Water Quality Changes in the Xingkai (Khanka) Lake, Northeast China, Driven by Climate Change and Human Activities: Insights from Published Data (1990–2020)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
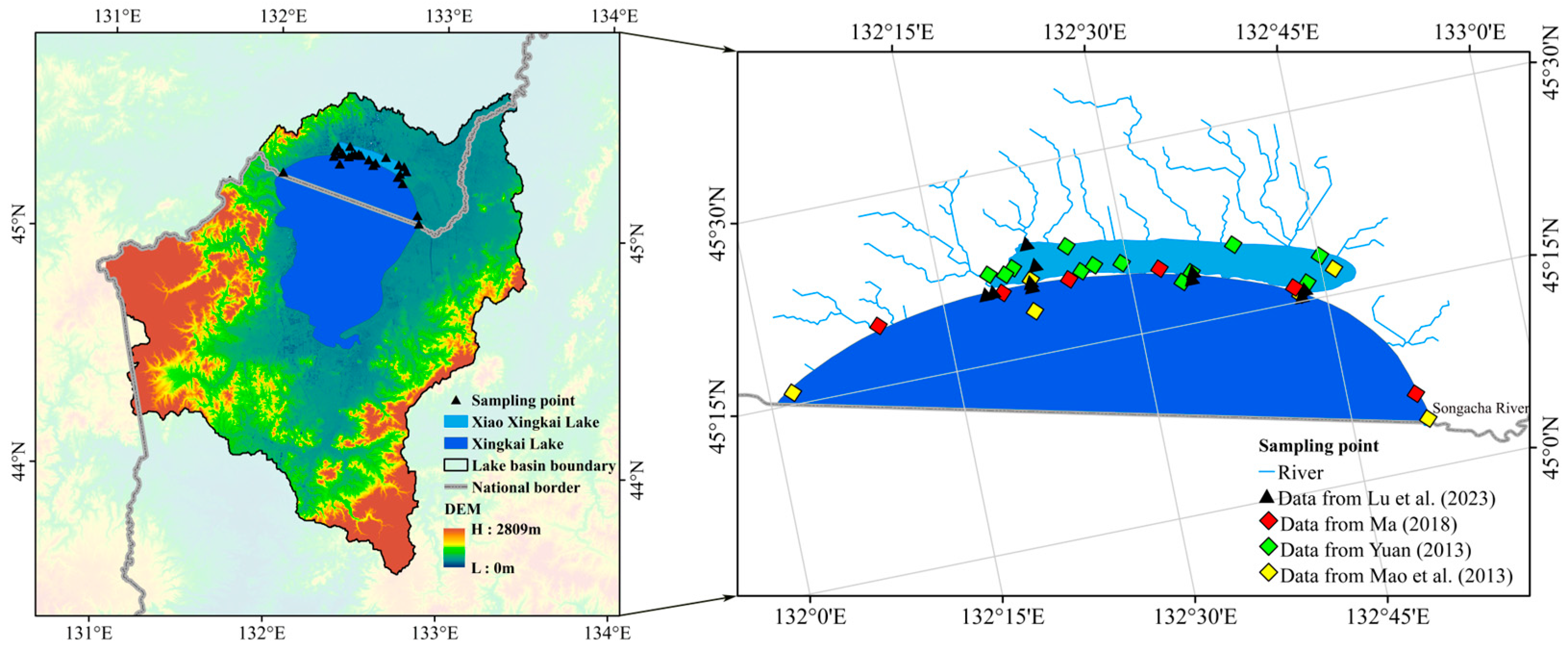
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Water Quality Evaluation
2.3.2. Heavy Metal Risk Evaluation
2.3.3. Data Analysis Methods
3. Results
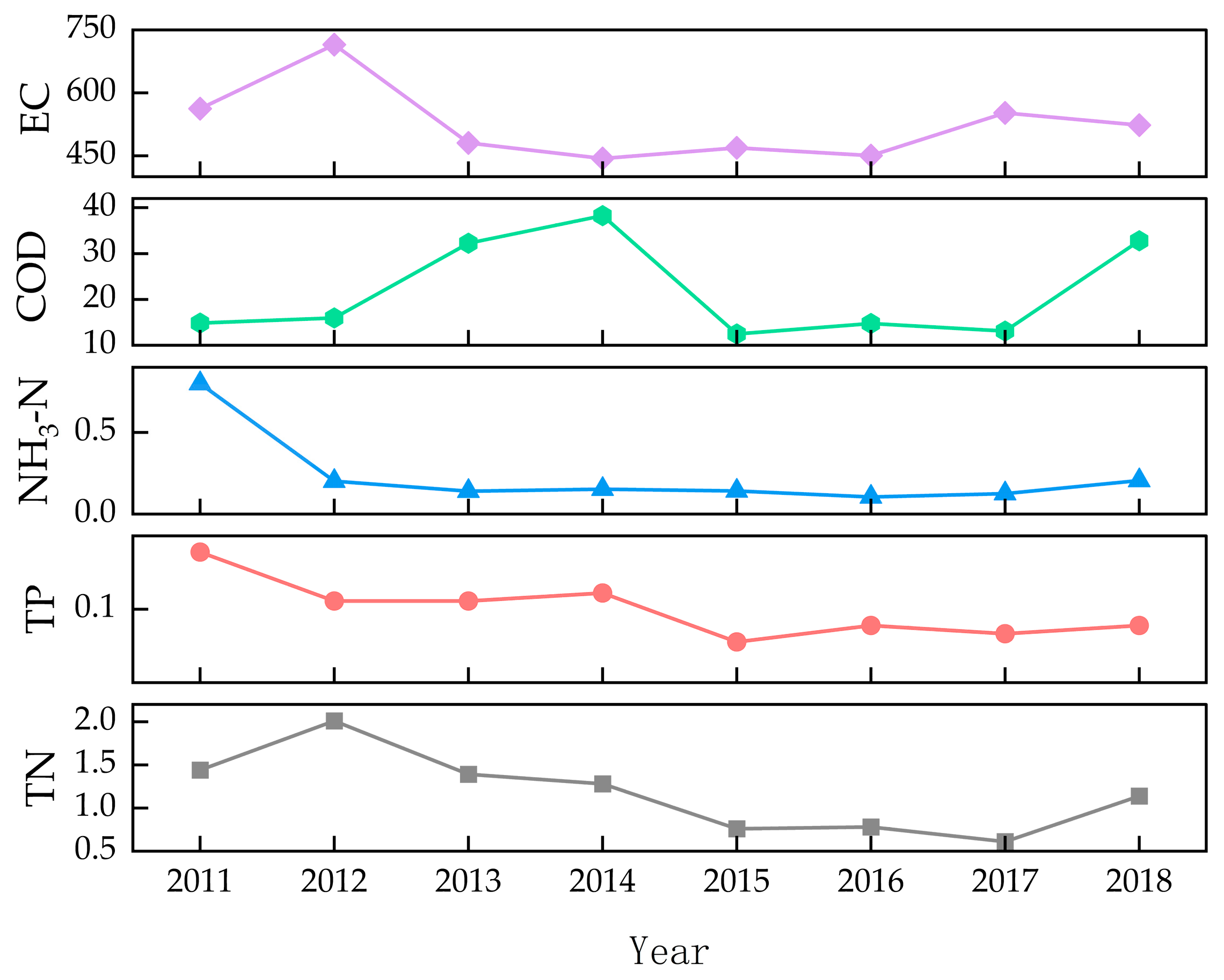
3.1. Temporal Variations in Water Quality
3.2. Heavy Metals and Nutrients in Sediments
3.3. Impact of Human Activities and Climate Factors on Water Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterization of Water Quality Trends and Sediment Contamination
4.2. Water Quality Changes in Response to Climate Change and Human Activities
4.3. Water Environmental Management Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, F.F.; Livneh, B.; Rajagopalan, B.; Wang, J.D.; Crétaux, J.F.; Wada, Y.; Berge-Nguyen, M. Satellites reveal widespread decline in global lake water storage. Science 2023, 380, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, K.; McGowan, S.; Capo, E.; Shen, J. Synergistic impacts of nutrient enrichment and climate change on long-term water quality and ecological dynamics in contrasting shallow-lake zones. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 3271–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszelewski, W.; Jokiel, P.; Pius, B.; Tomalski, P. River thermal seasons in the Central European Plain and their changes during climate warming. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaqout, T.; Andradóttir, H.O. Impacts of climate change on winter flood mechanisms: Spatial variability, trends, and bivariate frequency of rain-on-snow and soil frost. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Cui, S.Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, F.Z.; Jeppessen, E. Human impact on current environmental state in Chinese lakes. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shear, H.; Stadler-Salt, N.; Bertram, P.E.; Horvatin, P.J. The Development and Implementation of Indicators of Ecosystem Health in the Great Lakes Basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2003, 88, 119–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.A.; Moura, A.D. Ecological impacts of freshwater algal blooms on water quality, plankton biodiversity, structure, and ecosystem functioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotama, R.; Baker, D.M.; Guibert, I.; Mcilroy, S.E.; Russell, B.D. How a coastal megacity affects marine biodiversity and ecosystem function: Impacts of reduced water quality and other anthropogenic stressors. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Wang, X.H.; Jia, S.Q.; Mao, B.Y. Multi-methods to investigate spatiotemporal variations of nitrogen-nitrate and its risks to human health in China’s largest fresh water lake (Poyang Lake). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.J.; Feng, L.; Dai, Y.H.; Hu, C.A.M.; Gibson, L.; Tang, J.; Lee, Z.P.; Wang, Y.; Cai, X.B.; Liu, J.G.; et al. Global mapping reveals increase in lacustrine algal blooms over the past decade. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-y.; Zhou, B.; Huang, B. A continuing 30-year decline in water quality of Jiaojiang Estuary, China. Water Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, D.K.; Mohan, K.; Rajarajeswaran, J.; Divya, D.; Thanigaivel, S.; Zhang, S.B. Toxic effects of organophosphate pesticide monocrotophos in aquatic organisms: A review of challenges, regulations and future perspectives. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damseth, S.; Thakur, K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Mahajan, D.; Kumari, H.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, A.K. Assessing the impacts of river bed mining on aquatic ecosystems: A critical review of effects on water quality and biodiversity. HydroResearch 2024, 7, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.N.; Li, Y.P.; Ji, D.B.; Nwankwegu, A.S.; Lai, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.J.; Wang, K.; Wei, J.; Norgbey, E. Study on nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in Xiangxi Bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Resz, M.A.; Tanaselia, C.; Cadar, O. Assessing microbiological and heavy metal pollution in surface waters associated with potential human health risk assessment at fish ingestion exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Han, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, C.; Yao, Z.; Chen, K. Internal loading regulates the phosphorus concentration in a diversion input shallow lake in the semi-humid region of North China: Differentiated processes in littoral wetland and open water areas. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Leavitt, P.R.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Anthropogenic eutrophication of shallow lakes: Is it occasional? Water Res. 2022, 221, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.X.; Mwagona, P.C.; Yu, H.X.; Sun, X.W.; Liang, L.Q.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A. Seasonal dynamics of zooplankton functional group and its relationship with physico-chemical variables in high turbid nutrient-rich Small Xingkai Wetland Lake, Northeast China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2019, 34, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Wu, T.X.; Li, X.T.; Wang, S.D.; Shen, Q. A new method for accurate inversion of Forel-Ule index using MODIS images—Revealing the water color evolution in China’s large lakes and reservoirs over the past two decades. Water Res. 2024, 255, 121560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.X.; Jiang, M.; Liu, X.T.; Yu, H.X.; Otte, M.L.; Ma, C.X.; Her, Y.G. Environmental variables influencing phytoplankton communities in hydrologically connected aquatic habitats in the Lake Xingkai basin. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.X.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, X.Y.; Yu, H.X.; Otte, M.L. Interactions between Fe and light strongly affect phytoplankton communities in a eutrophic lake. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.L.; Li, X.Y.; Wen, B.L.; Chen, G.S.; Hartleyc, A.; Jiang, M.; Li, X.J. Characterization of Water Quality in Xiao Xingkai Lake: Implications for Trophic Status and Management. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.Y.; Wang, Q.C.; Tian, X.; Zhu, X.Y.; Dong, X.Q.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, Y.X. Spatiotemporal variation and ecological risk assessment of sediment heavy metals in two hydrologically connected lakes. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 1005194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Z.; Zou, Y.C.; Zhao, Z.C.; Zhang, T. A dataset of water physical and chemical properties in Xingkai Lake from 2011 to 2018. China Sci. Data 2023, 8, 196–203, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y. Effects of Flood Discharge on Physicochemical Properties and NitrogenTransformation of Lake Xingkai. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2018. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.X. Phytoplankton Community Structure and Analysis of Correlations with Environmental Factors in Xiaoxingkai Lake. Master’s Thesis, Northeastern Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2013. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Xu, Q.G.; Wei, Z.M.; Xuan, P.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. Temporal and spatial distribution of bacteria in XingKai Lake. J. Northeast. Agric. Univ. 2013, 44, 56–60, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.H.; Jin, X.C. Study on Lake Eutrophication and Its Countermeasure in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001; p. 210. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Piao, D.X.; Wang, F.K. Environmental conditions and the protection countermeasures for waters of Lake Xingkai. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 196–202, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.X.; Yao, W.D. Investigation and analysis of changes in water quality status of fisheries in Xingkai Lake. North. Chin. Fish. 2009, 25–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Dong, C.Z.; Zhao, C.X.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, P.R. Physico-chemical characteristics of different waters in Heilongjiang system. J. Fish. China 2003, 364–370, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.X.; Dong, C.Z.; Zhan, P.R. Water quality and evaluation of fishery waters of Heilongjiang. Chin. J. Fish. 2002, 69–73, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, C.X.; Chen, Z.X.; Wang, H.T.; Zhan, P.R. Analysis of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Contents and Assessment on Potential Eutrophication of Water in Xinkai Lake. Heilongjiang Sci. 2011, 2, 1–3, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.X.; Bian, S.W.; Yu, H.X.; Qu, C. Correlation Between Phytoplankton Abundance and Environmental Factors in Xingkai Lake. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2012, 40, 78–80, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C. Biodiversity and Community of Phytoplankton in Xingkai Lake. Master’s Thesis, Northeastern Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2009. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. Community Structure of Metazoan Zooplankton in Xingkai Lake. Master’s Thesis, Northeastern Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2009. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.Y.; Liu, T.L.; Liu, J.; Li, J.M.; Pan, F.Q. Investigation and Study on Water Quality and Pollution Condition in Lake Xingkai of China. Environ. Monit. China 2013, 29, 79–84, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.L.; Li, X.J.; Li, X.Y.; Wen, B.L. Evaluation of Water Quality of Xiaoxingkai Lake. Wetl. Sci. 2013, 11, 466–469, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.M. Zooplankton Community Structure and Analysis of Correlations with Environmental Factors in Xiaoxingkai Lake. Master’s Thesis, Northeastern Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2014. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Y.F. Biodiversity of Aquatic Organisms and Ecosystem Health Assessment of Xiaoxingkai Lake. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeastern Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2018. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.S. The Water Quality Change and Driving Force Analysis in Xiaoxingkai Lake. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.S.; Jiang, M.; Yuan, Y.X. Spatial Heterogeneity of Water Quality in Xiaoxingkai Lake. Wetl. Sci. 2015, 13, 166–170, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.L.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, J.T.; Chen, G.S.; Li, X.J. Phsophorus sorption capacity of surface sediments and risk assessment of potential phosphorus release in Lake Xiaoxingkai, China. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 2078–2085, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.L. The Research on Phosphorus Release Characteristics of Surficial Sediment and Its Effects on Eutrophication in Lake Xiaoxingkai, China. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.L.; Li, X.J.; Chen, G.S.; Zhang, J.T.; Yang, Y.L.; Yan, Y.; Lu, X.R.; Zhang, C.Y. Analysis of Eutrophication and Terrestrialization of Xiaoxingkai Lake. Wetl. Sci. 2016, 14, 271–275, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M. Zooplankton Community Structure and Analysis of Correlations with Environmental Factors in Daxiaoxingkai Lake. Master’s Thesis, Northeastern Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2015. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- An, R. Characteristics and Environmental Effect of Plankton Functional Groups in Sanjiang Plate Wetland. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeastern Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2016. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.X.; Tian, X.; Jiang, M. Structure of Phytoplankton Community in Xiaoxingkai Lake in July 2014 and Its Influence Factors. Wetl. Sci. 2017, 15, 221–228, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.J.; Zhou, H.X.; Xie, X.Y.; Li, X.K.; Zhang, D.Y.; Jia, L.M.; Wei, Q.B.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.M.; Ma, Y.Y. Effects of floodgates operation on nitrogen transformation in a lake based on structural equation modeling analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L. Effect of Artificial Aeration on Carbon and Phosphorus in Glyceria spiculosa Wetland of Xiaoxingkaihu Lake by Inputting Different Iron Dosage. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.Y.; Tian, Z.J.; Zhang, D.J.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L.H. Effect of iron-rich farmland drainage on phosphorus adsorption and release in sediments of Xiaoxingkai Lake. Chin. J. Ecol. 2022, 41, 1128–1134, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.Y.; Tian, Z.J.; Zhang, D.J.; Jiang, M. Physical and Chemical Characteristic and Phosphorus Adsorption Efficiency of Surface Sediment in Xiaoxingkai Lake. Wetl. Sci. 2021, 19, 577–584, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Q.; Li, S.J.; Tao, Z.; Song, K.S.; Wen, Z.D.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.F. Remote Sensing of Chlorophyll-a in Xinkai Lake Using Machine Learning and GF-6 WFV Images. Remote Sen. 2022, 14, 5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.Y. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Drivers of Phytoplankton Community Structure During Ice-Covered Period in Xingkai Lake. Master’s Thesis, Changchun Normal University, Changchun, China, 2023. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Z.J.; Sun, D.X.; Li, C.H.; Ye, C.; Wang, W.Q.; Wei, W.W.; Wang, H. Phosphorus morphology characteristics and its response to climate change in Xingkai Lake. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1965–1975, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Huo, S.L.; Xi, B.D.; Zhang, J.T.; Wu, F.C. Heavy metal contamination in sediments from typical lakes in the five geographic regions of China: Distribution, bioavailability, and risk. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.Y. Effects of Iron Input on Phosphorus Adsorption of Wetlands—Sediment System in Xiaoxingkai Lake. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.X.; Xie, Z.J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, C.; Li, C.H.; Wei, W.W.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X.Y. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of nutrients in sediments of Xingkai Lake. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1976–1986, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.J.; Zhao, R.B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, C.H.; Yu, Z.L.; Ye, C. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of nutrients in sediments of Xingkai Lake. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1987–1996, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, S.R.; Su, B.L.; Wu, H.X.; Wang, G.Q. Understanding the water quality change of the Yilong Lake based on comprehensive assessment methods. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, C.; Tan, L.; Cai, Q.H.; Ye, L. Long-term (2003–2021) evolution trend of water quality in the Three Gorges Reservoir: An evaluation based on an enhanced water quality index. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 169819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Ren, L.J.; Hua, C.Y.; Tian, Y.R.; Yong, X.; Fang, S.M. Identification of toxic metal contamination in surface sediments of the Xiaoqing River under a long-term perspective (1996–2020): Risks, sources and driving factors. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Francés, F.; Martínez-Graña, A.; Zarza, C.A.; Sánchez, A.G.; Rojo, P.A. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals and the Environmental Quality of Soil in the Northern Plateau of Spain by Geostatistical Methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.M.; Xu, L.B.; Wang, Q.R.; Guo, L.J.; Miao, Y.X.; Shen, Z.Y. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Dai, H.M.; Wei, M.H.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.H.; Liang, S. Soil geochemical baseline values and background values in Xunke Plain of HeiLongJiang Province. Geol. Bull. China 2024, 43, 1–15, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.A.C.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, J.P.; Liu, L.F.; Lan, Y.C. Temporal analysis of land degradation and urban expansion in central Yunnan Province using remote sensing for supporting sustainable development goals 11/15. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, N.C.; Newnham, G.J.; England, J.R.; Guerschman, J.; Cox, S.J.D.; Roxburgh, S.H. Good Practice Guidance. SDG Indicator 15.3.1, Proportion of Land That Is Degraded over Total Land Area. Version 2.0.; United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD): Bonn, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jixi Government. Regulations on Water Environment Protection in Heilongjiang Xingkai Lake National Nature Reserve. In Jixi Daily; 2011. Available online: https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%BB%91%E9%BE%99%E6%B1%9F%E5%85%B4%E5%87%AF%E6%B9%96%E5%9B%BD%E5%AE%B6%E7%BA%A7%E8%87%AA%E7%84%B6%E4%BF%9D%E6%8A%A4%E5%8C%BA%E6%B0%B4%E7%8E%AF%E5%A2%83%E4%BF%9D%E6%8A%A4%E8%A7%84%E5%AE%9A/4285417 (accessed on 2 September 2024). (In Chinese)
- Dippong, T.; Resz, M.A. Heavy metal contamination assessment and potential human health risk of water quality of lakes situated in the protected area of Tisa, Romania. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieniawski, S.; Macdonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G. A Guidance Manual to Support the Assessment of Contaminated Sediments in Freshwater Ecosystems; United States Environmental Protection Agency, Great Lakes National Program Office: Chicago, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Du, Y.H.; Yin, H.B.; Fan, C.X.; Chen, K.N.; Zhong, J.C.; Gu, X.Z. Exchanges of nitrogen and phosphorus across the sediment-water interface influenced by the external suspended particulate matter and the residual matter after dredging. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, S.M. Nutrient exchanges at the sediment-water interface and the responses to environmental changes in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Eutrophication control of large shallow lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Yu, T.; You, Y.H.; Dou, L.; Li, K. Impacts of parent material on distributions of potentially toxic elements in soils from Pearl River Delta in South China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Fang, T.T.; He, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Guo, G.L. Analysis of driving factors of spatial distribution of heavy metals in soil of non-ferrous metal smelting sites: Screening the geodetector calculation results combined with correlation analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.J.; Zhao, R.B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, C.H.; Yu, Z.L.; Ye, C. Ecological risk assessment and pollution characteristic analysis of heavy metals in sediments of xingkai lake. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1987–1996, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onakpa, M.M.; Njan, A.A.; Kalu, O.C. A Review of Heavy Metal Contamination of Food Crops in Nigeria. Ann. Glob. Health 2018, 84, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.M.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchlik, M.; Piekutin, J.; Dyczewska, K. Analysis of the Impact of Climate Change on Surface Water Quality in North-Eastern Poland. Energies 2022, 15, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranskaya, N.A.; Fuksova, T.V. Long-term Changes in the Main Components of Lake Khanka Water Regime. Russ Meteorol Hydro+ 2018, 43, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Fu, C.S. Impacts of land use/land cover and climate change on hydrological cycle in the Xiaoxingkai Lake Basin. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2023, 47, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.M.; Wang, K.L.; Yang, N.; Li, F.; Zou, Y.A.; Chen, X.S.; Deng, Z.M.; Xie, Y.H. Spatiotemporal water quality variations and their relationship with hydrological conditions in Dongting Lake after the operation of the Three Gorges Dam, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.L.; Bu, H.M. The impact of climate change on the water quality of Baiyangdian Lake (China) in the past 30 years (1991-2020). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Merchant, C.J. Worldwide alteration of lake mixing regimes in response to climate change. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakulopa, F.; Bärlund, I.; Borchardt, D. How a reservoir modulates downstream water quality under declining upstream loading and progressing climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavan, M.; Ceglar, A.; Pintar, M. Assessing the impacts of climate change on water quantity and quality modelling in small Slovenian Mediterranean catchment—Lesson for policy and decision makers. Hydrol. Process 2015, 29, 3124–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.Y.; Gao, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J.; Razlustkij, V.; Rudstam, L.G.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, X.F. Effects of Elevated Temperature on Resources Competition of Nutrient and Light Between Benthic and Planktonic Algae. Front. Env. Sci-Switz. 2022, 10, 908088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hien, H.N.; Hoang, B.H.; Huong, T.T.; Than, T.T.; Ha, P.T.T.; Toan, T.D.; Son, N.M. Study of the Climate Change Impacts on Water Quality in the Upstream Portion of the Cau River Basin, Vietnam. Environ. Model. Assess. 2016, 21, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, L.X.; Yang, L.Z.; Zhang, F.S.; Norse, D.; Zhu, Z.L. Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in China: Causes and Mitigation Measures. Ambio 2012, 41, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Xie, Z.J.; Wang, H.; Li, C.H.; Li, J.; Wei, W.W.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, C. Effect of land use on the water quality of rivers flowing into xingkai lake and ecological restoration strategies. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.T.; Sen, S.; Sahoo, D. State of Indian Northwestern Himalayan lakes under human and climate impacts: A review. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.H.; Wang, Q.J.; Guo, L.; Lin, H.; Chen, X.P.; Sun, Y.; Ning, S.R. An enhanced rainfall-runoff model with coupled canopy interception. Hydrol. Process 2020, 34, 1837–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.J. Influence of water body area on water quality in the southern Jiangsu Plain, eastern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.J.; Liu, L.J.; Tao, Z.Z.; Wan, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tang, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.Y. Effect of urbanization and urban forests on water quality improvement in the Yangtze River Delta: A case study in Hangzhou, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Liu, Q.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Jan, A.U.; Sharif, H.M.A.; Ditta, A.; Wang, G.; Cheng, H.F. Sources, impacts, factors affecting Cr uptake in plants, and mechanisms behind phytoremediation of Cr-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NO. | Period | WT/°C | pH | EC/ μs/cm | NH3-N/ mg/L | COD/ mg/L | TN/ mg/L | TP/ mg/L | Chl-a/ μg/L | DO/ mg/L | Data from Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1985–1998 | 0.04–2.43 | [28] | ||||||||
| 2 | 1994–1998 | 7.0–7.53 | 4.09, 4.73 | 0.09–2.65 | 0.01–0.07 | [29] | |||||
| 3 | 1998-2007 | 7.05–7.81 | 8.89–10.32 | [30] | |||||||
| 4 | May, Jul., and Sept. 2001 | 21 | 7.3–7.8 | 0.003–1.79 | 4.25–7.31 | 0.09–2.65 | 7.3–7.8 | [31,32,33] | |||
| 5 | May, Jul., and Sept. 2007 | 18.7–22.23 | 7.95–8.89 | 120–215 | 1.8–162.2 | 8.05–11.61 | [34,35,36] | ||||
| 6 | May 2008 | 8.37–8.89 | 130–160 | 8.05–10.75 | [34] | ||||||
| 7 | Jan.–Feb., May–Jun, Aug., and Oct. 2010 | 7.42–7.97 | 185–550 | 6.6–14.84 | [27] | ||||||
| 8 | 2010 | 0.5–0.7 | 0.07–0.08 | [37] | |||||||
| 9 | Jan. and May–Sept. 2011 | 0.4–2.45 | 0.04–0.22 | [26,37] | |||||||
| 10 | Sept. 2012 | 6.9–9.62 | 0.14–0.7 | 0.16–44.48 | 0.49–8.35 | 0.01–0.38 | 6–117 | 8.07–15.57 | [38] | ||
| 11 | 2012–2014 | 5.86–9.62 | 33.9–260.1 | 0.00–0.9 | 0.16–85.60 | 0.16–12.29 | 0.01–0.97 | 1.03–65.13 | 0.11–14.21 | [22] | |
| 12 | May and Jul.–Nov. 2013 | 6.19–9.4 | 20–240 | 0.001–0.02 | 2.24–78.5 | 0.38–5.55 | 0.03–0.18 | 1.19–99.98 | 1.38–12.29 | [39,40,41,42,43,44,45] | |
| 13 | Apr., May, and Sept.–Dec. 2014 | 7.85–9.41 | 250 | 0.01–0.87 | 31.66 | 0.76–1.81 | 0.07–0.29 | 2.7–9.1 | 4.05–4.21 | [40,46,47,48] | |
| 14 | 2013–2014 | 8.17 | 170 | 42.2 | 1.38 | 0.11 | [20,21] | ||||
| 15 | Jul.–Sept. 2015 | 15.61–16.63 | 7.6–7.94 | 0.20–0.46 | 18.34–20.7 | 0.63–2.3 | 3.45–5.42 | 7.1–9.16 | [25,49] | ||
| 16 | Jul. 2016 | 8.12 | 7.94 | [50] | |||||||
| 17 | May, Jul., Sept., and Oct. 2018 | 37.22–111.9 | 1.28–1.79 | 0.07–0.12 | [51,52] | ||||||
| 18 | 2011–2018 | 15.66–19.67 | 5.86–8.71 | 315.34–763.2 | 0.01–2.64 | 1.6–93.35 | 0.26–4.47 | 0.01–1.07 | [24] | ||
| 19 | Oct. 2020 | 0.85–1.37 | 0.12–0.2 | 1.46–4.51 | [53] | ||||||
| 20 | Aug.–Nov. 2021 | 16.75–19.33 | 9.93–11.4 | 136.1–257.2 | 0.05–0.19 | 3.47–5.72 | 0.34–9.66 | 0.04–0.36 | 0.81–346.44 | 8.79–10.99 | [23,54] |
| 21 | Jan. and May 2022 | 61.31–270.29 | 0.001–0.24 | 2.94–5.75 | 0.18–3.46 | 0.03–0.2 | 3.28–380.4 | 12.81–18.35 | [54,55] |
| NO. | Period | TN/ mg/kg | TP/ mg/kg | Mn/ mg/kg | Cr/ mg/kg | Ni/ mg/kg | Cu/ mg/kg | Zn/ mg/kg | As/ mg/kg | Cd/ mg/kg | Pb/ mg/kg | Hg/ mg/kg | Data from Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2011 | 650 | 75.95 | 23.35 | 19.65 | 60.35 | 0.14 | 21.63 | [56] | ||||
| 2 | Jul. 2013 | 188.73–3224.79 | 181.02–805.73 | [43,44] | |||||||||
| 3 | Sept. 2016 | 84.76–1421.79 | 330 | [57] | |||||||||
| 4 | Sept. 2018 | 84.76–1305 | [51] | ||||||||||
| 5 | Jul. 2021 | 210.30–4718.41 | 14.41–1272.23 | 28.6–73.8 | 11.6–32.9 | 9–29.1 | 17–59.7 | 2.9–13.2 | 0.08–0.2 | 14.2–22.8 | 0.01–0.13 | [58,59] | |
| 6 | Jan., May, Jul., and Sept. 2021 | 256.5–12361 | 142.9–1989 | 28.58–262.3 | 3.12–28.05 | 18.21–90.73 | 2.58–14.35 | 0.05–0.21 | 10.87–58.85 | 0.003–0.14 | [23] |
| Parameter | Mean | Range | Number of Samples/n | CV/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water temperature in Sept./°C | 17.12 | 15.62~22.23 | 117 | 9 |
| pH | 7.94 | 5.86~11.40 | 386 | 8 |
| Electrical conductivity (EC)/(μs/cm) | 277.89 | 20~763.20 | 221 | 54 |
| Ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N)/(mg/L) | 0.23 | 0.001~2.64 | 256 | 165 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD)/(mg/L) | 22.48 | 0.16~111.90 | 306 | 80 |
| Total nitrogen (TN)/(mg/L) | 1.19 | 0.09~12.29 | 366 | 58 |
| Total phosphorus (TP)/(mg/L) | 0.12 | 0.01~1.07 | 362 | 46 |
| Year | Annual Average | Average Value in May | Average Value in Sept. | Water Quality Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 72 | 74.66 | 69.33 | IV |
| 2012 | 62.67 | 64 | 61.33 | III |
| 2013 | 56 | 60 | 52 | III |
| 2014 | 58.67 | 52 | 65.33 | III |
| 2015 | 47.33 | 45.33 | 49.33 | II |
| 2016 | 48 | 45.33 | 50.66 | II |
| 2017 | 49.34 | 46.67 | 52 | II |
| 2018 | 51.34 | 50.67 | 52 | III |
| Parameter | Z | P | Variation Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water temperature in Sept. | 0.72 | 0.02 | Significant increase |
| pH | −0.33 | 0.32 | Decreasing trend, but not significant |
| EC | −0.14 | 0.71 | Decreasing trend, but not significant |
| TN | −0.64 | 0.03 | Significant decrease |
| TP | −0.52 | 0.1 | Decreasing trend, but not significant |
| NH3-N | −0.36 | 0.27 | Decreasing trend, but not significant |
| COD | 0 | 1 | No trend |
| Annual average WQI | −0.5 | 0.11 | Decreasing trend, but not significant |
| Average WQI (May) | −0.62 | 0.04 | Significant decrease |
| Average WQI (Sept.) | −0.42 | 0.2 | Decreasing trend, but not significant |
| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Northeast Plains Soil Background Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn/(mg/kg) | 330 | 650 | 490 | 616.85 |
| Cr/(mg/kg) | 28.58 | 75.95 | 62.97 | 52 |
| Cu/(mg/kg) | 3.12 | 29.1 | 14.99 | 18.27 |
| Zn/(mg/kg) | 17 | 90.73 | 49.4 | 55.39 |
| As/(mg/kg) | 2.58 | 14.35 | 7.96 | 8.04 |
| Cd/(mg/kg) | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.1 |
| Hg/(mg/kg) | 0.003 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.028 |
| Pb/(mg/kg) | 10.87 | 58.86 | 19.62 | 22.42 |
| Ni/(mg/kg) | 22.9 | 25.3 | 23.73 | 21.84 |
| Parameter | Igeo Value | Contamination Level | Contamination Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn/(mg/kg) | −0.68 | 0 | Uncontaminated |
| Cr/(mg/kg) | 1.29 | 2 | Moderately contaminated |
| Cu/(mg/kg) | −0.22 | 0 | Uncontaminated |
| Zn/(mg/kg) | −0.18 | 0 | Uncontaminated |
| As/(mg/kg) | −0.06 | 0 | Uncontaminated |
| Cd/(mg/kg) | 0.22 | 1 | Uncontaminated to moderately contaminated |
| Hg/(mg/kg) | 1.32 | 2 | Moderately contaminated |
| Pb/(mg/kg) | 0.38 | 1 | Uncontaminated to moderately contaminated |
| Ni/(mg/kg) | −0.19 | 0 | Uncontaminated |
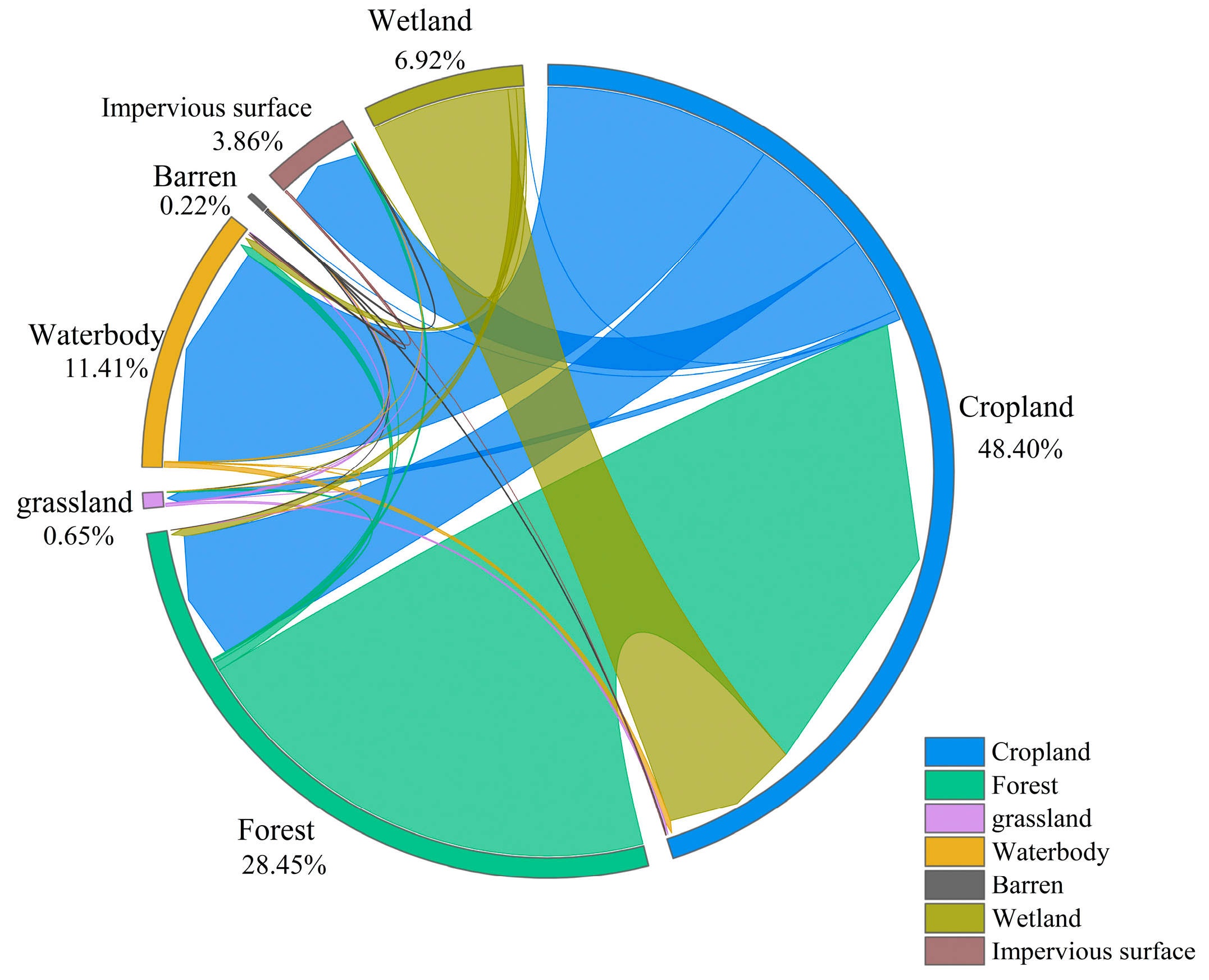
| In Target Year (2020) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland /km² | Forest /km² | Grassland /km² | Waterbody /km² | Barren /km² | Impervious Surface /km² | Wetland /km² | ||
| In baseline year (1990) | Cropland | 2043.49 | 41.74 | 3.23 | 75.02 | 0.03 | 25.78 | 0.01 |
| Forest | 160.31 | 218.01 | 0.46 | 2.78 | 0.02 | 0.92 | 0.00 | |
| Grassland | 0.75 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.00 | |
| waterbody | 1.84 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 1227.14 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.00 | |
| Barren | 0.43 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.63 | 0.00 | |
| Impervious surface | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.68 | 0.00 | 12.71 | 0.00 | |
| Wetland | 45.38 | 2.68 | 0.09 | 2.39 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.84 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, P.; Wang, R.; Shamov, V.V.; Zhu, A.-X.; Deng, C. Water Quality Changes in the Xingkai (Khanka) Lake, Northeast China, Driven by Climate Change and Human Activities: Insights from Published Data (1990–2020). Water 2024, 16, 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213080
Wu Y, Chen D, Liu Y, Li F, Wang P, Wang R, Shamov VV, Zhu A-X, Deng C. Water Quality Changes in the Xingkai (Khanka) Lake, Northeast China, Driven by Climate Change and Human Activities: Insights from Published Data (1990–2020). Water. 2024; 16(21):3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213080
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yaping, Dan Chen, Yu Liu, Fujia Li, Ping Wang, Rui Wang, Vladimir V. Shamov, A-Xing Zhu, and Chunnuan Deng. 2024. "Water Quality Changes in the Xingkai (Khanka) Lake, Northeast China, Driven by Climate Change and Human Activities: Insights from Published Data (1990–2020)" Water 16, no. 21: 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213080
APA StyleWu, Y., Chen, D., Liu, Y., Li, F., Wang, P., Wang, R., Shamov, V. V., Zhu, A.-X., & Deng, C. (2024). Water Quality Changes in the Xingkai (Khanka) Lake, Northeast China, Driven by Climate Change and Human Activities: Insights from Published Data (1990–2020). Water, 16(21), 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213080