An Optimization Study of Advanced Fenton Oxidation Methods (UV/Fenton–MW/Fenton) for Treatment of Real Epoxy Paint Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin of Epoxy Paint Wastewater (EPW) and Characteristics
2.2. Chemicals and Treatment Procedure
2.3. Box–Behnken Experimental Design
3. Results
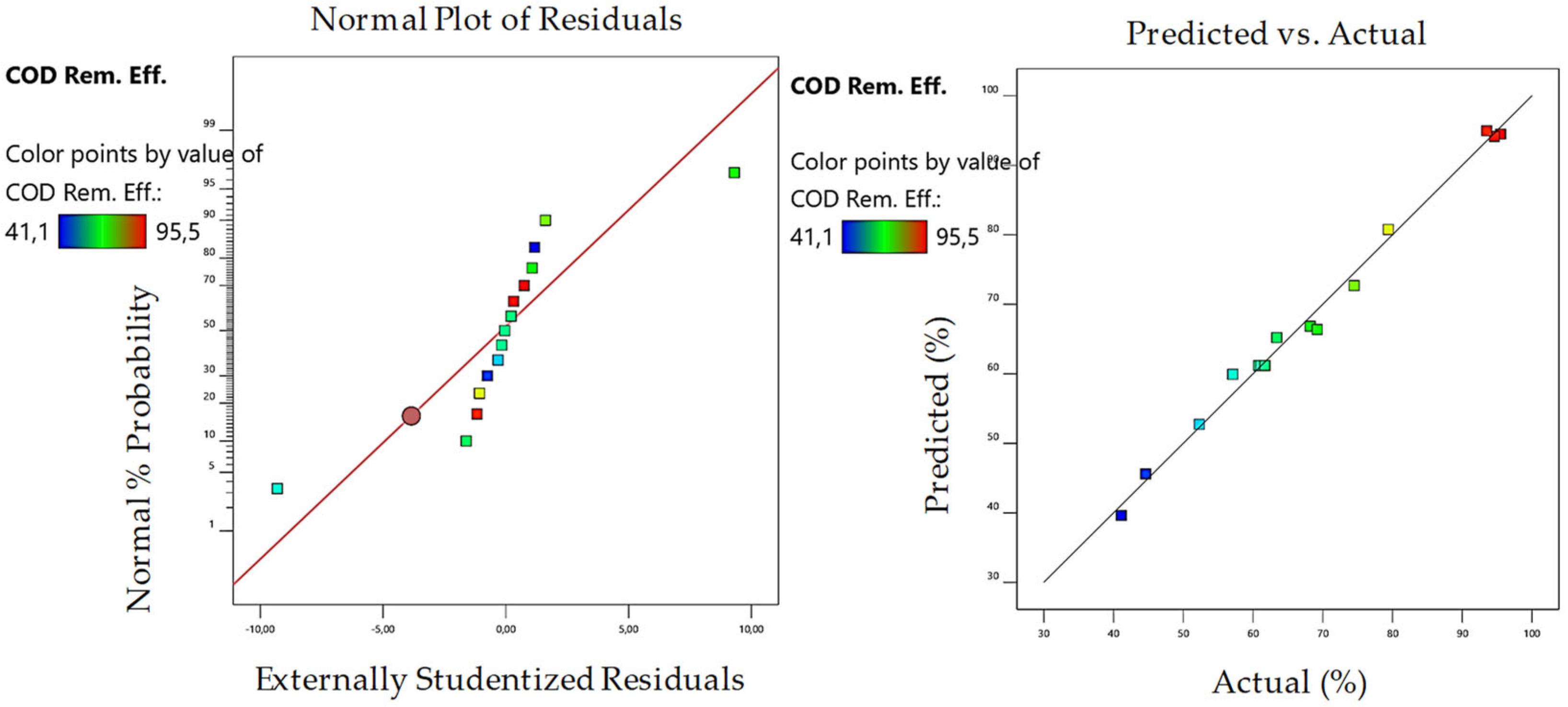
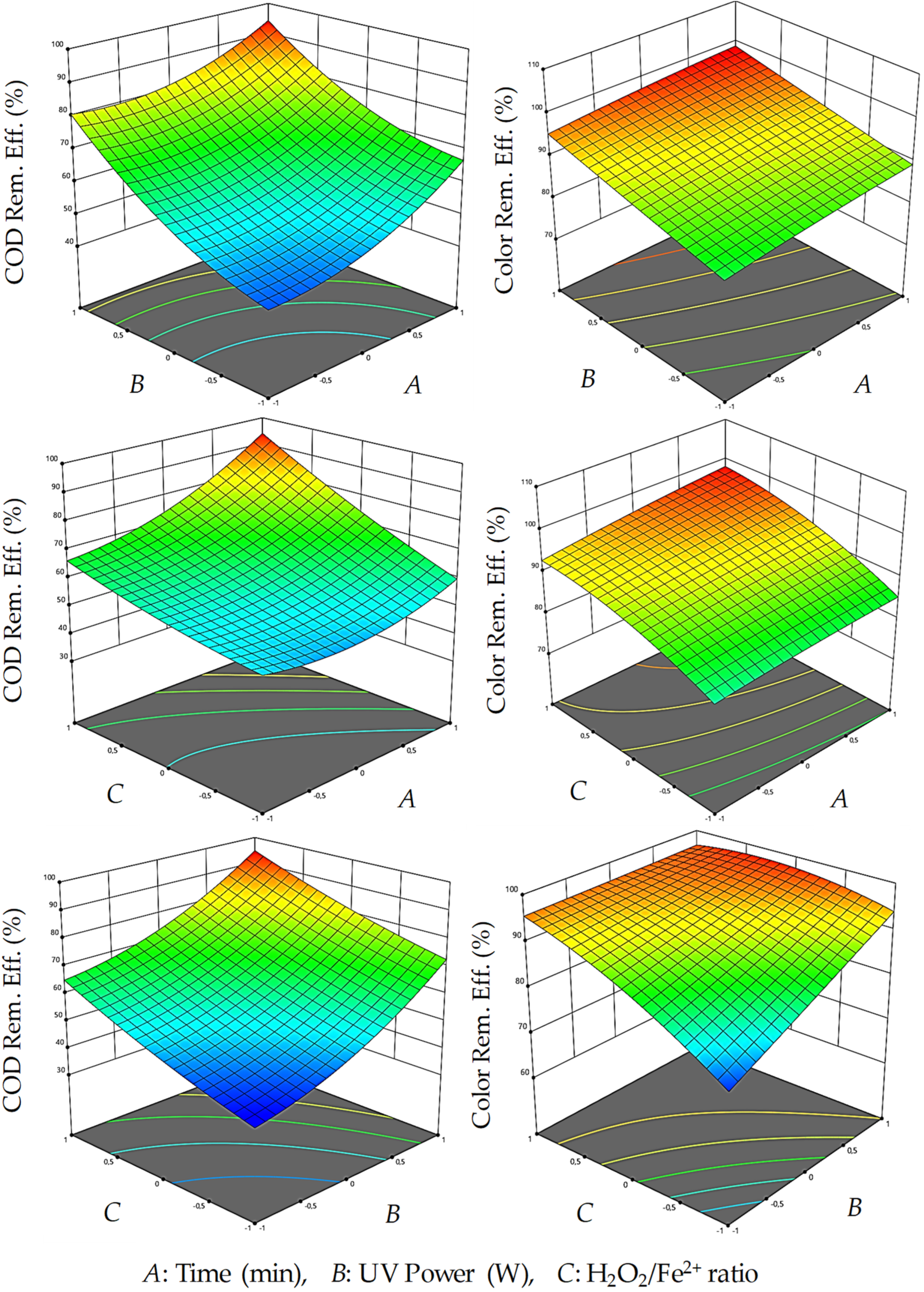
3.1. Optimization of UV/Fenton Process
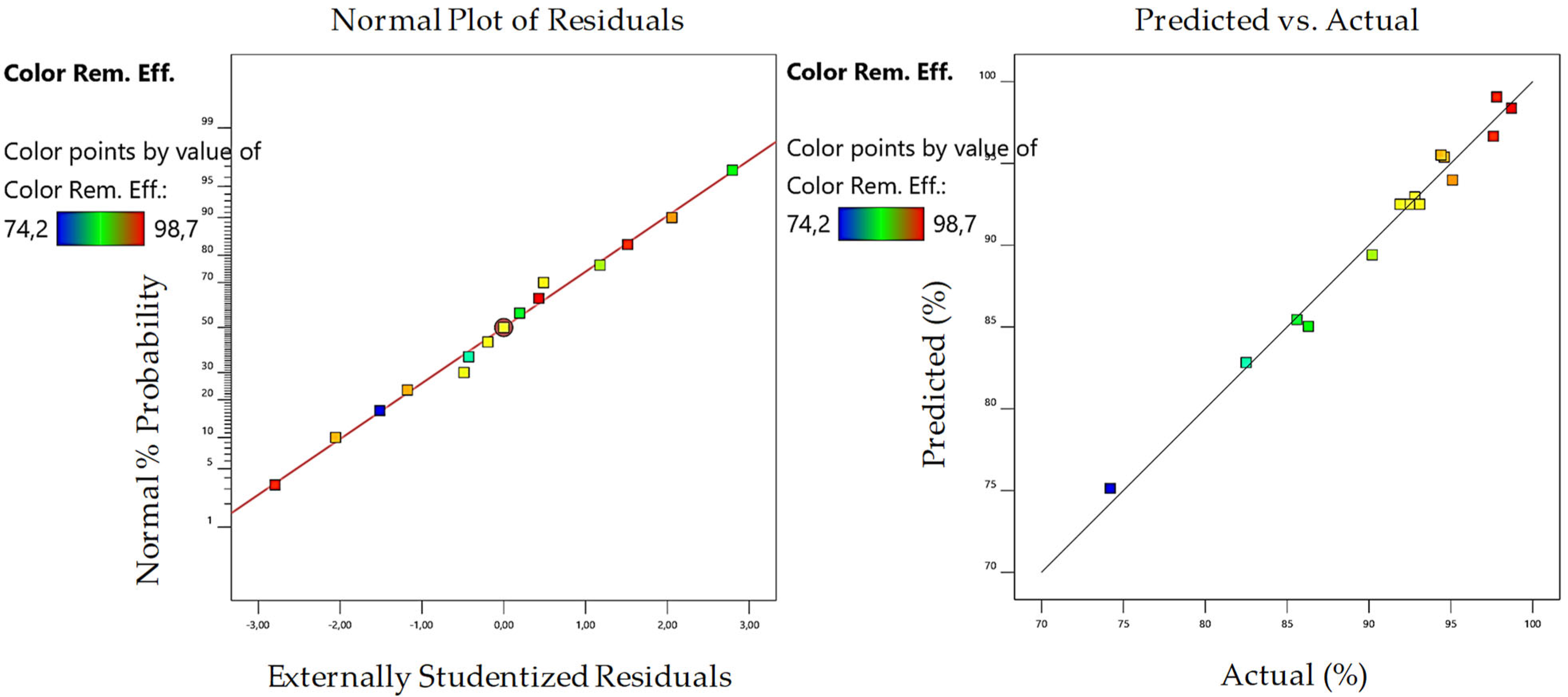
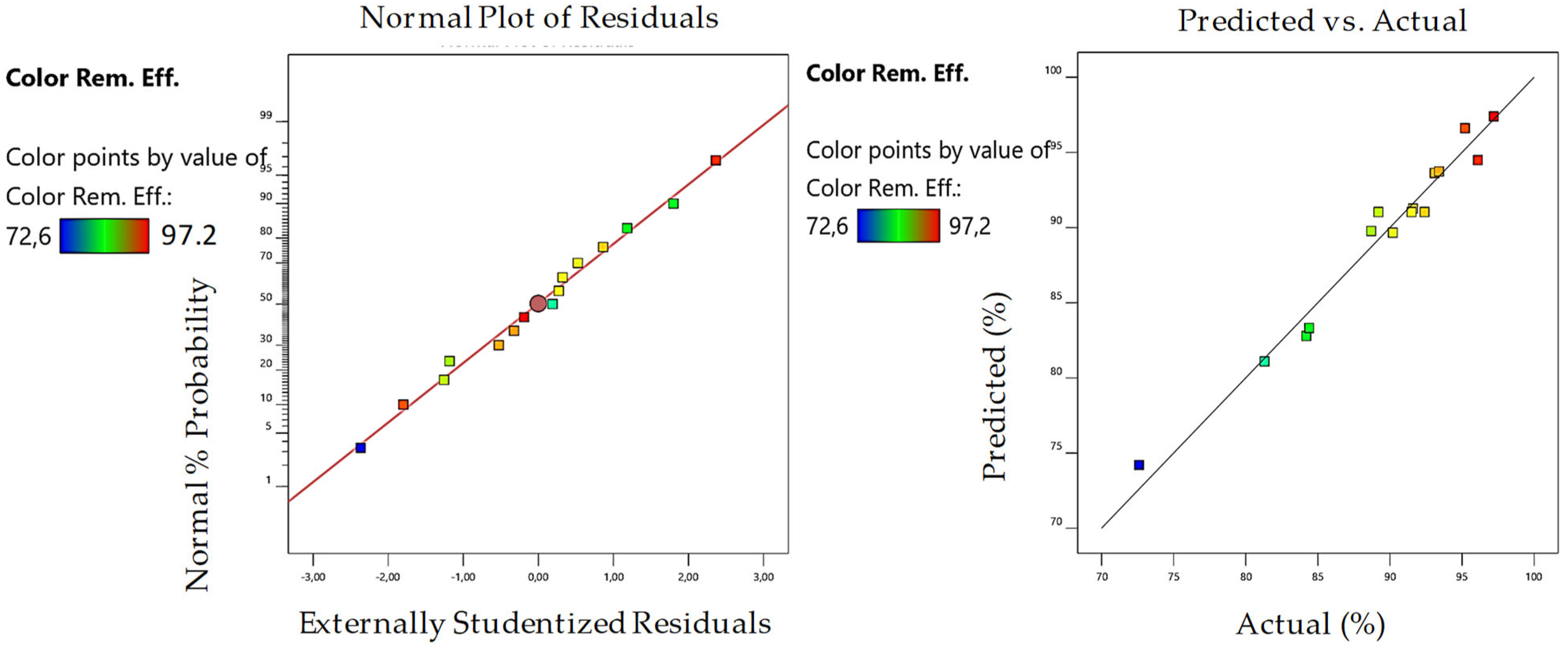
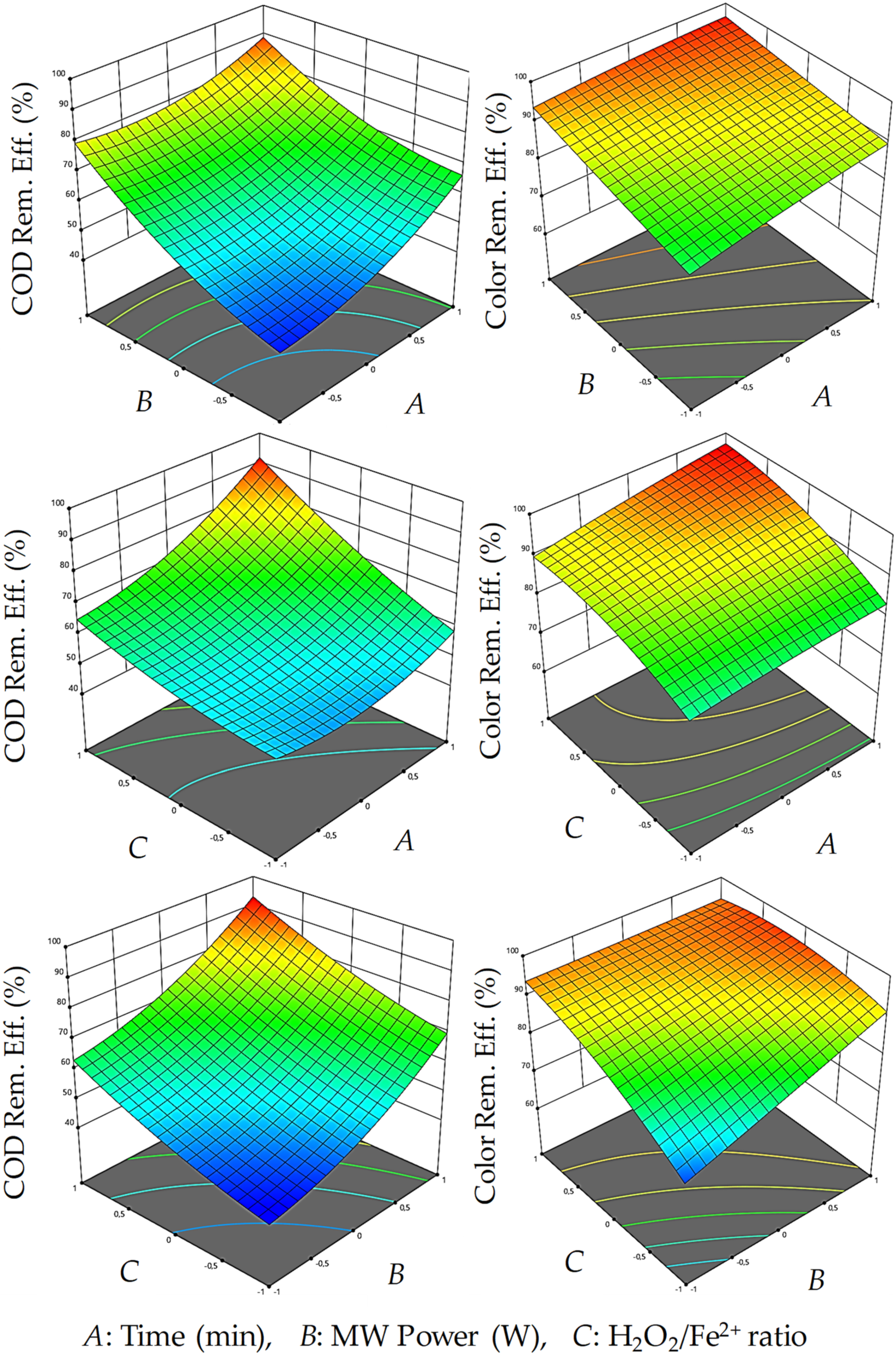
3.2. Optimization of MW/Fenton Process
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erkuş, A.; Oygun, E.; Türkmenoğlu, M.; Aldemir, A. Characterization of paint industry wastewater. Yüzüncü Yil Univ. J. Inst. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2018, 23, 308–319. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/593509 (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Bal, K.; Ünlü, K.C.; Acar, I.; Güçlü, G. Epoxy-based paints from glycolysis products of postconsumer PET bottles: Synthesis, wet paint properties and film properties. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.A. (Ed.) Epoxy Resins: Chemistry and Technology, 2nd ed.; Revised and Expanded; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, B. Wet air oxidation of epoxy acrylate monomer industrial wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adar, E.; Ilhan, F.; Aygun, A. Different methods applied to remove pollutants from real epoxy paint wastewater: Modeling using the response surface method. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 149, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbahti, B.K.; Aktas, N.; Tanyolac, A. Optimization of electrochemical treatment of industrial paint wastewater with response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viktoryová, N.; Szarka, A.; Hrouzková, S. Recent developments and emerging trends in paint industry wastewater treatment methods. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, A. Treatment of paint manufacturing wastewater by electrocoagulation. Desalination 2012, 285, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijałkowska, A.; Kurowski, R.; Rajczykowski, K.; Chmielarz, A. Advantages of continuous Fenton reaction over the traditional batch process in wastewater treatment in a single and two-step mode. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 231, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhatab, S.; El-Qanni, A.; Marei, N.N.; Hmoudah, M.; El-Hamouz, A. Sustainable competitive adsorption of methylene blue and acid red 88 from synthetic wastewater using NiO and/or MgO silicate based nanosorbcats: Experimental and computational modeling studies. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35483–35498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.F.; Chu, C.H.; Xu, W.T.; Chen, B.Z.; Ju, X.H.; Xing, W.; Sun, S.P. Amphibian-inspired amino acid ionic liquid functionalized nanofiltration membranes with high water permeability and ion selectivity for pigment wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 586, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, S.A.; Murshed, M.F.; Md Akil, H.; Ismail, N.; Md Rasib, S.Z.; Al-Gheethi, A.A.S. The application of modified natural polymers in toxicant dye compounds wastewater: A review. Water 2020, 12, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscanesi, M.; Russo, V.; Medici, A.; Giarra, A.; Hmoudah, M.; Di Serio, M.; Trifuoggi, M. Heterogeneous photodegradation for the abatement of recalcitrant COD in synthetic tanning wastewater. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hadary, E.H.A.; El-Feky, H.H.; El-Qanni, A.; Nassar, I.M.; Nassar, M.Y. CdO nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye in aqueous media. Asian J. Chem. Sci. 2023, 13, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consejo, C.; Ormad, M.P.; Sarasa, J.; Ovelleiro, J.L. Treatment of wastewater coming from painting processes: Application of conventional and advanced oxidation technologies. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2005, 27, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armando, P.; Lunardi, V.B.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Putro, J.N.; Santoso, S.P.; Wijaya, C.J.; Lie, J.; Irawaty, W.; Yuliana, M.; Shuwanto, H.; et al. Preparation of Fe-based MOFs composite as an adsorptive photocatalyst with enhanced photo-Fenton degradation under LED light irradiation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J. A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan-Alaton, I. A review of the effects of dye-assisting chemicals on advanced oxidation of reactive dyes in wastewater. Color. Technol. 2003, 119, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.H.; Dong, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, D.X.; Meng, D. A review on Fenton process for organic wastewater treatment based on optimization perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D.; Munoz, M.; Garcia, J.; Cirés, S.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Quesada, A.; Casas, J.A. Photo-Fenton oxidation of cylindrospermopsin at neutral pH with LEDs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 21598–21607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, R.M.R.; de Velásquez, M.T.O.; Moreno, A.D.; de la Torre, J.M. Characterisation and conditioning of Fenton sludges issued from wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E. A review on the photoelectro-Fenton process as efficient electrochemical advanced oxidation for wastewater remediation. Treatment with UV light, sunlight, and coupling with conventional and other photo-assisted advanced technologies. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palas, B.; Ersöz, G.; Atalay, S. Photo Fenton-like oxidation of Tartrazine under visible and UV light irradiation in the presence of LaCuO3 perovskite catalyst. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 111, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karale, R.S.; Manu, B.; Shrihari, S. Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation processes for degradation of 3-aminopyridine from water. APCBEE Procedia 2014, 9, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, S.A.; Um, W.; Corkhill, C.L.; Hyatt, N.C. Fenton and Fenton-like wet oxidation for degradation and destruction of organic radioactive wastes. npj Mater. Degrad. 2021, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. Advanced oxidation of phenol: A comparison between Fenton, electro-Fenton, sono-electro-Fenton and photo-electro-Fenton processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Amr, S.S.; Aziz, H.A. New treatment of stabilized leachate by ozone/Fenton in the advanced oxidation process. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basturk, E.; Karatas, M. Advanced oxidation of Reactive Blue 181 solution: A comparison between Fenton and Sono-Fenton Process. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1881–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Huang, Y.F.; Chang, P.S.; Chen, C.Y. Comparative study of oxidation of dye-Reactive Black B by different advanced oxidation processes: Fenton, electro-Fenton and photo-Fenton. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.J.; Ma, G.C.; Duan, X.J.; Zhuo, H.T.; Xu, J.B.; Chen, H. Poly(acrylic acid-butyl acrylate)-based physical hydrogel for adsorption and microwave-assisted Fenton degradation of cationic dye. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2003, 5, 6390–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.E.; Mulai, T.; Kharmawphlang, W.; Sharan, R.N.; Sahoo, M.K. The efficiency of Fenton, Fenton/MW and UV/oxidant processes in the treatment of a mixture of higher concentrations of azo dyes. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 15, 100515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabour, M.R.; Amiri, A. Comparative study of ANN and RSM for simultaneous optimization of multiple targets in Fenton treatment of landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2017, 65, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrades, F.; García-Montaño, J. Using central composite experimental design to optimize the degradation of real dye wastewater by Fenton and photo-Fenton reactions. Dyes Pigm. 2014, 100, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajo, J.; Silveira, J.E.; Pliego, G.; Zazo, J.A.; Casas, J.A. Increasing photo-Fenton process efficiency: The effect of high temperatures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 271, 118876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Shi, S.; Liu, Y. Microwave enhanced Fenton-like process for the treatment of high concentration pharmaceutical wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, I.; Pandey, R. Oxidative Degradation of Rhodamine B Dye in Wastewater Using Microwave-Assisted Fentons Reaction. In Recent Trends in Civil Engineering. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Sil, A., Kontoni, D.P.N., Pancharathi, R.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, Y. Microwave-enhanced Mn-Fenton process for the removal of BPA in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 294, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, U.; Avsar, Y.; Gonullu, M.T. Treatability of water-based paint wastewater with Fenton process in different reactor types. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vengris, T.; Binkiene, R.; Butkiene, R.; Ragauskas, R.; Stoncius, A.; Manusadzianas, L. Treatment of water-based wood paint wastewater with Fenton process. Chemija 2012, 23, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, A.D.; Franson, M.A.H.; Clesceri, L.S.; Rice, E.W.; Greenberg, A.E. (Eds.) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water & Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, A.D.; da Silva, L.F.; de Paula, H.M.; Romualdo, L.L.; Sadoyama, G.; Andrade, L.S. Combined use of coagulation (M. oleifera) and electrochemical techniques in the treatment of industrial paint wastewater for reuse and/or disposal. Water Res. 2018, 145, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldeamanuale, T.B.; Hassen, A.S. Toxicity study of heavy metals pollutants and physico-chemical characterization of effluents collected from different paint industries in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. J. Forensic Sci. Crim. Investig. 2017, 5, 555685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, Y.; Priya, L.; Sonawane, S.H.; Shyam, P. Comparative performance of Fenton and cavitation assisted Fenton techniques for effective treatment of greywater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cüce, H.; Özçelik, D. Application of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI)-based tools for modelling and enhancing sustainable optimization of the classical/photo-Fenton processes for the landfill leachate treatment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbacher, A.; von Sonntag, C.; Schmidt, T.C. Hydroxyl radical yields in the Fenton process under various pH, ligand concentrations and hydrogen peroxide/Fe(II) ratios. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, U. Investigation of Treatability of Domestic Wastewater by Fenton and Electrochemical Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Science, Department of Environmental Engineering, Yildiz Technical University, Istanbul, Turkey, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Bruns, R.E.; Ferreira, H.S.; Matos, G.D.; David, J.M.; Brandão, G.C.; da Silva, E.G.P.; Portugal, L.A.; dos Reis, P.S.; Souza, A.S.; et al. Box-Behnken design: An alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, C.; Gupta, A.K. Optimization of photocatalytic degradation of methyl blue using silver ion doped titanium dioxide by combination of experimental design and response surface approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirugnanasambandham, K.; Sivakumar, V. Microwave assisted extraction process of betalain from dragon fruit and its antioxidant activities. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2017, 16, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, J. Optimization of wheat bran acid pretreatment by response surface methodology. Chin. J. Bioprocess Eng. 2018, 16, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Yetilmezsoy, K.; Demirel, S.; Vanderbei, R.J. Response surface modeling of Pb (II) removal from aqueous solution by Pistacia vera L.: Box–Behnken experimental design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, F.; Yetilmezsoy, K.; Kabuk, A.H.; Ulucan, K.; Coskun, T.; Akoglu, B. Evaluation of operational parameters and its relation on the stoichiometry of Fenton’s oxidation to textile wastewater. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2017, 23, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydin, O.; Kurt, U.; Ilhan, F. Investigation of the synergistic effect of the Fenton process on the paint industry wastewater treatment and optimization of independent process parameters. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 386, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, N.; Sönmez, G. Removal of COD and color from textile wastewater by the Fenton and UV/H2O2 oxidation processes and optimization. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Yang, B.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.-G.; You, W.-D.; Ying, G.-G. Enhanced photo–Fenton removal efficiency with core-shell magnetic resin catalyst for textile dyeing wastewater treatment. Water 2021, 13, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumalo, S.M.; Bakare, B.F.; Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S. Application of response surface methodology on brewery wastewater treatment using chitosan as a coagulant. Water 2023, 15, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.; Lombraña, J.I.; De Luis, A.M.; Ortueta, M.; Varona, F. Microwave and Fenton’s reagent oxidation of wastewater. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2003, 1, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Shin, D.S.; Lee, J.K. Treatment of high-strength animal industrial wastewater using photo-assisted Fenton oxidation coupled to photocatalytic technology. Water 2019, 11, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messele, S.A.; Bengoa, C.; Stüber, F.E.; Giralt, J.; Fortuny, A.; Fabregat, A.; Font, J. Enhanced degradation of phenol by a Fenton-like system (Fe/EDTA/H2O2) at Circumneutral pH. Catalysts 2019, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cüce, H.; Cagcag Yolcu, O.; Aydın Temel, F. Combination of ANNs and heuristic algorithms in modelling and optimizing of Fenton processes for industrial wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 6065–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkyilmaz, M.; Kucukcongar, S. A comparison of endosulfan removal by photocatalysis process under UV-A and visible light irradiation: Optimization, degradation byproducts and reuse. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2023, 21, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Ban, Y.; Ren, B. A comparative study of UV–Fenton, UV–H2O2 and Fenton reaction treatment of landfill leachate. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, H.; Kaçar Kunukcu, Y.; Linden, K.G. Degradation of the pharmaceutical metronidazole via UV, Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.E. A full-scale biological aerated filtration system application in the treatment of paints industry wastewater. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 14159–14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutluay, G.; Babuna, F.G.; Eremektar, G.; Orhon, D. Treatability of water-based paint industry effluents. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2004, 13, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Mamadiev, M.; Yilmaz, G. Treatment and recycling facilities of highly polluted water-based paint wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 26, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucan-Altuntas, K.; Ilhan, F. Enhancing biodegradability of textile wastewater by ozonation processes: Optimization with response surface methodology. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapıcıoğlu, P. Investigation of environmental-friendly technology for a paint industry wastewater plant in Turkey. Süleyman Demirel Univ. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2018, 22, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Liu, M.; Zhang, F.G.; Li, D.; Du, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.Y. Removal of disinfection byproducts and toxicity of chlorinated water by post-treatments of ultraviolet/hydrogen peroxide and ultraviolet/peroxymonosulfate. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 352, 131563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | COD | Color | pH | Conductivity | Salinity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values/Units | 4600 ± 90 mg/L | 114 ± 4 Pt-Co | 7.5 ± 0.5 | 1810 ± 60 µS/cm | 1.11 ± 0.02% |
| Processes | Factors | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | +1 | ||
| UV/Fenton | Time (min) (A) | 20 | 40 | 60 |
| UV (W) (B) | 20 | 30 | 40 | |
| H2O2/Fe2+ (C) | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.60 | |
| MW/Fenton | Time (min) (A) | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| MW (W) × 10 (B) | 30 | 45 | 60 | |
| H2O2/Fe2+ (C) | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.60 | |
| Run | Levels | UV/Fenton COD Rem. (%) | UV/Fenton Color Rem. (%) | MW/Fenton COD Rem. (%) | MW/Fenton Color Rem. (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 74.5 | 95.1 | 71.6 | 91.6 |
| 2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 69.2 | 92.8 | 67.4 | 88.7 |
| 3 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 52.3 | 82.5 | 51.7 | 81.3 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 57.1 | 85.6 | 56.1 | 84.4 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 61.7 | 91.9 | 61 | 89.2 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 68.2 | 90.2 | 67.5 | 90.2 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 95.5 | 97.8 | 89.6 | 95.2 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 61.1 | 93.1 | 59.6 | 92.4 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60.8 | 92.5 | 58.2 | 91.5 |
| 10 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 63.4 | 94.4 | 61.4 | 93.4 |
| 11 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 79.4 | 94.6 | 78.6 | 93.1 |
| 12 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 41.1 | 74.2 | 42.2 | 72.6 |
| 13 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 94.6 | 98.7 | 92.7 | 97.2 |
| 14 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 93.5 | 97.6 | 91.6 | 96.1 |
| 15 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 44.6 | 86.3 | 42.5 | 84.2 |
| Processes/Parameters | UV/Fenton COD | UV/Fenton Color | MW/Fenton COD | MW/Fenton Color | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coded | Real | Coded | Real | Coded | Real | Coded | Real | |
| R2 | 0.9918 | 0.9841 | 0.9917 | 0.9697 | ||||
| p Value | 0.0001 | 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 0.0028 | ||||
| Time (min) (A) | 1 | 60 | 1 | 60 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 |
| UV (W) (B) | 0.9 | 38 | 0.9 | 38 | - | - | - | - |
| MW (W) (B) | - | - | - | - | 0.8 | 570 | 0.8 | 570 |
| H2O2/Fe2+ (C) | 0.4 | 0.48 | 0.4 | 0.48 | 0.8 | 0.56 | 0.8 | 0.56 |
| Model Predictions | 97.35 | 98.44 | 99.89 | 97.2 | ||||
| Experimental Results | 96.41 | 97.89 | 95.25 | 97.5 | ||||
| Wastewater | Treatment Method | COD Removal Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paint wastewater | Biological (Aerobic) | 43% | [64] |
| Epoxy paint wastewater | Chemical Coagulation | 44% | [5] |
| Epoxy paint wastewater | Electrocoagulation | 48% | [5] |
| Water-based paint wastewater | Adsorption | 62% | [65] |
| Water-based paint wastewater | Electrooxidation | 68% | [6] |
| Water-based paint wastewater | Fenton | 80% | [38] |
| Water-based paint wastewater | UV/Fenton | 81% | [66] |
| Epoxy paint wastewater | UV/Fenton MW/Fenton | 96.4% 95.3% | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balcioglu Ilhan, E.B.; Ilhan, F.; Kurt, U.; Yetilmezsoy, K. An Optimization Study of Advanced Fenton Oxidation Methods (UV/Fenton–MW/Fenton) for Treatment of Real Epoxy Paint Wastewater. Water 2024, 16, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040605
Balcioglu Ilhan EB, Ilhan F, Kurt U, Yetilmezsoy K. An Optimization Study of Advanced Fenton Oxidation Methods (UV/Fenton–MW/Fenton) for Treatment of Real Epoxy Paint Wastewater. Water. 2024; 16(4):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040605
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalcioglu Ilhan, Esra Billur, Fatih Ilhan, Ugur Kurt, and Kaan Yetilmezsoy. 2024. "An Optimization Study of Advanced Fenton Oxidation Methods (UV/Fenton–MW/Fenton) for Treatment of Real Epoxy Paint Wastewater" Water 16, no. 4: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040605
APA StyleBalcioglu Ilhan, E. B., Ilhan, F., Kurt, U., & Yetilmezsoy, K. (2024). An Optimization Study of Advanced Fenton Oxidation Methods (UV/Fenton–MW/Fenton) for Treatment of Real Epoxy Paint Wastewater. Water, 16(4), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040605







