Simulation of Diurnal Evolution of Evaporation Zone during Soil Drying after Rainfall
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
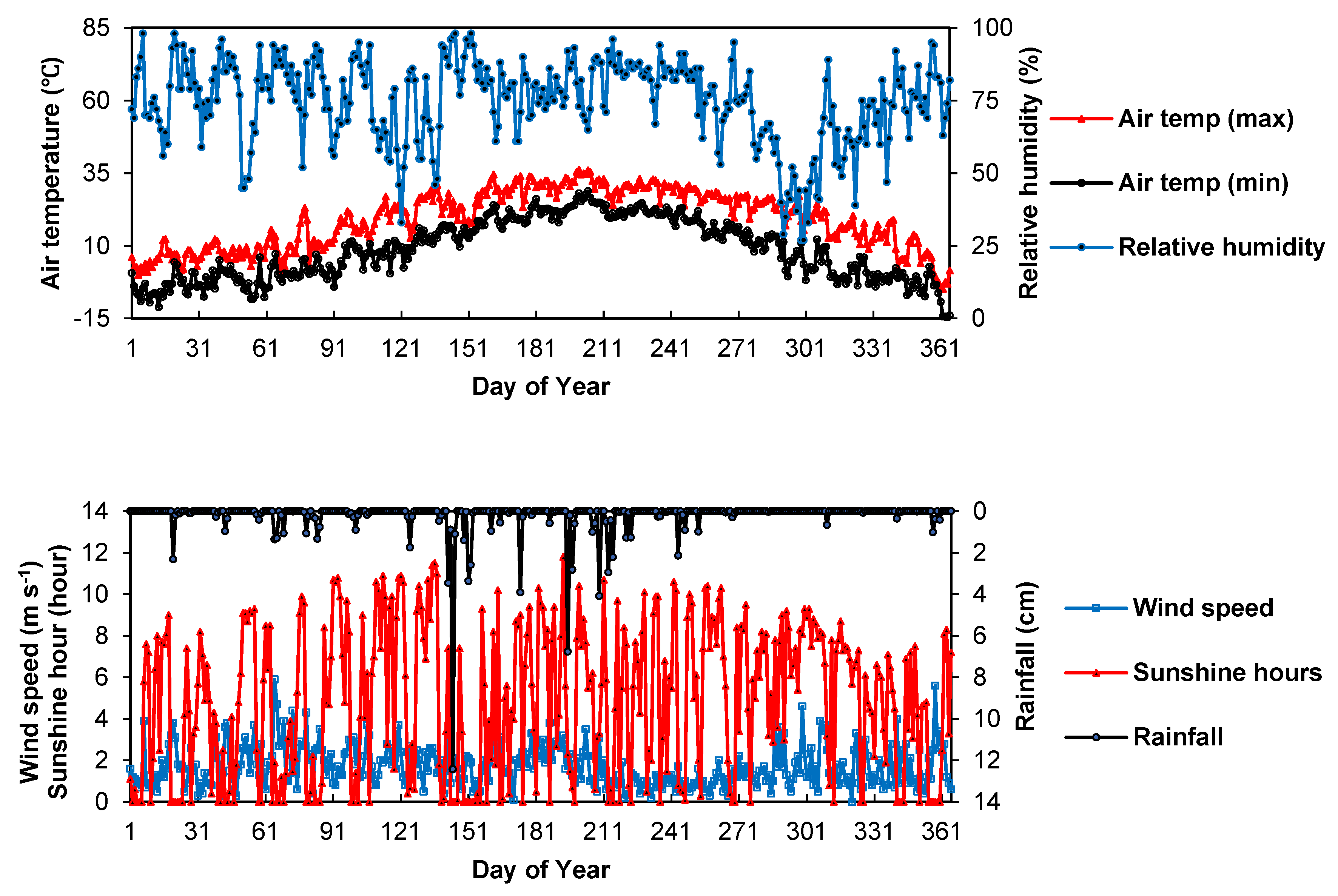
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Water Flow Equations
2.3. Heat Transport Equations
2.4. Initial and Boundary Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
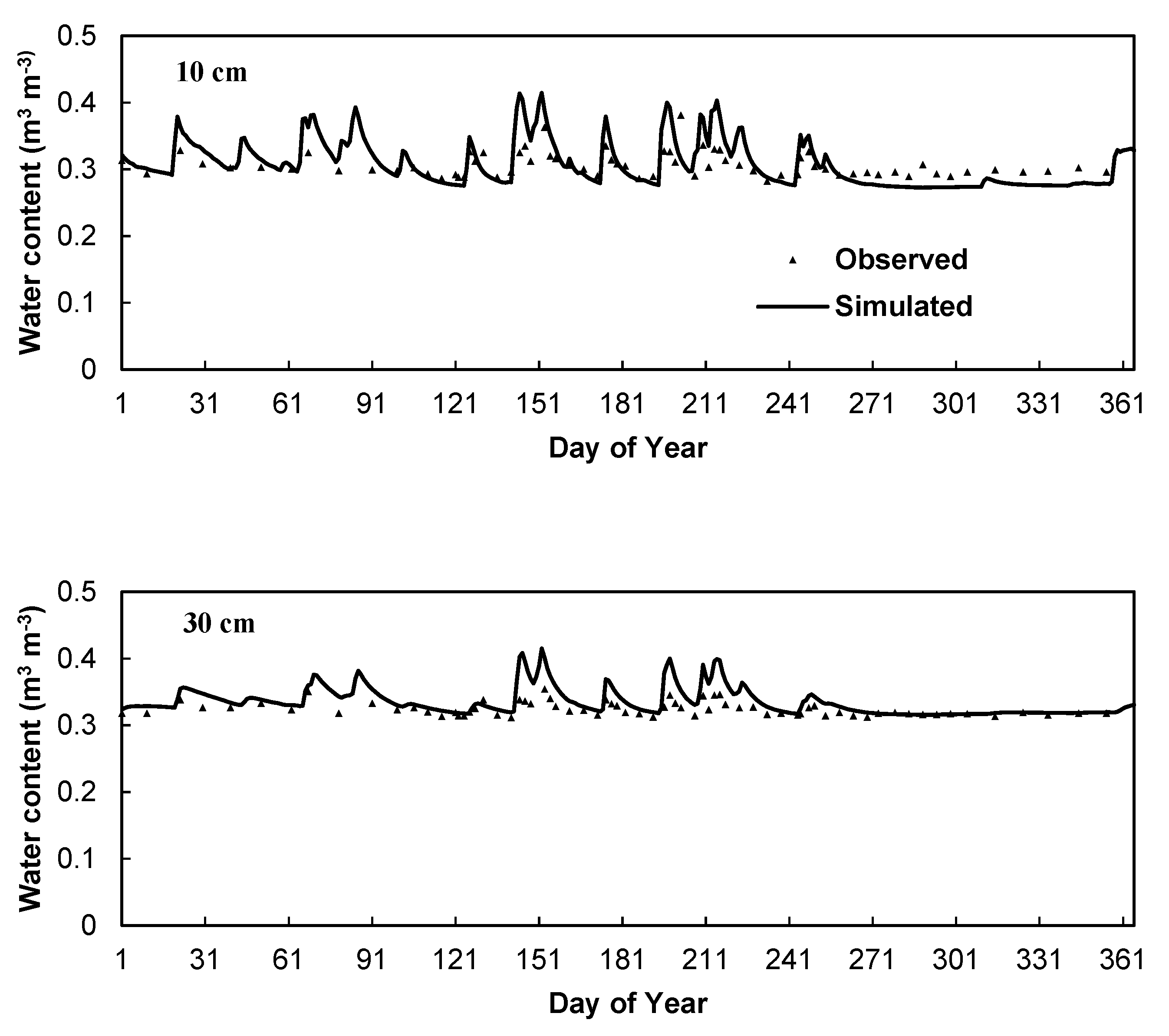
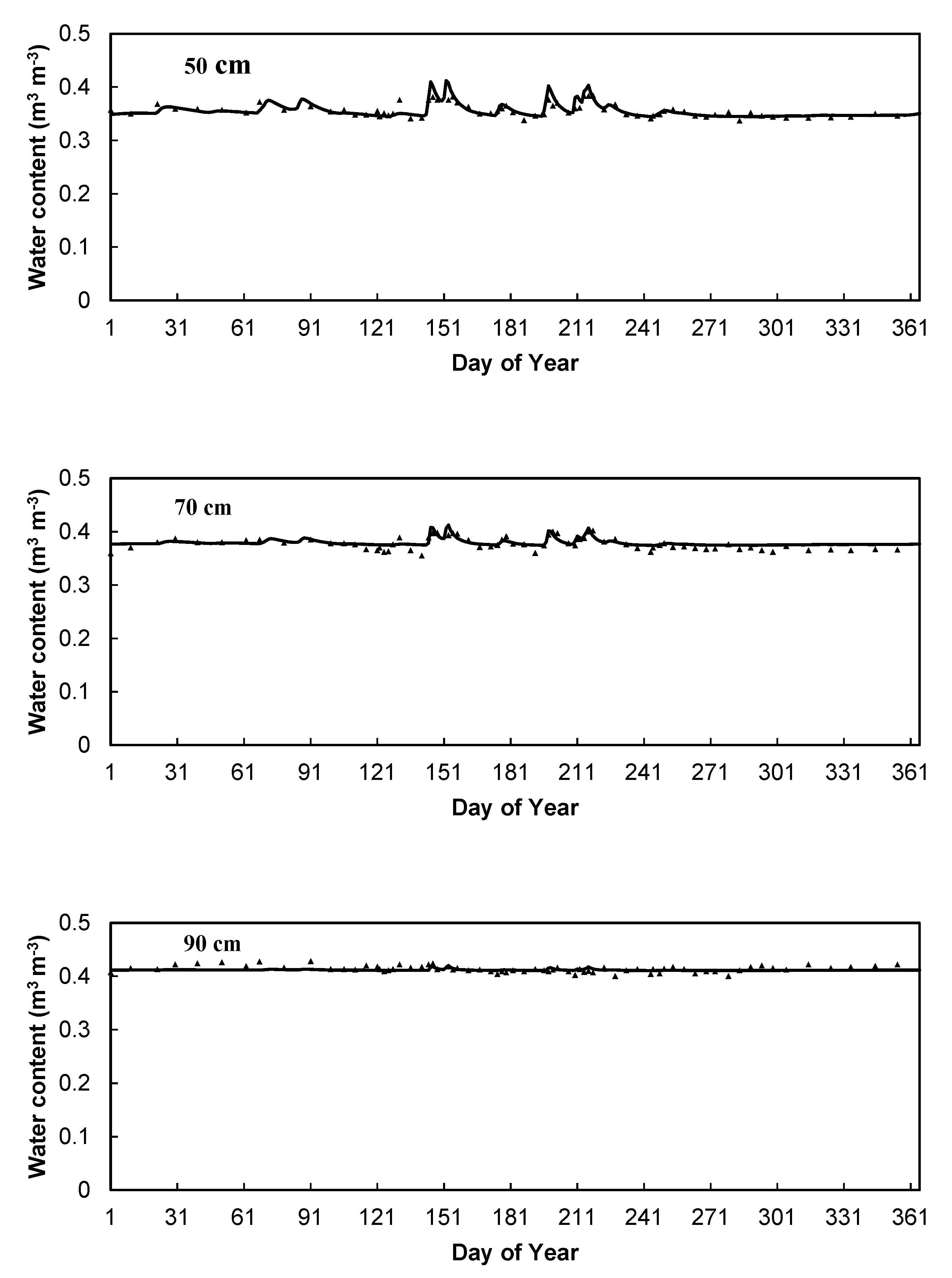
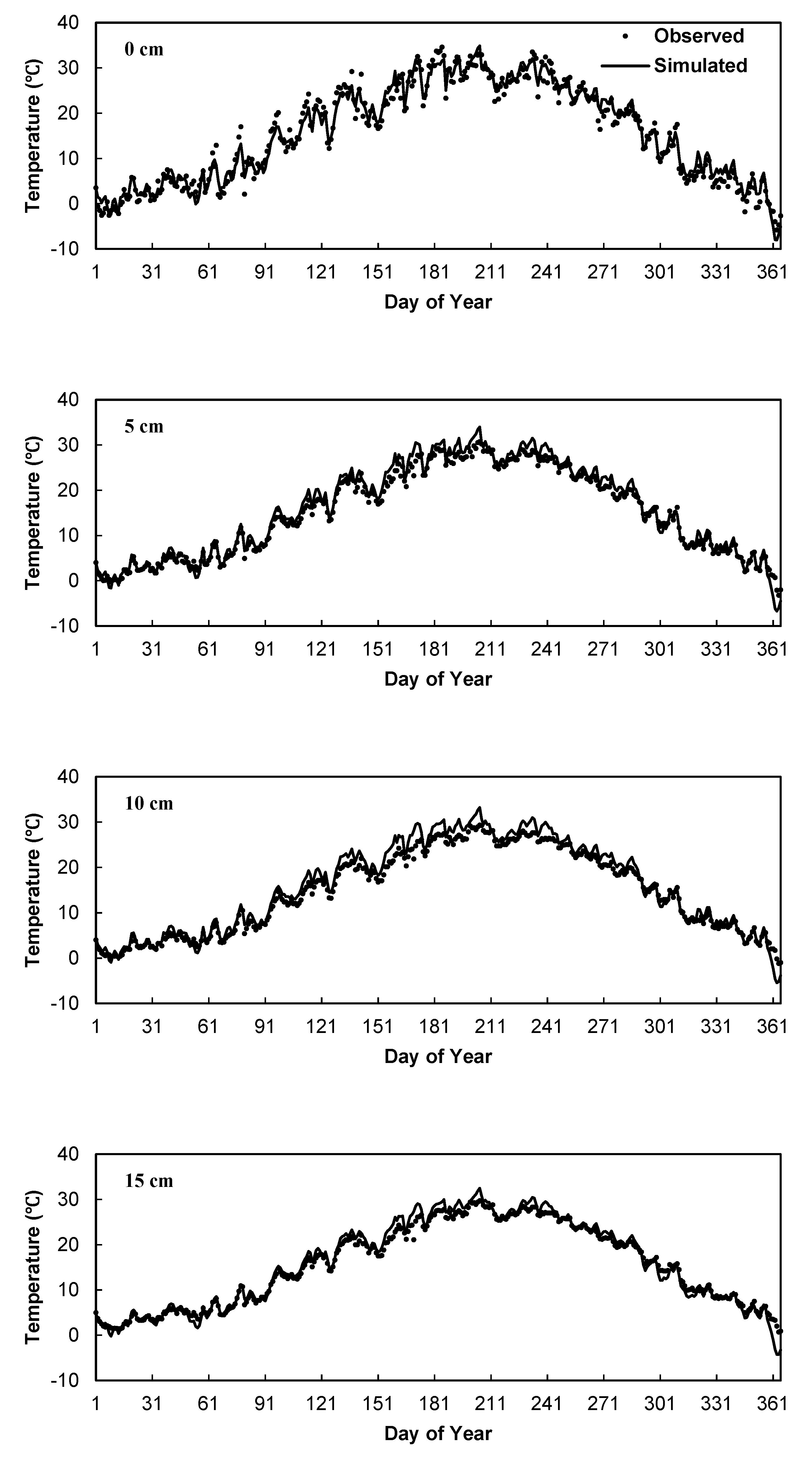
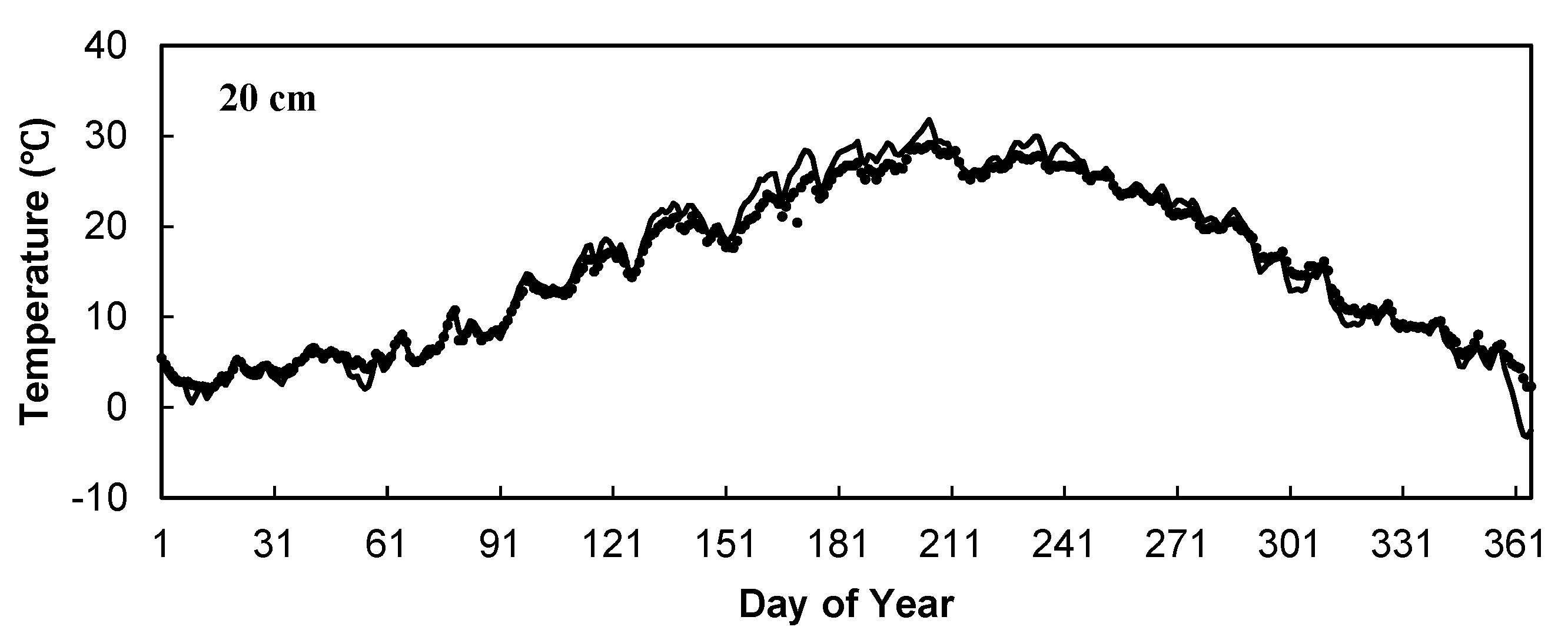
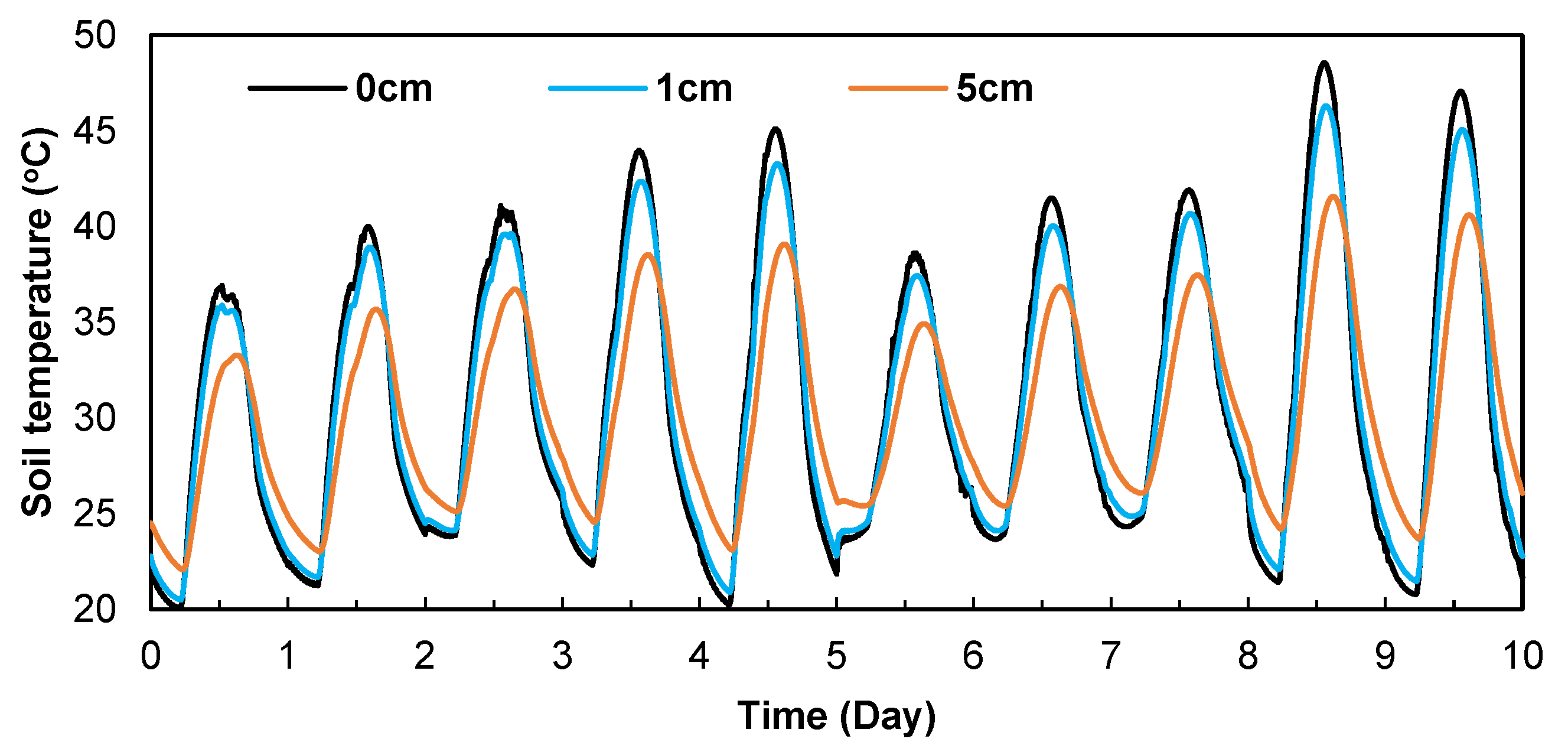
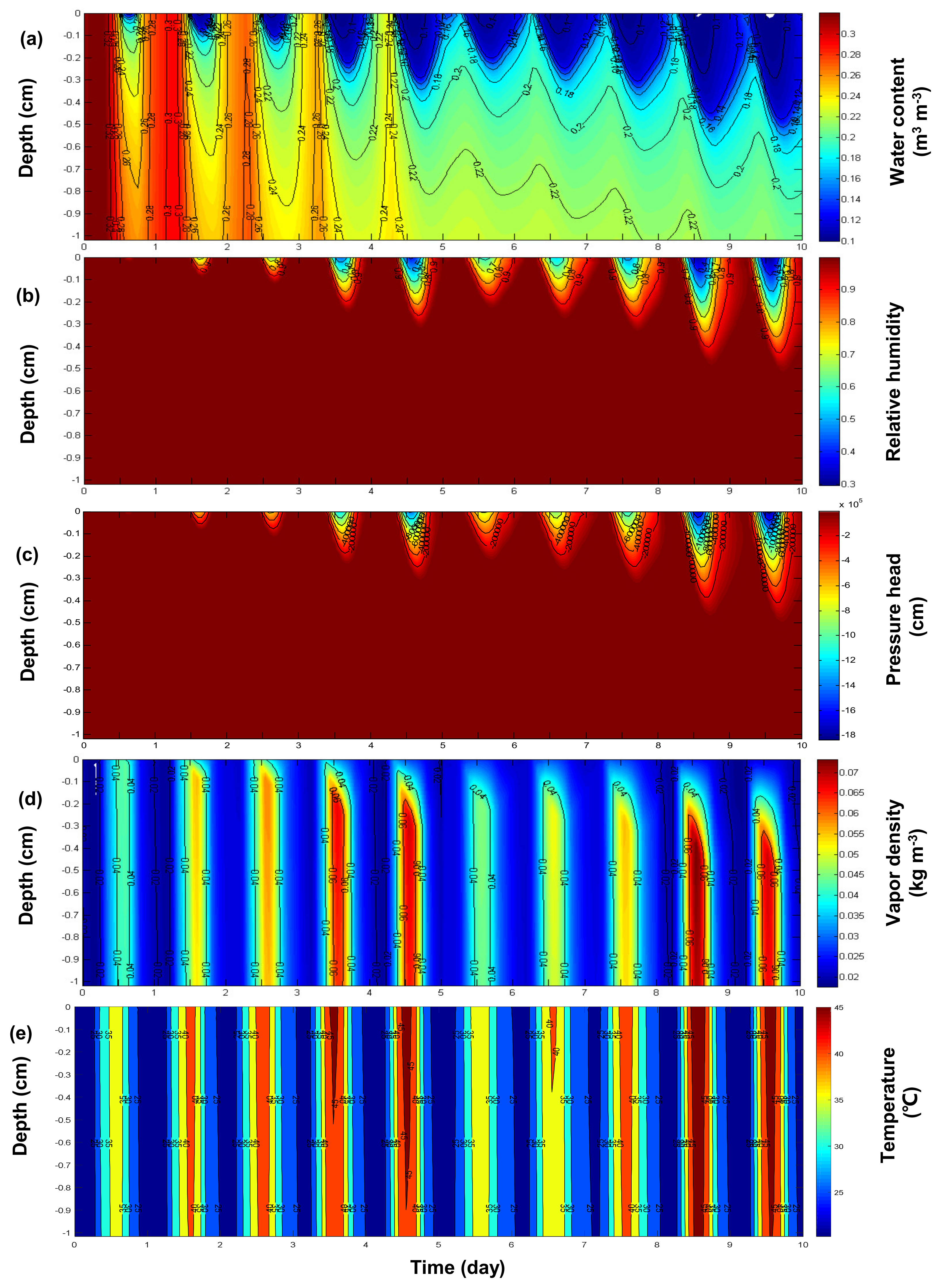
3.1. Comparisons between Observed and Simulated Soil Water Contents and Temperatures
3.2. Surface Energy Balance Components
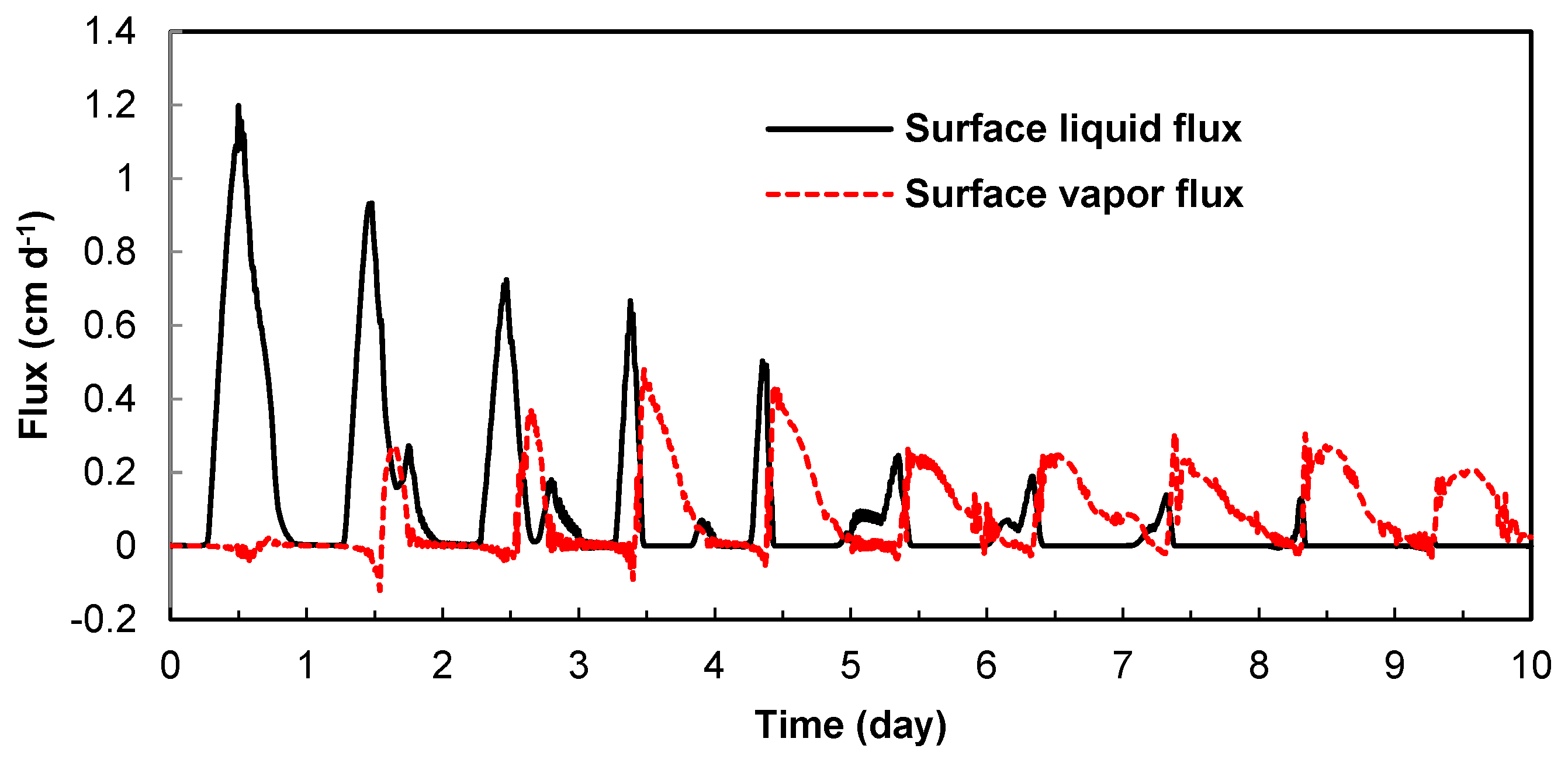
3.3. Surface Liquid and Vapor Fluxes
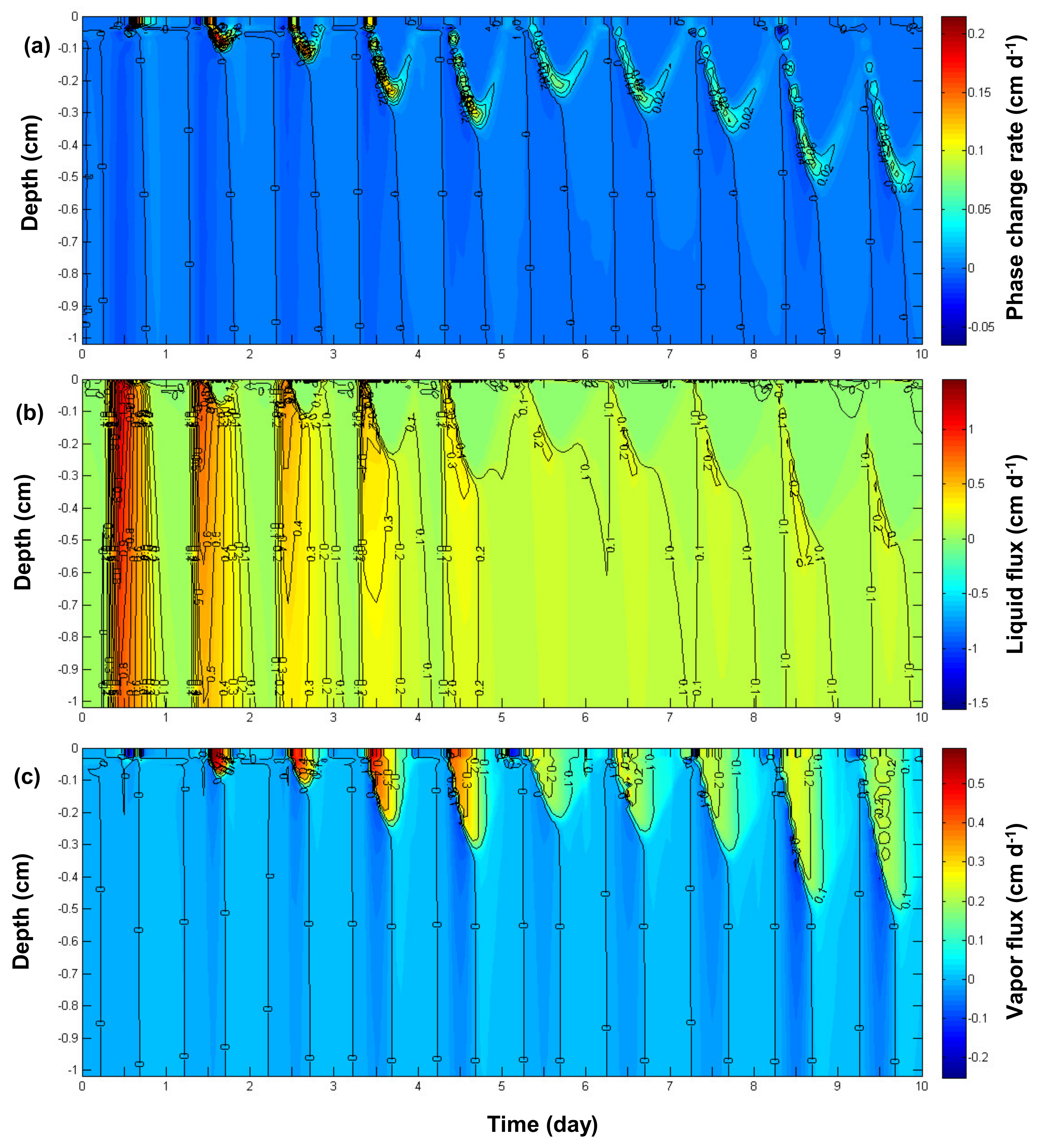
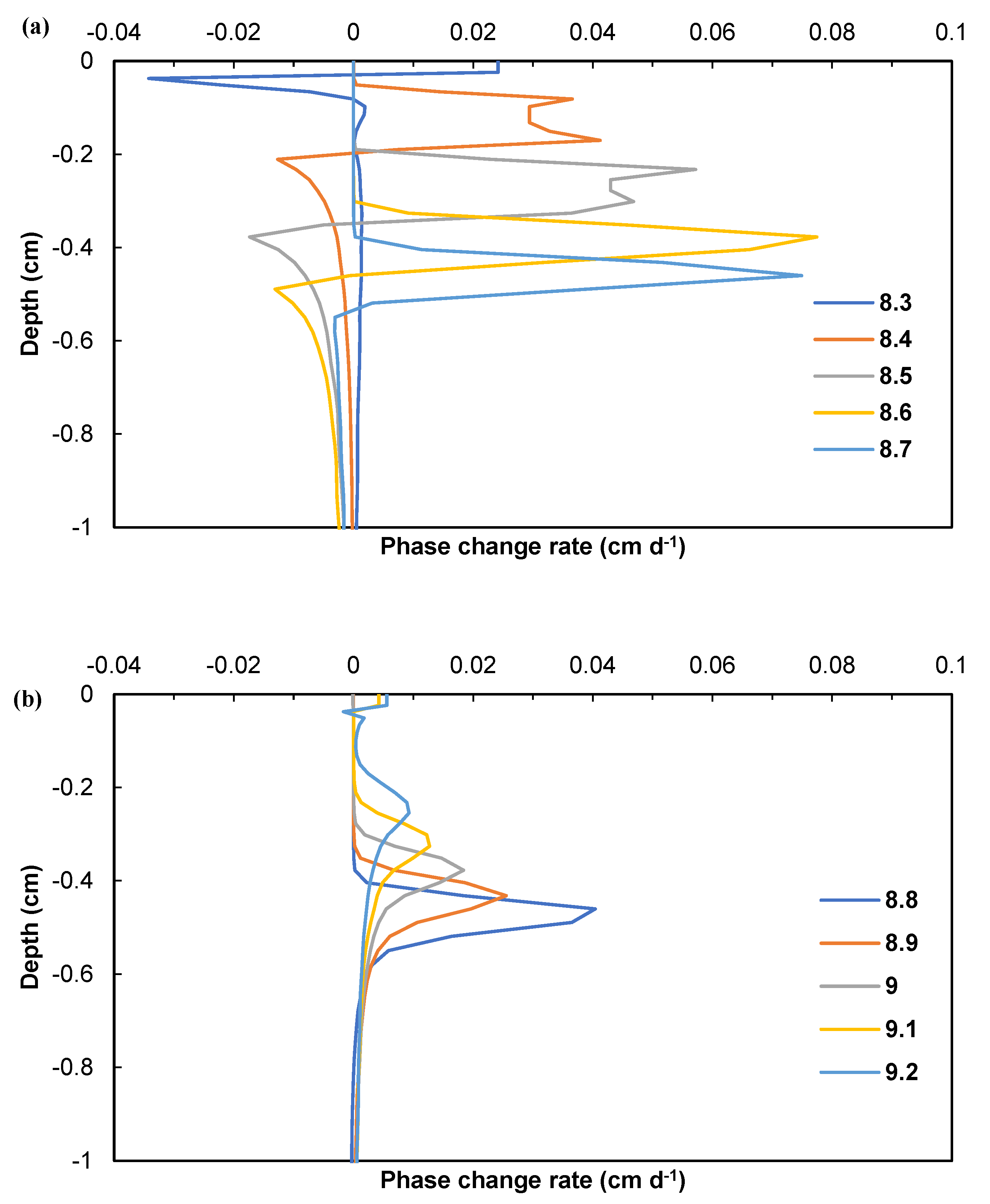
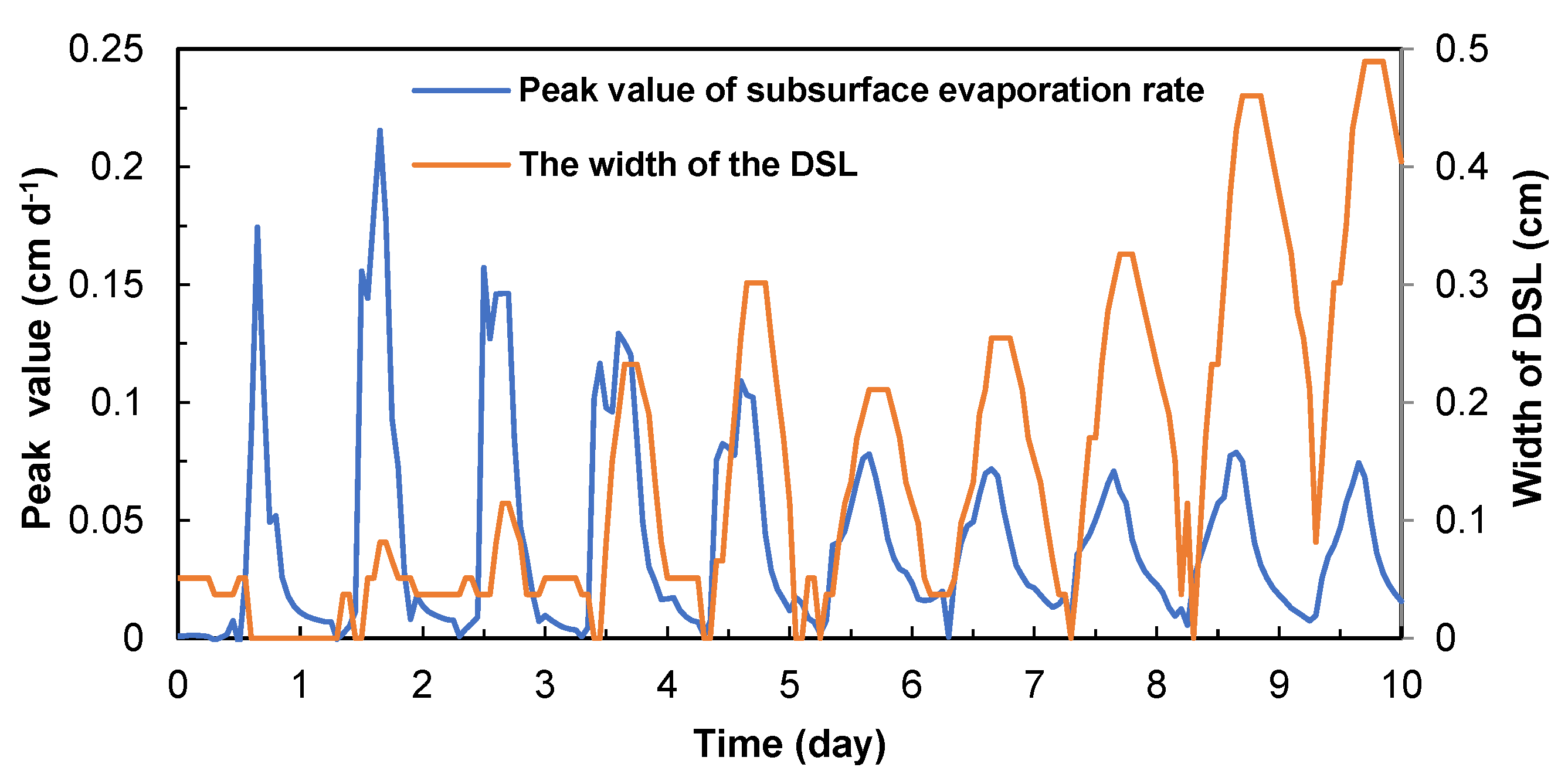
3.4. Evaporation Zone Dynamics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shukla, J.; Mintz, Y. Influence of land-surface evapotranspiration on the Earth’s climate. Science 1982, 215, 1498–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Ingram, W.J. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature 2002, 419, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiotis, A.G.; Tsimpanogiannis, I.N.; Stubos, A.K.; Yortsos, Y.C. Pore-network study of the characteristic periods in the drying of porous materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, P.; Assouline, S.; Or, D. Characteristic lengths affecting evaporative drying of porous media. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 77, 056309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Water and Heat Transport in Shallow Subsurface Soil and Across the Soil-Air Interface: Simulation, Experiments and Parameterization. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, E.A. Some factors affecting the evaporation of water from soil. J. Agric. Sci. 1923, 13, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvucci, G.D. Soil and moisture independent estimation of stage-two evaporation from potential evaporation and albedo or surface temperature. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviany, M.; Mittal, M. Funicular state in drying of a porous slab. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 1987, 30, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Or, D.; Lehmann, P.; Shahraeeni, E.; Shokri, N. Advances in Soil Evaporation Physics—A Review. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, vzj2012.0163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Toride, N.; Simunek, J. Water and vapor movement with condensation and evaporation in a sandy column. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.D. Dynamics of the near-surface evaporation zone and corresponding effects on the surface energy balance of a drying bare soil. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gran, M.; Carrera, J.; Olivella, S.; Saaltink, M.W. Modeling evaporation processes in a saline soil from saturation to oven dry conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2077–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Vanderborght, J.; Smits, K.M. Evaluation of model concepts to describe water transport in shallow subsurface soil and across the soil–air interface. Transp. Porous Media 2019, 128, 945–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, N.; Lehmann, P.; Vontobel, P.; Or, D. Drying front and water content dynamics during evaporation from sand delineated by neutron radiography. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W06418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, N.; Or, D. What determines drying rates at the onset of diffusion controlled stage-2 evaporation from porous media? Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W09513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deol, P.; Heitman, J.; Amoozegar, A.; Ren, T.; Horton, R. Quantifying nonisothermal subsurface soil water evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W11503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balugani, E.; Lubczynski, M.; Metselaar, K. Evaporation through a dry soil layer: Column experiments. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitman, J.L.; Horton, R.; Sauer, T.J.; Desutter, T.M. Sensible heat observations reveal soil-water evaporation dynamics. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitman, J.L.; Xiao, X.; Horton, R.; Sauer, T.J. Sensible heat measurements indicating depth and magnitude of subsurface soil water evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W00D05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Jones, S.B.; Tuller, M. Numerical evaluation of subsurface soil water evaporation derived from sensible heat balance. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W02547. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Vapor Flow Resistance of Dry Soil Layer to Soil Water Evaporation in Arid Environment: An Overview. Water 2015, 7, 4552–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.R.; De Vries, D.A. Moisture movement in porous materials under temperature gradients. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1957, 38, 222–232. [Google Scholar]
- Milly, P.C.D. Moisture and heat transport in hysteretic, inhomogeneous porous media: A matric head-based formulation and a numerical model. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, I.N.; Horton, R. Water transport in unsaturated nonisothermal salty soil: II. Theoretical development. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, I.N.; Horton, R. Simultaneous Transfer of Heat, Water, and Solute in Porous Media: I. Theoretical Development. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Simunek, J.; Mohanty, B.P. Numerical analysis of coupled water, vapor, and heat transport in the vadose zone. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 784–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekshmi, S.; Singh, D.N.; Shojaei Baghini, M. A critical review of soil moisture measurement. Measurement 2014, 54, 92–105. [Google Scholar]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.O.; Horton, R. Soil heat and water flow with a partial surface mulch. Water Resour. Res. 1987, 23, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, R.M.; Chow, F.K.; Kollet, S.J. The groundwater-land-surface-atmosphere connection: Soil moisture effects on the atmospheric boundary layer in fully-coupled simulations. Adv. Water Res. 2007, 30, 2447–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, G.; Braud, I.; Vauclin, M. Study of the mechanisms of evaporation under arid conditions using a detailed model of the soil-atmosphere continuum. Application to the EFEDA I experiment. J. Hydrol. 1997, 193, 114–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noborio, K.; McInnes, K.J.; Heilman, J.L. Two-dimensional model for water, heat, and solute transport in furrow-irrigated soil: I. Theory. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bavel, C.H.M.; Hillel, D.I. Calculating potential and actual evaporation from a bare soil surface by simulation of concurrent flow of water and heat. Agric. Meteorol. 1976, 17, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Sejna, M. The HYDRUS-1D Software Package for Simulating the Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably Saturated Media, version 3.0, HYDRUS Software Series 1; University of California Riverside: Riverside, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.; Wierenga, P.J. Estimating the soil heat flux from observations of soil temperature near the surface. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.K.; Shukla, M.K.; Mexal, J.G. Numerical Modeling of Water Fluxes in the Root Zone of a Mature Pecan Orchard. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.K.; Shukla, M.K.; Sharma, P.; Mexal, J.G. Coupled Liquid Water, Water Vapor, and Heat Transport Simulations in an Unsaturated Zone of a Sandy Loam Field. Soil Sci. 2011, 176, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, T.; Takeda, A.; Shimada, J. Evaporation beneath the soil surface: Some observational evidence and numerical experiments. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hydraulic Conductivity | Parameter | Expression/Constant |
|---|---|---|
| Effective liquid saturation Se | (θL − θr)/(θs − θr) | |
| Pore connectivity coefficient l | 0.5 | |
| Dynamic viscosity of liquid μ (m2 s−1) | exp(−6.434 − 2414/T + 667.3/T2) | |
| Gain factor GwT | 7 | |
| Surface tension of soil water γ (g s−2) | 75.6 − 0.1425 T − 2.38 × 10−4 T2 | |
| Surface tension at 25 °C γ0 (g s−2) | 71.89 | |
| Vapor diffusivity in soil D (m2 s−1) | DaΩθair | |
| Tortuosity factor in gas phase Ω | θair2/3 | |
| Vapor diffusivity in air Da (m2 s−1) | 2.12 × 10−5((T + 273.15)/273.15)2 | |
| Density of liquid water ρL (kg m−3) | 1000 − 7.3 × 10−3(T − 4)2+3.79 × 10−5(T − 4)3 | |
| Saturation vapor density ρsv (kg m−3) | 10−3 × exp(19.84 − 4975.9/(T + 273.15)) | |
| Relative humidity in soil Hr | exp(hMg/R/(T + 273.15)) | |
| Molecular weight of water M (kg mol−1) | 0.01805 | |
| Gravitation acceleration g (m s−2) | 9.81 | |
| Universal gas constant R (J mol−1 K−1) | 8.314 | |
| Enhancement factor η | 9.5 + 3θL/θs − 8.5exp(−((1 + 2.6/fc0.5)θL/θs)4) | |
| Mass fraction of clay fc | 0.03 |
| Day | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 6.5 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 9.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net radiation flux | 471.0 | 420.5 | 355.1 | 373.8 | 400.0 | 213.0 | 247.0 | 238.7 | 366.8 | 380.6 |
| Sensible heat flux | 63.9 | 44.8 | 14.8 | 63.6 | 96.5 | 40.9 | 47.0 | 46.7 | 86.4 | 109.2 |
| Latent heat flux | 340.9 | 265.6 | 118.6 | 131.0 | 97.9 | 64.9 | 49.8 | 44.7 | 61.6 | 52.3 |
| Ground heat flux | 66.2 | 110.1 | 221.7 | 179.2 | 205.6 | 107.2 | 150.2 | 147.3 | 218.8 | 219.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Han, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, L. Simulation of Diurnal Evolution of Evaporation Zone during Soil Drying after Rainfall. Water 2024, 16, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050639
Han J, Han H, Lin J, Zhang L. Simulation of Diurnal Evolution of Evaporation Zone during Soil Drying after Rainfall. Water. 2024; 16(5):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050639
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jiangbo, Hongtao Han, Jin Lin, and Lu Zhang. 2024. "Simulation of Diurnal Evolution of Evaporation Zone during Soil Drying after Rainfall" Water 16, no. 5: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050639
APA StyleHan, J., Han, H., Lin, J., & Zhang, L. (2024). Simulation of Diurnal Evolution of Evaporation Zone during Soil Drying after Rainfall. Water, 16(5), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050639







