Combining SWAT with Machine Learning to Identify Primary Controlling Factors and Their Impacts on Non-Point Source Pollution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
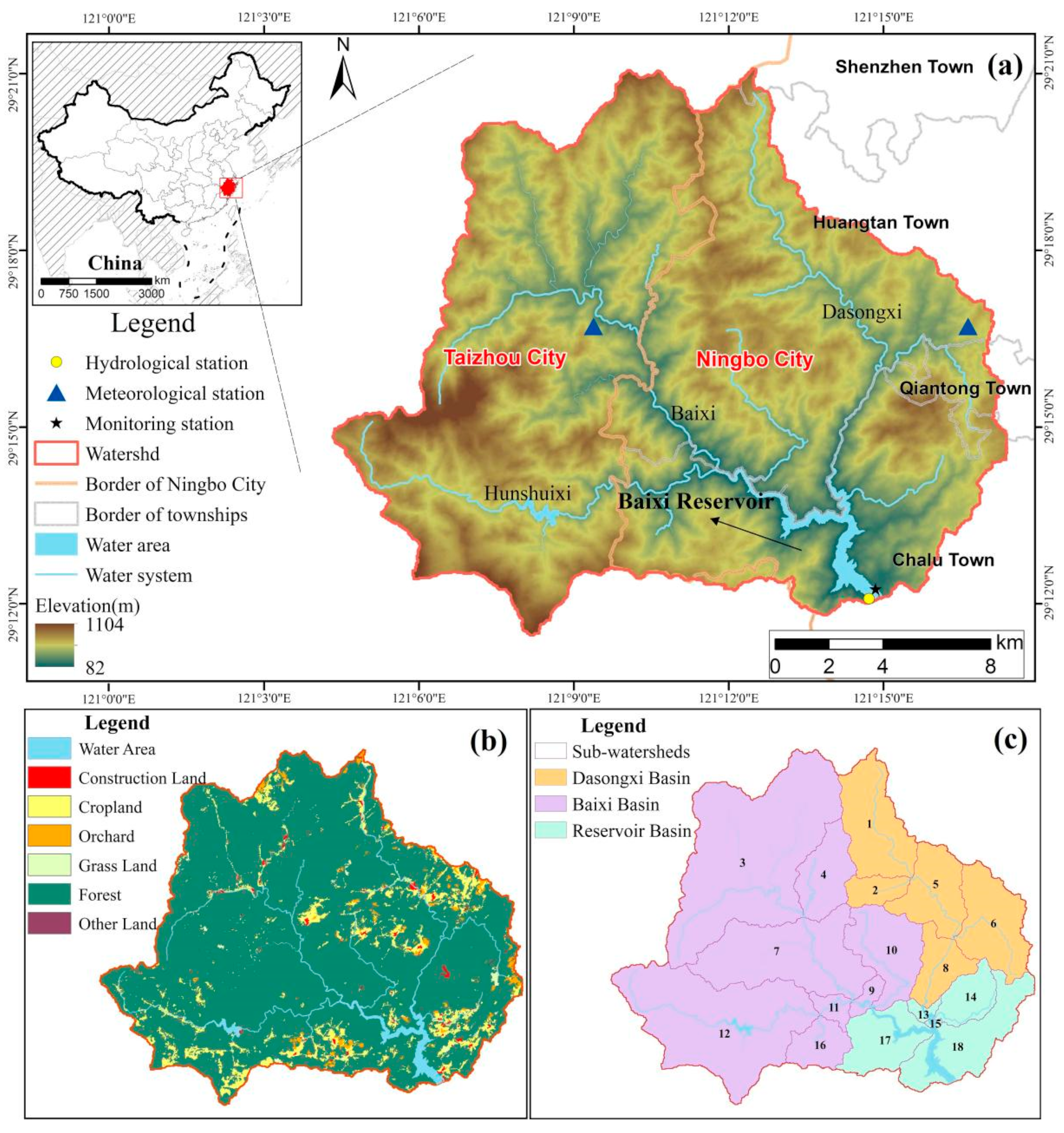
2.1. Study Area
2.2. SWAT Model Data Sources and Processing
2.3. SWAT Model Calibration
2.4. Calculation of TN and TP
2.5. The Coefficient of Variation (CV) and Absolute Change Rate ()
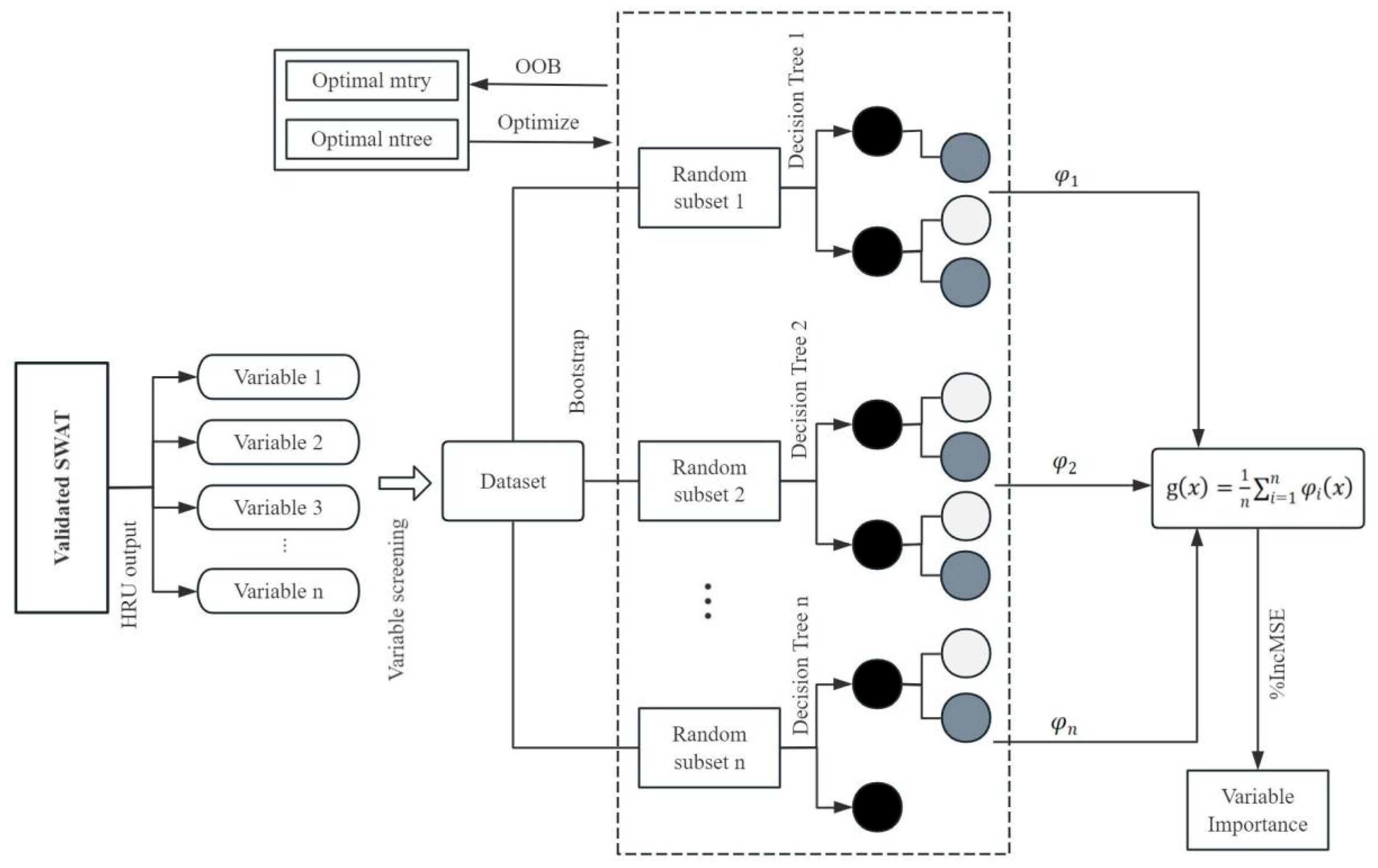
2.6. Random Forest Modeling
2.7. Partial Dependency Plot (PDP)
3. Results and Discussion
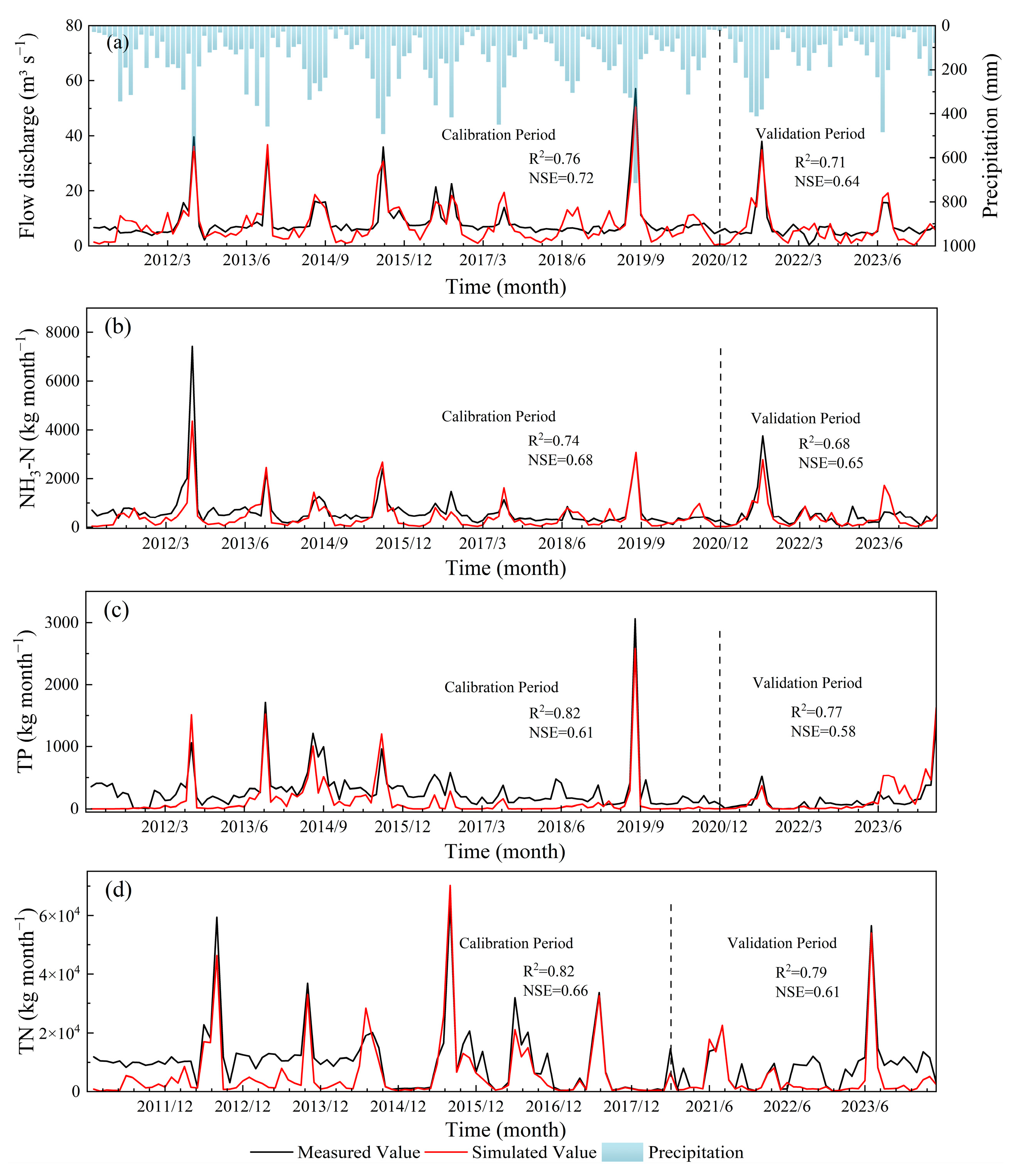
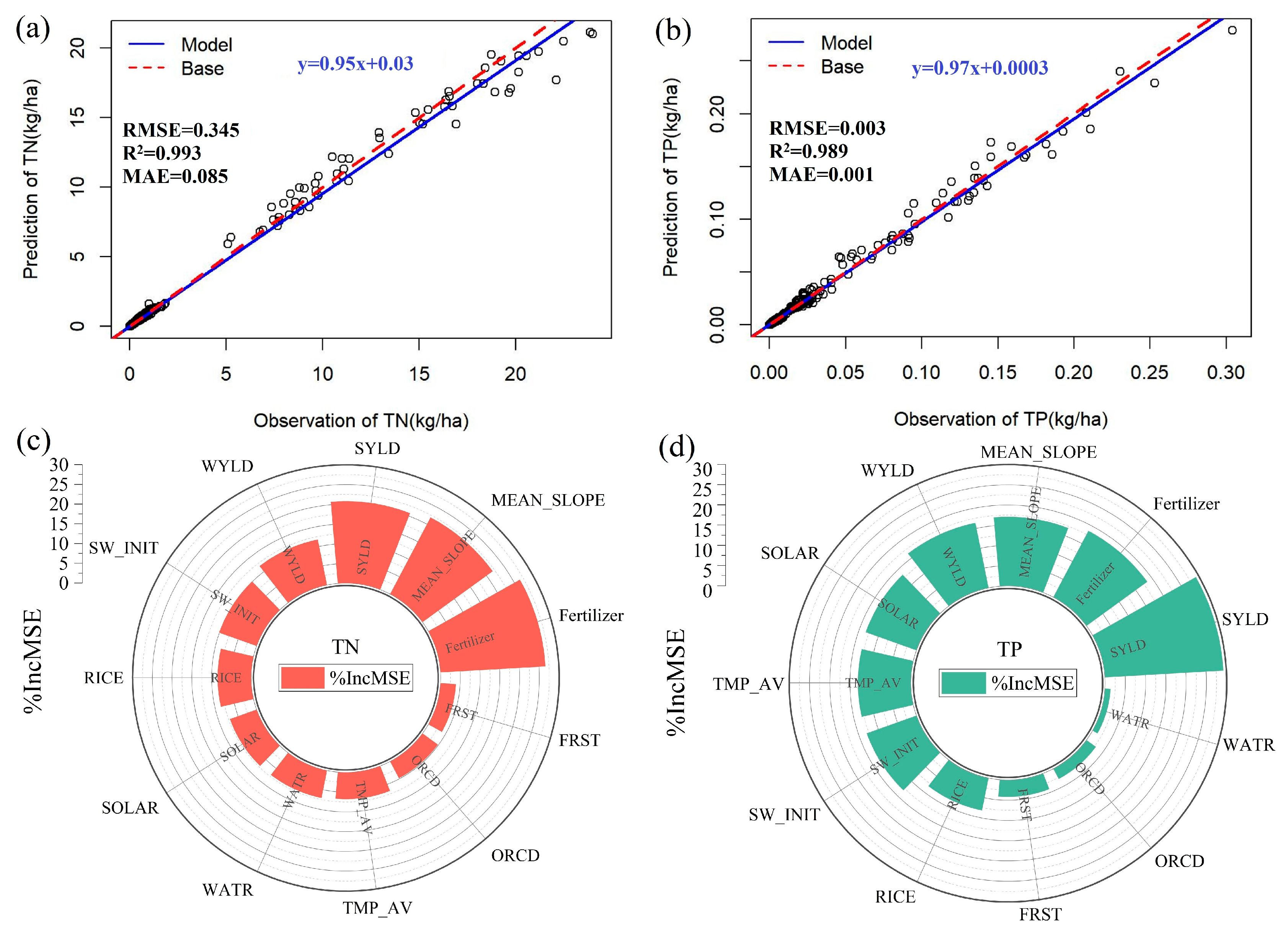
3.1. SWAT Model Validation
3.2. Spatiotemporal Distribution of NPS in the Watershed
3.2.1. Temporal Distribution of NPS
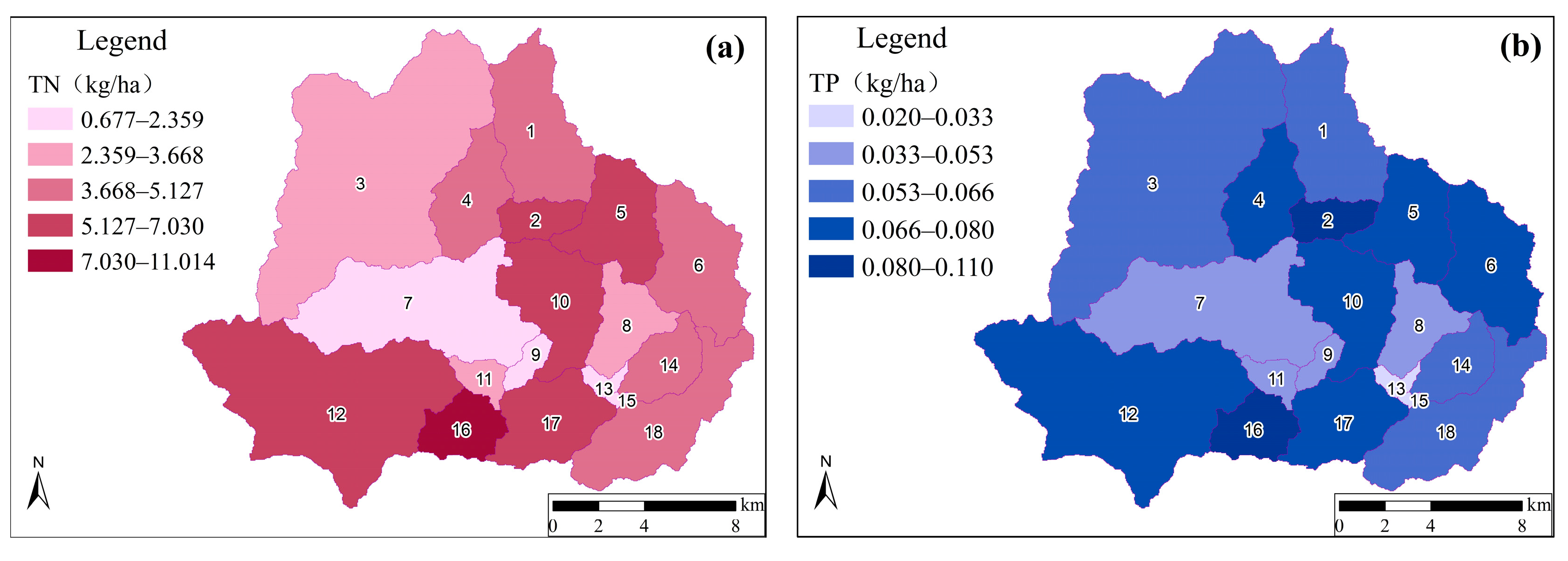
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution of NPS
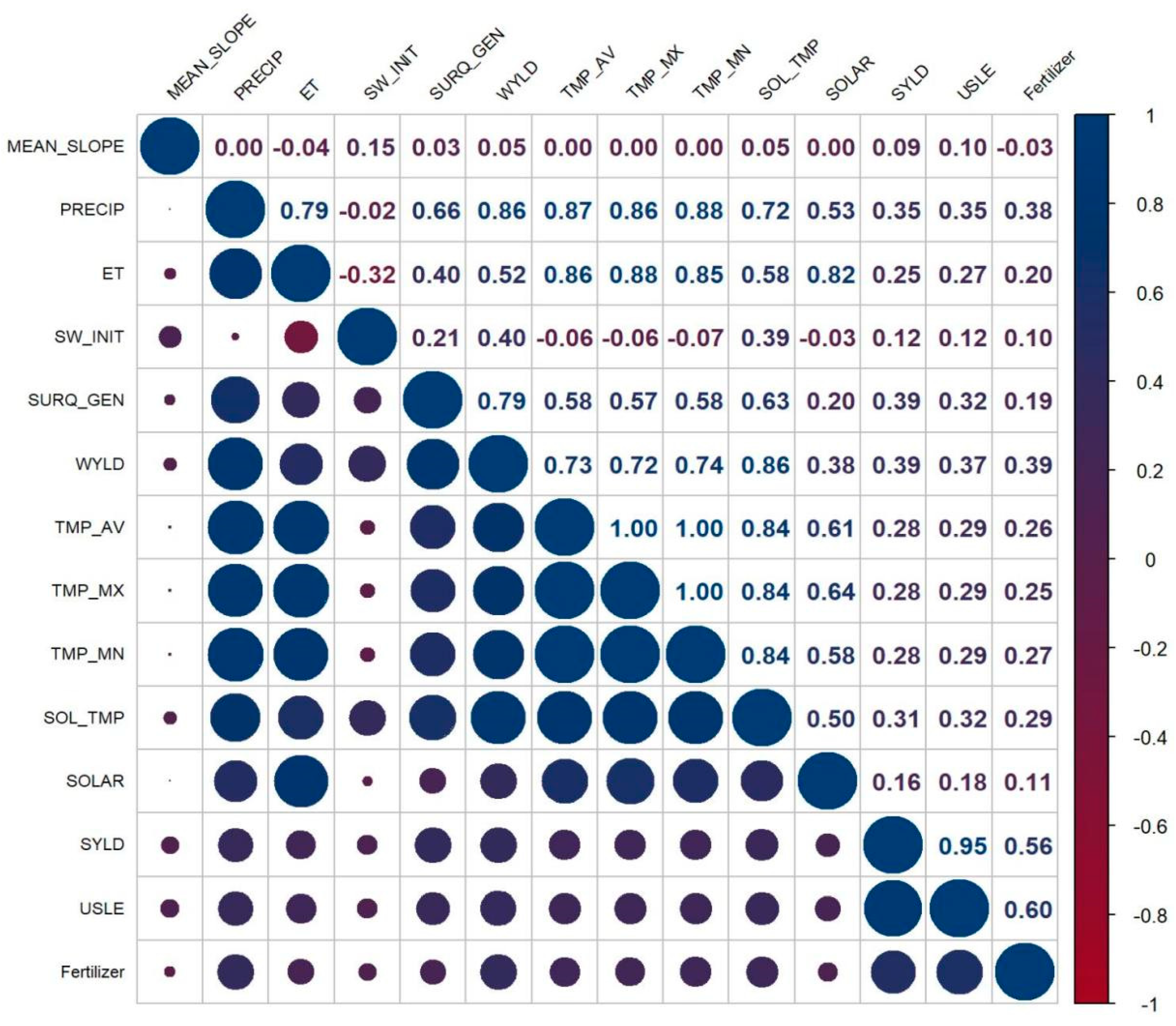
3.3. Correlation Analysis by Pearson
3.4. Variable Importance of the RF Model for TN and TP
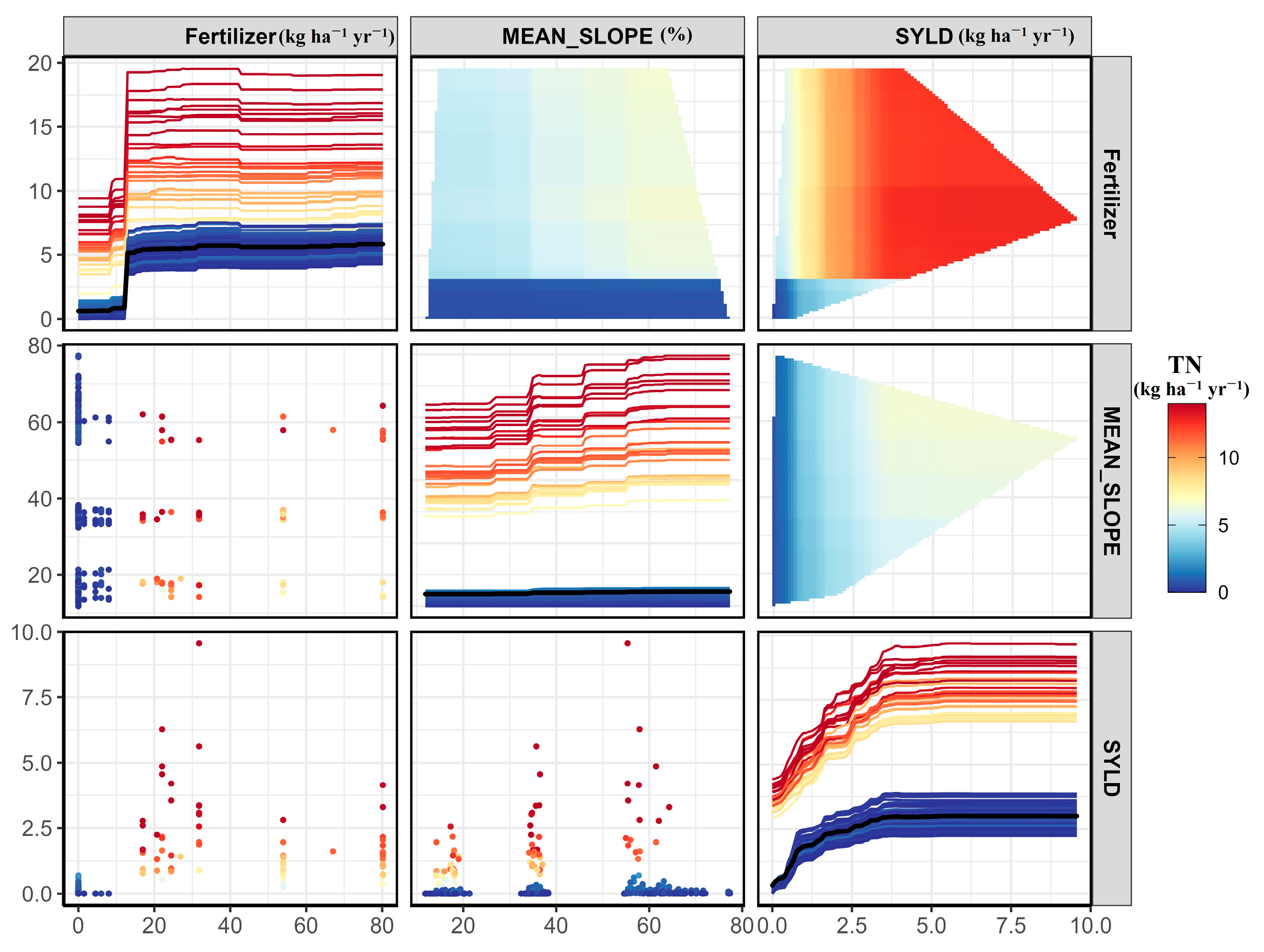
3.5. Impacts of Primary Controlling Factors on TN and TP
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, X.; Shen, W.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.; He, Y. Response of Non-Point Source Pollution Loads to Land Use Change under Different Precipitation Scenarios from a Future Perspective. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 3987–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Bouwman, A.F.; Van Gils, J.; Vilmin, L.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, Z.; Ran, X. Hindcasting Harmful Algal Bloom Risk Due to Land-Based Nutrient Pollution in the Eastern Chinese Coastal Seas. Water Res. 2023, 231, 119669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fianko, J.R.; Korankye, M.B. Quality Characteristics of Water Used for Irrigation in Urban and Peri-Urban Agriculture in Greater Accra Region of Ghana: Health and Environmental Risk. West Afr. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 28, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, M.C. The Effects of Recreational Water Exposure on Human Skin: Toxin Penetration and Microbiome Alteration. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Irvine, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, V.; Arockiaraj, J. Unveiling the Trifecta of Cyanobacterial Quorum Sensing: LuxI, LuxR and LuxS as the Intricate Machinery for Harmful Algal Bloom Formation in Freshwater Ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Liu, G.; Lombardi, G.V.; Su, M.; Yang, Z. Uncovering the Risk Spillover of Agricultural Water Scarcity by Simultaneously Considering Water Quality and Quantity. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 343, 118209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Li, Y.P.; Wang, C.X.; Huang, G.H. An Inexact Simulation-Based Stochastic Optimization Method for Identifying Effluent Trading Strategies of Agricultural Nonpoint Sources. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 152, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, P.M.; Stephenson, K.; Collick, A.S.; Easton, Z.M. Targeting for Nonpoint Source Pollution Reduction: A Synthesis of Lessons Learned, Remaining Challenges, and Emerging Opportunities. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ouyang, W.; Zhu, J.; Lin, C.; He, M. Discharge Dynamics of Agricultural Diffuse Pollution under Different Rainfall Patterns in the Middle Yangtze River. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y. Analysis of Agricultural Pollution by Flood Flow Impact on Water Quality in a Reservoir Using a Three-Dimensional Water Quality Model. J. Hydroinform. 2013, 15, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedláček, J.; Bábek, O.; Nováková, T. Sedimentary Record and Anthropogenic Pollution of a Complex, Multiple Source Fed Dam Reservoirs: An Example from the Nové Mlýny Reservoir, Czech Republic. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1456–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, B.; Xu, D.; Gao, L.; Yin, S. Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediments of the Largest Reservoir (Three Gorges Reservoir) in China: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20844–20858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, L.; Zhu, S.; Sun, A.; Wang, H.; Ding, Z. Identifying the Critical Areas and Primary Sources for Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Management of an Emigrant Town within the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L. Assessing Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Loads in Typical Basins of Upper Yellow River by Incorporating Critical Impacting Factors. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 177, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Qi, C.; Zhang, W. Distribution Characteristics of Non-Point Source Pollution of TP and Identification of Key Source Areas in Nanyi Lake (China) Basin: Based on InVEST Model and Source List Method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 117464–117484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Liu, L. Long-Term Effects of Anthropogenic Factors on Nonpoint Source Pollution in the Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, D.S.; Chaube, U.C.; Ekube Hailu, A.; Aberra Gudeta, D.; Tegene Kassa, M. Estimation and Comparision of Curve Numbers Based on Dynamic Land Use Land Cover Change, Observed Rainfall-Runoff Data and Land Slope. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Hu, C. A Comprehensive Study of the Effect of Input Data on Hydrology and Non-Point Source Pollution Modeling. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1505–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, D.; He, X. Predictive Modeling of Groundwater Nitrate Pollution and Evaluating Its Main Impact Factors Using Random Forest. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, S.; Langendoen, E.; Keesstra, S.; Ploeg, M.v.d.; Gelagay, H.; Lemma, H.; van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M. Susceptibility to Gully Erosion: Applying Random Forest (RF) and Frequency Ratio (FR) Approaches to a Small Catchment in Ethiopia. Water 2021, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avand, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Mirchooli, F.; Kavian, A.; Tiefenbacher, J.P. A New Approach for Smart Soil Erosion Modeling: Integration of Empirical and Machine-Learning Models. Environ. Model. Assess. 2023, 28, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Bai, Z.; He, P.; Jiang, R.; Huang, S.; Xu, X. Statistical Analysis of Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Northeast China Using Multiple Linear Regression and Random Forest. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 3637–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysanova, V.; White, M. Advances in Water Resources Assessment with SWAT—An Overview. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanief, A.; Laursen, A.E. Meeting Updated Phosphorus Reduction Goals by Applying Best Management Practices in the Grand River Watershed, Southern Ontario. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 130, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Fu, C.; Wang, X.; Dong, L.; Yao, S.; Xue, B.; Wu, H.; Wu, H. Decoding the Dramatic Hundred-Year Water Level Variations of a Typical Great Lake in Semi-Arid Region of Northeastern Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, B.; Kuemmerlen, M.; Kiesel, J.; Cai, Q.; Jähnig, S.C.; Fohrer, N. Impacts of Land Use Changes on Hydrological Components and Macroinvertebrate Distributions in the Poyang Lake Area. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 1119–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Ji, W. Relating Landscape Characteristics to Non-Point Source Pollution in Mine Waste-Located Watersheds Using Geospatial Techniques. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 82, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuemmerlen, M.; Schmalz, B.; Cai, Q.; Haase, P.; Fohrer, N.; Jähnig, S.C. An Attack on Two Fronts: Predicting How Changes in Land Use and Climate Affect the Distribution of Stream Macroinvertebrates. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.Y.; Jung, C.G.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.J. Evaluation of Watershed Scale Aquatic Ecosystem Health by SWAT Modeling and Random Forest Technique. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matomela, N.; Li, T.; Zhang, P.; Ikhumhen, H.O.; Lopes, N.D.R. Role of Landscape and Land-Use Transformation on Nonpoint Source Pollution and Runoff Distribution in the Dongsheng Basin, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jin, R.; Zhu, W. Quantification of Effects of Natural Geographical Factors and Landscape Patterns on Non-Point Source Pollution in Watershed Based on Geodetector: Burhatong River Basin, Northeast China as An Example. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, R.M.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Gao, S.H.; Sun, C.C.; Shen, Z.Y.; Ou, S.Z.; Chen, S.L. An Integrated Simulation-Monitoring Framework for Nitrogen Assessment: A Case Study in the Baixi Watershed, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1076–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tan, M.L.; Ficklin, D.L.; Dixon, B.; Yusop, Z.; Chaplot, V. Impacts of DEM Resolution, Source, and Resampling Technique on SWAT-Simulated Streamflow. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, W.; Guo, Q.; Wu, S. Effects of Landuse Change on Surface Runoff and Sediment Yield at Different Watershed Scales on the Loess Plateau. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2010, 25, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, M.C.H. Soil Processes and Current Trends in Quality Assessment; BoD—Books on Demand; Intechopen: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1029-3. [Google Scholar]
- Aouissi, J.; Benabdallah, S.; Chabaâne, Z.L.; Cudennec, C. Evaluation of Potential Evapotranspiration Assessment Methods for Hydrological Modelling with SWAT—Application in Data-Scarce Rural Tunisia. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 174, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, J.; Maximov, I.; Siber, R.; Bogner, K.; Mieleitner, J.; Zobrist, J.; Srinivasan, R. Modelling Hydrology and Water Quality in the Pre-Alpine/Alpine Thur Watershed Using SWAT. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Total Nitrogen and Ammonia Nitrogen in the Water Source of the Middle Route of the South-To-North Water Diversion Project. Water 2020, 12, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.E.; Siciliano, G. A Comprehensive Review of Constraints to Improved Management of Fertilizers in China and Mitigation of Diffuse Water Pollution from Agriculture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; Griensven, A.V.; Liew, M.W.V.; et al. SWAT: Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Dar, A.Q.; Jain, M.K. Modelling Streamflow Using the SWAT Model and Multi-Site Calibration Utilizing SUFI-2 of SWAT-CUP Model for High Altitude Catchments, NW Himalaya’s. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiyong, W.; Chaopu, T.; Liangjie, W.; Lei, D.; Yongqiu, X.; Xiaoyuan, Y. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics and Key Sources of Nitrogen Pollution in a Typical Agricultural Watershed Based on SWAT Model. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jia, R.; Shi, X.; Liang, J.; Dang, J. Feature Selection and Hyper Parameters Optimization for Short-Term Wind Power Forecast. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 6752–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibin, R.; Sudheer, K.P.; Chaubey, I. Sensitivity and Identifiability of Stream Flow Generation Parameters of the SWAT Model. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xu, F.; Zhang, P.; Yu, W.; Men, C. Identifying Non-Point Source Critical Source Areas Based on Multi-Factors at a Basin Scale with SWAT. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamian, R.; Jaleh, A.; Majid, A.; Mousavi, S.-F.; Heidarpour, M.; Jalalian, A.; Mikayilov, F. Application of a SWAT Model for Estimating Runoff and Sediment in Two Mountainous Basins in Central Iran. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, K.T.; Park, C.Y.; Lee, S.; Heo, T.-Y. Interpretation of Ensemble Learning to Predict Water Quality Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, A.; Parnell, A.; Hurley, C.B. Visualizing Variable Importance and Variable Interaction Effects in Machine Learning Models. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2022, 31, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Josefson, M. Temporal Variations of Suspended Sediment Transport in Oneida Creek Watershed, Central New York. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426–427, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedt, M.; Schäffer, A.; Smith, K.E.C.; Nabel, M.; Roß-Nickoll, M.; van Dongen, J.T. Comparing Straw, Compost, and Biochar Regarding Their Suitability as Agricultural Soil Amendments to Affect Soil Structure, Nutrient Leaching, Microbial Communities, and the Fate of Pesticides. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, P.B.; Nelson, N.O.; Frees, L.D.; Mankin, K.R. Comparison of AnnAGNPS and SWAT Model Simulation Results in USDA-CEAP Agricultural Watersheds in South-Central Kansas. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongley, E.D.; Xiaolan, Z.; Tao, Y. Current Status of Agricultural and Rural Non-Point Source Pollution Assessment in China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobre, R.L.; Caliman, A.; Cabral, C.R.; de Carvalho Araújo, F.; Guerin, J.; Dantas, F.D.; Quesado, L.B.; Venticinque, E.M.; Guariento, R.D.; Amado, A.M.; et al. Precipitation, Landscape Properties and Land Use Interactively Affect Water Quality of Tropical Freshwaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, M.A.; Lander, J.; Levine-Silverman, S. Diagnosing and Dealing with Multicollinearity. West. J. Nurs. Res. 1990, 12, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alin, A. Multicollinearity. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H. Multicollinearity and Misleading Statistical Results. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2019, 72, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahouda, M.K.; Joe, I. A Deep-Learned Embedding Technique for Categorical Features Encoding. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 114381–114391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yang, D.; Hu, H.; Gao, B. Detecting the Effect of Land-Use Change on Streamflow, Sediment and Nutrient Losses by Distributed Hydrological Simulation. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; Penn, C.J.; King, K.W.; McAfee, S.J. Surface-to-Tile Drain Connectivity and Phosphorus Transport: Effect of Antecedent Soil Moisture. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yue, F.; Wang, Y.; Qin, C.; Ding, H.; Xue, L.-L.; Li, S. The Effect of Heavy Rainfall Events on Nitrogen Patterns in Agricultural Surface and Underground Streams and the Implications for Karst Water Quality Protection. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 266, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Huang, D.; Zhou, L. Differences in Sediment Provenance from Rainfall and Snowmelt Erosion in the Mollisol Region of Northeast China. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 2442–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, J. Landscape Patterns Regulate Non-Point Source Nutrient Pollution in an Agricultural Watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wang, J. Effect on Water Consumption and Non-Point Source Pollutants Loss under Different Water and Nitrogen Regulation of Paddy Field in Southern China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Wei, C.; Xie, D. GIS-Based Prediction of Nutrient Loss from a Small Watershed. ACTA Pedol. Sin. 2013, 41, 837–844. [Google Scholar]
- Panuska, J.C.; Moore, I.D.; Kramer, L.A. Terrain Analysis: Integration into the Agricultural Nonpoint Source (AGNPS) Pollution Model. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, M.A.; McGrath, G.; Leopold, M. The Impact of Soil Water Repellency and Slope upon Runoff and Erosion. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterholz, W.; Simpson, Z.; Williams, M.; Shedekar, V.; Penn, C.; King, K. New Phosphorus Losses via Tile Drainage Depend on Fertilizer Form, Placement, and Timing. J. Environ. Qual. 2024, 53, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Category | Description | Precision | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | Provides elevation and slope data, crucial for simulating runoff, flow direction, and watershed boundaries [34]. | 90 m | http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/ (accessed on 8 October 2022) |
| Land Use | Describes land utilization (e.g., forest, agriculture), critical for estimating runoff and sediment yield [35]. | 1:100,000 | Ningbo Municipal Bureau of Land and Resources |
| Soil | Includes texture, organic matter, and hydraulic properties, key for water retention and nutrient cycling [36]. | 1:1,000,000 | Nanjing Institute of Soil Science |
| Meteorology | Weather data (e.g., precipitation, temperature) affects processes like runoff and evapotranspiration [37]. | Daily Average | Ningbo Meteorological Bureau |
| Hydrology | Streamflow and groundwater data for calibrating and validating model predictions [38]. | Daily Average | Baixi Reservoir Management Bureau, Ningbo |
| TN, TP, NH3-N | These nutrients are key indicators of water pollution, particularly in relation to agricultural runoff and waste management [39]. | Monthly Average | Ningbo Ecology and Environment Bureau, Ninghai Branch |
| Fertilizer | Fertilizer application data are used to simulate nitrogen and phosphorus runoff, impacting water quality [40]. | / | Ninghai Statistical Yearbook, Field Surveys |
| Category | Parameter Name | Range | Fitted Value | Sensitivity Rank | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | ||||
| Vegetation and Management | FRT_SURFACE | 0 | 1 | 0.49 | 6 |
| BIOMIX | 0 | 1 | 0.4 | 25 | |
| Soil | SOL_NO3(1) | 0 | 100 | 22.08 | 1 |
| SOL_ORGN(1) | 0 | 1800 | 1357.25 | 3 | |
| SOL_K(1) | 0 | 2000 | 1158.19 | 11 | |
| SOL_ORGP(1) | 0 | 600 | 345.95 | 12 | |
| SOL_BD(1) | 0.9 | 2.5 | 1.14 | 16 | |
| SOL_Z(1) | 0 | 800 | 385.96 | 20 | |
| SOL_AWC(1) | 0 | 1 | 0.47 | 26 | |
| Nutrient Transport | PHOSKD | 100 | 200 | 198.34 | 4 |
| NPERCO | 0 | 1 | 0.35 | 8 | |
| PPERCO | 10 | 17.5 | 15.43 | 9 | |
| Hydrological Process | ESCO | 0 | 1 | 0.02 | 14 |
| SURLAG | 0.05 | 24 | 6.86 | 15 | |
| CN2 | 35 | 98 | 66.94 | 19 | |
| Groundwater | ALPHA_BF | 0 | 1 | 0.22 | 2 |
| REVAPMN | 0 | 500 | 352.63 | 5 | |
| GW_DELAY | 0 | 500 | 22.5 | 7 | |
| GW_REVAP | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.18 | 10 | |
| GWQMN | 0 | 5000 | 1310.36 | 13 | |
| RCHRG_DP | 0 | 1 | 0.13 | 18 | |
| Channel and Erosion | CH_K2 | −0.01 | 500 | 235.71 | 17 |
| USLE_P | 0 | 1 | 0.39 | 21 | |
| CH_N2 | −0.01 | 0.3 | 0.16 | 22 | |
| ERORGN | 0 | 5 | 3.57 | 23 | |
| ERORGP | 0 | 5 | 0.03 | 24 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Y.; Hong, Q.; Jia, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Cheng, J. Combining SWAT with Machine Learning to Identify Primary Controlling Factors and Their Impacts on Non-Point Source Pollution. Water 2024, 16, 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213026
Yin M, Wu Z, Zhang Q, Su Y, Hong Q, Jia Q, Wang X, Wang K, Cheng J. Combining SWAT with Machine Learning to Identify Primary Controlling Factors and Their Impacts on Non-Point Source Pollution. Water. 2024; 16(21):3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213026
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Maowu, Zaijun Wu, Qian Zhang, Yangyang Su, Qiao Hong, Qiongqiong Jia, Xiao Wang, Kan Wang, and Junrui Cheng. 2024. "Combining SWAT with Machine Learning to Identify Primary Controlling Factors and Their Impacts on Non-Point Source Pollution" Water 16, no. 21: 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213026
APA StyleYin, M., Wu, Z., Zhang, Q., Su, Y., Hong, Q., Jia, Q., Wang, X., Wang, K., & Cheng, J. (2024). Combining SWAT with Machine Learning to Identify Primary Controlling Factors and Their Impacts on Non-Point Source Pollution. Water, 16(21), 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213026





