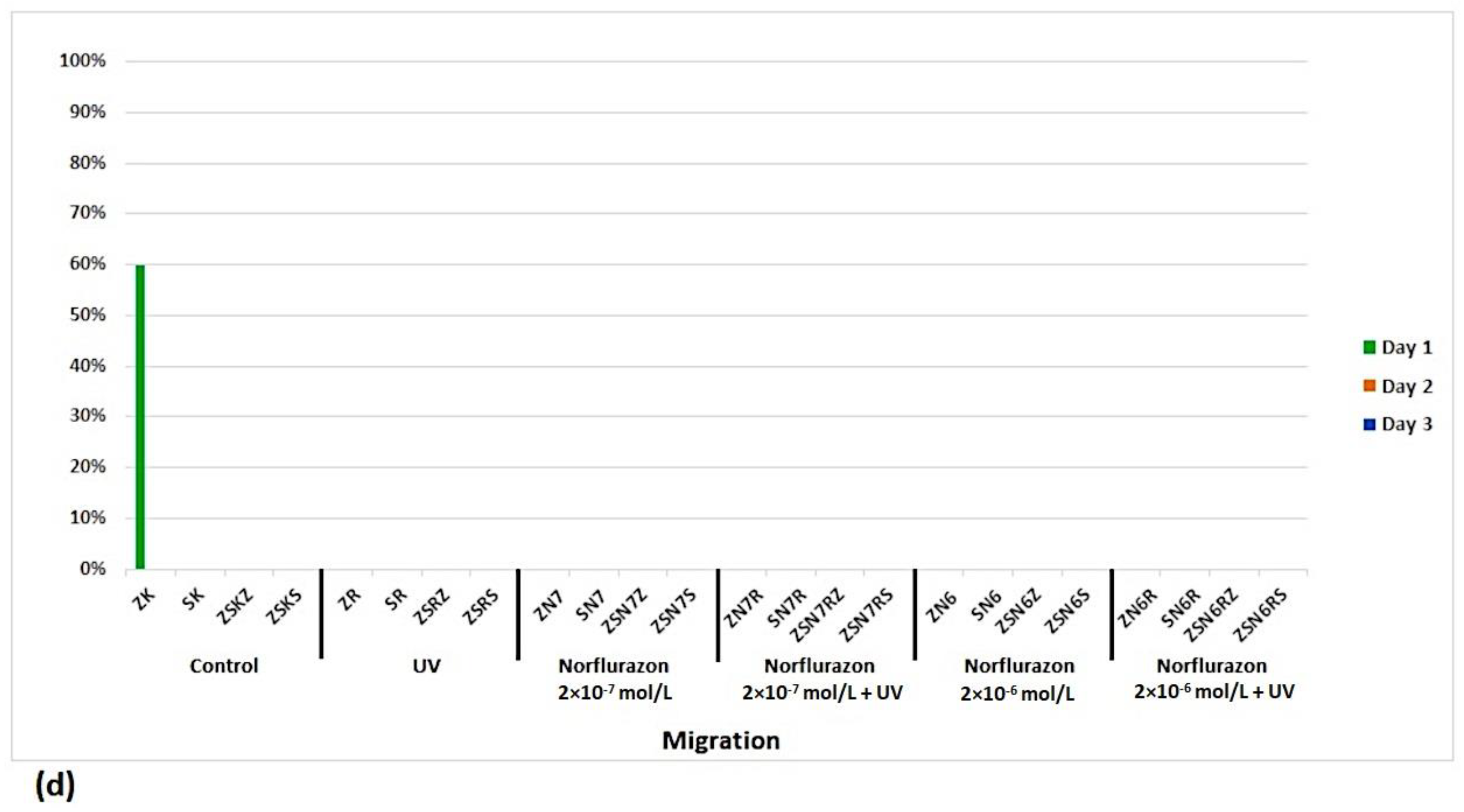
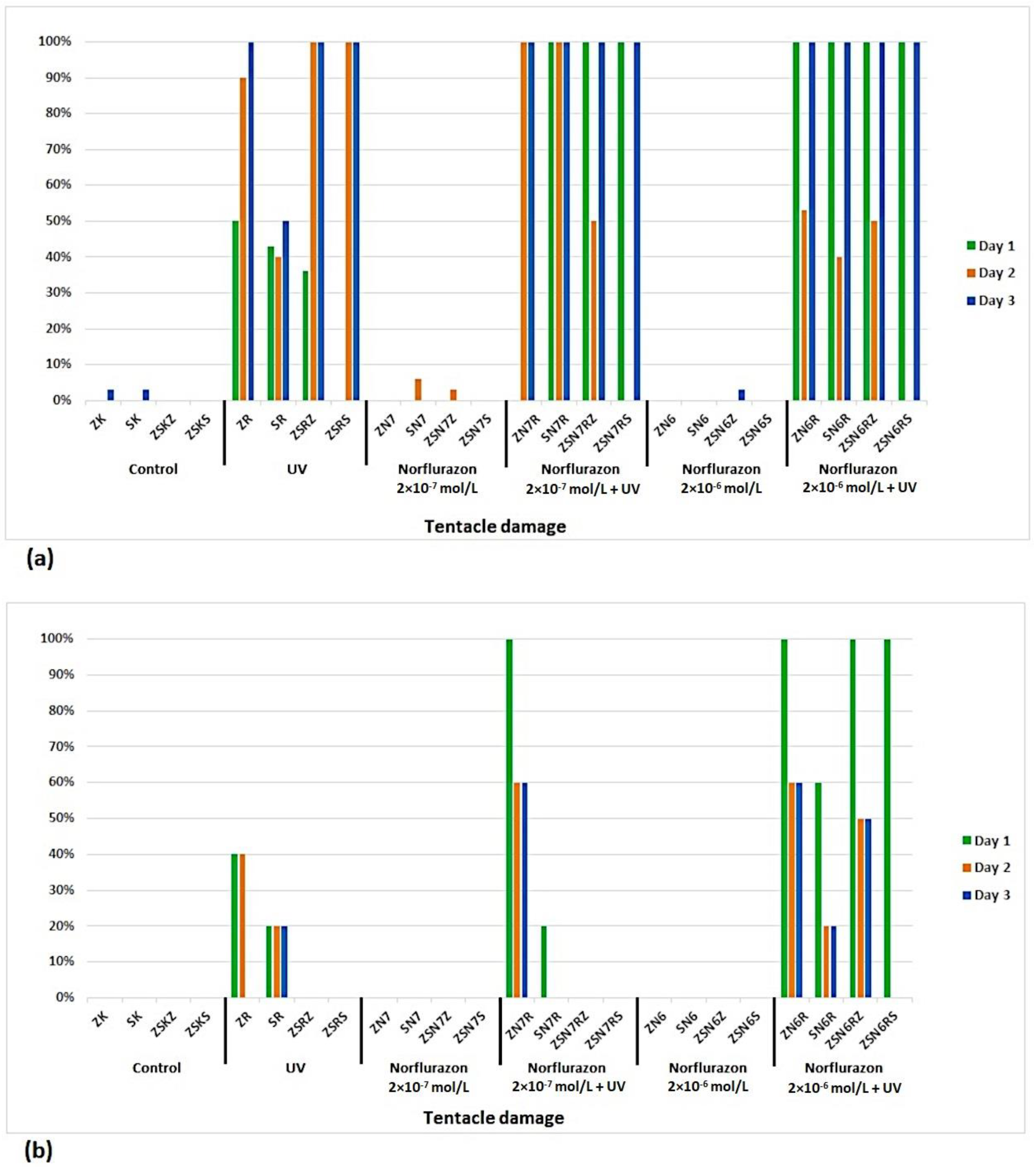
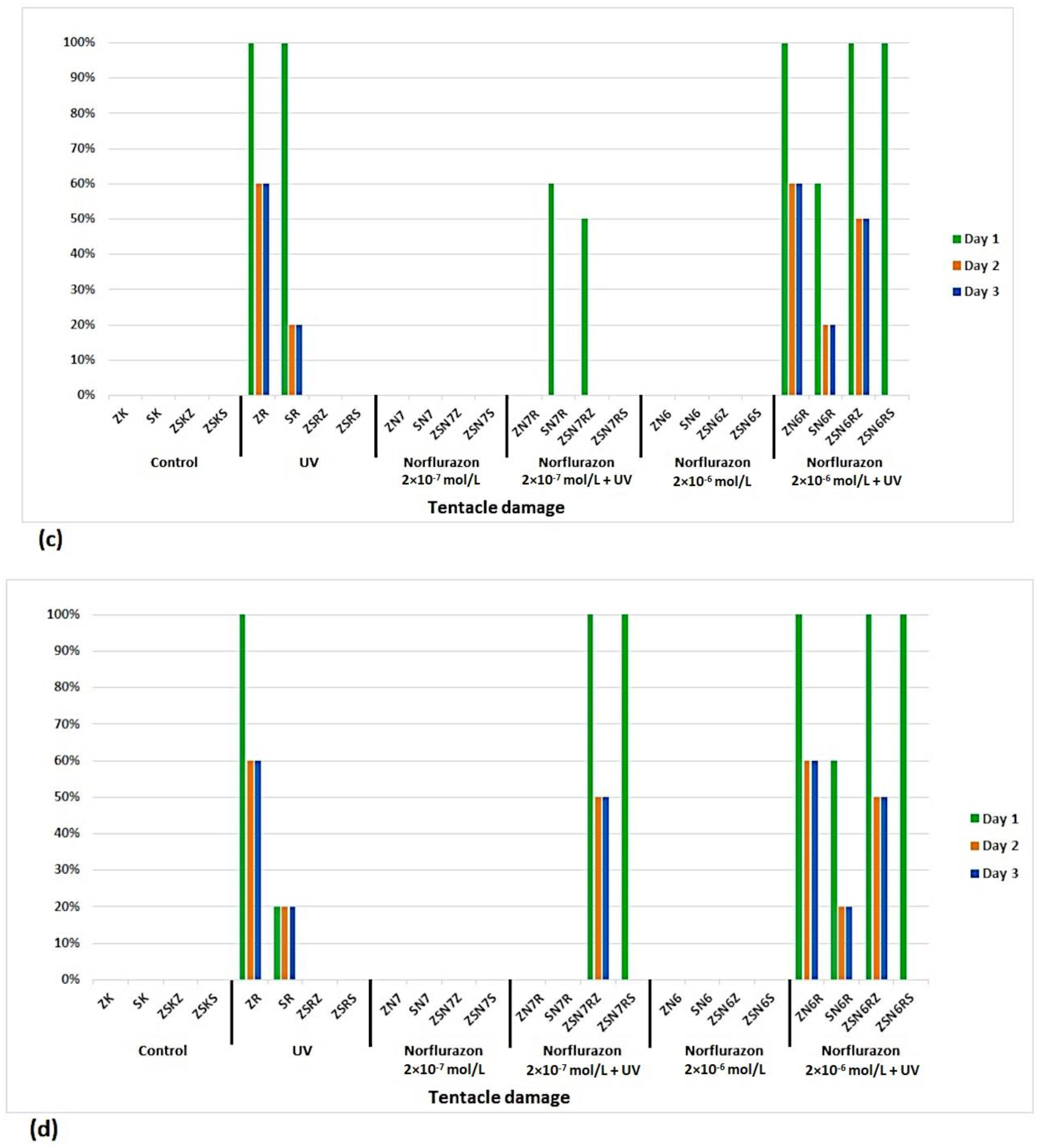
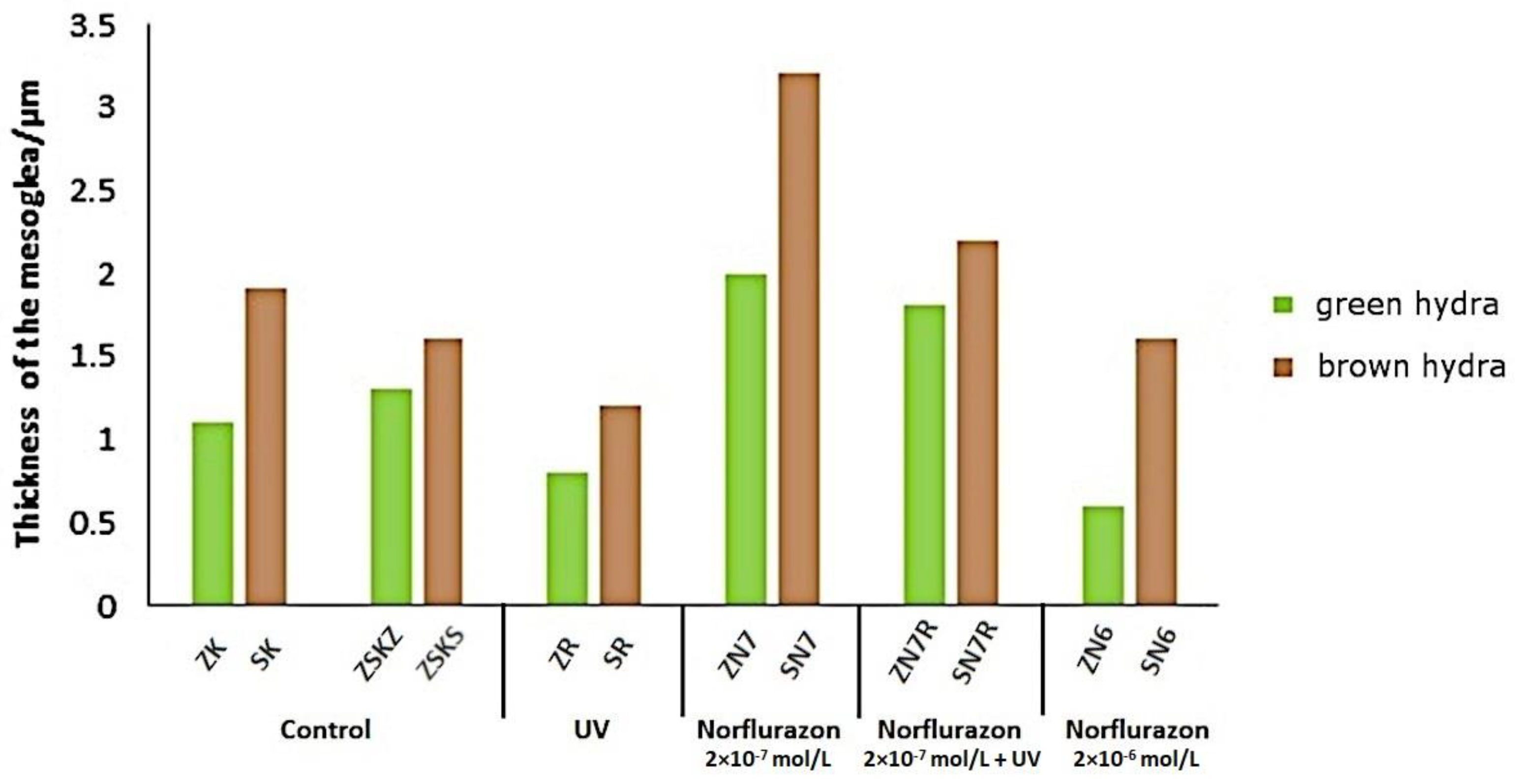
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
- For easier understanding of the abbreviations, in the figures and the table, we used combinations of the below listed terms. Abbreviations ending in Z or S indicate the observation of Z or S in the mixed sample of Z and S.
| CV | Chlorella vulgaris Beij. [K&H, 1992] |
| CZ | Mychonastes homosphaera (Chlorophyceae) (Skuja) Kalina et Punčochářová |
| Z | Green hydra |
| S | Brown hydra |
| K | Control |
| N6 | Norflurazon 2 × 10−6 mol/L |
| N7 | Norflurazon 2 × 10−7 mol/L |
| R | Irradiated |
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| HPF | High-pressure freezing |
| FS | Freeze substitution |
References
- Žnidarić, D. Comparison of the regeneration of the hypostome with the budding process in Hydra littoralis. Roux Arch. 1970, 166, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Sarras, M.P., Jr. Biogenesis of hydra mesoglea and its functions in regeneration. In Abstract Book of the International Workshop Hydra and the Molecular Logic of Regeneration; Bosch, T.C.G., Holstein, T.W., David, C.N., Eds.; DFG: Tutzing, Germany, 2005; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, B.P. Carbon metabolism of endosymbiotic algae. In Endocytobiology. Endosymbiosis and Cell Biology. Vol. I. A Synthesis of Recent Research; Schwemmler, W., Schenk, H.E.A., Eds.; WdeG: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Jelenčić, B.; Franjević, D. Endosymbiotic alga as the stronger evolutionary partner in green hydra symbiosis. J. Endocyt. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, G.; Franjević, D.; Jelenčić, B.; Kalafatić, M. Isolation and cultivation of endosymbiotic algae from green hydra and phylogenetic analysis of 18S rDNA sequences. Folia Biol. 2010, 58, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G. Value of the Hydra model system for studying symbiosis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivšić, M.; Kovačević, G. Evaluation of Algae Farming Using the Chlorella Bioassay. Croat. J. Fish. 2018, 76, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, T.C.G. Understanding complex host-microbe interactions in Hydra. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Bosch, T.C.G. Hydra’s Lasting Partnership with Microbes: The Key for Escaping Senescence? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, M.J.; Pascoe, D. The role of Hydra vulgaris (Pallas) in assessing the toxicity of freshwater pollutants. Water Res. 1998, 32, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafatić, M.; Kopjar, N. Response of Green Hydra to the Treatment with Different Pesticides under Laboratory Conditions. Z. Angew. Zool. 1994, 2, 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatić, M. Regeneration and asexual reproduction of Hydra oligactis treated with different pesticides. Biologia 1997, 52, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Ljubešić, N.; Šunjić, H. The effect of chloramphenicol on the symbiosis between alga and hydra. Biologia 2001, 56, 605–610. [Google Scholar]
- Arkhipchuk, V.V.; Blaise, C.; Malinovskaya, M.V. Use of hydra for chronic toxicity assessment of waters intended for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachamim, T.; Sher, D. What Hydra can teach us about chemical ecology—How a simple, soft organism survives in a hostile aqueous environment. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonge, C.M. Ecology and physiology of reef building corals. In Perspectives in Marine Biology; Buzzati-Traverso, A., Ed.; University California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA; Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1958; pp. 117–136. [Google Scholar]
- Bode, H.R. The interstitial cell lineage of hydra: A stem cell system that arose early in evolution. J. Cell Sci. 1996, 109 Pt 6, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradkin, M.; Kakis, H.; Campbell, R. Effects of γ irradiation on hydra: Elimination of interstitial cells from viable hydra. Radiat. Res. 1978, 76, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.R.; Wright, K.; Baillie, A.C. The Biochemical Mode of Action of Pesticides; Academic Press Inc.: London, UK, 1984; pp. 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, I.C.; Robertson, D.S. Role of carotenoids in protecting chlorophyll from photodestruction. Plant Physiol. 1960, 35, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savin, M.C.; Amador, J.A. Mineralization of Norflurazon in a Cranberry Bog Soil: Laboratory Evaluations of Management Practices. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giry, G.; Ayele, J. Study of norflurazon behavior in soils-Influence of formulation additives upon sorption parameters. Agronomie 2002, 22, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böger, P. Mode of action of herbicides affecting carotenogenesis. J. Pestic. Sci. 1996, 21, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamovitz, D.; Pecker, I.; Sandmann, G.; Böger, P.; Hirschberg, J. Cloning a gene coding for norflurazon resistance in cyanobacteria. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 1990, 45, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamovitz, D.; Sandman, G.; Hirschberg, J. Molecular and biochemical characterization of herbicide-resistant mutants of cyanobacteria reveals that phytoene desaturation is a rate-limiting step in carotenoid biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 17348–17353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandman, G.; Vique, A. Phylogeny of carotenogenic genes and enzymes in cyanobacteria. In The Phototrophyc Prokaryotes, Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Phototrophyc Prokaryotes: Structural and Functional Analyses of Cyanobacterial Photosystem, Vienna, Austria, 6–12 September 1997; Peschek, A., Löffelhardt, W., Schwetterer, G., Eds.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: Vienna, Austria, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wrischer, M.; Ljubešić, N.; Modrušan, Z. Development of calcelaria chromoplasts in the presence of herbicides affecting carotenoid biosyn-thesis. Acta Bot. Croat. 1991, 50, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Burkard, G.; Grumbach, K.H.; Meier, D. Physiological effects of photosystem II-herbicides on the development of the photosynthetic apparatures. Photosynth. R 1980, 1, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, E.M.; Bastian, K.C.; Mollhagen, T. Occurrence of cotton herbicides and insecticides in playa lakes of the High Plains of West Texas. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 248, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, J.; Marade, J.; Spurlock, F. Empirical Modeling of Spatial Vulnerability Applied to a Norflurazon Retrospective Well Study in California. J. Environ. Qual. 1999, 28, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Differential Sensitivity to 30 Herbicides among Populations of Two Green Algae Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 68, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, S.; Zheng, R.; Jin, S.; Huang, S.; Huang, Y. Toxicity of 40 Herbicides to the Green Alga Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2002, 51, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceljski, M.; Hrlec, G.; Ostojić, Z.; Cvjetković, B. Pregled sredstava za zaštitu bilja u Republici Hrvatskoj za 1997. godinu. Glas. Zašt. Bilja 1997, 3–4, 93–212. [Google Scholar]
- Tschiersh, H.; Ohomann, E.; Döge, M. Modification of the thylacoid structure of Euglena gracilis by norflurazon treatment: Consequences for fluorescence quenching. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2002, 47, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzlyak, M.N.; Khozin, I.; Cohen, Z. Spectro-photometric Analysis of Carotenoids in Plant Extracts Based on Elimination of Chlorophyll Absorption. Phytochem. Anal. 1996, 7, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.C.; Koch, R. Influence of Exposure Concentration and Duration on Effects and Recovery of Lemna minor Exposed to the Herbicide Norflurazon. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrous, O.; Benhassaine-Kesri, G.; Tremolieres, A.; Mazijak, P. Effect of norflurazon on lipid metabolism in soya seedlings. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salopek, B.; Ljubešić, N. The fine structure of pepper chloroplasts: The effect of bleaching herbicides. Acta Bot. Croat. 1994, 53, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Vecchia, F.D.; Barbato, R.; Rocca, N.L.; Moro, I.; Rascio, N. Responses to bleaching herbicides by leaf chloroplasts of maize plants grown at different temperatures. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 357, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Ljubešić, N. Effects of Norflurazon on Green and Brown Hydra. Folia Biol. 2009, 57, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, T.; Kalafatić, M.; Kopjar, N.; Kovačević, G. Toxicity testing of herbicide norflurazon on an aquatic bioindicator species—The planarian Polycelis felina (Daly.). Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 73, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECHA. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/notification-details/2240/1767154 (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Friedberg, E.C. DNA Damage and Repair. Nature 2003, 421, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalafatić, M.; Kovačević, G.; Zupan, I.; Franjević, D. Effect of repeated UV-irradiation on Hydra oligactis Pallas. Period. Biol. 2003, 105, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, G.; Petrinec, D.; Tramontana Ljubičić, P.; Reipert, S.; Sirovina, D.; Špoljar, M.; Peharec Štefanić, P.; Želježić, D. Formation of Microalgal Hunting Nets in Freshwater Microcosm Food Web: Microscopic Evidence. Water 2023, 15, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaskadbi, S.S.; Shetye, L.; Chiplonkar, S.; Ghaskadbi, S. Ultraviolet irradiation initiates ectopic foot formation in regenerating hydra and promotes budding. J. Biosci. 2005, 30, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, I.; Alves, M.; Malheiro, C.; Silva, A.R.R.; Loureiro, S.; Henriques, I.; González-Alcaraz, M.N. Short-Term Responses of Soil Microbial Communities to Changes in Air Temperature, Soil Moisture and UV Radiation. Genes 2022, 13, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonntag, B.; Summerer, M.; Sommaruga, R. Are freshwater mixotrophic ciliates less sensitive to solar ultraviolet radiation than heterotrophic ones? J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2011, 58, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, S.; Beattie, G.A.C.; Holford, P.; Yang, C.; Cen, Y. Susceptibility of Diaphorina citri to Irradiation with UV-A and UV-B and the Applicability of the Bunsen-Roscoe Reciprocity Law. Insects 2023, 14, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, S.; Christer, B.; Lars-Anders, H.; Marcus, L. Fitness cost from fluctuating ultraviolet radiation in Daphnia magna. Biol. Lett. 2021, 17, 20210261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshun-Wilson, F.; Wolf, R.; Andersen, T.; Hessen, D.O.; Sperfeld, E. UV radiation affects antipredatory defense traits in Daphnia pulex. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 14082–14097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.N.; Mahamed, A.H.; Alarcon, J.F.; Al Suwailem, A.; Agustí, S. Adverse Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation on Growth, Behavior, Skin Condition, Physiology, and Immune Function in Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannaki, D.; Medana, C.; Binetti, R.; Calza, P.; Roslev, P. Effect of UV-A, UV-B and UV-C irradiation of glyphosate on photolysis and mitigation of aquatic toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, P.C.; Boman, B.; Foos, J.F. Norflurazon and Simazine Losses in Surface Runoff Water from Flatwoods Citrus Production Areas. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 78, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reipert, S.; Goldammer, H.; Richardson, C.; Goldberg, M.W.; Hawkins, T.J.; Hollergschwandtner, E.; Kaufmann, W.A.; Antreich, S.; Stierhof, Y.D. Agitation modules: Flexible means to accelerate automated freeze substitution. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2018, 66, 903–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldammer, H.; Hollergschwandtner, E.; Elisabeth, N.H.; Frade, P.R.; Reipert, S. Automatized freeze substitution of algae accelerated by a novel agitation module. Protist 2016, 167, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, J.; Giepmans, B.N.G. Neodymium as an alternative contrast for uranium in electron microscopy. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 153, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Želježić, D.; Horvatin, K.; Kalafatić, M. Morphological features and comet assay of green and brown hydra treated with aluminium. Symbiosis 2009, 44, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, G.; Gregorović, G.; Matijević, A.; Kalafatić, M. Toxic effects of iron on green and brown hydra. Curr. Sci. 2016, 110, 502–504. [Google Scholar]
- Hyne, R.V.; Rippon, G.D.; White, J.; Ellender, G. Accumulation of uranium by freshwater hydra into discharged nematocysts. Aquat. Toxicol. 1992, 23, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimalkumar, K.; Sangeetha, S.; Felix, L.; Kay, P.; Pugazhendhi, A. A systematic review on toxicity assessment of persistent emerging pollutants (EPs) and associated microplastics (MPs) in the environment using the Hydra animal model. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 256, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, K.T.; Huebner, H.J.; Li, Y.; Phillips, T.D.; Raushel, F.M. Organophosphate nerve agent toxicity in Hydra attenuata. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekamge, S.; Miranda, A.F.; Abraham, A.N.; Li, V.V.; Shukla, R.; Bansal, V.; Nugegoda, D. The Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) to Three Freshwater Invertebrates with Different Life Strategies: Hydra vulgaris, Daphnia carinata, and Paratya australiensis. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.H. Organic Pollutants—An Ecotoxicological Perspective; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/reregistration/fs_PC-105801_1-Jul-96.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2024).
- Wilson, P.C.; Wilson, S.B.; Haunert, D. Toxicity of the norflurazon to the aquatic macrophyte Vallisneria americana (Michx.). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 69, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, E.A.; Miller, S.W. Bioindicators: Using organisms to measure environmental impacts. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2011, 2, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Karntanut, W.; Pascoe, D. The toxicity of copper, cadmium and zinc to four different Hydra (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). Chemosphere 2002, 47, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, A.L. Biology of Hydra; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoh Kam, J.; Hogg, C.; Fosbury, R.; Shinhmar, H.; Jeffery, G. Mitochondria are specifically vulnerable to 420 nm light in drosophila which undermines their function and is associated with reduced fly mobility. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Ljubešić, N. New Observations on Green Hydra Symbiosis. Folia Biol. 2007, 55, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, C.A.; Woodley, C.M.; Fauth, J.E.; Knutson, S.; Burtscher, M.M.; May, L.A.; Avadanei, A.R.; Higgins, J.L.; Ostrander, G.K. A survey of environmental pollutants and cellular-stress markers of Porites astreoides at six sites in St. John, U.S. Virgin Islands. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1914–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z. Why Algae Release Volatile Organic Compounds—The Emission and Roles. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizdaroglu, M.; Coskun, E.; Jaruga, P. Repair of oxidatively induced DNA damage by DNA glycosylases: Mechanisms of action, substrate specificities and excision kinetics. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 771, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohnert, G.; Steinke, M.; Tollrian, R. Chemical cues, defence metabolites and the shaping of pelagic interspecific interactions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leflaive, J.; Ten-Hage, L. Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: A comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Song, X.; Fan, Y. Characterization and antioxidant activity of the oligo-maltose fraction from Polygonum cillinerve. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Baky, H.H.; Shallan, M.; Baroty, G.E.; El-Baz, F.K. Volatile Compounds of the Microalga Chlorella vulgaris and Their Phytotoxic Effect. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2002, 5, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lafarge, C.; Cayot, N. Insight on a comprehensive profile of volatile compounds of Chlorella vulgaris extracted by two “green” methods. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.M.; Bell, T.; West, S.A. Multicellular group formation in response to predators in the alga Chlorella vulgaris. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, M.D.; Borin, J.M.; Boswell, J.C.; Walker, J.; Chen, I.K.; Knox, C.A.; Boyd, M.; Rosenzweig, F.; Ratcliff, W.C. De novo origins of multicellularity in response to predation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venuleo, M.; Raven, J.A.; Giordano, M. Intraspecific chemical communication in microalgae. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapsetaki, S.E.; Fisher, R.M.; West, S.A. Predation and the formation of multicellular groups in algae. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2016, 17, 651–669. [Google Scholar]
- Kević, N.; Radić Brkanac, S.; Vincek, N.; Peharec Štefanić, P.; Faraguna, F.; Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Franjević, D. Endosymbiotic green algae in European Hydra strains show quantitative difference on morphological and isoenzyme level. Symbiosis 2019, 77, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Zheng, Y. Overview of Microalgal Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) and Their Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutry, J.; Buysse, M.; Tissot, S.; Cazevielle, C.; Hamede, R.; Dujon, A.M.; Ujvari, B.; Giraudeau, M.; Klimovich, A.; Thomas, F.; et al. Spontaneously occurring tumors in different wild-derived strains of hydra. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Richa; Kumar, A.; Tyagi, M.B.; Sinha, R.P. Molecular Mechanisms of Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced DNA Damage and Repair. J. Nucleic Acids 2010, 2010, 592980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousry, C.; Saber, M.M.; Abd-Elsalam, W.H. Cosmeceutical Topical Water-in-Oil Nanoemulsion of Natural Bioactives: Design of Experiment, in vitro Characterization, and in vivo Skin Performance Against UVB Irradiation-Induced Skin Damages. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 2995–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Wei, M.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y. The mechanism for the formation of OH radicals in condensed-phase water under ultraviolet irradiation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 21453–21460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.P.; Williamson, C.E.; Wängberg, S.; Rautio, M.; Rose, K.C.; Gao, K.; Helbling, E.W.; Sinha, R.P.; Worres, R. Effects of UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with other environmental factors. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.S.; Newmark, P.A. The cell biology of regeneration. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Walker, G.C. Mechanisms of DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, J.S.; Baird, B.J.; Redon, C.E.; Avdoshina, V.; Palchik, G.; Wu, J.; Kondratyev, A.; Bonner, W.M.; Olga, A. Martin Susceptibility to bystander DNA damage is influenced by replication and transcriptional activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10274–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žnidarić, D.; Lui, A. Regeneration of hydra damaged by zolone PM insecticide. Z. Mikrosk. Anat. Forsch. 1983, 97, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Domazet-Lošo, T.; Klimovich, A.; Anokhin, B.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Hamm, M.J.; Lange, C.; Bosch, T.C.G. Naturally occurring tumours in the basal metazoan Hydra. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4222–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafatić, M.; Kovačević, G.; Ljubešić, N.; Šunjić, H. Effects of ciprofloxacin on green hydra and endosymbiotic alga. Period. Biol. 2011, 103, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Žnidarić, D.; Ante, L.; Kalafatić, M. Regeneration and reproduction of irradiated green hydra (Cnidaria). Period. Biol. 1992, 2, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lyndby, N.H.; Murray, M.C.; Trampe, E.; Meibom, A.; Kühl, M. The mesoglea buffers the physico-chemical microenvironment of photosymbionts in the upside-down jellyfish Cassiopea sp. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1112742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarras, M.P., Jr.; Yan, L.; Grens, A.; Zhang, X.; Agbas, A.; Huff, J.K.; St John, P.L.; Abrahamson, D.R. Cloning and biological function of laminin in Hydra vulgaris. Dev. Biol. 1994, 164, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stidwill, R.P.; Christen, M. Alteration of fibronectin affinity during differentiation modulates the in vitro migration velocities of Hydra nematocytes. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 1998, 41, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber-Muller, S.; Studer, R.; Muller, P.; Yanze, N.; Schmid, V. Integrin and talin in the jellyfish Podocoryne carnea. Cell Biol. Int. 2001, 25, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, M.G.; Grimaldi, A.; Baranzini, N.; La Corte, C.; Dara, M.; Parrinello, D.; Cammarata, M. Mesoglea Extracellular Matrix Reorganization during Regenerative Process in Anemonia viridis (Forskål, 1775). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV | CZ | CVCZ | CV | CZ | CVCZ | CV | CZ | CVCZ | ||
| Control | Z | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| S | + | green − | + | + | green − | + | + | green − | + | |
| ZS | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Irradiated | Z | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ |
| S | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| ZS | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | |
| Norflurazon 2 × 10−7 mol/L | Z | green − | ++ | ++ | green − | ++ | ++ | green − | ++ | ++ |
| S | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| ZS | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Norflurazon 2 × 10−6 mol/L | Z | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ |
| S | green + | green + | + | green + | green + | + | green + | green + | + | |
| ZS | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | + | |
| Norflurazon 2 × 10−7 mol/L Irradiated | Z | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| S | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | |
| ZS | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | |
| Norflurazon 2 × 10−6 mol/L Irradiated | Z | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| S | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| ZS | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovačević, G.; Matijević, A.; Korać, P.; Želježić, D.; Reipert, S.; Caput Mihalić, K.; Sirovina, D.; Peharec Štefanić, P.; Ivšić, M. Effects of Norflurazon and UV Radiation on Symbiotic and Free-Living Hydra. Water 2024, 16, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050645
Kovačević G, Matijević A, Korać P, Želježić D, Reipert S, Caput Mihalić K, Sirovina D, Peharec Štefanić P, Ivšić M. Effects of Norflurazon and UV Radiation on Symbiotic and Free-Living Hydra. Water. 2024; 16(5):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050645
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovačević, Goran, Ana Matijević, Petra Korać, Davor Želježić, Siegfried Reipert, Katarina Caput Mihalić, Damir Sirovina, Petra Peharec Štefanić, and Martina Ivšić. 2024. "Effects of Norflurazon and UV Radiation on Symbiotic and Free-Living Hydra" Water 16, no. 5: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050645
APA StyleKovačević, G., Matijević, A., Korać, P., Želježić, D., Reipert, S., Caput Mihalić, K., Sirovina, D., Peharec Štefanić, P., & Ivšić, M. (2024). Effects of Norflurazon and UV Radiation on Symbiotic and Free-Living Hydra. Water, 16(5), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050645







