Linking Water Quality Indicators in Stable Reservoir Ecosystems: Correlation Analysis and Ecohydrological Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Research Sites
2.2. Research Method
2.2.1. Main Equipment
- JPBJ-608 Portable Dissolved Oxygen Analyzer (Shanghai Yideng Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China)
- HCA-101 Standard COD Digester (Jiangsu Taizhou Huachen Instrument Co., Ltd., Taizhou, Jiangsu, China)
- TU-1810D UV-Visible Spectrophotometer (Beijing Puyang General Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China)
- Burette
2.2.2. Water Sample Treatment Procedures
- Dissolved oxygen: measured according to “Determination of Dissolved Oxygen in Water Quality—Electrochemical Probe Method” (HJ 506-2009) [24].
- Chemical oxygen demand (COD): determined using the “Rapid Digestion Spectrophotometric Method” (HJ 828-2017) [25].
- Permanganate index (CODMn): determined using the “Determination of Permanganate Index in Water Quality” (GB/T 11892-1989) [26].
- Ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N): measured using the “Nessler Reagent Spectrophotometry Method” (HJ 535-2009) [30].
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Correlation Analysis Using Univariate Linear Regression
2.3.2. Correlation Coefficient (R) Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
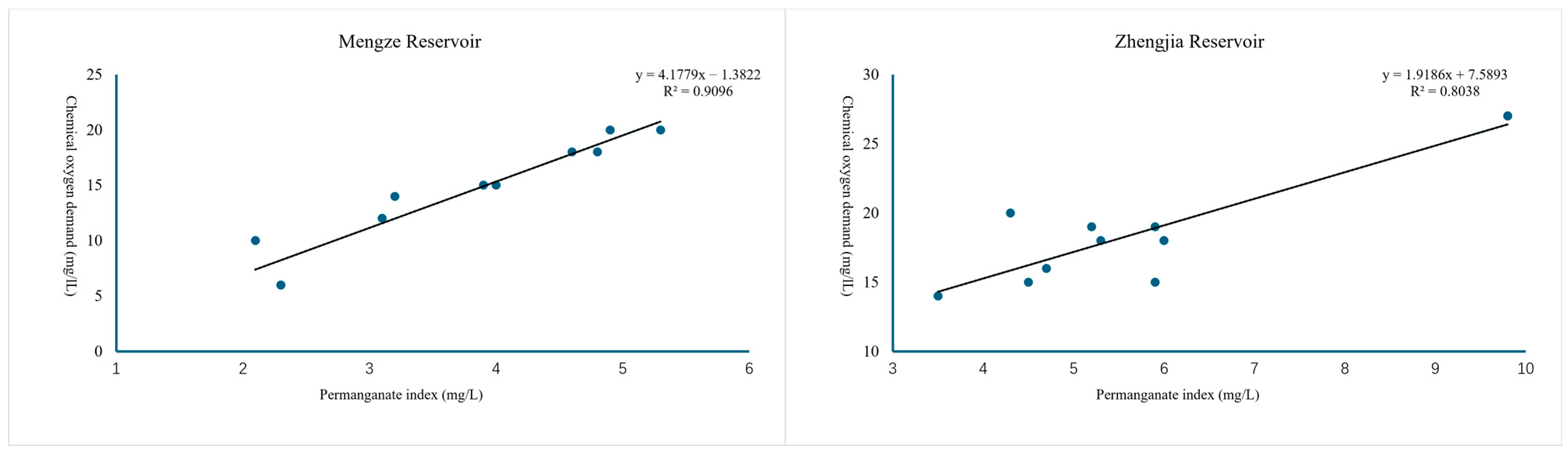
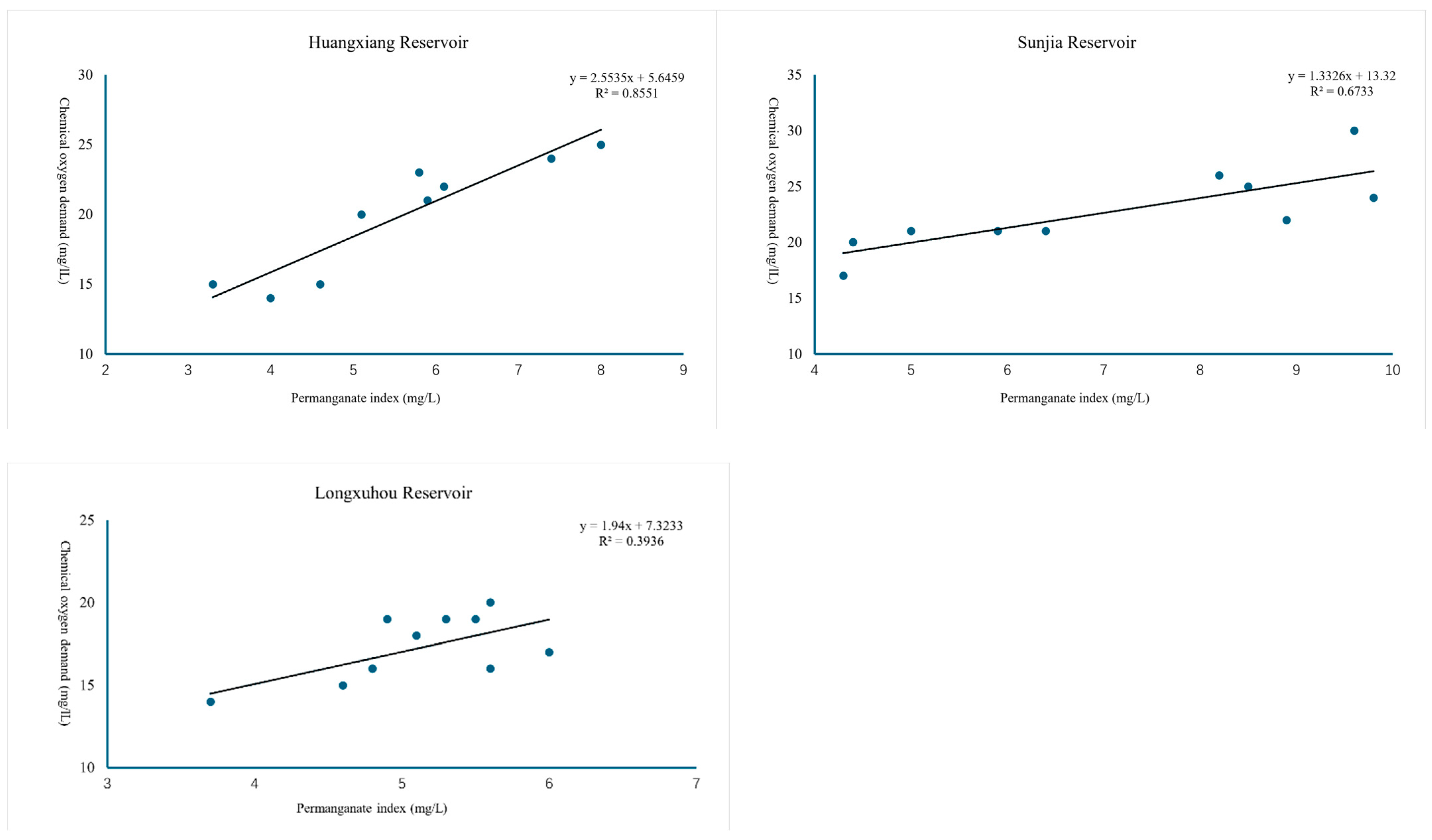
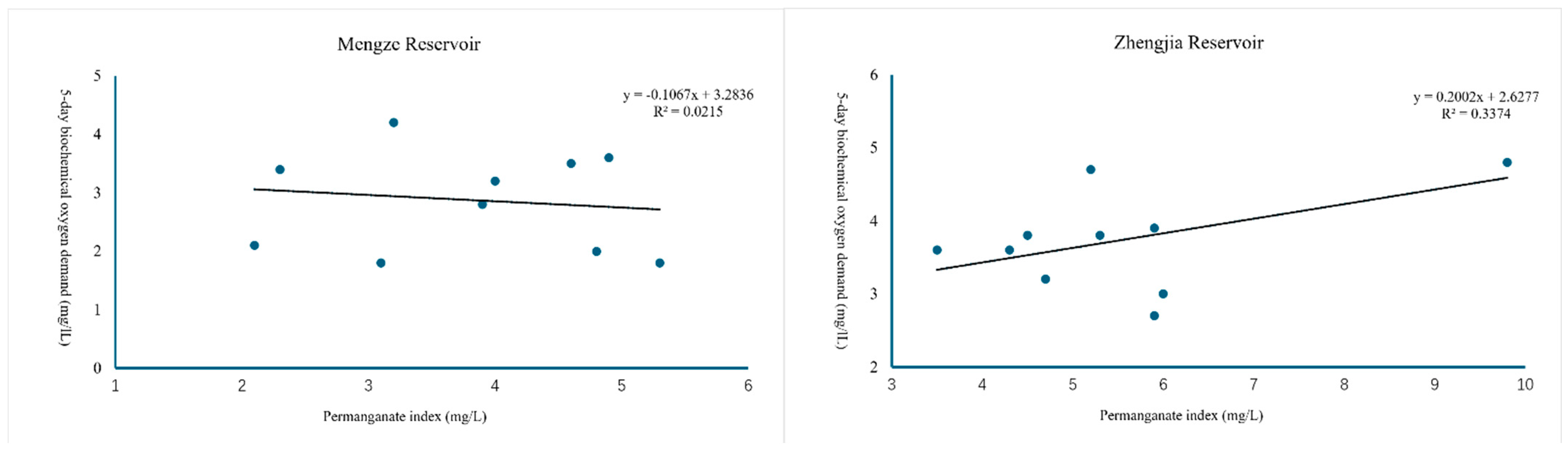
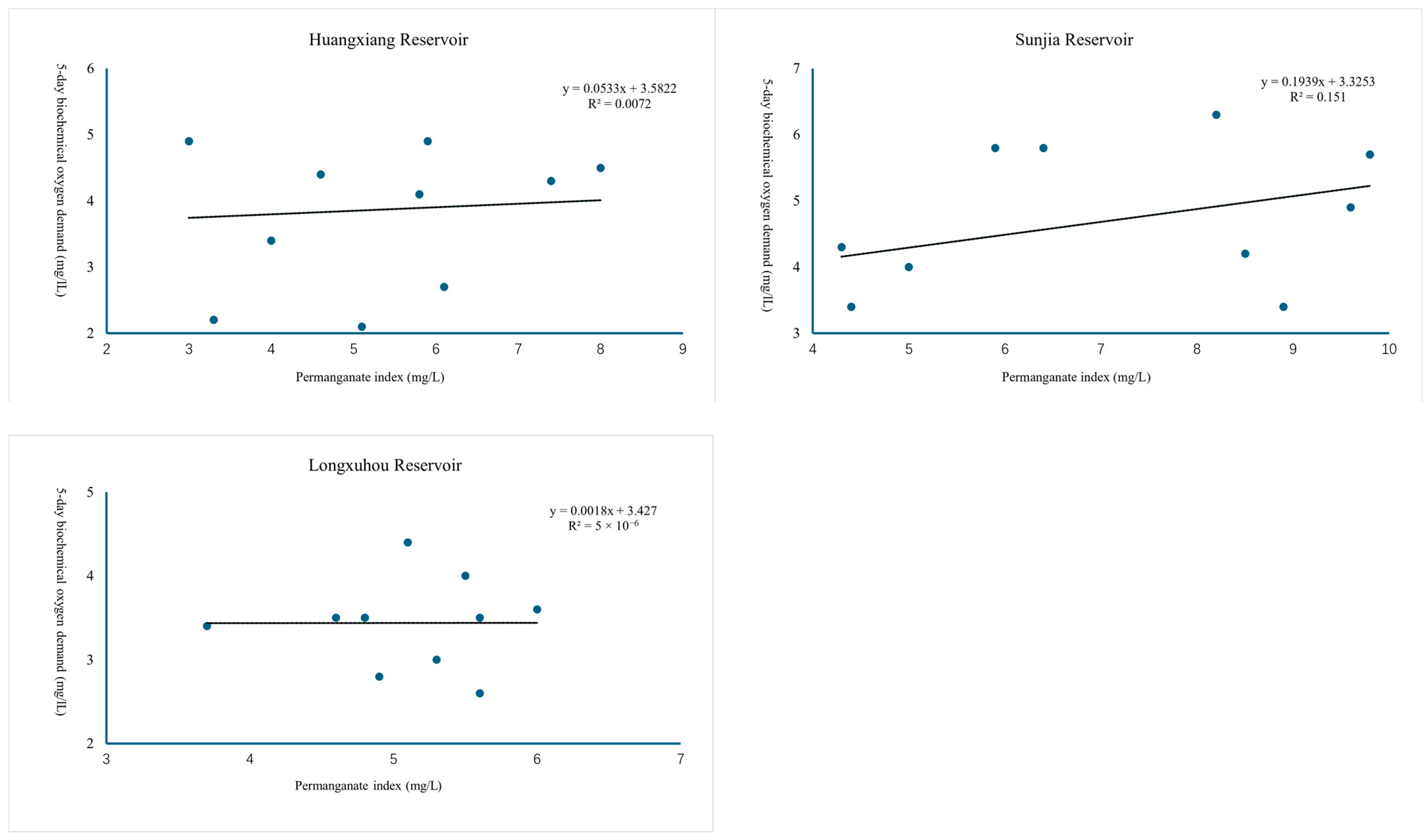
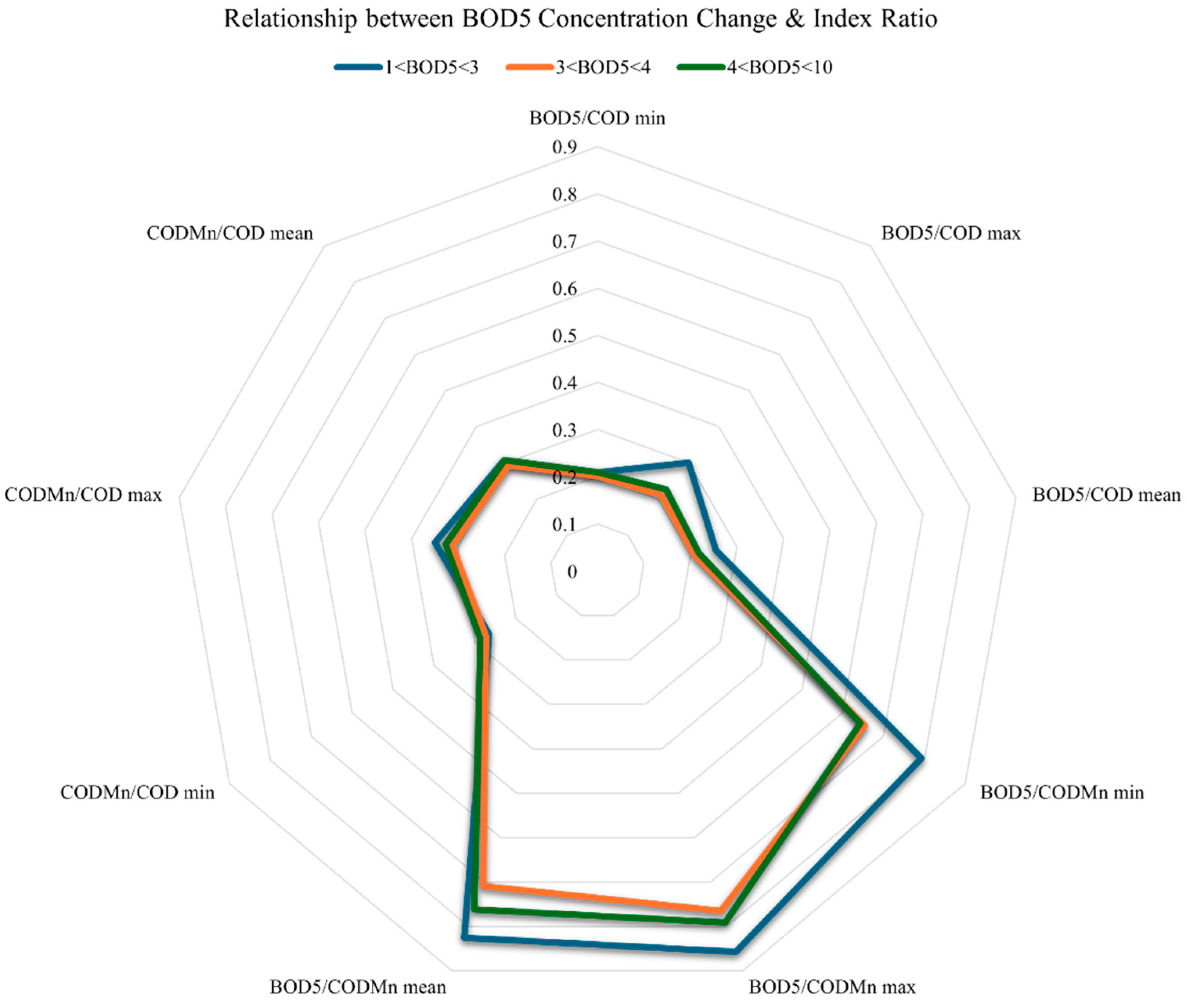
3.1. Correlation Outcome Statistics of BOD5, COD, and CODMn
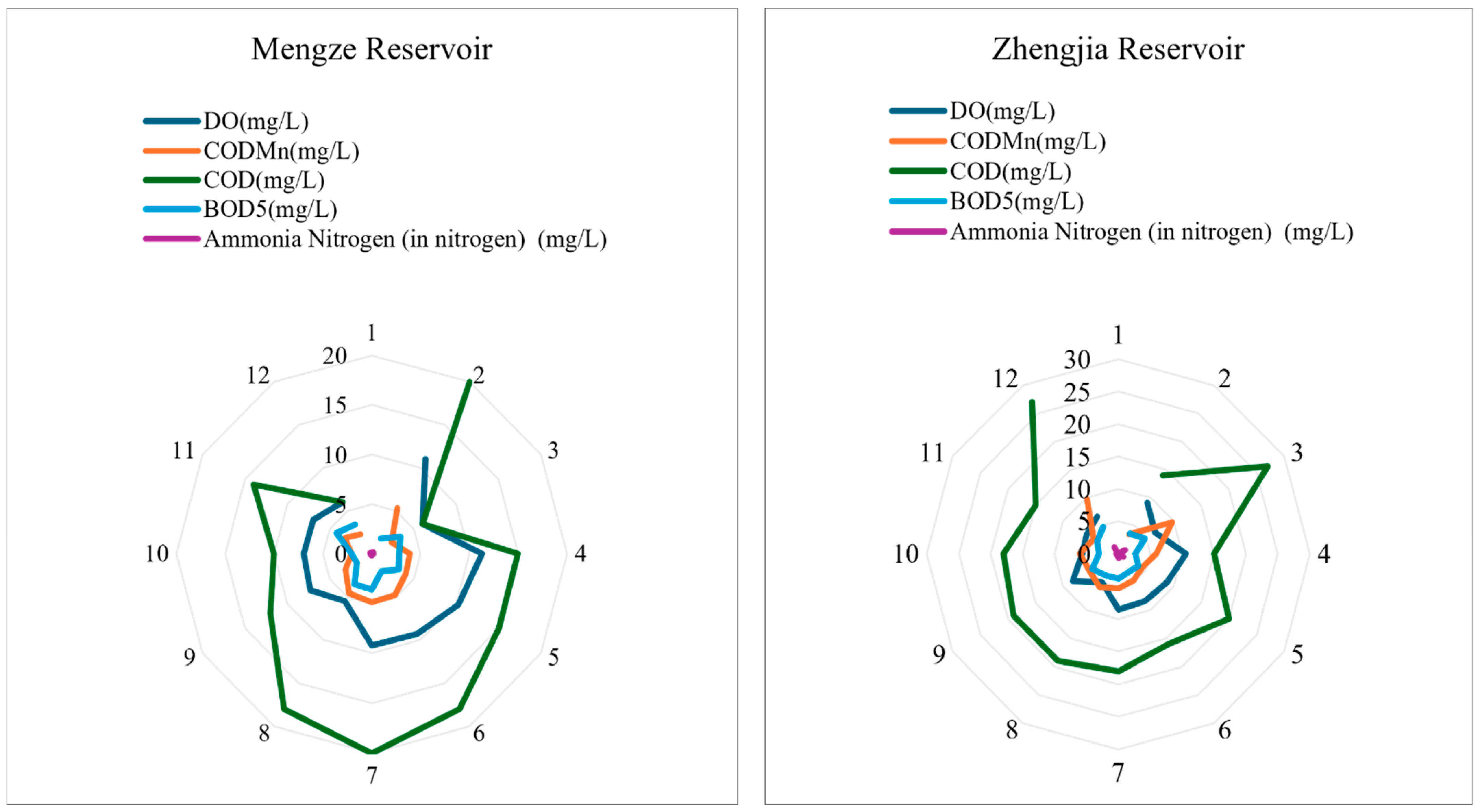
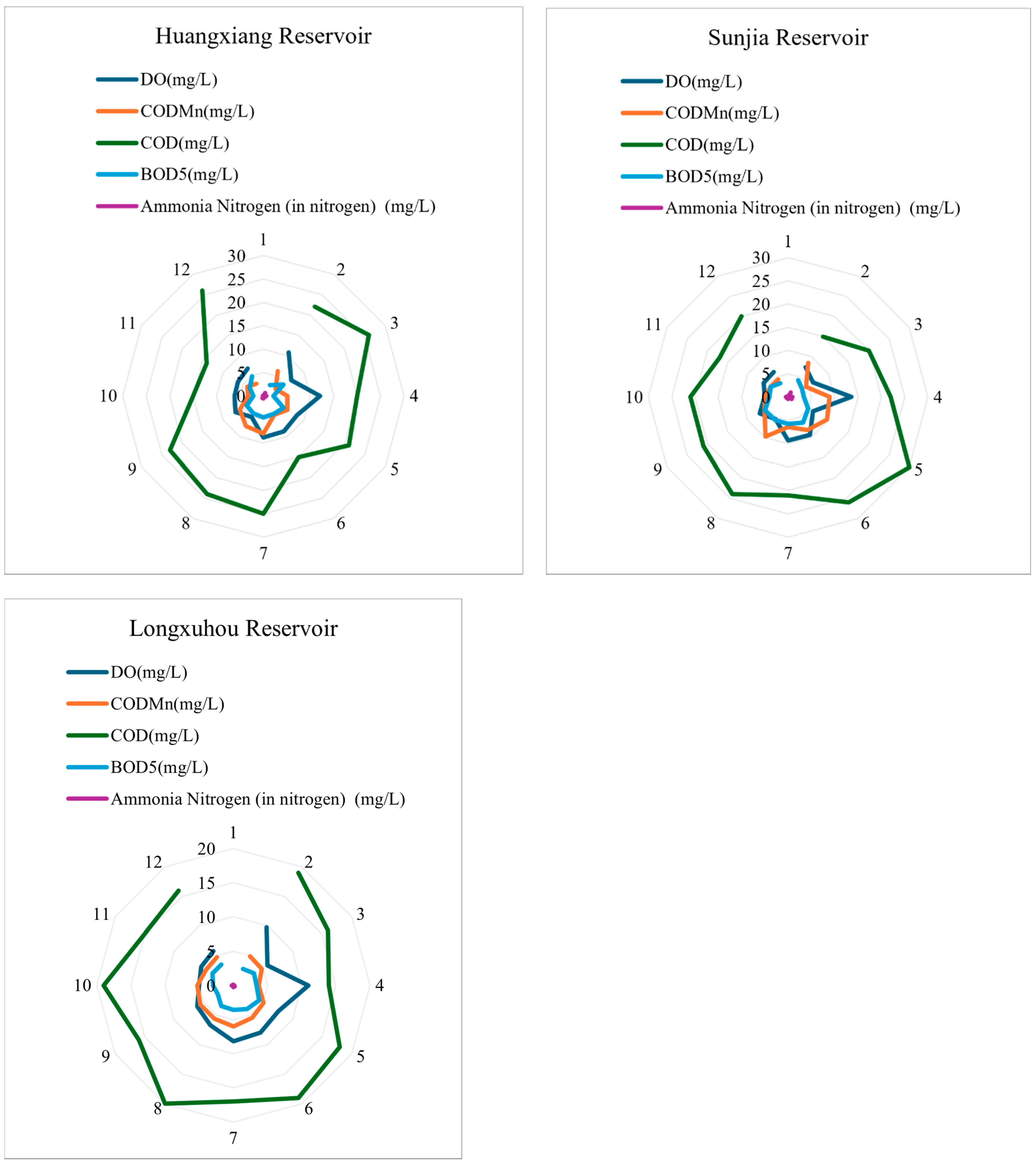
3.2. Statistics Results of DO, BOD5, COD, CODMn, and NH3-H
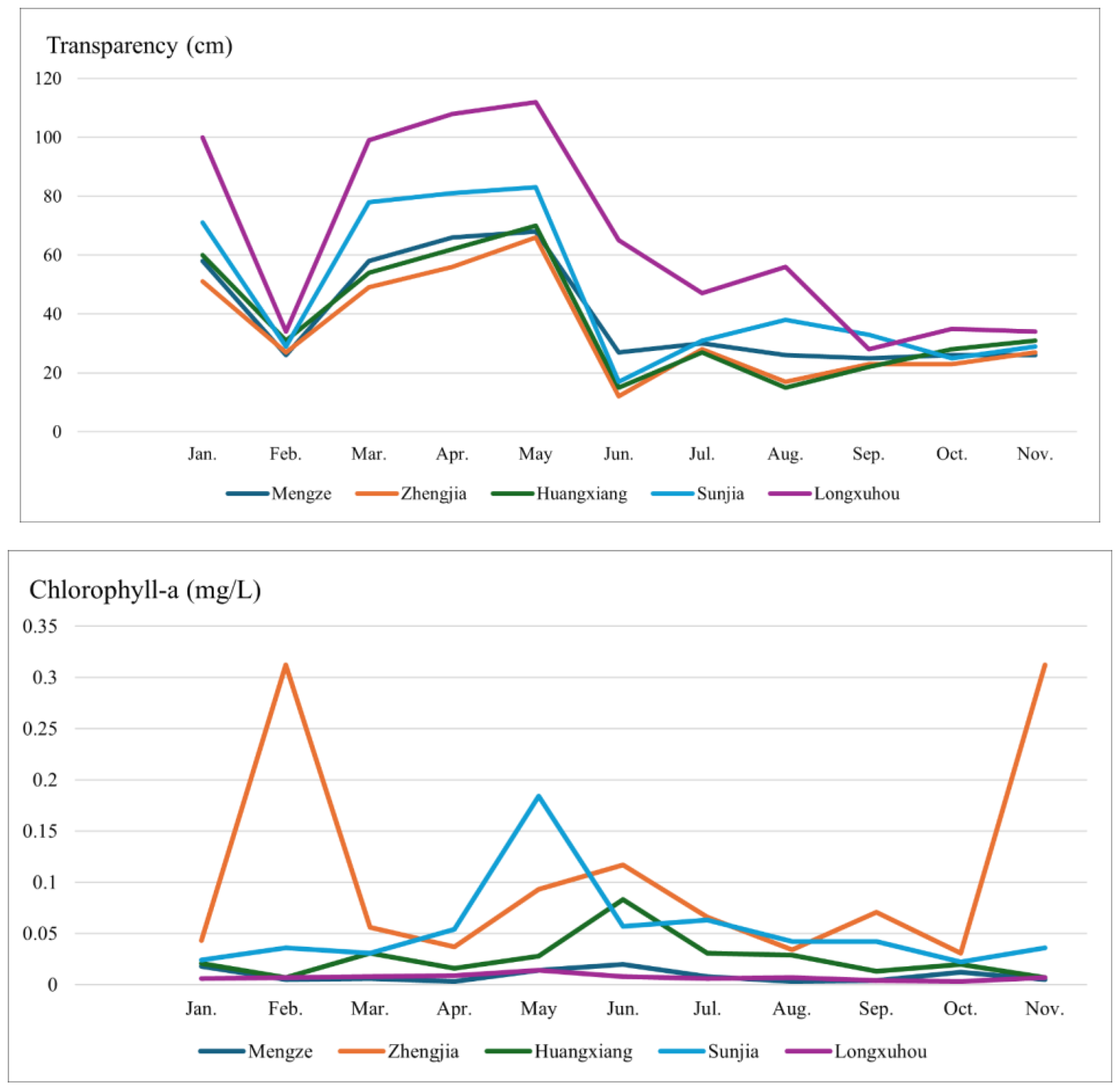
3.3. Analysis of Water Temperature, Chlorophyll-a, Transparency, and Turbidity Dynamics in the Reservoirs
4. Conclusions, Recommendations, and Research Limitations
Research Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Chu, X.; Chen, Y. Spatial and temporal distribution of dissolved oxygen in surface water environment of megacities. J. East China Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 6, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W. Variation of dissolved oxygen with depth in Dudang Reservoir. Straits Sci. 2012, 6, 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yan, L. Variation characteristics of dissolved oxygen and its correlation with water temperature in Changtan Reservoir, Zhejiang Province. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Jane, S.F.; Hansen, G.J.A.; Kraemer, B.M.; Leavitt, P.R.; Mincer, J.L.; North, R.L.; Pilla, R.M.; Stetler, J.T.; Williamson, C.E.; Woolway, R.I.; et al. Widespread deoxygenation of temperate lakes. Nature 2021, 594, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Klump, J.V.; Guo, L. Dynamics of dissolved and particulate phosphorus influenced by seasonal hypoxia in Green Bay, Lake Michigan. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotner, J.B.; Anderson, N.J.; Osburn, C. Accumulation of recalcitrant dissolved organic matter in aerobic aquatic systems. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2022, 7, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xie, Y.; Hashim, S.; Akhtar Khan, A.; Wang, X.; Xu, H. Application of Microbial Technology Used in Bioremediation of Urban Polluted River: A Case Study of Chengnan River, China. Water 2018, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhai, W.; Shan, B. Oxygen microprofile in the prepared sediments and its implication for the sediment oxygen consuming process in a heavily polluted river of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8634–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, H.; Yin, W.; Shao, S.; Lv, S.; Hu, Y. Water Quality and Microbial Community Changes in an Urban River after Micro-Nano Bubble Technology in Situ Treatment. Water 2019, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, X.; Chao, L.; Zhang, W.; You, T.; Zhang, J. Diversity change of microbial communities responding to zinc and arsenic pollution in a river of northeastern China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2014, 15, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, D. Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) determination methods. China Environ. Monit. 2004, 20, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, J.; Liu, H. Progress in determination of Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5). Hebei Chem. Ind. 2006, 1, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P. Application of inoculated fluid to five-day biochemical oxygen demand detection. Environ. Res. Monit. 2008, 21, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.T.K.; Viet, L.H.; Giao, N.T. Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Variations of Surface Water Quality in the Southern Province of Vietnamese Mekong Delta Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, D.; Huang, C.; Rutherford, S.; Dwirahmadi, F.; Chu, C.; Wang, X.; Nguyen, M.; Nguyen, N.H.; Do, C.M.; Nguyen, T.H.; et al. Temporal and spatial assessment of river surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A study in Can Tho City, a Mekong Delta area, Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ren, F.; Liu, J.; Shi, N.; Wang, H.; You, X. Evaluation of Wastewater Pollution and Treatment Efficiencies in China During Urbanization Based on Dynamic Exogenous Variable Data Envelopment Analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 585718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Duan, N.; Wu, X.; Fang, H. COD Discharge Limits for Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants in China Based on Statistical Methods. Water 2018, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Hua, M.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, P.; Ye, Z.; Huang, M.; Jin, Q. Sustainability efficiency assessment of wastewater treatment plants in China: A data envelopment analysis based on cluster benchmarking. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, E.P.A. Editorial Committee of Monitoring and Analysis Methods of Water and Wastewater State Environmental Protection Administration. In Monitoring and Analysis Methods of Water and Wastewater; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, J.; Ni, L.; Shen, H.; Xie, P. A Novel and Convenient Method for Early Warning of Algal Cell Density by Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters and Its Application in a Highland Lake. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-J.; Ruddick, K.; Lacroix, G. Detection of algal blooms in European waters based on satellite chlorophyll data from MERIS and MODIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 6567–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, J.; Cusack, C.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M.; Silke, J.; McElligott, D.; Davidson, K. Applied simulations and integrated modelling for the understanding of toxic and harmful algal blooms (ASIMUTH): Integrated HAB forecast systems for Europe’s Atlantic Arc. Harmful Algae 2016, 53, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wei, Y.; Wang, L.; Zeng, C.; Ma, X.; Wu, H. Impact of industrialization on water protection in the Huai River Basin within Shandong Province, China. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Pan, Z.; Wang, A. Determination of dissolved oxygen in water by iodometry. Chem. Anal. Metrol. 2021, 2, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Z.; Zhu, L. Influence of chloride ion on COD determination. Pollut. Control Technol. 2011, 24, 50–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Cheng, W. Correlation analysis of permanganate index, biochemical oxygen demand and chemical oxygen demand in surface water. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2016, 41, 134–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Liang, D. Development and Implementation of Machining Technology; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- China Environmental Science Press. Water Quality Five-day Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD5) Determination Dilution and Inoculation Method; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, Y. Health Standard for Smoke and Dust in Welding Workshops; National Group Standards Information Platform: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Guo, Z.; Shang, W. Determination method of ammonia nitrogen in water. Water Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 3, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiei, V.; Nejadhashemi, A.P.; Mushtaq, S.; Bailey, R.T.; An-Vo, D.A. Groundwater-surface water interactions at wetland interface: Advancement in catchment system modeling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 152, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, F.; Kung, H.T.; Yushanjiang, A. Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Composition and Water Quality Evaluation for Different Water Bodies in the Ebinur Lake Watershed, Northwestern China. Water 2019, 11, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Guo, M.; Cao, X.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Yue, W. Hydrochemical and Isotopic Characterization of the Impact of Water Diversion on Water in Drainage Channels, Groundwater, and Lake Ulansuhai in China. Water 2021, 13, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Miao, Q.; Li, Z.; Akae, T. A Study on Water and Salt Transport, and Balance Analysis in Sand Dune-Wasteland-Lake Systems of Hetao Oases, Upper Reaches of the Yellow River Basin. Water 2020, 12, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Jin, Q. Analysis and research on the correlation between Chemical oxygen Demand, permanganate index and Biochemical oxygen demand in China. In Environmental Engineering Technology Innovation and Application Sub-Forum, Proceedings of the 2019 Annual Science and Technology Conference of the Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences, Xi’an, China, 23–25 August 2019; Environmental Engineering Branch of Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences, Editorial Department of Environmental Engineering: Beijing, China, 2019; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Chen, W. Chlorophyll a and primary productivity of phytoplankton in Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 15, 2127–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Xiong, F.; Li, W. Spatial and temporal variation of transparency and its influencing factors in Fuxian Lake, Yunnan Province. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 681–686. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.; Gu, H.; Lou, C. Multiple regression analysis of water eutrophication factors in Beijing Zoo. Beijing Water Aff. 2012, 15, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D. Relationship between water transparency and eutrophication in Yudong Reservoir. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 34, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.-Q.; Tian, B.-H.; Xin, L.-H. Relationship between phytoplankton community structure and water quality factors in autumn in Yuqiao Reservoir. Environ. Pollut. Control 2011, 33, 64–68. [Google Scholar]



| Reservoir Name | Geographic Location | Detection Number | Depth at Which Water Samples Were Collected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mengze | E 113°41′12.72″, N 31°1′20.30″ | S2290001 | 0.35 m |
| Zhengjia | E 113°40′8.40″, N 31°1′0.83″ | S2290002 | 0.42 m |
| Huangxiang | E 113°45′50.50″, N 31°14′6.37″ | S2290003 | 0.38 m |
| Sunjia | E 113°47′1.65″, N 31°31′31″ | S2290004 | 0.39 m |
| Longxuhou | E 113°50′17.86″, N 31°0′24.75″ | S2290005 | 0.40 m |
| Monitoring Index | Standard Method | Standard Number |
|---|---|---|
| BOD5 | Water quality–determination of BOD5–dilution and inoculation method | HJ 505-2009 [8] |
| COD | Water quality–determination of COD–rapid digestion spectrophotometric method | HJ/T 399-2007 [9,10] |
| CODMn | Water quality–determination of CODMn | GB/T 11892-1989 [11] |
| Correlation Index | Reservoir Name | Linear Relation | R-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD-CODMn | Mengze | y = 4.1779x − 1.3822 | 0.9537 |
| Zhengjia | y = 1.9186x + 7.5839 | 0.8965 | |
| Huangxiang | y = 2.5535x + 5.6459 | 0.9247 | |
| Sunjia | y = 0.9901x + 14.759 | 0.5315 | |
| Longxuhou | y = 1.94x + 7.3233 | 0.6274 | |
| BOD5-CODMn | Mengze | y = −0.1067x + 3.2836 | 0.1466 |
| Zhengjia | y = 0.2002x + 2.6277 | 0.5809 | |
| Huangxiang | y = 0.0533x + 3.5822 | 0.0849 | |
| Sunjia | y = 0.1939x + 3.3253 | 0.3886 | |
| Longxuhou | y = 0.0018x + 3.427 | 0.0022 | |
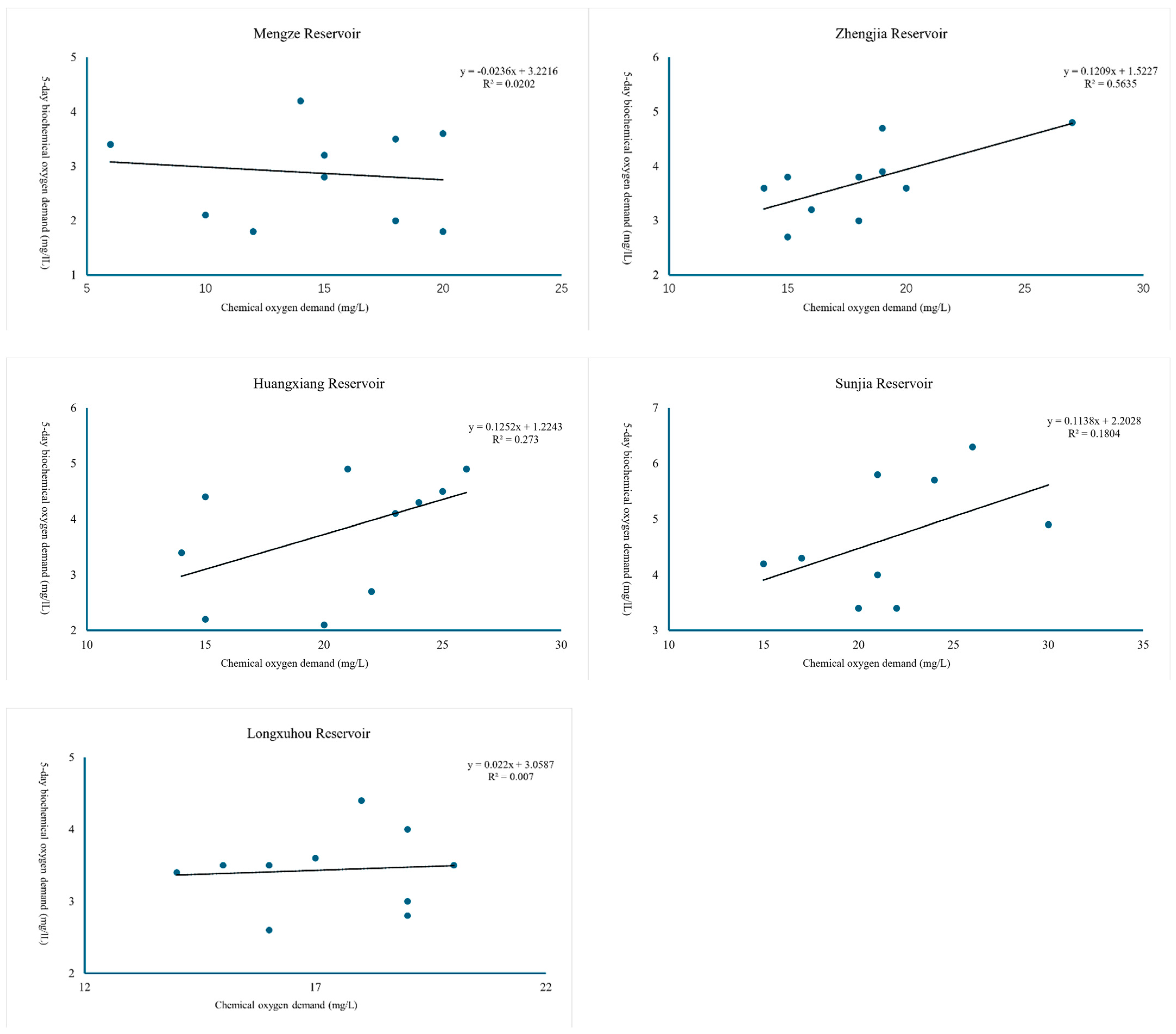
| COD-BOD5 | Mengze | y = −0.0236x + 3.2216 | 0.1421 |
| Zhengjia | y = 0.1209x + 1.5227 | 0.7507 | |
| Huangxiang | y = 0.1252x + 1.2243 | 0.5225 | |
| Sunjia | y = 0.1138x + 2.2028 | 0.4247 | |
| Longxuhou | y = 0.022x + 3.0587 | 0.0837 |
| Index | Mengze | Zhengjia | Huangxiang | Sunjia | Longxuhou | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD5 | max | 4.2000 | 4.8000 | 4.9000 | 6.3000 | 4.4000 |
| min | 1.8000 | 2.7000 | 2.1000 | 3.4000 | 2.6000 | |
| mean | 2.9077 | 3.8000 | 3.8000 | 4.6846 | 3.4462 | |
| COD | max | 20.0000 | 27.0000 | 26.0000 | 30.0000 | 20.0000 |
| min | 6.0000 | 14.0000 | 14.0000 | 15.0000 | 14.0000 | |
| mean | 13.8462 | 19.1538 | 20.8462 | 21.6923 | 17.1538 | |
| CODMn | max | 5.3000 | 9.8000 | 8.0000 | 9.8000 | 6.0000 |
| min | 2.1000 | 3.5000 | 3.0000 | 4.3000 | 3.7000 | |
| mean | 3.6818 | 6.0154 | 5.1692 | 6.8846 | 5.0462 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, P.; Wan, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Razzaq, A. Linking Water Quality Indicators in Stable Reservoir Ecosystems: Correlation Analysis and Ecohydrological Implications. Water 2024, 16, 3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243600
Du J, Yang X, Xu P, Wan X, Wang P, Wang D, Yang Q, Wang Q, Razzaq A. Linking Water Quality Indicators in Stable Reservoir Ecosystems: Correlation Analysis and Ecohydrological Implications. Water. 2024; 16(24):3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243600
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Juan, Xiao Yang, Peng Xu, Xiang Wan, Pan Wang, Ding Wang, Qi Yang, Qiu Wang, and Amar Razzaq. 2024. "Linking Water Quality Indicators in Stable Reservoir Ecosystems: Correlation Analysis and Ecohydrological Implications" Water 16, no. 24: 3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243600
APA StyleDu, J., Yang, X., Xu, P., Wan, X., Wang, P., Wang, D., Yang, Q., Wang, Q., & Razzaq, A. (2024). Linking Water Quality Indicators in Stable Reservoir Ecosystems: Correlation Analysis and Ecohydrological Implications. Water, 16(24), 3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243600








