Prediction of Reference Crop Evapotranspiration in China’s Climatic Regions Using Optimized Machine Learning Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
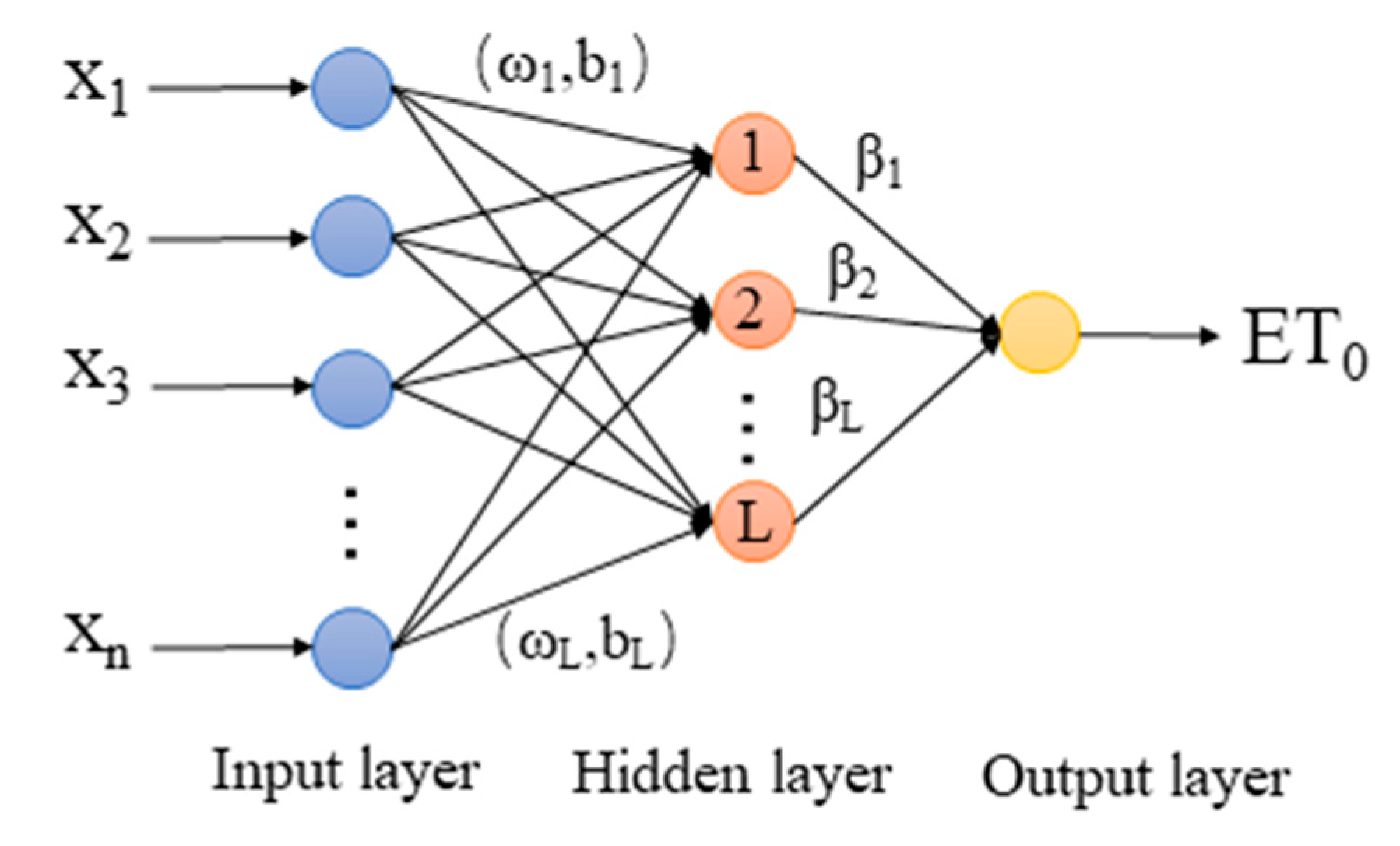
2.3. Extreme Learning Machine Model (ELM)
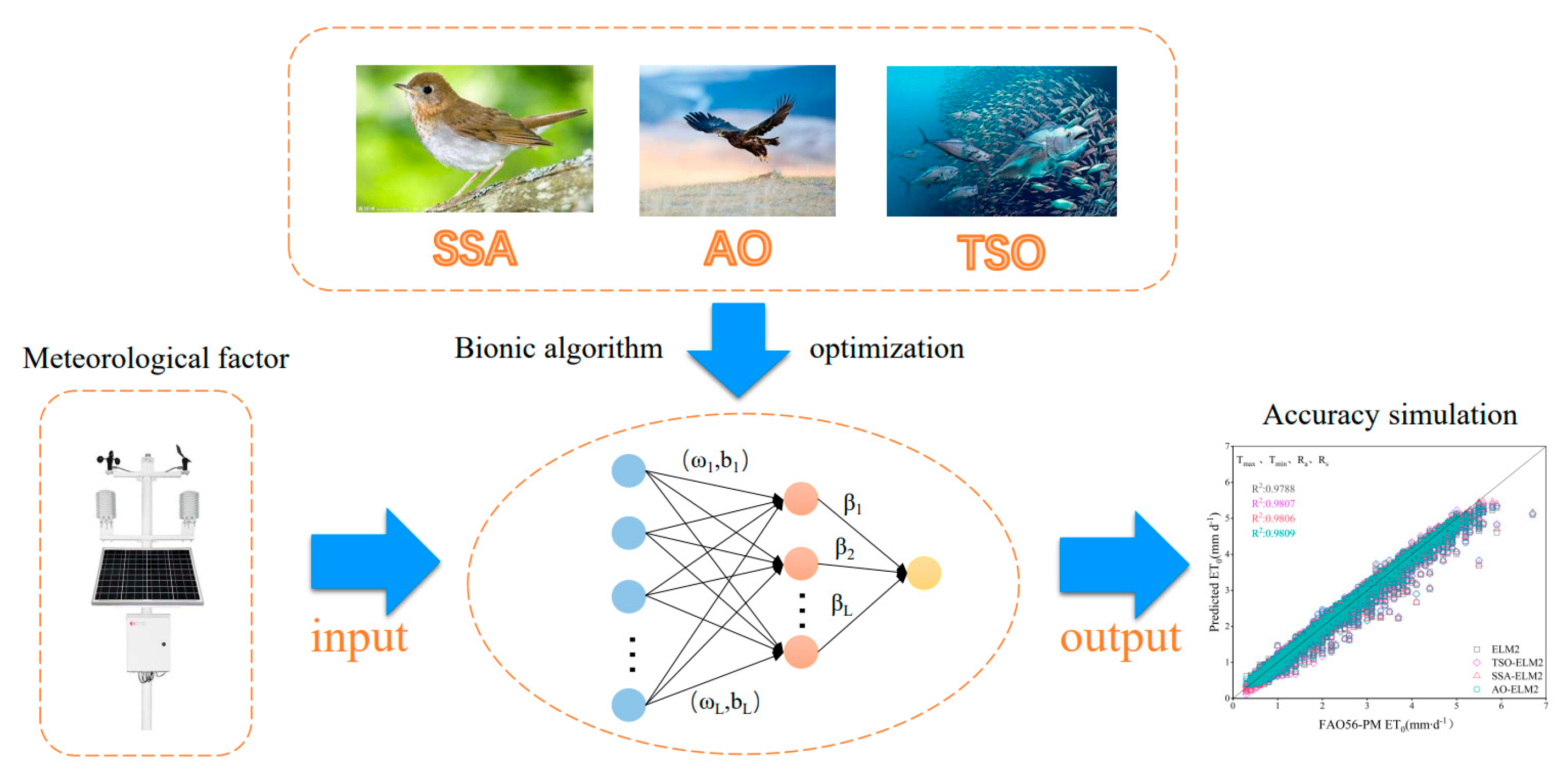
2.4. Novel Bionic Algorithm
2.4.1. Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA)
- Initialization of sparrow population:
- 2.
- Discoverer Update:
- 3.
- Follower Updates:
- 4.
- Danger warning:
2.4.2. Tuna Swarm Optimization (TSO)
- Population initialization:
- 2.
- Spiral predation:
2.4.3. Aquila Optimizer (AO)
- Extended Search (X1):
- 2.
- Narrowing Down the Search (X2):
- 3.
- Expansion Development (X3):
- 4.
- Scaling Down Development (X4):
2.5. Refer to Crop Evapotranspiration Calculation Model
2.5.1. FAO-56 Penman–Monteith Equation
2.5.2. Model Accuracy Verification
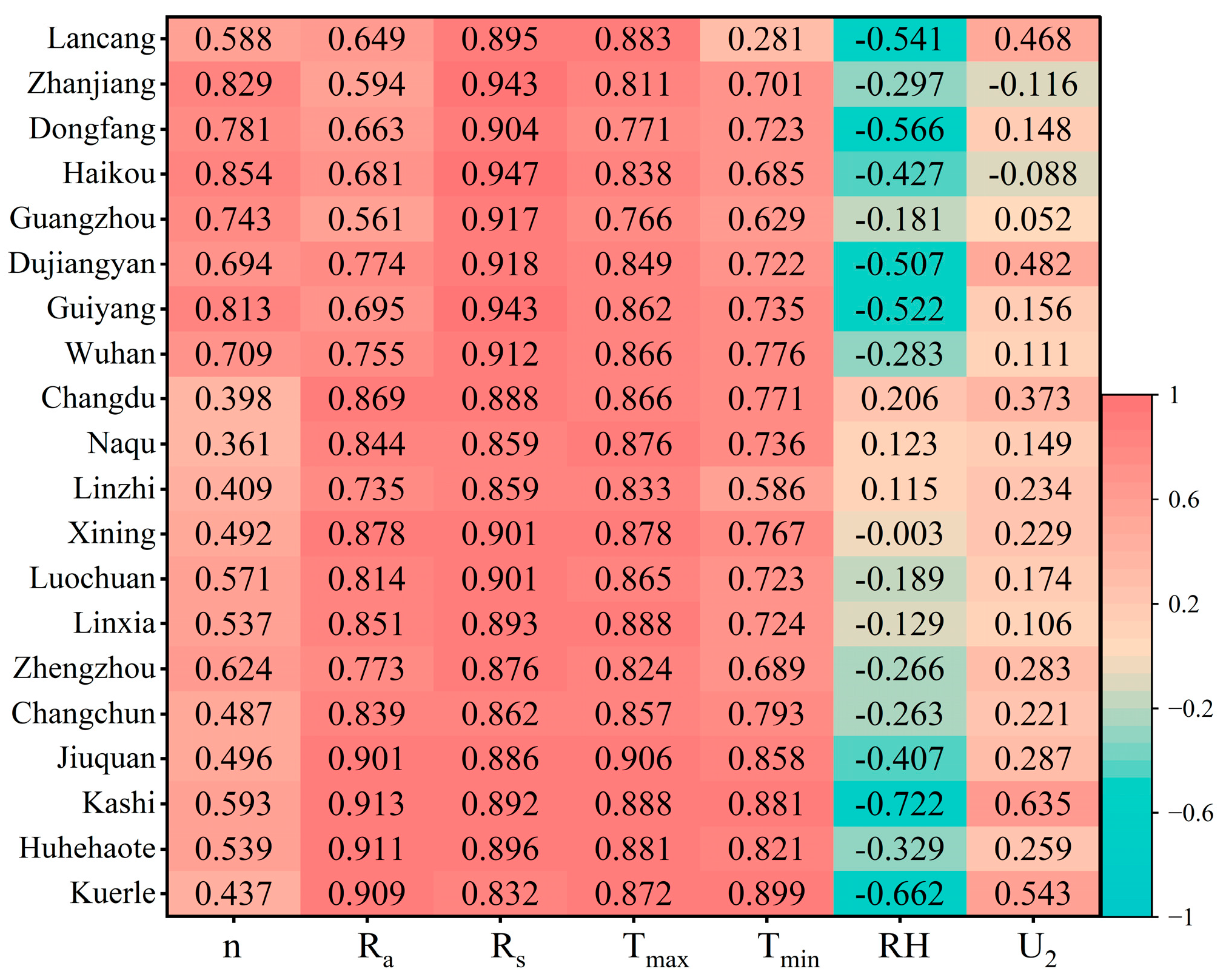
2.6. The Importance of Meteorological Factors for ET0 as Determined by the Through Analysis Method
3. Results and Analysis
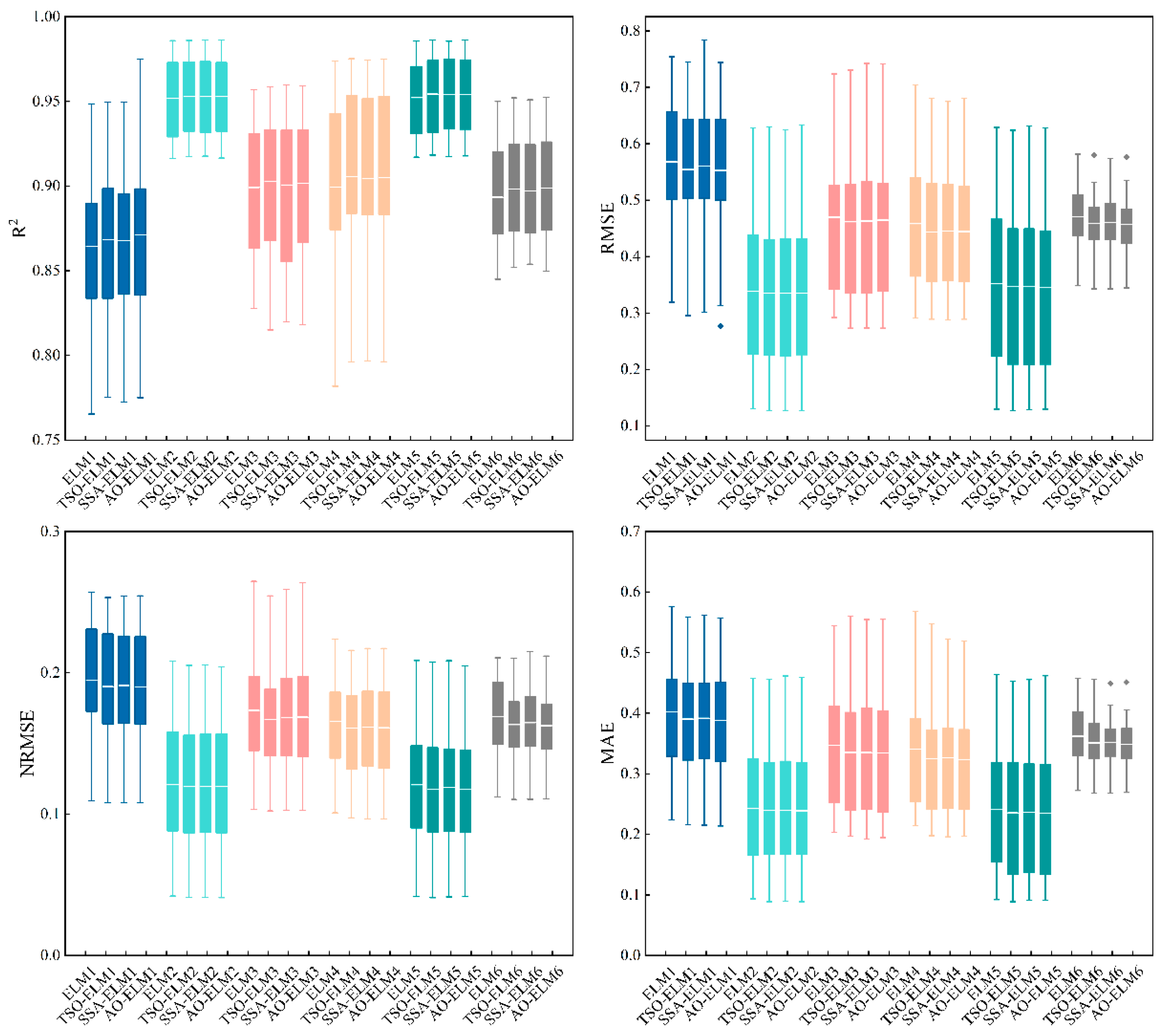
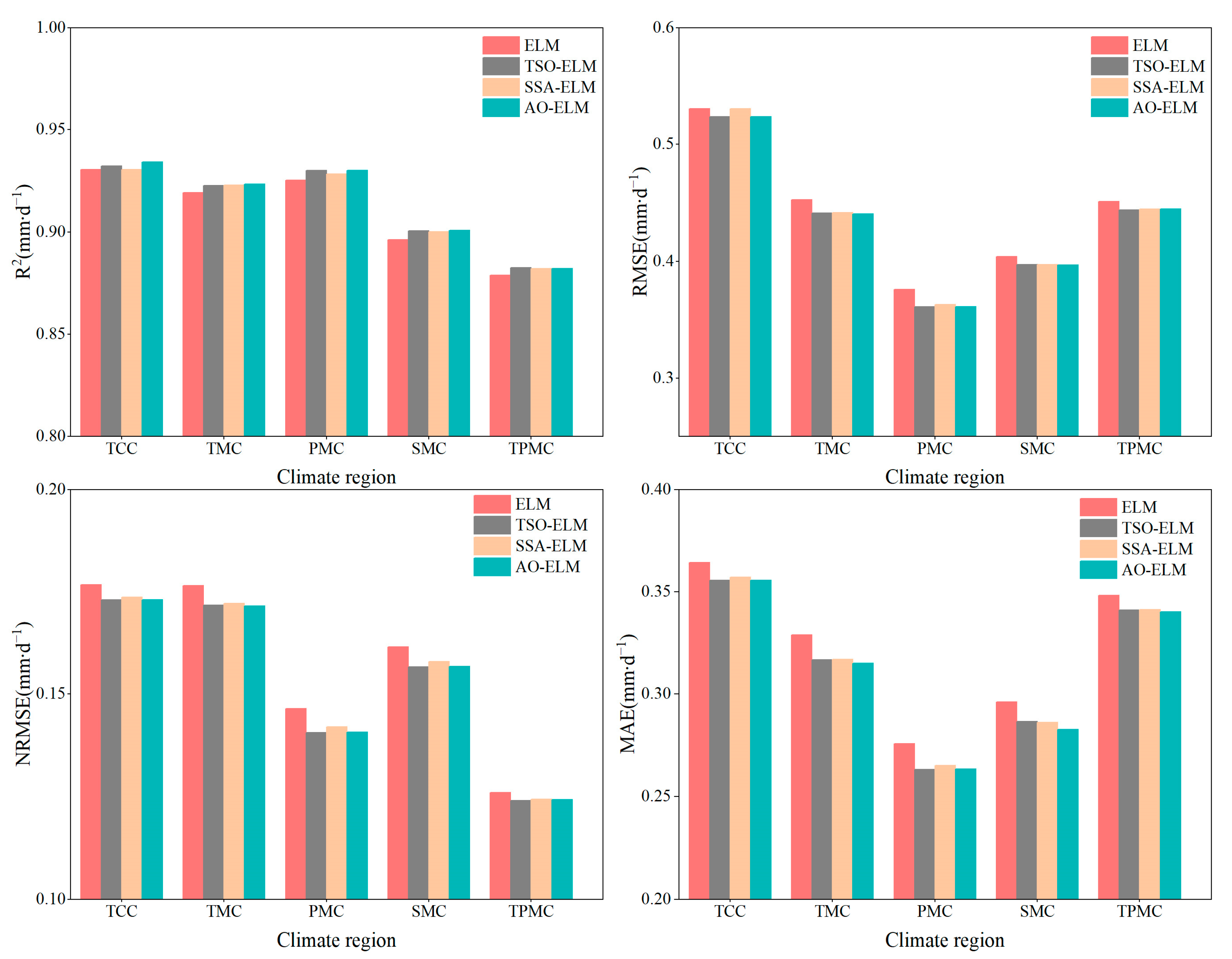
3.1. Comparison of Performance Differences of Machine Learning Models in Different Climate Regions
3.2. Comparison of the Stability of Each Machine Learning Model
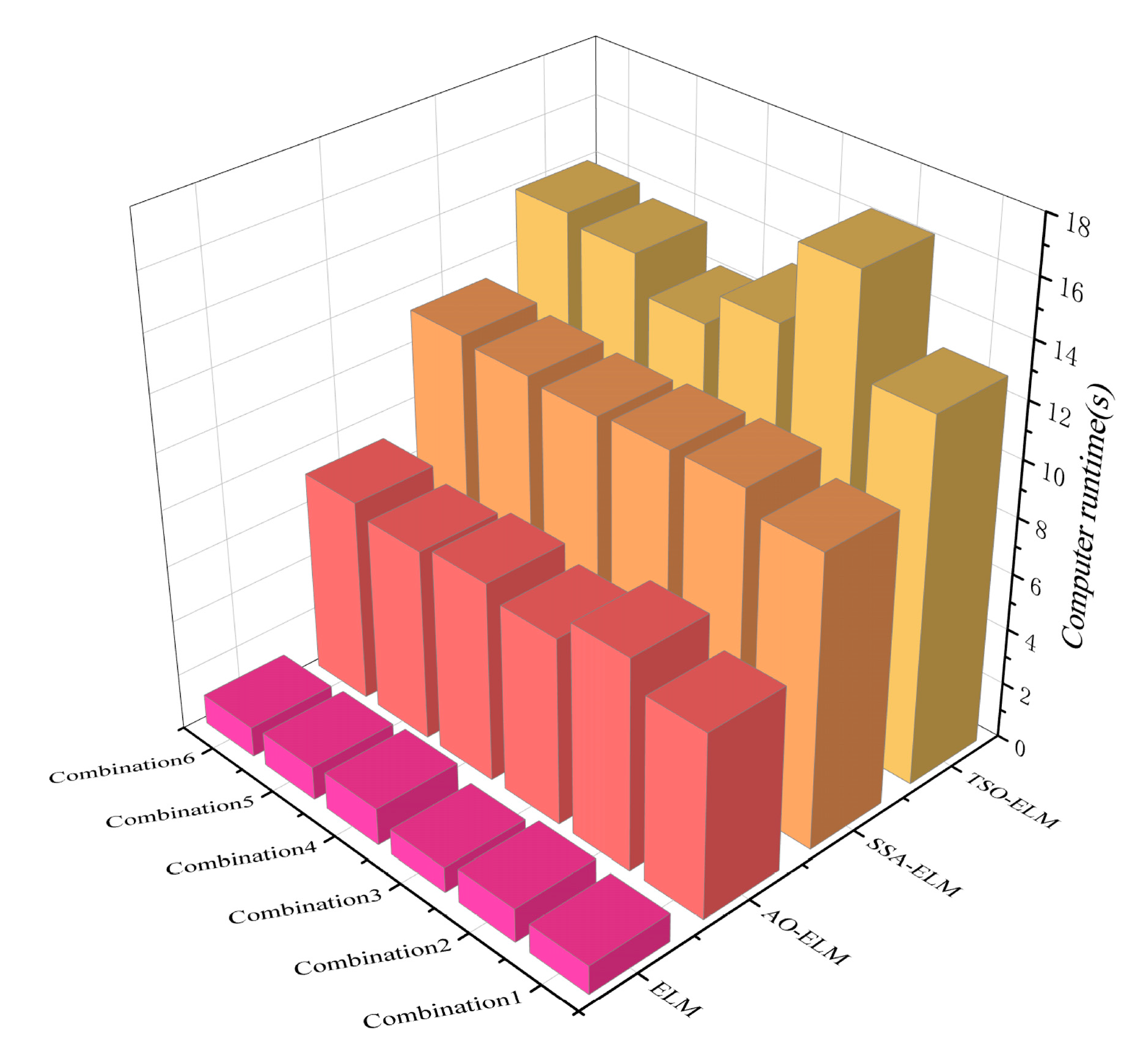
3.3. Comparison of Computational Costs of Various Machine Learning Models
3.4. Selection of the Best Model for Each Climate Region
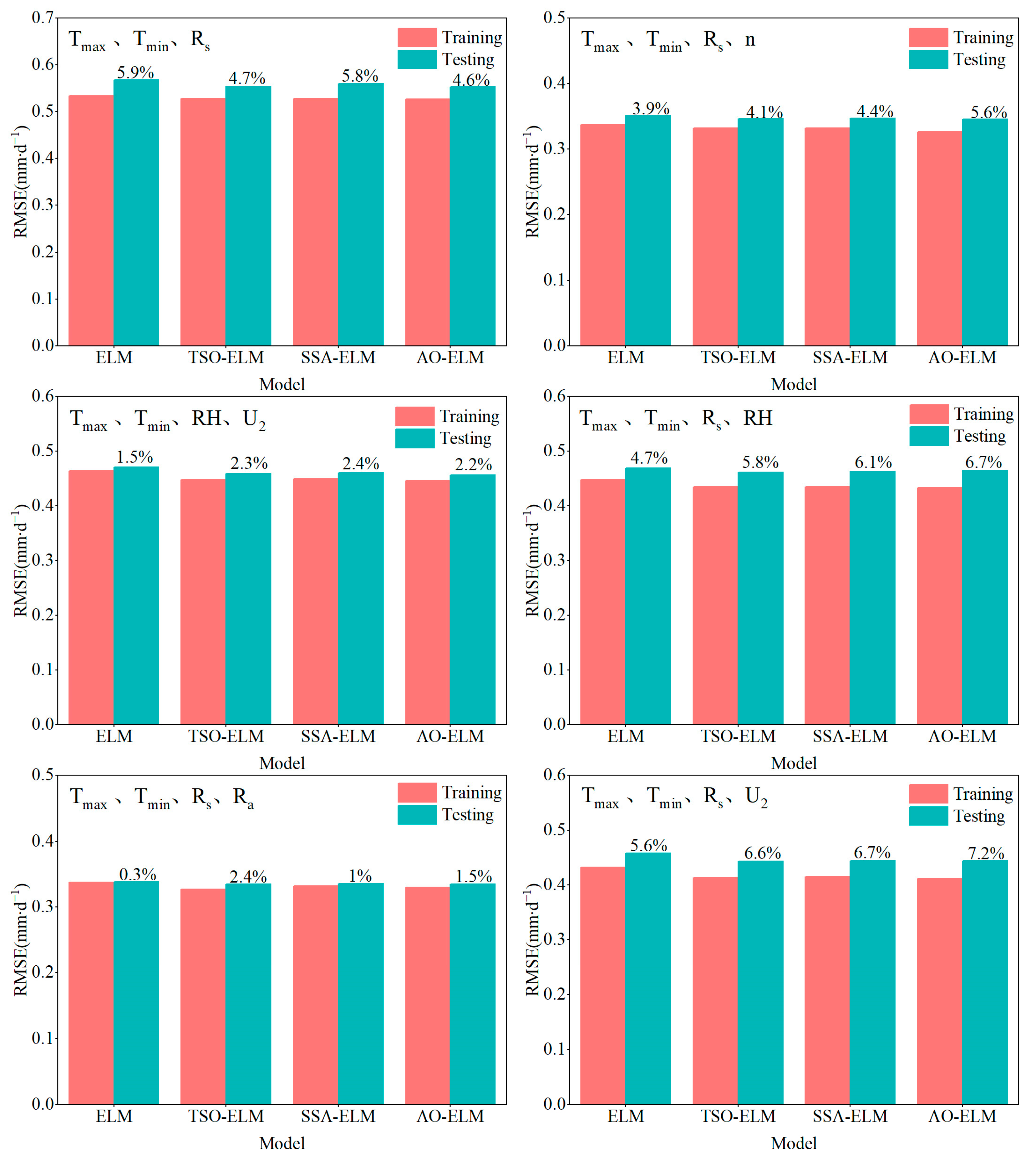
3.5. Improving ET0 Predictions More Effectively
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- During the testing phase, the three hybrid models demonstrated satisfactory prediction accuracy across different climatic regions. Among them, the AO-ELM model exhibited superior predictive performance compared to the SSA-ELM and TSO-ELM models.
- (2)
- In scenarios where complete meteorological data are unavailable, the combination of the Tmax, Tmin, and Rs parameters with U2 as an input parameter yield better ET0 predictions in temperate continental monsoon climate regions. Conversely, using n as an input parameter provided satisfactory ET0 predictions in the other climate regions.
- (3)
- Stations located in highland mountain climate regions exhibited excellent simulation performance, while those in tropical monsoon climate regions showed the poorest performance. This suggests that local climate conditions significantly influence the overall model performance.
- (4)
- For model selection, the AO-ELM model demonstrated superior predictive performance when applied on a large scale. Regarding the optimal combination of input parameters, apart from the superior prediction accuracy of the combination4 in the temperate continental monsoon (TCC) region, the combination5 performed better in the remaining four climatic regions. Therefore, AO-ELM4 (utilizing Tmax, Tmin, Rs, and U2 as inputs) was chosen for the temperate continental climate (TCC) region, and AO-ELM5 (utilizing Tmax, Tmin, Rs and n as inputs) was chosen for the tropical monsoon climate (TMC), plateau mountain climate (PMC), subtropical monsoon climate (SMC), and temperate monsoon climate (TPMC) regions when determining the most suitable model for each climatic region with limited meteorological data.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, R.G. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO Irrig. Drain. Pap. 1998, 56, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Shiri, J.; Kisi, Ö.; Landeras, G.; López, J.J.; Nazemi, A.H.; Stuyt, L. Daily reference evapotranspiration modeling by using genetic programming approach in the Basque Country (Northern Spain). J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cui, N.; Feng, Y.; Gong, D.; Hu, X. Improvement of Makkink model for reference evapotranspiration estimation using temperature data in Northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jia, Y.; Cui, N.; Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Gong, D. Calibration of Hargreaves model for reference evapotranspiration estimation in Sichuan basin of southwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 181, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, R.S.; Han, C.T.; Liu, Z.W. Evaluation of 18 models for calculating potential evapotranspiration in different climatic zones of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.H.; Sun, X.H.; Ma, J.J. Prediction of daily crop reference evapotranspiration (ET0) values through a least-squares support vector machine model. Hydrol. Res. 2011, 42, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gong, D.; Cui, N. National-scale assessment of pan evaporation models across different climatic zones of China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.L.; Gong, D.Z.; Cui, N.B.; Lv, M.; Feng, Y. Evaluation of bio-inspired optimization algorithms hybrid with artificial neural network for reference crop evapotranspiration estimation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 190, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.B.; Da Cunha, F.F.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Fernandes, E.I. Estimation of reference evapotranspiration in Brazil with limited meteorological data using ANN and SVM—A new approach. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Zheng, J.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, F.C. Estimation of daily maize transpiration using support vector machines, extreme gradient boosting, artificial and deep neural networks models. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Mehdizadeh, S. Modeling daily reference evapotranspiration via a novel approach based on support vector regression coupled with whale optimization algorithm. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, A.T.; Ella, V.B.; Lampayan, R.M.; Reaño, C.E. Modeling Reference Crop Evapotranspiration Using Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) in Region IV-A, Philippines. Water 2022, 14, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.H.; Si, J.H.; He, Z.B.; Wu, J.; Shao, H.B.; Yu, H.J. Support-Vector-Machine-Based Models for Modeling Daily Reference Evapotranspiration With Limited Climatic Data in Extreme Arid Regions. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 3195–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladlani, I.; Houichi, L.; Djemili, L.; Heddam, S.; Belouz, K. Modeling daily reference evapotranspiration (ET0) in the north of Algeria using generalized regression neural networks (GRNN) and radial basis function neural networks (RBFNN): A comparative study. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2012, 118, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Peng, Y.; Cui, N.B.; Gong, D.Z.; Zhang, K.D. Modeling reference evapotranspiration using extreme learning machine and generalized regression neural network only with temperature data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 136, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Cui, N.B.; Gong, D.Z.; Zhang, Q.W.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of random forests and generalized regression neural networks for daily reference evapotranspiration modelling. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lian, J.J.; Peng, Y.Z.; Hu, B.Q.; Chen, H.S. Generalized reference evapotranspiration models with limited climatic data based on random forest and gene expression programming in Guangxi, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, H.W.; Xue, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.G.; Yan, D.; Gui, D.W. Estimating evapotranspiration by coupling Bayesian model averaging methods with machine learning algorithms. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Ren, J.; Wang, K.; Guo, X. Estimation of reference evapotranspiration via machine learning algorithms in humid and semiarid environments in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 5091–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spontoni, T.A.; Ventura, T.M.; Palacios, R.S.; Curado, L.; Fernandes, W.A.; Capistrano, V.B.; Fritzen, C.L.; Pavao, H.G.; Rodrigues, T.R. Evaluation and Modelling of Reference Evapotranspiration Using Different Machine Learning Techniques for a Brazilian Tropical Savanna. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, Y.; Kumar, M.; Ananthakrishnan, S.; Kumarapuram, G. Evapotranspiration Modeling Using Different Tree Based Ensembled Machine Learning Algorithm. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagappan, M.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Alagappan, M. Prediction of reference evapotranspiration for irrigation scheduling using machine learning. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 2669–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.F.; Peng, Y.W.; Fan, J.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Huang, G.M. A novel kernel extreme learning machine model coupled with K-means clustering and firefly algorithm for estimating monthly reference evapotranspiration in parallel computation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Cui, N.B.; Zhao, L.; Hu, X.T.; Gong, D.Z. Comparison of ELM, GANN, WNN and empirical models for estimating reference evapotranspiration in humid region of Southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Yue, W.J.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, F.C.; Cai, H.J.; Wang, X.K.; Lu, X.H.; Xiang, Y.Z. Evaluation of SVM, ELM and four tree-based ensemble models for predicting daily reference evapotranspiration using limited meteorological data in different climates of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 263, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gong, D.Z.; Mei, X.R.; Cui, N.B. Estimation of maize evapotranspiration using extreme learning machine and generalized regression neural network on the China Loess Plateau. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.L.; Feng, Q.; Yang, L.S.; Deo, R.C.; Wen, X.H.; Si, J.H.; Xiao, S.C. Future Projection with an Extreme-Learning Machine and Support Vector Regression of Reference Evapotranspiration in a Mountainous Inland Watershed in North-West China. Water 2017, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.S.; Malek, M.A.; Abdullah, N.S.; Kisi, O.; Yap, K.S. Extreme Learning Machines: A new approach for prediction of reference evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, M.Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Koo, C.H. Swarm-based optimization as stochastic training strategy for estimation of reference evapotranspiration using extreme learning machine. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.S.; Wu, Z.J.; Cui, N.B.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, Y.S.; Hu, X.T.; Gong, D.Z.; Zheng, S.S. Genetic Algorithm-Optimized Extreme Learning Machine Model for Estimating Daily Reference Evapotranspiration in Southwest China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Feng, Y.; Gong, D.Z.; Jiang, S.Z.; Zhao, L.; Cui, N.B. Hybrid particle swarm optimization with extreme learning machine for daily reference evapotranspiration prediction from limited climatic data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 173, 105430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Han, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.R.; Han, B.; Tang, A.D. Tuna Swarm Optimization: A Novel Swarm-Based Metaheuristic Algorithm for Global Optimization. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 9210050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abualigah, L.; Yousri, D.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Ewees, A.A.; Al-qaness, M.; Gandomi, A.H. Aquila Optimizer: A novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 157, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Shen, B. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: Sparrow search algorithm. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2020, 8, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, F.C.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Zheng, J. Climate change effects on reference crop evapotranspiration across different climatic zones of China during 1956–2015. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhu, Q.; Siew, C. Extreme learning machine: A new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.F.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.N.; Xu, X.Z.; Nie, R. Extreme learning machine: Algorithm, theory and applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2015, 44, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.H.; Liu, X.G.; Huang, G.M.; Fan, J.L.; Wu, L.F.; Wu, J. Comparison of four bio-inspired algorithms to optimize KNEA for predicting monthly reference evapotranspiration in different climate zones of China. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 186, 106211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.C.; Wu, L.F.; Fan, J.L.; Zhang, F.C.; Zou, Y.F.; Wu, Y. A novel hybrid WOA-XGB model for estimating daily reference evapotranspiration using local and external meteorological data: Applications in arid and humid regions of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Z.; Liang, C.; Cui, N.B.; Zhao, L.; Du, T.S.; Hu, X.T.; Feng, Y.; Guan, J.; Feng, Y. Impacts of climatic variables on reference evapotranspiration during growing season in Southwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 216, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.F.; Fan, J.L. Comparison of neuron-based, kernel-based, tree-based and curve-based machine learning models for predicting daily reference evapotranspiration. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVicar, T.R.; Roderick, M.L.; Donohue, R.J.; Li, L.T.; Van Niel, T.G.; Thomas, A.; Grieser, J.; Jhajharia, D.; Himri, Y.; Mahowald, N.M.; et al. Global review and synthesis of trends in observed terrestrial near-surface wind speeds: Implications for evaporation. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, R.M.; Dai, H.L.; Mostafa, R.R.; Islam, A.; Kisi, O.; Elbeltagi, A.; Zounemat-Kermani, M. Application of novel binary optimized machine learning models for monthly streamflow prediction. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, R.R.; Kisi, O.; Adnan, R.M.; Sadeghifar, T.; Kuriqi, A. Modeling Potential Evapotranspiration by Improved Machine Learning Methods Using Limited Climatic Data. Water 2023, 15, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Climate Regions | Station | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | Elevation (m) | Tmax (℃) | Tmin (℃) | N (h) | RH (%) | U2 (m·s−1) | Rs (MJ m−2·d−1) | Ra (MJ m−2·d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCC | Kuerle | 41.75 | 86.17 | 937 | 18.31 | 6.09 | 7.89 | 45.21 | 1.30 | 15.97 | 27.61 |
| Kashi | 39.47 | 75.99 | 1281 | 18.49 | 6.02 | 7.71 | 49.93 | 1.01 | 16.32 | 28.41 | |
| Jiuquan | 39.75 | 98.51 | 1476 | 15.07 | 1.24 | 8.42 | 47.10 | 1.25 | 16.91 | 28.31 | |
| Huhehaote | 40.81 | 111.62 | 1074 | 13.46 | 0.93 | 7.72 | 52.16 | 1.06 | 15.96 | 27.93 | |
| TMC | Changchun | 43.83 | 125.29 | 215 | 11.34 | 0.83 | 7.14 | 62.76 | 2.07 | 14.56 | 26.78 |
| Zhengzhou | 34.72 | 113.64 | 107 | 20.40 | 9.89 | 5.80 | 64.29 | 1.39 | 14.77 | 30.02 | |
| Linxia | 35.60 | 103.21 | 1882 | 14.49 | 1.69 | 6.66 | 66.33 | 0.71 | 15.60 | 29.75 | |
| Luochuan | 35.76 | 109.43 | 1166 | 15.63 | 4.83 | 6.89 | 61.76 | 1.19 | 15.85 | 29.69 | |
| PMC | Xining | 36.65 | 101.77 | 2249 | 14.05 | 0.08 | 7.27 | 56.24 | 0.82 | 16.14 | 29.42 |
| Linzhi | 29.64 | 94.36 | 3100 | 16.29 | 4.05 | 5.48 | 63.19 | 0.94 | 14.90 | 31.57 | |
| Naqu | 31.48 | 92.05 | 4500 | 7.13 | −7.73 | 7.58 | 51.76 | 1.48 | 17.38 | 31.04 | |
| Changdu | 31.14 | 97.18 | 3244 | 16.82 | 0.93 | 6.56 | 50.31 | 0.64 | 16.15 | 31.14 | |
| SMC | Wuhan | 30.60 | 114.03 | 48 | 21.46 | 13.22 | 5.26 | 77.02 | 1.08 | 14.76 | 31.30 |
| Guangzhou | 23.16 | 113.27 | 21 | 26.56 | 18.99 | 4.57 | 76.98 | 1.02 | 14.57 | 33.23 | |
| Guiyang | 26.68 | 106.62 | 1100 | 19.63 | 12.12 | 3.15 | 77.53 | 1.26 | 12.47 | 32.41 | |
| Dujiangyan | 30.99 | 103.65 | 1019 | 19.28 | 12.65 | 2.52 | 79.68 | 0.66 | 11.15 | 31.18 | |
| TPMC | Haikou | 20.03 | 110.33 | 15 | 28.11 | 21.55 | 5.61 | 83.18 | 1.53 | 16.50 | 33.93 |
| Dongfang | 19.10 | 108.65 | 73 | 28.71 | 22.26 | 7.07 | 78.78 | 2.42 | 18.61 | 34.10 | |
| Lancang | 22.56 | 99.93 | 1054 | 27.45 | 14.69 | 5.91 | 77.41 | 0.48 | 16.45 | 33.38 | |
| Zhanjiang | 21.27 | 110.37 | 23 | 26.84 | 20.76 | 5.24 | 81.89 | 1.62 | 15.80 | 33.69 |
| Models | Input Combinations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELM | TSO-ELM | SSA-ELM | AO-ELM | |
| ELM1 | TSO-ELM1 | SSA-ELM1 | AO-ELM1 | Tmax, Tmin, Rs |
| ELM2 | TSO-ELM2 | SSA-ELM2 | AO-ELM2 | Tmax, Tmin, Rs, Ra |
| ELM3 | TSO-ELM3 | SSA-ELM3 | AO-ELM3 | Tmax, Tmin, Rs, RH |
| ELM4 | TSO-ELM4 | SSA-ELM4 | AO-ELM4 | Tmax, Tmin, Rs, U2 |
| ELM5 | TSO-ELM5 | SSA-ELM5 | AO-ELM5 | Tmax, Tmin, Rs, n |
| ELM6 | TSO-ELM6 | SSA-ELM6 | AO-ELM6 | Tmax, Tmin, RH, U2 |
| Training | Testing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | |
| ELM1 | 0.9022 | 0.6259 | 0.2178 | 0.4219 | 0.9046 | 0.6251 | 0.2060 | 0.4265 |
| TSO-ELM1 | 0.9041 | 0.6197 | 0.2155 | 0.4155 | 0.9016 | 0.6402 | 0.2118 | 0.4151 |
| SSA-ELM1 | 0.9038 | 0.6208 | 0.2160 | 0.4163 | 0.9010 | 0.6721 | 0.2123 | 0.4162 |
| AO-ELM1 | 0.9043 | 0.6191 | 0.2153 | 0.4144 | 0.9015 | 0.6402 | 0.2117 | 0.4150 |
| ELM2 | 0.9304 | 0.5233 | 0.1730 | 0.3592 | 0.9282 | 0.5475 | 0.1807 | 0.3659 |
| TSO-ELM2 | 0.9337 | 0.5136 | 0.1771 | 0.3519 | 0.9280 | 0.5481 | 0.1807 | 0.3628 |
| SSA-ELM2 | 0.9332 | 0.5157 | 0.1778 | 0.3546 | 0.9281 | 0.5478 | 0.1806 | 0.3637 |
| AO-ELM2 | 0.9340 | 0.5127 | 0.1768 | 0.3522 | 0.9278 | 0.5489 | 0.1810 | 0.3644 |
| ELM3 | 0.9349 | 0.5107 | 0.1773 | 0.3540 | 0.9238 | 0.5632 | 0.1924 | 0.3957 |
| TSO-ELM3 | 0.9370 | 0.5021 | 0.1743 | 0.3466 | 0.9235 | 0.5642 | 0.1851 | 0.3929 |
| SSA-ELM3 | 0.9372 | 0.5016 | 0.1742 | 0.3450 | 0.9150 | 0.5675 | 0.1862 | 0.3952 |
| AO-ELM3 | 0.9375 | 0.5002 | 0.1736 | 0.3433 | 0.9230 | 0.5657 | 0.1856 | 0.3916 |
| ELM4 | 0.9612 | 0.3794 | 0.1353 | 0.2527 | 0.9607 | 0.3948 | 0.1321 | 0.2720 |
| TSO-ELM4 | 0.9667 | 0.3542 | 0.1259 | 0.2225 | 0.9658 | 0.3724 | 0.1242 | 0.2450 |
| SSA-ELM4 | 0.9669 | 0.3537 | 0.1257 | 0.2214 | 0.9656 | 0.3734 | 0.1245 | 0.2466 |
| AO-ELM4 | 0.9671 | 0.3524 | 0.1241 | 0.2205 | 0.9659 | 0.3717 | 0.1240 | 0.2445 |
| ELM5 | 0.9317 | 0.5214 | 0.1797 | 0.3596 | 0.9277 | 0.5494 | 0.1812 | 0.3671 |
| TSO-ELM5 | 0.9332 | 0.5154 | 0.1776 | 0.3531 | 0.9284 | 0.5467 | 0.1803 | 0.3620 |
| SSA-ELM5 | 0.9333 | 0.5146 | 0.1777 | 0.3532 | 0.9279 | 0.5504 | 0.1815 | 0.3631 |
| AO-ELM5 | 0.9336 | 0.5143 | 0.1773 | 0.3533 | 0.9280 | 0.5481 | 0.1807 | 0.3639 |
| ELM6 | 0.9425 | 0.4715 | 0.1667 | 0.3535 | 0.9440 | 0.4818 | 0.1597 | 0.3635 |
| TSO-ELM6 | 0.9463 | 0.4560 | 0.1612 | 0.3430 | 0.9467 | 0.4701 | 0.1560 | 0.3567 |
| SSA-ELM6 | 0.9459 | 0.4578 | 0.1618 | 0.3448 | 0.9461 | 0.4728 | 0.1568 | 0.3583 |
| AO-ELM6 | 0.9468 | 0.4538 | 0.1604 | 0.3408 | 0.9472 | 0.4677 | 0.1552 | 0.3545 |
| Training | Testing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | |
| ELM1 | 0.8833 | 0.5658 | 0.2173 | 0.4026 | 0.8866 | 0.5426 | 0.2107 | 0.3924 |
| TSO-ELM1 | 0.8869 | 0.5570 | 0.2140 | 0.3940 | 0.8901 | 0.5345 | 0.2076 | 0.3833 |
| SSA-ELM1 | 0.8868 | 0.5573 | 0.2142 | 0.3945 | 0.8905 | 0.5338 | 0.2075 | 0.3838 |
| AO-ELM1 | 0.8876 | 0.5555 | 0.2135 | 0.3930 | 0.8903 | 0.5340 | 0.2075 | 0.3844 |
| ELM2 | 0.9289 | 0.4387 | 0.1676 | 0.3032 | 0.9458 | 0.3749 | 0.1462 | 0.2671 |
| TSO-ELM2 | 0.9312 | 0.4312 | 0.1647 | 0.2988 | 0.9481 | 0.3666 | 0.1429 | 0.2625 |
| SSA-ELM2 | 0.9311 | 0.4317 | 0.1648 | 0.2988 | 0.9479 | 0.3673 | 0.1432 | 0.2616 |
| AO-ELM2 | 0.9319 | 0.4293 | 0.1639 | 0.2966 | 0.9482 | 0.3661 | 0.1426 | 0.2605 |
| ELM3 | 0.9254 | 0.4561 | 0.1739 | 0.3259 | 0.9097 | 0.4769 | 0.1836 | 0.3509 |
| TSO-ELM3 | 0.9299 | 0.4370 | 0.1684 | 0.3109 | 0.9092 | 0.4700 | 0.1786 | 0.3423 |
| SSA-ELM3 | 0.9301 | 0.4366 | 0.1682 | 0.3105 | 0.9094 | 0.4799 | 0.1774 | 0.3517 |
| AO-ELM3 | 0.9306 | 0.4351 | 0.1677 | 0.3105 | 0.9097 | 0.4743 | 0.1721 | 0.3412 |
| ELM4 | 0.9324 | 0.4310 | 0.1690 | 0.3012 | 0.9195 | 0.4589 | 0.1802 | 0.3223 |
| TSO-ELM4 | 0.9341 | 0.4104 | 0.1610 | 0.2763 | 0.9243 | 0.4447 | 0.1746 | 0.3001 |
| SSA-ELM4 | 0.9378 | 0.4139 | 0.1623 | 0.2789 | 0.9241 | 0.4455 | 0.1749 | 0.3026 |
| AO-ELM4 | 0.9394 | 0.4083 | 0.1601 | 0.2735 | 0.9249 | 0.4431 | 0.1738 | 0.2987 |
| ELM5 | 0.9288 | 0.4391 | 0.1678 | 0.3042 | 0.9455 | 0.3762 | 0.1467 | 0.2676 |
| TSO-ELM5 | 0.9313 | 0.4315 | 0.1649 | 0.2985 | 0.9473 | 0.3695 | 0.1440 | 0.2629 |
| SSA-ELM5 | 0.9310 | 0.4323 | 0.1871 | 0.2992 | 0.9476 | 0.3682 | 0.1436 | 0.2628 |
| AO-ELM5 | 0.9322 | 0.4286 | 0.1637 | 0.2962 | 0.9486 | 0.3649 | 0.1423 | 0.2590 |
| ELM6 | 0.9215 | 0.4566 | 0.1865 | 0.3522 | 0.9089 | 0.4874 | 0.1919 | 0.3731 |
| TSO-ELM6 | 0.9290 | 0.4352 | 0.1714 | 0.3305 | 0.9181 | 0.4631 | 0.1825 | 0.3505 |
| SSA-ELM6 | 0.9284 | 0.4378 | 0.1720 | 0.3325 | 0.9176 | 0.4644 | 0.1830 | 0.3509 |
| AO-ELM6 | 0.9294 | 0.4338 | 0.1708 | 0.3292 | 0.9194 | 0.4595 | 0.1810 | 0.3468 |
| Training | Testing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | |
| ELM1 | 0.9018 | 0.3669 | 0.1505 | 0.2734 | 0.8935 | 0.4895 | 0.1658 | 0.3187 |
| TSO-ELM1 | 0.9032 | 0.3638 | 0.1492 | 0.2699 | 0.9017 | 0.4483 | 0.1522 | 0.2950 |
| SSA-ELM1 | 0.9034 | 0.3635 | 0.1491 | 0.2698 | 0.8990 | 0.4503 | 0.1564 | 0.2979 |
| AO-ELM1 | 0.9036 | 0.3630 | 0.1489 | 0.2693 | 0.9020 | 0.4440 | 0.1516 | 0.2943 |
| ELM2 | 0.9570 | 0.2368 | 0.0973 | 0.1744 | 0.9608 | 0.2594 | 0.1122 | 0.2216 |
| TSO-ELM2 | 0.9619 | 0.2128 | 0.0880 | 0.1717 | 0.9614 | 0.2580 | 0.1117 | 0.2158 |
| SSA-ELM2 | 0.9582 | 0.2336 | 0.0961 | 0.1724 | 0.9613 | 0.2580 | 0.1115 | 0.2155 |
| AO-ELM2 | 0.9587 | 0.2321 | 0.0954 | 0.1710 | 0.9618 | 0.2575 | 0.1111 | 0.2149 |
| ELM3 | 0.9265 | 0.3182 | 0.1304 | 0.2399 | 0.9219 | 0.3672 | 0.1689 | 0.2721 |
| TSO-ELM3 | 0.9311 | 0.3083 | 0.1260 | 0.2300 | 0.9284 | 0.3507 | 0.1598 | 0.2517 |
| SSA-ELM3 | 0.9306 | 0.3085 | 0.1264 | 0.2309 | 0.9268 | 0.3512 | 0.1608 | 0.2520 |
| AO-ELM3 | 0.9315 | 0.3065 | 0.1256 | 0.2287 | 0.9245 | 0.3522 | 0.1614 | 0.2541 |
| ELM4 | 0.9344 | 0.3018 | 0.1237 | 0.2127 | 0.9317 | 0.3649 | 0.1589 | 0.3018 |
| TSO-ELM4 | 0.9387 | 0.2920 | 0.1196 | 0.2015 | 0.9358 | 0.3592 | 0.1561 | 0.2954 |
| SSA-ELM4 | 0.9383 | 0.2932 | 0.1201 | 0.2031 | 0.9338 | 0.3619 | 0.1571 | 0.3004 |
| AO-ELM4 | 0.9390 | 0.2912 | 0.1193 | 0.2003 | 0.9346 | 0.3619 | 0.1562 | 0.2955 |
| ELM5 | 0.9559 | 0.2396 | 0.0985 | 0.1774 | 0.9615 | 0.3313 | 0.1070 | 0.2149 |
| TSO-ELM5 | 0.9580 | 0.2338 | 0.0961 | 0.1722 | 0.9652 | 0.3155 | 0.1017 | 0.2032 |
| SSA-ELM5 | 0.9580 | 0.2342 | 0.0963 | 0.1725 | 0.9638 | 0.3180 | 0.1029 | 0.2049 |
| AO-ELM5 | 0.9582 | 0.2125 | 0.0959 | 0.1724 | 0.9650 | 0.3148 | 0.1014 | 0.2028 |
| ELM6 | 0.8839 | 0.4036 | 0.1649 | 0.3172 | 0.8825 | 0.4436 | 0.1658 | 0.3248 |
| TSO-ELM6 | 0.8917 | 0.3887 | 0.1588 | 0.3020 | 0.8867 | 0.4354 | 0.1621 | 0.3180 |
| SSA-ELM6 | 0.8903 | 0.3914 | 0.1600 | 0.3037 | 0.8852 | 0.4387 | 0.1635 | 0.3201 |
| AO-ELM6 | 0.8921 | 0.3882 | 0.1587 | 0.3009 | 0.8868 | 0.4352 | 0.1617 | 0.3171 |
| Training | Testing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | |
| ELM1 | 0.8486 | 0.5191 | 0.2049 | 0.3722 | 0.8326 | 0.5707 | 0.2181 | 0.4119 |
| TSO-ELM1 | 0.8529 | 0.5116 | 0.2019 | 0.3622 | 0.8344 | 0.5659 | 0.2168 | 0.4009 |
| SSA-ELM1 | 0.8533 | 0.5111 | 0.2017 | 0.3628 | 0.8363 | 0.5627 | 0.2152 | 0.4005 |
| AO-ELM1 | 0.8534 | 0.5109 | 0.2016 | 0.3619 | 0.8361 | 0.5629 | 0.2159 | 0.3882 |
| ELM2 | 0.9678 | 0.2386 | 0.0953 | 0.1639 | 0.9671 | 0.2360 | 0.0891 | 0.1605 |
| TSO-ELM2 | 0.9690 | 0.2346 | 0.0938 | 0.1606 | 0.9678 | 0.2335 | 0.0881 | 0.1608 |
| SSA-ELM2 | 0.9686 | 0.2349 | 0.0939 | 0.1609 | 0.9676 | 0.2344 | 0.0884 | 0.1611 |
| AO-ELM2 | 0.9692 | 0.2340 | 0.0936 | 0.1601 | 0.9678 | 0.2341 | 0.0882 | 0.1606 |
| ELM3 | 0.8853 | 0.4521 | 0.1778 | 0.3254 | 0.8770 | 0.4450 | 0.1830 | 0.3335 |
| TSO-ELM3 | 0.8941 | 0.4361 | 0.1713 | 0.2818 | 0.8858 | 0.4318 | 0.1744 | 0.3146 |
| SSA-ELM3 | 0.8941 | 0.4359 | 0.1717 | 0.3081 | 0.8866 | 0.4298 | 0.1745 | 0.3082 |
| AO-ELM3 | 0.8939 | 0.4365 | 0.1717 | 0.3072 | 0.8851 | 0.4329 | 0.1753 | 0.3076 |
| ELM4 | 0.8753 | 0.4754 | 0.1868 | 0.3476 | 0.8632 | 0.5013 | 0.1982 | 0.3546 |
| TSO-ELM4 | 0.8851 | 0.4548 | 0.1788 | 0.3238 | 0.8701 | 0.4853 | 0.1945 | 0.3421 |
| SSA-ELM4 | 0.8845 | 0.4564 | 0.1794 | 0.3254 | 0.8684 | 0.4884 | 0.1960 | 0.3456 |
| AO-ELM4 | 0.8859 | 0.4536 | 0.1784 | 0.3222 | 0.8693 | 0.4872 | 0.1956 | 0.3421 |
| ELM5 | 0.9679 | 0.2392 | 0.0957 | 0.1649 | 0.9675 | 0.2281 | 0.0937 | 0.1586 |
| TSO-ELM5 | 0.9689 | 0.2347 | 0.0938 | 0.1609 | 0.9705 | 0.2329 | 0.0896 | 0.1539 |
| SSA-ELM5 | 0.9689 | 0.2352 | 0.0948 | 0.1609 | 0.9705 | 0.2320 | 0.0918 | 0.1565 |
| AO-ELM5 | 0.9691 | 0.2343 | 0.0937 | 0.1605 | 0.9707 | 0.2304 | 0.0882 | 0.1533 |
| ELM6 | 0.8758 | 0.4789 | 0.1889 | 0.3621 | 0.8705 | 0.4425 | 0.1870 | 0.3585 |
| TSO-ELM6 | 0.8850 | 0.4595 | 0.1813 | 0.3477 | 0.8754 | 0.4328 | 0.1775 | 0.3477 |
| SSA-ELM6 | 0.8849 | 0.4596 | 0.1813 | 0.3431 | 0.8719 | 0.4354 | 0.1817 | 0.3460 |
| AO-ELM6 | 0.8857 | 0.4583 | 0.1807 | 0.3426 | 0.8764 | 0.4289 | 0.1762 | 0.3435 |
| Training | Testing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | NRMSE | MAE | |
| ELM1 | 0.8047 | 0.5948 | 0.1697 | 0.4685 | 0.8097 | 0.5892 | 0.1647 | 0.4656 |
| TSO-ELM1 | 0.8056 | 0.5881 | 0.1679 | 0.4607 | 0.8140 | 0.5825 | 0.1629 | 0.4578 |
| SSA-ELM1 | 0.8050 | 0.5889 | 0.1681 | 0.4620 | 0.8129 | 0.5843 | 0.1634 | 0.4601 |
| AO-ELM1 | 0.8058 | 0.5877 | 0.1678 | 0.4599 | 0.8137 | 0.5830 | 0.1631 | 0.4577 |
| ELM2 | 0.9626 | 0.2524 | 0.0712 | 0.1807 | 0.9579 | 0.2765 | 0.0762 | 0.2006 |
| TSO-ELM2 | 0.9653 | 0.2438 | 0.0689 | 0.1726 | 0.9599 | 0.2700 | 0.0745 | 0.1952 |
| SSA-ELM2 | 0.9651 | 0.2444 | 0.0691 | 0.1731 | 0.9598 | 0.2703 | 0.0745 | 0.1954 |
| AO-ELM2 | 0.9656 | 0.2427 | 0.0684 | 0.1715 | 0.9601 | 0.2691 | 0.0743 | 0.1942 |
| ELM3 | 0.8573 | 0.5025 | 0.1446 | 0.3897 | 0.8637 | 0.4969 | 0.1392 | 0.3823 |
| TSO-ELM3 | 0.8632 | 0.4918 | 0.1416 | 0.3859 | 0.8664 | 0.4920 | 0.1380 | 0.3749 |
| SSA-ELM3 | 0.8625 | 0.4930 | 0.1419 | 0.3799 | 0.8643 | 0.4960 | 0.1391 | 0.3796 |
| AO-ELM3 | 0.8639 | 0.4905 | 0.1412 | 0.3767 | 0.8653 | 0.4938 | 0.1386 | 0.3778 |
| ELM4 | 0.8148 | 0.5742 | 0.1638 | 0.4511 | 0.8218 | 0.5708 | 0.1594 | 0.4532 |
| TSO-ELM4 | 0.8244 | 0.5593 | 0.1596 | 0.4380 | 0.8311 | 0.5555 | 0.1552 | 0.4397 |
| SSA-ELM4 | 0.8243 | 0.5593 | 0.1423 | 0.4379 | 0.8308 | 0.5561 | 0.1554 | 0.4362 |
| AO-ELM4 | 0.8257 | 0.5572 | 0.1591 | 0.4358 | 0.8295 | 0.5584 | 0.1560 | 0.4353 |
| ELM5 | 0.9638 | 0.2491 | 0.0704 | 0.1779 | 0.9592 | 0.2725 | 0.0752 | 0.1973 |
| TSO-ELM5 | 0.9649 | 0.2475 | 0.0692 | 0.1735 | 0.9596 | 0.2707 | 0.0747 | 0.1961 |
| SSA-ELM5 | 0.9650 | 0.2449 | 0.0692 | 0.1733 | 0.9600 | 0.2697 | 0.0744 | 0.1946 |
| AO-ELM5 | 0.9653 | 0.2427 | 0.0688 | 0.1717 | 0.9601 | 0.2693 | 0.0743 | 0.1948 |
| ELM6 | 0.8531 | 0.5098 | 0.1467 | 0.3957 | 0.8609 | 0.5003 | 0.1408 | 0.3905 |
| TSO-ELM6 | 0.8573 | 0.5023 | 0.1446 | 0.3883 | 0.8647 | 0.4936 | 0.1388 | 0.3830 |
| SSA-ELM6 | 0.8578 | 0.5014 | 0.1444 | 0.3876 | 0.8653 | 0.4925 | 0.1386 | 0.3820 |
| AO-ELM6 | 0.8587 | 0.4999 | 0.1439 | 0.3859 | 0.8645 | 0.4936 | 0.1389 | 0.3819 |
| Regions | Station | Model ID | R2 | RMSE | MAE | NRMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCC | Kuerle | TSO-ELM4 | 0.9752 | 0.3453 | 0.2202 | 0.1055 |
| Kashi | AO-ELM4 | 0.9725 | 0.3717 | 0.2516 | 0.1163 | |
| Jiuquan | AO-ELM4 | 0.9628 | 0.3651 | 0.2351 | 0.1267 | |
| Huhehaote | TSO-ELM4 | 0.9537 | 0.4003 | 0.2648 | 0.1460 | |
| TMC | Changchun | TSO-ELM3 | 0.9307 | 0.4550 | 0.3199 | 0.1852 |
| Zhengzhou | AO-ELM5 | 0.9291 | 0.4485 | 0.3373 | 0.1488 | |
| Linxia | AO-ELM5 | 0.9809 | 0.1942 | 0.1290 | 0.0869 | |
| Luochuan | AO-ELM5 | 0.9569 | 0.3311 | 0.2311 | 0.1285 | |
| PMC | Xining | AO-ELM5 | 0.9864 | 0.1655 | 0.1306 | 0.0704 |
| Linzhi | AO-ELM5 | 0.9471 | 0.4417 | 0.2909 | 0.1231 | |
| Naqu | AO-ELM2 | 0.9736 | 0.2219 | 0.2391 | 0.1022 | |
| Changdu | AO-ELM5 | 0.9765 | 0.2098 | 0.0929 | 0.1201 | |
| SMC | Wuhan | TSO-ELM2 | 0.9803 | 0.2265 | 0.1542 | 0.0862 |
| Guangzhou | TSO-ELM5 | 0.9567 | 0.2617 | 0.1777 | 0.0865 | |
| Guiyang | AO-ELM5 | 0.9733 | 0.2077 | 0.1365 | 0.0918 | |
| Dujiangyan | SSA-ELM2 | 0.9739 | 0.1921 | 0.1286 | 0.0927 | |
| TPMC | Haikou | AO-ELM5 | 0.9532 | 0.3192 | 0.2167 | 0.0898 |
| Dongfang | SSA-ELM5 | 0.9387 | 0.3731 | 0.2883 | 0.0886 | |
| Lancang | AO-ELM2 | 0.9834 | 0.1271 | 0.0886 | 0.0409 | |
| Zhanjiang | AO-ELM5 | 0.9662 | 0.2536 | 0.1825 | 0.0768 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Ma, R.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Mao, H. Prediction of Reference Crop Evapotranspiration in China’s Climatic Regions Using Optimized Machine Learning Models. Water 2024, 16, 3349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233349
Hu J, Ma R, Jiang S, Liu Y, Mao H. Prediction of Reference Crop Evapotranspiration in China’s Climatic Regions Using Optimized Machine Learning Models. Water. 2024; 16(23):3349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233349
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jian, Rong Ma, Shouzheng Jiang, Yuelei Liu, and Huayan Mao. 2024. "Prediction of Reference Crop Evapotranspiration in China’s Climatic Regions Using Optimized Machine Learning Models" Water 16, no. 23: 3349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233349
APA StyleHu, J., Ma, R., Jiang, S., Liu, Y., & Mao, H. (2024). Prediction of Reference Crop Evapotranspiration in China’s Climatic Regions Using Optimized Machine Learning Models. Water, 16(23), 3349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233349






