Abstract
Constructed wetlands are a versatile technology for various treatment approaches, especially in emerging countries. The research aims to study and optimize the hybridizing process of a vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland with adsorption technology to provide energy-efficient and sustainable removal of heavy metals and bulk organics before their discharge into water bodies or water reuse for irrigation. This study focuses on the adsorption of selected heavy metals present in sewage from Kanpur, India, a cluster of tanning industries and other relevant industrial polluters, investigating the pollutant adsorption onto activated carbon and zeolites in batch and column tests. The results of the batch tests indicated high zeolite loading rates for lead (91.6 mg/g), chromium (60.8 mg/g) and copper (47.4 mg/g). In the column tests applying different adsorbent combinations and ratios, the average removal rates were as follows: 54.6% for cadmium, 14.1% for chromium, 52.4% for copper, 2.2% for iron, 29.2% for manganese, 26.6% for nickel, 35.2% for lead and 44.6% for zinc. The column tests conducted in preparation for field testing in pilot wetlands showed that shorter retention times and background bulk organic concentrations, as well as high ammonium concentrations, negatively affected heavy metal removal by reducing the adsorption and ion exchange capacity of the adsorbents.
1. Introduction
Access to water is a basic human right and an essential factor for human health. Therefore, it must be accessible and safe for everyone, regardless of origin, status, or economic opportunities [1]. Heavy metal (HM) pollution is already detectable in about 40% of the world’s rivers and lakes [2]. Although several heavy metals are essential for living organisms in lower concentrations, they can lead to serious and chronic health issues and potentially endanger natural ecosystems due to their accumulative and non-biodegradable properties [3]. In particular, arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), mercury (Hg), nickel (Ni) and lead (Pb) are the main critical pollutants due to their presence in drinking water sources and their potential effects on the human body [4]. Iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn) can also cause issues when consumed in higher concentrations. Different approaches, such as chemical precipitation, electrochemical methods or membrane filtration, are commonly used to reduce HM contamination in wastewater, but are complex to operate, costly and energy-intensive [5]. Seeking nature-based, cost-effective, and largely self-sufficient technologies, constructed wetlands (CWs) and soil filters can make a valuable contribution to the elimination of trace compounds from municipal, industrial, and domestic wastewater.
The removal of particle-bound HMs is mainly achieved by precipitation processes, ion-exchange, sedimentation and filtration [6]. To increase the removal efficiency of dissolved HMs, three natural zeolites, and six activated carbons (ACs) are tested in this study. Natural zeolite is mainly used for the treatment of wastewater and landfill leachate. It is favourable, has a good availability, stability, chemical reactivity, reversible dehydration, and a high ion-exchange capacity making it suitable to remove cationic compounds such as HMs or ammonium (NH4+) from wastewater [7,8]. AC has a large specific surface area, is very resistant, reusable, insoluble in water and has a high adsorption potential for (in)organic compounds and colloid particles [8,9,10]. In addition, it can also indirectly promote the removal by enhancing biological processes [11]. Thus, the combination of zeolite and AC in CWs can enhance the removal or inorganic and organic compounds from wastewater. Additionally, zeolites have ion-exchanging properties that allow for the recovery of cationic compounds, such as ammonium or heavy metals that are bound to them.
Previous studies with zeolite-enhanced vertical subsurface flow CW (VSSF-CW), showed promising results but were not tested for the treatment of primary effluent. Abedi et al. [12] investigated the removal rates of 99.9% for Pb and Mn in a VSSF-pilot-scale-CW planted with Phragmites australis (common reed) and enhanced with a combination of biochar and zeolite, treating synthetic wastewater. The conventional approach with gravel, on the other hand, only achieved 52.4% for Pb, and 59.7% for Mn. Similar results for the removal of Pb were investigated by Zhou et al. [13], who also used zeolite as substrate in a VSSF-CW. Further HM removal rates were 98.2% for Cu, 75.1% for Cr, and 67% for Zn. However, as the operating time increased, Zn and Cu were desorbed and re-released again. Another VSSF-lab-scale-CW study with a vermiculite enhanced approach observed removal rates of 65.71 ± 1.34% for Cu, 64.29 ± 1.29% for Pb and 81.67 ± 3.26% for Cd during a 60 day operation [14]. In the study conducted by A et al., it was observed that heavy metals, such as Cd, Cr, Ni, Pb, and Zn, predominantly accumulated in the upper and middle layers of an unplanted constructed wetland. However, in planted CWs featuring reed and rush, the accumulation shifted primarily to the top layer. This shift indicates the passive role of plants in constructed wetlands, facilitating the removal of heavy metals [15]. Zhan et al. investigated the competitive effects of combining zeolite and AC to remove NH4+ and Zn2+. The study aimed to determine the effectiveness of this combination in removing both pollutants and focused on competitive effects. At higher Zn2+ concentrations, the combination of zeolite and AC demonstrated higher removal rates compared to lower Zn2+ concentrations, indicating superior removal potential with the combined adsorbent approach [16].
The focus of this case study is the wastewater-irrigated region of Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, specifically the Jajmau sewage treatment plant (STP). Designed based on activated sludge technology, this STP is engineered to treat 130 million litres of municipal wastewater per day (MLD). It consists of primary sedimentation tanks, aeration tanks (surface aeration), clarifiers, sludge digestion and mechanical sludge dewatering. Following secondary treatment, the effluent from the STP is blended with industrial effluent sourced from a common effluent treatment plant (CETP). This combined effluent is then transported to around 2500 ha of peri-urban agricultural land via a 4 km concrete irrigation channel, underlining the necessity for enhanced treatment methods to facilitate water reuse [17]. The treatment plant is located near a tannery cluster whose effluents are characterised by a high concentration of salts, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD), as well as various potentially toxic elements, such as HMs, especially Cr3+ [18,19].
Therefore, this study primarily examines the heavy metal and organic compound removal of a VSSF-CW in column studies, treating municipal wastewater from the STP Jajmau, impacted by unidentified discharges from tanneries. Different ratios of zeolite to AC were tested to observe changes in removal rates and determine optimal ratios for future pilot-scale water reuse applications. Preliminary batch tests were performed to identify the most effective adsorbents for the removal of HMs and bulk organics for subsequent column testing. As the pH influences the speciation of HMs and, consequently, the adsorption ability, mobility, and toxicity, the effects of different pH values on solubility was studied in batch tests with HM-spiked STP effluent. In addition, it can be determined whether retention is primarily due to precipitation or adsorptive processes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
Six different activated carbons and three zeolites were tested in batch tests, treating HM spiked STP effluent in Germany (Table 1 and Table 2). Based on these findings, two zeolites and two granulated activated carbons (GACs) were selected to conduct lab-scale column tests using filtered primary effluent from the STP Jajmau in Kanpur, India representing a wastewater with ambient HM concentrations (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn) after settling.

Table 1.
Properties of the used zeolites for batch and column tests according to the suppliers.

Table 2.
Properties of the used activated carbons for batch and column tests according to the suppliers.
2.2. Pre-Processing of Adsorbents
To yield the desired fraction of ≈375 μm, the chosen adsorbents were crushed by a swing mill (Emax, Retsch GmbH, Haan, Germany). The particle size was chosen to achieve adequate bed volumes, while preventing clogging of the column. The crushed material was then sieved using a sieve inset with the needed mesh sizes. The smallest fractions < 45 μm were kept for performing the batch tests. The fraction of ≈375 μm was washed until runoff was clear to remove the attached fine dust. The sieved materials were subsequently dried at 100 ± 2 °C for 24 h to achieve a constant weight, and finally stored in Schott bottles without additional treatment until usage (Oven: UE 500, Memmert GmbH, Schwabach, Germany). The particle size was determined by microscope (VHX 2000, Keyence, Osaka, Japan) and laser diffraction technology (Mastersizer 2000, Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK).
2.3. Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
To determine the CEC, 1 g of the natural zeolites were dried and transferred into a 250 mL, 1 M ammonium acetate. (NH4Ac) solution (EMSURE ACS, Reag. Ph. Eur., Supelco, Merck GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany). A blind approach was also conducted to determine undesired ammonium losses through stripping or sorption on the glassware. The samples were shaken for 24 h on a lab shaker (Universal Shaker SM 30, Edmund Bühler, Bodelshausen, Germany) with 180 rounds per minute (RPM) and subsequently separated by filtration with a pore size of 0.1 μm filter and analysed for desorbed alkali and alkaline earth metals using inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) (Optima 8300, PerkinElmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). To remove non-adsorbed ammonium, the zeolites were rinsed with a 70% ethanol solution until no residual ammonium was detected in the residue. The loaded zeolites were then regenerated with 1 M potassium chloride (KCl) (GPR RECTAPUR, VWR International, Radnor, PA, USA) solution. Shaking, sampling and analysis procedure were the same as described above. The resulting solution was analysed for ammonium via photometry (WTW photoLab S12, Xylem Inc., Washington, DC, USA) using cell tests (Test kits, ammonium, Spectroquant, Supelco, Merck GmbH, Germany). The cation exchange capacity indicates the quantity of cations exchanged through ammonium.
2.4. Heavy Metal Precipitation Pre-Tests
Since some heavy metals tend to precipitate even under lower pH values, precipitation batch tests were conducted using STP effluent spiked with cadmium nitrate tetrahydrate, 98.5% min (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), copper(II) nitrate trihydrate GPR RECTAPUR (VWR International, Radnor, PA, USA), chromium(III) nitrate nonahydrate, 99% (Acros Organics BV, Geel, Belgium), Nickel(II) nitrate hexahydrate, 98% (Alfa Aesar, Ward Hill, MA, USA), lead(II) nitrate AnalaR Normapur (VWR International, Radnor, PA, USA) and zinc hexahydrate, 98%, extra pure (Acros Organics BV, Geel, Belgium) (Table 3). The pH was adjusted with 1 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (VWR International, Radnor, PA, USA) and 1 M nitric acid (HNO3) (VWR International, Radnor, PA, USA) to four different values ranging from acidic to neutral (4, 5, 6, 7). The HM concentrations were set to 5 mg/L. Besides a blank sample, 250 mg of zeolite < 45 µm was added to the solution. To evaluate the results, the speciation of the HMs as a function of pH was simulated by using the software Hydra/Spana [20]. After shaking for one day on a lab shaker (Universal Shaker SM 30, Edmund Bühler, Germany) with 180 RPM, the samples were filtered with membrane syringe filters (pore size 0.45 µm). For the heavy metal analysis, the samples were directly acidified to a pH < 2 with HNO3 and stored at 4 °C until analysis using ICP-OES (Optima 8300, PerkinElmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) according to DIN EN ISO 11885:2009-09 [21]. Each experiment was executed in triplicate.

Table 3.
Parameters of HM spiked STP effluent for precipitation and adsorption batch tests.
2.5. Adsorption Batch Tests
To evaluate the most promising adsorbents for the column tests, batch tests were conducted beforehand in Germany. The adsorption capacity for heavy metals and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) of three different natural zeolites (Zeogran K 80, ZeoAqua and Carpathian Zeolite), four fresh (Filtrasorb 400, HPC Super 830. Norit GAC 830W and Norit GAC 1240W) and two reactivated ACs (Cyclecarb 401 and Cyclecarb 501) was determined using the same HM-spiked STP effluent as in the precipitation pre-tests after 24 h of shaking with 180 RPM. Adsorbent concentration was set to 50, 100, 250, 500 and 1000 mg/L, with a particle diameter of <45 µm.
Based on the results of the precipitation tests, the pH in each sample was adjusted to 4 with HNO3 to maintain the heavy metals in a dissolved state. Heavy metal analysis was conducted in the same way as the precipitation pre-tests. The catalytic oxidation method (TOC-L, Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) used for the analysis of DOC was according to DIN EN 1484:2019-04 [22].
2.6. Constructed Wetlands Column Tests
Utilizing the findings from the adsorption batch test results, zeolites Zeogran K 80 and ZeoAqua and ACs Cyclecarb 401 and HPC Super 830 were selected. To avoid clogging in the glass columns, the used primary effluent from the STP Jajmau in Kanpur, India, was pre-filtered by a hollow fibre membrane (pore size: 0.1 μm). The concentrations of the filtered primary effluent are given in Table 4. Custom-made glass columns with an inner diameter of 10 mm (Goetec-Labortechnik GmbH, Bickenbach, Germany) were filled with different adsorbents and backing support layers, consisting of two filter plates (100 μm), glass wool, and glass beads to create a proper flow regime and prevent an outwash of the adsorbents.

Table 4.
STP Jajmau primary effluent and pre filtered primary effluent parameters (March 2022).
The columns were calculated to achieve 40,800 treated bed volumes at an empty bed contact time (EBCT) of 15 min, according to the constant diffusivity model with Equation (1) [23]. The raw water was fed continuously at a flow rate of 7.48 mL/min in down-flow mode using a peristaltic pump (Masterflex L/S, Cole-Parmer, Vernon Hills, IL, USA). The experimental set-up is given in Figure 1. DOC and HM analysis were performed in the same way as batch testing, except for adding Fe and Mn to the analysed parameters using ICP-OES (iCAP PRO X Duo, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA).
where EBCTSC is the empty bed contact time in the small-scale system [min], EBCTLC is the empty bed contact time in the large-scale system [min], RSC is the adsorbent particle size for the small-scale system, RLC is the adsorbent particle size for the large-scale system, tSC the running time for the small-scale system and tLC is the running time for the large-scale system.
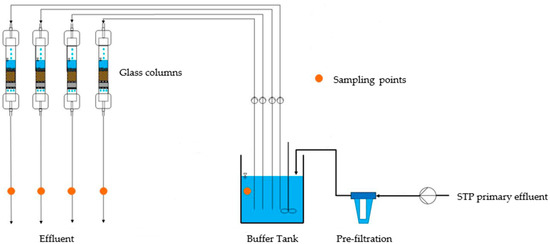
Figure 1.
Constructed wetland column test set-up for the treatment of primary effluent of the STP Jajmau in Kanpur, India.
2.7. Data Evaluation
HM capacities, indicating the sorbent’s metal content, were calculated for each sorbent in the batch experiments by analysing HM concentrations before and after the shaking time using the following Equation (2). Overall removal [%] was calculated for DOC in the batch experiments and for each column test with Equation (3):
where qe (mg/g) is the adsorbed amount of HM on the respective sorbent, Ci (mg/L) is the initial HM concentration in the solution, Ce (mg/L) is the HM equilibrium concentration in the solution after shaking, VL is the solution volume and ma (g) is the adsorbent dosage.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Zeolite Cation Exchange Capacity
Ammonium was chosen to determine the CEC, because adjusting the pH to the acidic level required to keep HMs dissolved would promote competitive interactions with H+ ions. These interactions could adversely impact the CEC. The CEC for the three different zeolites is shown in Table 5. The adsorbed ammonium amount ranged between 114–127 meq/100 g with a similar amount of desorbed alkali and alkaline earth cations, which indicates stoichiometric ion exchange. Zeogran K 80 adsorbed the highest amount of ammonium with 127.1 meq/100 g followed by ZeoAqua with 125.3 meq/100 g and Carpathian Zeolite with 114.1 meq/100 g. The elution order for Zeogran K 80 and ZeoAqua was Ca2+ > K+ > Na+ > Mg2+ and for Carpathian Zeolite Ca2+ > K+ > Mg2+ > Na+. Zeogran K 80 effectively exchanged the highest amount of ammonium for alkali and alkaline earth ions.

Table 5.
Adsorbed ammonium and exchanged cations by the tested zeolites.
A slightly higher CEC was observed by Malekian et al. [24] ranging from 140 to 165 meq/100 g for both millimetre- and nanometre-sized particles of Iranian zeolite. Wasielewski et al. [25] applied a comparable method to assess the CEC of three natural zeolites. They examined CECs ranging from 119 to 132 meq/100 g. Their approach differed in the shaking duration, lasting 30 min compared to this study’s 24 h. Nonetheless, they repeated the contact with (NH4Ac) and KCl three times using fresh solutions, potentially resulting in slightly higher outcomes.
3.2. Effects of pH on HM Precipitation
The speciation of HMs in solution depends on the pH of the solution, which strongly influences the adoption and ion exchange processes. Figure 2 shows the concentrations of dissolved HMs under the pH values 4, 5, 6 and 7 for the blank samples. The HM concentrations for all HMs decline with rising pH to varying degrees. Particularly, Cr, Cu, and Pb tend to precipitate already under mild acidic conditions. At a pH of 6, 98.0% of Cr, 89.3% of Cu and 98.3% of Pb are removed from the solution. To a lower degree, Cd (46.9% at pH 7) and Zn (73.0% at pH 7) also precipitate, while Ni showed only a reduction of 9.5% at a pH of 7. As the increase in the pH is a result of an increase in OH−-ions in the solution, the HMs predominantly co-/precipitate as metal oxides/hydroxides.
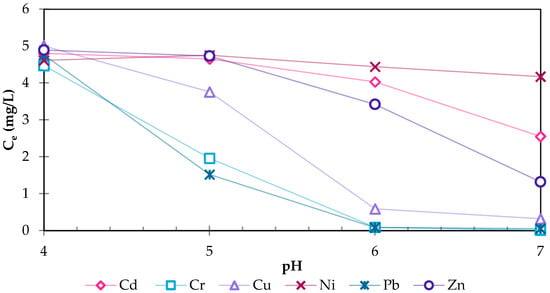
Figure 2.
Concentrations of dissolved HMs at pH 4, 5, 6, and 7 for the blank samples with an initial concentration of 5 mg/L per HM.
According to the modelling software Hydra/Spana, the water-soluble Cu2+ and copper sulphate CuSO4 react at increasing pH to form crystalline copper oxide CuO and solid brochantite Cu4[(OH)6|(SO4)]. Zn and Cr form a water-insoluble complex. According to the experimental results, the formation of zinc chromite ZnCr2O4 occurs at a pH value above 5 and not, as in the simulation, at 3.5. However, Zn and Cr did not alter into a solid complex in the same quantity. Zn remains water-soluble even at a pH value of 6 with a proportion of approximately 38%, while Cr precipitates completely. The reason for this is the zinc chromite molecule, which has twice as many Cr atoms as Zn atoms, and that Cr also precipitates as hydroxide. Pb primarily forms pyromorphite Pb5(PO4)3Cl precipitates within the pH range of 3.3 to 8.5. Beyond this range, it precipitates as hydroxide Pb(OH)2 due to the excess of OH− ions. Cd and Ni begin to precipitate as hydroxides at the pH of 8.5 and 7.5, respectively, according to the simulation. It is possible that the precipitation of Cd in the test is due to an unspecified substance in the wastewater. Except for Cd, the experimental data and the simulated HM speciation are in accordance.
The precipitation test with 250 mg/L (Figure 3) added zeolite showed similar results for Cd, Cu, Ni and Zn as they remain approximately as high as the initial concentration at a pH of 4. Cr (51.6% at pH 4) and Pb (93.7% at pH 4) concentrations on the other hand decrease under this condition, indicating an affinity of the zeolite to adsorb or exchange ions with Cr and Pb. Accordingly, the decreasing effect of acidic conditions on the ion exchange, caused by the competition of hydrogen and metal ions for binding sites on the zeolite, is minor in the concentration range investigated. It should also be noted that low pH values change the sorption processes and increase the mobility and remobilization of already adsorbed HMs, re-releasing them into the environment [26]. However, the increased ion solubility under acidic conditions enhances plant uptake, which is another removal pathway of HMs in constructed wetlands [27,28].
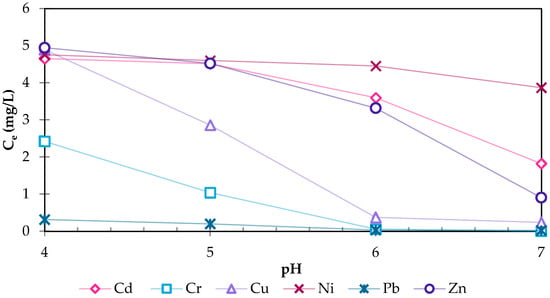
Figure 3.
Concentrations of dissolved HMs at pH 4, 5, 6, and 7 for the 250 mg zeolite samples with an initial concentration of 5 mg/L per HM.
The formation of insoluble carbonates, sulphides, oxides, and hydroxides is also coupled with the pH, directly effecting the precipitation and co-precipitation. While the formation of sulphides has a relatively broad pH range, the formation of carbonates, oxides, and hydroxides increases with rising pH values [29]. Besides the pH, the prerequisite is the presence of the required anions. With higher pH values, the surface charge of substrates becomes more negative, favouring the adsorption of metal cations and mitigating the adsorption of oxygen-containing ions like As, Sb, and Se, due to the excess of OH− ions [30].
In conclusion, alkaline conditions favour the adsorption and co-precipitation of HM cations and acidic conditions the adsorption and removal of oxygenated anions. Kong et al. [31] investigated the contrary results in Cr(VI) adsorption tests using artificial zeolite spheres loaded with nano Fe–Al bimetallic oxide. The expectation is that OH− ions serve as an electron donor for reducing Cr(VI) to Cr(III) and, subsequently, precipitate as Cr(OH)n [32]. In this case, the removal was facilitated under acidic conditions, possibly due to the excess H+ concentration neutralising or converting the negative into positive charge. The positively charged Fe-Al bimetallic oxides then adsorb HCrO4− existing under acidic conditions [31].
3.3. Removal Efficiency and Loading Rates in Batch Tests
All activated carbons showed similar results and rising DOC removal rates with increasing adsorbent doses up to 91.7% for Filtrasorb 400, 96.2% for HPC super 830, 95.1% for Norit GAC 830W, 95.3% for Norit GAC 1240W, 93.8% for Cyclecarb 401 and 93.6% for Cyclecarb 501 (Figure 4). Since zeolites are not expected to provide higher organic removal rates, only one zeolite (ZeoAqua) was tested for comparison. The DOC removal by zeolite does not exceed 31.8% at an adsorbent dose of 100 mg/L, even at higher concentrations, and is far below the removal achieved by ACs as projected. Zeolites exhibit consistently sized pores ranging from 0.4 to 1.3 nm. DOC constituents are typically larger molecules. Therefore, effective adsorbents for these applications need pores in the lower meso-scale range (2–50 nm). Thus, the smaller pore size of zeolites limits their effectiveness in removing bulk organic substances [33].
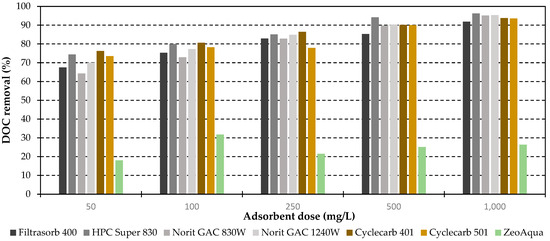
Figure 4.
DOC removal rates in dependence of the adsorbent dose. Regenerated ACs are highlighted in shades of brown.
Figure 5 depicts the loading rates of the three different natural zeolites as a function of the adsorbent dose for the six tested HMs. Maximum loading rates were reached for all zeolites at 50 mg/L of adsorbent dose, except for Zn and Cu (Zeogran K 80). The loading behaviour can be separated in three groups. High loading rate: Cr, Cu and Pb; Medium loading rate: Cd and Ni and Low/Negative loading rate: Zn. Compared to other HMs, the stronger relative binding strengths of Pb and Cr and Cu as well as the small hydrated radius of Pb led to a higher loading rate [34,35]. This observation is consistent with the precipitation pre-test results using added zeolite, indicating high retention of Pb (93.8%) and Cr (51.6%) compared to other heavy metals at pH 4, where no precipitation occurred. Additionally, Cu removal increased from 24.8% (without zeolite) to 42.8% (with zeolite) at pH 5 in the pre-tests, demonstrating enhanced removal facilitated by zeolite. The negative removal of Zn up to an adsorbent dosage of 250 mg/L is discussed further below. Moreover, with rising adsorbent dose, Zeogran K 80 showed increasing removal and loading rates compared to the other tested zeolites.
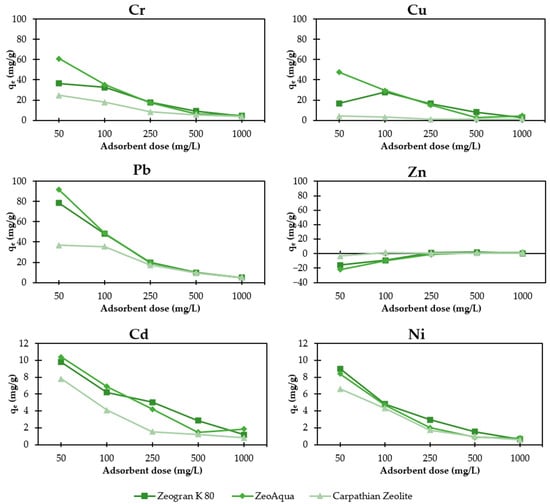
Figure 5.
Loading rates of the tested zeolites in dependence of the adsorbent dosage.
Selectivity for zeolite was: Pb > Cr > Cu > Cd = Ni > Zn. For higher adsorbent doses, the selectivity altered to: Pb > Cr > Cu > Cd > Ni = Zn. Zeogran K 80 and ZeoAqua showed similar maximum removal rates distinctively higher than Carpathian Zeolite. Highest loading was achieved for Pb with 91.6 mg/g (ZeoAqua), 60.8 mg/g for Cr (ZeoAqua), 47.4 mg/g for Cu (ZeoAqua), 10.4 mg/g for Cd (ZeoAqua) and 9 mg/g for Ni (Zeogran K 80). Negative loading rates for Zn occurred for all zeolites below adsorbent doses of 250 mg/L which indicate possible cross-contamination of the used zeolites or glassware. A review of Yuna et al. [36] regarding the removal of HMs from wastewater with zeolites summarised the following loading rates for natural zeolites: 4.1 mg/g for Cr, 4.1–13.5 mg/g for Cd, 2.9–5.3 mg/g for Cu, 10–91.2 mg/g for Pb, 3.1–22 mg/g for Zn and 2 mg/g for Ni. In comparison, the zeolites tested in this study showed higher loading rates for Cr, Cu, Ni, nearly identical loading rates for Cd and Pb and a lower loading rate for Zn.
Selectivity for AC was: Pb > Cr > Ni > Cd = Cu > Zn at an adsorbent concentration of 50 mg/L altering to: Pb = Cr > Cu > Cd > Ni = Zn at 1 g/L adsorbent concentration, showing similar HM affinity as zeolites (Figure 6). The maximum loading rates were: 44.4 mg/g (Cyclecarb 401) for Pb, 31.4 mg/g for Cr (Cyclecarb 401), 10.4 mg/g for Cu (Cyclecarb 401), 8.6 mg/g for Cd (Norit GAC 1240W), 15 mg/g for Ni (Filtrasorb 400), and 1.4 for Zn (Cyclecarb 401). It should also be emphasised that a higher AC adsorbent dosage had no impact on the removal of Cu and Zn, which may be caused by strong the leachability of these HMs [13].
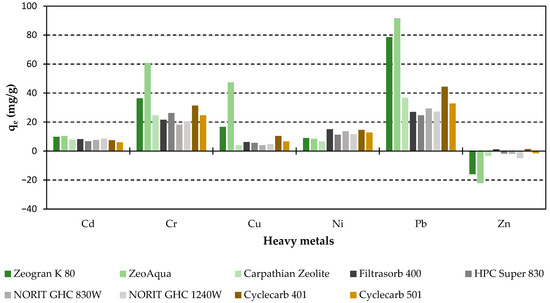
Figure 6.
Maximum heavy metal loading rates for 50 mg/L adsorbent dose concentration (C0/HM = 5 mg/L). Regenerated ACs are highlighted in shades of brown.
The zeolites achieved a maximum removal of 99.2 ± 1.6% for Pb, 85.6 ± 11.1% for Cr, 63.5 ± 29.6% for Cu, 27.2 ± 8.6% for Cd, 13.7 ± 2.1% for Ni and 19.1 ± 5.5% for Zn. The ACs achieved a removal rate of 99.1 ± 0.5% for Pb, 97.0 ± 2.9% for Cr, 91.3 ± 5.4% for Cu, 25.5 ± 6.9% for Cd, 18.4 ± 3.2% for Ni and 20.3 ± 18.9% for Zn (Figure 7). However, there was no or negative removal for Zn below adsorbent dosages of 250 mg/L. The low loading and removal rates of Zn for all adsorbents are caused by competitive effects, mainly between Zn and Cu. Both mainly exist in an exchangeable state and have strong leachability and bioavailability which results in competitive adsorption resulting in the desorption of Zn [13,37].
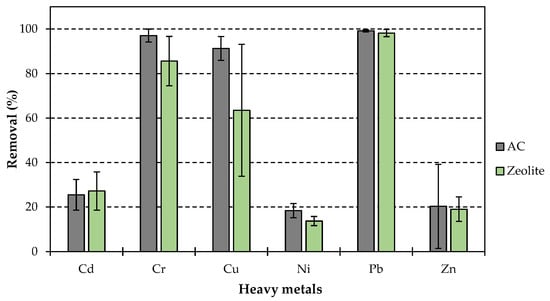
Figure 7.
Maximum HM removal rates with standard deviation of zeolite and AC in the batch tests.
The high removal rates observed with the tested activated carbons are attributed to a pH increase, inducing precipitation processes during the testing period. This phenomenon occurs because activated carbon adsorbs acidic compounds, indirectly raising the pH level. Especially for the 1 g/L adsorbent dose samples the increase in pH is between 2.2–2.3 for all tested ACs whereas zeolites did not affect the pH during the experiment.
3.4. Removal Efficiency in Column Tests
Most of the studied heavy metals were found in low concentrations of below 0.1 mg/L in the primary effluent of the STP Jajmau, close to or below the Indian water reuse standards [38]. For Pb, the second test run could not be evaluated due to the concentrations in the influent being below the detection limit. To prevent clogging caused by particulate matter in the columns, the primary effluent of the STP Jajmau was filtered with a 0.1 μm membrane. Figure 8 shows the %-proportion pre- and post-filtration of DOC and the various tested HMs. The reduction was 68.36% for DOC, 76.14% for Cd, 82.50% for Cr, 74.88% for Cu, 59.24% for Fe, 69.15% for Mn, 61.91% for Ni, 76.69% for Pb, and 66.09% for Zn, indicating that the majority of the HMs are present in colloidal form in the effluent of the STP Jajmau.
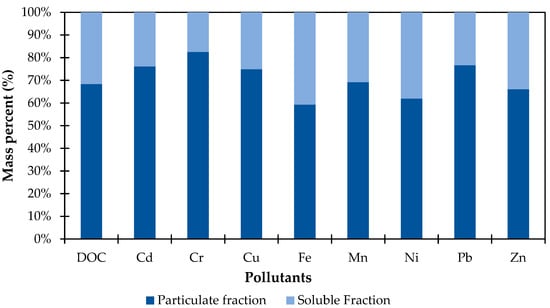
Figure 8.
Fractionation of DOC and selected HMs in STP primary effluent by filtration (0.1 μm membrane; soluble and particulate fraction of total amount in mass percent).
The column tests with different GAC/zeolite ratios (Figure 9) showed a wide range of results due to fluctuating feed concentrations. The blue shading indicates the first experimental campaign, while the yellow shading represents the second one. Contrary to the expectations, a higher zeolite ratio had no positive effect on the removal of most HMs. The high TDS of 1516 ± 285 mg/L in the influent can explain this phenomenon. The dissolved solids clog the smaller pore-sized zeolites’ channels, reducing both adsorption and ion-exchange potential. The mixtures with the regenerated Cyclecarb 401 showed a higher removal rate than the fresh carbon HPC Super 830, except for Mn, which is consistent with the batch test results where Cyclecarb 401 reached the highest loading rates. The highest average removal was 54.6% for Cd (Zeogran K 80/Cyclecarb 401; 50:50), 14.1% for Cr (Zeogran K 80/Cyclecarb 401; 50:50), 52.4% for Cu (Zeogran K 80/Cyclecarb 401; 50:50), 2.2% for Fe (ZeoAqua/Cyclecarb 401; 50:50), 29.2% for Mn (Zeogran K 80/HPC Super 830 80:20), 26.6% for Ni (ZeoAqua/Cyclecarb 401; 50:50), 35.2% for Pb (ZeoAqua/Cyclecarb 401 80:20) and 44.6% for Zn (Zeogran K 80/Cyclecarb 401; 50:50).
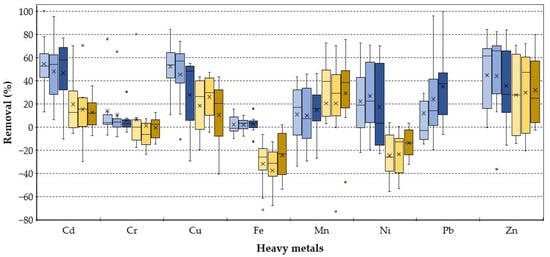
Figure 9.
Boxplots of heavy metal removal with different Zeolite/GAC ratios in the column tests.
Contrary to the batch test results, the removal of Cr, Cu and Pb was distinctly lower, and the removal of Cd and Zn was distinctly higher. The higher pH values in the column test favour the removal of Zn, since a major retention mechanism is the precipitation as carbonate under alkaline conditions [39,40]. The lower overall removal rates compared to the batch test findings can be explained by the shorter contact time between the contaminated water and the filter material and the different composition of wastewater. Therefore, a lower hydraulic loading rate (HLR) and a higher hydraulic retention time (HRT) are beneficial to the removal performance and the establishment of a suitable microbial community, as well as ensuring sufficient oxygen supply in CWs [41,42,43]. In a study conducted by Yadav et al. [44], the removal of Cr, Zn, Cu, Co, and Ni was investigated in a lab-scale VSSF-CW. The results showed that the removal efficiency for all heavy metals increased as the HRT was extended in all instances.
In addition, the results were affected by an increased ammonium concentration of 90.2 mg/L NH4+ in column tests compared to 4.44 mg/L NH4+ in batch tests. With increasing concentrations of the positively charged NH4+, competitive effects with the cationic HMs increasingly occur by decreasing the number of potential binding sites [16]. The combination of zeolite and activated carbon enhances the removal of NH4+ ions but diminishes zeolites’ ability to eliminate HMs due to the alkaline conditions induced by activated carbon. This leads to the creation of hydrated HM hydroxides with larger ion sizes, preventing their penetration into zeolite channels [16]. The adsorption-reducing effects of high NH4+ concentrations were also investigated in other studies. The removal of As, Cu and Zn from biogas slurry were investigated by [45] in a VSSF-CW. Due to the high NH4+ content, the removal rates of 8–23% for Zn, 35–83% for As, and below 1% for Cu, stress the importance of a prior NH4+ removal for maximum heavy metal retention via ion exchange with zeolites.
Negative removal occurred for most adsorbent variations, especially for Fe and Ni within the second experimental campaign (yellow shaded columns). The influent of the second campaign showed higher TDS levels of 1700 ± 231 mg/L and conductivity levels of 2533 ± 346 µs/cm compared to the first campaign’s TDS levels of 1501 ± 265 mg/L and conductivity levels of 1912 ± 214 µs/cm. These findings suggest that the influent had higher salinity, which could have led to increased desorption effects. Furthermore, the pH in the second campaign was slightly lower at 7.83 ± 0.20 compared to the first campaign’s pH of 8.17 ± 0.20. This increases the solubility and mobility of the metals and can lead to the re-release of absorbed HMs. Ni showed a low ion-exchange affinity with the zeolites in batch tests, so desorption is more likely than for more affine HMs. The desorption of the Fe2O3-containing zeolite can cause the release of Fe. As adsorption plays a crucial role in the removal process, a partial displacement of previously adsorbed Fe and Ni took place as the remaining capacity decreased. This resulted in effluent concentrations surpassing those of the influent.
4. Conclusions
The tested zeolites, Zeogran K 80 and ZeoAqua, showed high affinity to HMs such as Cr, Cu and Pb, even at low adsorbent doses. In contrast, Carpathian Zeolite demonstrated considerably lower removal and loading rates, highlighting substantial disparities among the tested zeolites. The ACs showed a similar removal capacity for the studied HMs; however, with lower loading rates compared to the zeolites and no major differences among themselves. The results indicated that an increase in pH, e.g., through the addition of AC, not only influences adsorption and ion exchange processes but also leads to increased co-/precipitation as metal oxides/hydroxides, which results in higher removal rates. When evaluating the HM loading rates in ACs, this aspect should be carefully considered. Negative removal rates of Zn at low adsorbent doses, especially for Zeogran K 80 and ZeoAqua, may be caused by cross-contamination or other external factors of the adsorbent and require further investigation.
Column tests revealed that shorter contact times, elevated background organic concentrations, along with high NH4+ and TDS levels, had an adverse impact on HM removal. TDS and DOC hampered the adsorption and ion-exchange capabilities of the adsorbents because the molecules involved were generally larger than the zeolite pore size, leading to the blockage of the zeolite channels. NH4+ ions competed with the cationic heavy metals, thereby impacting both the removal efficiency, and loading capacity. This can be seen as higher zeolite ratio had no positive effect on the removal of most HMs. Therefore, the used zeolites need a proper pretreatment to fully use their potential in removing cationic compounds such as HMs.
The present study indicated a good removal potential of the used adsorbents. However, it is important to note that results from lab-scale testing may differ from large-scale applications under natural conditions in CWs. This is due to complex removal processes in CWs, such as plant uptake, microbial processes, and complexation, as well as environmental factors such as redox potential, temperature, and seasonality, which influence pollutant removal.
Author Contributions
L.M.O.: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing; C.K.: conceptualization, methodology, validation, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision; P.B.: methodology, validation, resources, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the European Commission within the project “Pavitra Ganga” (GA No. 821051, call H2020 SC5-12-2018) and the Government of India (DBT) in course of the EU-India cooperation in H2020.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support from the Emschergenossenschaft, Essen, the lab teams at IIT Kanpur and Fraunhofer IEG, Bochum as well as the STP Jajmau staff in Kanpur. Many thanks also to Florian Voss and Andreas Bauer for their contributions to this paper as well as Thomas Wintgens for the final revision of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
References
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 9789241549950. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Ding, X.; Bian, H.; Yao, X. Total concentrations and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Liu, H. A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.; Badenberg, S.; Wulff, M.; Drewes, J.; Helmreich, B. Evaluation of Factors Influencing Lab-Scale Studies to Determine Heavy Metal Removal by Six Sorbents for Stormwater Treatment. Water 2016, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Dong, H.; Zeng, G. Application of zeolite in removing salinity/sodicity from wastewater: A review of mechanisms, challenges and opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Sheng, S.; Pan, F.; Chen, F.; Fu, J. Comprehensive evaluation of substrate materials for contaminants removal in constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.; Yan, Y.; Ran, J. Adsorption materials for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and the key factors for VOCs adsorption process: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Cao, J.; Ye, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Bate, B. Content and morphology of lead remediated by activated carbon and biochar: A spectral induced polarization study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 124605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Lee, W.-N.; Coleman, C.; Meyer, M.; Carter, J.; Nowack, K.; Huang, C.-H. Pilot investigation of two-stage biofiltration for removal of natural organic matter in drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, T.; Mojiri, A. Constructed wetland modified by biochar/zeolite addition for enhanced wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 16, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gu, T.; Yi, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y. The release mechanism of heavy metals from lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands treating road runoff. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 16588–16595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Li, H. Aquatic toxicity of heavy metal-containing wastewater effluent treated using vertical flow constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, A.; Oka, M.; Fujii, Y.; Soda, S.; Ishigaki, T.; Machimura, T.; Ike, M. Removal of heavy metals from synthetic landfill leachate in lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; You, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hao, N.; Bate, B. A study on the competitive adsorption process of NH4+ and Zn2+ on activated carbon and zeolite. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 20, 6039–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Government; Australian High Commission New Delhi; Victorian Government; Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur; National Mission for Clean Ganga and World Bank. Jajmau Tannery Industry Road Map to Sustainable Waste Management: A Model for the Ganga Basin; Earth Systems: Melbourne, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Younas, F.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Afzal, M.; Hussain, K.; Shahid, M.; Aslam, Z.; Bashir, S.; Hussain, M.M.; Bundschuh, J. Constructed wetlands as a sustainable technology for wastewater treatment with emphasis on chromium-rich tannery wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Yadav, A.; Dwivedi, P.D.; Das, M. Toxic hazards of leather industry and technologies to combat threat: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigdomènech, I.; Colàs, E.; Grivé, M.; Campos, I.; García, D. A tool to draw chemical equilibrium diagrams using SIT: Applications to geochemical systems and radionuclide solubility. MRS Proc. 2014, 1665, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN ISO 11885:2009-09; Water Quality—Determination of Selected Elements by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) (ISO 11885:2007). German Version EN ISO 11885:2009. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2009.
- DIN EN 1484:2019-04; Water Analysis—Guidelines for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) and Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC). German Version EN 1484:1997. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2019.
- Crittenden, J.C.; Trussell, R.R.; Hand, D.W.; Howe, K.J.; Tchobanoglous, G. MWH’s Water Treatment: Principles and Design, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781118103777. [Google Scholar]
- Malekian, R.; Abedi-Koupai, J.; Eslamian, S.S.; Mousavi, S.F.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Afyuni, M. Ion-exchange process for ammonium removal and release using natural Iranian zeolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 51, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasielewski, S.; Rott, E.; Minke, R.; Steinmetz, H. Evaluation of Different Clinoptilolite Zeolites as Adsorbent for Ammonium Removal from Highly Concentrated Synthetic Wastewater. Water 2018, 10, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, A. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water and Wastewaters by Sulfur-Containing Precipitation Agents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, J.; Jović, M.; Smičiklas, I.; Pezo, L.; Šljivić-Ivanović, M.; Onjia, A.; Popović, A. Chemical speciation of metals in unpolluted soils of different types: Correlation with soil characteristics and an ANN modelling approach. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 165, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Bonten, L.T.; Koopmans, G.F.; Song, J.; Luo, Y.; Temminghoff, E.J.; Comans, R.N. Solubility of trace metals in two contaminated paddy soils exposed to alternating flooding and drainage. Geoderma 2016, 261, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.K.; Vaccari, D.A.; Li, Y.; Shammas, N.K. Chemical Precipitation. Physicochemical Treatment Processes; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 141–197. [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, L.; Mench, M.; Jacob, D.L.; Otte, M.L. Metal and metalloid removal in constructed wetlands, with emphasis on the importance of plants and standardized measurements: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3447–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by artificial zeolite spheres loaded with nano Fe–Al bimetallic oxide in constructed wetland. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Gao, Y. Mechanisms of Cr(VI) removal by FeCl3-modified lotus stem-based biochar (FeCl3@LS-BC) using mass-balance and functional group expressions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 551, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zou, L.; Wang, L. Photocatalytic TiO2/adsorbent nanocomposites prepared via wet chemical impregnation for wastewater treatment: A review. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 371, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dai, Y.; Tang, X.; Tao, R.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Tai, Y. Effect of heavy metals in mixed domestic-industrial wastewater on performance of recirculating standing hybrid constructed wetlands (RSHCWs) and their removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinraide, T.B.; Yermiyahu, U. A scale of metal ion binding strengths correlating with ionic charge, Pauling electronegativity, toxicity, and other physiological effects. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2007, 101, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuna, Z. Review of the Natural, Modified, and Synthetic Zeolites for Heavy Metals Removal from Wastewater. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.Y.; Chou, C.C.; Pan, C.T. Heavy metal removal within pilot-scale constructed wetlands receiving river water contaminated by confined swine operations. Desalination 2009, 249, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellenberg, T.; Subramanian, V.; Ganeshan, G.; Tompkins, D.; Pradeep, R. Wastewater Discharge Standards in the Evolving Context of Urban Sustainability–The Case of India. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luca, G.A.; Maine, M.A.; Mufarrege, M.M.; Hadad, H.R.; Sánchez, G.C.; Bonetto, C.A. Metal retention and distribution in the sediment of a constructed wetland for industrial wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Kröpfelová, L. Wastewater Treatment in Constructed Wetlands with Horizontal Sub-Surface Flow; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 9781402085802. [Google Scholar]
- Si, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Cao, X.; Zhang, X.; Sand, W. Mechanism and performance of trace metal removal by continuous-flow constructed wetlands coupled with a micro-electric field. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.; Sun, G. A review on nitrogen and organics removal mechanisms in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Dependency on environmental parameters, operating conditions and supporting media. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Xu, J. Improving Winter Performance of Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment in Northern China: A Review. Wetlands 2014, 34, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Abbassi, R.; Kumar, N.; Satya, S.; Sreekrishnan, T.R.; Mishra, B.K. The removal of heavy metals in wetland microcosms: Effects of bed depth, plant species, and metal mobility. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Cui, X.; Li, H. Effects of fillers combined with biosorbents on nutrient and heavy metal removal from biogas slurry in constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).