Water–Energy Nexus-Based Optimization of the Water Supply Infrastructure in a Dryland Urban Setting
Abstract
1. Introduction
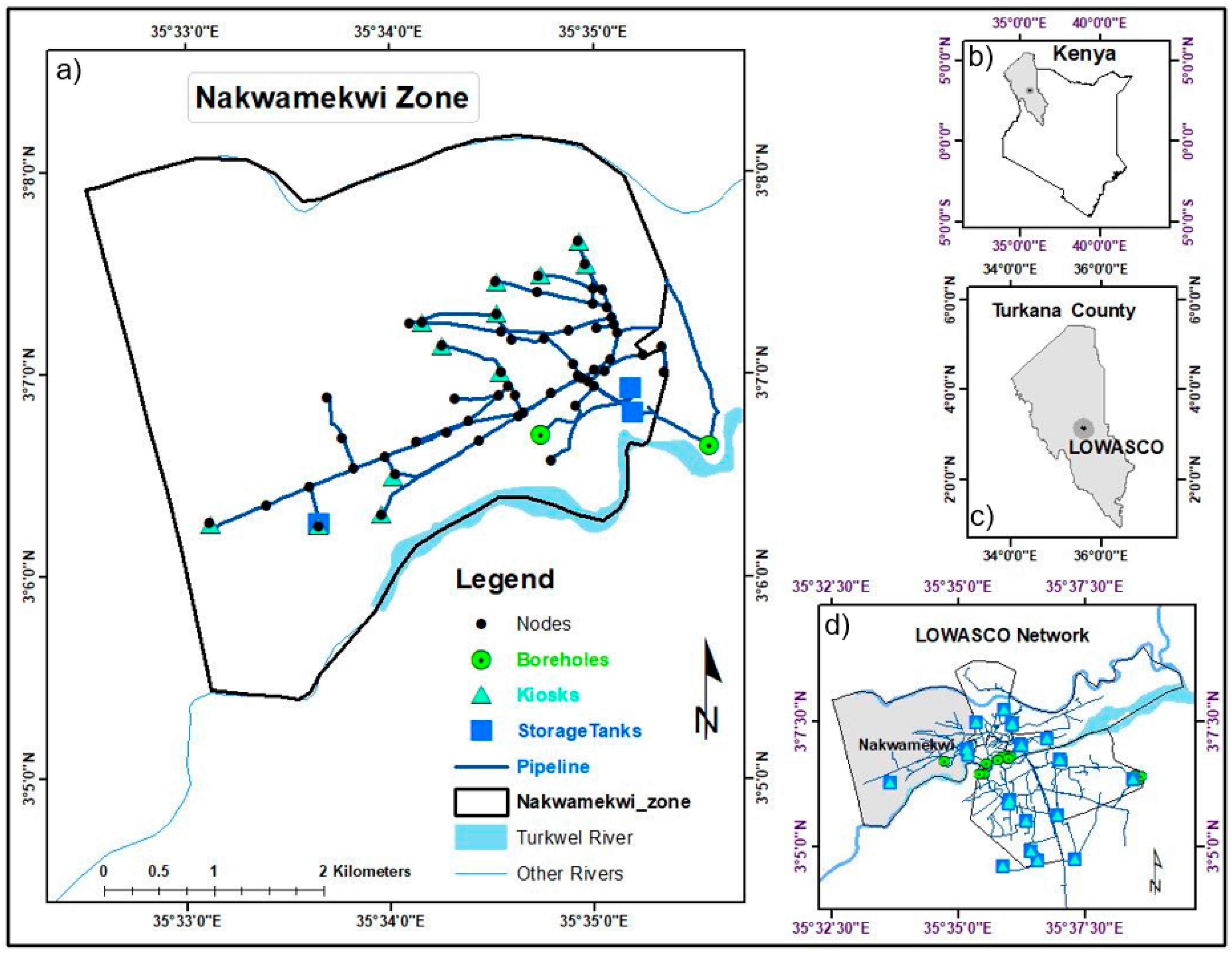
2. Data and Study Area Description
3. Methodology
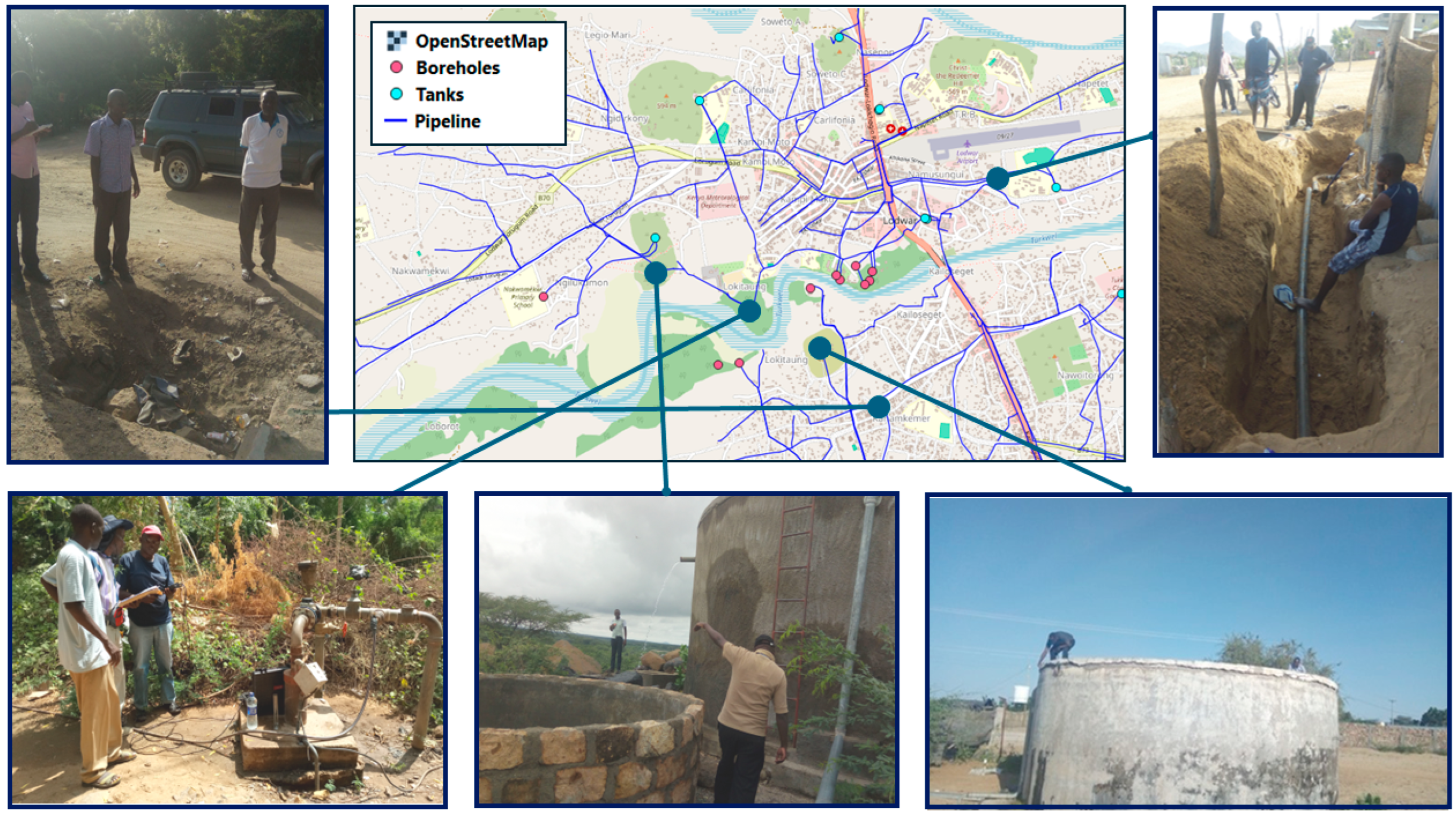
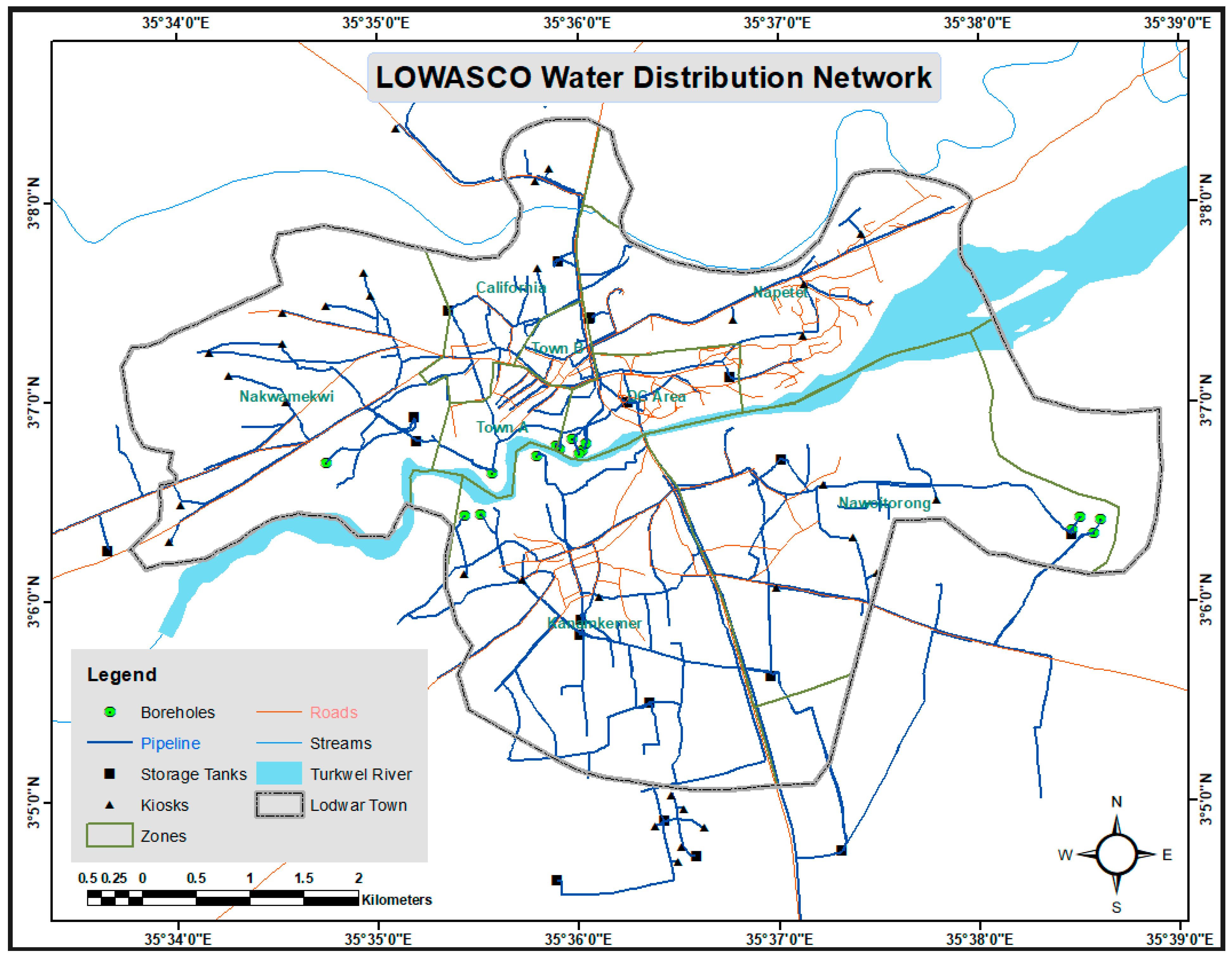
3.1. Water Network Distribution Mapping
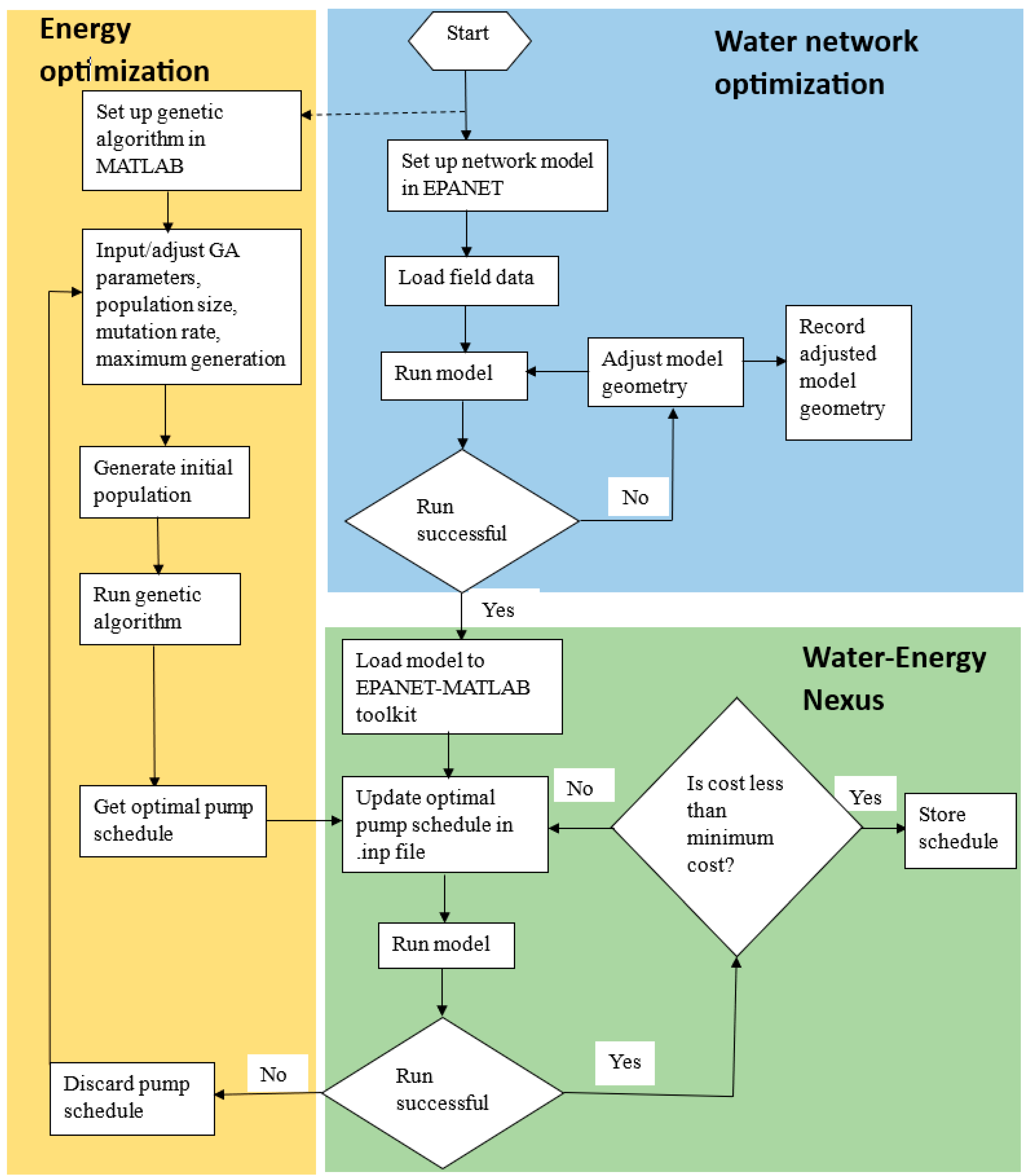
3.2. WDN Simulation and Optimization
3.2.1. Water Network Optimization
3.2.2. Energy Optimization
3.2.3. Water–Energy Nexus
4. Results and Discussion
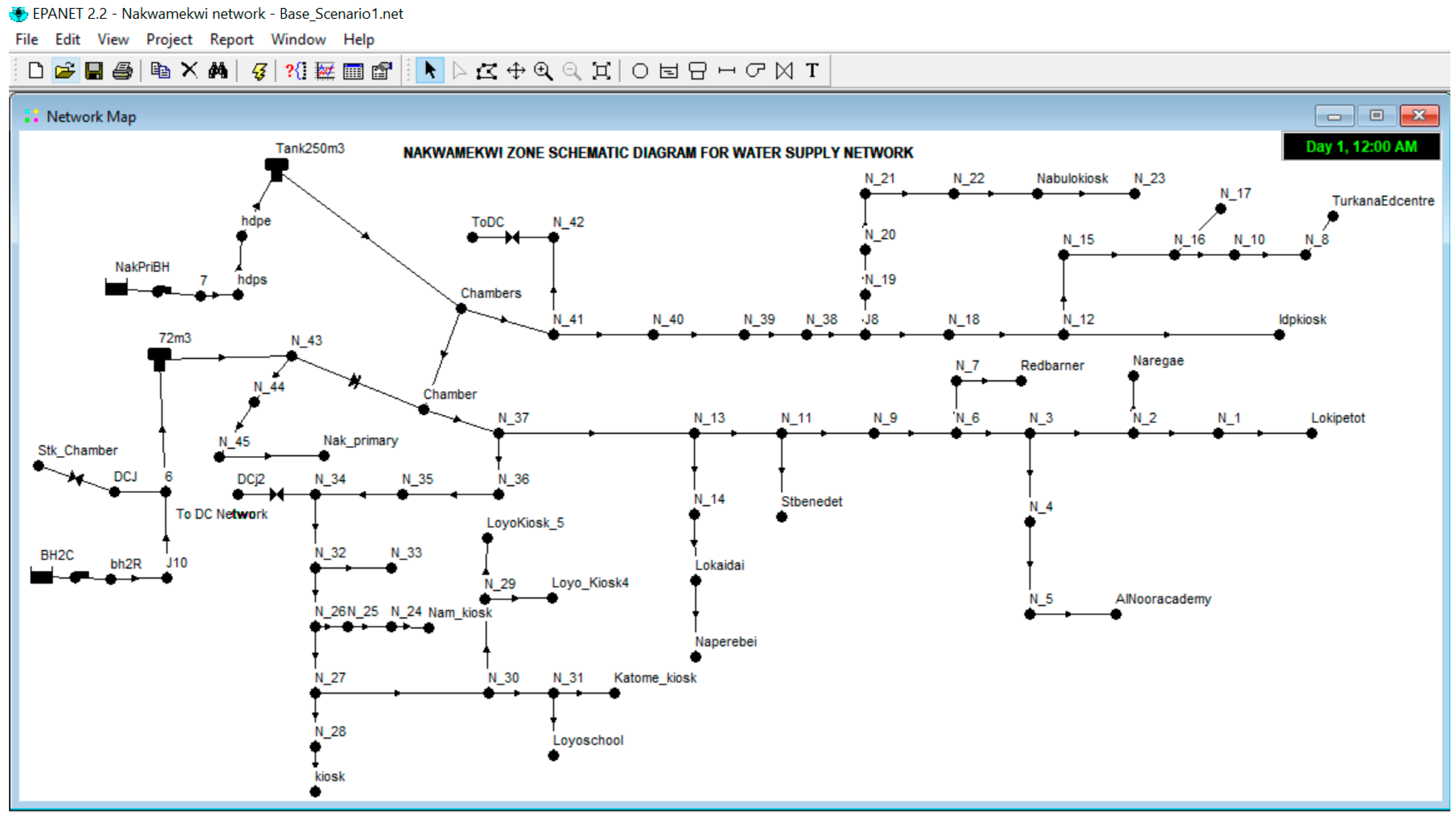
4.1. Water Distribution Network Mapping Results
4.2. Water Distribution Network Optimization Results
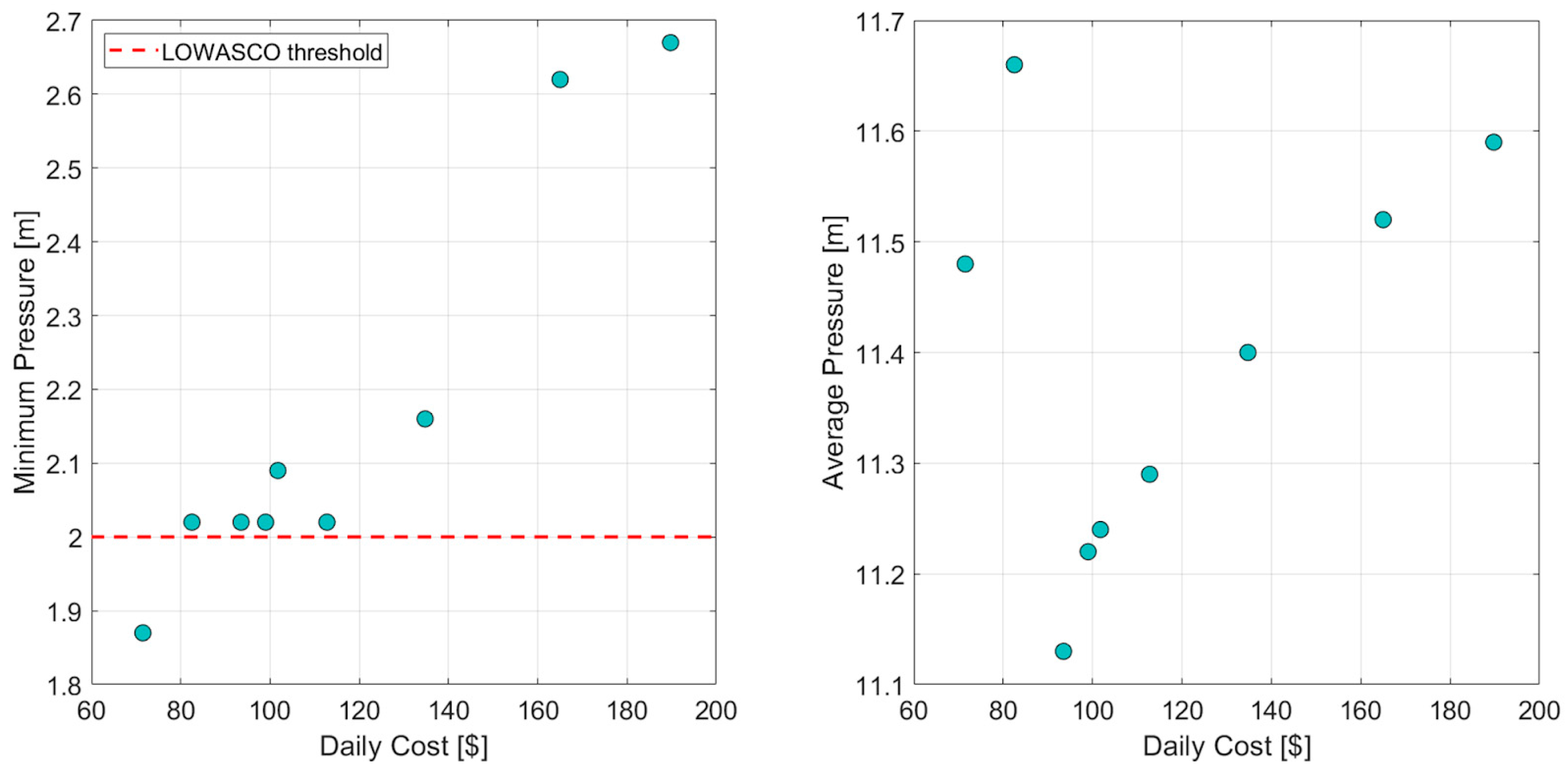
4.3. Water–Energy Nexus Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stringer, L.C.; Mirzabaev, A.; Benjaminsen, T.A.; Harris, R.M.; Jafari, M.; Lissner, T.K.; Stevens, N.; der Pahlen, C.T.-V. Climate change impacts on water security in global drylands. One Earth 2021, 4, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroulis, A.G. Dryland changes under different levels of global warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 482–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.; Barchiesi, S.; Ogali, C.J.; Welling, R.; Dalton, J.; Laban, P. Water in Drylands: Adapting to Scarcity Through Integrated Management; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2016; 44p. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Program/Global Resource Information Database (UNEP/GRID). Global Digital Datasets for Land Degradation Studies: A GIS Approach; UNEP/GRID: Geneva, Switzerland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Cities and Drylands: Managing the Complex Relationship Between Cities and Their Dryland Ecosystems; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): Nairobi, Kenya, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Singh, R.K.; Liu, H.; Song, X.; Xu, Z.; Cui, X. Exploring the evolving landscape of COVID-19 interfaced with livelihoods. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olago, D.O. Constraints and solutions for groundwater development, supply, and governance in urban areas in Kenya. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 27, 1031–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremaninejad, F.; Hoseini, E.; Fereidounfar, S. Cities in drylands as artificial protected areas for plants. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bakri, J.T.; Shawash, S.; Ghanim, A.; Abdelkhaleq, R. Geospatial Techniques for Improved Water Management in Jordan. Water 2016, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.K.; Giupponi, C.; Wada, Y. Measuring global water security towards sustainable development goals. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 124015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Costa, L.; Rybski, D.; Lucht, W.; Kropp, J.P. A systematic study of sustainable development goal (SDG) interactions. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoff, C. Water Security and Sustainable Growth in Drylands. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Development of Drylands, Jodhpur, India, 11–14 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, M.N.; Haider, H.; Farahat, A.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. Water–energy nexus for water distribution systems: A literature review. Environ. Rev. 2019, 27, 519–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, N.K.; Wang, L.K. Water Engineering: Hydraulics, Distribution, and Treatment; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-470-39098-6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Ma, J.; Blanckaert, K.; Wan, Z. Water saving and energy reduction through pressure management in urban water distribution networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 3715–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaibi, M.T.; Soussi, M.; Karnib, A. Enhancing community well-being in African drylands through technology-based solutions in the water–energy–food–ecosystems nexus. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2024, 10, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, T.; Keulertz, M.; Woertz, E. The water–energy–food nexus: An introduction to nexus concepts and some conceptual and operational problems. In The Water-Energy-Food Nexus in the Middle East and North Africa; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bideris-Davos, A.A.; Vovos, P.N. Comprehensive Review for Energy Recovery Technologies Used in Water Distribution Systems Considering Their Performance, Technical Challenges, and Economic Viability. Water 2024, 16, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahe, S.; Sharif, A.; Joda, F.; Avami, A.; Kianbakhsh, A. Water-energy nexus in the combined cycle power plant using energy, exergy, economic and environmental analyses. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 293, 117493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vairavamoorthy, K.; Akinpelu, E.; Lin, Z.; Ali, M. Design of Sustainable Water Distribution Systems in Developing Countries; Water Development Research Unit, Faculty of the Built Environment South Bank University: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fath, B.; Chen, B. Energy-water nexus under energy mix scenarios using input-output and ecological network analyses. Appl. Energy 2019, 233–234, 827–839. [Google Scholar]
- Abegaz, B.W.; Datta, T.; Mahajan, S.M. Sensor technologies for the energy-water nexus—A review. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.; Loureiro, D.; Cabral, M.; Covas, D. Comprehensive Resilience Assessment Framework for Water Distribution Networks. Water 2024, 16, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpitella, S.; Brentan, B.; Montalvo, I.; Izquierdo, J.; Certa, A. Multi-criteria analysis applied to multi-objective optimal pump scheduling in water systems. Water Supply 2019, 19, 2338–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mala-Jetmarova, H.; Sultanova, N.; Savić, D. Lost in Optimisation of Water Distribution Systems? A Literature Review of System Design. Water 2018, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S. Engineering Optimization: Theory and Practice, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sangroula, U.; Han, K.-H.; Koo, K.-M.; Gnawali, K.; Yum, K.-T. Optimization of Water Distribution Networks Using Genetic Algorithm Based SOP–WDN Program. Water 2022, 14, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Modeling resilience in a water supply system: Contrasting conditions of drought and flood. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual Conference of International Institute for Infrastructure, Renewal and Reconstruction: International Conference on Disaster Management (IIIRR 2012), Kumamoto, Japan, 24–26 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sahely, H.R.; Kennedy, C.A.; Adams, B.J. Developing sustainability criteria for urban infrastructure systems. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2005, 32, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, O.M.; Okolie, S.T.A.; Fayomi, O.S.I. Optimization of Water Distribution Systems: A Review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1378, 022068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaze, S.; Kumar, R.; Khan, J.N.; Al-Ansari, N.; Parvaze, S.; Vishwakarma, D.K.; Elbeltagi, A.; Kuriqi, A. Optimization of Water Distribution Systems Using Genetic Algorithms: A Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 4209–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, D.P.; Van Beek, E. Water Resources Systems Planning and Management: An introduction to Methods, Models and Applications; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Behandish, M.; Wu, Z.Y. Concurrent pump scheduling and storage level optimization using meta-models and evolutionary algorithms. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackle, G.; Savic, D.; Walters, G. Application of Genetic Algorithms to Pump Scheduling for Water Supply. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Genetic Algorithms in Engineering Systems: Innovations and Applications, Sheffield, UK, 12–14 September 1995; pp. 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y.; Mori, K. Optimizing pump operation scheduling for water supply systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), Shanghai, China, 11–13 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, G.; Zhao, X. State Estimation of Municipal Water Supply Network Based on BP Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Internet Computing and Information Services, Hong Kong, China, 17–18 September 2011; pp. 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, T.; Ribau, J.; Figueiredo, D.; Alves, R. Improving energy efficiency in water supply systems with pump scheduling optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.H.M.; Ramos, H.M.; de Castro, M.A.H. Hybrid genetic algorithm in the optimization of energy costs in water supply networks. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2010, 10, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari-Asl, J.; Monfared, S.A.H.; Abolfathi, S. Reducing Water Conveyance Footprint through an Advanced Optimization Framework. Water 2024, 16, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mala-Jetmarova, H.; Sultanova, N.; Savic, D. Lost in Optimisation of Water Distribution Systems? A Literature Review of System Operation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 93, 209–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiyo, F.; Nyangito, M.; Wasonga, O.P. Trend analysis of rainfall and temperature variability in the arid environment of Turkana, Kenya. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 8, 30–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hirpa, F.A.; Dyer, E.; Hope, R.; Olago, D.O.; Dadson, S.J. Finding sustainable water futures in data-sparse regions under climate change: Insights from the Turkwel River basin, Kenya. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 19, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanui, F.; Olago, D.; Dulo, S.; Ouma, G.; Kuria, Z. Hydrogeochemistry of a strategic alluvial aquifer system in a semi-arid setting and its implications for potable urban water supply: The Lodwar Alluvial Aquifer System (LAAS). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Republic of Kenya. Kenya Population and Housing Census Volume IA. Population Distribution by Administrative Units; KNBS: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Republic of Kenya. Kenya Population and Housing Census Volume II, Distribution of Population by Administrative Units; KNBS: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Korzenevica, M.; Ng’Asike, P.O.; Ngikadelio, M.; Lokomwa, D.; Ewoton, P.; Dyer, E. From fast to slow risks: Shifting vulnerabilities of flood-related migration in Lodwar, Kenya. Clim. Risk Manag. 2024, 43, 100584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodwar Water and Sanitation Company Ltd. Performance Report 2019. Lodwar Water and Sanitation Company Ltd.: Lodwar, Kenya, (unpublished).
- Maxwell, C.O.; Dulo, S.; Olago, D.O.; Odira, P.M.A. Water Availability Analysis of Multiple Source Groundwater Supply Systems in Water Stressed Urban Centers: Case of Lodwar municipality, Kenya. J. Civil. Environ. Eng. 2020, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Services Regulatory Board. A Performance Report of Kenya’s Water Services Sector 2020/2021. Available online: https://wasreb.go.ke/impact-reports-issue-no-14/ (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Rossman, L.; Woo, H.; Tryby, M.; Shang, F.; Janke, R.; Haxton, T. EPANET 2.2 User Manual; EPA/600/R-20/133; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ávila, C.A.M.; Sánchez-Romero, F.-J.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. Improve leakage management to reach sustainable water supply networks through by green energy systems. Optimized case study. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 83, 103994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliades, D.G.; Kyriakou, M.; Vrachimis, S.; Polycarpou, M.M. EPANET-MATLAB Toolkit: An Open-Source Software for Interfacing EPANET with MATLAB. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Computing and Control for the Water Industry (CCWI), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 7–9 November 2016; p. 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodwar Water and Sanitation Company Ltd. Borehole Summary Report 2016. Lodwar Water and Sanitation Company Ltd.: Lodwar, Kenya, (Unpublished company report).
- Republic of Kenya. Practice Manual for Water Supply Services in Kenya; Ministry of Water and Irrigation: Nairobi, Kenya, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ürkmez, M.; Kallesøe, C.; Bendtsen, J.D.; Leth, J. Scenario Based Cost Optimization of Water Distribution Networks Powered by Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA), Bridgetown, Barbados, 16–18 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Yan, D.; Yang, H.; Ma, L.; Kou, C. Multi-objective optimization of water distribution networks based on non-dominated sequencing genetic algorithm. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; van Zyl, J.E.; Walters, G.A.; Savic, D.A. Genetic algorithm optimisation of level-controlled pumping station operation. In Water Network Modelling for Optimal Design and Management; Centre for Water Systems: Exeter, UK, 2000; pp. 79–90. [Google Scholar]


| Service Type | No. of Connections | Estimated Average Population Per Connection | Total Population | Per Capita in Liters/Day | Daily Demand in Liters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | 1309 | 5 | 6545 | 75 | 490,875 |
| Water kiosk | 12 | 50 households ×5 | 3000 | 20 | 60,000 |
| Standpipe | 20 | 10 households ×5 | 1000 | 20 | 20,000 |
| School/Institution | 5 | 300 | 1500 | 5 | 7500 |
| Business/Commercial | 10 | 500 | 5000 | ||
| Total | 1356 | 12,045 | 620 | 583,375 |
| Element Name | Properties Set |
|---|---|
| Junction (Node) | id, elevation, base demand, demand pattern |
| Reservoir | id, description, total head |
| Tank | id, elevation, initial, minimum and maximum level, and diameter |
| Pipe | id, start and end node, length, diameter, roughness |
| Pump | id, pump curve, pattern |
| Valve | id, start and end node, diameter, type, fixed status |
| Label | Text, font |
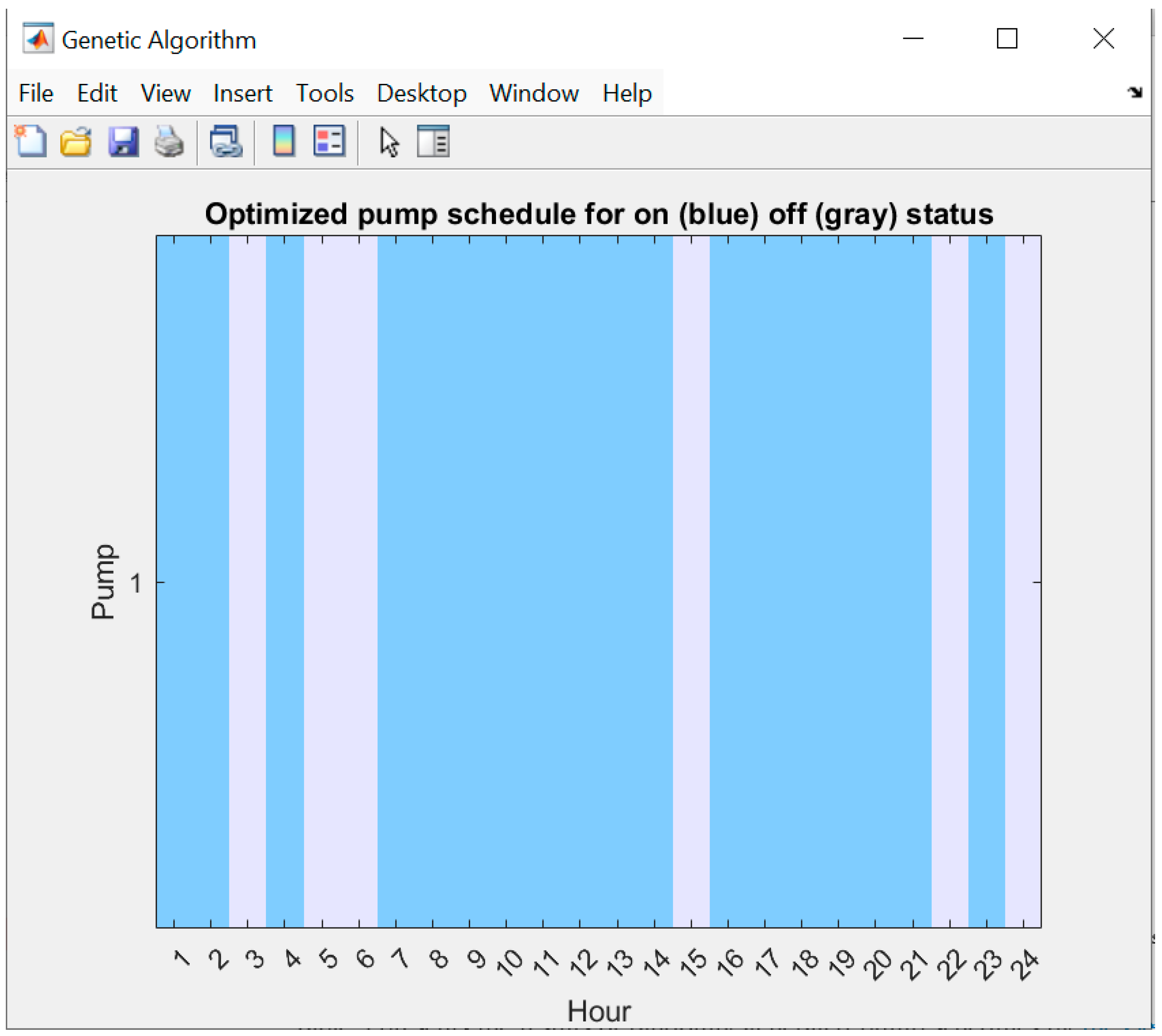
| No | GA Generated Pump Schedule in 24 h Period of Hybrid Pumping | Successful Run? | Actual Cost in USD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | |||
| 1 | 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 | Yes | 71.5 |
| 2 | 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 | Yes | 82.5 |
| 3 | 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 | Yes | 93.5 |
| 4 | 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 | Yes | 99 |
| 5 | 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 | Yes | 101.75 |
| 6 | 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 | Yes | 112.75 |
| 7 | 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 | Yes | 134.75 |
| 8 | 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 | Yes | 165 |
| 9 | 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 | Yes | 189.75 |
| 10 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 | No | 24.75 |
| 12 | 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 | No | 101.75 |
| 13 | 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 | No | 93.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maxwell, C.O.; Oonge, Z.I.; Odira, P.M.A.; Ouma, G.O.; Lompi, M.; Pacetti, T.; Bacco, M.D.; Caporali, E. Water–Energy Nexus-Based Optimization of the Water Supply Infrastructure in a Dryland Urban Setting. Water 2024, 16, 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213073
Maxwell CO, Oonge ZI, Odira PMA, Ouma GO, Lompi M, Pacetti T, Bacco MD, Caporali E. Water–Energy Nexus-Based Optimization of the Water Supply Infrastructure in a Dryland Urban Setting. Water. 2024; 16(21):3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213073
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaxwell, Charles Odira, Zablon Isaboke Oonge, Patts M. A. Odira, Gilbert Ong’isa Ouma, Marco Lompi, Tommaso Pacetti, Mario Di Bacco, and Enrica Caporali. 2024. "Water–Energy Nexus-Based Optimization of the Water Supply Infrastructure in a Dryland Urban Setting" Water 16, no. 21: 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213073
APA StyleMaxwell, C. O., Oonge, Z. I., Odira, P. M. A., Ouma, G. O., Lompi, M., Pacetti, T., Bacco, M. D., & Caporali, E. (2024). Water–Energy Nexus-Based Optimization of the Water Supply Infrastructure in a Dryland Urban Setting. Water, 16(21), 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213073






