Microplastic Contamination in Shrimps from the Negombo Lagoon—Sri Lanka
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. Tissue Digestion and Filtration
2.3. Identification and Characterization of Microplastics
2.4. Quality Control
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Abundance of Microplastics
3.2. Sizes of Microplastics
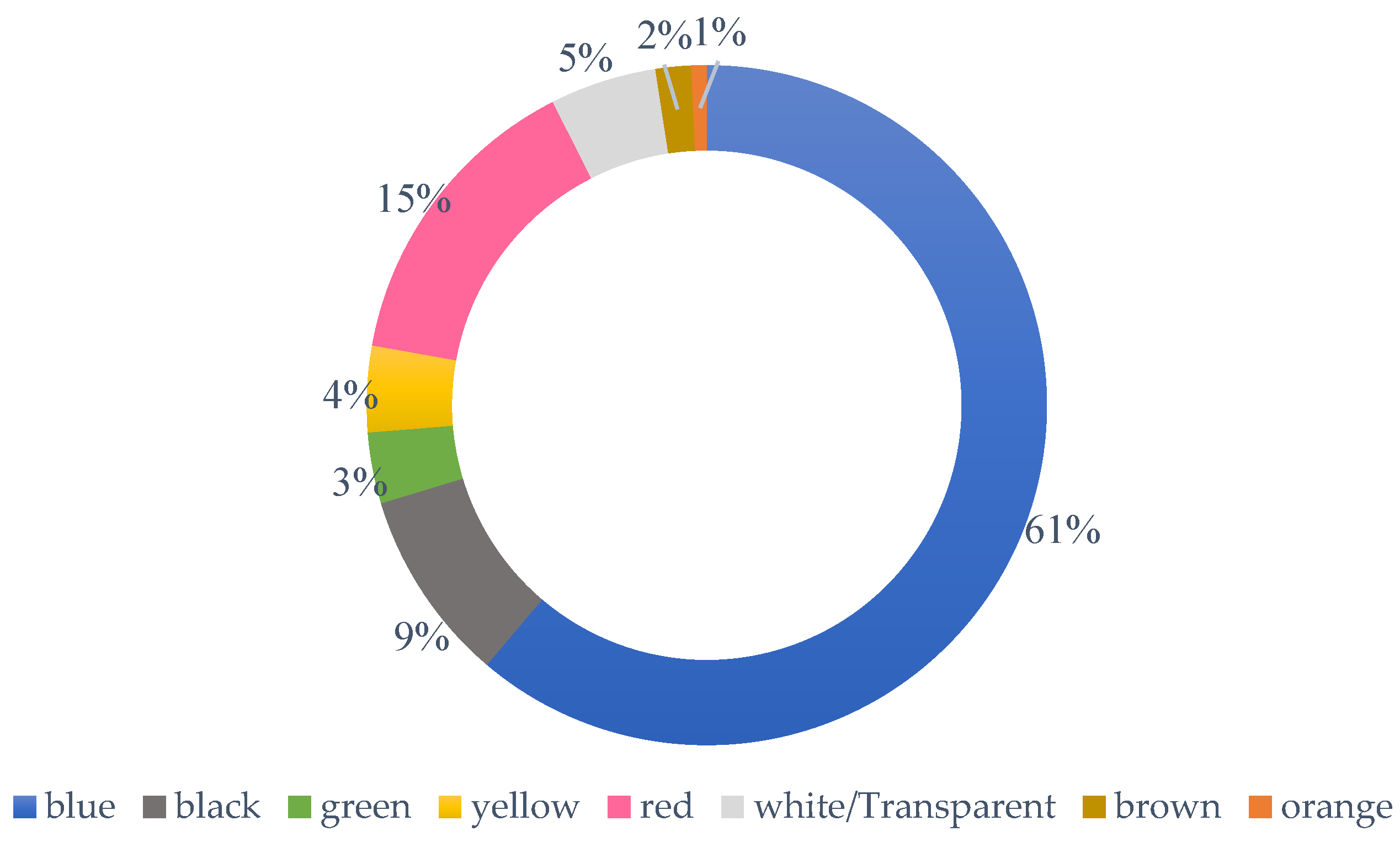
3.3. Color of Microplastics
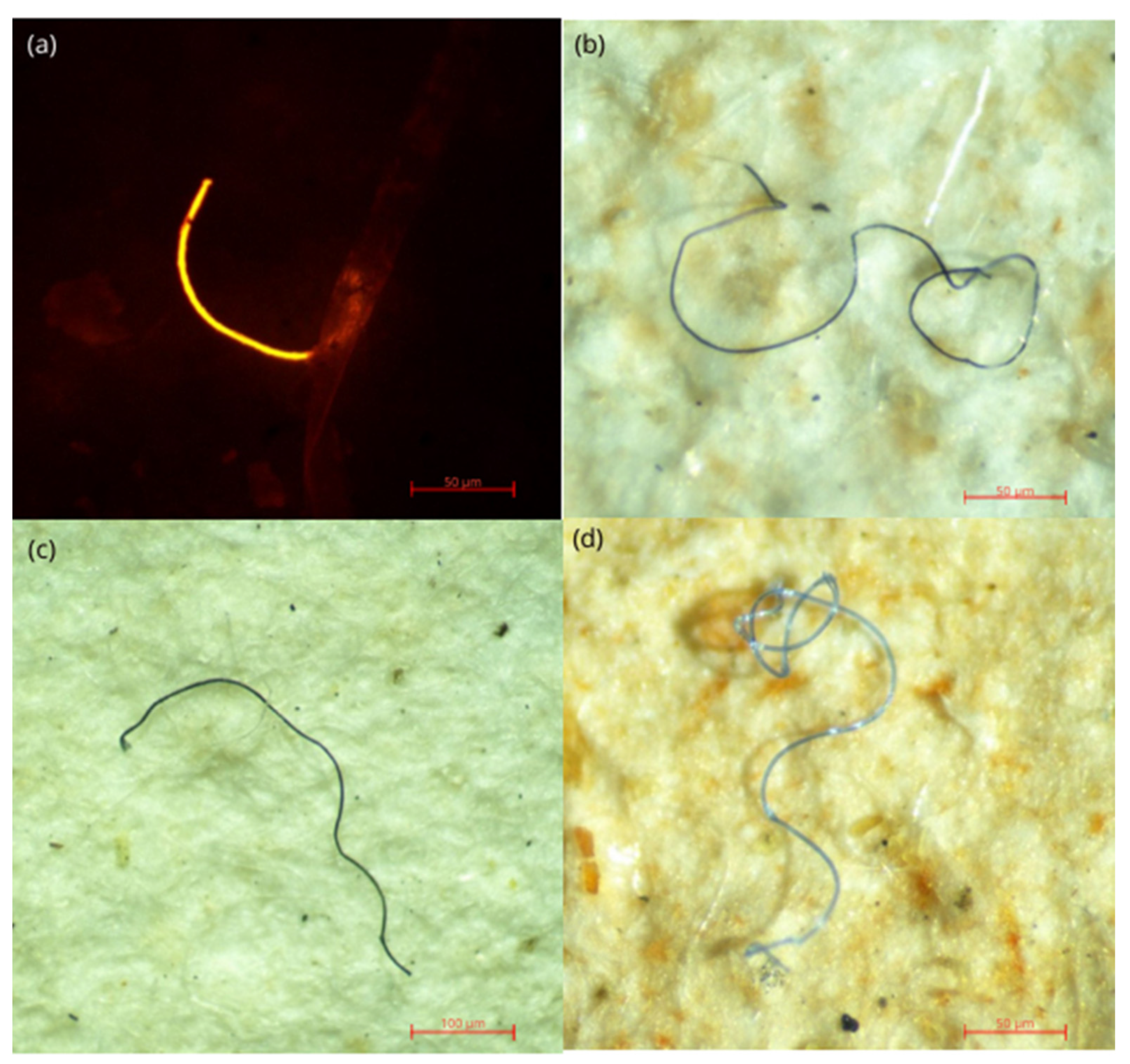
3.4. Types and Shapes of MPs
| Species | Study Area | Abundance (Items/g) | Tissue Examined | Type of Dominant MPs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paratya australiensis | Victoria, Australia | 24 ± 31 | WB | Fibers | (Nun et al., 2020) [39] |
| Litopenaeus vannamei | Shrimp farm, Guangdong Province, China | 14.1 ± 5.7 | GI | Fibers | (Curren et al., 2020) [37] |
| Metapenaeus monoceros | Northern Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh | 3.87 ± 1.05 | GI | Fibers | (Hossain et al., 2020) [38] |
| Penaeus monodon | Northern Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh | 3.40 ± 1.23 | GI | Fibers | (Hossain et al., 2020) [38] |
| Parapenaeopsis stylifera | Northeastern Arabian Sea | 64.8 ± 24.6 | GI | Fibers | (Gurjar et al., 2021) [47] |
| Metapenaeus monoceros | Northeastern Arabian Sea | 78.5 ± 48.4 | GI | Fibers | (Gurjar et al., 2021) [47] |
| Penaeus indicus | Northeastern Arabian Sea | 47.5 ± 38.0 | GI | Fibers | (Gurjar et al., 2021) [47] |
| Parapenaeopsis hardwickii | Xiangshan Bay, China | 0.25 ± 0.08 | GI | Fibers | (Wu et al., 2020) [40] |
3.5. Polymer Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plastics Europe. Plastics—The Fast Facts 2023; Plastics Europe: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Prasannamedha, G. Biological and Chemical Impacts on Marine Biology. In Modern Treatment Strategies for Marine Pollution; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 11–27. ISBN 978-0-12-822279-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Hossini, H.; Makhdoumi, P. Review of Microplastic Occurrence and Toxicological Effects in Marine Environment: Experimental Evidence of Inflammation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 142, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Arthur, C. Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for Quantifying Synthetic Particles in Waters and Sediments; NOAA Marine Debris Division: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Santos, T.; Duarte, A.C. (Eds.) Characterization and Analysis of Microplastics; Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-444-63898-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kühn, S.; Van Franeker, J.A. Quantitative Overview of Marine Debris Ingested by Marine Megafauna. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Franeker, J.A. Plastic Ingestion in the North Atlantic Fulmar. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1985, 16, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Yu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, R. Sorption Behaviors of Phenanthrene on the Microplastics Identified in a Mariculture Farm in Xiangshan Bay, Southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, V.; Blázquez, G.; Calero, M.; Quesada, L.; Martín-Lara, M.A. The Potential of Microplastics as Carriers of Metals. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowley, J.; Baker-Austin, C.; Porter, A.; Hartnell, R.; Lewis, C. Oceanic Hitchhikers—Assessing Pathogen Risks from Marine Microplastic. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakib, M.R.J.; Sarker, A.; Ram, K.; Uddin, M.G.; Walker, T.R.; Chowdhury, T.; Uddin, J.; Khandaker, M.U.; Rahman, M.M.; Idris, A.M. Microplastic Toxicity in Aquatic Organisms and Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussarellu, R.; Suquet, M.; Thomas, Y.; Lambert, C.; Fabioux, C.; Pernet, M.E.J.; Le Goïc, N.; Quillien, V.; Mingant, C.; Epelboin, Y.; et al. Oyster Reproduction Is Affected by Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umamaheswari, S.; Priyadarshinee, S.; Kadirvelu, K.; Ramesh, M. Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated P53 Signaling Pathway in Zebrafish. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 345, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Jia, H.; Sun, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L. Long-Term Phototransformation of Microplastics under Simulated Sunlight Irradiation in Aquatic Environments: Roles of Reactive Oxygen Species. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, N.C.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, J.L.; Thiel, M. Amberstripe Scad Decapterus muroadsi (Carangidae) Fish Ingest Blue Microplastics Resembling Their Copepod Prey along the Coast of Rapa Nui (Easter Island) in the South Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, N.C.; Gallardo, C.; Lenz, M.; Thiel, M. Capture, Swallowing, and Egestion of Microplastics by a Planktivorous Juvenile Fish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvan, K.; Pandurangan, P.; Velu, R.; Robinson, J. Occurrence of Microplastics in Gastrointestinal Tracts of Planktivorous Fish from the Thoothukudi Region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 44723–44731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, T. Toward an Improved Understanding of the Ingestion and Trophic Transfer of Microplastic Particles: Critical Review and Implications for Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1119–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brander, S.M.; Renick, V.C.; Foley, M.M.; Steele, C.; Woo, M.; Lusher, A.; Carr, S.; Helm, P.; Box, C.; Cherniak, S.; et al. Sampling and Quality Assurance and Quality Control: A Guide for Scientists Investigating the Occurrence of Microplastics Across Matrices. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 1099–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeque, P.K.; Cole, M.; Coppock, R.L.; Lewis, C.N.; Miller, R.Z.; Watts, A.J.R.; Wilson-McNeal, A.; Wright, S.L.; Galloway, T.S. Are We Underestimating Microplastic Abundance in the Marine Environment? A Comparison of Microplastic Capture with Nets of Different Mesh-Size. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The Physical Impacts of Microplastics on Marine Organisms: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liang, W.; Liu, Q.-X.; Fu, S.; Ma, C.; Chen, Q.; Su, L.; Craig, N.J.; Shi, H. Fish Ingest Microplastics Unintentionally. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10471–10479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch, S.; Friedrich, C.; Brinker, A. Uptake Routes of Microplastics in Fishes: Practical and Theoretical Approaches to Test Existing Theories. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, L.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Potential Adverse Health Effects of Ingested Micro- and Nanoplastics on Humans. Lessons Learned from in Vivo and in Vitro Mammalian Models. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2020, 23, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, O.M.L.; Basheer, A.A.; Khattab, R.A.; Ali, I. Health and Environmental Effects of Persistent Organic Pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; O’Brien, J.W.; Galloway, T.; Thomas, K.V. Accumulation and Fate of Nano- and Micro-Plastics and Associated Contaminants in Organisms. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Maiti, S.K. Evaluation of Potential Human Health Risks from Toxic Metals via Consumption of Cultured Fish Species Labeo Rohita: A Case Study from an Urban Aquaculture Pond. Expo. Health 2019, 11, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volschenk, C.M.; Gerber, R.; Mkhonto, M.T.; Ikenaka, Y.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Nakayama, S.; Ishizuka, M.; Van Vuren, J.H.J.; Wepener, V.; Smit, N.J. Bioaccumulation of Persistent Organic Pollutants and Their Trophic Transfer through the Food Web: Human Health Risks to the Rural Communities Reliant on Fish from South Africa’s Largest Floodplain. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, Seafood & Crustacean Exports from Sri Lanka—EDB Sri Lanka. Available online: https://www.srilankabusiness.com/sea-food/sri-lankan-sea-food-products.html (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Athukorala, D.; Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y.; Matsushita, B. Impacts of Urbanization on the Muthurajawela Marsh and Negombo Lagoon, Sri Lanka: Implications for Landscape Planning towards a Sustainable Urban Wetland Ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, A.; Aluwihare, L.; Youngs, S.; DiBenedetto, M.H.; Ward, C.P.; Michel, A.P.M.; Colson, B.C.; Mazzotta, M.G.; Walsh, A.N.; Nelson, R.K.; et al. The M/V X-Press Pearl Nurdle Spill: Contamination of Burnt Plastic and Unburnt Nurdles along Sri Lanka’s Beaches. ACS Environ. Au 2022, 2, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaeman; Herlinah; Parenrengi, A. The Consumption Rate of Tiger Prawns (Penaeus monodon) on Alive Amphipod-Crustacean. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 564, 012087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hamidian, A.H.; Tubić, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.K.H.; Wu, C.; Lam, P.K.S. Understanding Plastic Degradation and Microplastic Formation in the Environment: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partow, H.; Lacroix, C.; Floch, S.L.; Alcaro, L. X-Press Pearl Maritime Disaster Sri Lanka—Report of the UN Environmental Advisory Mission; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Curren, E.; Leaw, C.P.; Lim, P.T.; Leong, S.C.Y. Evidence of Marine Microplastics in Commercially Harvested Seafood. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 562760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Uddin, M.N.; Sharifuzzaman, S.M.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Sarker, S.; Nawaz Chowdhury, M.S. Microplastic Contamination in Penaeid Shrimp from the Northern Bay of Bengal. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, B.; Su, L.; Kellar, C.; Craig, N.J.; Keough, M.J.; Pettigrove, V. Identification of Microplastics in Surface Water and Australian Freshwater Shrimp Paratya Australiensis in Victoria, Australia. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Leung, J.Y.S.; Huang, W.; Zeng, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, A.; Yu, X.; Xu, X.; et al. Accumulation of Microplastics in Typical Commercial Aquatic Species: A Case Study at a Productive Aquaculture Site in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; Alves, J.R.; Da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Major Factors Influencing the Quantification of Nile Red Stained Microplastics and Improved Automatic Quantification (MP-VAT 2.0). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; Reis, V.; Matos, J.T.V.; Da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. A New Approach for Routine Quantification of Microplastics Using Nile Red and Automated Software (MP-VAT). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leistenschneider, C.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Mani, T.; Primpke, S.; Taubner, H.; Gerdts, G. Microplastics in the Weddell Sea (Antarctica): A Forensic Approach for Discrimination between Environmental and Vessel-Induced Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15900–15911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athukorala, A.; Amarathunga, A.A.D.; De Silva, D.S.M.; Bakir, A.; McGoran, A.; Sivyer, D. Occurrence and Abundance of Microplastics in Surface Waters and Sediments from the Negombo Lagoon, Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on the Environmental Effects of Nanoparticles and Nanomaterials, Plymouth, UK, 5–8 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Barrows, A.P.W.; Cathey, S.E.; Petersen, C.W. Marine Environment Microfiber Contamination: Global Patterns and the Diversity of Microparticle Origins. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, O.; Gökdağ, K.; Jovanović, B.; Kıdeyş, A.E. Microplastic Litter Composition of the Turkish Territorial Waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and Its Occurrence in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Fish. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjar, U.R.; Xavier, M.; Nayak, B.B.; Ramteke, K.; Deshmukhe, G.; Jaiswar, A.K.; Shukla, S.P. Microplastics in Shrimps: A Study from the Trawling Grounds of Northeastern Part of Arabian Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48494–48504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodall, L.C.; Sanchez-Vidal, A.; Canals, M.; Paterson, G.L.J.; Coppock, R.; Sleight, V.; Calafat, A.; Rogers, A.D.; Narayanaswamy, B.E.; Thompson, R.C. The Deep Sea Is a Major Sink for Microplastic Debris. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2014, 1, 140317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia-Castañeda, G.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Frías-Espericueta, M.G.; Rivera-Hernández, J.R.; Green-Ruiz, C.R.; Páez-Osuna, F. Microplastics in the Tissues of Commercial Semi-Intensive Shrimp Pond-Farmed Litopenaeus Vannamei from the Gulf of California Ecoregion. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
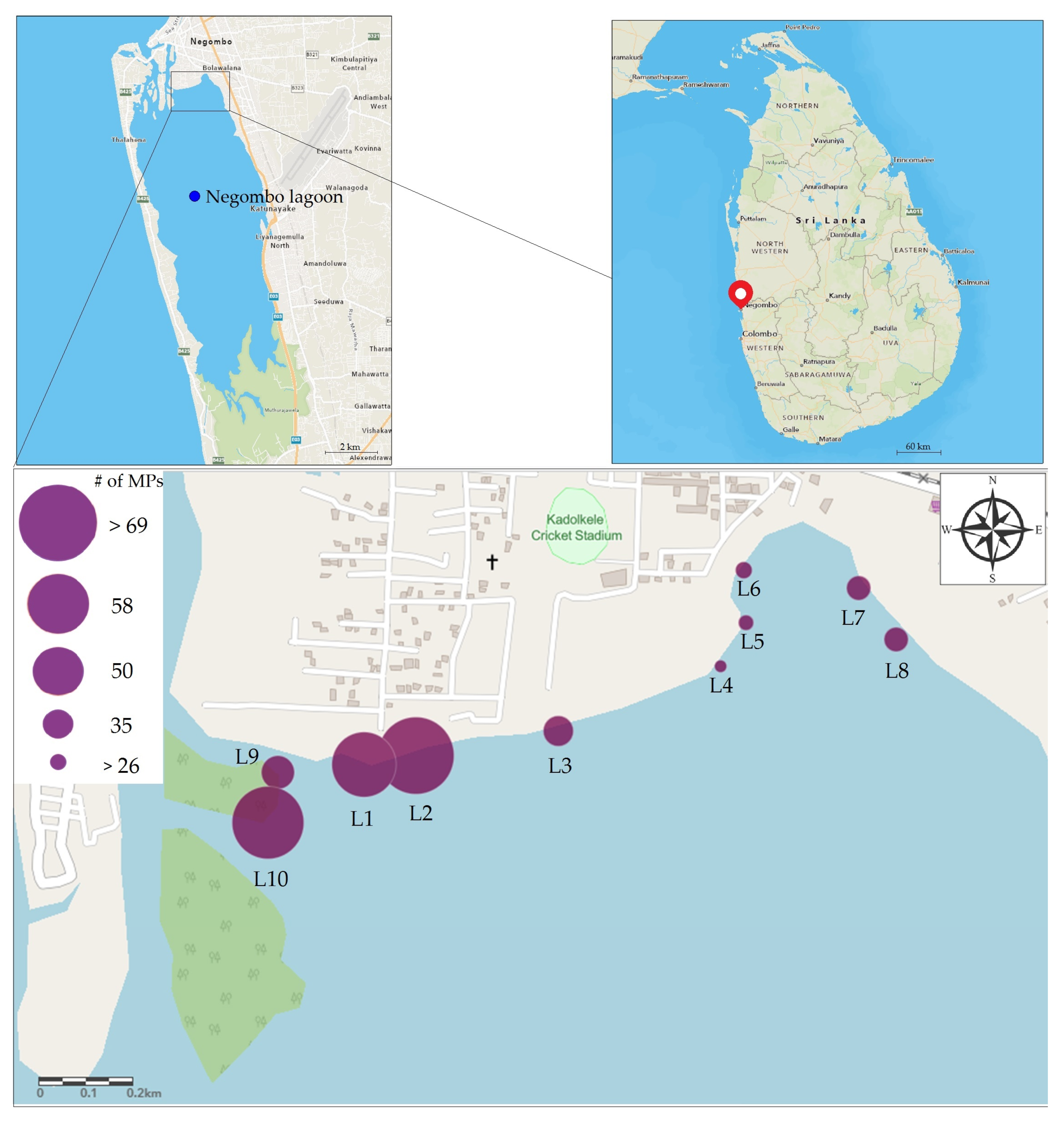
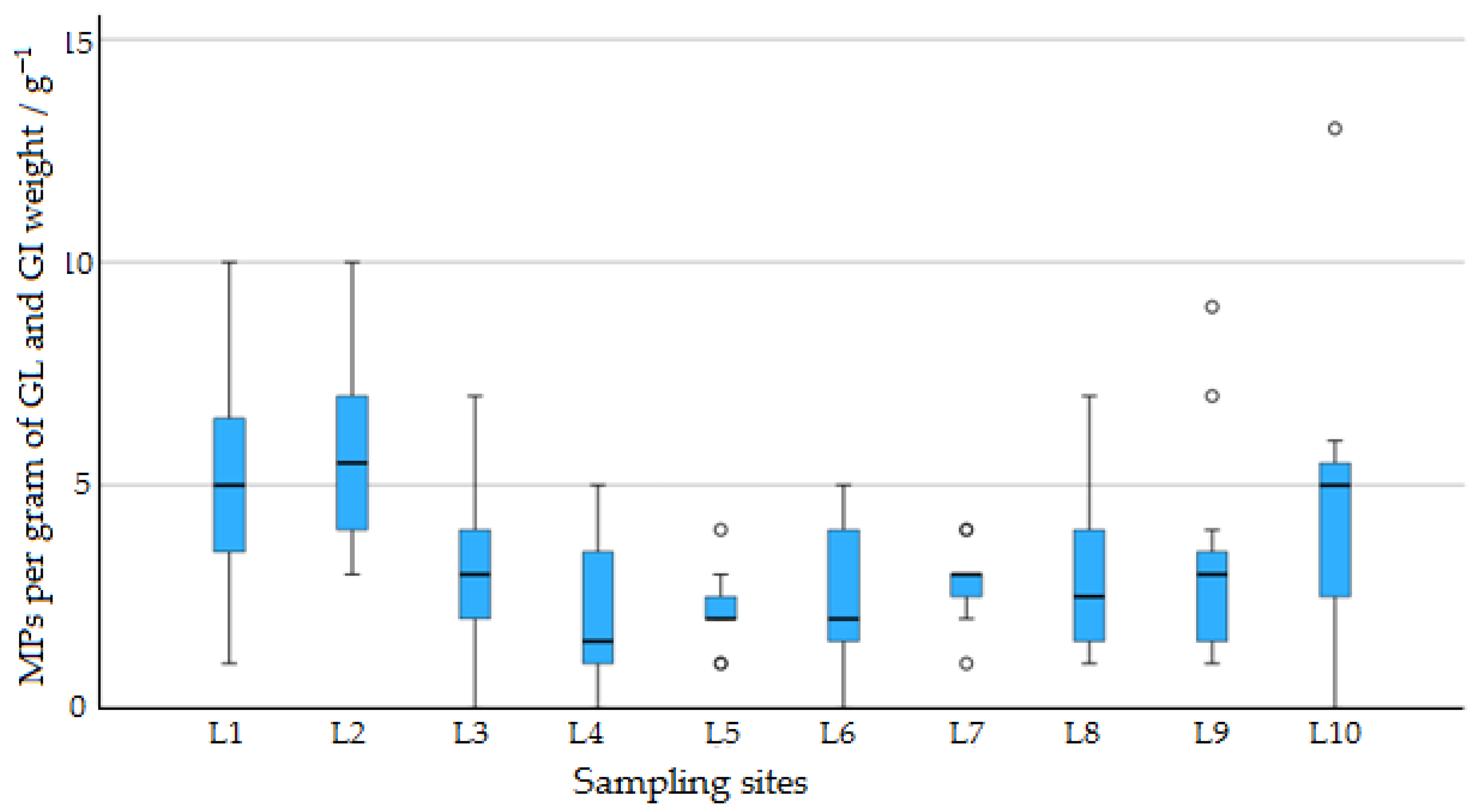

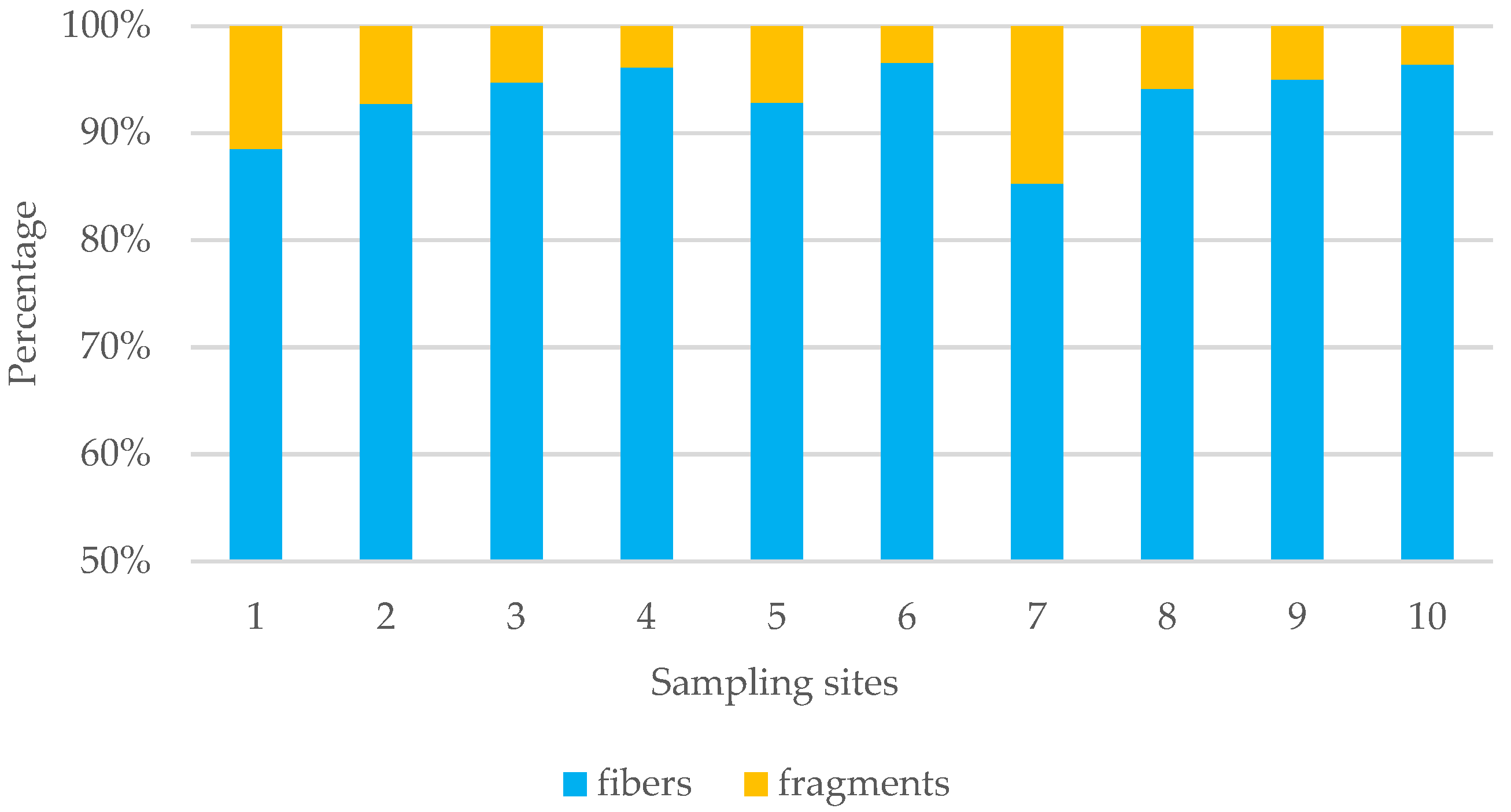

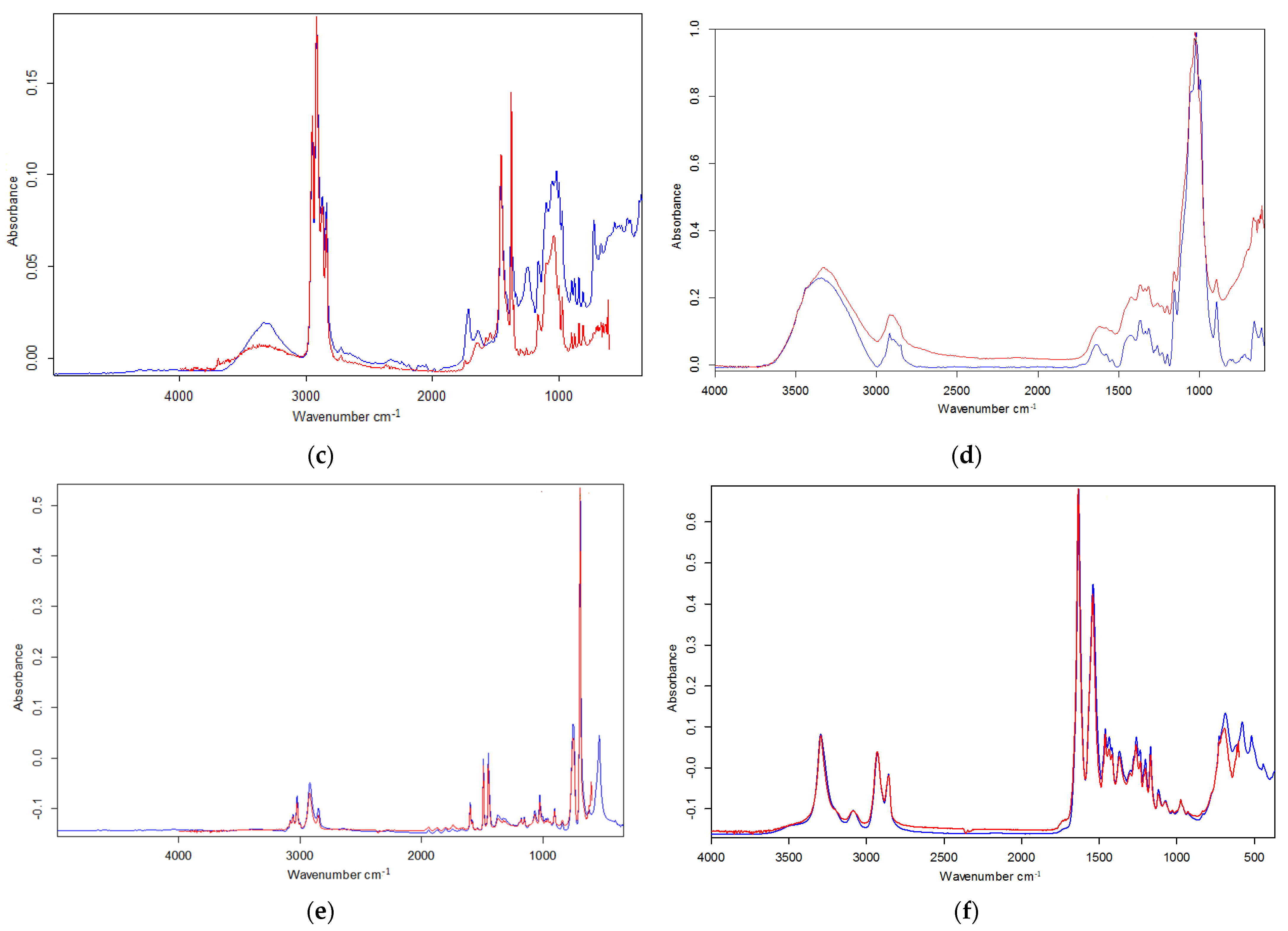
| Sampling Site | Sample Count | MPs per Gram of GL and GI Weight—(g)−1 | Identified MPs Count | Body Weight—(g) | GL + GI Weight— (g) | Total/Extended Length—(mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. monodon | P. indicus | ||||||
| L1 | 2 | 10 | 9.54 ± 4.61 | 61 | 4.99 ± 0.86 | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 78.83 ± 4.70 |
| L2 | 2 | 10 | 10.42 ± 3.93 | 69 | 5.35 ± 2.98 | 0.55 ± 0.03 | 84.25 ± 11.25 |
| L3 | 3 | 9 | 5.71 ± 3.45 | 38 | 5.57 ± 1.04 | 0.54 ± 0.03 | 89.5 ± 6.02 |
| L4 | 1 | 11 | 3.94 ± 2.88 | 26 | 5.42 ± 0.89 | 0.54 ± 0.02 | 93.75 ± 13.28 |
| L5 | 0 | 12 | 4.17 ± 1.80 | 28 | 5.51 ± 0.55 | 0.55 ± 0.04 | 89.25 ± 10.28 |
| L6 | 4 | 8 | 4.34 ± 2.63 | 29 | 5.50 ± 0.44 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 97.33 ± 7.90 |
| L7 | 2 | 10 | 5.12 ± 1.44 | 34 | 5.92 ± 0.67 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 94.25 ± 13.90 |
| L8 | 4 | 8 | 5.09 ± 2.95 | 34 | 5.32 ± 0.69 | 0.55 ± 0.02 | 87.66 ± 12.98 |
| L9 | 4 | 8 | 5.90 ± 3.93 | 40 | 5.62 ± 0.69 | 0.55 ± 0.03 | 83.58 ± 9.60 |
| L10 | 3 | 9 | 8.12 ± 5.32 | 56 | 5.80 ± 0.57 | 0.57 ± 0.57 | 83.83 ± 10.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lawan, P.L.M.J.H.; De Silva, D.S.M.; Amarathunga, A.A.D.; McGoran, A.; Bakir, A.; Sivyer, D.B.; Reeve, C. Microplastic Contamination in Shrimps from the Negombo Lagoon—Sri Lanka. Water 2024, 16, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030447
Lawan PLMJH, De Silva DSM, Amarathunga AAD, McGoran A, Bakir A, Sivyer DB, Reeve C. Microplastic Contamination in Shrimps from the Negombo Lagoon—Sri Lanka. Water. 2024; 16(3):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030447
Chicago/Turabian StyleLawan, P. L. M. J. H., D. S. M. De Silva, A. A. D. Amarathunga, A. McGoran, A. Bakir, D. B. Sivyer, and C. Reeve. 2024. "Microplastic Contamination in Shrimps from the Negombo Lagoon—Sri Lanka" Water 16, no. 3: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030447
APA StyleLawan, P. L. M. J. H., De Silva, D. S. M., Amarathunga, A. A. D., McGoran, A., Bakir, A., Sivyer, D. B., & Reeve, C. (2024). Microplastic Contamination in Shrimps from the Negombo Lagoon—Sri Lanka. Water, 16(3), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030447








