The Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole via the Fe2+/Ultraviolet/Sodium Percarbonate Advanced Oxidation Process: Performance, Mechanism, and Back-Propagate–Artificial Neural Network Prediction Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
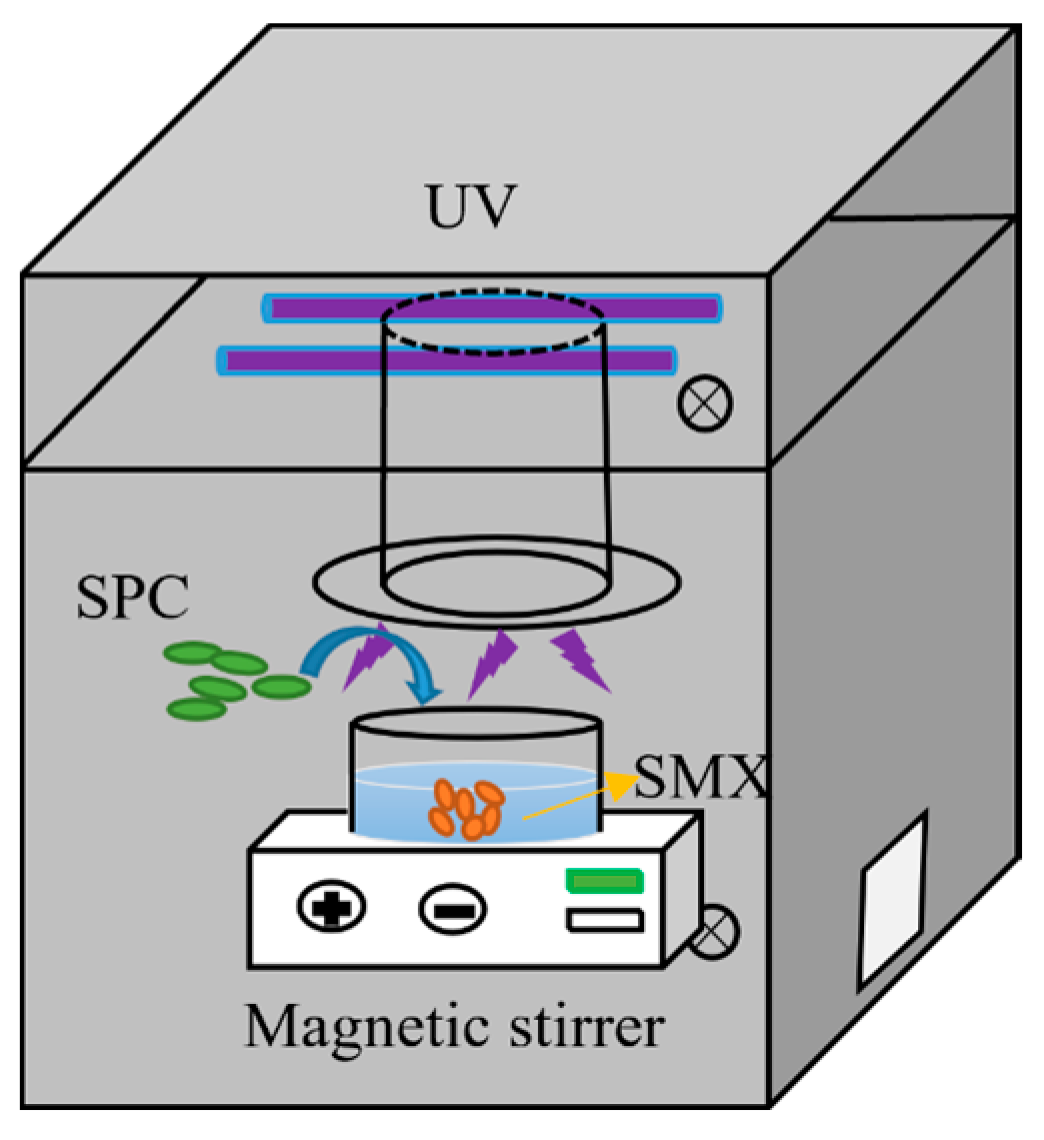
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Theoretical Calculation
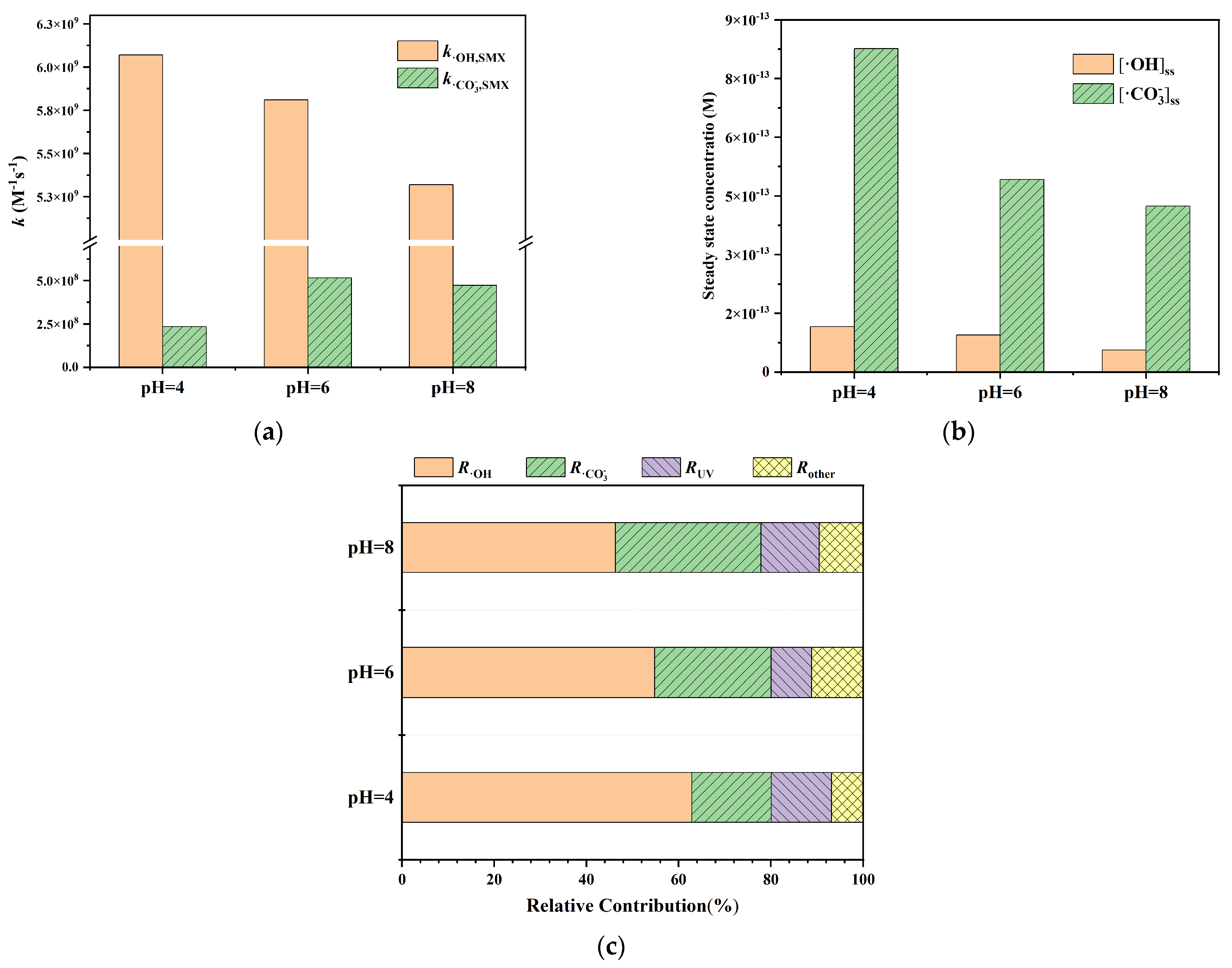
2.4.1. Rate Constants and Contribution of Free Radicals
2.4.2. Response Surface Model
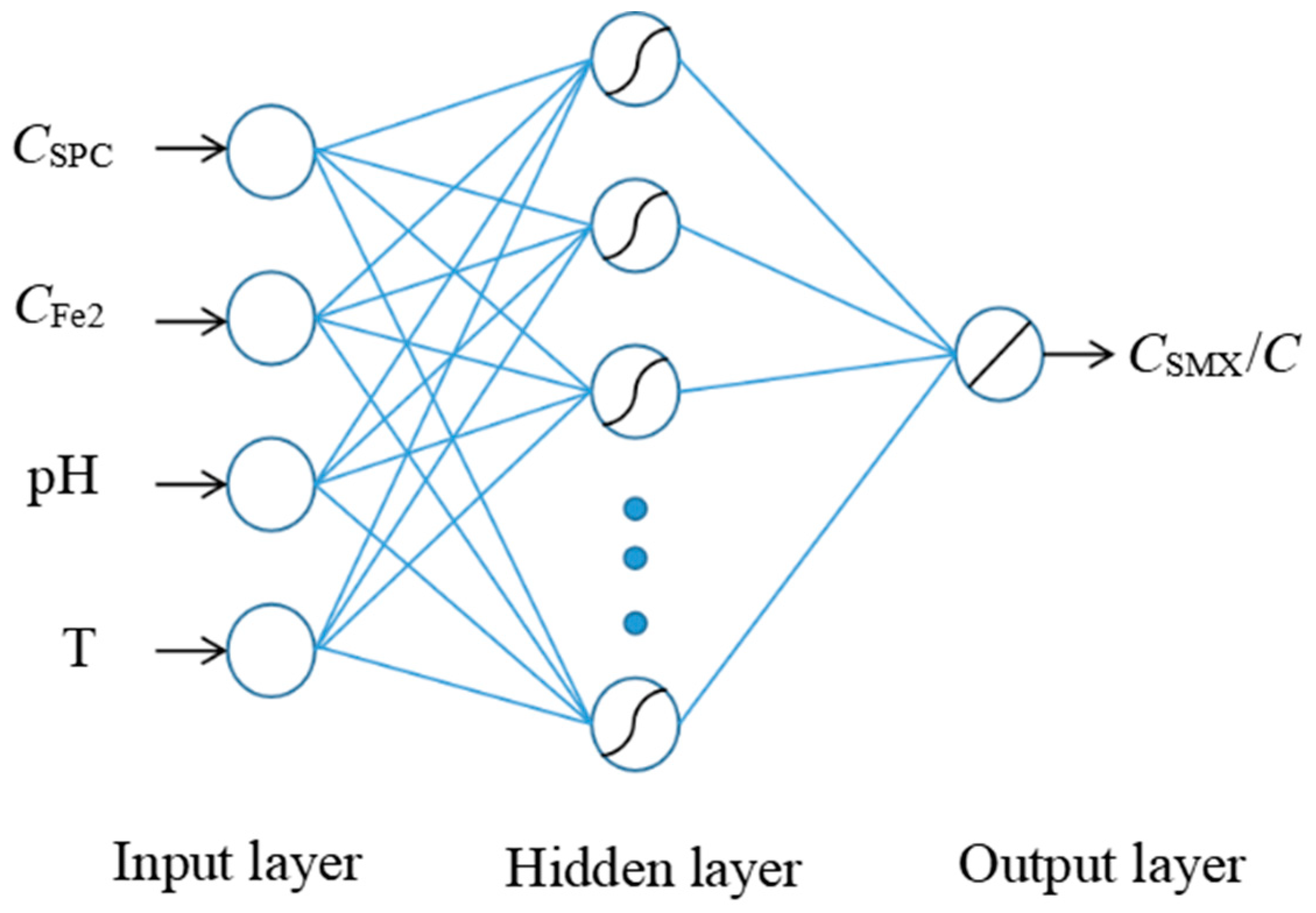
2.5. Construction of BP Neural Network Model
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Feasibility and Mechanism of SMX Degradation Enhanced via Fe2+/UV/SPC System
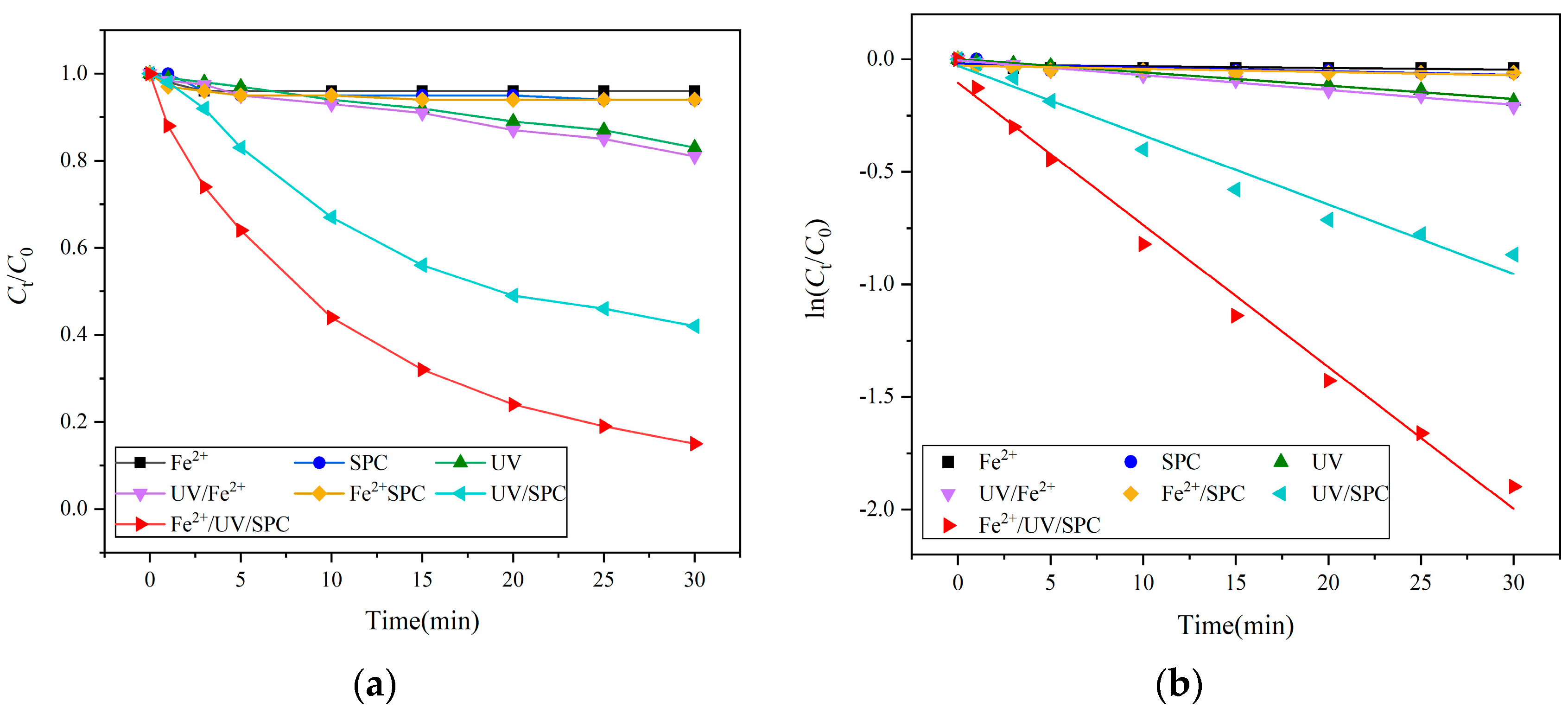
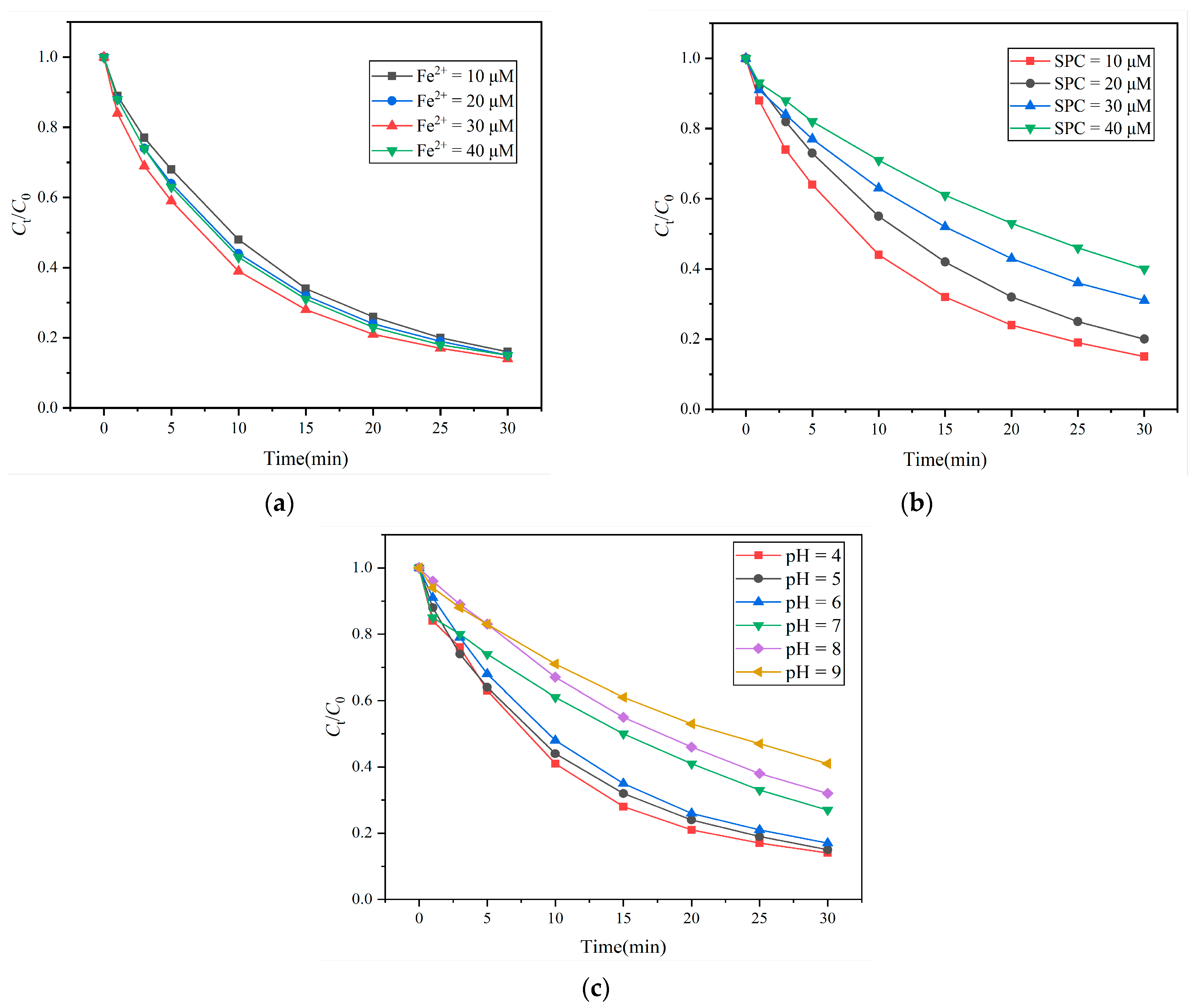
3.1.1. Degradation Efficiency of Fe2+/UV/SPC System
3.1.2. Optimization Analysis of Fe2+/UV/SPC System
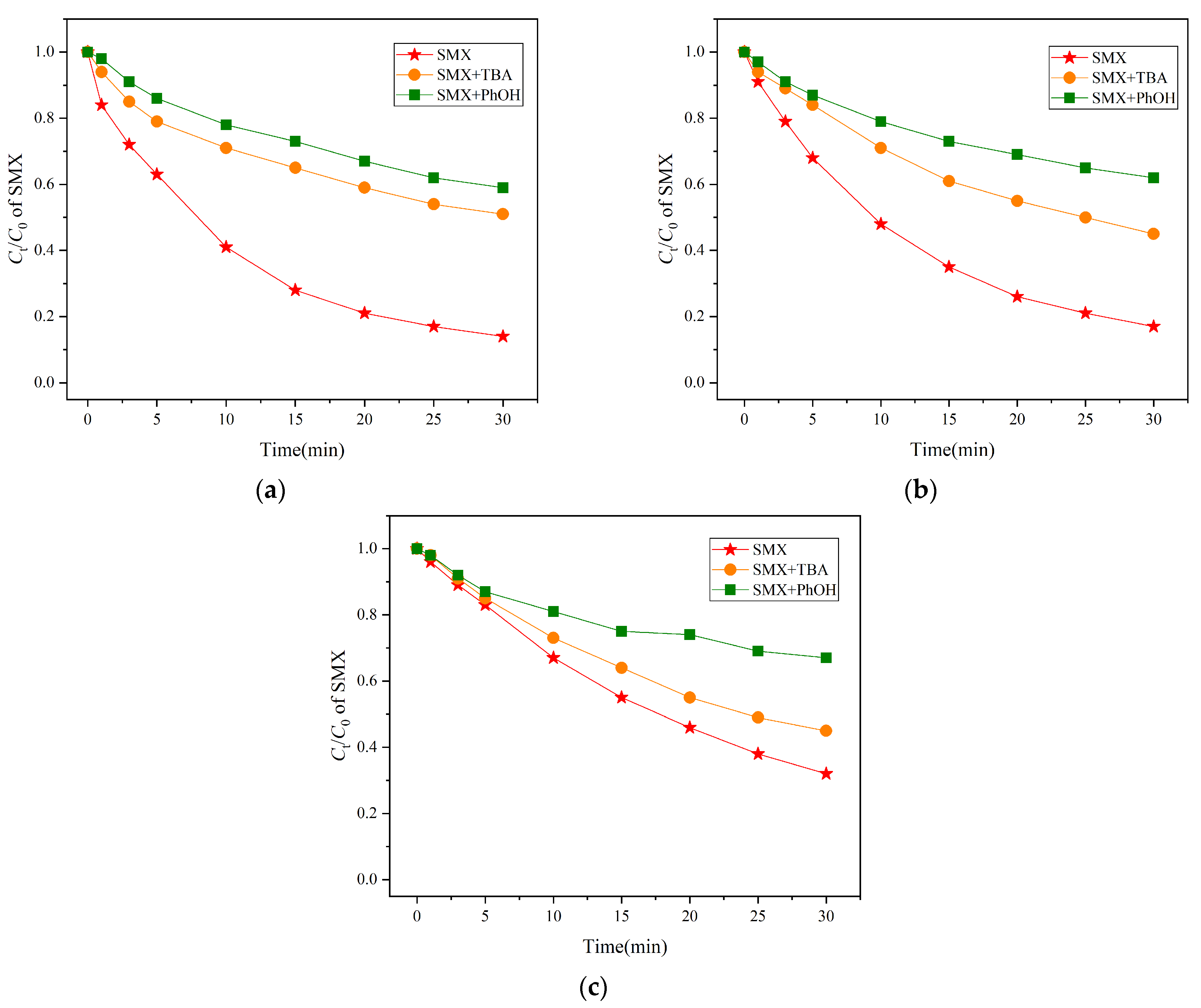
3.1.3. Degradation Mechanism of SMX via Fe2+/UV/SPC System
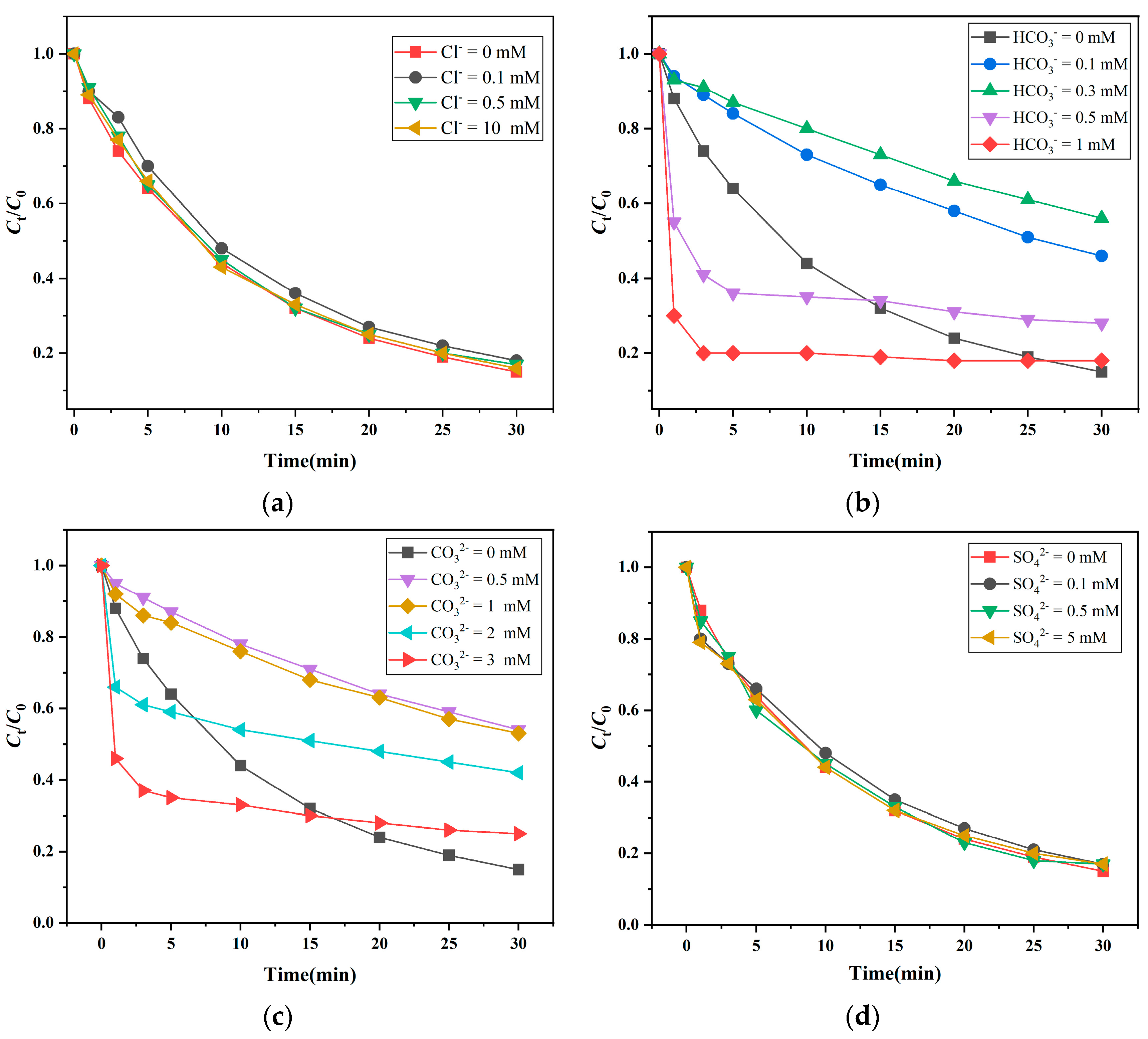
3.1.4. Influence of Anions on the SMX Degradation via Fe2+/UV/SPC System
3.2. Predictions Models for the SMX Degradation via Fe2+/UV/SPC System
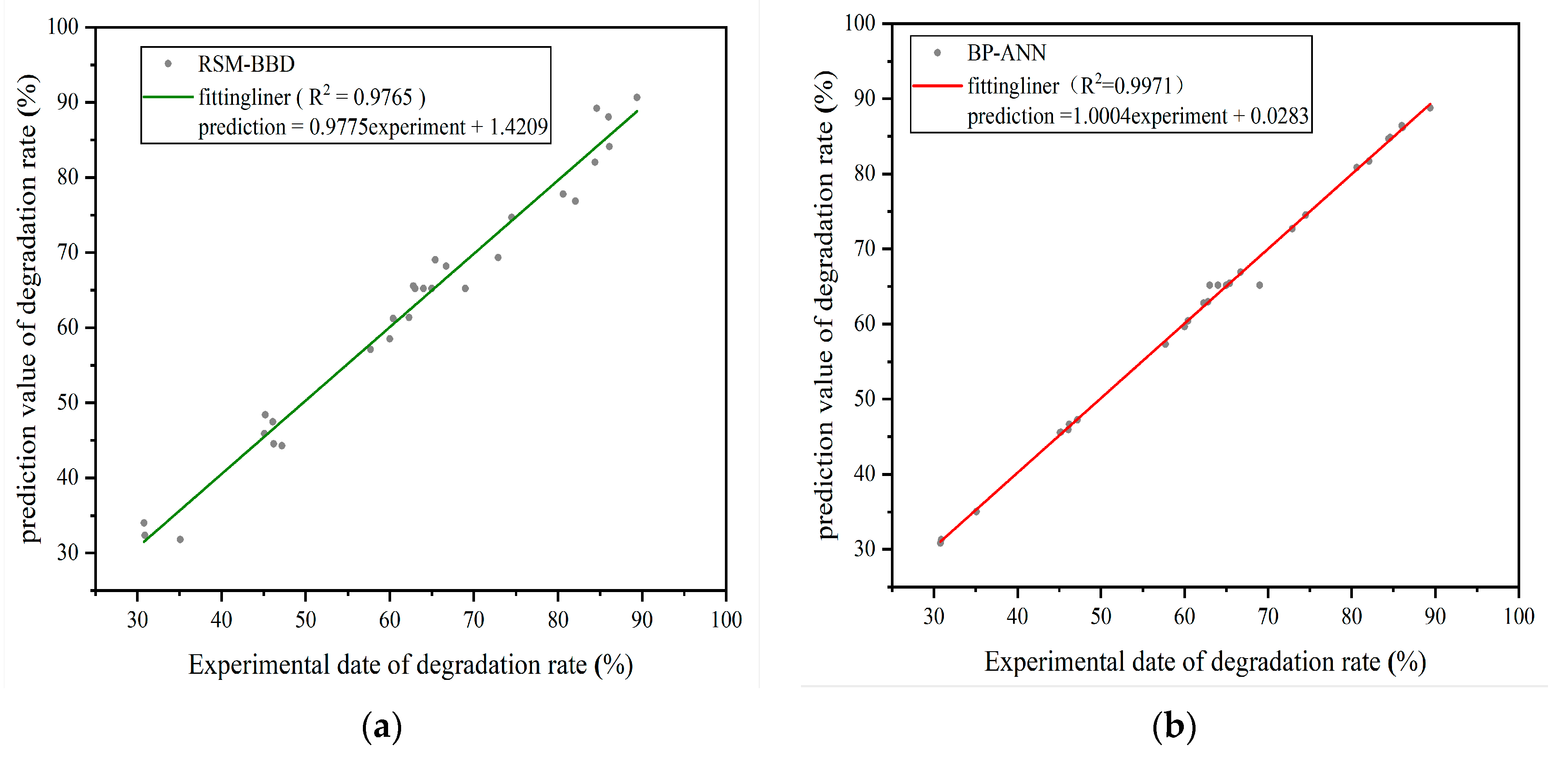
3.2.1. Evaluation of RSM-BBD Model
3.2.2. Evaluation of BP-ANN Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y.; Nan, J.; Ma, J.; Nagarajan, D.; Chang, J.S. Antibiotics degradation by advanced oxidation process (AOPs): Recent advances in ecotoxicity and antibiotic-resistance genes induction of degradation products. Chemosphere 2022, 311, 136977. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Juan, P.P.L.; Elisa, D.M.; André, A. Characteristics and ways of treating cosmetic wastewater generated by Brazilian industries: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 168, 601–612. [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran, J.; Karthikeyan, B.S.; Jost, J.; Samal, A. An atlas of fragrance chemicals in children’s products. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corbel, V.; Stankiewicz, M.; Pennetier, C.; Fournier, D.; Stojan, J.; Girard, E.; Dimitrov, M.; Molgó, J.; Hougard, J.-M.; Lapied, B. Evidence for inhibition of cholinesterases in insect and mammalian nervous systems by the insect repellent deet. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, Q.; Cao, X.; Lu, S.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, G. Occurrence, sources and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the groundwater: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2015, 1, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Guo, Y.; Lu, S.; Yan, P.; Sui, Q. Recent advances in pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the surface water and sediments in China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esplugas, S.; Bila, D.M.; Krause, L.G.; Dezotti, M. Ozonation and advanced oxidation technologies to remove endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in water effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 631–642. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, W.; Adamek, E.; Ziemiańska, J.; Sobczak, A. Effects of the presence of sulfonamides in the environment and their influence on human health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aukidy, M.; Verlicchi, P.; Jelic, A.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelò, D. Monitoring release of pharmaceutical compounds: Occurrence and environmental risk assessment of two WWTP effluents and their receiving bodies in the Po Valley Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Shi, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence, distribution and bioaccumulation of antibiotics in the Haihe River in China. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajard, L.; Adamovsky, O.; Audouze, K.; Baken, K.; Barouki, R.; Beltman, J.B.; Beronius, A.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C.; Cano-Sancho, G.; de Baat, M.L.; et al. Application of AOPs to assist regulatory assessment of chemical risks Case studies, needs and recommendations. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singa, P.K.; Isa, M.H.; Sivaprakash, B.; Ho, Y.C.; Lim, J.W.; Rajamohan, N. PAHs remediation from hazardous waste landfill leachate using Fenton, photo—Fenton and electro—Fenton oxidation processes—Performance evaluation under optimized conditions using RSM and ANN. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116191. [Google Scholar]
- Lojo-López, M.; Andrades, J.A.; Egea-Corbacho, A. Degradation of simazine by photolysis of hydrogen peroxide Fenton and photo-Fenton under darkness, sunlight and UV light. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keisuke, I.; Mohamed, G.E.D. Aqueous pesticide degradation by hydrogen peroxide/ultraviolet irradiation and Fenton-type advanced oxidation processes: A review. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 5, 81–135. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Lian, J.; Ren, Z.; Hou, C.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Luo, C.; Wu, D.; Liang, H. Coupling sodium percarbonate (SPC) oxidation and coagulation for membrane fouling mitigation in algae-laden water treatment. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, A.; Ghanbari, F. COD removal from petrochemical wastewater by UV/hydrogen peroxide, UV/persulfate and UV/percarbonate: Biodegradability improvement and cost evaluation. J. Water Reuse Desal. 2016, 6, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Sui, Q.; Lyu, S.; Hao, H.; Schröder, H.F.; Gebhardt, W. Elucidation of the oxidation mechanisms and pathways of sulfamethoxazole degradation under Fe(II) activated percarbonate treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Z.; Tan, Z.; Liang, J.; Guan, Z.; Liao, X.; Jian, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Dai, W.; Sun, S. Iron-rich sludge biochar triggers sodium percarbonate activation for robust sulfamethoxazole removal: Collaborative roles of reactive oxygen species and electron transfer. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borre, K. Neural networks and their applications. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1994, 65, 1803–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Duan, X.; O’Shea, K.; Dionysiou, D.D. Degradation and transformation of bisphenol A in UV/Sodium percarbonate: Dual role of carbonate radical anion. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Jin, X.; Li, M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, R.; Yin, A.; Shi, J.; Sun, J.; Zhu, L. Mechanism and security of UV driven sodium percarbonate for sulfamethoxazole degradation using DFT and metabolomic analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaron, M.A.; Aaron, J.J. Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: Principles and applications. A Review. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tec. 2014, 44, 2577–2641. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.R.; Li, X.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Li, H.B. Degradation of melatonin by UV, UV/H2O2, Fe2+/H2O2 and UV/Fe2+/H2O2 processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 68, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pillai, S.C. Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts: A review of recent advances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Gu, X.; Lu, S.; Miao, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Sui, Q. Benzene depletion by Fe2+-catalyzed sodium percarbonate in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, N.; Bates, G.W. The formation of Fe3+-transferrin-CO32− via the binding oxidation of Fe2+. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 12034–12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carena, L.; Vione, D.; Minella, M.; Canonica, S.; Schönenberger, U. Inhibition by phenolic antioxidants of the degradation of aromatic amines and sulfadiazine by the carbonate radical (). Water Res. 2022, 209, 117867. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, J.; Lin, T.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, F.; Chen, H. Effects of Fe(II)-activated persulfate/sodium percarbonate (PS/SPC) pretreatment on ultrafiltration membrane fouling control and mechanisms. Desalination 2023, 547, 116258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Kang, C. Hydroxyl radical dominated ibuprofen degradation by UV/percarbonate process: Response surface methodology optimization, toxicity, and cost evaluation. Chemosphere 2023, 329, 138681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, G.; Geng, J.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Ren, H. Kinetics and modeling of artificial sweeteners degradation in wastewater by the UV/persulfate process. Water Res. 2019, 150, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Burbano, A.A.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Suidan, M.T.; Richardson, T.L. Oxidation kinetics and effect of pH on the degradation of MTBE with Fenton reagent. Water Res. 2005, 39, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Xi, H.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Z. Bicarbonate-activated hydrogen peroxide and efficient decontamination of toxic sulfur mustard and nerve gas simulants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lin, L.; Lin, Z.; Guo, G.; Lin, J.M. Chemiluminescence arising from the decomposition of peroxymonocarbonate and enhanced by CdTe quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 10049–10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, N.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, J. Recent advances in bicarbonate-activated hydrogen peroxide system for water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127332. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Liu, M. Singlet oxygen generated from the decomposition of peroxymonocarbonate andits observation with chemiluminescence method. Spectrochim. Acta A 2009, 72, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Duan, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Sedlak, D.L. Impact of peroxymonocarbonate on the transformation of organic contaminants during hydrogen peroxide in situ chemical oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 781–786. [Google Scholar]
- Estahbanati, M.R.K.; Feilizadeh, M.; Iliuta, M.C. Photocatalytic valorization of glycerol to hydrogen: Optimization of operating parameters by artificial neural network. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 209, 483–492. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Tang, J.; Yuan, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, Y. Elimination of humic acid in water: Comparison of UV/PDS and UV/PMS. RSC Adv. 2020, 30, 17627–17634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.R.; Mirzajani, O. UV/peroxydisulfate oxidation of, C.I. Basic Blue 3: Modeling of key factors by artificial neural network. Desalination 2010, 251, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Z.; Shin, Y.; Yu, J.; Kim, G.; Hwang, S. Development of NOx removal process for LNG evaporation system: Comparative assessment between response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 74, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


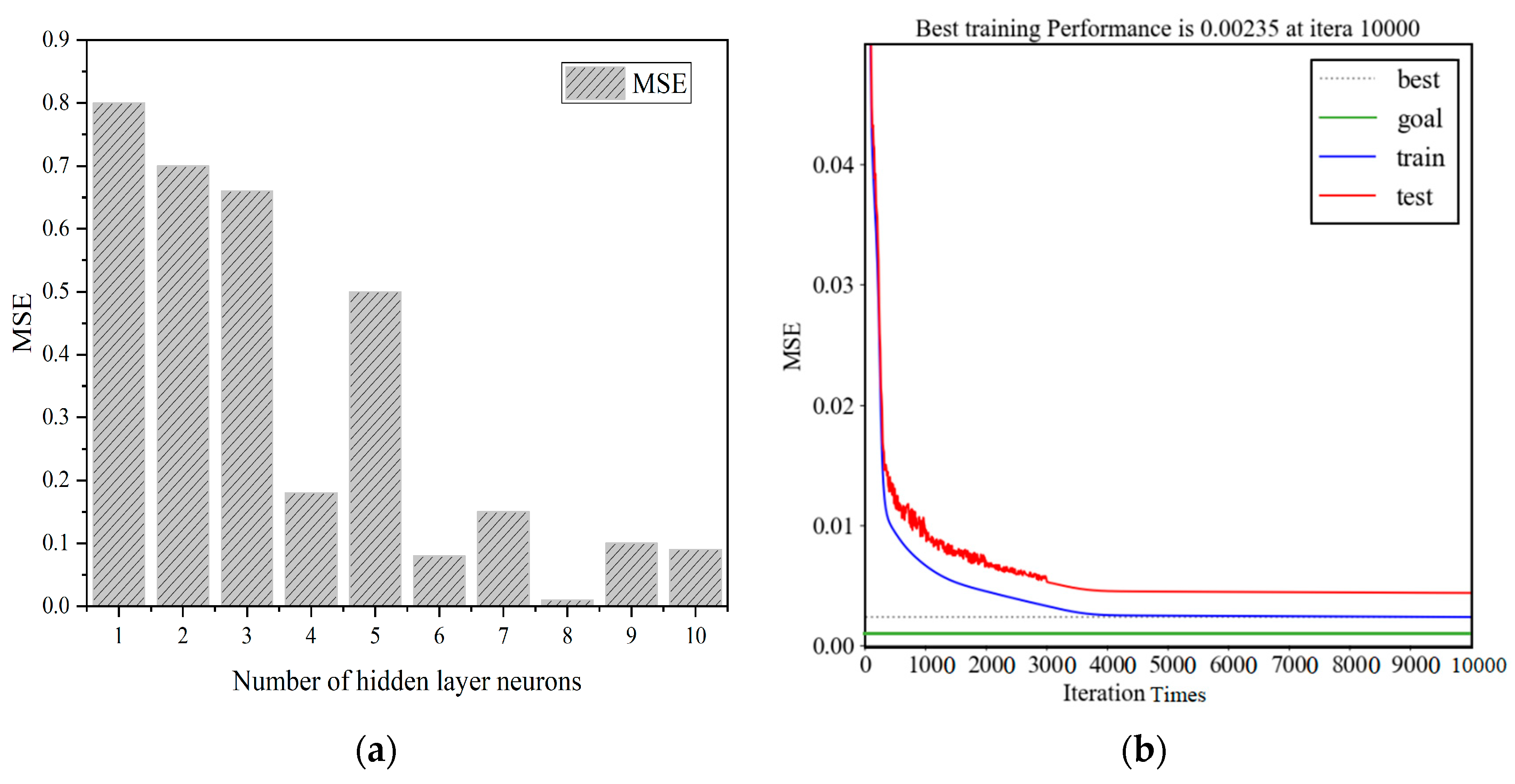
| Type | Quadratic Sum | DOF | MSE | F | p | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 7818 | 14 | 558.43 | 43.42 | <0.0001 | significant |
| (CSPC) | 667.52 | 1 | 667.52 | 51.9 | <0.0001 | significant |
| () | 548.1 | 1 | 548.1 | 42.61 | <0.0001 | significant |
| (pH) | 2700 | 1 | 2700 | 209.91 | <0.0001 | significant |
| (t) | 2494.08 | 1 | 2494.08 | 193.9 | <0.0001 | significant |
| 23.04 | 1 | 23.04 | 1.79 | 0.2021 | ||
| 97.02 | 1 | 97.02 | 7.54 | 0.0158 | significant | |
| 2.25 | 1 | 2.25 | 0.17 | 0.6821 | ||
| 56.25 | 1 | 56.25 | 4.37 | 0.0552 | ||
| 0.0025 | 1 | 0.0025 | 0.000194 | 0.9891 | ||
| 57 | 1 | 57 | 4.43 | 0.0538 | ||
| 18.56 | 1 | 18.56 | 1.44 | 0.2496 | ||
| 70.28 | 1 | 70.28 | 5.46 | 0.0348 | significant | |
| 430.41 | 1 | 430.41 | 33.46 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| 452.71 | 1 | 452.71 | 35.2 | <0.0001 | significant | |
| Residual error | 180.08 | 14 | 12.86 | |||
| Disfitting term | 159.28 | 10 | 15.93 | 3.06 | 0.146 | insignificant |
| Pure error | 20.8 | 4 | 5.2 | |||
| Sum | 7998.07 | 28 |
| Wih | Who | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hidden Layer | CSPC | pH | t | ||
| 1 | 0.443 | −0.309 | −0.434 | 0.175 | 0.500 |
| 2 | −0.020 | 0.299 | −0.805 | 0.313 | 0.913 |
| 3 | −0.103 | 0.167 | 0.019 | −1.937 | −0.576 |
| 4 | −1.334 | −0.502 | 1.900 | −0.479 | 0.590 |
| 5 | −0.658 | −1.380 | −0.208 | −0.184 | −1.080 |
| 6 | −0.009 | 0.507 | 2.594 | 0.512 | −1.780 |
| 7 | −1.053 | 0.501 | −1.101 | −0.462 | 1.376 |
| 8 | 1.547 | −0.566 | 1.893 | 1.389 | 2.401 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Ruan, C.; Xie, W.; Dai, C.; Gao, Y.; Liao, Z.; Gao, N. The Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole via the Fe2+/Ultraviolet/Sodium Percarbonate Advanced Oxidation Process: Performance, Mechanism, and Back-Propagate–Artificial Neural Network Prediction Model. Water 2024, 16, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040532
Chen J, Ruan C, Xie W, Dai C, Gao Y, Liao Z, Gao N. The Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole via the Fe2+/Ultraviolet/Sodium Percarbonate Advanced Oxidation Process: Performance, Mechanism, and Back-Propagate–Artificial Neural Network Prediction Model. Water. 2024; 16(4):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040532
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Juxiang, Chong Ruan, Wanying Xie, Caiqiong Dai, Yuqiong Gao, Zhenliang Liao, and Naiyun Gao. 2024. "The Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole via the Fe2+/Ultraviolet/Sodium Percarbonate Advanced Oxidation Process: Performance, Mechanism, and Back-Propagate–Artificial Neural Network Prediction Model" Water 16, no. 4: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040532
APA StyleChen, J., Ruan, C., Xie, W., Dai, C., Gao, Y., Liao, Z., & Gao, N. (2024). The Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole via the Fe2+/Ultraviolet/Sodium Percarbonate Advanced Oxidation Process: Performance, Mechanism, and Back-Propagate–Artificial Neural Network Prediction Model. Water, 16(4), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040532







