Abstract
This study investigated the degradation of sulfolane using pressurized ozonation under varying initial concentrations and the influence of different catalysts and peroxymonosulfate activation methods on the degradation efficiency. Initial sulfolane concentrations of 1 mg L−1, 20 mg L−1, and 100 mg L−1 were tested over 120 min, revealing a degradation efficiency of 73%, 41%, and 18%, respectively. The addition of various metal ions (Zn2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Co2+) demonstrated that only zinc and magnesium enhanced degradation, with zinc achieving a 92% removal efficiency and magnesium achieving 86%. Different doses of magnesium and zinc were further tested, showing optimal degradation at specific concentrations. The combination of PMS with ozonation was explored, revealing that zinc activation did not significantly enhance degradation, while NaOH activation achieved near-total degradation, with a 100 mg L−1 NaOH concentration. Varying PMS concentrations indicated that altering pH was more effective than changing PMS dosage. Finally, the impact of pH changes in both reverse osmosis water and tap water matrices confirmed that higher pH levels significantly improved degradation efficacy, achieving up to 98% removal with NaOH concentrations of 50 mg L−1 in reverse osmosis water. These results suggest that optimizing pH and catalyst type are critical for enhancing sulfolane degradation in pressurized ozonation systems.
1. Introduction
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), as innovative wastewater treatment technologies, have gained widespread use [1,2,3,4]. Ozone, with a redox potential (ORP) of 2.07 V, has gathered significant attention due to its potent oxidation and disinfection capabilities [3]. Its extensive application is primarily attributed to its unique dipole structure, which facilitates reactions with electron-rich organic compounds like phenols, amines, and olefins [5]. Given its high oxidation capacity against various pollutants, ozone holds promise in treating wastewater from various industries including pulp and paper production, detergent and surfactant production, municipal wastewater, and pharmaceutical production, among others [6,7,8,9]. However, some organic compounds cannot be effectively mineralized or degraded by ozonation alone, necessitating enhancing the efficacy of ozonation.
Ozonation enhancement can be achieved by increasing hydroxyl radical generation, which can occur through various methods such as ozonation in alkaline solutions (O3/OH−), the photolysis of ozone (O3/UVC), peroxone (O3/H2O2), and catalytic ozonation [10,11,12,13]. Alternatively, enhancement can be attained through a combination of ozone with sulfate radical oxidants, such as ozone/peroxymonosulfate (O3/PMS) or ozone/sodium perdisulfate (O3/PDS), and persulfate/O3/UVC [14,15,16,17]. Through the advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), dissolved ozone in water decomposes into hydroxyl radicals (•OH) and superoxide radicals (O2•−). The generation of hydroxyl radicals increases at higher pH levels [10,11]. Catalytic ozonation holds significant potential for enhancing the ozonation removal efficacy of emerging contaminants [10,18,19,20]. Various catalysts, including transition metals, metal oxides, and activated carbon, have been investigated for catalytic ozonation across a wide range of organic compounds. The mechanisms of catalytic ozonation remain complex and not yet fully understood [20,21]. However, it is generally acknowledged that certain catalysts can enhance the oxidation of organic compounds through two primary mechanisms: (i) by promoting the transformation of ozone to hydroxyl radicals (•OH), and (ii) by reacting with organic compounds to form complexes that are more readily oxidized by ozone [10,13,22,23].
To generate sulfate radicals (SO4•−) for ozonation enhancement, the activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) or persulfate (PS) is required [24]. Many studies have mainly focused on homogeneous or heterogeneous activation methods involving transition metals, UV light, and heat [25,26,27]. Recently, Yang et al. [14] discovered that PMS can be activated by O3 to generate •OH, achieving radical yields of 0.43 and 0.45 simultaneously, while sodium perdisulfate (PDS) cannot directly react with O3, due to the peroxy group (O–O) in PDS, which is resistant to O3 [15,28]. The combination of O3 and PMS is highly effective in degrading refractory micropollutants such as para-chlorobenzoic acid (pCBA) and ibuprofen (IBP) [29,30]. Among the reported synergistic ozonation methods, O3/PMS has demonstrated significantly higher radical yields compared to both ozonation alone and the O3/H2O2 combination [31].
In recent years, groundwater contamination by sulfolane has been reported in Canada, US, and Australia [32]. Sulfolane (C4H8O2S), also known as 2,3,4,5-tetrahydrothiophene-1,1-dioxide, is a highly polar organic solvent that is water-miscible and colorless. In natural gas processing plants, it is extensively used to remove polar compounds from sour gas streams [33]. A few different treatment methods can be used for sulfolane degradation, among which advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have received attention recently. The reported AOP-based system for sulfolane treatment encompasses Fenton and Fenton-like processes, TiO2 photocatalysis, ultraviolet-C (UVC)/H2O2, UVC/O3, UVC/persulfate, and various ozone-based methods. These systems are characterized by their ability to generate highly reactive oxidative species, primarily hydroxyl radicals [34,35,36,37,38,39]. Yu et al. (2016) [36] discussed the use of various oxidative techniques, including UVA and UVC irradiation in conjunction with photoactive oxidants such as ozone, H2O2, and TiO2 photocatalysis, for the degradation of sulfolane in aqueous solutions. Mehrabani-Zeinabad et al. [37] examined the mineralization of sulfolane using a combination of UV, ozone, and hydrogen peroxide (UV/O3/H2O2) within a tubular reactor. Izadifard et al. [17] investigated the synergistic effects of persulfate/UVC and O3/persulfate/UVC on sulfolane degradation. The introduction of O3 to the system reduced the reaction time, and in both scenarios, higher persulfate concentrations resulted in greater sulfolane degradation.
This paper investigates the enhancement in pressurized ozonation for sulfolane degradation in aqueous media in a bench-scale system using various oxidative techniques. This study begins by examining the effect of sulfolane concentration on a pressurized ozonation system. Subsequently, experiments are conducted by combining homogenous metal ions with ozonation and peroxymonosulfate with ozonation. Finally, the performance of pressurized ozonation processes at high-pH conditions across different water matrices is compared. To the best of our knowledge, the synergistic effect of pressurized ozonation with homogenous metal ions, peroxymonosulfate, and varying pH levels to improve degradation has not been previously explored.
2. Materials and Methods
Sulfolane with 99% purity was purchased from Alfa Aesar (Fisher Scientific Inc., Canada). Potassium peroxymonosulfate ((HKO5S)(0.5HKO4S)(0.5K2O4S)), magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2·6H2O, 99%), cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2·6H2O) reagent grade, nickel (II) chloride (NiCl2, 98%), copper(II) chloride (CuCl2, 99%), and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich, Oakville, ON, Canada. Analytical-grade zinc chloride (ZnCl2) was obtained from VWR Chemicals, Canada. High-purity oxygen was obtained from Air Liquide. Except for different water matrices, all experiments used reverse osmosis (RO) water and were conducted in a 4.5 L cylinder reactor with a 3.5 L solution in batch mode as depicted in Figure S1. The initial sulfolane concentration was set to 1 mg L−1 for all experiments unless studying the dependence on initial concentrations, which was 20 mg L−1 and 100 mg L−1. Solutions were prepared by diluting a 5000 mg L−1 stock solution of sulfolane in 3.5 L of reverse osmosis (RO) water. Samples were filtered with 0.45 mm PVDF filter paper prior to analytical measurements. All experiments were conducted at a temperature of 21 °C.
All experiments were performed in triplicate, and they were carried out with a 0.6 L min−1 ozone flow rate, 20 psi (137.9 kPa) of pressure, an ozone percentage of 100%, and an ozone concentration of 2.86 mg L−1. An ozone generator (A2Z 3-G LAB, A2Z O3 systems Inc., Louisville, KY, USA) was connected to the pure oxygen cylinder to introduce ozone into the system. At fixed time intervals (10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 90, and 120 min), 2.5 mL samples were collected and extracted with 1.5 mL of dichloromethane (DCM). The extracted sulfolane samples were analyzed using a Shimadzu GCMS-QP2010 SE gas chromatograph–mass spectrometer, equipped with a ZB 5MSI column. Helium with a purity of 99.999% was employed as the carrier gas at a steady flow rate of 1.07 mL min−1. Samples were injected in splitless mode with a volume of 1.0 µL, and the injection port was maintained at 250 °C. The oven temperature program began at 90 °C for 2 min and then increased to 160 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min, followed by a ramp to 280 °C at 20 °C/min, where it was held for 2 min. The mass spectrometer scanned for ions with m/z values of 41, 56, and 120, and the GCMS had a detection limit of 10 µg L−1. Zinc and magnesium ion concentrations were simultaneously analyzed using an inductive coupled plasma (ICP) spectrometer (iCAP 7000 SERIES, Thermo SCIENTIFIC, Cambridge, UK) instrument.
The ozone concentration in the solution was determined using the iodometric method. In this process, a sample of ozonated water is mixed with a buffered potassium iodide (KI) solution. The mixture is then acidified with diluted sulfuric acid to initiate the reaction. The resulting solution is titrated with a standardized sodium thiosulfate solution until it turns pale yellow. At this point, a starch indicator is added, causing the solution to turn blue. The titration continues until the blue color disappears, signifying the completion of the reaction. The volume of sodium thiosulfate used during titration corresponds to the ozone concentration in the water sample.
3. Results
3.1. Sulfolane Degradation with Different Initial Concentrations
This study investigated the normalized sulfolane concentrations over degradation times during pressurized ozonation treatment, as depicted in Figure 1. Degradation times ranging from 0 to 120 min, with various initial sulfolane concentrations of 1 mg L−1, 20 mg L−1, and 100 mg L−1, were tested. The initial concentration study involved spiking reverse osmosis (RO) water samples with different sulfolane concentrations. It was observed that with increasing time, sulfolane degradation increased, while an increase in initial sulfolane concentration led to decreased degradation. Sulfolane removal percentages of 73%, 41%, and 18% were found for initial concentrations of 1 mg L−1, 20 mg L−1, and 100 mg L−1, respectively. Furthermore, a second-order kinetic model was adopted to examine experimental data, and the effects of different sulfolane concentrations on the kinetics of degradation are summarized in Table 1. The degradation rate constant of samples decreased from 0.0230 (mg L−1)−1 min−1 to 0.2 × 10−4 (mg L−1)−1 min−1, indicating the influence of initial concentration.
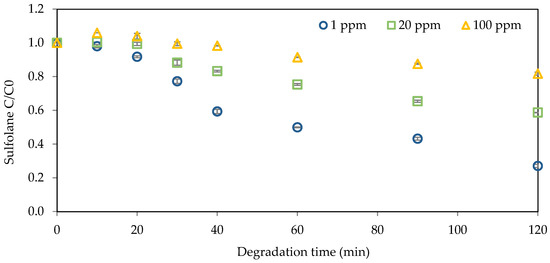
Figure 1.
Sulfolane degradation with different initial concentrations (initial Csulfolane = 1, 20, and 100 mg L−1; ozone flow rate = 0.6 L min−1; system pressure = 20 psi; and ozone percentage = 100%).

Table 1.
Sulfolane degradation rate constant with different initial concentrations.
These findings are like those of Mehrabani-Zeinabad et al. [37], who investigated sulfolane degradation using UV/O3/H2O2 across different initial sulfolane concentrations (ranging from 10 mg L−1 to 500 mg L−1). They reported an increase in degradation kinetics as the initial concentration decreased. Similarly, Khan et al. [38] examined the impact of initial sulfolane concentration (ranging from 0.56 mg L−1 to 200 mg L−1) on sulfolane degradation using UVC/H2O2. They observed a decrease in degradation rate with increasing initial concentrations and noted that the degradation rate became nearly independent of sulfolane concentration when the initial concentration was below 30 mg L−1.
Increasing the initial concentration of sulfolane decreases the degradation efficacy, indicating that pressurized ozonation alone may not be effective at high concentrations. Therefore, methods to enhance sulfolane degradation are needed. The performance of the ozonation system can be improved by various methods, such as catalytic ozonation and hybrid ozonation processes, which will be explained in the following sections.
3.2. Different Homogeneous Metal Ions Impact on Sulfolane Degradation
In Figure 2, the impact of different metal ions (alkaline earth metal and transition metals) on sulfolane degradation was investigated, and the normalized sulfolane concentration within 120 min is shown. Zinc, magnesium, cobalt, copper, and nickel with an initial concentration of 2 mg L−1 were added as metal ions to a sample with a 1 mg L−1 sulfolane concentration. All results were compared with a control sample with no metal ions, which showed a 73% degradation efficacy after 120 min. The degradation percentages when zinc, magnesium, copper, nickel, and cobalt ions were added were 92%, 86%, 42%, 36%, and 35%, respectively. These results revealed that among the metals, only zinc and magnesium positively impacted sulfolane degradation and enhanced removal efficacy. In contrast, it is hypothesized that the other metal ions might rapidly consume ozone and hydroxyl radicals through secondary reactions, such as the formation of metal-hydroxo complexes or metal oxide precipitates. This consumption reduced the availability of reactive species necessary for sulfolane degradation, and the scavenging effect may explain the observed decrease in degradation efficacy. Nickel notably decreased sulfolane degradation throughout the experiment. For copper and cobalt, the figures show that for the first 20 min, the sulfolane degradation increased, but after that, the degradation decreased compared to the control sample. Due to the improvement in sulfolane degradation after adding magnesium and zinc, the impact of changes in the initial dosage of zinc ions (magnesium ions results represented in the Supplementary Information, Section S2) was investigated.
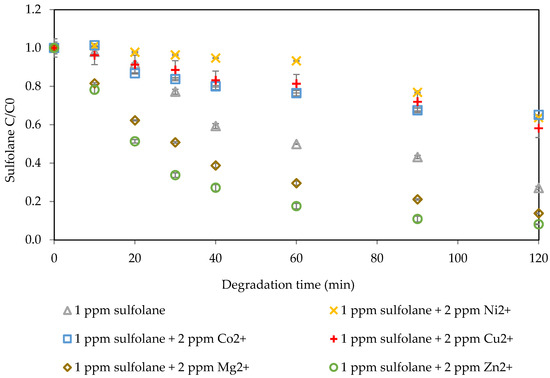
Figure 2.
Impact of homogenous metals on sulfolane degradation (initial Csulfolane = 1 mg L−1, ozone flow rate = 0.6 L min−1, system pressure = 20 psi, and ozone percentage = 100%).
Different Zn2+ Catalyst Dosages
The effect of zinc concentration on sulfolane degradation was analyzed by varying the initial zinc concentration while the sulfolane concentration was fixed at 1 mg L−1. The results are presented in Figure 3, with initial zinc concentrations of zero, 2 mg L−1, 10 mg L−1, and 50 mg L−1. The experiments were conducted over 120 min. The results showed that the final degradation percentages were 73%, 92%, 78%, and 62% for initial dosages of zero, 2 mg L−1, 10 mg L−1, and 50 mg L−1, respectively. By increasing the exposure time, the degradation rate for each experiment increased. However, by increasing the zinc initial dosage, the degradation efficacy decreased, from 92% at a 2 mg L−1 concentration to 62% at a 50 mg L−1 concentration. In the 50 mg L−1 concentration, the sulfolane degradation percentage increased for the first 35 min to 35%, which is equal to the control sample without any zinc at this time. Then, the degradation rate decreased, and after 120 min, the degradation percentage was 62% compared to the control, which was 73%. It is important to note that according to Wang and Chen [13], extra metal ions can scavenge the generated ·OH. Therefore, the optimization of catalyst dosage is vital for the catalytic ozonation process. In a study by Tanatti [40], the efficacy of homogeneous and heterogenous forms of zinc catalysts (ZnSO4 and ZnO) in bisphenol-A (BPA) degradation was investigated. The results showed a 94.16% BPA removal with ZnSO4 and 98.52% for ZnO within 12.5 min under optimized conditions.
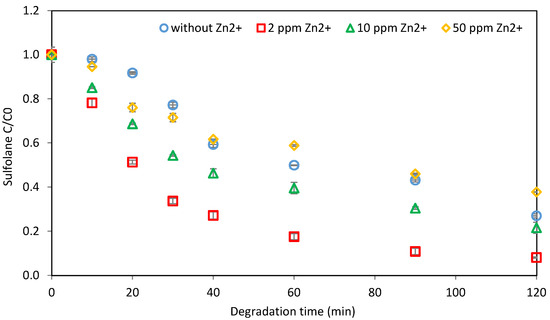
Figure 3.
Impact of different initial zinc concentrations on sulfolane degradation (initial Csulfolane = 1 mg L−1; Czinc = 2, 10, and 50 mg L−1; ozone concentration = 2.86 mg L−1).
To investigate possible reactions between zinc and sulfolane, different experiments were conducted under ambient and pressurized conditions in the absence of ozone. A significant enhancement in the rate of sulfolane degradation was observed in the presence of zinc under pressurized ozonation. However, zinc alone did not impact the sulfolane concentration in the solution, thereby ruling out possible zinc–sulfolane interactions. Furthermore, the ICP analysis showed no significant changes in the zinc concentration during the 120 min of the pressurized ozonation process.
3.3. Effects of O3/PMS on Sulfolane Degradation
Another method to enhance ozonation efficacy is to combine ozonation with peroxymonosulfate to increase radical formation. Prior to investigating the effects of peroxymonosulfate dosage on sulfolane degradation, a series of control experiments were conducted to account for the individual effects of the different parameters involved. The results showed that there was no reaction when only peroxymonosulfate was utilized without the activation of peroxymonosulfate. These results are consistent with those of Izadifard et al. [17], who found that persulfate/ozonation did not degrade sulfolane in the absence of UVC radiation.
3.3.1. Effects of O3/PMS Activated with (Zn2+)
According to the literature [14,27,30], the combination of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and ozone might increase the degradation efficacy due to the enhancement in hydroxyl radicals and sulfate radical formation. According to Bandala et al. [41], without a homogeneous catalyst, the organic pollutant remained undegraded regardless of the PMS concentration. This observation suggests that PMS alone is insufficient for generating free radicals. Therefore, PMS needs to be activated, and using transition metals is one of the activation methods. Since zinc, in combination with ozone, has shown good results for sulfolane degradation, as illustrated in Section 3.2, the activation of PMS with zinc was investigated. The effect of zinc as an activator with integrated ozonation and peroxymonosulfate during 120 min is depicted in Figure 4. The initial concentrations of sulfolane, peroxymonosulfate, and zinc were 1 mg L−1, 70 mg L−1, and 10 mg L−1, respectively. The results showed that the final removal percentages were zero for PMS alone without activation, 46% for O3/PMS, and 48% for O3/PMS/Zn2+. Activating PMS with zinc slightly increased sulfolane degradation efficacy, which is still low compared to the pressurized ozonation system efficacy. Therefore, PMS activation with zinc is not effective and another activation method needs to be explored.
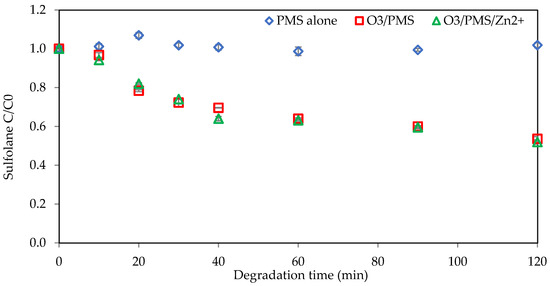
Figure 4.
Sulfolane degradation with PMS activated with zinc (initial Csulfolane = 1 mg L−1, CPMS = 70 mg L−1, Czinc = 10 mg L−1, ozone concentration = 2.86 mg L−1).
3.3.2. Effects of O3/PMS Activated with NaOH
Effect of NaOH Dosage
Another way to activate PMS is to change the pH of the solution. The effect of adding different NaOH concentrations as an activator with integrated ozonation and peroxymonosulfate to enhance sulfolane degradation is depicted in Figure 5. The initial concentration of sulfolane was 1 mg L−1, the peroxymonosulfate concentration was 70 mg L−1, and the sodium hydroxide concentrations were 10 mg L−1 and 100 mg L−1. The results showed that PMS/NaOH alone did not have any degradation, suggesting that PMS alone is not a reliable treatment method for sulfolane. The final removal percentages were 73% for O3, 100% for 100 mg L−1 of NaOH (pH = 10.56), and 95% for 10 mg L−1 of NaOH (pH = 9). Activation with 100 mg L-1 of NaOH resulted in the total degradation of sulfolane in less than 60 min, while for both 10 mg L−1 and 100 mg L−1, the degradation rate was higher in the first 40 min. Activating PMS by increasing the pH with NaOH significantly increased sulfolane degradation, indicating that increasing the pH increases the hydroxyl radical formation in the solution, thereby enhancing the degradation efficacy [10,11].
3 O3 + OH− + H+ → 2 •OH + 4 O2
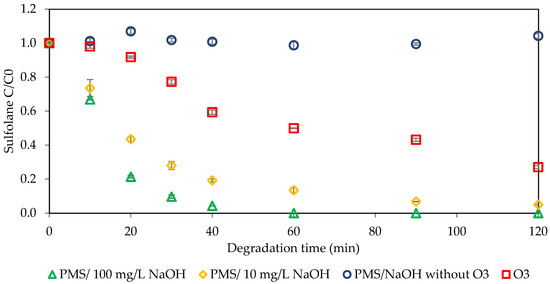
Figure 5.
Sulfolane degradation with PMS activated with NaOH (initial Csulfolane = 1 mg L−1, CPMS = 70 mg L−1, CNaOH = 10 and 100 mg L−1, ozone concentration = 2.86 mg L−1).
A similar trend took place with a lower PMS initial concentration (10 mg L−1), which is presented in the Supplementary Information (Section S3). By increasing the NaOH concentration from 10 mg L−1 to 100 mg L−1 the sulfolane degradation increased from 97% to complete degradation after 120 min of operation.
Effect of Different PMS Concentrations
The effect of initial PMS dosage on sulfolane degradation over time is presented in Figure 6. Two PMS dosages of 10 mg L−1 and 70 mg L−1 were tested. The degradation percentage increased from 0 to 120 min for both dosages. The combination of peroxymonosulfate and ozone increased the sulfolane degradation percentage compared to ozonation alone. Specifically, the degradations were reported as 95% and 97% with PMS-activated NaOH (10 mg L−1) for initial dosages of PMS of 70 mg L−1 and 10 mg L−1, respectively. Interestingly, there was no significant impact from changing the PMS concentration on the sulfolane degradation rate. Supplementary results, which are presented in the Supplementary Information (Section S4), confirmed these findings for different PMS concentrations activated with 100 mg L−1 of NaOH as well. The increment in the degradation efficacy is likely related to the sulfate radical formation.
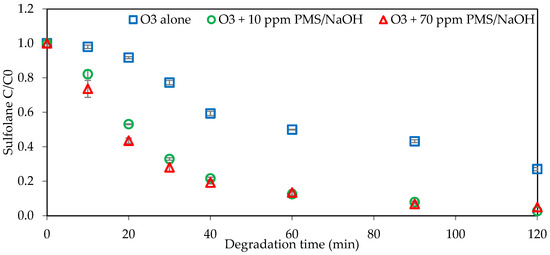
Figure 6.
Impact of initial PMS dosage on sulfolane degradation (initial Csulfolane = 1 mg L−1, CPMS = 10 and 70 mg L−1, CNaOH = 10 mg L−1, ozone concentration = 2.86 mg L−1).
Comparing the results of PMS activation with different PMS concentrations and NaOH concentrations, it appears that changing the pH could be a suitable method for improving ozonation efficacy on sulfolane degradation. Therefore, in the next section, the impact of pH changes is investigated.
3.4. Effect of Initial pH on Sulfolane Degradation with Different Water Matrices
3.4.1. Sulfolane Degradation in Reverse Osmosis (RO) Water Matrix
The efficacy and mechanism of ozonation and the stability of ozone molecules are typically influenced by the pH of the solution, so it plays a vital role in the oxidation process [31]. Therefore, the impact of pH change on sulfolane degradation was investigated by adding different NaOH concentrations (0, 10, 25, 50, and 100 mg L−1) to the sulfolane samples as presented in Table 2 and Figure 7. The changes were monitored over 120 min, and the results indicated significant improvements in sulfolane degradation with pH variations. Specifically, the degradation rate within the first 30 min was notably higher compared to the subsequent time intervals. With increasing NaOH concentration from 0 mg L−1 to 100 mg L−1, the degradation percentages changed from 73% for 0 mg L−1 to 96% for 10 mg L−1, 97% for 25 mg L−1, 98% for 50 mg L−1, and 96% for 100 mg L−1. The sulfolane degradation rate was significantly greater at alkaline pH values, suggesting increased ozone dissolution and breakdown, resulting in the production of a substantial amount of ˙OH in alkaline conditions. Also, at high pH levels, the hydroxide (−OH) ions in the solution facilitate the breakdown of ozone, hence increasing the production of ˙OH radicals.

Table 2.
Solution pH value with different NaOH concentrations.
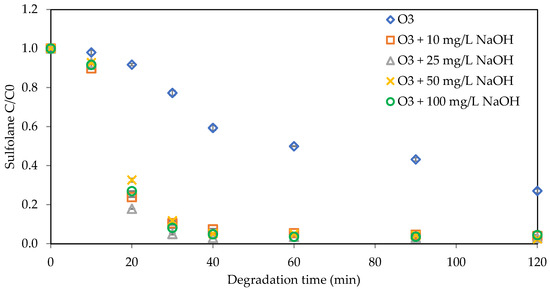
Figure 7.
Impact of NaOH on sulfolane degradation in reverse osmosis (RO) water (initial Csulfolane = 1 mg L−1, ozone concentration = 2.86 mg L−1).
The increase in pH leads to the formation of reaction intermediates like O3− and HO3−, which enhance the oxidation process [42]. In alkaline conditions, ozone decomposes more readily due to its lower oxidation potential, thereby producing a greater amount of ˙OH radicals. Furthermore, Kunz et al. [43] in a study on textile reactive dyes showed that the half-life of ozone decreases as the pH increases, which significantly impacts its reaction in the solution.
3.4.2. Sulfolane Degradation in Tap Water Matrix
In Figure 8, the impact of changes in pH in tap water on sulfolane degradation was investigated. NaOH concentrations ranged from 0 mg L−1 to 10 mg L−1, 50 mg L−1, 200 mg L−1, 400 mg L−1, and 800 mg L−1. The degradation rate increased from 73% to 98% as the pH of the solution was increased. Interestingly, in tap water, the NaOH concentrations of 400 mg L−1 and 800 mg L−1 achieved the same degradation percentage as ultra-pure water. The degradation efficacy was observed to be 73%, 80%, 91%, 92%, 98%, and 98% for NaOH concentrations of 0, 10 mg L−1, 50 mg L−1, 200 mg L−1, 400 mg L−1, and 800 mg L−1, respectively. The pH of the solution increased from 8 to 12.35 by increasing the NaOH concentration from 0 to 800 mg L−1 and is reported in Table 3.
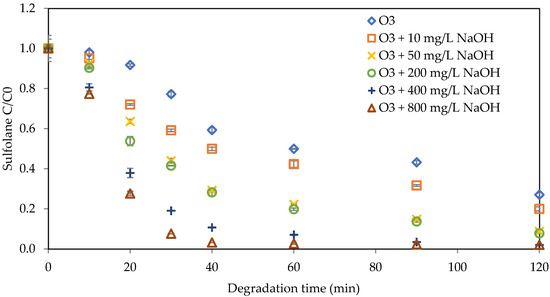
Figure 8.
Impact of NaOH on sulfolane degradation with tap water (initial Csulfolane = 1 mg L−1, ozone concentration = 2.86 mg L−1).

Table 3.
Solution pH values in tap water with different NaOH concentrations.
These findings are aligned with the previous chapter which confirmed that the presence of different inorganic ingredients in water (different water chemistries) would change the degradation rate and decrease the ozonation efficacy.
4. Conclusions
Improving the sulfolane degradation on a bench-scale setup using a pressured ozonation system was the objective of this study. It was demonstrated that an increment in the initial sulfolane concentration in aquatic solution can decrease the pressurized ozonation system efficacy. To overcome the decrease in degradation, the impacts of numerous hybrid ozonations, such as ozonation/metal ions, ozonation/peroxymonosulfate, and ozonation, at high pH were examined. It was observed that zinc and magnesium integrated with ozonation and also increasing pH have a significant role in accelerating the sulfolane degradation rate.
This study demonstrates that pressurized ozonation effectively degrades sulfolane, but the efficacy is significantly influenced by the initial sulfolane concentration. Lower initial concentrations of sulfolane led to higher degradation rates, while higher concentrations exhibited reduced efficacy, indicating a potential limitation of pressurized ozonation for treating heavily contaminated water. The addition of metal ions such as Zn2+ and Mg2+ positively impact the degradation process, enhancing the removal efficacy. However, other metals such as Ni2+, Cu2+, and Co2+ act as scavengers, thereby reducing the degradation rate. This suggests that the careful selection and optimization of metal ion types and dosages are crucial for improving the efficacy of the ozonation process.
Furthermore, this study highlights the potential of combining ozonation with peroxymonosulfate to enhance sulfolane degradation. While PMS alone without activation shows no significant degradation, the integration of PMS with NaOH as an activator markedly increases the degradation efficacy, achieving almost complete removal under optimal conditions. This enhancement is attributed to the increased formation of hydroxyl radicals at higher pH levels. However, the use of Zn2+ to activate PMS showed only a marginal improvement, indicating that alternative activation methods need exploration. Additionally, the impact of varying water matrices on the degradation process was investigated, with pH adjustments significantly improving the degradation rates in both reverse osmosis (RO) and tap water.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16223162/s1, Figure S1: Schematic of sulfolane degradation set-up; Figure S2: Impact of different initial magnesium concentration on sulfolane degradation; Figure S3: Impact of NaOH concentration for PMS activation on sulfolane degradation; Figure S4: Impact of initial PMS dosage on sulfolane degradation.
Author Contributions
N.Z.: Conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft preparation. G.A.: resources, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), Bonavista Energy Corp. and Enhance Energy, grant number 1009107.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), Bonavista Energy Corp. and Enhance Energy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this study received funding from National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), Bonavista Energy Corp. and Enhance Energy, grant number 1009107. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
References
- Khan, M.F.; Yu, L.; Achari, G. Field evaluation of a pressurized ozone treatment system to degrade sulfolane in contaminated groundwaters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.D.; Cozzens, R.A.; Kim, B.J. Effects of ozonation on the biodegradability of substituted phenols. Water Res. 1997, 31, 2655–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, A. Ozone technology of German industrial enterprises. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1999, 21, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zhang, F.; Hu, Y.; Feng, C.; Wu, H. Ozonation in water treatment: The generation, basic properties of ozone and its practical application. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2017, 33, 49–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Ma, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H. Characteristics and mechanisms of catalytic ozonation with Fe-shaving-based catalyst in industrial wastewater advanced treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De los Santos Ramos, W.; Poznyak, T.; Chairez, I. Remediation of lignin and its derivatives from pulp and paper industry wastewater by the combination of chemical precipitation and ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, C.G.; Farm, Y.Y.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Pang, C.K.; Nga, J.L.; Puma, G.L. Ozonation treatment processes for the remediation of detergent wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada-Vásquez, M.A.; Simarro-Gimeno, C.; Vidal-Barreiro, I.; Cardona-Gallo, S.A.; Pitarch, E.; Hernández, F.; Torres-Palma, R.A.; Chica, A.; Navarro-Laboulais, J. Application of catalytic ozonation using Y zeolite in the elimination of pharmaceuticals in effluents from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.N.; Leu, H.J.; Nguyen, V.N. Enhancing pharmaceutical wastewater treatment: Ozone-assisted electrooxidation and precision optimization via response surface methodology. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Ziółek, M.; Nawrocki, J. Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, K.; El-Din, M.G. Degradation of recalcitrant surfactants in wastewater by ozonation and advanced oxidation processes: A review. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2004, 26, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munter, R. Advanced oxidation processes–current status and prospects. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Chem. 2001, 50, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H. Catalytic ozonation for water and wastewater treatment: Recent advances and perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lu, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y. Production of sulfate radical and hydroxyl radical by reaction of ozone with peroxymonosulfate: A novel advanced oxidation process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7330–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shih, K.; Ying, G.G.; Feng, Y. Activation of ozone by peroxymonosulfate for selective degradation of 1, 4-dioxane: Limited water matrices effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniere, E.; Van Langenhove, H.; Van Hulle, S.; Demeestere, K. The ozone-activated peroxymonosulfate process for the removal of a mixture of TrOCs with different ozone reactivity at environmentally relevant conditions: Technical performance, radical exposure and online monitoring by spectral surrogate parameters. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadifard, M.; Achari, G.; Langford, C.H. Degradation of sulfolane using activated persulfate with UV and UV-Ozone. Water Res. 2017, 125, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Modelling of emerging contaminant removal during heterogeneous catalytic ozonation using chemical kinetic approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y. Catalytic ozonation of refractory O-isopropyl-N-ethylthionocarbamate collector with coexisted kaolinite in sulfide flotation wastewaters. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 198, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuge, S.P.; Saroha, A.K. Catalytic ozonation for the treatment of synthetic and industrial effluents-Application of mesoporous materials: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 211, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.; Luo, M.; Zhu, C.; Li, L. Removal of aqueous oxalic acid by heterogeneous catalytic ozonation with MnOx/sewage sludge-derived activated carbon as catalysts. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, S.; Dai, X.; Dong, B. Application, mechanism and prospects of Fe-based/Fe-biochar catalysts in heterogenous ozonation process: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 319, 138018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.J.; Rivas, F.J.; Montero-de-Espinosa, R. Iron type catalysts for the ozonation of oxalic acid in water. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3553–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.W.; Wang, W.L.; Lee, M.Y.; Wu, Q.Y.; Guan, Y.T. Synergistic effects of ozone/peroxymonosulfate for isothiazolinone biocides degradation: Kinetics, synergistic performance and influencing factors. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacławek, S.; Lutze, H.V.; Grübel, K.; Padil, V.V.; Černík, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.H.; Ma, J.; Ren, Y.M.; Liu, Y.L.; Xiao, J.Y.; Lin, L.Q.; Zhang, C. Efficient degradation of atrazine by magnetic porous copper ferrite catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation via the formation of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5431–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shad, A.; Chen, J.; Qu, R.; Dar, A.A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Allam, A.A.; Wang, Z. Degradation of sulfadimethoxine in phosphate buffer solution by UV alone, UV/PMS and UV/H2O2: Kinetics, degradation products, and reaction pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Sonntag, C.; Von Gunten, U. Chemistry of Ozone in Water and Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, J.; Wen, G.; Huang, T.; Deng, L.; Ma, J. Study on enhanced ozonation degradation of para-chlorobenzoic acid by peroxymonosulfate in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Sui, M.; Yuan, B.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Qin, J.; Xu, G. Degradation of ibuprofen using ozone combined with peroxymonosulfate. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.W.; Du, Y.; Ouyang, W.Y.; Wang, W.L. The promotions on radical formation and micropollutant degradation by the synergies between ozone and chemical reagents (synergistic ozonation): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, O.; Minnear, L. Sulfolane Technical Assistance and Evaluation Report; Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- CCME (Canadian Council of Minister of the Environment). Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines for Sulfolane: Water and Soil (Scientific Supporting Document. [Online]); CCME (Canadian Council of Minister of the Environment): Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Khan, M.F.; Achari, G. A review on physiochemical treatment of sulfolane in aqueous media. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharwadkar, S.; Yu, L.; Achari, G. Enhancement of LED based photocatalytic degradation of sulfolane by integration with oxidants and nanomaterials. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Mehrabani-Zeinabad, M.; Achari, G.; Langford, C.H. Application of UV based advanced oxidation to treat sulfolane in an aqueous medium. Chemosphere 2016, 160, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabani-Zeinabad, M.; Yu, L.; Achari, G.; Langford, C.H. Mineralisation of sulfolane by UV/O3/H2O2 in a tubular reactor. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 11, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Yu, L.; Achari, G.; Tay, J.H. Degradation of sulfolane in aqueous media by integrating activated sludge and advanced oxidation process. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadifard, M.; Achari, G.; Langford, C.H. Mineralization of sulfolane in aqueous solutions by Ozone/CaO2 and Ozone/CaO with potential for field application. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanatti, N.P. Treatability and kinetic analysis of BPA-containing wastewater by catalytic ozone processes using ZnSO4 and ZnO catalysts. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandala, E.R.; DomÍnguez, Z.; Rivas, F.; Gelover, S. Degradation of atrazine using solar driven fenton-like advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2007, 42, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elovitz, M.S.; von Gunten, U.; Kaiser, H.P. Hydroxyl radical/ozone ratios during ozonation processes, I.I. The effect of temperature, pH, alkalinity, and DOM properties. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2000, 22, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, A.; Mansilla, H.; Duran, N. A degradation and toxicity study of three textile reactive dyes by ozone. Environ. Technol. 2002, 23, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).