Origin of Intercrystalline Brine Formation in the Balun Mahai Basin, Qaidam: Constraints from Geochemistry and H-O-Sr Isotopes
Abstract
1. Introduction
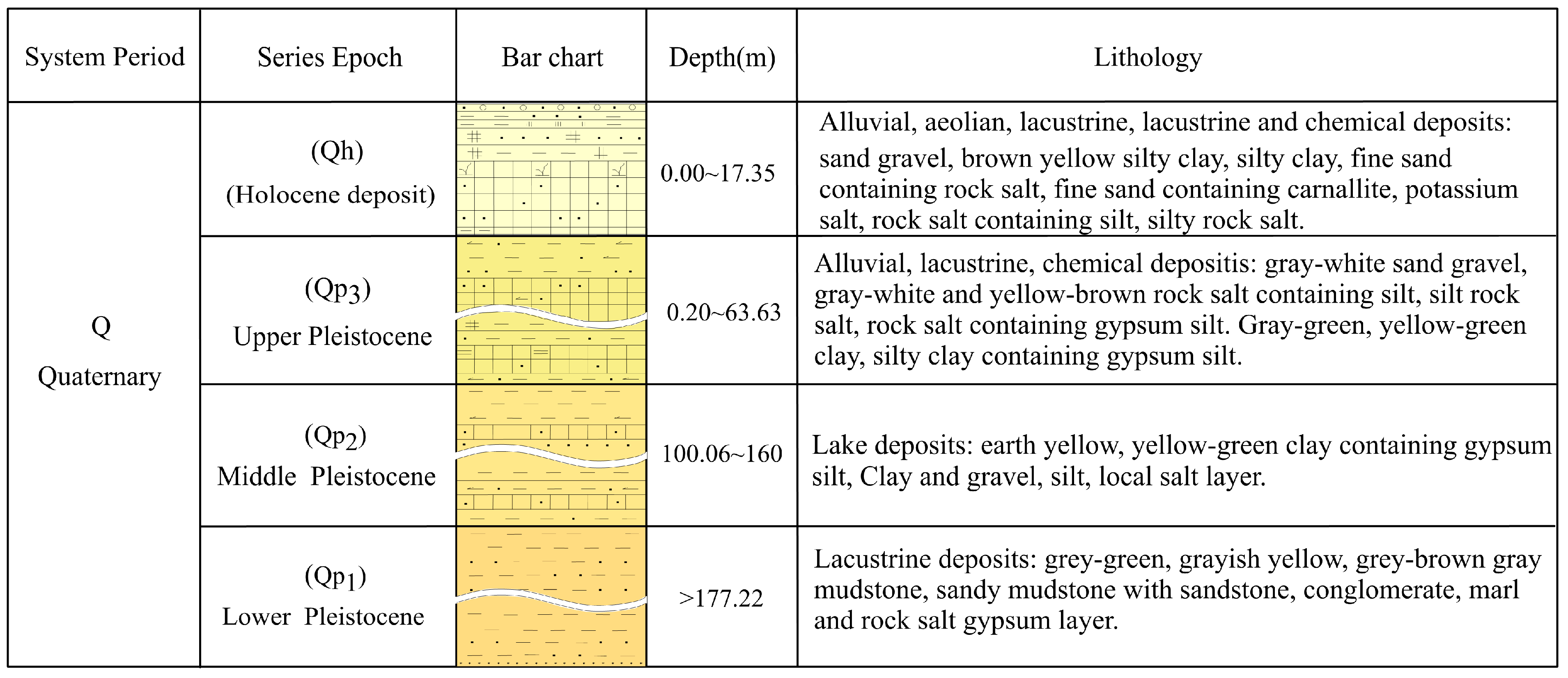
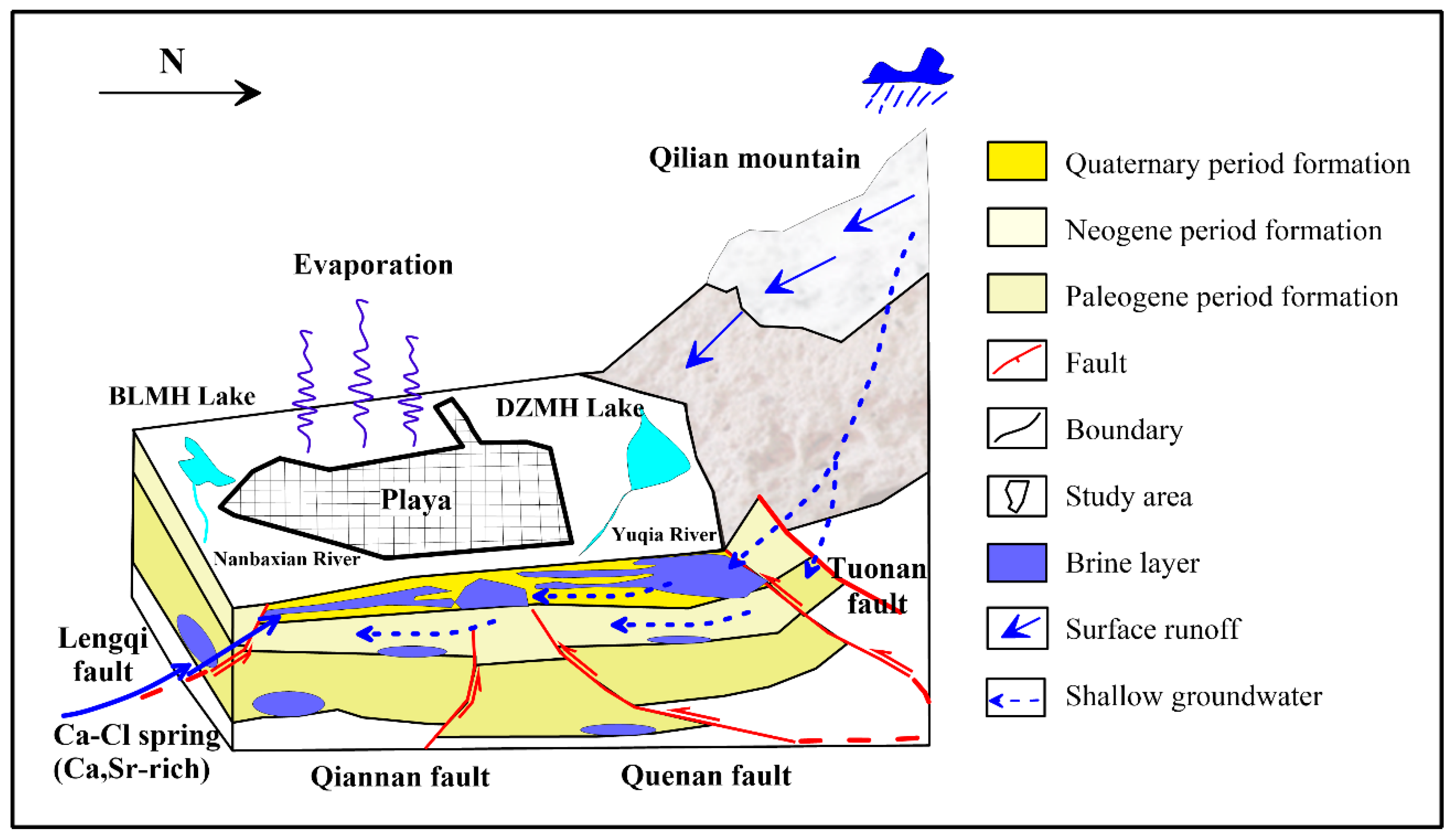
2. Geology and Hydrological Setting
3. Sampling and Analytical Methods
4. Results
4.1. Chemical Composition of Brine
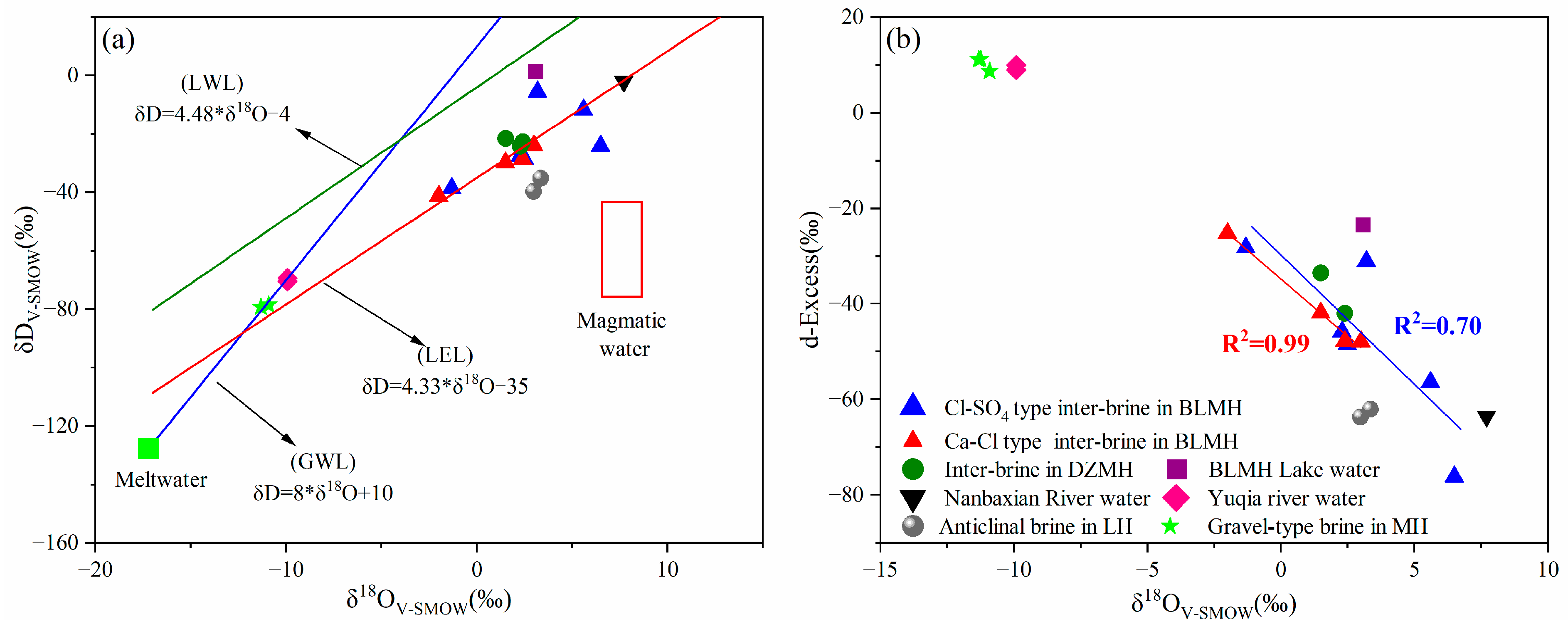
4.2. Isotope Composition of Brine
5. Discussion
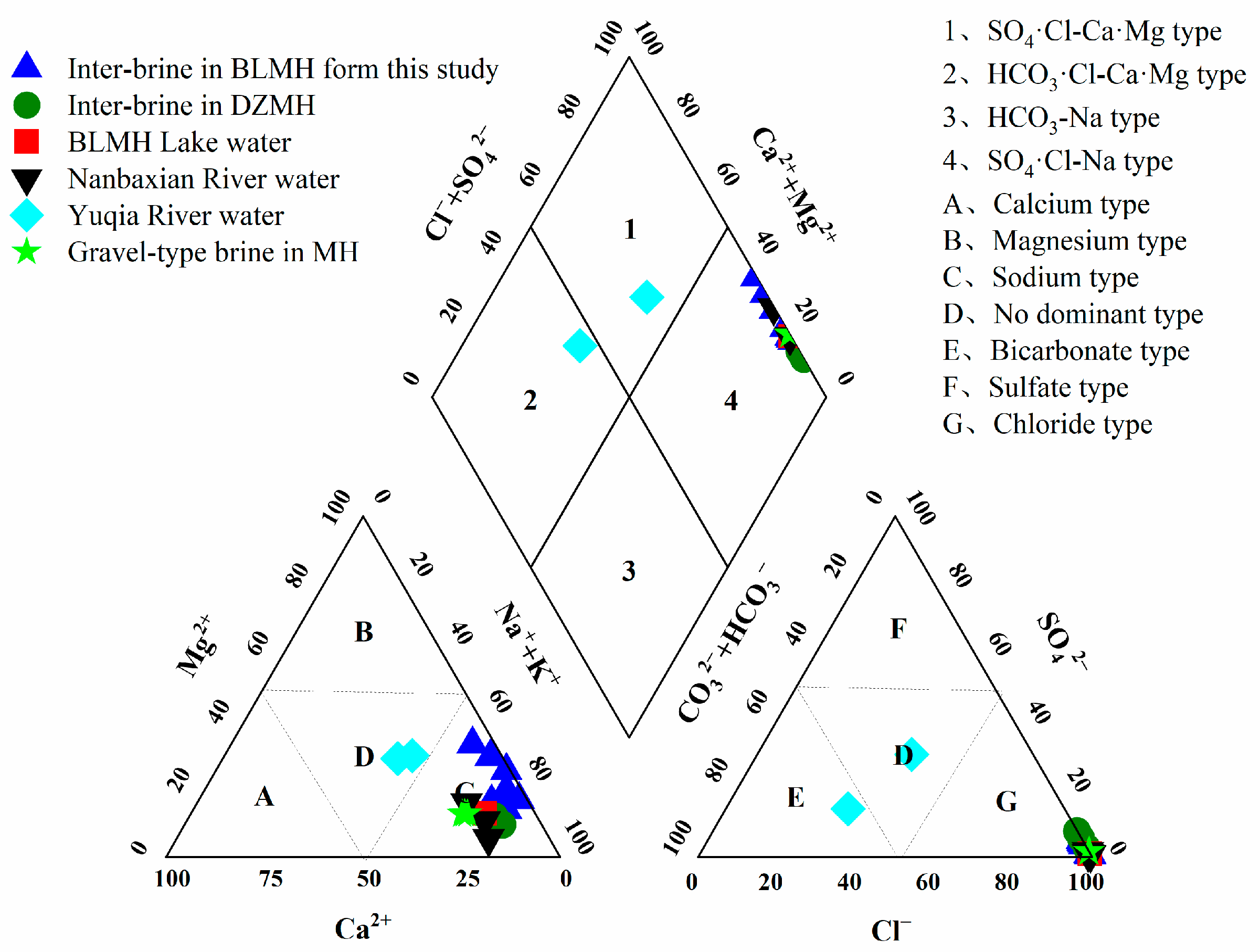
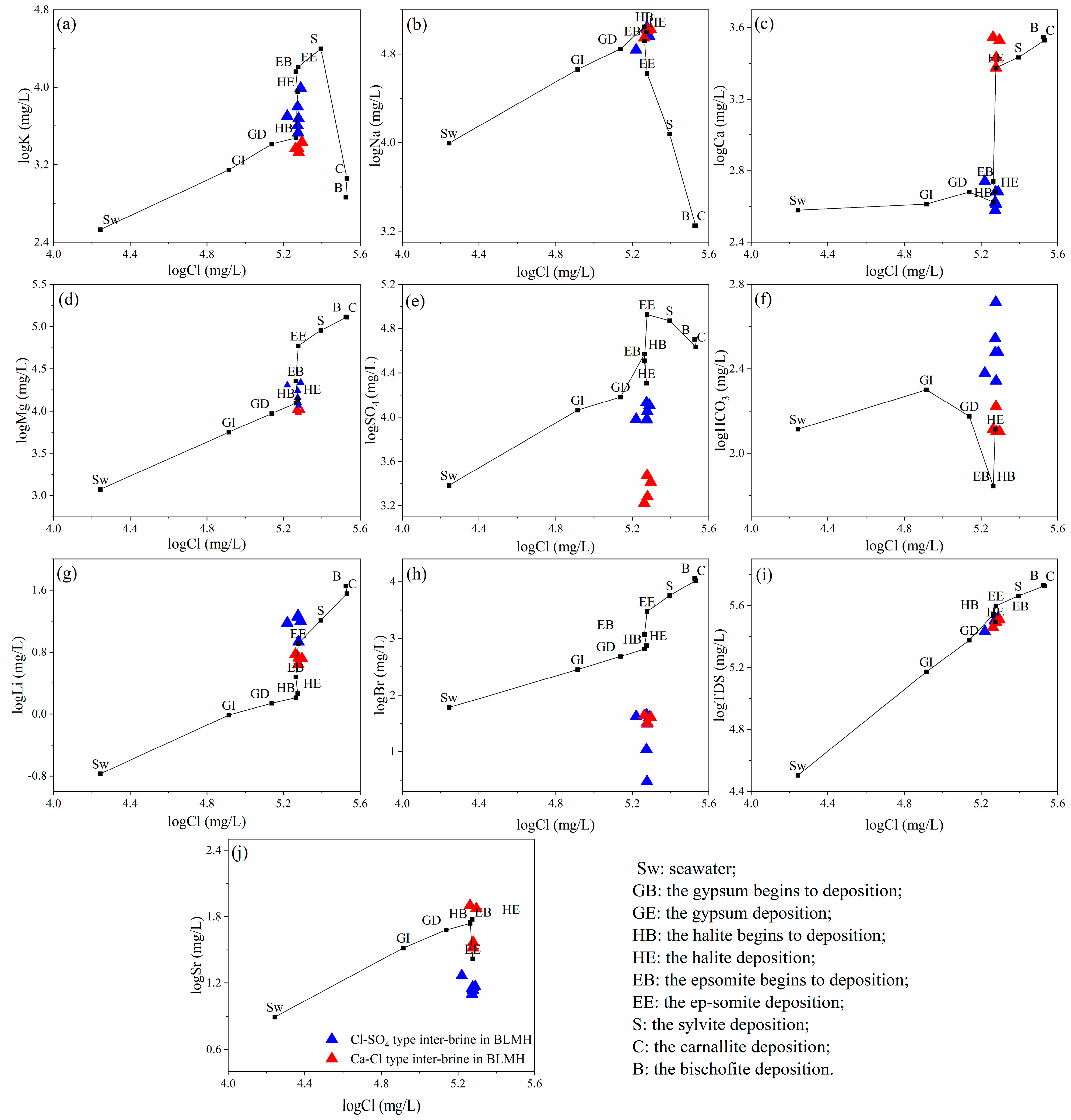
5.1. Hydrochemical Compositions
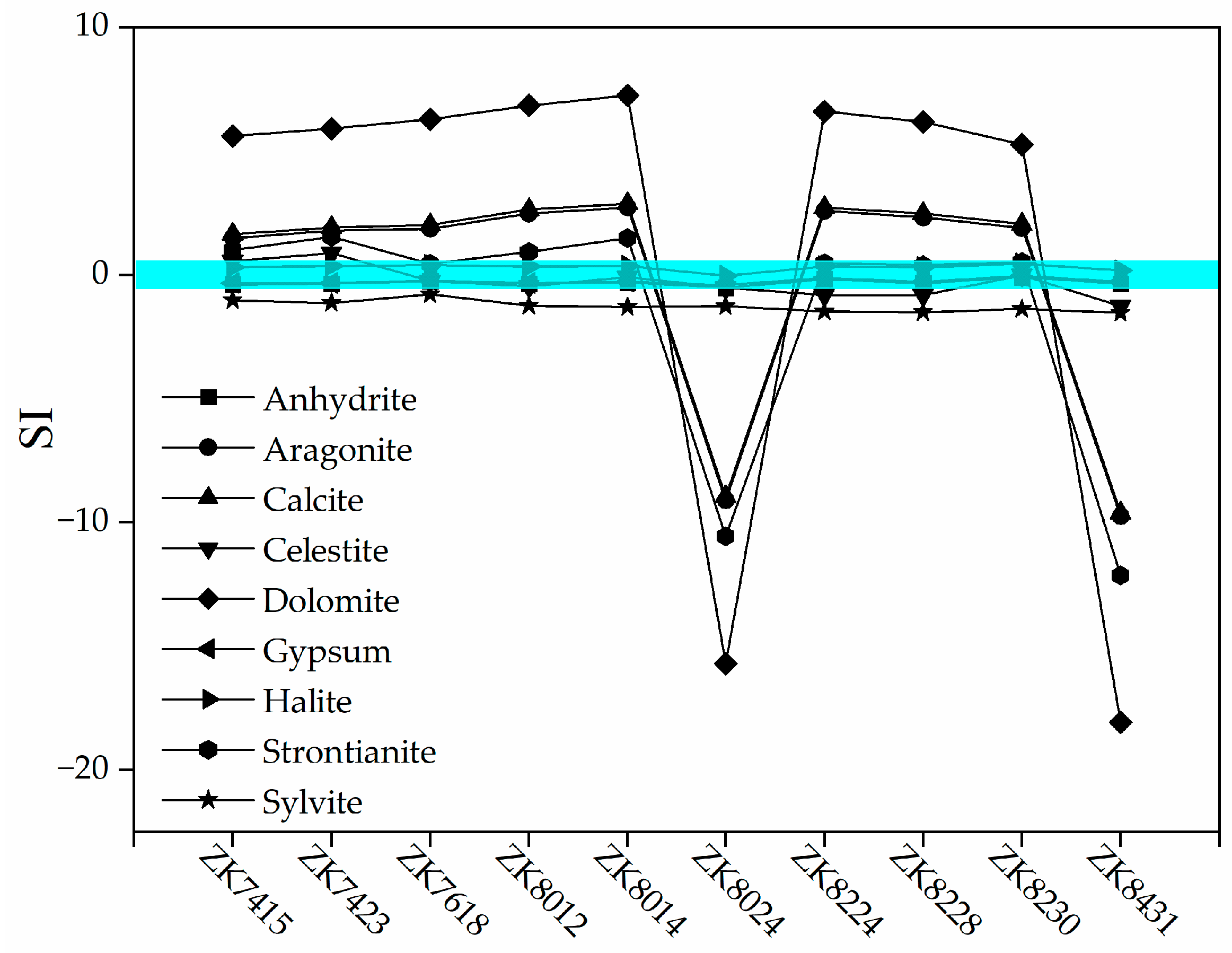
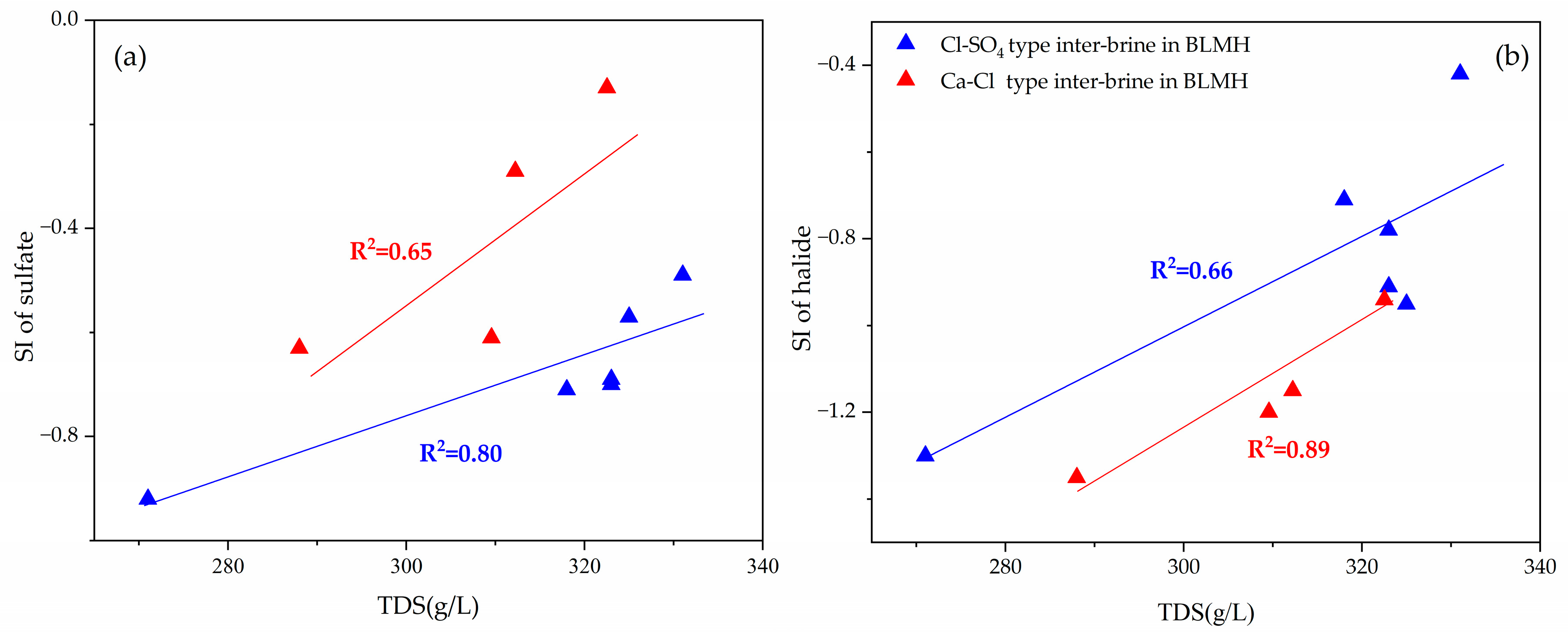
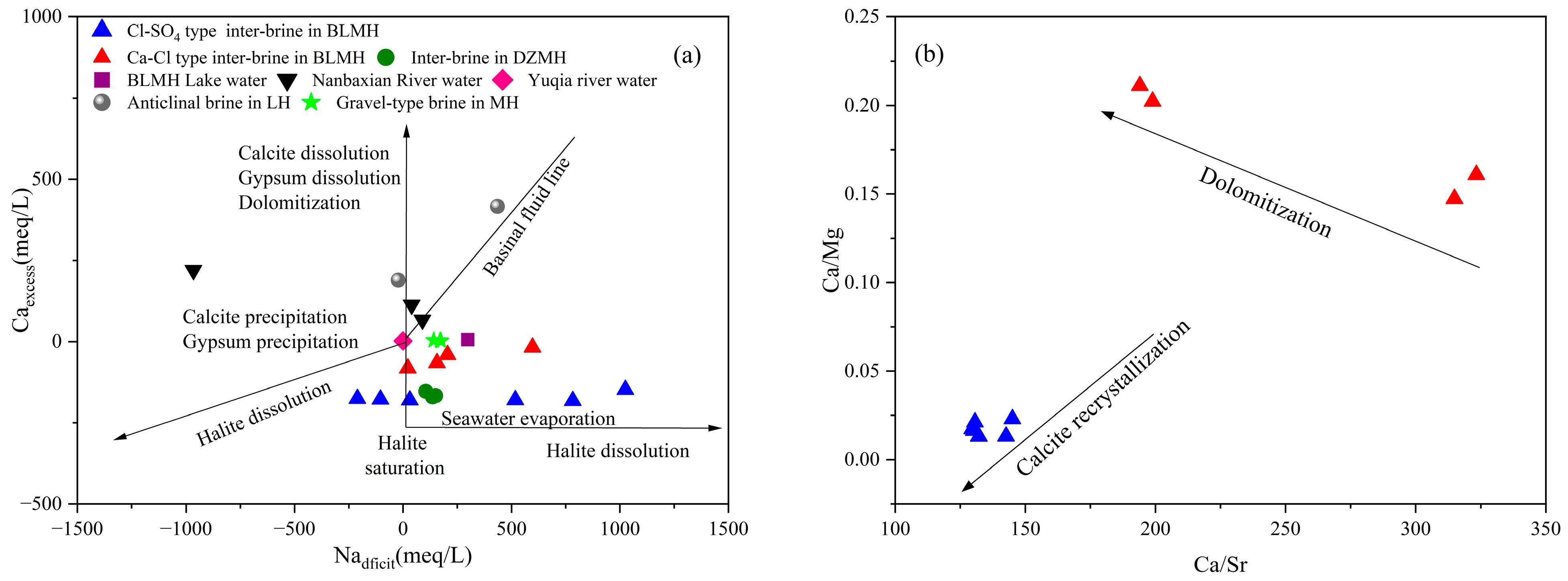
5.2. Hydrogeochemical Interactions
- (1)
- Ion Exchange Interaction
- (2)
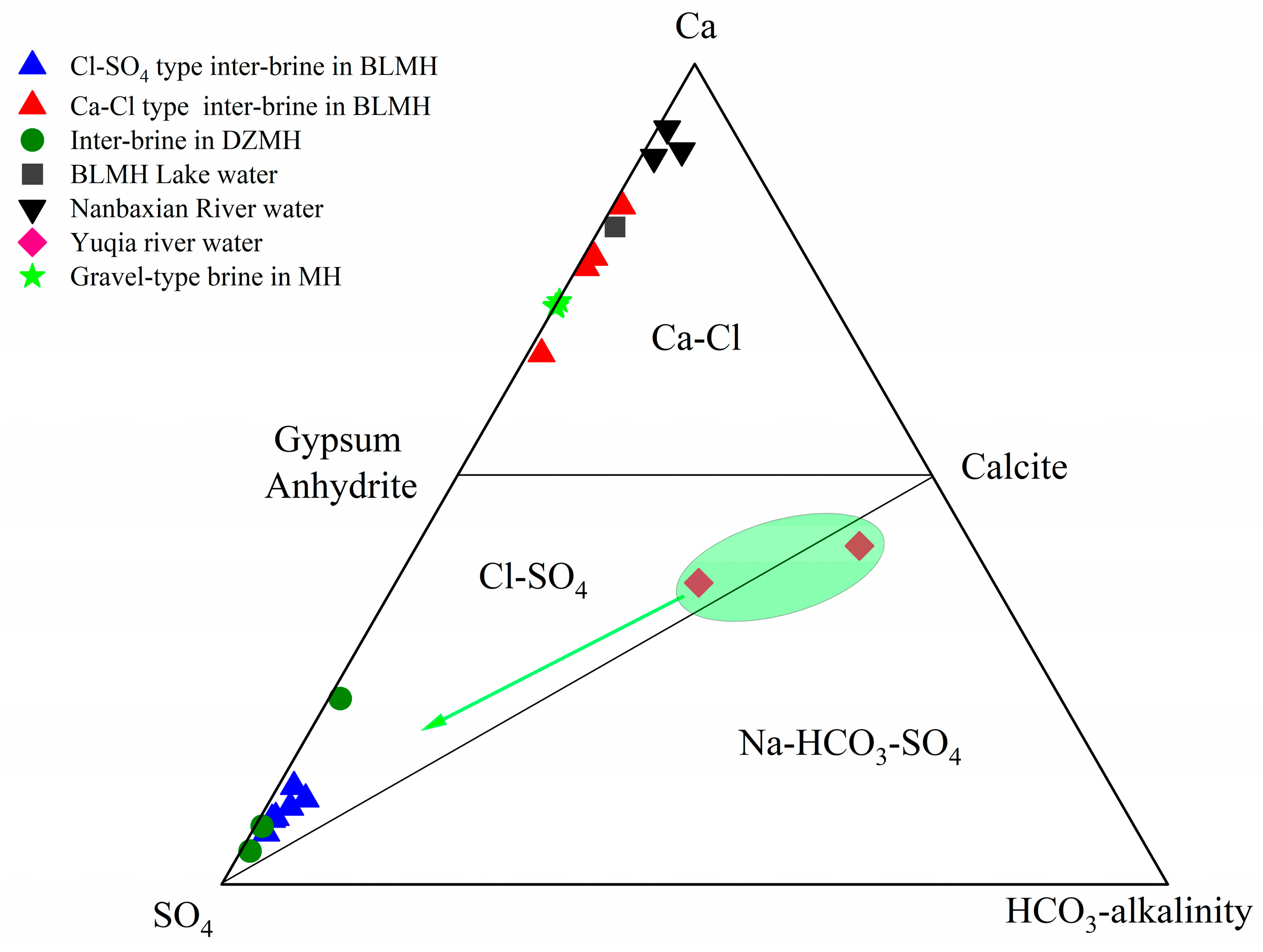
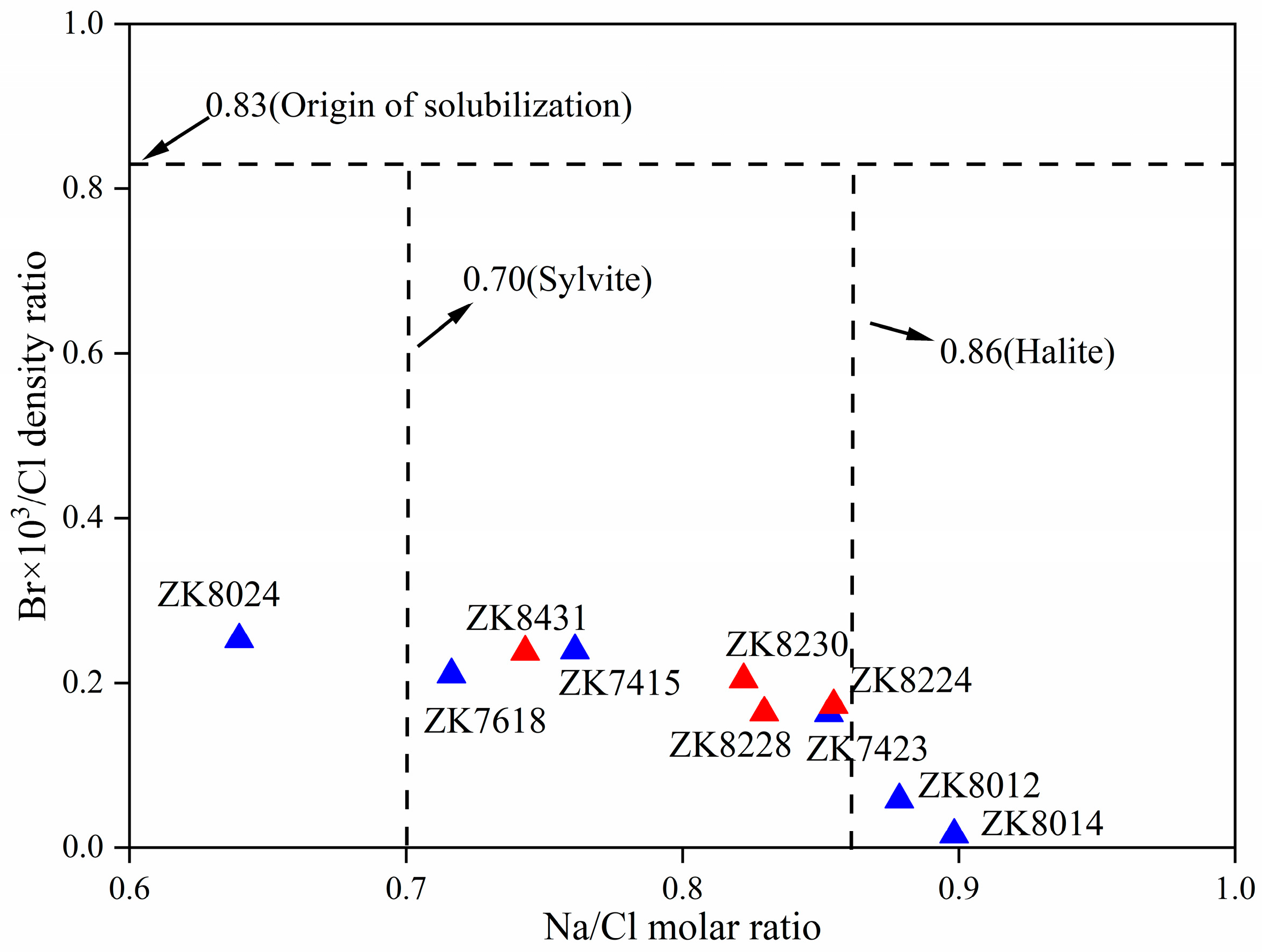
- Water–rock Interaction
5.3. Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes
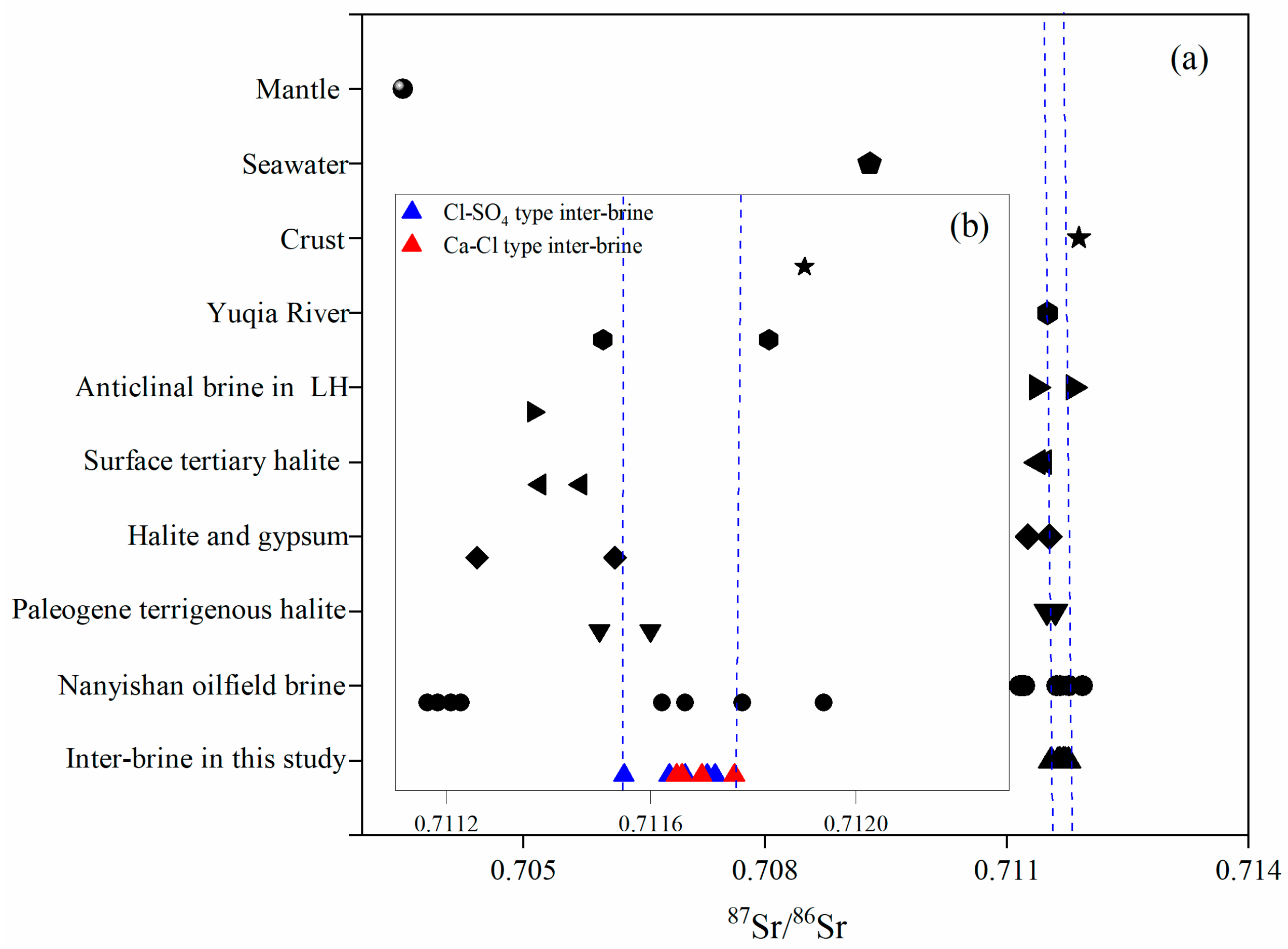
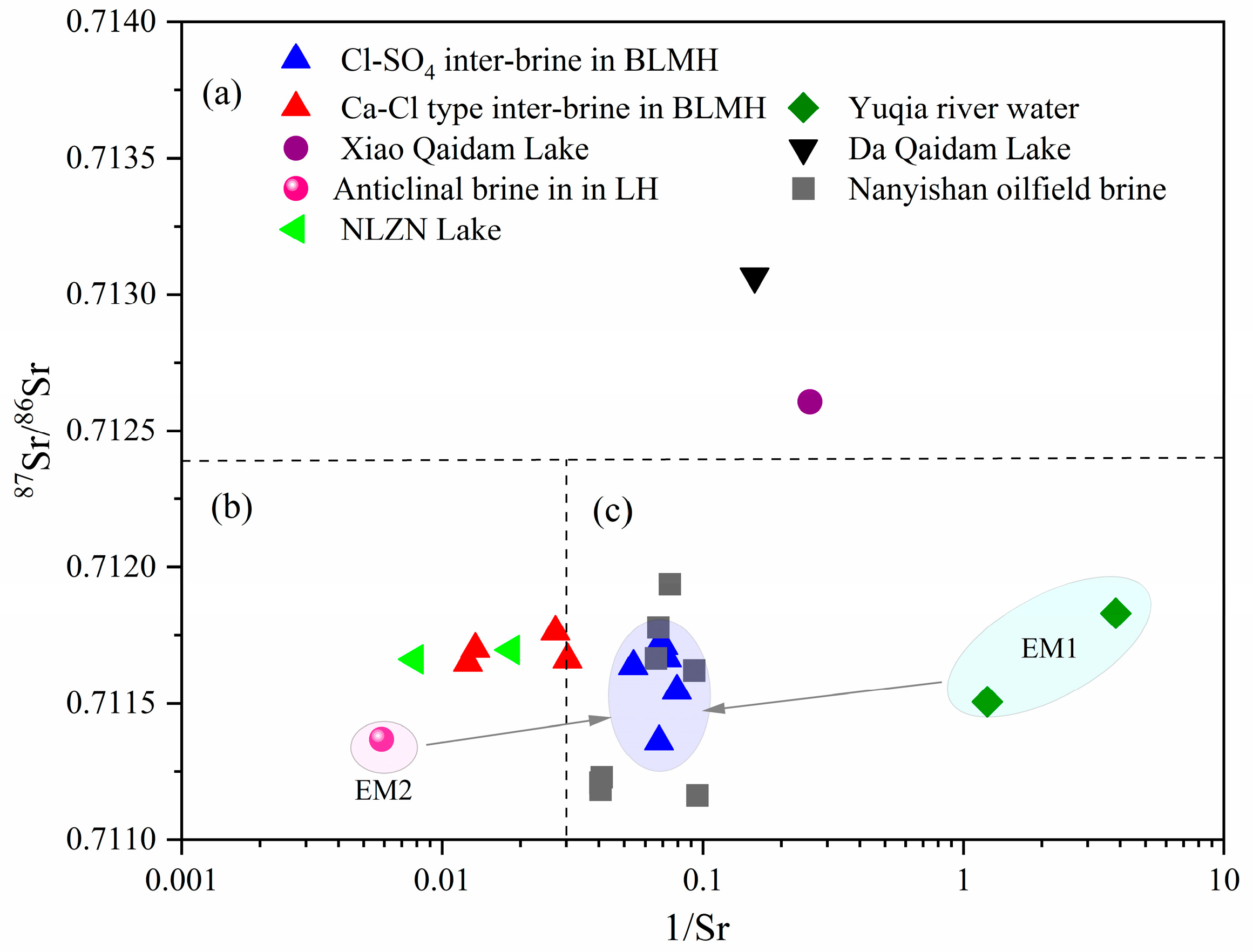
5.4. Strontium Isotopes
5.5. Formation and Evolution
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Hydrochemical characteristics suggest that the inter-brine in the study area belong to the high-salinity, weakly alkaline brine. The hydrochemical types are separated by the ZK7423-ZK8024 line, with Cl-SO4-type brine to the north and Ca-Cl-type brine to the north. The brine is mainly controlled by evaporation and concentration, rock salt dissolution, and ion exchange interaction. Dissolution of halite, sylvite, and gypsum provides a solute source for inter-brine.
- (2)
- Hydrogen and oxygen isotope studies suggest that the “low deuterium and high oxygen” inter-brine in the study area comes from atmospheric precipitation or meltwater of ice and snow. Isotope drift and deuterium surplus phenomena suggests that the brine is subject to water–rock interactions, evaporation, and concentration.
- (3)
- Studies on strontium isotopes suggests that the recharge and mixing of Ca-Cl water and Yuqia River water play a crucial role in forming and evolving Cl-SO4-type inter-brine in BLMH. A mass balance equation based on strontium isotopes allows for quantitatively estimating the contribution of the Yuqia River water as 58%~77% and the contribution of the anticline brine as 23%~42% in inter-brine.
- (4)
- The ionic ratios suggests that the inter-brine has poor sealing conditions. The water–rock and ion exchange interactions occur during the migration process. These features are typical of water of rock-salt-leaching origin, which can be summarized as the mixed origin model of “dissolution and filtration replenishment + deep replenishment” in BLMH.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al Rawashdeh, R. World peak potash: An analytical study. Resour. Policy 2020, 69, 101834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Lowenstein, T.K.; Wang, A.; Zheng, C.; Yu, J. Brine: Genesis and Sustainable Resource Recovery Worldwide. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2023, 48, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Z.; Li, M. Dynamic potassium flows analysis in China for 2010–2019. Resour. Policy 2022, 78, 102803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.P.; Hou, X.H.; Yu, C.Q.; Li, H.P.; Yi, W.H.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, X.L.; Zhang, Y.S.; Guo, T.W.; Wei, Z.; et al. The leading role of salt formation theory in the breakthrough and important progress in potash deposit prospecting. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2015, 36, 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Choubey, P.K.; Kim, M.S.; Srivastava, R.R.; Lee, J.C. Advance review on the exploitation of the prominent energy-storage element: Lithium. Part I: From mineral and brine resources. Mine. Eng. 2016, 89, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, L.A.; Hynek, S.A.; Bradley, D.C.; Boutt, D.; Labay, K.; Jochens, H. Lithium brines: A global perspective. Rev. Econ. Geol. 2016, 18, 339–365. [Google Scholar]
- Jurikova, H.; Ring, S.J.; Henehan, M.J.; Neugebauer, I.; Schröder, B.; Müller, D.; Schwab, M.J.; Tjallingii, R.; Brauer, A.; Blanchet, C. Boron geochemistry reveals the evolution of Dead Sea brines. Earth Planet. Sc. Lett. 2023, 622, 118403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.Q.; Huo, C.Y.; Cai, K.Q. The high mountain-deep basin saline environment—A now cenetic model of salt deposits. Geol. Rev. 1983, 29, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.G.; Xiao, Y.K.; Peng, Z.C.; An, Z.S.; He, X.X. Boron concentration and isotopic composition of halite from experiments and salt lakes in the Qaidam Basin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2000, 64, 2177–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.Y.; Luo, C.G.; Yang, H.J.; Kong, F.C.; Li, Y.L.; Deng, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, K.Y. Sources and a proposal for comprehensive exploitation of lithium brine deposits in the Qaidam Basin on the northern Tibetan Plateau, China: Evidence from Li isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 117, 103277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, P.; Gloaguen, E.; Labbe, J.F.; Melleton, J.; Piantone, P. Global lithium resources and sustainability issues. In Lithium Process Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gilalana, L.A.; Monge, M. Lithium: Production and estimated consumption. Evidence of persistence. Resour. Policy 2019, 60, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baspineiro, C.F.; Franco, J.; Flexer, V. Potential water recovery during lithium mining from high salinity brines. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Jiao, P.C.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhu, Z.G.; Hu, Y.F. Characteristics, reservoir physical properties and water-rich areas of Li-rich brine in Yiliping Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.C.; Yang, Y.K.; Luo, X.; Sha, Z.J.; Wang, J.P.; Ma, Y.J.; Ling, Z.Y.; He, B.Y.; Liu, W.P. Deep hydrothermal and shallow groundwater borne lithium and boron loadings to a mega brine lake in Qinghai Tibet Plateau based on multi-tracer models. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.H.; Li, B.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.T. Origin and evolution of inter-brine in the northern Qaidam Basin based on hydrochemistry and stable isotopes. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 211–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, L.M.; Stueber, A.M.; Huston, T.J. Br-Cl-Na systematics in Illionis basin fluids: Constraints on fluid origin and evolution. Geology 1990, 18, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Burchfiel, B.C. Late Cenozoic right-lateral movement along the Wenquan Fault and associated deformation: Implications for the kinematic history of the Qaidam Basin, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Int. Geol. Rev. 2004, 46, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Chen, J.Z.; Ding, C.W.; Ma, Y.L.; Liang, H.; Xue, S.; Zhang, T.; Du, X.C. Supernormal enrichment of lithium, rubidium and cesium in Salt Lake clays of Qaidam Basin and their development potential. Geol. China 2023, 50, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Hu, X.M.; Wu, Y.B.; Wang, C.Y. Sedimentology and evolution of sedimentary facies for the Cenozoic in the Mahai Region on the Northern Margin of the Qaidam Basin. Acta Geol. Sichuan 2011, 30, 129–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.W.; Ma, Y.L.; Chen, J.Z.; Ren, W.K.; Du, X.C.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, H.D.; Zhang, F.G. Mineralogy of clay deposits and geochemical characteristics of rare and scattered elements in the Balun Mahai Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. J. Salt Lake Sci. 2024, 32, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, S.Y.; Ge, W.; Zhang, Q.D.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.K. Main geological characteristics and genesis of clay-type lithium deposits deposited in lacustrine facies. Bull. Miner. Petro. Geochem. 2024, 43, 64–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.Y.; Zhao, Q.S.; Wang, G.C.; Zhang, J.W.; Feng, J. Hydrochemical dynamic characteristics and evolution of underground brine in the Mahai Salt Lake of the Qaidam Basin Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geol. Sin-Engl. 2018, 05, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhao, Y.J.; Xuan, Z.Q. Since the middle Pleistocene sedimentary characteristics and environment evolution and enrichment of brine in the east Salt Lake of Mohair. Geol. Chem. Miner 2018, 40, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.C. Study on Groundwater Circulation Model of Yuqia-Mahai Basin in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yuqia River. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.K.; Fan, Q.S.; Han, G.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, J.B.; Bai, H.K. Origin and Evolution of Deep K-Rich Confined Brine in Mahai Basin, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Aquat. Geochem. 2024, 30, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Miao, W.L.; Li, Y.S.; Tang, Q.L.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.Q. Hydrochemical charateristics of Oilfield Waters in Lenghu No. 3 Structure Area of North Edge of Qaidam Basin. J. Salt Lake Sci. 2016, 24, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Liu, X.X.; Lu, L.; Zhang, X.D.; Fan, Z.L.; Yu, X.L. Hydrochemical characteristics and origin of deep pore brine deposits in Mahai Baisn. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 37, 532–540. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, N.; Shen, L.J.; Li, R.Q.; Liu, C.L.; Jiao, P.C.; Hu, Y.F.; Zhao, X.F. Contribution of deep material sources to shallow potash formation of the Quaternary Mahai Salt Lake in the Qaidam Basin: Evidence from isotopes and trace elements. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 171, 106166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.D.; Yang, Y.B.; Song, B.W.; Galy, A.; Zhang, F.; Jin, Z.D.; Zhang, G.B.; Ye, C.C.; Fang, X.M. Hydrothermal systems with radiogenic Sr in the North Qaidam ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt, NE Tibetan Plateau and implications for regional dissolved Sr budget. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 138, 105214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, Y.S.; Tang, Q.L.; Miao, W.L.; Li, W.L.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y. Hydrochemical components and their distribution characteristics of oilfield waters in No. 4 structure of Lenghu, Qaidam Basin. J. Salt Lake Res. 2016, 24, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.W.; Li, J.S.; Fan, Q.S.; Wang, M.X.; Shan, F.S. Origin of Deep inter-brines from Dayantan Mine Area in Qaidam Basin. J. Salt Lake Res. 2019, 27, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hardie, L.A.; Eugster, H.P. The evolution of closed-basin brines. Mineral. Soc. Amer. Spec. Pap. 1970, 3, 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, A.B. Origin and Chemical Evolution of Brines in Sedimentary Basins. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 1–3 October 1978; p. 7504. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, C.J. Seawater evaporation trajectory and its application. Earth Sci. 1995, 4, 410–414. [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright, I.; Weaver, T.R.; Fifield, L.K. Cl/Br ratios and environmental isotopes as indicators of recharge variability and groundwater flow: An example from the southeast murray basin. Australia. Chem. Geol. 2006, 231, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.S.; Ma, H.Z.; Lai, Z.P.; Tan, H.B.; Li, T.W. Origin and evolution of oilfield brines from Tertiary strata in western Qaidam Basin: Constraints from 87Sr/86Sr, δD, δ18O, δ34S and water chemistry. Chin. J. Geochem. 2010, 29, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.S.; Lowenstein, T.K.; Wei, H.C.; Yuan, Q.; Qin, Z.J.; Shan, F.S.; Ma, H.Z. Sr isotope and major ion compositional evidence for formation of Qarhan Salt Lake, western China. Chem. Geol. 2018, 497, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risacher, F.; Alonso, H.; Salazar, C. The origin of brines and salts in Chilean salars: A hydrochemical review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2003, 63, 249–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risacher, F.; Alonso, H. Geoquimica del Salar de Atacama: 2. Evolucion de las aguas. Rev. Geol. Chile 1996, 23, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Jin, Z.D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. Hydrochemical characteristics, controlling factors and solute sources of groundwater within the Tarim River Basin in the extreme arid region, NW Tibetan Plateau. Quatern. Int. 2015, 380, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholler, H. Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In Methods and Techniques of Groundwater Investigation and Development; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1967; pp. 54–83. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.M.; Criss, R.E. Na-Ca-Cl Relations in Basinal Fluids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 1996, 60, 2743–2752. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.M.; Sun, T.; Shen, W.Z.; Shu, L.S.; Niu, Y.L. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution. Episodes 2006, 29, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazor, E.; Drever, J.I.; Finley, J. Hydrochemical implications of Groundwater Mixing: An from the southern Laramie Basin, Wyoming. Waer Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Raj, B.; Tiwari, A.K.; Mahato, M.K. Evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality in the Jhansi district of Bundelkhand region, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1225–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloppmann, W.; Négrel, P.; Casanova, J.; Klinge, H.; Schelkes, K.; Guerrot, C. Halite dissolution derived brines in the vicinity of a Permian salt dome (N German Basin). Evidence from boron, strontium, oxygen, and hydrogen isotopes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2001, 65, 4087–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaicha, F.; Dib, H.; Bouteraa, O.; Manchar, N.; Boufaa, K.; Chabour, N.; Demdoum, A. Geochemical assessment, mixing behavior and environmental impact of thermal waters in the Guelma geothermal system, Algeria. Acta Geochim. 2019, 38, 683–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, T.; Deines, P. Theoretical calculation of oxygen isotope fractionation factors in carbonate systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 3642–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotope in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Longinelli, A.; Sighinolfi, G.; de Michele, V.; Selmo, E. δ18O and chemical composition of Libyan Desert Glass, country rocks, and sands: New considerations on target material. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2011, 46, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.B.; Rao, W.B.; Ma, H.Z.; Chen, J.S.; Li, T.W. Hydrogen, oxygen, helium and strontium isotopic constraints on the formation of oilfield waters in the western Qaidam Basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.X. Salt Lake in Qaidam Basin; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987; pp. 1–235. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.B.; Xu, J.X.; Liu, J.B.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, K.; Ma, H.Z. Research progress of underground brine hydrogeology. J. Salt Lake Res. 2018, 26, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.S.; Ma, H.Z.; Tan, H.B.; Xu, J.X.; Li, T.W. Characteristics and genesis of brine in western Qaidam Basin. Geochemistry 2007, 06, 601–611. [Google Scholar]
- Fontes, J.C.; Matray, J.M. Geochemistry and origin of formation brines from the Paris Basin, France: 1. Brines associated with Triassic salts. Chem. Geol. 1993, 109, 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.S.; Ma, H.Z.; Tan, H.B.; Li, T.W.; Xu, J.X. Hydrochemical characteristics of brines and potassium-prospecting researches in Western Qaidam Basin. Acta Geo. Sin. 2007, 28, 446–455. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Cao, Q.; Yin, F.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, L.D.; Shen, Y. Characteristics of the brines and hot springs in the Triassic carbonates in the high and steep fold zone of the eastern Sichuan Basin. Acta Geolo. Sin. 2015, 89, 1908–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.K.; Fan, Q.S.; Wang, J.P.; Qin, Z.J.; Zhang, X.R.; Wei, H.C.; Du, Y.S.; Shan, F.S. Hydrochemistry, distribution and formation of lithium-rich brines in salt lakes on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Minerals 2019, 9, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.C.; Zhang, J.W.; Yao, F.J.; Zhao, L. Deep brine potassium exploration and research progress of Mahai Potash Deposit. Miner. Depos. 2016, 6, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.G.; Wei, J.H.; Li, Q.; Ayantobo, O.O. Regional Characteristics and Impact Factors of Change in Terrestrial Water Storage in Northwestern China from 2002 to 2020. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhou, P.P.; Wang, G.C.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Z.M.; Liao, F.; Li, B.; Chen, X.L.; Guo, L.; Dang, X.Y.; et al. Hydrochemical and isotopic interpretation of interactions between surface water and groundwater in Delingha, Northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Lv, A.F.; Jia, S.F.; Qi, S.S. Longterm multisource satellite data fusion reveals dynamic expansion of lake water area and storage in a hyperarid basin of China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.S.; Ma, H.Z.; Tan, H.B.; Li, T.W. Geochemistry Characteristics of Sulfur Isotope in Oilfield Brine of the Western Qaidam Basin. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2009, 28, 137–142. [Google Scholar]


| Num. | pH | TDS | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | Li+ | Br− | Sr2+ | δD | δ18O | 87Sr/86Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/L | g/L | g/L | g/L | g/L | g/L | g/L | g/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | ‰ | ‰ | |||
| ZK7415 | 7.86 | 318.00 | 6.27 | 92.70 | 0.38 | 17.30 | 188.00 | 13.50 | 0.30 | 18.20 | 45.00 | 12.60 | −5.50 | 3.20 | 0.711700 |
| ZK7423 | 7.64 | 323.00 | 4.76 | 105.00 | 0.41 | 11.60 | 190.00 | 11.30 | 0.22 | 8.50 | 31.00 | 13.75 | −27.40 | 2.30 | 0.711666 |
| ZK7618 | 8.07 | 331.00 | 9.79 | 90.50 | 0.48 | 21.80 | 195.00 | 12.80 | 0.30 | 15.80 | 41.00 | 14.75 | −24.10 | 6.50 | 0.711661 |
| ZK8012 | 7.99 | 323.00 | 3.99 | 107.00 | 0.42 | 14.50 | 188.00 | 9.47 | 0.35 | 17.90 | 11.00 | 14.20 | −38.60 | −1.30 | 0.711710 |
| ZK8014 | 8.05 | 325.00 | 3.37 | 110.00 | 0.48 | 12.50 | 189.00 | 9.53 | 0.52 | 18.40 | 3.00 | 14.50 | −11.60 | 5.60 | 0.711725 |
| ZK8024 | 7.40 | 271.00 | 5.02 | 68.80 | 0.55 | 20.20 | 166.00 | 9.58 | 0.24 | 15.00 | 42.00 | 18.50 | −28.50 | 2.50 | 0.711637 |
| ZK8224 | 7.72 | 312.21 | 2.34 | 105.05 | 2.37 | 9.66 | 189.71 | 2.98 | 0.17 | 4.40 | 32.85 | 33.00 | −41.20 | −2.00 | 0.711661 |
| ZK8228 | 7.78 | 309.54 | 2.12 | 102.23 | 2.71 | 10.11 | 190.20 | 1.91 | 0.13 | 5.30 | 31.20 | 36.75 | −29.80 | 1.50 | 0.711763 |
| ZK8230 | 7.72 | 322.54 | 2.70 | 105.50 | 3.38 | 10.03 | 198.09 | 2.58 | 0.13 | 5.20 | 40.50 | 74.50 | −23.90 | 3.00 | 0.711700 |
| ZK8431 | 7.55 | 288.00 | 2.32 | 88.10 | 3.52 | 10.00 | 183.00 | 1.67 | 0.13 | 5.90 | 43.50 | 79.50 | −28.60 | 2.40 | 0.711650 |
| L-1 | 7.32 | 252.50 | 2.06 | 80.50 | 3.45 | 7.21 | 157.00 | 1.89 | 0.20 | 3.90 | - | - | 1.30 | 3.09 | - |
| N-01 | 7.39 | 137.60 | 0.79 | 45.00 | 3.13 | 3.28 | 84.55 | 0.85 | 0.15 | 2.00 | 22.80 | - | −2.00 | 7.70 | - |
| N-02 | 7.40 | 73.85 | 0.44 | 23.90 | 3.21 | 0.85 | 44.59 | 0.58 | 0.43 | 0.60 | 2.50 | - | - | - | - |
| N-03 | 7.90 | 153.70 | 0.65 | 46.80 | 5.35 | 5.68 | 44.18 | 0.96 | 0.18 | 1.90 | 10.00 | - | - | - | - |
| Num. | ZK7415 | ZK7423 | ZK7618 | ZK8012 | ZK8014 | ZK8024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR | 71.65 | 64.29 | 63.20 | 73.81 | 77.06 | 58.01 |
| FS | 28.35 | 35.71 | 36.80 | 26.19 | 22.94 | 41.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, N.; Qin, X.; Ma, Y.; Pan, T.; Chen, J.; Ding, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; et al. Origin of Intercrystalline Brine Formation in the Balun Mahai Basin, Qaidam: Constraints from Geochemistry and H-O-Sr Isotopes. Water 2024, 16, 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223286
Feng N, Qin X, Ma Y, Pan T, Chen J, Ding C, Jiang Z, Zhang D, Liu C, Li Q, et al. Origin of Intercrystalline Brine Formation in the Balun Mahai Basin, Qaidam: Constraints from Geochemistry and H-O-Sr Isotopes. Water. 2024; 16(22):3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223286
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Ning, Xiwei Qin, Yuliang Ma, Tong Pan, Jianzhou Chen, Chengwang Ding, Ziwen Jiang, Dong Zhang, Chenglin Liu, Qingkuan Li, and et al. 2024. "Origin of Intercrystalline Brine Formation in the Balun Mahai Basin, Qaidam: Constraints from Geochemistry and H-O-Sr Isotopes" Water 16, no. 22: 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223286
APA StyleFeng, N., Qin, X., Ma, Y., Pan, T., Chen, J., Ding, C., Jiang, Z., Zhang, D., Liu, C., Li, Q., Ren, E., & Zhang, F. (2024). Origin of Intercrystalline Brine Formation in the Balun Mahai Basin, Qaidam: Constraints from Geochemistry and H-O-Sr Isotopes. Water, 16(22), 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223286