An Innovative Deep-Learning Technique for Fuel Demand Estimation in Maritime Transportation: A Step Toward Sustainable Development and Environmental Impact Mitigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Study Area Description
3.1. Jazan Port, Saudi Arabia
3.2. Fujairah Port, United Arab Emirates
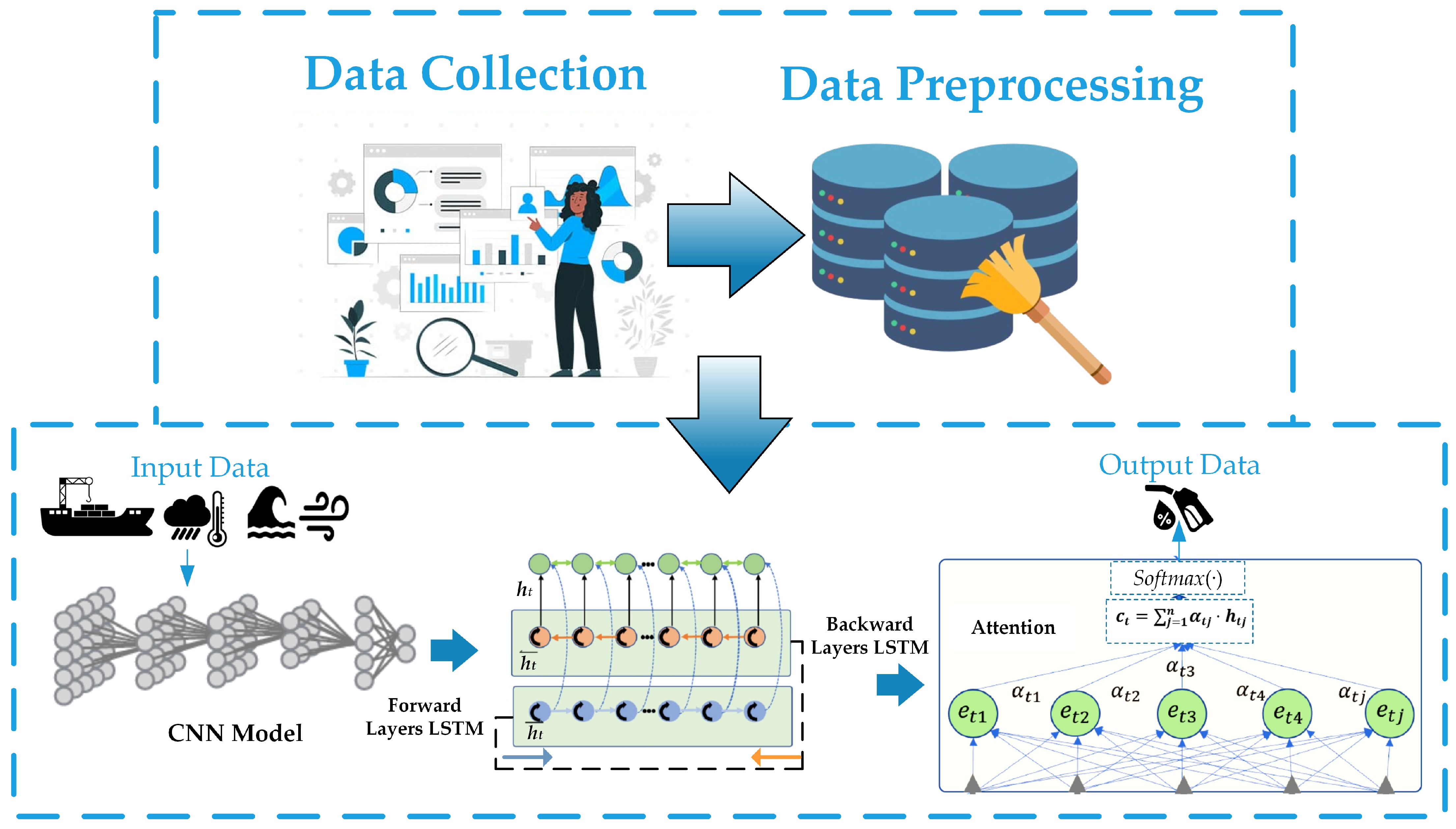
4. Methodology
4.1. CNNs
4.2. Bi-LSTM
4.3. Proposed Model
- Vessel Characteristics: type, size, weight, and engine specifications.
- Weather Conditions: wind speed and temperature.
- Sea states: wave height, current speed and direction.
- Navigation Specifics: distance traveled, speed, and port stay durations.
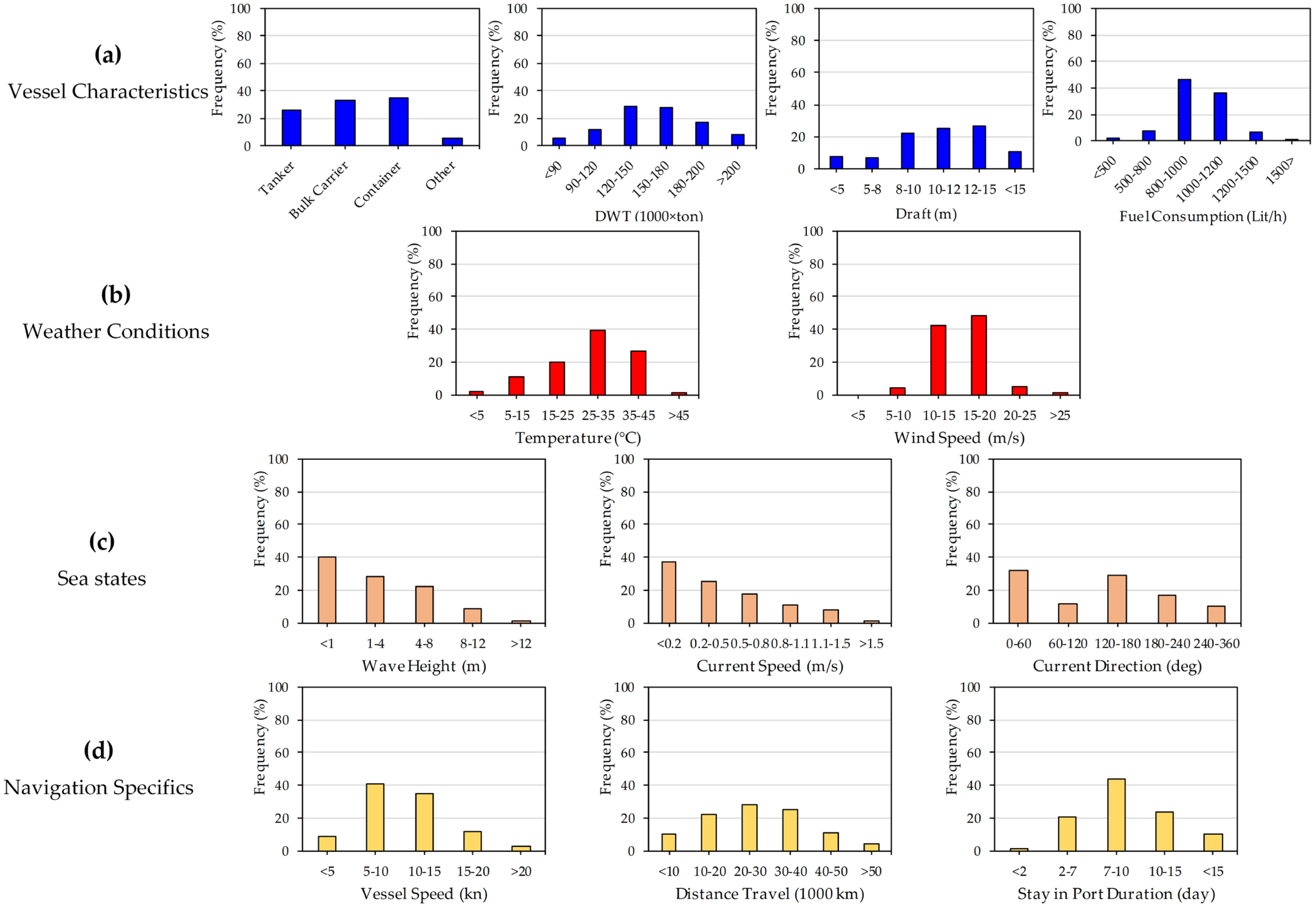
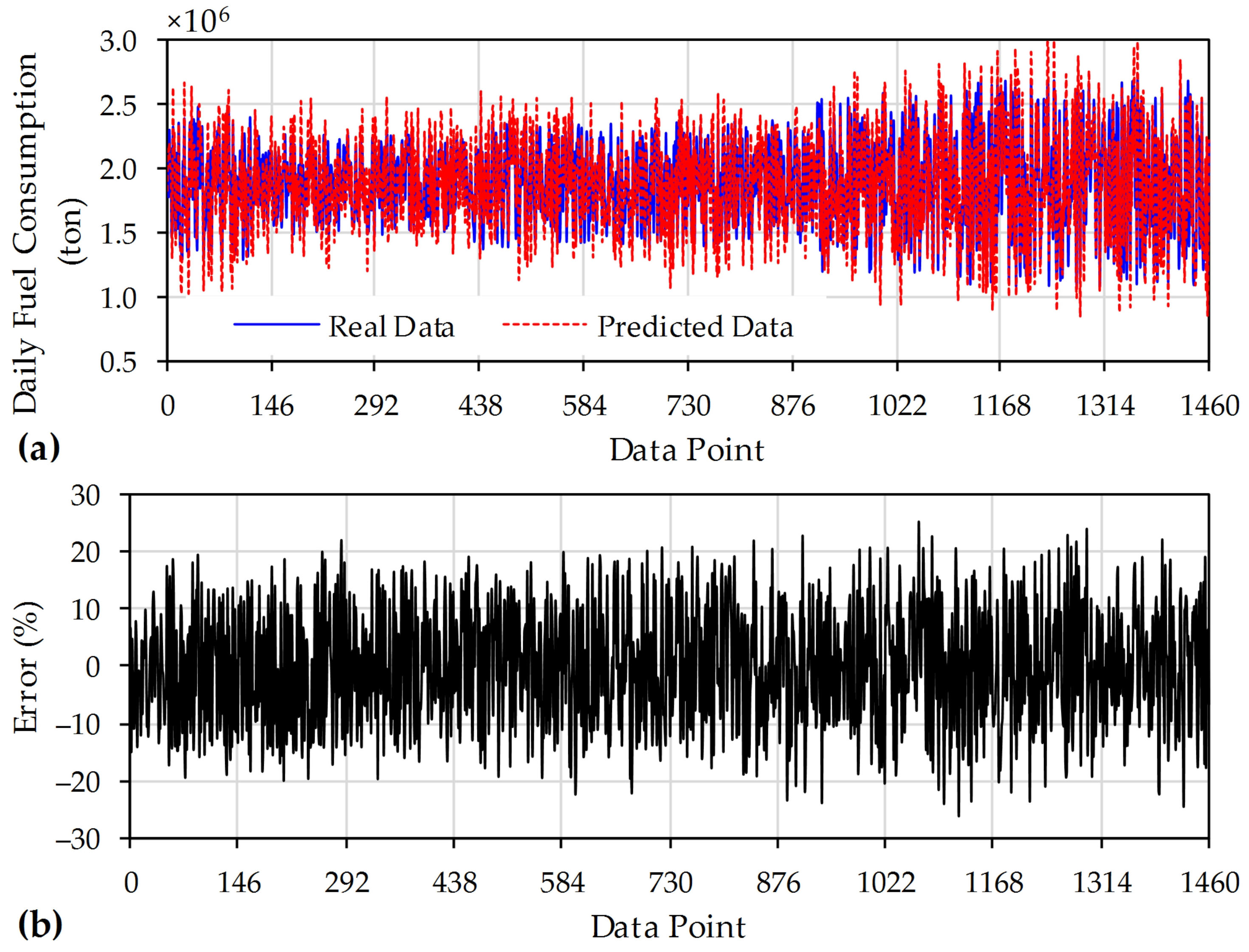
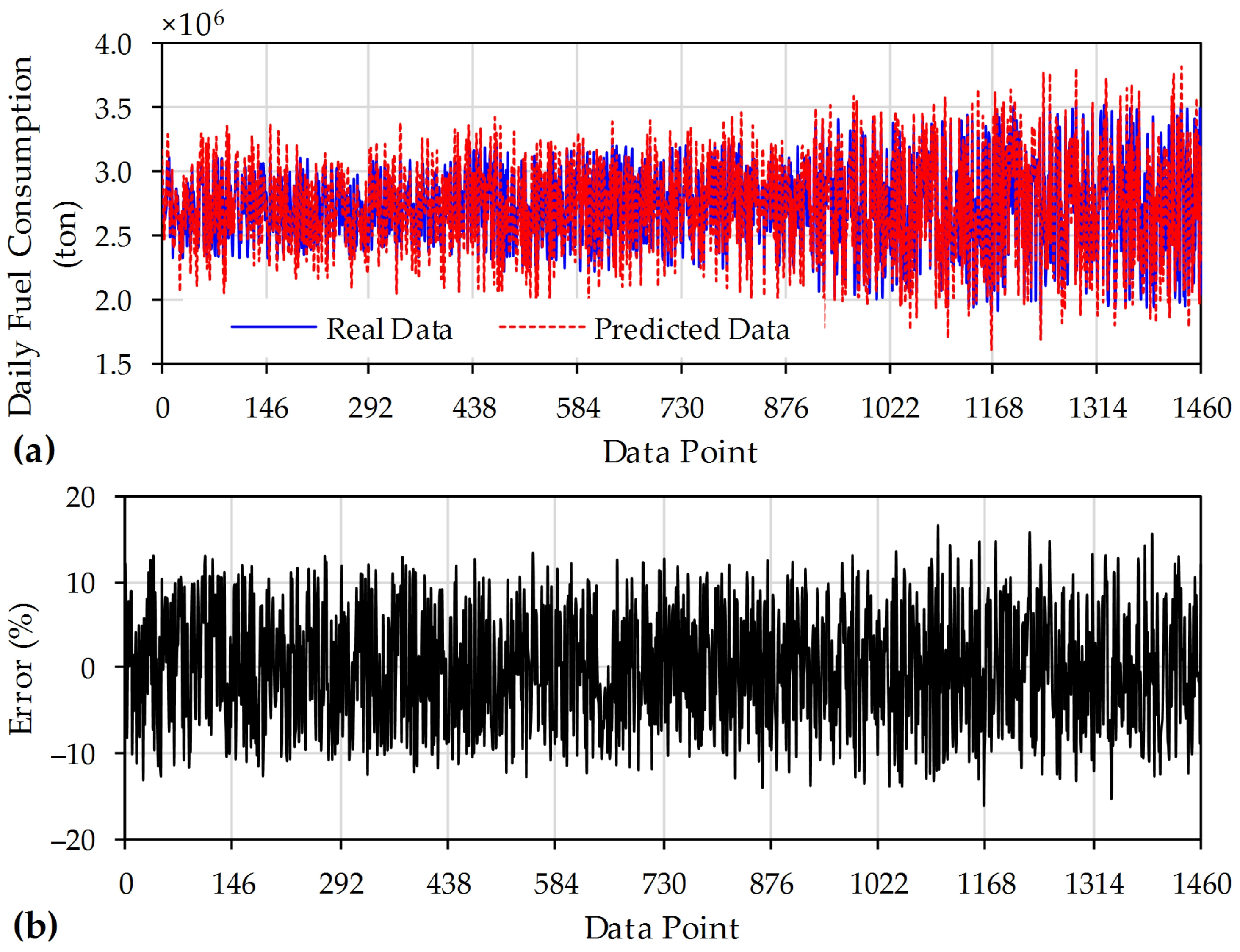
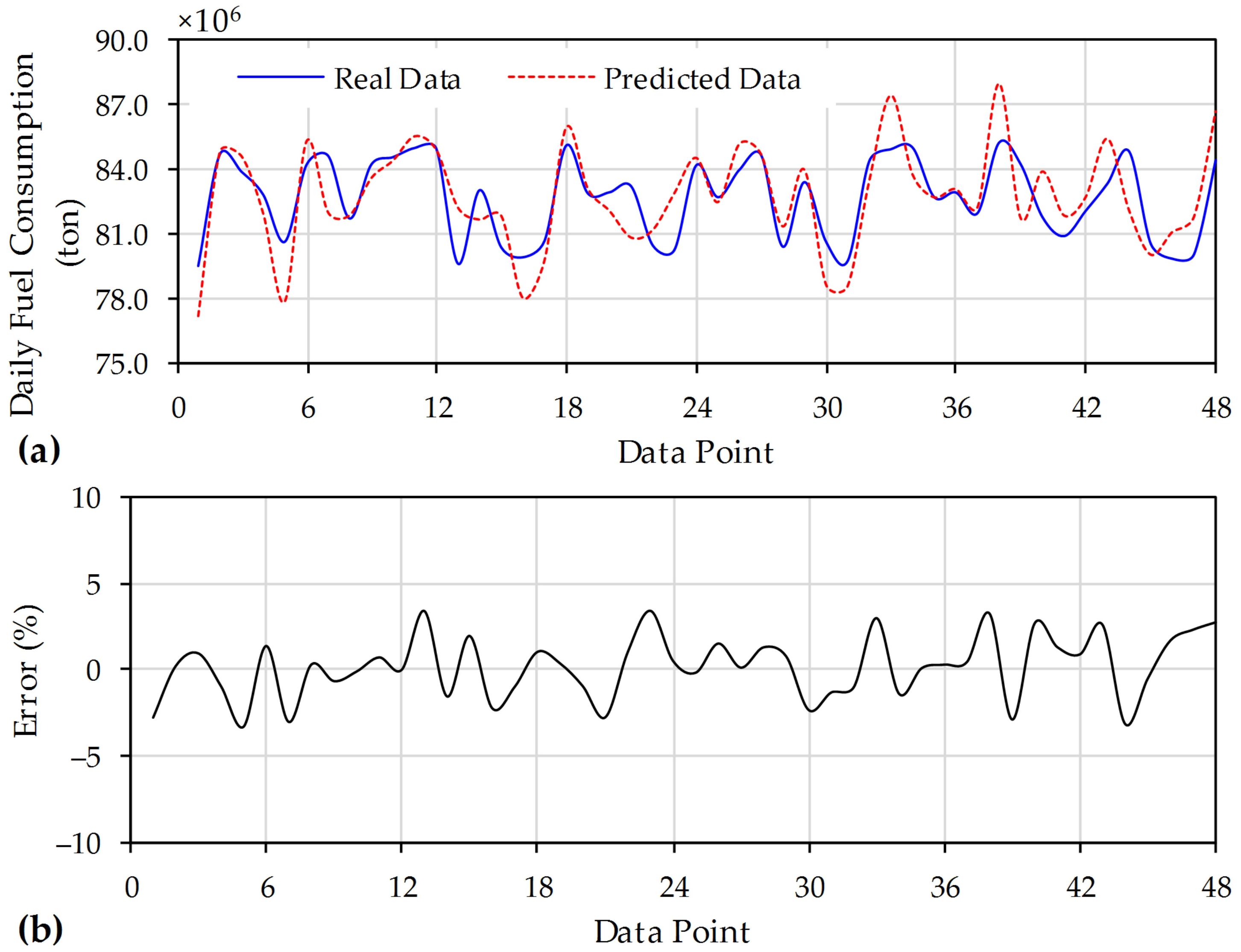
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saidi, S.; Mani, V.; Mefteh, H.; Shahbaz, M.; Akhtar, P. Dynamic Linkages between Transport, Logistics, Foreign Direct Investment, and Economic Growth: Empirical Evidence from Developing Countries. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 141, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, J.; Su, M.; Wan, S.; Zhang, Z. The Relationship between Freight Transport and Economic Development: A Case Study of China. Res. Transp. Econ. 2021, 85, 100885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.M.; Pretes, M. Maritime Dependency and Economic Prosperity: Why Access to Oceanic Trade Matters. Mar. Policy 2020, 121, 104180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, Y.H.V.; Lai, K.; Cheng, T.C.E.; Yang, D. International Trade and Shipping. In The Impact of the English Civil War on the Economy of London, 1642–1650; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 163–200. ISBN 9781315239057. [Google Scholar]
- Edih, U.O.; Faghawari, N.; Agboro, D.O. Port Operation’s Efficiency and Revenue Generation in Global Maritime Trade: Implications for National Growth and Development in Nigeria. J. Money Bus. 2023, 3, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omdehghiasi, H.; Mojtahedi, A.; Farajpour, I. A Parametric Stability Analysis of the Offshore Jacket Launch: A Case Study in the Persian Gulf. Mar. Syst. Ocean Technol. 2018, 13, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhou, A. Water Resource Utilization Assessment in China Based on the Dynamic Relationship between Economic Growth and Water Use. Water 2024, 16, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloruntobi, O.; Mokhtar, K.; Gohari, A.; Asif, S.; Chuah, L.F. Sustainable Transition towards Greener and Cleaner Seaborne Shipping Industry: Challenges and Opportunities. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 100628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Han, H.; Zeng, L. Artificial Intelligence, Resource Reallocation, and Corporate Innovation Efficiency: Evidence from China’s Listed Companies. Resour. Policy 2023, 81, 103324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratila (Adam), A.; Gavril (Moldovan), I.A.; Nita, S.C.; Hrebenciuc, A. The Importance of Maritime Transport for Economic Growth in the European Union: A Panel Data Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M. Impact of Port Infrastructure on Economic Development With Special Reference to Major Ports in India. Manag. Account. J. 2023, 58, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koilo, V. Sustainability Issues in Maritime Transport and Main Challenges of the Shipping Industry. Environ. Econ. 2019, 10, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargin, J. The Pathway to a Green Gulf: A Review and Analysis of the Evolution of Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates’ Climate Change Positions. Carbon Clim. Law Rev. 2021, 15, 313–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokatian-Beiragh, M.; Banan-Dallalian, M.; Golshani, A.; Allahdadi, M.N.; Samiee-Zenoozian, M. The Effectiveness of Mangrove Forests as a Nature-Based Solution against Flood Risk under an Extreme Weather Event. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 77, 103630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, S.; Gabarrell Durany, X.; Pedroso Tonon, A.; Rossi, S. Marine Microalgae Contribution to Sustainable Development. Water 2021, 13, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, J.; Zaragoza, S.; Diaz-Casas, V. Review of Ship Energy Efficiency. Ocean Eng. 2022, 257, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, M.P.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, J. Navigating Energy Efficiency: A Multifaceted Interpretability of Fuel Oil Consumption Prediction in Cargo Container Vessel Considering the Operational and Environmental Factors. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.S.; Lam, J.S.L.; Xiao, Z. Prediction of Harbour Vessel Fuel Consumption Based on Machine Learning Approach. Ocean Eng. 2023, 278, 114483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, A.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Wu, D.; Vladimir, N. A Review of Ship Fuel Consumption Models. Ocean Eng. 2022, 264, 112405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Hu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zhen, R. An Adaptive Hyper Parameter Tuning Model for Ship Fuel Consumption Prediction under Complex Maritime Environments. J. Ocean Eng. Sci. 2022, 7, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tsoulakos, N.; Kujala, P.; Hirdaris, S. A Deep Learning Method for the Prediction of Ship Fuel Consumption in Real Operational Conditions. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 130, 107425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, R.T.; Viktorelius, M.; Varvne, H.; Rasmussen, H.B.; von Knorring, H. Energy Efficiency in Ship Operations—Exploring Voyage Decisions and Decision-Makers. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 102, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durlik, I.; Miller, T.; Cembrowska-Lech, D.; Krzemińska, A.; Złoczowska, E.; Nowak, A. Navigating the Sea of Data: A Comprehensive Review on Data Analysis in Maritime IoT Applications. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y. Optimization of ship speed and fleet deployment under carbon emissions policies for container shipping. Transport 2019, 34, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelzaher, M.A.; Farahat, E.M.; Abdel-Ghafar, H.M.; Balboul, B.A.A.; Awad, M.M. Environmental Policy to Develop a Conceptual Design for the Water–Energy–Food Nexus: A Case Study in Wadi-Dara on the Red Sea Coast, Egypt. Water 2023, 15, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, L.; Pan, X.; Chen, X.; Chang, F.; Wan, D.; Liu, D.; Hu, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Y. Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water 2020, 12, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solakivi, T.; Paimander, A.; Ojala, L. Cost Competitiveness of Alternative Maritime Fuels in the New Regulatory Framework. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 113, 103500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wang, S. Introduction of Maritime Transportation. In Applications of Machine Learning and Data Analytics Models in Maritime Transportation; Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Lespier, L.; Long, S.; Shoberg, T.; Corns, S. A Model for the Evaluation of Environmental Impact Indicators for a Sustainable Maritime Transportation Systems. Front. Eng. Manag. 2019, 6, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasenko, L.; Niyazbekova, S.; Khalilova, M.; Andrianova, L.; Annenskaya, N.; Brovkina, N.; Guseva, I.; Abalakina, T.; Matrosov, S.; Abdusattarova, S. Development of Maritime Transport: Features and Financial Component in Market Conditions. Transp. Res. Procedia 2022, 63, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gutiérrez, J.; Calderay, F.; Saborido, N.; Boile, M.; Rodríguez Valero, R.; Durán-Grados, V. Methodologies for Estimating Shipping Emissions and Energy Consumption: A Comparative Analysis of Current Methods. Energy 2015, 86, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosasang, V.; Chandraprakaikul, W.; Kiattisin, S. A Comparison of Traditional and Neural Networks Forecasting Techniques for Container Throughput at Bangkok Port. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2011, 27, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuAl-Foul, B.M. Forecasting Energy Demand in Jordan Using Artificial Neural Networks. Top. Middle East. N. Afr. Econ. Electron. J. 2012, 14, 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Oludolapo, O.A.; Adisa, J.A.; Pule, K.A. Comparing Performance of MLP and RBF Neural Network Models for Predicting South Africa’s Energy Consumption. J. Energy S. Afr. 2012, 23, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialystocki, N.; Konovessis, D. On the Estimation of Ship’s Fuel Consumption and Speed Curve: A Statistical Approach. J. Ocean Eng. Sci. 2016, 1, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wang, S.; Du, Y. Development of a Two-Stage Ship Fuel Consumption Prediction and Reduction Model for a Dry Bulk Ship. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 138, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Lee, G.; Park, K.-S.; Kim, H. Neural Network-Based Fuel Consumption Estimation for Container Ships in Korea. Marit. Policy Manag. 2020, 47, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işıklı, E.; Aydın, N.; Bilgili, L.; Toprak, A. Estimating Fuel Consumption in Maritime Transport. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 124142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Sun, B.; Li, X.; Olsson, T.; Maleki, N.; Ahlgren, F. Fuel Consumption Prediction Models Based on Machine Learning and Mathematical Methods. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Lee, H.J.; Wang, X.; Bae, S.-H. Fuel Consumption Cost Prediction Model for Ro-Ro Carriers: A Machine Learning-Based Application. Marit. Policy Manag. 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gender Considerations and Entrepreneurship Development in Fujairah, United Arab Emirates. J. Entrep. Proj. Manag. 2023, 7, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.; Manaf Bohari, A. Adoption of Big Data Analytics in Medium-Large Supply Chain Firms in Saudi Arabia. Knowl. Perform. Manag. 2022, 6, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduardo, A.V.S.; Muhammad, K.R.; Sami, A.-G.; Jihad, S.; Mesfer, M.A.-Z.; Antonio, N. A Monumental Flood Mitigation Channel in Saudi Arabia. Stroit. Mater. 2022, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shan, Q.; Li, T. Large Port Energy Management Based on Distributed Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Information, Cybernetics, and Computational Social Systems (ICCSS), Guangzhou, China, 13–15 November 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Alshareef, M.H.; Aljahdali, B.M.; Alghanmi, A.F.; Sulaimani, H.T. Spatial Analysis and Risk Evaluation for Port Crisis Management Using Integrated Soft Computing and GIS-Based Models: A Case Study of Jazan Port, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; Fathi, H.; Abdalla, F.; Alshehri, F.; Eldeeb, H. An Integrated Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Approach for Groundwater Quality Assessment in Jazan, Saudi Arabia. Water 2023, 15, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi, A.; Albratty, M.; Al-Rajab, A.J.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Javed, S.A.; Ahsan, W.; Rehman, Z.; Hassani, R.; Alqahtani, S.S. Heavy Metal Contamination in Leafy Vegetables Grown in Jazan Region of Saudi Arabia: Assessment of Possible Human Health Hazards. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhmoudi, S.A.O.; Aldhanhani, H.R.A.; Ridouane, F.L.; Ateeg, M.; Al Moalla, A.; Mirza, S.B. Study the Impact of the Anthropogenic Activities on the Marine Environment of Fujairah Offshore Waters of UAE Based on Baseline Surveys and Buoy Data. J. Mar. Sci. 2024, 2024, 1998158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeghin, A.; Borriero, A.; Orsenigo, D.; Diano, M.; Méndez Guerrero, C.A.; Perotti, A.; Petri, G.; Tamietto, M. Convolutional Neural Networks for Vision Neuroscience: Significance, Developments, and Outstanding Issues. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1153572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh Javaran, M.R.; Rajabi, M.M.; Kamali, N.; Fahs, M.; Belfort, B. Encoder–Decoder Convolutional Neural Networks for Flow Modeling in Unsaturated Porous Media: Forward and Inverse Approaches. Water 2023, 15, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, R.; Zhao, H. Enhancing Dissolved Oxygen Concentrations Prediction in Water Bodies: A Temporal Transformer Approach with Multi-Site Meteorological Data Graph Embedding. Water 2023, 15, 3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Gao, H.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, L. Runoff Prediction in the Xijiang River Basin Based on Long Short-Term Memory with Variant Models and Its Interpretable Analysis. Water 2023, 15, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Bai, M.; Xu, Y.; Dong, S.; Rao, H.; Ming, W. A Comprehensive Review of Methods for Hydrological Forecasting Based on Deep Learning. Water 2024, 16, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Syed, M.A.; Ahmed, I. A CNN-LSTM Architecture for Marine Vessel Track Association Using Automatic Identification System (AIS) Data. Sensors 2023, 23, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansod, P.J.; Mohan, U.; Yadav, D.K.; Singh, Y.; Sharmila, P.; Chauhan, A. An Innovative Method for Fuel Consumption and Maintenance Cost of Heavy-Duty Vehicles Based on SR-GRU-CNN Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2023 2nd International Conference on Automation, Computing and Renewable Systems (ICACRS), IEEE, Pudukkottai, India, 11–13 December 2023; pp. 811–816. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Hou, J.; Gong, P.; Zhong, Y.; He, W.; Fu, Z. A Review of the Data-Driven Prediction Method of Vehicle Fuel Consumption. Energies 2023, 16, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Lyu, H.; Yin, Y.; Cheng, T.; Gao, X.; Zhang, W.; Jing, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L. Multi-Scale Object Detection Model for Autonomous Ship Navigation in Maritime Environment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, X. Urban Water Demand Prediction Based on Attention Mechanism Graph Convolutional Network-Long Short-Term Memory. Water 2024, 16, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. Fitting Analysis of Inland Ship Fuel Consumption Considering Navigation Status and Environmental Factors. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 187441–187454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-R.; Jung, M.; Park, J.-B. Development of a Fuel Consumption Prediction Model Based on Machine Learning Using Ship In-Service Data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyanık, T.; Karatuğ, Ç.; Arslanoğlu, Y. Machine Learning Approach to Ship Fuel Consumption: A Case of Container Vessel. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 84, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Port | Longitude | Latitude | Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jazan, KSA | 42.53° | 16.90° | X-large | [43] |
| Fujairah, UAE | 56.36° | 25.14° | Large | [44] |
| Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| Learning Rate | 0.001–0.01 |
| Batch Size | 32–128 |
| Number of Epochs | 50–200 |
| Optimization Algorithm | Adam, SGD, RMSprop |
| Activation Function (CNN) | ReLU |
| Activation Function (LSTM) | tanh, sigmoid |
| Loss Function | MSE |
| Framework | Training Time (hours) | Convergence (Epochs) |
|---|---|---|
| TensorFlow | 42 | 100 |
| PyTorch | 48 | 120 |
| Keras | 45 | 100 |
| Scikit-Learn | 65 | 150 |
| Theano | 58 | 130 |
| Input Feature | Vessel Size | Vessel Weight | Engine Specs | Wind Speed | Temperature | Wave Height | Current Speed | Current Direction | Distance Traveled | Vessel Speed | Stay in Port Durations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vessel Size | 1 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.15 |
| Vessel Weight | 0.45 | 1 | 0.42 | 0.2 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.1 | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.18 |
| Engine Specs | 0.5 | 0.42 | 1 | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.12 |
| Wind Speed | 0.13 | 0.2 | 0.09 | 1 | 0.55 | 0.43 | 0.5 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Temperature | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.55 | 1 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.3 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 0.22 |
| Wave Height | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 1 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.19 |
| Current Speed | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.48 | 0.37 | 1 | 0.32 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.28 |
| Current Direction | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0.3 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 1 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.14 |
| Distance Traveled | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.41 | 0.16 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.45 |
| Vessel Speed | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.3 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.33 | 0.18 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.55 |
| Stay in Port Durations | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.2 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alghanmi, A.F.; Aljahdali, B.M.; Sulaimani, H.T.; Turan, O.; Alshareef, M.H. An Innovative Deep-Learning Technique for Fuel Demand Estimation in Maritime Transportation: A Step Toward Sustainable Development and Environmental Impact Mitigation. Water 2024, 16, 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223325
Alghanmi AF, Aljahdali BM, Sulaimani HT, Turan O, Alshareef MH. An Innovative Deep-Learning Technique for Fuel Demand Estimation in Maritime Transportation: A Step Toward Sustainable Development and Environmental Impact Mitigation. Water. 2024; 16(22):3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223325
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlghanmi, Ayman F., Bassam M. Aljahdali, Hussain T. Sulaimani, Osman Turan, and Mohammed H. Alshareef. 2024. "An Innovative Deep-Learning Technique for Fuel Demand Estimation in Maritime Transportation: A Step Toward Sustainable Development and Environmental Impact Mitigation" Water 16, no. 22: 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223325
APA StyleAlghanmi, A. F., Aljahdali, B. M., Sulaimani, H. T., Turan, O., & Alshareef, M. H. (2024). An Innovative Deep-Learning Technique for Fuel Demand Estimation in Maritime Transportation: A Step Toward Sustainable Development and Environmental Impact Mitigation. Water, 16(22), 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223325







