Abstract
Prison populations are unlikely to have access to prompt, effective medical care as the general population. Therefore, vaccination and effective surveillance systems have been recommended to mitigate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) transmission in prison settings. This pilot study aimed to assess the application of wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) in a prison to act as an early warning tool for COVID-19 transmission. In this study, weekly wastewater samples (n = 21) were collected for 21 weeks from a prison facility in New Orleans, LA, USA, and analyzed for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and the results were compared with the number of confirmed cases during the same period. SARS-CoV-2 was concentrated using two methods and quantified via RT-qPCR using CDC N1 and N2 assays. Overall, SARS-CoV-2 was detected in eight samples (38%). An equal number of samples tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 using the two concentrating methods, indicating the effectiveness of both methods for building-scale WBE. Despite limited clinical testing in the studied prison facility, instances of SARS-CoV-2 detection in wastewater prior to the diagnosis of COVID-19 depict the potential use of wastewater surveillance in detecting the presence of early and averting outbreaks in asymptomatic COVID-19 patients.
1. Introduction
Despite the fact that COVID-19 is primarily transmitted via respiratory droplets, the shedding of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in the excrements of both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients [1,2] and the persistence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater [3] have led to the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater. Based on this principle, wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) has been widely implemented as a valuable tool that can complement clinical testing to estimate the number of COVID-19 cases or identify the circulating variant of SARS-CoV-2 in cities. Similarly, building-level WBE targeting congregate housing facilities can provide directions for strategic testing to identify asymptomatic patients and avert outbreaks. Previous studies have demonstrated the benefits of WBE in closed environments such as college campuses [4], long-haul transport vessels [5], nursing homes [6], hospitals [7], and schools [8]. Prisons are also often overcrowded, creating conditions that can facilitate COVID-19 transmission [9]. However, only one WBE study on SARS-CoV-2 in prisons has been reported [10] due to difficulties associated with access to prisons for researchers and the installation of sampling equipment [11].
WBE studies associated with prisons are often limited to evaluating substance use due to concerns for illicit drug and prescription abuse among prisoners [12,13]. Given that prisoners are likely to be aware of dates for routine urinalysis, a conventional approach to identifying drug abuse, resulting in biased results, WBE has been recommended as a cost-effective and highly sensitive approach to estimating substance abuse in prison facilities. In relation to COVID-19, a previous study conducted in the United States reported that the incidence rate of COVID-19 was significantly higher in the prison population compared to the general population [9]. The COVID-19 mortality rate per 100,000 persons was found to be 199.6 deaths in the prison population compared to 80.96 in the general population [14]. Although bias due to different testing rates could not be ruled out, incarcerated people are likely to have other medical conditions, making them more susceptible to severe COVID-19 illness. In addition, overcrowding, poor ventilation, and inadequate hygiene and sanitation can lead to potential infectious disease outbreaks in prisons. Prison populations are also unlikely to have access to prompt, effective medical care as the general population, and initiatives related to decarceration, vaccination, and the effective surveillance of COVID-19 have been recommended for prison facilities [14]. Based on this background, this pilot study aimed to determine SARS-CoV-2 levels in wastewater and utilize WBE as an early warning tool in prison facilities to provide information about the presence of asymptomatic COVID-19 cases before the appearance of symptoms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Collection
Wastewater originating from the prison facility in New Orleans was collected as grab samples from a wastewater tank, which collects all wastewater generated in the prison prior to treatment and drainage into sewer lines, once a week from mid-September 2020 to early March 2021, excluding the final two weeks of December (n = 21). All samples were collected in sterile bottles, transported to the laboratory in ice-filled containers, and processed within 6 h.
2.2. Virus Concentration and RNA Extraction
Two virus concentration methods, adsorption–extraction (Method A) and adsorption–elution (Method B), used in this study have been previously described in detail [15]. Briefly, both methods began with the addition of 2.5 M MgCl2 to 100 mL of wastewater sample prior to filtration through an electronegative membrane (90 mm diameter and 0.45 μm pore size; Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). In method A, nucleic acid was directly extracted from the filter. In method B, magnesium ions were first removed by the passage of 200 mL of 0.5 mM H2SO4 (pH 3.0) through the filter, and viruses were eluted with 10 mL of 1.0 mM NaOH (pH 10.8). The eluate was recovered in a tube containing 50 μL of 100 mM H2SO4 and 100 μL of 100× Tris-EDTA buffer for neutralization. It was then followed by centrifugation using a Centriprep YM-30 (Merck Millipore) containing an ultrafiltration membrane with an NMWL of 30 kDa (Merck Millipore) to obtain viral concentrates of approximately 650 μL. This viral concentrate was stored at −25 °C until RNA extraction.
2.3. RNA Extraction and Complementary DNA (cDNA) Preparation
Viral RNA was extracted from the concentrated samples and electronegative filter (200 μL) using an Allprep PowerViral DNA/RNA Kit (QIAGEN, Germantown, MD, USA) to obtain a final volume of 100 µL, according to the manufacturer’s protocol. In total, 30 μL of cDNA was prepared from 15 μL RNA using a High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The thermal conditions of the RT reaction were initial incubation at 25 °C for 10 min, followed by 37 °C for 120 min and 85 °C for 5 min to inactivate the enzyme.
2.4. RT-qPCR
RT-qPCR assays for SARS-CoV-2 were performed with BioRad CFX96 Real-Time PCR Instrument (BioRad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) using CDC N1 and N2 primers and probes. The reaction mixture (25 μL) consisted of 12.5 μL of PerfecTa qPCR ToughMix (Quantabio, Beverly, MA, USA), 0.1 μL each of 100 μM forward and reverse primers, 0.05 μL of 100 μM TaqMan probe, 2.5 μL of cDNA template, and 9.75 μL of PCR grade water. Details of PCR conditions and primer/probe information for CDC N1N2 and pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) assays were the same as described previously [7,15]. All qPCR reactions were conducted in duplicate, and the negative control comprised RNase-free water. Standard curves were generated using ten-fold serial dilutions of the gBlocks gene fragment of SARS-CoV-2 (Integrated DNA technologies, Coralville, IA, USA). Only samples with a cycle threshold value of <40 in both wells were considered positive.
2.5. Data Analysis
Deidentified COVID-19 data comprising the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases with clinical testing were kindly provided by the prison facility. All data were recorded in Microsoft Office Excel 2019 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA), and the average concentration was calculated in the sample sets where SARS-CoV-2 was detected by both assays.
3. Results and Discussion
In this study, a total of eight (38%) samples tested positive for the SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Comparisons between the two virus concentration methods revealed that seven (33%) samples tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 using both methods (Table 1). Among the samples concentrated with method A, four (19%) were positive when using the CDC N1 assay compared to five (23.8%) when using the CDC N2 assay. Similarly, six (28.6%) and four (19%) samples concentrated with method B were positive when tested using CDC N1 and N2, respectively. The proper implementation of WBE requires stringent virus concentration methods [16], and our findings suggest the effectiveness of the virus concentration method used in this study in testing SARS-CoV-2. Over the course of the pandemic, a significant number of studies have been carried out to assess the recovery of SARS-COV-2 using either pre-existing methods or novel virus concentration methods. The pre-existing methods were initially designed to attain the significant recovery of enteric viruses. Unlike enteric viruses, SARS-CoV-2 is an enveloped virus that is hydrophobic in nature and likely to adhere to solid particles. Therefore, a solid fraction of wastewater has also been demonstrated as an effective matrix for the recovery of SARS-CoV-2 [17]. Since high viral loads of SARS-CoV-2 (up to 1.2 × 105 per mL) in stool samples have been reported [1], one of the advantages of WBE in buildings is the lesser extent of SARS-CoV-2 decay in sewers compared to WBE studies conducted via sampling in a centralized wastewater treatment plant. This can assist in significant SARS-CoV-2 recovery using previously developed virus concentration techniques, and our results show that both methods are effective for building-level WBE. Nevertheless, other factors such as the volume of wastewater flow, number of COVID-19 cases, use of antiviral chemicals, and method of sampling can significantly impact SARS-CoV-2 detection in building-level WWS. During instances of a low number of COVID-19 cases, as seen in this study in a prison facility, grab sampling once a week is likely to be inadequate in maximizing the potential of WBE. It is generally accepted that composite sampling provides a time- or flow-integrated measure of the WW matrix, and it is better suited for WBE during periods of low disease prevalence or when conducting daily grab samplings as it provides greater sensitivity for viral detection [18]. Grab samplings can miss shedding events, and cheaper alternatives to autosamplers such as passive samplers can also be used as a potential sampling strategy in the future [19]. Interestingly, two samples that tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 using one assay tested positive when using another assay. Since SARS-CoV-2 RNA is likely to be present in low concentrations and is prone to fragmentation, we suggest the use of multiple assays to lower false negative results and improve the accuracy of WBE studies.

Table 1.
Positive ratio and concentration of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater.
Globally, more than 40% of laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases have been shown to be asymptomatic [20], highlighting potential transmission risks in communities and adding value to WBE. It is worth mentioning that institutional-scale WBE has generally been limited to universities after WBE detected SARS-CoV-2 in dormitory effluents, leading to the detection of two asymptomatic infected students [4]. This is in part due to the low adherence to social distancing measures by students and the high accuracy of WBE in predicting COVID-19 infection in residents at the building level [21]. The close monitoring of infection trends in communities via WBE has shown WBE to provide a lead time of 2–4 days in detecting variants of SARS-CoV-2 and surges in clinical cases and hospitalizations in Canada during a period of relatively higher testing intensity [22]. This finding was aided by the normalization of SARS-CoV-2 with PMMoV concentration. Normalization strategies, such as normalization with human fecal markers, can nullify the effect of unusual dilution events and improve the accuracy of WBE. The concentration of PMMoV in the wastewater of the prison ranged from 2.4 to 4.8 and 2.5 to 5.0 log10 copies/L using methods A and B, respectively. Figure 1 shows the number of new COVID-19 cases and PMMoV-normalized SARS-CoV-2 concentration in wastewater. Due to limited clinical and wastewater testing in the studied prison facility, we did not perform a correlation analysis between the number of COVID-19 cases and wastewater concentration of SARS-CoV-2. However, a WBE study conducted in UK prisons has reported a significant correlation between COVID-19 case numbers in prisons and the concentration of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater [23]. Furthermore, instances of SARS-CoV-2 detection in wastewater before, during, and after confirmation of the presence of a COVID-19 patient (during February 2021 in Figure 1) depict the potential use of WBE as an effective surveillance tool for identifying COVID-19 outbreaks and preventing further transmission of COVID-19. Recently, a study seeking the perspectives of prisoners during the COVID-19 pandemic also reported that most prisoners accepted integrating WBE to identify the COVID-19 outbreak rather than solely relying on clinical testing [24]. Taken altogether, we advocate the use of WBE to complement clinical surveillance in order to identify COVID-19 outbreaks in prisons.
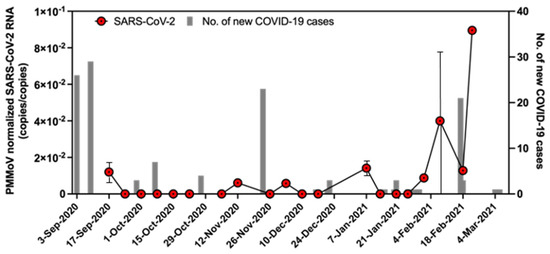
Figure 1.
Number of daily new cases in the prison facility and PMMoV-normalized SARS-CoV-2 concentrations in wastewater.
As demonstrated in Figure 1, SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected in wastewater, although there were no new cases of COVID-19 identified in the facility. This can be attributed to the continued shedding of SARS-CoV-2 by previously diagnosed or asymptomatic patients of COVID-19 and/or the persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in sewer lines. To minimize health risks associated with the handling of raw wastewater, one of the techniques adopted widely in water microbiology laboratories to inactivate pathogens involves preheating wastewater at 60 °C for 1 h. However, we did not preheat the samples used in our study to reduce the heat inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. As different variants of SARS-CoV-2 with high transmissibility continue to emerge, we recommend preheating samples to inactivate pathogens prior to sample processing if the significant loss of SARS-CoV-2 RNA due to the pasteurization of wastewater samples is not observed.
In conclusion, this study suggests both methods used in this study as suitable virus concentration methods for SARS-CoV-2 and suggests the use of multiple assays to successfully implement WBE at the building scale. Despite limited testing in prison settings and weekly wastewater samplings, our study highlights the potential of WBE as a complementary method for the surveillance of COVID-19 in vulnerable prison settings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, formal analysis, supervision, and project administration writing—original draft preparation, S.P.S.; writing—review and editing, S.S.; formal analysis, writing—original draft, formal analysis, and visualization, O.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by internal funding from the School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, Tulane University.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, P.; Poon, L.L.M.; Wang, Q. Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Tong, Z.; Wang, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, J.; Wu, W.; Yuan, C.; Yu, M.; Li, P.; et al. Detection of novel coronavirus by RT-PCR in stool specimen from asymptomatic child, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 26, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Bertsch, P.M.; Bibby, K.; Haramoto, E.; Hewitt, J.; Huygens, F.; Gyawali, P.; Korajkic, A.; Riddell, S.; Sherchan, S.P.; et al. Decay of SARS-CoV-2 and surrogate murine hepatitis virus RNA in untreated wastewater to inform application in wastewater-based epidemiology. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancourt, W.Q.; Schmitz, B.W.; Innes, G.K.; Prasek, S.M.; Pogreba Brown, K.M.; Stark, E.R.; Foster, A.R.; Sprissler, R.S.; Harris, D.T.; Sherchan, S.P.; et al. COVID-19 containment on a college campus via wastewater-based epidemiology, targeted clinical testing and an intervention. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 779, 146408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Bertsch, P.M.; Angel, N.; Bibby, K.; Bivins, A.; Dierens, L.; Edson, J.; Ehret, J.; Gyawali, P.; Hamilton, K.A.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in commercial passenger aircraft and cruise ship wastewater: A surveillance tool for assessing the presence of COVID-19 infected travellers. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27, taaa116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, E.; Torres, I.; López-Fernández, P.Á.; Ortí, R.; Maestre, J.F.; Sánchez, G.; Navarro, D. Early detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection cases or outbreaks at nursing homes by targeted wastewater tracking. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1061–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandukar, S.; Sthapit, N.; Thakali, O.; Malla, B.; Sherchan, S.P.; Shakya, B.M.; Shrestha, L.P.; Sherchand, J.B.; Joshi, D.R.; Lama, B.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater, river water, and hospital wastewater of Nepal. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 824, 153816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Gutierrez, V.; Hassard, F.; Vu, M.; Leitao, R.; Burczynska, B.; Wildeboer, D.; Stanton, I.; Rahimzadeh, S.; Baio, G.; Garelick, H.; et al. Monitoring occurrence of SARS-CoV-2 in school populations: A wastewater-based approach. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibowitz, A.I.; Siedner, M.J.; Tsai, A.C.; Mohareb, A.M. Association Between Prison Crowding and COVID-19 Incidence Rates in Massachusetts Prisons, April 2020–January 2021. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klevens, R.M.; Young, C.C.W.; Olesen, S.W.; Osinski, A.; Church, D.; Muten, J.; Chou, L.; Segal, T.; Cranston, K. Evaluation of wastewater surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 in Massachusetts correctional facilities, 2020–2022. Front. Water 2023, 5, 1083316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassard, F.; Smith, T.R.; Boehm, A.B.; Nolan, S.; O’Mara, O.; Di Cesare, M.; Graham, D. Wastewater surveillance for rapid identification of infectious diseases in prisons. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e556–e557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postigo, C.; de Alda, M.L.; Barceló, D. Evaluation of drugs of abuse use and trends in a prison through wastewater analysis. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, A.J.; Banta-Green, C.J.; Ort, C.; Robel, A.E.; Field, J. Wastewater testing compared with random urinalyses for the surveillance of illicit drug use in prisons. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2016, 35, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, N.; Ward, J.A.; Parish, K.; Saloner, B.; Dolovich, S. COVID-19 Incidence and Mortality in Federal and State Prisons Compared with the US Population, April 5, 2020, to April 3, 2021. JAMA 2021, 326, 1865–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherchan, S.P.; Shahin, S.; Patel, J.; Ward, L.M.; Tandukar, S.; Uprety, S.; Schmitz, B.W.; Ahmed, W.; Simpson, S.; Gyawali, P. Occurrence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Six Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants at the Early Stage of COVID-19 Pandemic in The United States. Pathogens 2021, 10, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, M.; Ahmed, W.; Bibby, K.; Carducci, A.; Gerba, C.P.; Hamilton, K.A.; Haramoto, E.; Rose, J.B. SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater: State of the knowledge and research needs. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 739, 139076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peccia, J.; Zulli, A.; Brackney, D.E.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Kaplan, E.H.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Ko, A.I.; Malik, A.A.; Wang, D.; Wang, M.; et al. Measurement of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater tracks community infection dynamics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrity, D.; Papp, K.; Stoker, M.; Sims, A.; Frehner, W. Early-pandemic wastewater surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Southern Nevada: Methodology, occurrence, and incidence/prevalence considerations. Water Res. X 2021, 10, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schang, C.; Crosbie, N.D.; Nolan, M.; Poon, R.; Wang, M.; Jex, A.; John, N.; Baker, L.; Scales, P.; Schmidt, J.; et al. Passive Sampling of SARS-CoV-2 for Wastewater Surveillance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10432–10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Kang, L.; Liu, R.; Jing, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, M. Global Percentage of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections Among the Tested Population and Individuals with Confirmed COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2137257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinez, A.; Hill, D.; Dandaraw, B.; Green, H.; Kilaru, P.; Middleton, F.; Run, S.; Kmush, B.L.; Larsen, D.A. High Sensitivity and Specificity of Dormitory-Level Wastewater Surveillance for COVID-19 during Fall Semester 2020 at Syracuse University, New York. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aoust, P.M.; Graber, T.E.; Mercier, E.; Montpetit, D.; Alexandrov, I.; Neault, N.; Baig, A.T.; Mayne, J.; Zhang, X.; Alain, T.; et al. Catching a resurgence: Increase in SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA identified in wastewater 48 h before COVID-19 clinical tests and 96 h before hospitalizations. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 770, 145319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobling, K.; Quintela-Baluja, M.; Hassard, F.; Adamou, P.; Blackburn, A.; Term Research Team; McIntyre-Nolan, S.; O’Mara, O.; Romalde, J.L.; Di Cesare, M.; et al. Comparison of gene targets and sampling regimes for SARS-CoV-2 quantification for wastewater epidemiology in UK prisons. J. Water Health 2024, 22, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riback, L.R.; Dickson, P.; Ralph, K.; Saber, L.B.; Devine, R.; Pett, L.A.; Clausen, A.J.; Pluznik, J.A.; Bowden, C.J.; Sarrett, J.C.; et al. Coping with COVID in corrections: A qualitative study among the recently incarcerated on infection control and the acceptability of wastewater-based surveillance. Health Justice 2023, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).