Impact of Thinning and Contour-Felled Logs on Overland Flow, Soil Erosion, and Litter Erosion in a Monoculture Japanese Cypress Forest Plantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Study Hillslope Soil Characteristics
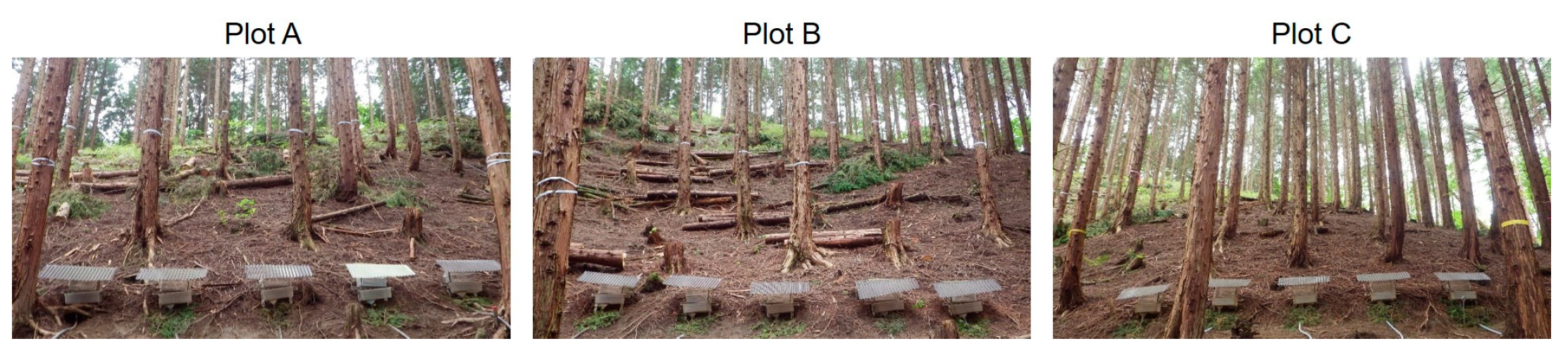
2.3. Study Plots
2.4. Small-Sized Trap Design
2.5. Data Collection and Processing
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Monthly Seasonal Variability
3.2. Paired-Plot and -Trap Analyses
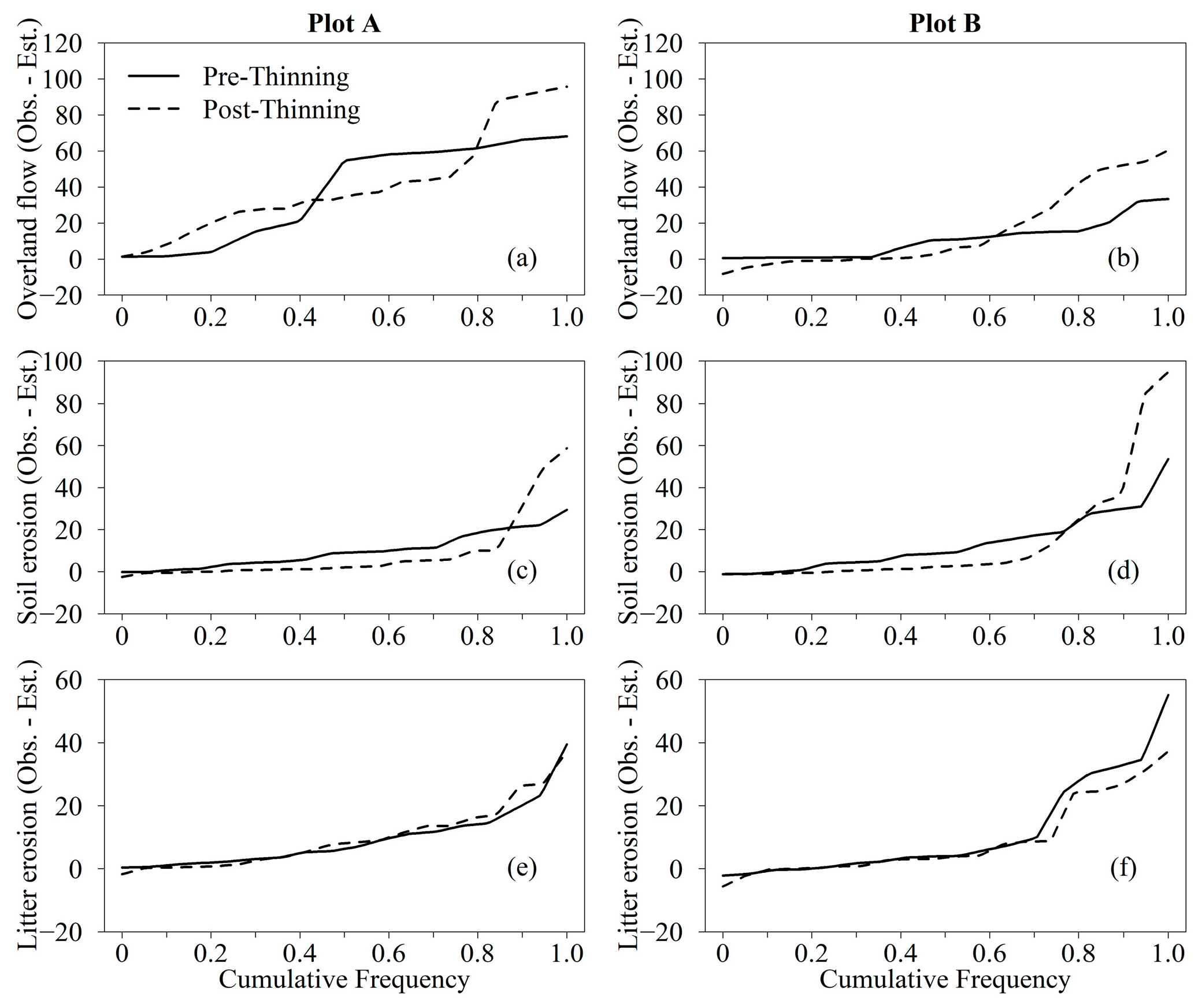
3.3. Cumulative Frequency Distribution
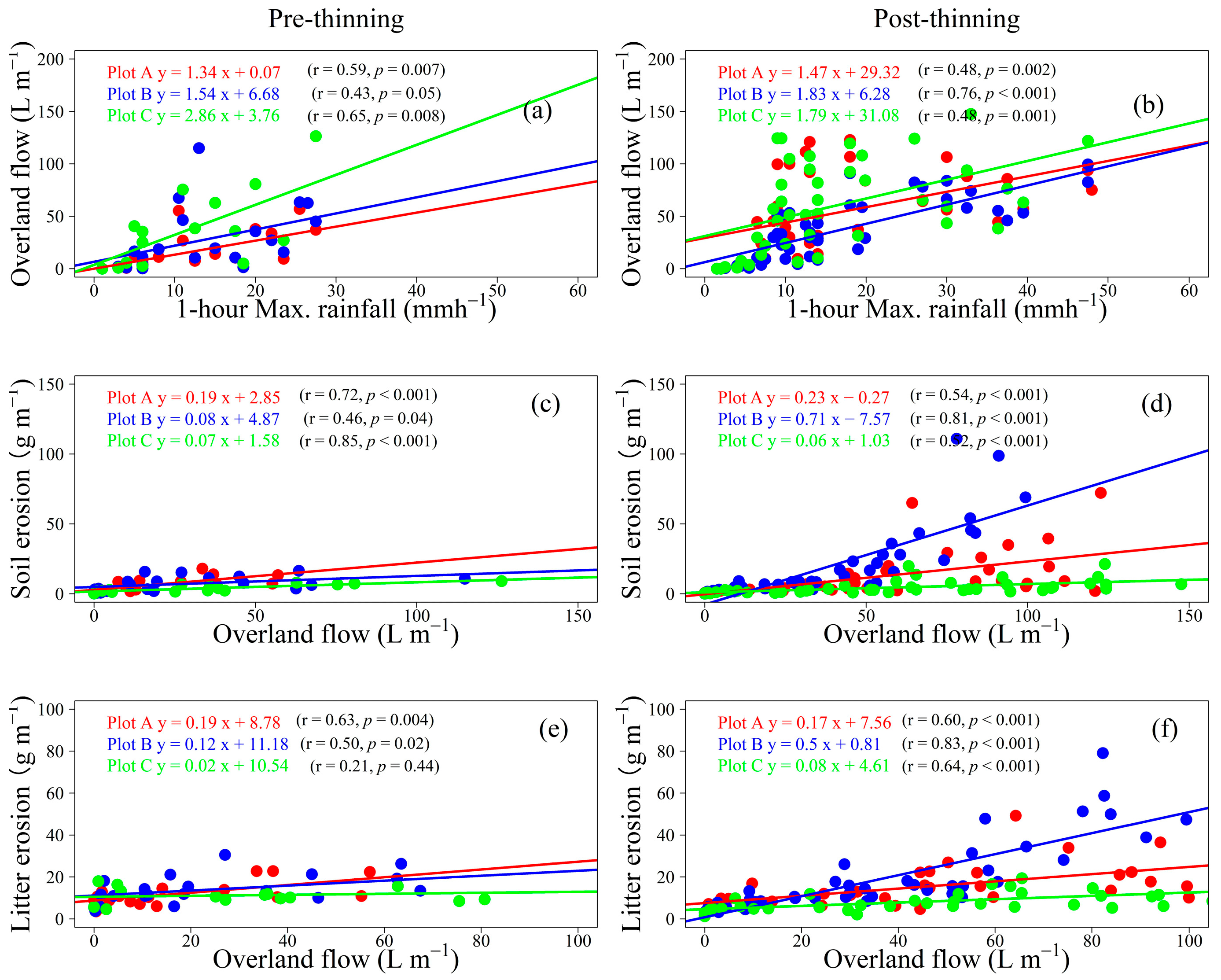
3.4. Driving Factors of Overland Flow and Soil and Litter Erosion
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Overland Flow Post-Thinning
4.2. Changes in Soil and Litter Erosion Post-Thinning
4.3. Changes in Hydrological and Erosional Processes Post-Thinning
4.4. Limitation of Our Study
4.5. Suggestions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, W.; Luo, Q.; Lu, H.; Wu, J.; Duan, W. The effect of litter layer on controlling surface runoff and erosion in rubber plantations on tropical mountain slopes, SW China. Catena 2017, 149, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, C.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X.; Liu, W.; Jiang, X. Can intercrops improve soil water infiltrability and preferential flow in rubber-based agroforestry system? Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Jordán, A.; Tarolli, P.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. The immediate effectiveness of barley straw mulch in reducing soil erodibility and surface runoff generation in Mediterranean vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahnak, M.; Tanaka, N.; Sato, T.; Nainar, A.; Gomyo, M.; Kuraji, K.; Suzaki, T.; Suzuki, H.; Nakane, Y. Enhancing Overland Flow Infiltration through Sustainable Well-Managed Thinning: Contour-Aligned Felled Log Placement in a Chamaecyparis obtusa Plantation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, J.; Kume, T.; Wakiyama, Y.; Higashi, N.; Chiwa, M.; Otsuki, K. Estimation of annual suspended sediment yield from a Japanese cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa) plantation considering antecedent rainfalls. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanko, K.; Mizugaki, S.; Onda, Y. Estimation of soil splash detachment rates on the forest floor of an unmanaged Japanese cypress plantation based on field measurements of throughfall drop sizes and velocities. Catena 2008, 72, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizugaki, S.; Nanko, K.; Onda, Y. The effect of slope angle on splash detachment in an unmanaged Japanese cypress plantation forest. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahnak, M.; Mitsuyasu, K.; Jeong, S.; Otsuki, K.; Chiwa, M.; Sadeghi, S.M.M.; Kume, A. Soil hydraulic conductivity differences between upslope and downslope of two coniferous trees on a hillslope. J. For. Res. 2019, 24, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidle, R.C.; Ziegler, A.D.; Negishi, J.N.; Nik, A.R.; Siew, R.; Turkelboom, F. Erosion processes in steep terrain—Truths, myths, and uncertainties related to forest management in Southeast Asia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 224, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.A.; Nainar, A.; Annammala, K.V.; Sugumaran, D.; Jamal, M.H.; Yusop, Z. Soil erosion in disturbed forests and agricultural plantations in tropical undulating terrain: In situ measurement using a laser erosion bridge method. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2020, 11, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; de Jong, W.; Kakizawa, H.; Kawase, M.; Matsushita, K.; Sato, N.; Takayanagi, A. New frontiers in Japanese Forest Policy: Addressing ecosystem disservices in the 21st century. Ambio 2021, 50, 2272–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japan Forestry Agency. Annual Report on Forest and Forestry in Japan Fiscal Year 2022 (Summary), Japan (Tokyo): Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries; Japan Forestry Agency: Chiyoda, Japan, 2023; p. 42. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/e/data/publish/attach/pdf/index-193.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Onda, Y.; Gomi, T.; Mizugaki, S.; Nonoda, T.; Sidle, R.C. An overview of the field and modelling studies on the effects of forest devastation on flooding and environmental issues. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M. Effect of raindrops on the breakdown of cypress litter into small pieces. J. Jpn. For. Assoc. Kansai Branch 1988, 39, 43–46. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, J. Downhill movement of litter and its implication for ecological studies in three types of forest in Japan. Ecol. Res. 1991, 6, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, S.; Abe, T.; Kobayashi, C.; Tamai, K. Effect of forest floor coverage on reduction of soil erosion in Hinoki plantation. Bull. For. For. Prod. Res. Inst. 1992, 362, 1–34, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Miura, S.; Yoshinaga, S.; Yamada, T. Protective effect of floor cover against soil erosion on steep slopes forested with Chamaecyparis obtusa (hinoki) and other species. J. For. Res. 2003, 8, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao, K.; Motoyoshi, T.; Sato, T.; Fukuzondo, T.; Seo, K.; Ikeda, S. Factors determining residents’ preparedness for floods in modern megalopolises: The case of the Tokai flood disaster in Japan. J. Risk Res. 2004, 7, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, T. Living with Forests; Maruzen: Tokyo, Japan, 2000. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Tsuboyama, Y.; Nobuhiro, T. Effects of thinning on canopy interception loss, evapotranspiration, and runoff in a small headwater Chamaecyparis obtusa catchment in Hitachi Ohta Experimental Watershed in Japan. Bull. For. For. Prod. Res. Inst. 2018, 17, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, X.B.; Miyata, S.; Gomi, T. Effect of forest thinning on overland flow generation on hillslopes covered by Japanese cypress. Ecohydrology 2011, 4, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakiri, K.; Ito, S.; Mitsuda, Y.; Hirata, R. Short-term effects of different thinning methods on degradation and recovery of understory vegetation of a hinoki (Chamaecyparis obtuse) plantation. Veg. Sci. 2019, 36, 43–59, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, T.; Sidle, R.C.; Ueno, M.; Miyata, S.; Kosugi, K.I. Characteristics of overland flow generation on steep forested hillslopes of central Japan. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, V.; Khuder, H.; Mickovski, S.B.; Spanos, I.A.; Norris, J.E.; Dorren, L.; Nicoll, B.C.; Achim, A.; Rubio, J.; Jouneau, L.; et al. Ecotechnological solutions for unstable slopes: Ground bio-and eco-engineering techniques and strategies. In Slope Stability and Erosion Control: Ecotechnological Solutions; Spinger: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 211–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Van Stan, J.T.; Heydari, M.; Omidipour, R.; Rocha, F.; Plaza-Alvarez, P.A.; Zema, D.A.; Muñoz-Rojas, M. Post-fire restoration with contour-felled log debris increases early recruitment of Spanish black pine (Pinus nigra Arn. ssp. salzmannii) in Mediterranean forests. Restor. Ecol. 2021, 29, e13338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourgholami, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Tavankar, F.; Picchio, R. Effectiveness of three post-harvest rehabilitation treatments for runoff and sediment reduction on skid trails in the Hyrcanian forests. Croat. J. For. Eng. J. Theory Appl. For. Eng. 2020, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Vega, J.A. Are erosion barriers and straw mulching effective for controlling soil erosion after a high severity wildfire in NW Spain? Ecol. Eng. 2016, 87, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, P.R.; Wagenbrenner, J.W.; Brown, R.E.; Wohlgemuth, P.M.; Beyers, J.L. Evaluating the effectiveness of contour-felled log erosion barriers as a post-fire runoff and erosion mitigation treatment in the western United States. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenbrenner, J.W.; MacDonald, L.H.; Rough, D. Effectiveness of three post-fire rehabilitation treatments in the Colorado Front Range. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2989–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Plaza-Álvarez, P.A.; Yáñez, M.D.C.; Miralles, I.; Ortega, R.; Soria, R.; Candel-Pérez, D.; Zema, D.A. Long-term evaluation of soil functionality in Mediterranean forests after a wildfire and post-fire hillslope stabilisation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 555, 121715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraji, K.; Gomyo, M.; Nainar, A. Thinning of cypress forest increases subsurface runoff but reduces peak storm-runoff: A lysimeter observation. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2019, 13, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostadinov, S.; Braunović, S.; Dragićević, S.; Zlatić, M.; Dragović, N.; Rakonjac, N. Effects of erosion control works: Case study—Grdelica Gorge, the South Morava River (Serbia). Water 2018, 10, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, A. The effect of organic matter content on soil erosion in simulated rainfall experiments in W. Sussex, UK. Soil Use Manag. 1994, 10, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, V.H.D.; Pleguezuelo, C.R.R. Soil-erosion and runoff prevention by plant covers: A review. Agron. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momiyama, H.; Kumagai, T.O.; Egusa, T. Model analysis of forest thinning impacts on the water resources during hydrological drought periods. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 499, 119593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Kasahara, T.; Otsuki, K.; Tateishi, M.; Saito, T.; Onda, Y. Effects of thinning on flow peaks in a forested headwater catchment in western Japan. Water 2017, 9, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, H.; Kume, T.; Shinohara, Y.; Miyazawa, Y.; Otsuki, K. Did annual run-off and low flow decrease with reduced forestry practices in Japan? Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 2440–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, C.J.C.; Yokoyama, K.; Sakai, H.; Koizumi, A.; Sakai, K. Decadal Changes in Soil Water Storage Characteristics Linked to Forest Management in a Steep Watershed. Water 2022, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JMA (Japan Meteorological Agency). The Normal Value of Toyota City, Aichi Prefecture. 2020. Available online: https://www.data.jma.go.jp/stats/etrn/view/nml_amd_ym.php?prec_no=51&block_no=0464&year=&month=&day=&view= (accessed on 26 September 2024). (In Japanese).
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World reference base for soil resources 2014, update 2015: International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. World Soil Sci. Res. 2015, 106, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Tobe, H.; Chigira, M.; Doshida, S. Comparisons of landslide densities between rock types in weathered granitoid in Obara village, Aichi prefecture. J. Jpn. Soc. Eng. Geol. 2007, 48, 66–79, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Tanaka, N.; Nainar, A.; Kuraji, K.; Gomyo, M.; Suzuki, H. Soil erosion and overland flow in Japanese cypress plantations: Spatio-temporal variations and a sampling strategy. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 2322–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahnak, M.; Sato, T.; Otani, Y.; Kuraji, K.; Suzaki, T. The Differences in Water Repellency in Root Mat (Biomat) and Soil Horizons of Thinned and Non-thinned Chamaecyparis obtusa (Siebold et Zucc.) Endl. Plantations. Forests 2023, 14, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidle, R.C.; Hirano, T.; Gomi, T.; Terajima, T. Hortonian overland flow from Japanese forest plantations—An aberration, the real thing, or something in between? Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 3237–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/IEC 1539-1:1997; Information Technology–Programming Languages–Fortran–Part 1: Base Language. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- Bombino, G.; D’Agostino, D.; Marziliano, P.A.; Pérez Cutillas, P.; Praticò, S.; Proto, A.R.; Manti, L.M.; Lofaro, G.; Zimbone, S.M. A Nature-Based Approach Using Felled Burnt Logs to Enhance Forest Recovery Post-Fire and Reduce Erosion Phenomena in the Mediterranean Area. Land 2024, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Onda, Y.; Kato, H.; Gomi, T.; Liu, X. Estimation of throughfall with changing stand structures for Japanese cypress and cedar plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 402, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, B.X.; Gomi, T.; Miyata, S.; Sidle, R.C.; Kosugi, K.; Onda, Y. Runoff responses to forest thinning at plot and catchment scales in a headwater catchment draining Japanese cypress forest. J. Hydrol. 2012, 444, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.G.; Shin, K.; Joo, K.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Shin, S.S.; Choung, Y. Effects of soil conservation measures in a partially vegetated area after forest fires. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 399, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, K.V.; Dixon, J.L.; Wilcox, A.C.; McWethy, D. Fire-produced coarse woody debris and its role in sediment storage on hillslopes. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2023, 48, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, R.P.; Bladon, K.D.; Wagenbrenner, J.W.; Coe, D.B. Hillslope sediment production after wildfire and post-fire forest management in northern California. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 5242–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S.; Kosugi, K.I.; Gomi, T.; Mizuyama, T. Effects of forest floor coverage on overland flow and soil erosion on hillslopes in Japanese cypress plantation forests. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W06402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, M.D.; Marshall, R.M.; O’Donnell, F.; Smith, E.B.; Haney, J.A.; Gori, D.F. Effects of climate variability and accelerated forest thinning on watershed-scale runoff in southwestern USA ponderosa pine forests. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourgholami, M.; Karami, S.; Tavankar, F.; Lo Monaco, A.; Picchio, R. Effects of slope gradient on runoff and sediment yield on machine-induced compacted soil in temperate forests. Forests 2020, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourgholami, M.; Khajavi, S.; Labelle, E.R. Mulching and water diversion structures on skid trails: Response of soil physical properties six years after harvesting. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 123, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainar, A.; Kishimoto, K.; Takahashi, K.; Gomyo, M.; Kuraji, K. How do ground litter and canopy regulate surface runoff?—A paired-plot investigation after 80 years of broadleaf forest regeneration. Water 2021, 13, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


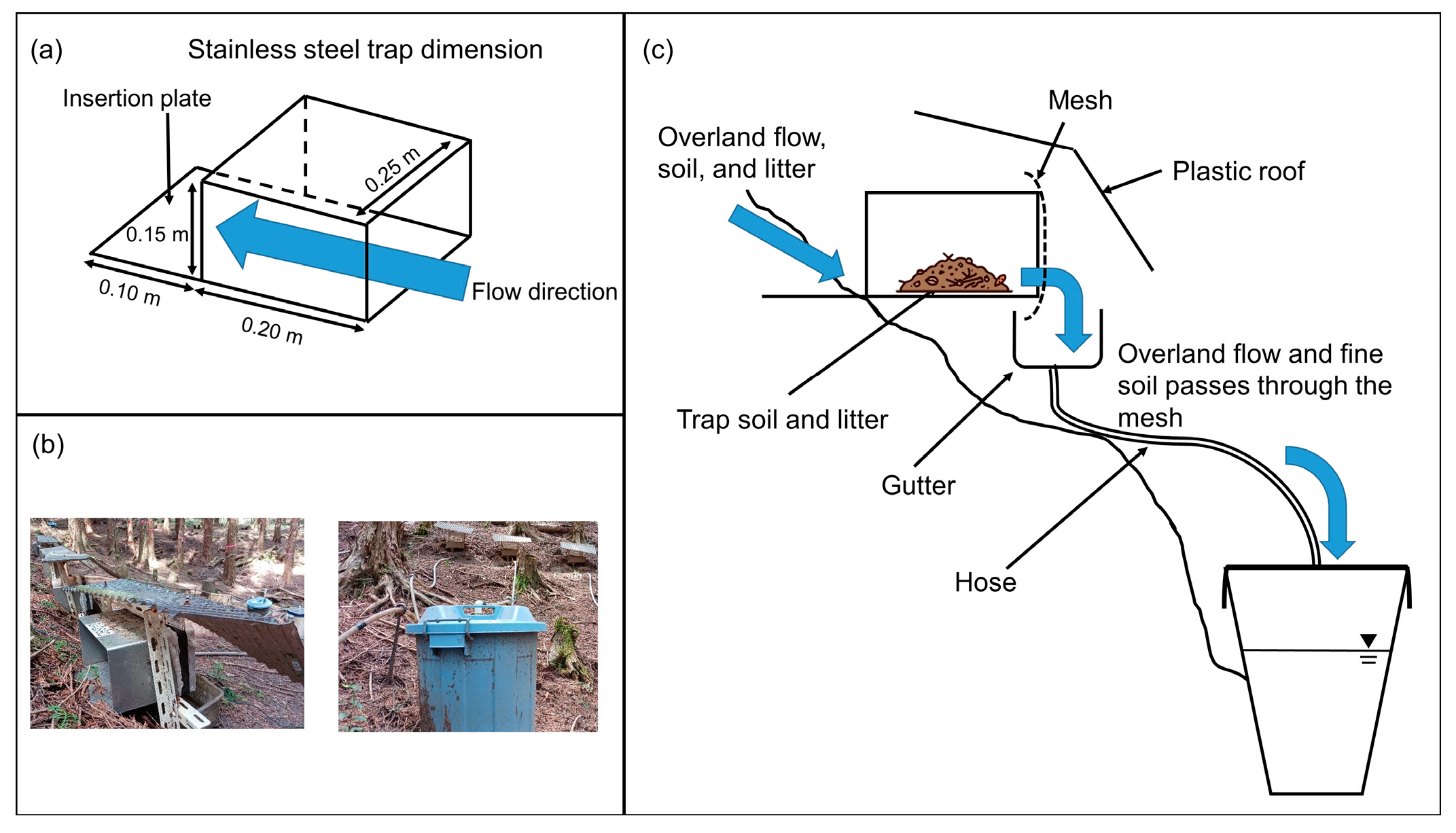
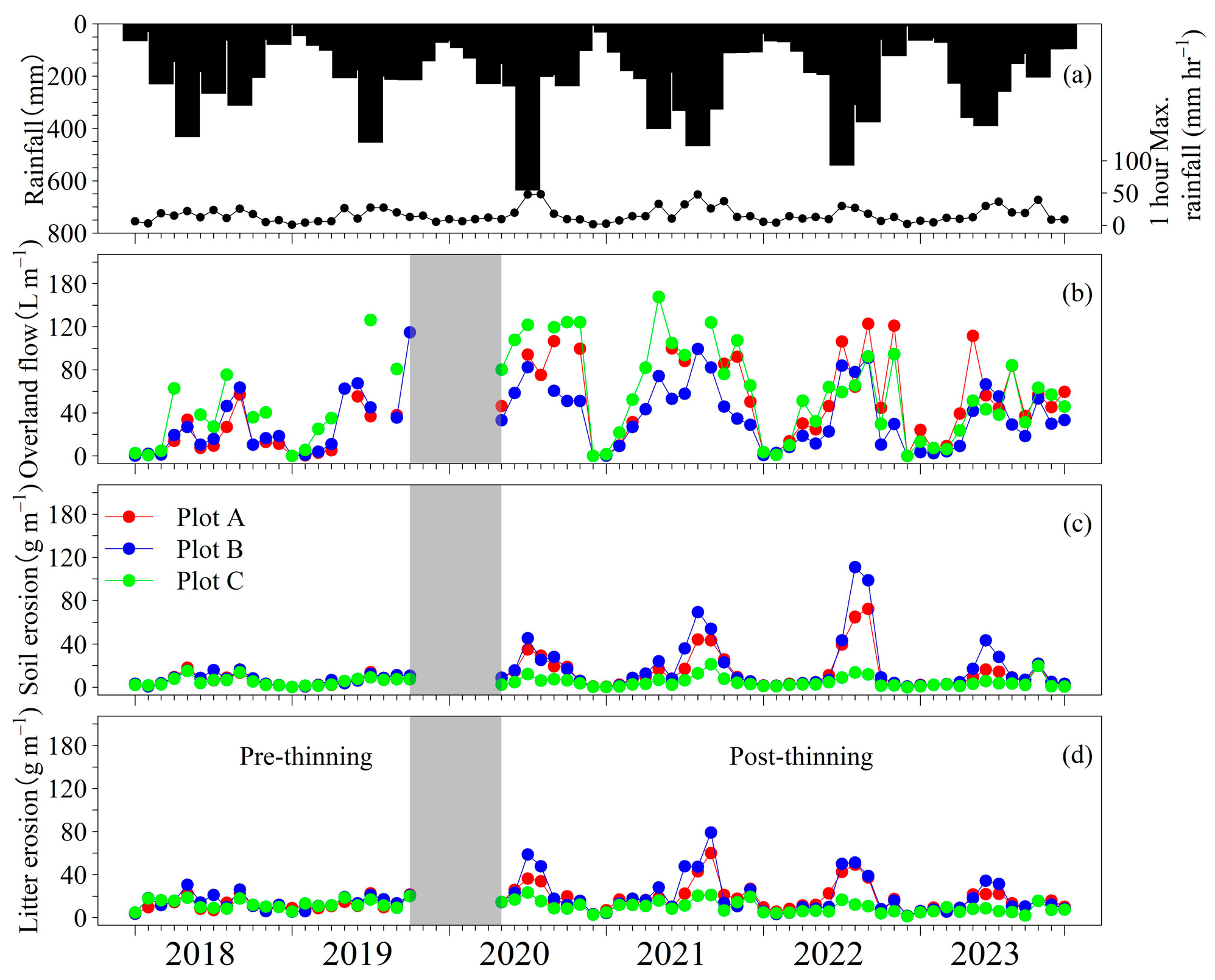
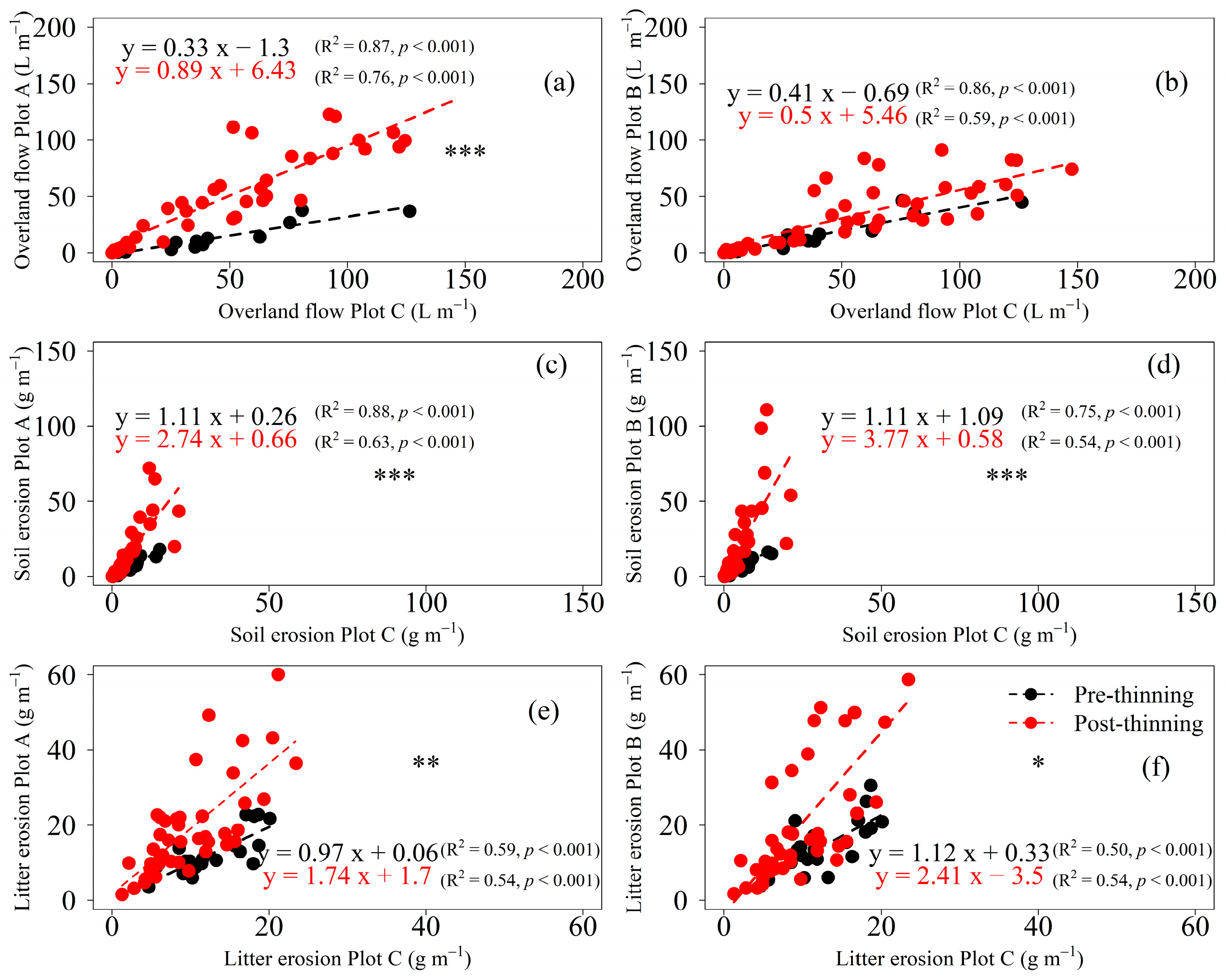
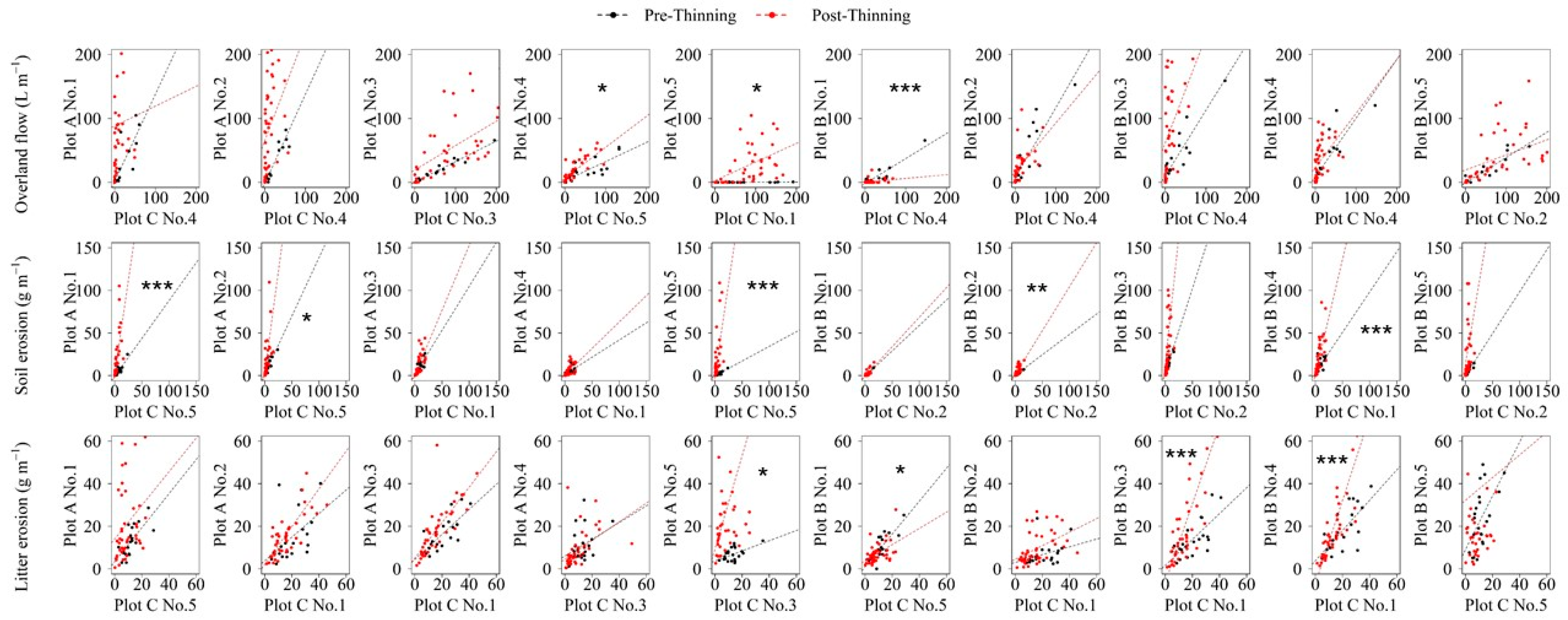
| Period | Plot | Tree Height (m) | DBH 1 (cm) | Tree Density (Tree ha−1) | Average Slope Angle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before thinning | A | 15.7 ± 0.7 | 20.0 ± 3.7 | 1800 | 34.8° |
| B | 16.81 ± 1.0 | 20.4 ± 2.7 | 2000 | 31.9° | |
| C | 16.4 ± 0.5 | 20.2 ± 2.5 | 1520 | 30.1° | |
| After thinning | A | 15.79 ± 0.8 | 20.6 ± 4.0 | 1100 | 34.8° |
| B | 17.1 ± 1.1 | 21.0 ± 2.9 | 1200 | 31.9° | |
| C | 16.4 ± 0.5 | 20.2 ± 2.5 | 1520 | 30.1° |
| Period | Year | OEF (mm) | OMS | TMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before thinning | 2018 | 2091.5 | 1862.5 | 1599.5 |
| 2019 | 1713.5 | 1605 | 1623.5 | |
| After thinning | 2020 | 1782 | 1976.5 | 1696.0 |
| 2021 | 2593 | 2044.5 | 1719.0 | |
| 2022 | 2098 | 1749.0 | 1476.0 | |
| 2023 | 2110.6 | 1885 | 1522.5 | |
| Mean | 2064.8 | 1853.7 | 1606.08 | |
| Period | Year | Plot | Overland Flow (L m−1) | Soil Erosion (g m−1) | Litter Erosion (g m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-thinning | 2018 | A | 186.0 | 83.2 | 143.7 |
| B | 231.8 | 93.8 | 180.1 | ||
| C | 288.5 | 70.3 | 150.6 | ||
| 2019 | A | 139.1 | 56.2 | 129.4 | |
| B | 341.8 | 62.7 | 139.3 | ||
| C | 273.0 | 49.7 | 129.2 | ||
| Post-thinning | 2020 | A | 422.0 | 131.2 | 165.3 |
| B | 337.1 | 146.7 | 192.7 | ||
| C | 678.3 | 43.6 | 102.7 | ||
| 2021 | A | 458.3 | 187.4 | 273.5 | |
| B | 556.2 | 250.9 | 314.6 | ||
| C | 876.9 | 71.9 | 157.9 | ||
| 2022 | A | 579.9 | 206.3 | 22.7 | |
| B | 358.4 | 287.0 | 207.7 | ||
| C | 503.5 | 51.7 | 83.4 | ||
| 2023 | A | 573.3 | 90.0 | 161.3 | |
| B | 347.8 | 146.1 | 170.2 | ||
| C | 465.3 | 46.5 | 86.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farahnak, M.; Sato, T.; Tanaka, N.; Nainar, A.; Mohd Ghaus, I.; Kuraji, K. Impact of Thinning and Contour-Felled Logs on Overland Flow, Soil Erosion, and Litter Erosion in a Monoculture Japanese Cypress Forest Plantation. Water 2024, 16, 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202874
Farahnak M, Sato T, Tanaka N, Nainar A, Mohd Ghaus I, Kuraji K. Impact of Thinning and Contour-Felled Logs on Overland Flow, Soil Erosion, and Litter Erosion in a Monoculture Japanese Cypress Forest Plantation. Water. 2024; 16(20):2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202874
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarahnak, Moein, Takanori Sato, Nobuaki Tanaka, Anand Nainar, Ibtisam Mohd Ghaus, and Koichiro Kuraji. 2024. "Impact of Thinning and Contour-Felled Logs on Overland Flow, Soil Erosion, and Litter Erosion in a Monoculture Japanese Cypress Forest Plantation" Water 16, no. 20: 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202874
APA StyleFarahnak, M., Sato, T., Tanaka, N., Nainar, A., Mohd Ghaus, I., & Kuraji, K. (2024). Impact of Thinning and Contour-Felled Logs on Overland Flow, Soil Erosion, and Litter Erosion in a Monoculture Japanese Cypress Forest Plantation. Water, 16(20), 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202874








