Assessment of Ecological Hazards in the Inaouen Wadi and Its Tributaries Using the Presence of Potentially Toxic Elements in Its Sediments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
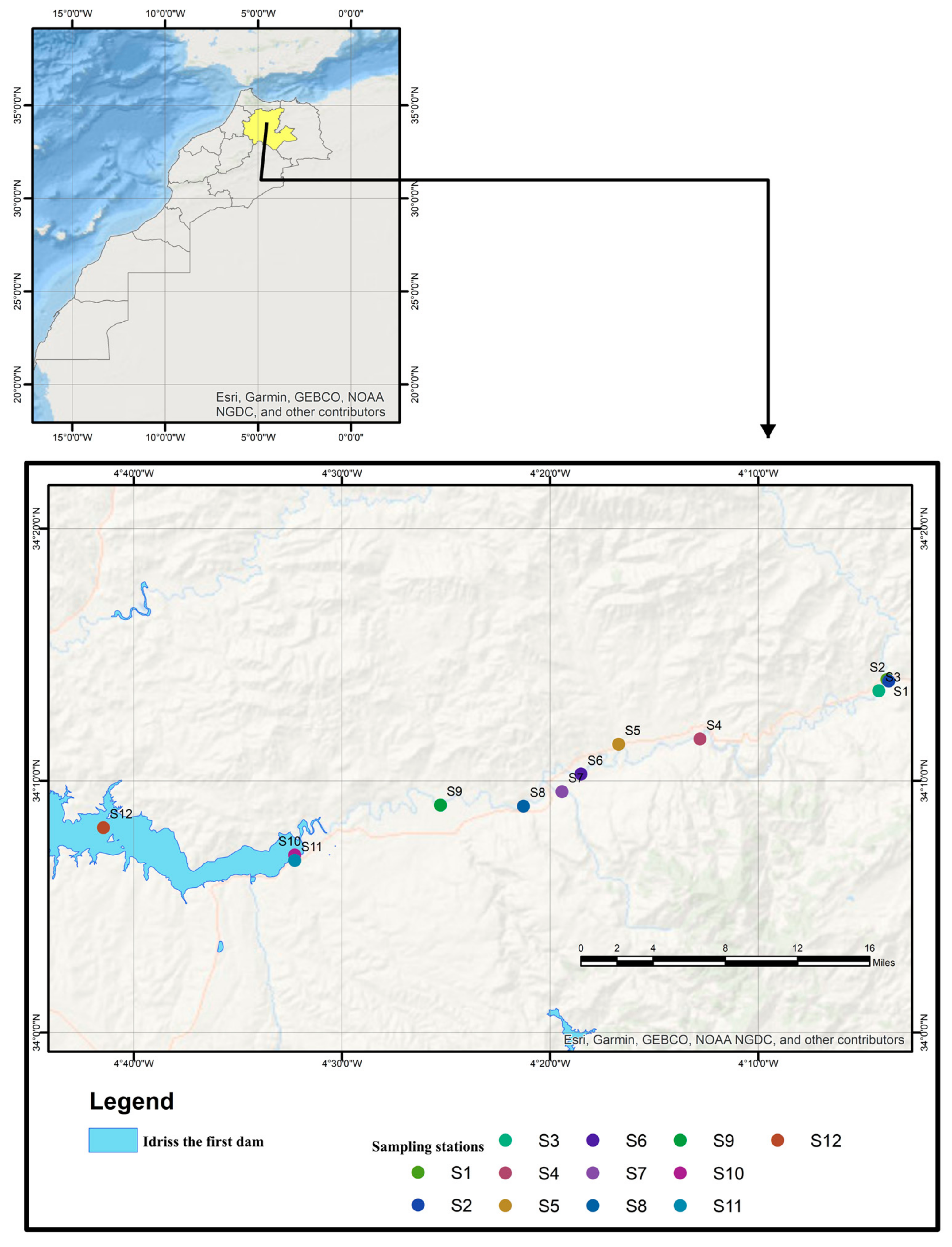
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Pre-Processing of Samples
2.3. Physicochemical Treatments and Analyses
2.4. Quality Indexes
2.4.1. The Enrichment Factor (EF) and Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
2.4.2. Ecological Hazard Factor (Eh), Potential Ecological Hazard Index (RI) and Modified Potential Ecological Risk Index (MRI)
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
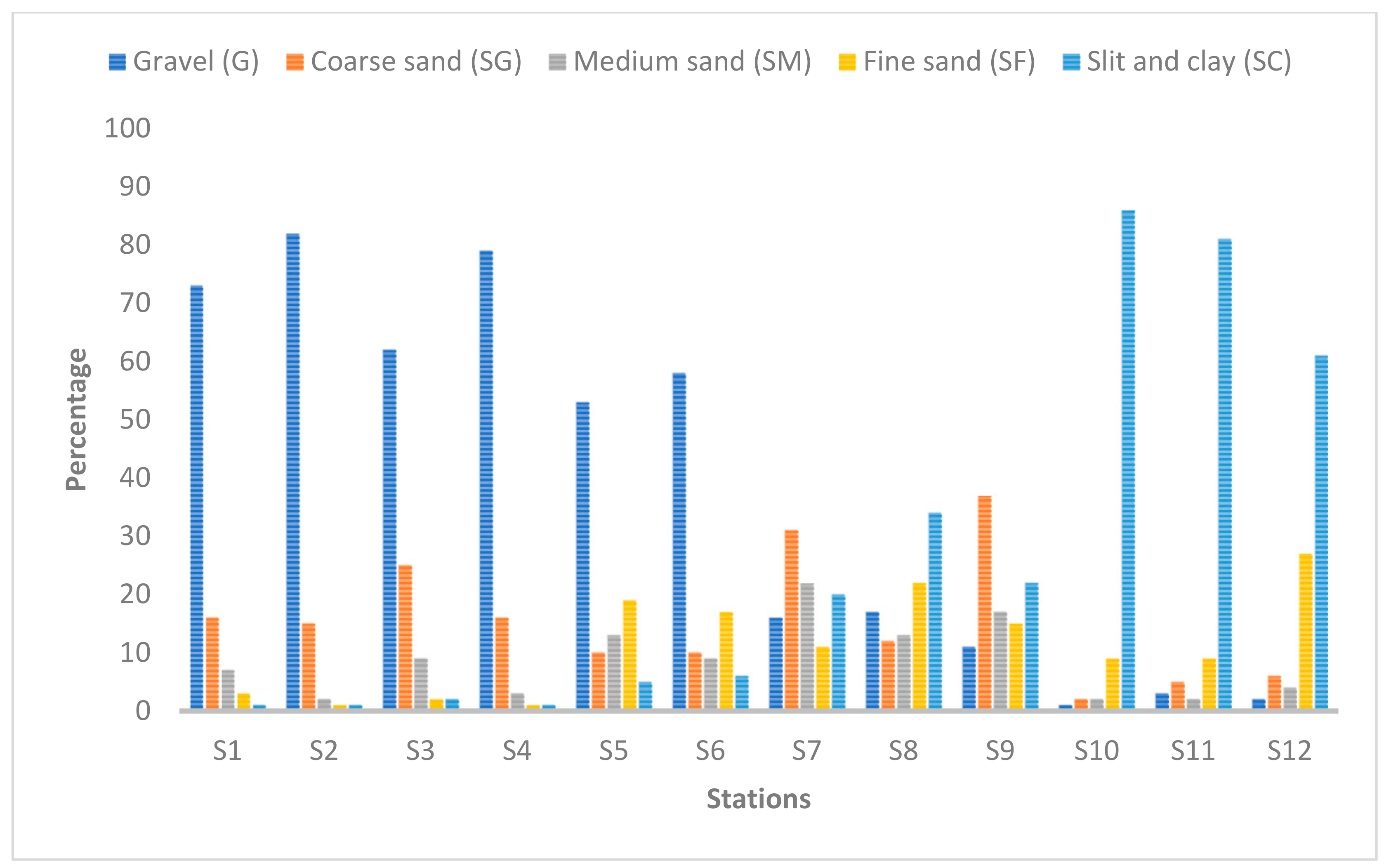
3.1. Sediment Grain Size
3.2. Trace Elements in Sediments
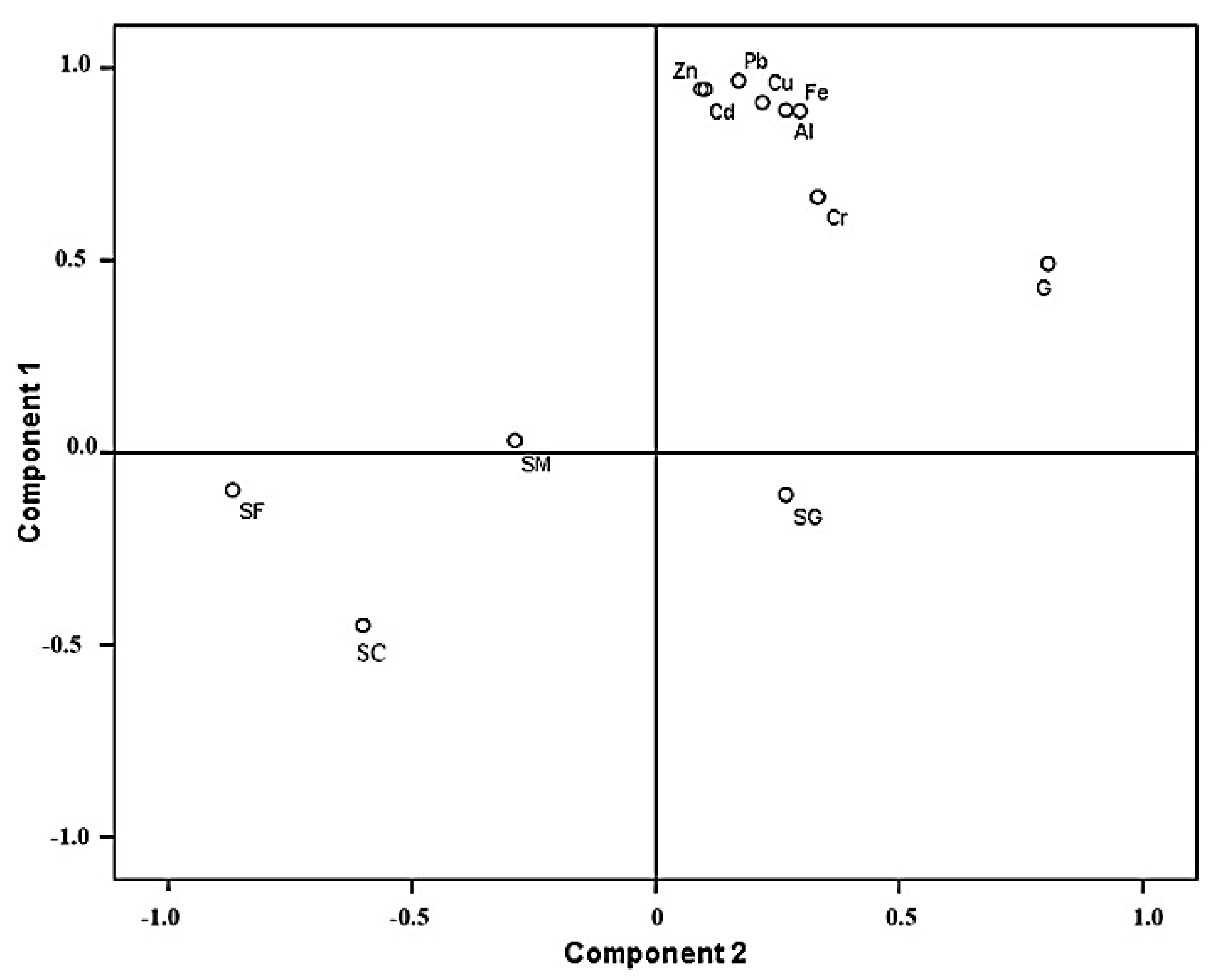
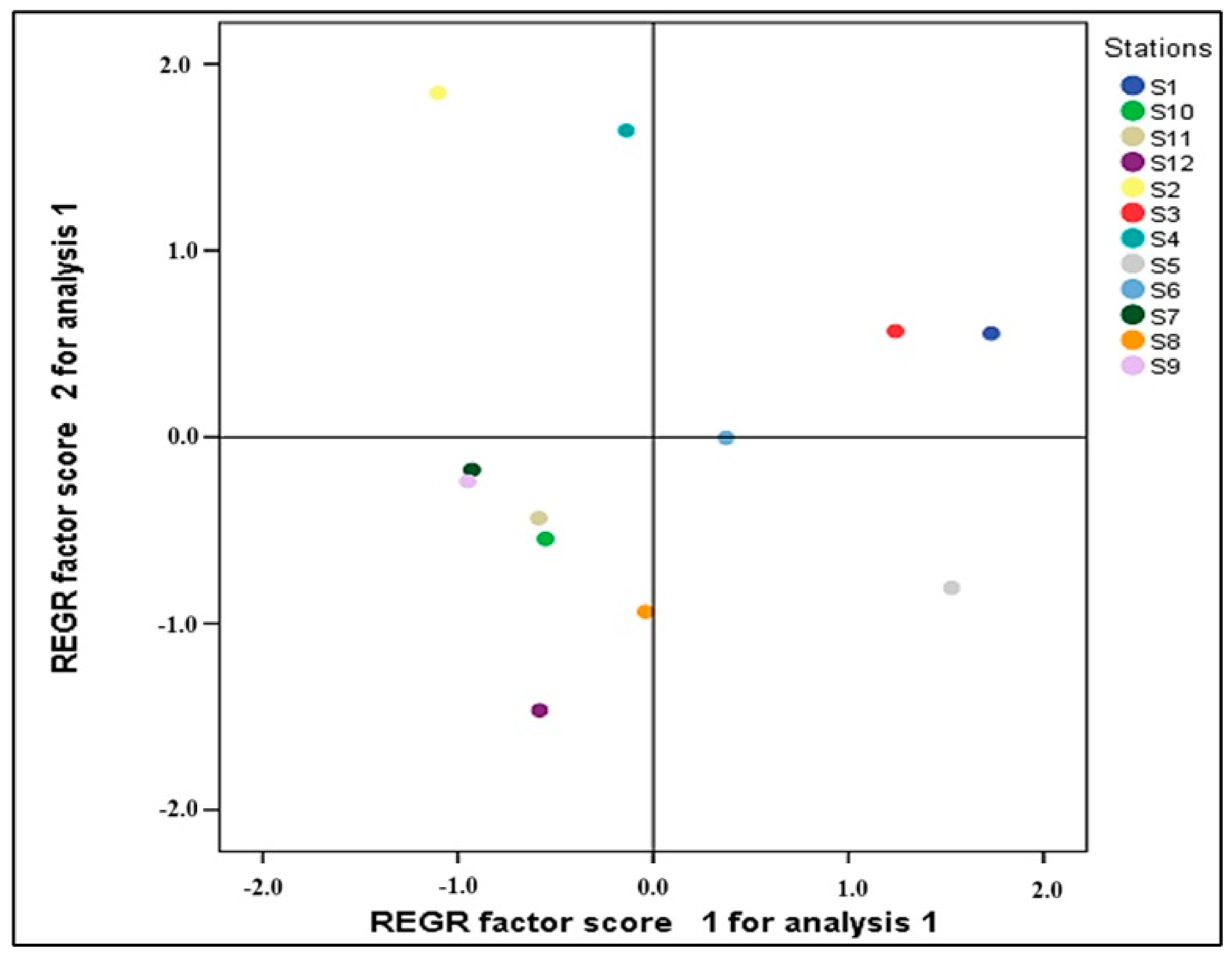
3.3. Statistical Analysis
3.4. Pollution Indexes and Ecological Hazards
3.4.1. The Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
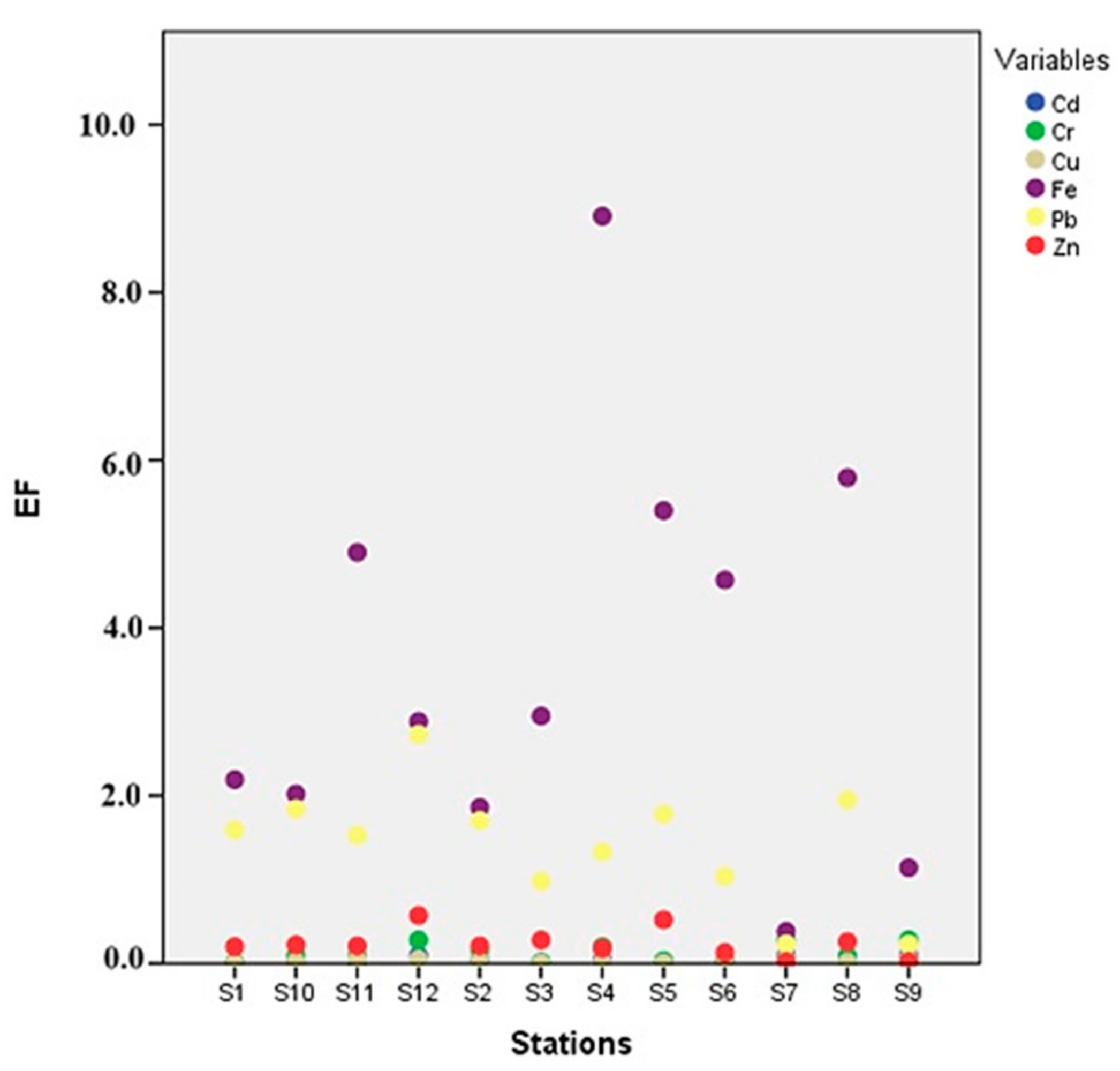
3.4.2. The Enrichment Factor (EF)
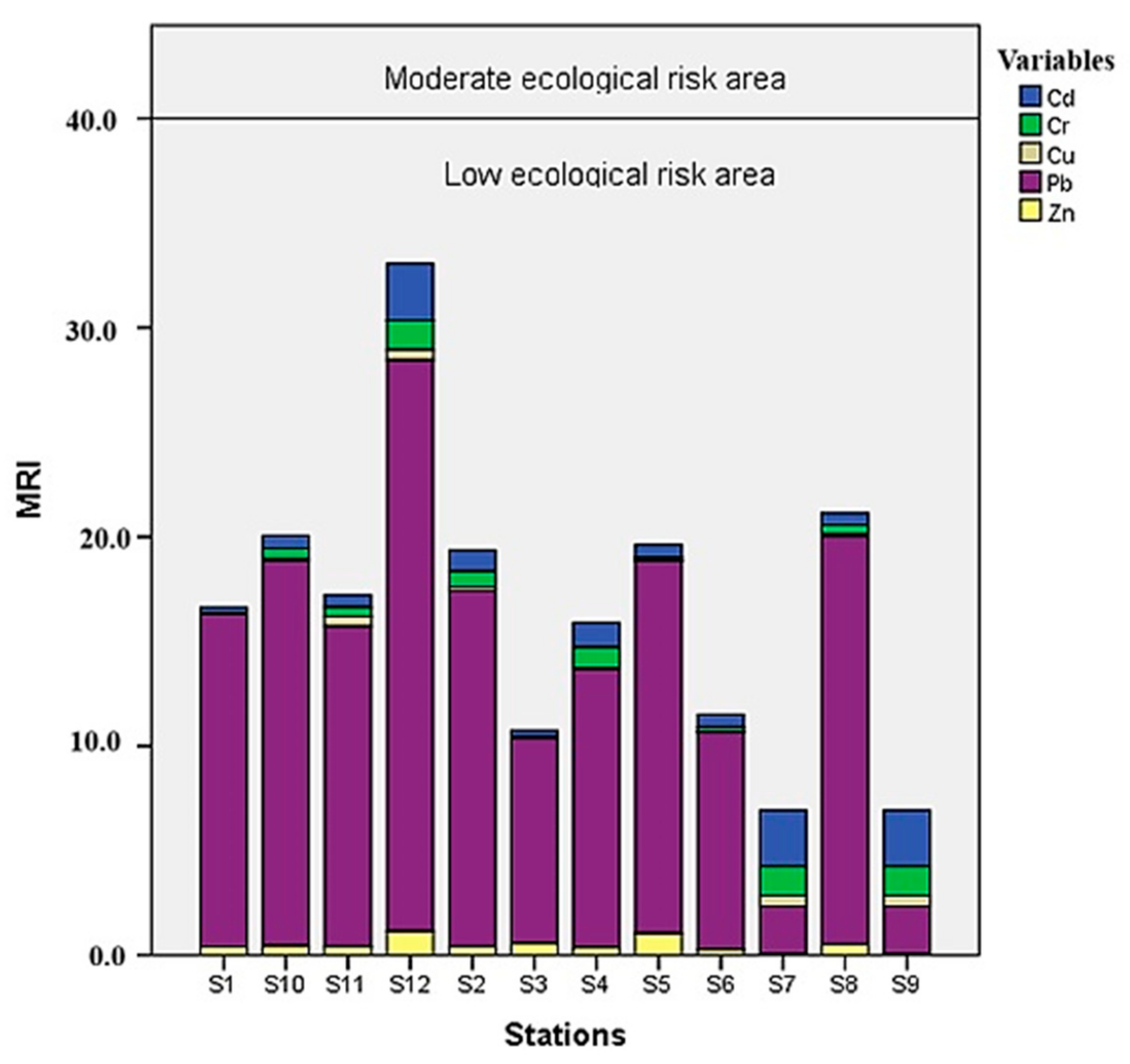
3.4.3. Ecological Hazard Assessment by Potential Ecological Hazard Index and Modified Potential Ecological Hazard Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Description of the Sampling Stations and Their Characteristics
| Presentation of the Stations | Geographic Coordinates | Description of the Stations | ||
| LATITUDE N | LONGITUDE W | |||
| S1 | Larbaa wadi | 34°13′58.841″ | 4°3′42.36″ | The blackish color of the water, along with its unpleasant odor and visual nuisance, indicated the influence of wastewater discharge. Additionally, the presence of solid waste accumulated at the edge of the watercourse further exacerbates environmental impact. |
| S2 | Lahdar wadi | 34°14′3.659″ | 4°3′50.099″ | The right bank is fed by tributaries that collect runoff from the pre-Rifian hills and are characterized by Jurassic marl and limestone formations. |
| S3 | Upstream of Inaouene wadi | 34°13′40.942″ | 4° 4′7.528″ | Upstream of the Inaouene wadi, the waters exhibit a blackish color, accompanied by olfactory and visual nuisances. |
| S4 | Inaouene wadi located in Ghiata Al Gharbia | 34°11′57.611″ | 4°12′24.865″ | The presence of agricultural activity was used to estimate the degree of self-purification of the watercourses. |
| S5 | Amlil wadi | 34°11′17.293″ | 4°16′39.879″ | The right bank of the Inaouene wadi, characterized by a blackish water color and olfactory and visual nuisance, helped to detect the influence of wastewater discharge and was affected by uncontrolled dumping. |
| S6 | Inaouene wadi | 34°11′16.967″ | 4°16′39.88″ | The detection of wastewater discharge helped estimate the degree of self-purification of the watercourses. |
| S7 | Zirg wadi | 34°09′54.2″ | 4°20′24.5″ | Presence of agricultural activity. |
| S8 | Inaouene wadi after Zirg | 34°09′54.5″ | 4°20′24.4″ | The degree of self-purification of the watercourses was estimated. |
| S9 | Bouhlou wadi | 34°07′56.4″ | 4°24′33.8″ | The tributary of the left bank of the Inaouene wadi, fed by the Tazekka massif and the limestone of the Middle Atlas, is little affected by anthropic and agricultural factors and has a bottom made up of coarse gravel. |
| S10 | Metmata wadi | 34°07′00.6″ | 4°32′17.4″ | This region is a tributary of the left bank of the Inaouene wadi and was little affected by agricultural and anthropic activity. |
| S11 | Downstream of Inaouene wadi sidi abd jlil | 34°08′16.2″ | 4°30′09.6″ | The color and odor of the water seemed to be acceptable. |
| S12 | Idriss 1st dam | 34°7′31.989″ | 4°39′50.032″ | All parameters seemed to be acceptable. |
References
- Chedadi, M.; Bassouya, M.; Agour, A.; Asmi, H.E.; Merzouki, M.; Bari, A. Assessment of sediments contamination by potential toxic elements, in relationships with the physicochemical characteristics of Moroccan Oued Fez river. Sci. Afr. 2023, 22, e01949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobi, K.K.; Nayek, S.; Gope, M.; Rai, A.K.; Saha, R. Sources evaluation, ecological and health risk assessment of potential toxic metals (PTMs) in surface soils of an industrial area, India. Env. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 4159–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholkappian, M.; Ravisankar, R.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Jebakumar, J.P.P.; Kanagasabapathy, K.; Prasad, M.; Satapathy, K. Assessing heavy metal toxicity in sediments of Chennai Coast of Tamil Nadu using Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (EDXRF) with statistical approach. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayzoun, H.; Garnier, C.; Durrieu, G.; Lenoble, V.; Le Poupon, C.; Angeletti, B.; Ouammou, A.; Mounier, S. Organic carbon, and major and trace element dynamic and fate in a large river subjected to poorly-regulated urban and industrial pressures (Sebou River, Morocco). Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faouzi, J.; Bedoui, I.; Rezouki, S.; Moubchir, T.; Allali, A.; EloutassI, N.; Lahkimi, A. Vertical transfer of bacteriological and parasitological pollutants from irrigation water to soil and crops. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2023, 24, 93–103. Available online: https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/yadda/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-0ef0576d-5dd7-4d24-ab67-4db7b4207fa7 (accessed on 10 July 2024). [CrossRef]
- Moubchir, T.; Eloutassi, N.; Bendaoud, A.; Belkhiri, A.; Maai, M.; Moubchir, M.; Zahir, I. Heavy metals analysis and quality evaluation in drinking groundwater around an abandoned mine Area of Ouichane (Nador’s Province, Morocco). J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 118–127. Available online: https://bibliotekanauki.pl/articles/24201772.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Qiu, Y.-W. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals both in wild and mariculture food chains in Daya Bay, South China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezouki, S.; El-Haji, S.; Moubchir, T.; Faouzi, J.; Bendaoud, A.; Beniaich, G.; Allali, A.; Eloutassi, N. Evaluation of the impact of anthropic activities on the physico-chemical and microbiological parameters of the water of the wadi inaouene and its tributaries. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2023, 24, 282–294. Available online: https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/yadda/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-688757fd-6e59-42cf-8af8-e6108b4e6956 (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Volpe, M.; La Cara, F.; Volpe, F.; De Mattia, A.; Serino, V.; Petitto, F.; Zavalloni, C.; Limone, F.; Pellecchia, R.; De Prisco, P.; et al. Heavy metal uptake in the enological food chain. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, M.; Shirazy, A.; Shirazi, A.; Pour, A.B. Processing and interpretation of geochemical data for mineral exploration. In Geospatial Analysis Applied to Mineral Exploration; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 171–188. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323956086000044 (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Zhang, S.; Chen, B.; Du, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, H.; Wang, F. Distribution, assessment, and source of heavy metals in sediments of the Qinjiang River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z. Ecological and environmental risks of heavy metals in sediments in Dingzi Bay, South Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’guessan, Y.M.; Probst, J.L.; Bur, T.; Probst, A. Trace elements in stream bed sediments from agricultural catchments (Gascogne region, SW France): Where do they come from? Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2939–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral Pinto, M.M.S.; Silva, M.M.V.G.; Ferreira da Silva, E.A.; Dinis, P.A.; Rocha, F. Transfer processes of potentially toxic elements (PTE) from rocks to soils and the origin of PTE in soils: A case study on the island of Santiago (Cape Verde). J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 183, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Tueros, I.; Borja, A.; Belzunce, M.; Franco, J.; Solaun, O.; Valencia, V.; Zuazo, A. Maximum likelihood mixture estimation to determine metal background values in estuarine and coastal sediments within the European Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G. Determination of sediment metal background concentrations and enrichment in marine environments–a critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Mohan, D.; Singh, V.K.; Malik, A. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—A tributary of the Ganges, India. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leleyter, L.; Probst, J.-L. A New Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Speciation of Particulate Trace Elements in River Sediments. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1999, 73, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charriau, A.; Lesven, L.; Gao, Y.; Leermakers, M.; Baeyens, W.; Ouddane, B.; Billon, G. Trace metal behaviour in riverine sediments: Role of organic matter and sulfides. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, C.; Casas, J.M.; Rosas, H. Heavy metals and metalloids in sediments from the Llobregat basin, Spain. Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassimi, H.; Taleb, A.; Bouezmarni, M.; Karzazi, O.; Taleb, M.; Kherbeche, A.; Debbaut, V. The effect of the physicochemical conditions variations on the behavior of heavy metals trapped in polluted fluvial system sediments: The case of Oued Sebou, Morocco. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabdelkader, A.; Taleb, A.; Probst, J.; Belaidi, N.; Probst, A. Anthropogenic contribution and influencing factors on metal features in fluvial sediments from a semi-arid Mediterranean river basin (Tafna River, Algeria): A multi-indices approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, J.R.; Andrade, E.M.; Palácio, H.A.; Sales, M.M.; Maia, A.R. Influence of land use/occupation on water quality in the Trussu river valley, Ceará, Brazil. Rev. Ciência Agronômica 2017, 48, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Moubchir, T.; Faouzi, J.; Loukili, E.H.; Bendaoud, A.; Belkhiri, A.; Rezouki, S.; Eloutassi, N.; Zahir, I. Investigation of the Hydrochemistry Quality of the Ouichane Groundwater (Morocco) Using Multivariate Statistical Methods and Diagram Analysis. Moroc. J. Chem. 2024, 12, 734–746. [Google Scholar]
- Branchu, P.; Badin, A.L.; Bechet, B.; Eisenlohr, L.; Priol, T.L.; Marseille, F.; Trielli, E. Pollution D’origine Routière et Environnement de Proximité. VertigO-La Rev. Électronique En Sci. De L’environnement 2013, 15. Available online: https://journals.openedition.org/vertigo/12775 (accessed on 10 July 2024). [CrossRef]
- Lionard, E.; Coquery, M.; Lyon, I. Échantillonnage des Sédiments: Préparation d’un Essai Collaborative; Hal Inrae: Paris, France, 2013; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Montarges-Pelletier, E.; Jeanneau, L.; Faure, P.; Bihannic, I.; Barres, O.; Lartiges, B.S. The junction of Fensch and Moselle rivers, France; mineralogy and composition of river materials. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, Y.J.A.B.; Nascimento, C.W.A.D.; Biondi, C.M. Comparison of USEPA digestion methods to heavy metals in soil samples. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepel, E.A.; Stefansson, K.M.; Zoller, W.H. The enrichment of volatile elements in the atmosphere by volcanic activity: Augustine volcano 1976. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1978, 83, 6213–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinex, S.A.; Helz, G.R. Regional geochemistry of trace elements in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Environ. Geol. 1981, 3, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo J. 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- McLennan, S.M. Chapter 7. Rare Earth Elements in Sedimentary Rocks: Influence of Provenance and Sedimentary Processes. In Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 189, pp. 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K.; Giesy, J.; Jones, P. Probabilistic risk assessment of agrochemicals in the environment. Crop. Prot. 2000, 19, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-N.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Zeng, G.-M.; Jiang, M.; Liang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yin, J.; Huang, H.-J.; Liu, Z.-F.; Jiang, H.-W. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port based on modified potential ecological risk index. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzougagh, B.; Meshram, S.G.; Baamar, B.; Dridri, A.; Boudad, L.; Sadkaoui, D.; Mimich, K. Relationship between landslide and morpho-structural analysis: A case study in Northeast of Morocco. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Belem, T.; Mbonimpa, M. Mécanismes de rétention des métaux lourds en phase solide: Cas de la stabilisation des sols contaminés et des déchets industriels. VertigO-La Rev. Électronique En Sci. De L’environnement 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, B.A.; Callender, E.; Axtmann, E.V. Effects of colloids on metal transport in a river receiving acid mine drainage, upper Arkansas River, Colorado, U.S.A. Appl. Geochem. 1995, 10, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, H.A.; Liberati, M.R.; Huang, C.P. Competitive Adsorption of Heavy Metals by Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 1986, 15, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geesey, G.; Borstad, L.; Chapman, P. Influence of flow-related events on concentration and phase distribution of metals in the lower Fraser River and a small tributary stream in British Columbia, Canada. Water Res. 1984, 18, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, N.T.; Tabatabai, M.A. Effect of cropping systems on adsorption of metals by soils: II. Effect of pH. Soil Sci. 1992, 153, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbouih, H.; Nassali, H.; Ei Abdellaoui, A.; Srhiri, A. Speciation chimique du zinc et du cuivre dans les sediments du lac Fouarat au Maroc. J. Soc. Chim. De Tunis. 2001, 4, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, P.G.C. Associate Committee on Scientific. Biologically Available Metals in Sediments; National Research Council of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1988; Volume 27694. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, M.; Nyary, I.; Toth, L. The microelement content of some submerged and floating aquatic plants. Acta. Bot. Hung. 1984, 30, 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- Rezouki, S.; Allali, A.; Touati, N.; Mansouri, D.; Eloutassi, N.; Fadli, M. Spatio-temporal evolution of the physico-chemical parameters of the Inaouen wadi and its tributaries. J. Chem. 2021, 9, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yongming, H.; Peixuan, D.; Junji, C.; Posmentier, E.S. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 355, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C. Riverine Composition and Estuarine Geochemistry of Particulate Metals in China—Weathering Features, Anthropogenic Impact and Chemical Fluxes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 1051–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Liu, E.; Zhang, E.; Li, K.; Shen, J. Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China. CATENA 2016, 145, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Y. Heavy metal pollution in reservoirs in the hilly area of southern China: Distribution, source apportionment and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajjami, S.; Abriak, N.-E.; Souabi, S.; El Alami, M. +Study of Metallic Contamination of Oued Sebou Sediments, Morocco. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaraj, M.; Benaabidate, L.; Mesnage, V. Assessment of inaouene river pollution for potable water supply, Northern Morocc. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 68–80. Available online: https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/baztech/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-7a14f851-1dc6-4bf7-afbc-0d81c8bf73f9 (accessed on 3 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Iqbal, J.; Akhter, G.; Shah, M.H. Fractionation, bioavailability, contamination and environmental risk of heavy metals in the sediments from a freshwater reservoir, Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H. Spatial variation of heavy metal contamination in the riparian sediments after two-year flow regulation in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.A., Jr. Sediment quality criteria in use around the world. Limnology 2002, 3, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badassan, T.E.; Avumadi, A.M.; Ouro-Sama, K.; Gnandi, K.; Jean-Dupuy, S.; Probst, J.L. Geochemical composition of the Lomé lagoon sediments, Togo: Seasonal and spatial variations of major, trace and rare earth element concentrations. Water 2020, 12, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvier, A.; Leleyter, L.; Probst, A.; Probst, J.-L.; Prunier, J.; Pourcelot, L.; Le Roux, G.; Lemoine, M.; Reinert, M.; Baraud, F. Why comparison between different chemical extraction procedures is necessary to better assess the metals availability in sediments. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 225, 106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leleyter, L.; Rousseau, C.; Biree, L.; Baraud, F. Comparison of EDTA, HCl and sequential extraction procedures, for selected metals (Cu, Mn, Pb, Zn), in soils, riverine and marine sediments. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 116–117, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baize, D. Teneurs totales en éléments traces métalliques dans les sols (France): Références et stratégies d’interprétation. Programme ASPITET 1997, 1–410. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S.; Lai, M.; Lin, C. Influence of solution acidity and CaCl2 concentration on the removal of heavy metals from metal-contaminated rice soils. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Site | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % of Metal in Carbonate and Exchangeable Fractions (A) | % Pb | 50 | 65 | 50 | 59 | 67 | 46 | 64 | 57 | 48 | 55 | 66 | 45 |
| % Cd | 83 | 50 | 63 | 67 | 67 | 60 | 40 | 71 | 50 | 40 | 69 | 67 |
| % of Metal in the Carbonate and Exchangeable Fraction (A) | ∂ |
|---|---|
| >50 | 1.60 |
| 31–50 | 1.40 |
| 11–30 | 1.20 |
| 1–10 | 1.00 |
| <1 | 1.00 |
| Potential Toxic Elements (mg kg−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Cu | Pb | Zn | Fe | Reference | |
| World’s rivers | 0.0003 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.11 | - | [42] |
| Sebou wadi | 0.00001–0.011 | 0.47–77.5 | 12.5–625 | 0.5–19 | 30–1250 | 19–30.300 | [43] |
| Moulouya wadi | 0.19–0.8 | - | 19.4–27.88 | 19.2–710 | 81–949 | - | [44] |
| Khmiss wadi | 0.05–0.67 | 4.15–67.5 | 31–87 | 10–57 | 41.25–200 | 2087–7800 | [45] |
| Rdom wadi | 0–0.01 | 1–1.9 | 0.2–2.1 | 1.2–2.7 | 1–3.8 | 178–468 | [46] |
| Tislit-Talsint wadi | 0.35 | 33.30 | 58.54 | 85.84 | 142.65 | 39.390 | [47] |
| Sebou wadi | - | 77.93–119 | - | - | 79.27–121 | 33.330–44.190 | [48] |
| Hassar wadi | 1.5–17.4 | 107.7–258.9 | 165.4–326.6 | 15.03–148.2 | 458.02–1768.9 | 1700–2500 | [49] |
| Inaouene wadi | 90–0.1 | 10–113 | 1.1–11 | 1–7012 | 2.1–1900 | 82–19.905 | Present study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezouki, S.; Moubchir, T.; El Hanafi, L.; Flouchi, R.; Zahir, I.; Alzain, M.N.; El Guerrouj, B.; Noman, O.; Shahat, A.A.; Allali, A. Assessment of Ecological Hazards in the Inaouen Wadi and Its Tributaries Using the Presence of Potentially Toxic Elements in Its Sediments. Water 2024, 16, 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202936
Rezouki S, Moubchir T, El Hanafi L, Flouchi R, Zahir I, Alzain MN, El Guerrouj B, Noman O, Shahat AA, Allali A. Assessment of Ecological Hazards in the Inaouen Wadi and Its Tributaries Using the Presence of Potentially Toxic Elements in Its Sediments. Water. 2024; 16(20):2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202936
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezouki, Sanae, Tarik Moubchir, Laila El Hanafi, Rachid Flouchi, Ilham Zahir, Mashail N. Alzain, Bouchra El Guerrouj, Omar Noman, Abdelaaty A. Shahat, and Aimad Allali. 2024. "Assessment of Ecological Hazards in the Inaouen Wadi and Its Tributaries Using the Presence of Potentially Toxic Elements in Its Sediments" Water 16, no. 20: 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202936
APA StyleRezouki, S., Moubchir, T., El Hanafi, L., Flouchi, R., Zahir, I., Alzain, M. N., El Guerrouj, B., Noman, O., Shahat, A. A., & Allali, A. (2024). Assessment of Ecological Hazards in the Inaouen Wadi and Its Tributaries Using the Presence of Potentially Toxic Elements in Its Sediments. Water, 16(20), 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202936







