The Performance and Mechanism of Solvothermal Synthesis of a Ca-Fe-La Composite for Enhanced Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
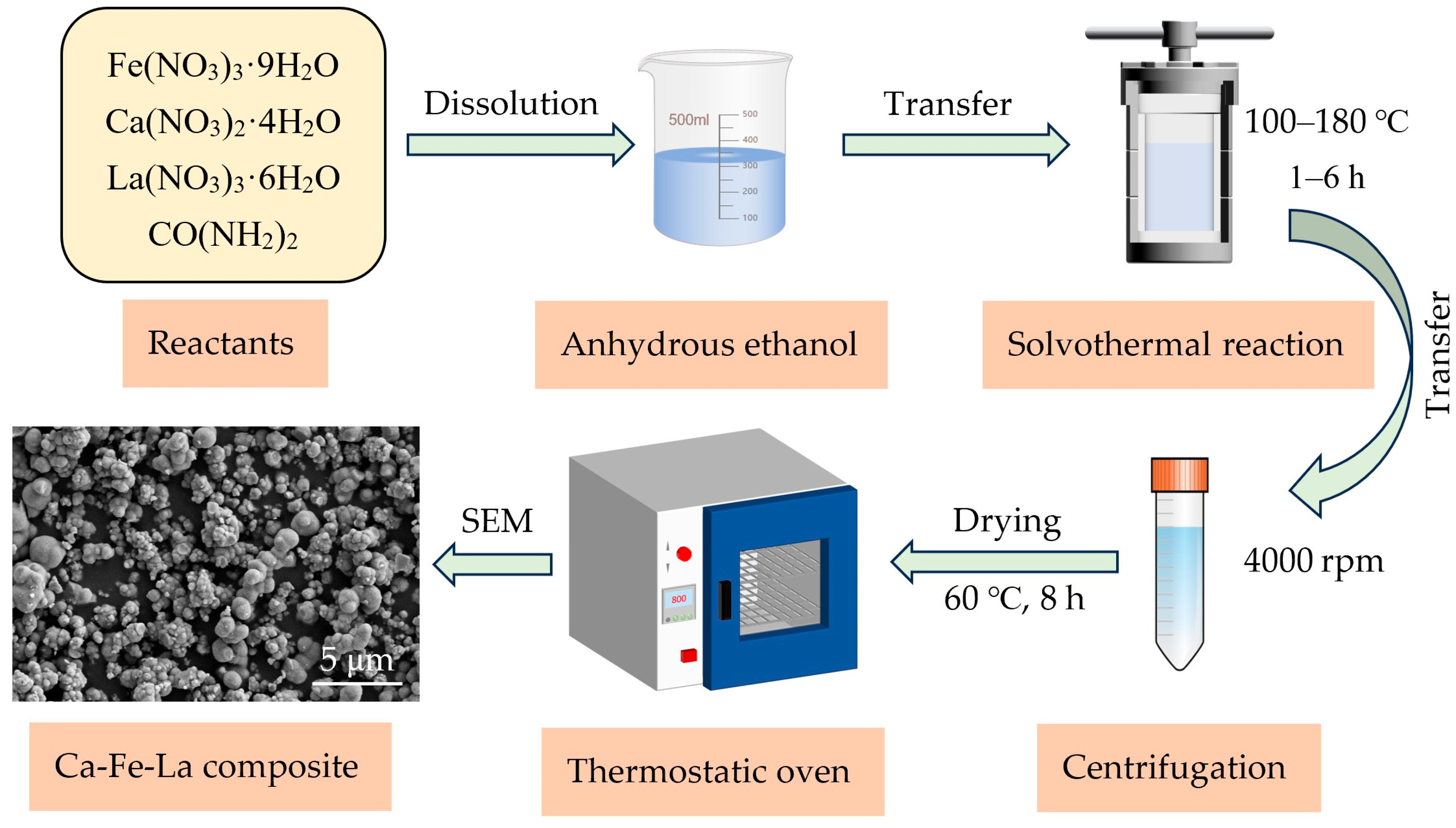
2.1. Adsorbent Preparation
2.2. Batch Experiments
2.3. Kinetic and Isotherm Studies
2.4. Error Analysis
2.5. Adsorbent Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
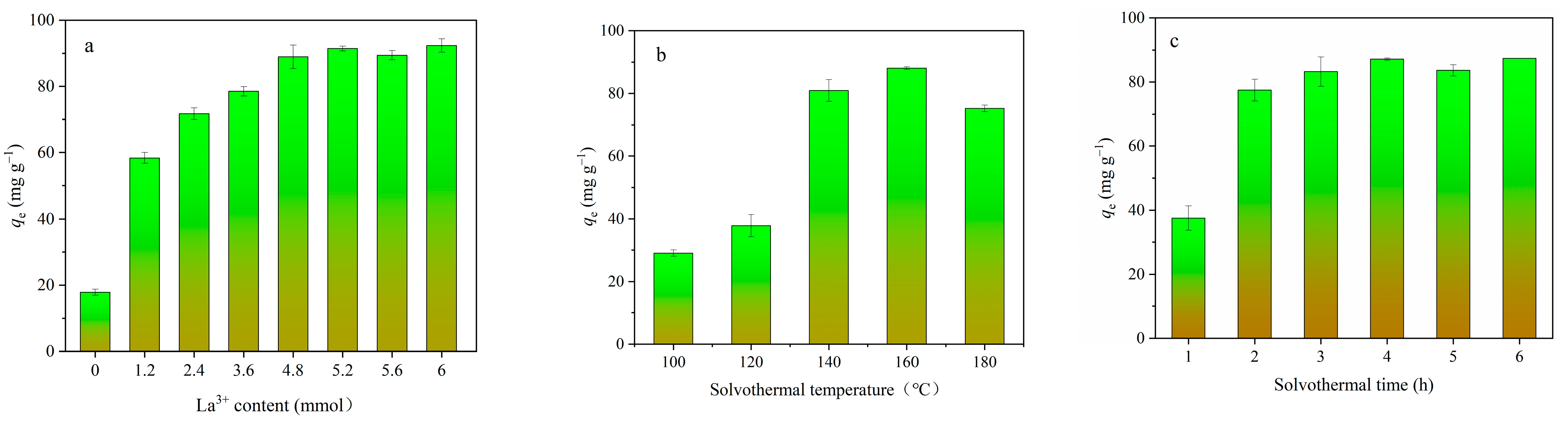
3.1. Optimization of the Ca-Fe-La Composite
3.2. Physical Properties of Ca-Fe and Ca-Fe-La Composites
3.3. Adsorption Processes
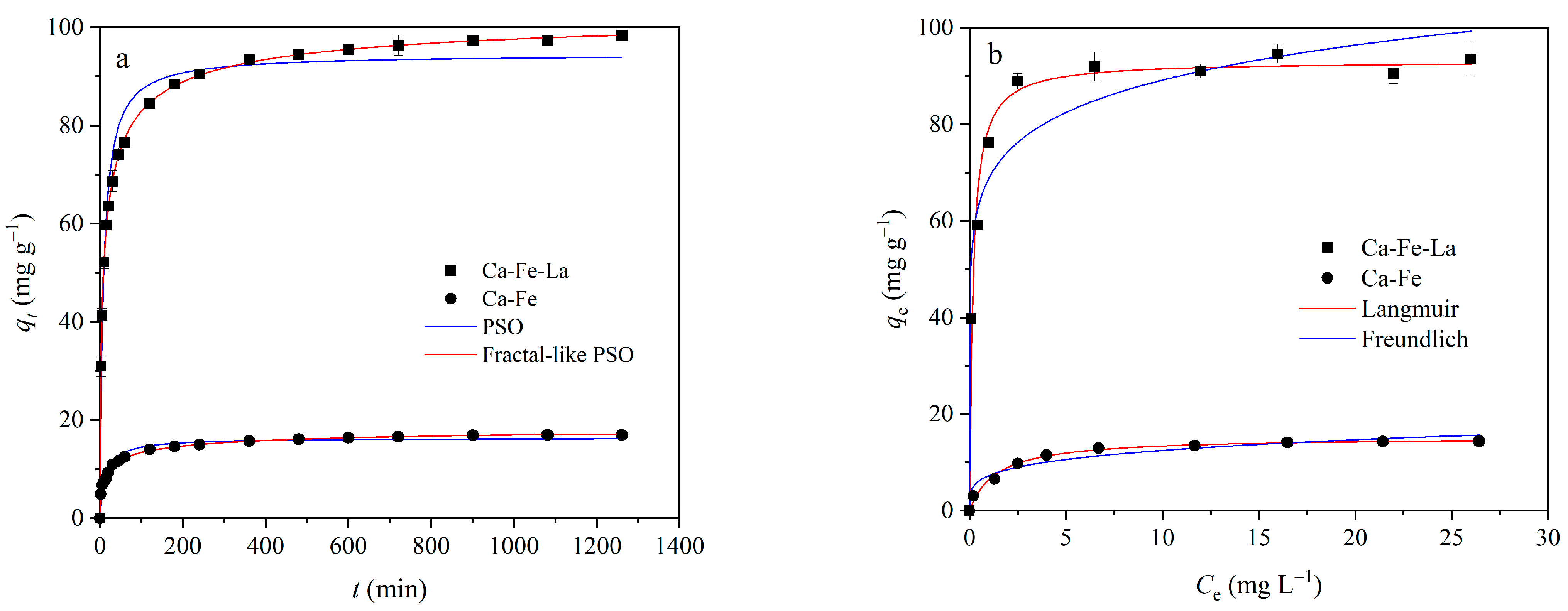
3.3.1. Kinetic Studies
3.3.2. Isotherm Studies
3.3.3. Effect of pH
3.3.4. Effect of Coexisting Anions
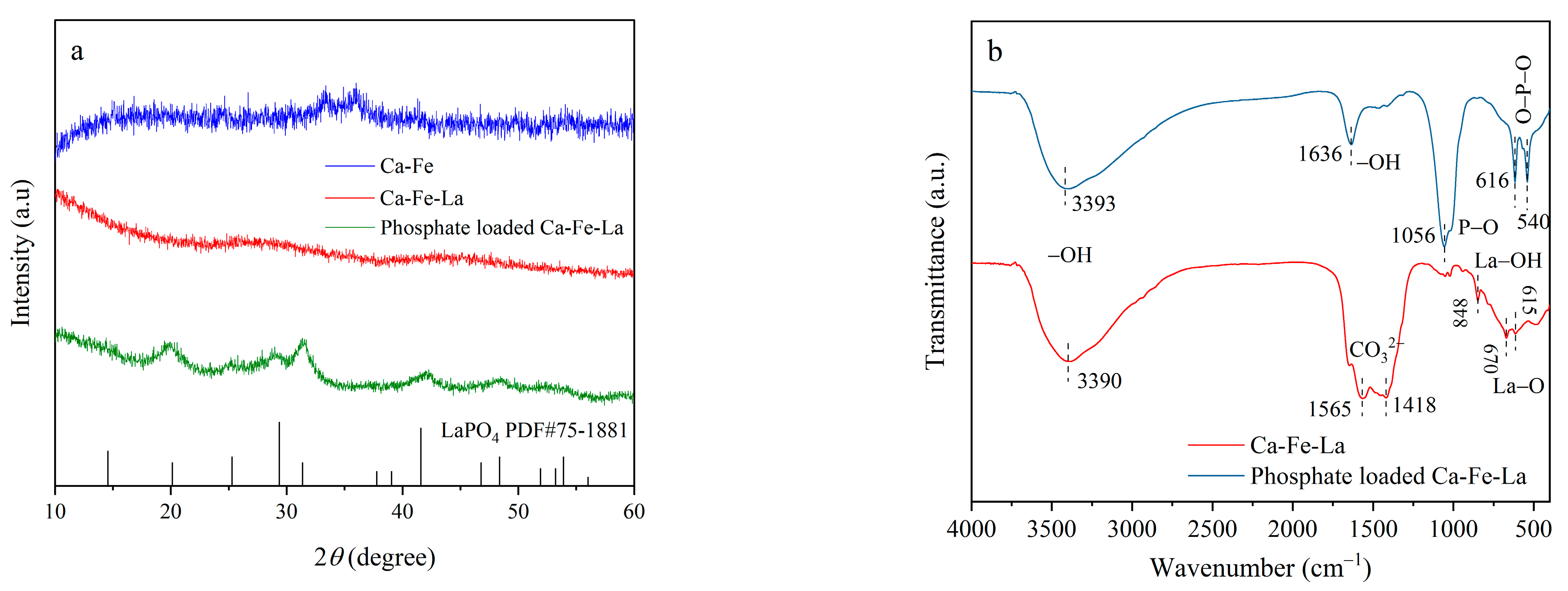
3.4. Adsorption Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ulrich, A.E.; Frossard, E. On the history of a reoccurring concept: Phosphorus scarcity. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Shen, T.; Wang, N.; Wang, P. Critical review of La(III)-based absorbents toward phosphate adsorption from aqueous solutions: Mechanisms, adsorbent design, and prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fu, J.; Tang, Y.; Smith, R.L.; Qi, X. Mg-coordinated self-assembly of MgO-doped ordered mesoporous carbons for selective recovery of phosphorus from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Yu, W.; Young, B. A novel lanthanum carbonate for low-level phosphorus removal: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Pei, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, S.; Feng, C. Facile preparation of oxygen vacancy-rich magnesium oxide for advanced removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 66, 106080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Manchanda, A.; Khan, T.A. Adsorption of Coomassie brilliant blue on a novel eco-friendly nanogel from simulated water: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202304927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, B.; Yu, W.; Huang, H.; Han, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X.; Young, B.; Wang, G. Lanthanum-based adsorbents for phosphate reutilization: Interference factors, adsorbent regeneration, and research gaps. Sustain. Horiz. 2022, 1, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.T.; Wu, T. Magnetic porous NiLa-Layered double oxides (LDOs) with improved phosphate adsorption and antibacterial activity for treatment of secondary effluent. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanassra, I.W.; McKay, G.; Kochkodan, V.; Ali Atieh, M.; Al-Ansari, T. A state of the art review on phosphate removal from water by biochars. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shao, J.; Ma, B.; Wu, B.; Hu, C. Oxygen defects of MgLa-LDH enhancing electrostatic attraction and inner-sphere complexation during phosphate adsorption from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatrista, G.; Pratt, C.; El Hanandeh, A. Phosphate adsorption by metal organic frameworks: Insights from a systematic review, meta-analysis, and predictive modelling with artificial neural networks. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, B. NaLa(CO3)2 hybridized with Fe3O4 for efficient phosphate removal: Synthesis and adsorption mechanistic study. Water Res. 2019, 155, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Lo, I.M.C. Surface functional group engineering of CeO2 particles for enhanced phosphate adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4601–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, S.; Fu, W.; Zhang, K.; Guo, H.; Wang, F. Green synthesis of CaxLa1-xMnO3 with modulation of mesoporous and vacancies for efficient low concentration phosphate adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, B.; Lo, I.M.C. Selective phosphate removal from water and wastewater using sorption: Process fundamentals and removal mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaweil, A.S.; Ibrahim, K.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; El-Subruiti, G.M.; Omer, A.M. Phosphate removal by Lanthanum-doped aminated graphene oxide@aminated chitosan microspheres: Insights into the adsorption mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Qin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, P.; Liang, W. Fabrication and mechanism of La/Al bimetallic organic frameworks for phosphate removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Pei, X. Development of fractal-like Furusawa–Smith and fractal-like Boyd models for modeling of phosphate adsorption: Statistical evaluation and comparison. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 59, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerifar, M.; Azizian, S. Fractal-like adsorption kinetics at the solid/solution interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 13111–13119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanassra, I.W.; Kochkodan, V.; Subeh, M.; McKay, G.; Atieh, M.; Al-Ansari, T. Phosphate removal from synthetic and treated sewage effluent by carbide derive carbon. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 36, 101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnaro, F.; Balsamo, M. Modelling CO2 adsorption dynamics onto amine-functionalised sorbents: A fractal-like kinetic perspective. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 192, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, R.D. Curve-fit errors in Langmuir adsorption maxima, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari Majd, M.; Kordzadeh-Kermani, V.; Ghalandari, V.; Askari, A.; Sillanpää, M. Adsorption isotherm models: A comprehensive and systematic review (2010−2020). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Zhao, D.; Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, F. Adsorption performance and mechanism of Ca–Al-LDHs prepared by oyster shell and pop can for phosphate from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dithmer, L.; Nielsen, U.G.; Lundberg, D.; Reitzel, K. Influence of dissolved organic carbon on the efficiency of P sequestration by a lanthanum modified clay. Water Res. 2016, 97, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Shen, W. Recovery of phosphate from aqueous solution by dewatered dry sludge biochar and its feasibility in fertilizer use. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yu, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, S.; Fu, J. Lanthanum ion modification of aminated cyclomatrix poly-phosphazene-coated porous carbon nanosheets for rapid, efficient and selective removal of phosphate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 593, 153359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Shang, Y.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q. Selective removal of phosphate by dual Zr and La hydroxide/cellulose-based bio-composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 533, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Le, M.; Nguyen, X.H.; Nguyen, T.P.; Tran, T.H.; Cuong, D.X.; Thai Van, N.; Nghiem Le, H.; Tap Van, H.; Nguyen, L.H. Lychee peels-derived biochar-supported CaFe2O4 magnetic nanocomposite as an excellent adsorbent for effective removal of nitrate and phosphate from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, K.; Jellali, S.; Jeguirim, M.; Trabelsi, A.B.H.; Limousy, L. Investigations on phosphorus recovery from aqueous solutions by biochars derived from magnesium-pretreated cypress sawdust. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, M.; Yang, R.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W. Synchronous phosphate and fluoride removal from water by 3D rice-like lanthanum-doped La@MgAl nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, S. Adsorption of phosphate in water by defective UiO-66/Ce2(CO3)3 composite: Adsorption characteristics and mechanisms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 640, 158459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yue, X.; Zhang, S.; Geng, Q.; Zheng, J.; Xu, X.; Li, T.; Pu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y.; et al. La(III) loaded Fe(III) cross–linked chitosan composites for efficient removal of phosphate from wastewater: Performance and mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Tao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic, and adsorption mechanism studies of La(OH)3-modified exfoliated vermiculites as highly efficient phosphate adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Xia, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Song, S. Simultaneous sorption of arsenate and fluoride on calcined Mg-Fe-La hydrotalcite-like compound from water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16287–16297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Liu, J.; Usman, M.; Chen, Q.; He, H. Superior adsorption of phosphate by ferrihydrite-coated and lanthanum decorated magnetite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, M.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Li, J. Needle-like Mg-La bimetal oxide nanocomposites derived from periclase and lanthanum for cost-effective phosphate and fluoride removal: Characterization, performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lou, S.; Zeng, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. High-efficiency adsorption of phosphate by Fe-Zr-La tri-metal oxide composite from aqueous media: Performance and mechanism. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 4587–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Chen, R.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Yuan, J.; Chen, L.; Xia, S. Efficient phosphate elimination from aqueous media by La/Fe bimetallic modified bentonite: Adsorption behavior and inner mechanism. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Huang, D.; Pan, J.; Li, W. Optimized Ca-Al-La modified biochar with rapid and efficient phosphate removal performance and excellent pH stability. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Fang, L.; Fortner, J.D.; Guan, X.; Lo, I.M.C. Highly efficient and selective phosphate removal from wastewater by magnetically recoverable La(OH)3/Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Water Res. 2017, 126, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Song, X.; Tao, L.; Sarkar, B.; Sarmah, A.K.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Q.; Xiao, R.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H. Novel Fe-Mn binary oxide-biochar as an adsorbent for removing Cd(II) from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hou, J.; Pan, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhang, M.; Yin, X.; Wu, J.; Miao, L.; Liu, Q. A novel La(OH)3 decorated co-graft tannin and polyethyleneimine co-coating magnetic adsorbent for effective and selective phosphate removal from natural water and real wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Ren, Q.; Wang, X.; Chi, Y.; Yuan, H.; Wang, S.; Ren, Y. Phosphate adsorption using calcium aluminate decahydrate to achieve low phosphate concentrations: Batch and fixed-bed column studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Absorbent | BET Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Micropores | Mesopores | Macropores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca-Fe composite | 73.31 | 3.72 | 0.067 | 8.9% | 87% | 3.8% |
| Ca-Fe-La composite | 278.41 | 3.51 | 0.197 | 21.5% | 72.5% | 6.0% |
| Models | Parameters | Ca-Fe-La | Ca-Fe | Models | Parameters | Ca-Fe-La | Ca-Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | (mg g−1) | 94.5 | 16.3 | Fractal-like PSO | (mg g−1) | 104.3 | 19.2 |
(g mg−1 min−1)) | 1.28 × 10−3 | 4.77 × 10−3 | (g mg−1 min−(1−h)) | 1.50 × 10−3 | 5.73 × 10−3 | ||
| Adj. R2 | 0.9689 | 0.9539 | h | 0.423 | 0.486 | ||
| RMSE | 4.78 | 1.05 | Adj. R2 | 0.9996 | 0.9961 | ||
| RMSE | 0.575 | 0.303 | |||||
| Langmuir | (mg g−1) | 93.0 | 15.2 | Freundlich | (L1/n g−1 mg−(1+1/n)) | 68.7 | 7.26 |
(L mg−1) | 5.69 | 0.72 | n | 8.87 | 4.26 | ||
| Adj. R2 | 0.9882 | 0.9897 | Adj. R2 | 0.9320 | 0.9388 | ||
| RMSE | 3.40 | 0.523 | RMSE | 8.14 | 1.27 |
| Adsorbents | Dosage (g L−1) | Concentration (mg L−1) | Temperature (°C) | pH | Reaction Time (h) | qmax (mg g−1) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OMC-MgO | 1.0 | 0–400 | 25 | 5 | 24 | 107 | [3] |
| LC-80 | 0.02 | 0.2–3.0 | 23.0 ± 0.5 | − | 5 | 82.7 | [4] |
| ML-10 | 0.33 | 25–200 | 25 | 7 | 24 | 67.6 | [10] |
| MLC | 0.1 | 0.5–50 | 25 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 24 | 77.85 | [12] |
| CeO2 (2 mL H2O) | 0.1 | 1–20 | 25 | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 24 | 80.5 | [13] |
| Ca0.4La0.6MnO3 | 0.4 | 5–100 | 25 | 5 | 24 | 63.01 | [14] |
| Ca-Fe-La composite | 0.5 | 20–120 | 25 | − | 24 | 93.0 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Hu, Q.; Qu, W.; Liu, H.; He, Z. The Performance and Mechanism of Solvothermal Synthesis of a Ca-Fe-La Composite for Enhanced Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solutions. Water 2024, 16, 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202932
Xu X, Hu Q, Qu W, Liu H, He Z. The Performance and Mechanism of Solvothermal Synthesis of a Ca-Fe-La Composite for Enhanced Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solutions. Water. 2024; 16(20):2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202932
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaojun, Qili Hu, Weiyi Qu, Hengyuan Liu, and Zhihao He. 2024. "The Performance and Mechanism of Solvothermal Synthesis of a Ca-Fe-La Composite for Enhanced Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solutions" Water 16, no. 20: 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202932
APA StyleXu, X., Hu, Q., Qu, W., Liu, H., & He, Z. (2024). The Performance and Mechanism of Solvothermal Synthesis of a Ca-Fe-La Composite for Enhanced Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solutions. Water, 16(20), 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202932







