Integrated Modeling Approach to Assess Freshwater Inflow Impact on Coastal Water Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Description of SWAT and EFDC Models and Their Coupling Process
2.3. Water Quality Parameters
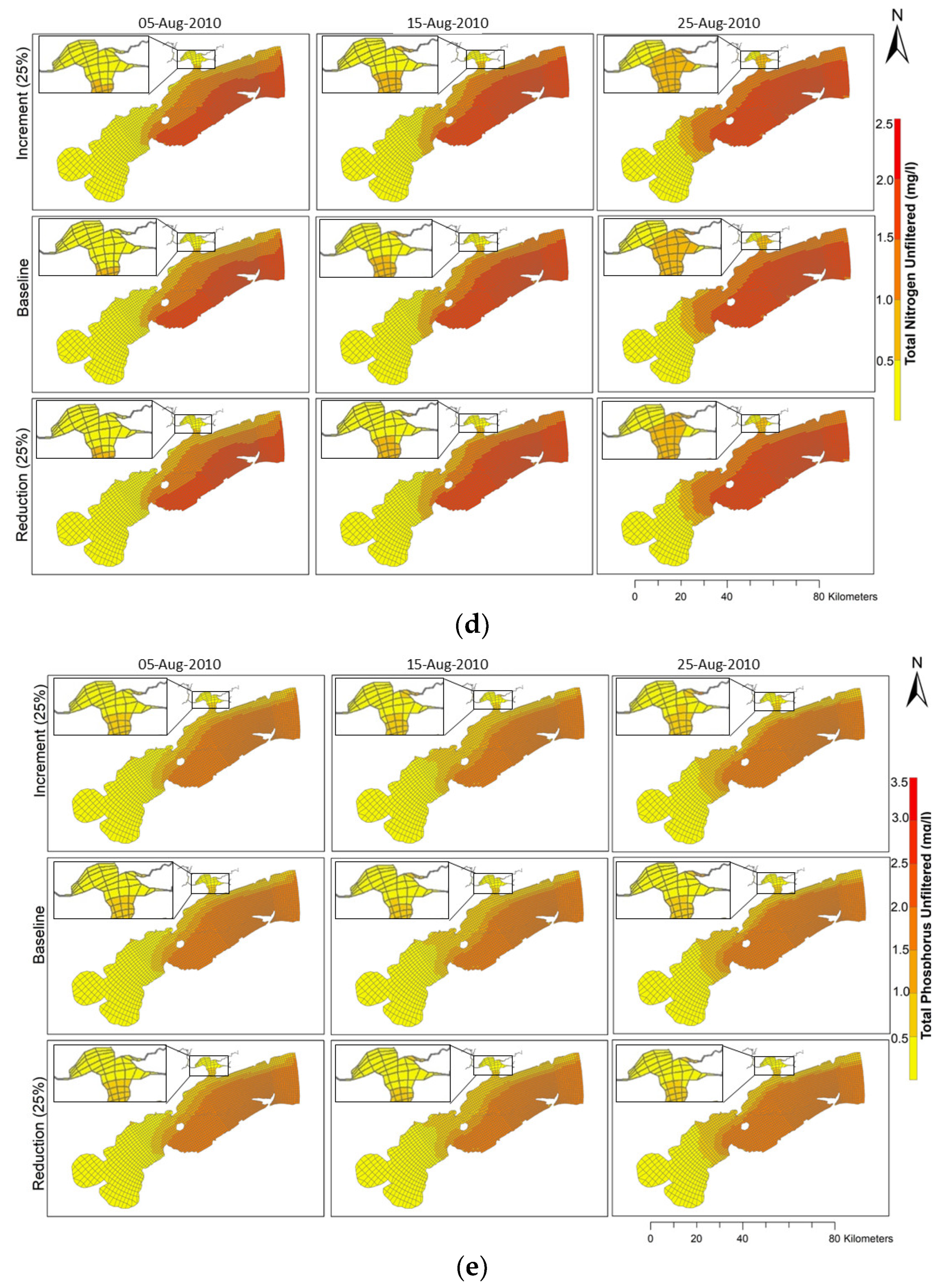
3. Results
3.1. Flow Assessment: Calibration and Validation
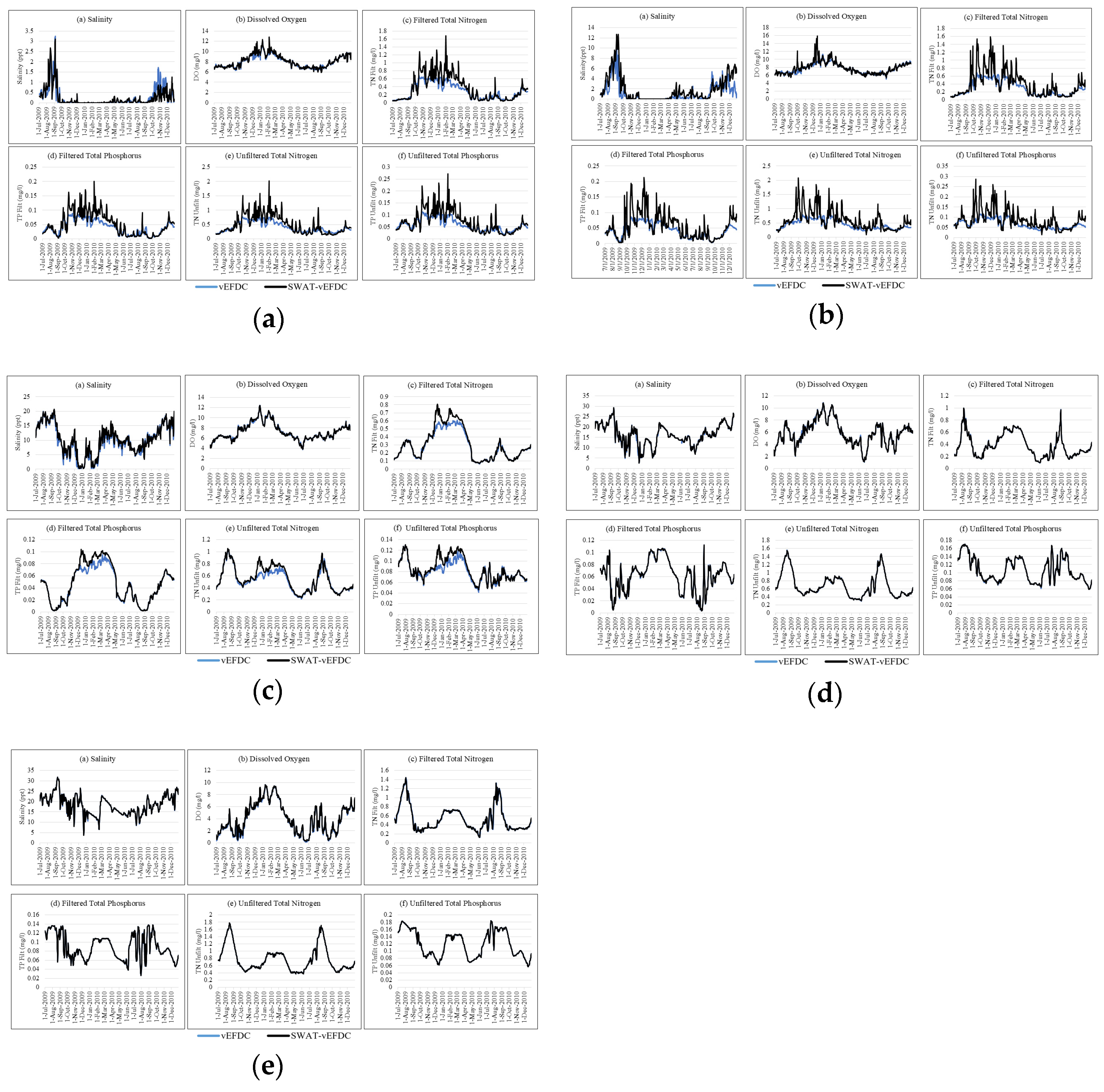
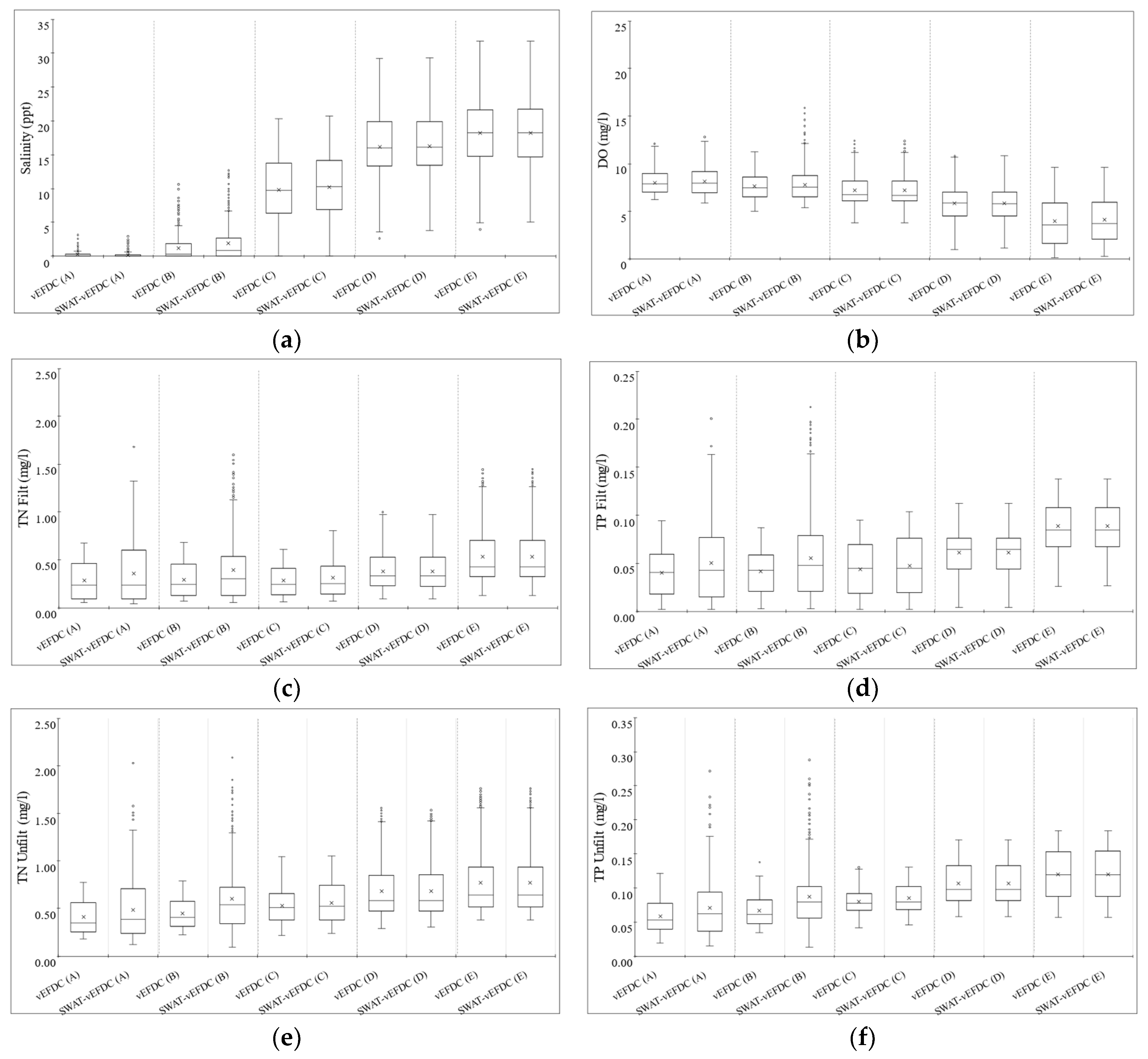
3.2. Water Quality Assessment
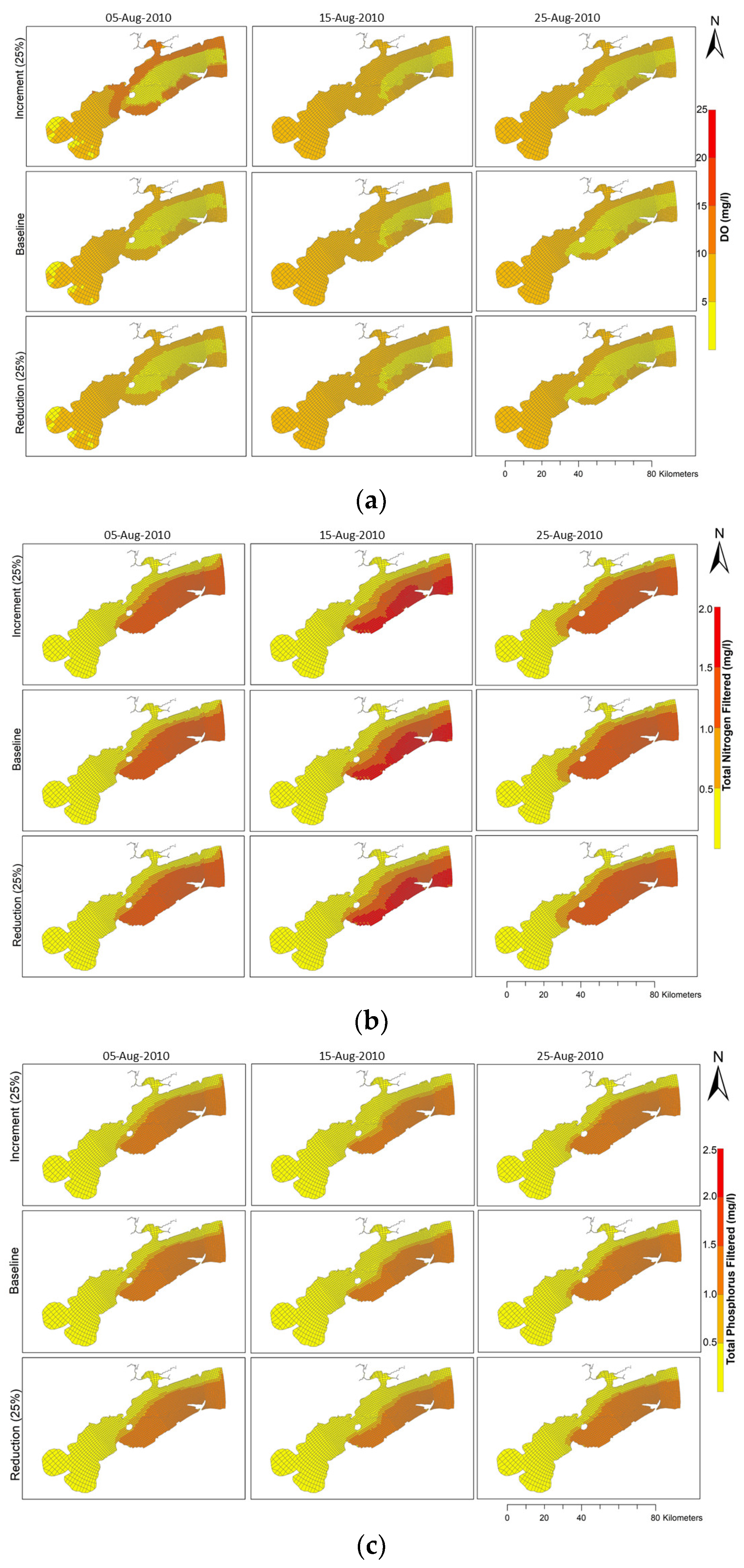
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jordan, S.J.; Benson, W.H. Introduction Sustainable Watersheds: Integrating Ecosystem Services and Public Health Supplementary Issue: Ecosystem Services and Environmental Health. Environ. Health Insights 2015, 9, EHI-S19586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshesha, T.W.; Wang, J.; Melaku, N.D. Modelling Spatiotemporal Patterns of Water Quality and Its Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystem in the Cold Climate Region of Alberta, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.B.K.; Long, W.; Zhang, X.; Wood, R.J.; Murtugudde, R. Predicting Dissolved Oxygen in the Chesapeake Bay: Applications and Implications. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhusal, A.; Ghimire, A.B.; Thakur, B.; Kalra, A. Evaluating the Hydrological Performance of Integrating PCSWMM and NEXRAD Precipitation Product at Different Spatial Scales of Watersheds. Model. Earth Syst. Env. 2023, 9, 4251–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, P.S.; Kwon, H.-H.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, J.-H. Modeling, Challenges, and Strategies for Understanding Impacts of Climate Extremes (Droughts and Floods) on Water Quality in Asia: A Review. Env. Res. 2023, 225, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flipo, N.; Gallois, N.; Schuite, J. Regional Coupled Surface–Subsurface Hydrological Model Fitting Based on a Spatially Distributed Minimalist Reduction of Frequency Domain Discharge Data. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2023, 16, 353–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, U.; Bhusal, A.; Babu Ghimire, A.; Shin, S. Comparing HEC-HMS, PCSWMM, and Random Forest Models for Rainfall-Runoff Evaluation to Extreme Flooding Events. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2023: Adaptive Planning and Design in an Age of Risk and Uncertainty–Selected Papers from World Environmental and Water Resources Congress, Henderson, NV, USA, 21–24 May 2023; pp. 1250–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wei, X.; Hao, L.; Sanchis, M.G.; Hou, Y.; Yousefpour, R.; Tang, R.; Zhang, Z. Forest Hydrology Modeling Tools for Watershed Management: A Review. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 530, 120755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpanelli, A.; Paris, A.; Sichangi, A.W.; O’Loughlin, F.; Papa, F. Water Resources in Africa: The Role of Earth Obser vation Data and Hydrodynamic Modeling to Derive River Discharge. Surv. Geophys. 2022, 44, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Jun, S.M.; Song, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Kang, M.S. Application of the SWAT-EFDC Linkage Model for as sessing Water Quality Management in an Estuarine Reservoir Separated by Levees. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Jun, S.M.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.; Kwak, J.; Kang, M.S. Development of a Framework for Evaluating Water Quality in Estuarine Reservoir Based on a Resilience Analysis Method. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 62, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Hwang, S.; Lee, H.; Kwak, J.; Song, J.H.; Jun, S.M.; Kang, M.S. Impact Assessment of Water-Level Management on Water Quality in an Estuary Reservoir Using a Watershed-Reservoir Linkage Model. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 280, 108234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, Z.; Ding, X.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, D.Q. Research on Water Environmental Capacity Accounting of the Yongzhou Section of Xiangjiang River Basin Based on the SWAT-EFDC Coupling Model. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2022, 13, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Javed, A.; Arhonditsis, G.B. An Ensemble Modeling Framework to Study the Effects of Climate Change on the Trophic State of Shallow Reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J.R. SWAT2000 User’s Manual VERSION 2000. 2005. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/145722143/SWAT2000-User-s-Manual (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Tetra Tech Inc. The Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code User Manual US EPA, Version 1.01; Tetra Tech Inc.: Fairfax, VA, USA, 2007.
- Tetra Tech Inc. The Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code Theory and Computation Volume 3: Water Quality Module; Tetra Tech Inc.: Fairfax, VA, USA, 2007; Volume 2, p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Mississippi Commission on Environmental Quality. Regulations for Surface Water Quality Criteria for Intrastate, Interstate, and Coastal Waters; MDEQ: Jackson, MI, USA, 2021; pp. 39289–40385.
- Armandei, M.; Linhoss, A.C.; Camacho, R.A. Hydrodynamic Modeling of the Western Mississippi Sound Using a Linked Model System. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetra Tech Inc. Visual EFDC 2.0 User’s Guide, A Grid Generation, Editing, Pre- and Post-Processing Tool for EFDC Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Modeling 2018; Tetra Tech Inc.: Fairfax, VA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bazgirkhoob, H.; Linhoss, A.; Armandei, M. A Numerical Tool for Dissolved Oxygen Simulation in the Western Mississippi Sound. J. Coast. Res. 2022, 38, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.; Parajuli, P.B. Best Management Practices Affect Water Quality in Coastal Watersheds. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large Area Hydrologic Modeling and Assessment Part 1: Model Development1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Xie, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, D.; Yang, S. Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Model: A Systemic Review. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 93, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.; Parajuli, P.B.; To, F. Comparison of Flood Frequency at Different Climatic Scenarios in Forested Coastal Watersheds. Climate 2023, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venishetty, V.; Parajuli, P.B.; To, F. Assessing the Effect of Spatial Variation in Soils on Sediment Loads in Yazoo River Watershed. Hydrology 2023, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venishetty, V.; Parajuli, P.B. Assessment of BMPs by Estimating Hydrologic and Water Quality Outputs Using SWAT in Yazoo River Watershed. Agriculture 2022, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, W.; Srinivasan, R.; Pérez-Miñana, E.; Willcock, S.P.; Quintero, M. Using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to Model Ecosystem Services: A Systematic Review. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Yao, H.; Chen, Y. A Coupled Modeling Approach to Evaluate Nitrogen Retention within the Shanmei Reservoir Watershed, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 166, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, P.B.; Risal, A. Evaluation of Climate Change on Streamflow, Sediment, and Nutrient Load at Watershed Scale. Climate 2021, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C. SWAT-CUP 2012: SWAT Calibration and Uncertainty Programs—A User Manual; Eawag: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 106. [Google Scholar]
- Saline Water and Salinity|U.S. Geological Survey. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/special-topics/water-science-school/science/saline-water-and-salinity (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Tang, X.; Xie, G.; Deng, J.; Shao, K.; Hu, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, G. Effects of Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities on Lake Environmental Dynamics: A Case Study in Lake Bosten Catchment, NW China. J. Env. Manag. 2022, 319, 115764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesh, I.V.; Khlebovich, V.V. Principal Processes within the Estuarine Salinity Gradient: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 61, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Peng, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H. Effects of Dissolved Oxygen and Nutrient Loading on Phosphorus Fluxes at the Sediment–Water Interface in the Hai River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 130, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Han, X.; Brookes, J.D.; Qin, B. High Probability of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Co-Limitation Occurring in Eutrophic Lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, W.H. Recent Advances in Information and Communications Technology (ICT) and Sensor Technology for Monitoring Water Quality. Water 2020, 12, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P.; Gitau, M.W.; Member, A.; Moriasi, D.N. Hydrologic and Water Quality Models: Performance Measures and Evaluation Criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.; Jiang, K.; Chen, X.; Li, H. Comprehensive Study on Parameter Sensitivity for Flow and Nutrient Modeling in the Hydrological Simulation Program Fortran Model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20982–20994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Her, Y.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Yu, X. Quantifying the Contribution of External Loadings and Internal Hydrodynamic Processes to the Water Quality of Lake Okeechobee. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
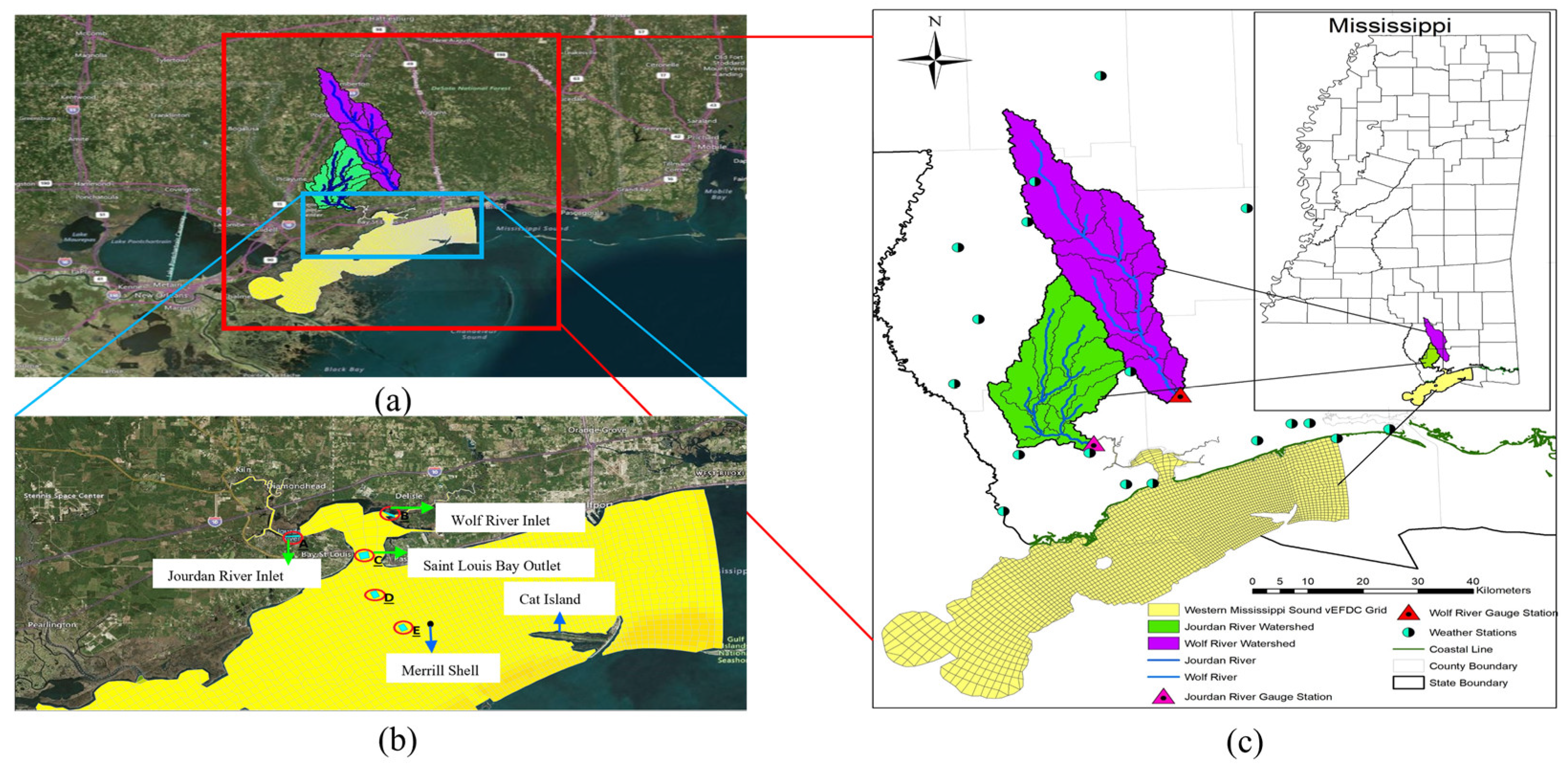




| S. No. | Data | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Elevation Data: Digital Elevation Model (DEM) (30 m × 30 m) (2020) | United States Geological Survey (USGS) (https://apps.nationalmap.gov/viewer/) (accessed on 4 October 2022) |
| 2 | Land-use and Land-cover Data: Cropland Data Layer (CDL) (2010) | United States Department of Agriculture-National Agricultural Statistics Service (USDA-NASS) (https://nassgeodata.gmu.edu/CropScape/) (accessed on 4 October 2022) |
| 3 | Soil Data: USSURGO (2020) | United States Soil Survey Geographic Database (US-SSURGO) SWAT-USSURGO (https://swat.tamu.edu/data/) (accessed on 4 October 2022) |
| 4 | Weather Data: NOAA (1995–2010) Precipitation, Maximum Temperature, Minimum Temperature | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) SWAT—Climate Data (https://swat.tamu.edu/data/) (accessed on 4 October 2022) |
| 5 | Discharge Data: -USGS 02481660 (2002–2005) (Jourdan River Nr Bay St Louis) -USGS 02481510 (1997–2010) (Wolf River Nr Landon) | United States Geological Survey (USGS) (https://waterdata.usgs.gov/ms/nwis/) (accessed on 5 October 2022) |
| Location | Salt | DO | TN Filt | TP Filt | TN Unfilt | TP Unfilt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | NSE | R2 | NSE | R2 | NSE | R2 | NSE | R2 | NSE | R2 | NSE | |
| A | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.32 | 0.82 | 0.23 | 0.76 | −0.3 | 0.75 | −0.3 |
| B | 0.76 | 0.39 | 0.76 | 0.57 | 0.75 | − 0.35 | 0.71 | −0.6 | 0.54 | −2.4 | 0.50 | −2.3 |
| C | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1 | 1 | 0.97 | 0.9 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.9 | 0.89 | 0.76 |
| D | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| E | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhattarai, S.; Parajuli, P.; Linhoss, A. Integrated Modeling Approach to Assess Freshwater Inflow Impact on Coastal Water Quality. Water 2024, 16, 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213012
Bhattarai S, Parajuli P, Linhoss A. Integrated Modeling Approach to Assess Freshwater Inflow Impact on Coastal Water Quality. Water. 2024; 16(21):3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213012
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhattarai, Shreeya, Prem Parajuli, and Anna Linhoss. 2024. "Integrated Modeling Approach to Assess Freshwater Inflow Impact on Coastal Water Quality" Water 16, no. 21: 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213012
APA StyleBhattarai, S., Parajuli, P., & Linhoss, A. (2024). Integrated Modeling Approach to Assess Freshwater Inflow Impact on Coastal Water Quality. Water, 16(21), 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213012






