Abstract
Steroid hormones, recognized as emerging environmental contaminants, have garnered increasing attention in recent years. The present work studied the distribution characteristics in the environment, bioaccumulation in aquatic products, and the associated environmental and health risks of typical steroid hormones from commercial freshwater aquaculture farms operating under different aquaculture modes (monoculture and polyculture). Totals of 9 and 14 steroid hormones were detected in water and sediment samples, with concentrations ranging from 0.66 ± 0.17 ng/L to 40.5 ± 5.08 ng/L and from 0.36 ± 0.08 ng/g to 123 ± 19.9 ng/g, respectively. Hazard index (HI) calculations indicated that all sampling locations were identified as medium or high risk for both water and sediment matrices. Nineteen steroids were detected in at least one type of tissue, with the concentrations in the bile, plasma, muscle, liver, and gill ranging from <LOQ to 52.6 ± 4.82 ng/L, from <LOQ to 41.9 ± 4.80 ng/L, from 0.36 ± 0.07 ng/g to 321 ± 19.1 ng/g, from <LOQ to 1140 ± 107 ng/g, and from 0.36 ± 0.03 ng/g to 1450 ± 239 ng/g, respectively. Furthermore, four synthetic steroid hormones exhibited significant bioaccumulation across various tissues, such as MLA in bile and 5α-DHP in muscle, liver, and gill (BAF > 5000 L/kg). Notably, despite low estimated daily intakes (EDIs) (0.43–6.43 ng/day/person to 18.7 ng/day/person) and hazard quotients (HQs) (below 4.188 × 10−7), the high bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) underscore the necessity for stringent regulatory measures by local governments. Additionally, a comparison of EDI results across different aquaculture modes and fish species revealed that steroid hormone-related health risks to humans are influenced by both the fish species and the aquaculture mode. This study indicated that the consumption of poly-cultured fish (e.g., bighead carp) may pose a greater steroid-related health risk, compared to the consumption of mono-cultured fish.
1. Introduction
Steroid hormones, recognized as typical environmental endocrine disruptors, have received increasing attention due to their bioaccumulation [1], endocrine-disrupting effects [2,3], and potential carcinogenicity [4,5]. Both natural and synthetic steroid hormones are extensively utilized in various human activities, such as contraception, treatment of gynecological diseases, and in large-scale animal husbandry, including aquaculture, for inducing ovulation and promoting growth [6,7,8]. The incomplete removal by sewage treatment plants and direct discharge from some animal farms contribute to the frequent detection of these steroid hormones in environmental matrices and aquatic organisms, with concentrations ranging from ng/L (ng/g) to μg/L (μg/g) [9]. Studies have reported reproductive and behavioral disturbances in fish associated with exposure to steroid hormones at ng/L levels [10,11,12]. Moreover, these compounds can accumulate in humans via food chain transfer, leading to adverse health effects, including developmental and reproductive abnormalities. Despite their beneficial effects in promoting growth and treating diseases, the prevalence of steroid hormones in aquaculture [13] settings merits significant concern.
Recent investigations have identified and quantified various natural and synthetic steroid hormones, including the transformation products, in aquaculture environments at concentrations ranging from sub-nanogram per liter to tens of nanograms per liter [14,15,16]. Advances in environmental analytical techniques have enabled the quantification of steroid hormone concentrations in aquatic products. Based on literature, steroid hormones are expected to be present at ng/g levels in marine organisms, especially fish [17,18]. Both field observations and laboratory studies have indicated that synthetic steroid hormones may disrupt reproductive functions in fish, inducing feminization in males. [14,17]. Notably, 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2) in concentrations below 0.035 ng/L have been demonstrated to adversely affect fish reproductive performance [19]. These steroid hormones accumulate in the edible tissues of aquatic products consumed by humans, such as fish, shrimp, and crab [20]. Furthermore, studies have shown that hormone residues in food are resistant to thermal inactivation or removal [21]. Consequently, consumption of animal-derived foods containing these hormones could expose consumers to additional hormonal effects, impacting physiological processes and public health [22]. However, current research on the bioaccumulation characteristics and ecological risks of steroid hormones, particularly in various fish species, remains limited and predominantly focuses on marine and wild freshwater environments [23,24], with scant attention to freshwater aquaculture systems.
In response, six fish species from commercial freshwater aquaculture farms, employing either monoculture or polyculture systems, were sampled to investigate the bioaccumulation of steroid hormones in bile, plasma, liver, gill, and muscle tissues. The ecological risks associated with these steroid hormones and their cumulative effects on human health through fish consumption were evaluated. This study enhanced our understanding of steroid hormone bioaccumulation in fish tissues and informed about more effective management strategies in aquaculture environments.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Sample Collection
High purity standards of 47 natural and synthetic steroids, including 14 androgens, 5 glucocorticoids, 21 progestagens, and 7 isotope-labeled internal standards, namely testosterone-16, 16, 17-d3 (T-d3), stanozolol-d3 (S-d3), melengestrol acetate-d3 (MGA-d3), mifepristone-d3 (MFST-d3), norethindrone-d6 (NTD-d6), progesterone-d9 (PGT-d9), and cortisol-d2 (CRL-d2), were purchased from different chemical suppliers (Table S1). The detailed information on chemicals and materials is summarized in the Supplementary Information.
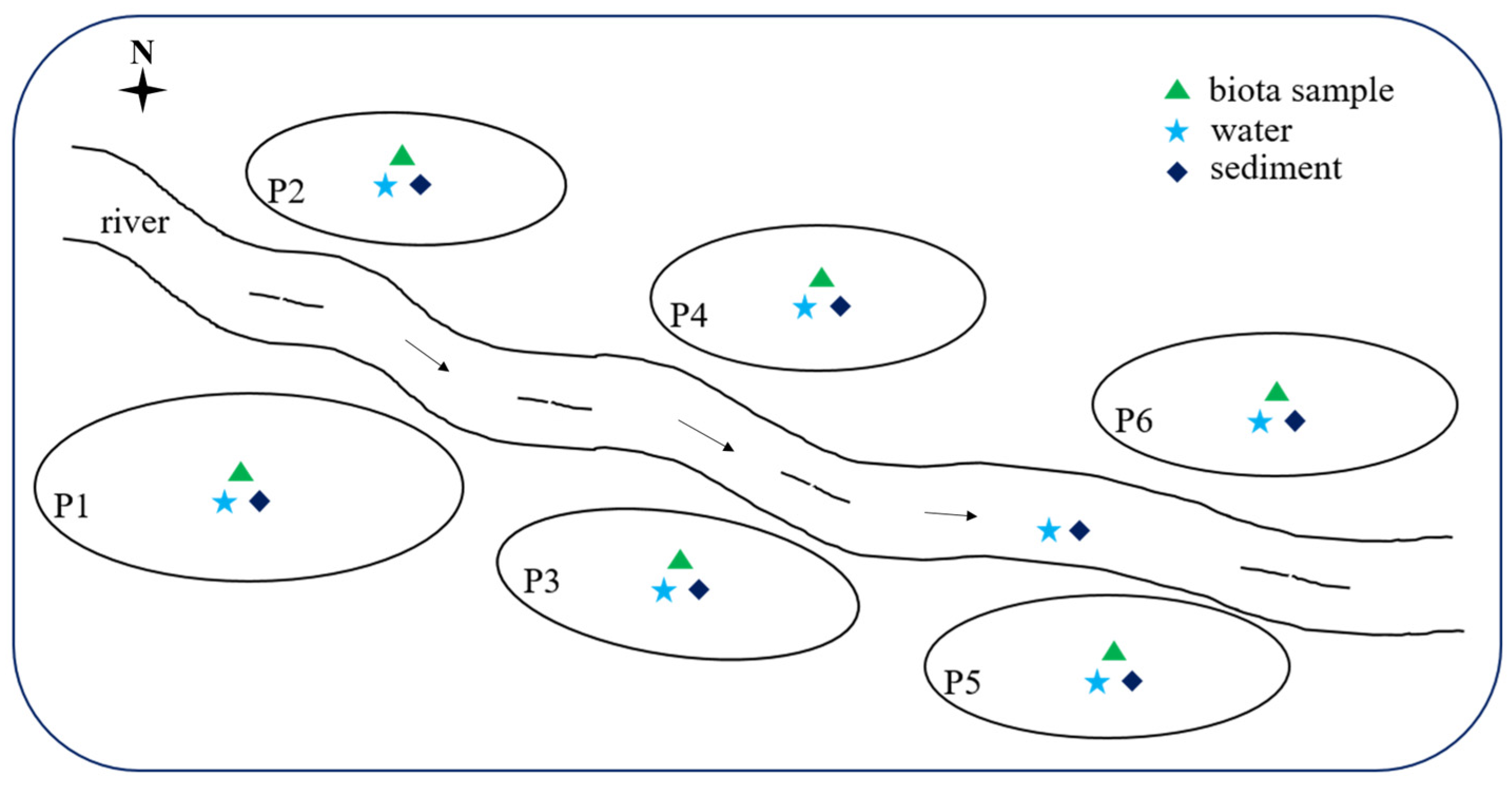
Six representative freshwater aquaculture ponds (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, and P6) situated in Shunde, Foshan, an essential aquaculture region in Guangdong, China, were selected for this study. Shunde District is situated in the central region of the Pearl River Delta Plain, between 113°1′ E longitude and 22°40′ to 23°20′ N latitude. The district encompasses a total area of 806 square kilometers, with water bodies (including rivers and fish ponds) comprising 37.4% of this area. It is characterized by a south subtropical monsoon climate. The aquaculture in these fish ponds represents a significant source of freshwater fish products in southern China. The schematic is shown in Figure 1. Pond P1 followed a polyculture system, accommodating 70,000 fish, comprising 20,000 crucian carp (Carassius auratus), 35,000 grass carp (Ctenopharynodon idellus), and 15,000 bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). In contrast, Ponds P2 through P6 adopted monoculture systems, housing approximately 60,000 weevers (Lateolabrax japonicus), 50,000 snakeheads (Channa argus), 50,000 mud carps (Cirrhinus molitorella), 60,000 crucian carp crucian carps (Carassius auratus), and 50,000 bighead carps (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis), respectively. All selected farms are privately owned and operated under the guidance of technical personnel. The influent for each pond was sourced from adjacent rivers.
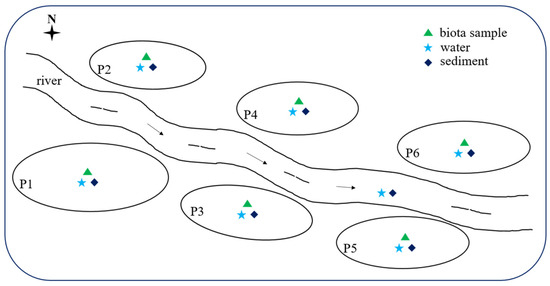
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of sampling sites.
Water samples, including both river and pond water, were collected in 1 L pre-cleaned brown glass bottles in triplicate for each site. Approximately 50 mL of methanol was added to suppress microbial activity, and the pH was adjusted to 3 using 4 M H2SO4. Sediment samples (0–30 cm depth) were obtained using a bottom sampler and stored in 1 L brown glass jars, also in triplicate. One gram of sodium azide was added to inhibit microbial growth. All samples were refrigerated and promptly transported to the laboratory. Water samples were processed within 24 h. Sediment samples were freeze-dried, homogenized, sieved through a 60-mesh standard sieve, and then kept at −20 °C in the dark until extraction.
Fish were transported alive in 25 L polypropylene containers filled with pond water and continuously oxygenated, ensuring immediate transfer to the laboratory. The targeted species included crucian carp (Carassius auratus), weever (Lateolabrax japonicus), grass carp (Ctenopharynodon idellus), mud carp (Cirrhinus molitorella), snakehead (Channa argus), and bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Blood was drawn via the caudal vein using a heparinized syringe (Jiangxi Fenglin Medical Devices Co., Ltd., Fuzhou, China). Plasma samples were separated post-centrifugation (10 min at 10,000× g) and stored in polypropylene tubes. Fish were then dissected. Bile was extracted from the gallbladder with a syringe and stored in polypropylene tubes. The gill, liver, and muscle tissues were excised using surgical scissors (Anqisheng Medical Technology (Xuzhou) Co., Ltd., Xuzhou, China). All samples were kept at −20 °C until chemical analysis.
2.2. Sample Extraction and Instrumental Analysis
Sample extraction and instrumental analysis were carried out according to our previous studies [25], and the detailed method information is given in the Supplementary Information (SI Tables S1 and S2). Briefly, water samples were extracted by solid-phase extraction using Waters Oasis HLB cartridges (500 mg, 6 mL) (Waters, Milford, MA, USA). Solid samples were subjected to ultrasonication extraction utilizing ethyl acetate. Subsequently, sediment and feed extracts were purified using silica gel columns prior to analysis. For biota samples, initial purification involved a two-layer SAX/PSA cartridge (SAX = strong anion exchange; PSA = primary secondary amine) (ANPEL Laboratory Technologies (Shanghai) Inc., Shanghai, China) to eliminate bile acid in bile and lipid in liver and muscle samples [25]. Target steroid hormones were then enriched using HLB solid-phase extraction (SPE) cartridges (Waters, Milford, MA, USA). Dissected gill, liver, and muscle tissues were homogenized at 35,000 rpm and extracted with methanol/water-0.1 M acetic acid (50:50, v/v) through ultrasonication. The extracts were enriched with HLB cartridges for gill samples and SAX/PSA-HLB tandem cartridges for liver and muscle samples. Plasma and bile samples were extracted using HLB and SAX/PSA-HLB tandem cartridges, respectively. The determination of target steroid hormone compounds was performed using an Agilent 1200 LC coupled with an Agilent 6460 QQQ (RRLC–MS/MS) (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source. Quantification was executed in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode, employing isotope-labeled compounds as internal standards. For further details on the extraction and analysis procedures, please consult the Supplementary Information.
2.3. Data Analysis
The aquatic acute median effective concentration (EC50) or chronic no observed effect concentration (NOEC) values for chemicals were utilized to derive predicted no effect concentration (PNEC) values [26]. The RQ approach was used to perform an ecological risk assessment of steroid hormones in water samples [26]. The bioaccumulation factor (BAF) of a steroid hormone was calculated as the ratio of the concentration of a steroid hormone in fish tissue to the concentration of the steroid hormone in the corresponding water sample. The estimated daily intake (EDI) of selected steroid hormones through fish consumption by local residents or global consumers was determined based on the maximum concentration of the steroid hormone in fish muscle and the average daily fish consumption for an adult. Consumption data were obtained from a dietary survey conducted in South China [27] and from the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations [28]. Hazard quotients (HQs) for human exposure to steroid hormones were calculated as the ratio of the EDI to the acceptable daily intake (ADI) for adults. HQ values exceeding 1 indicated a significant risk of adverse health effects.
Basic statistics, including concentration range, mean, standard deviation, and median values, were employed to characterize the contamination profiles of steroid hormones across different media, such as water, sediment, and tissue samples. These analyses were conducted using Microsoft Excel 2021. For concentrations below the limit of quantitation (LOQ), values were replaced with half the LOQ, and not-detected (ND) data were set to zero for the purposes of calculating total concentrations and visualizing data.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Occurrence of Steroid Hormones in Water and Sediment Samples
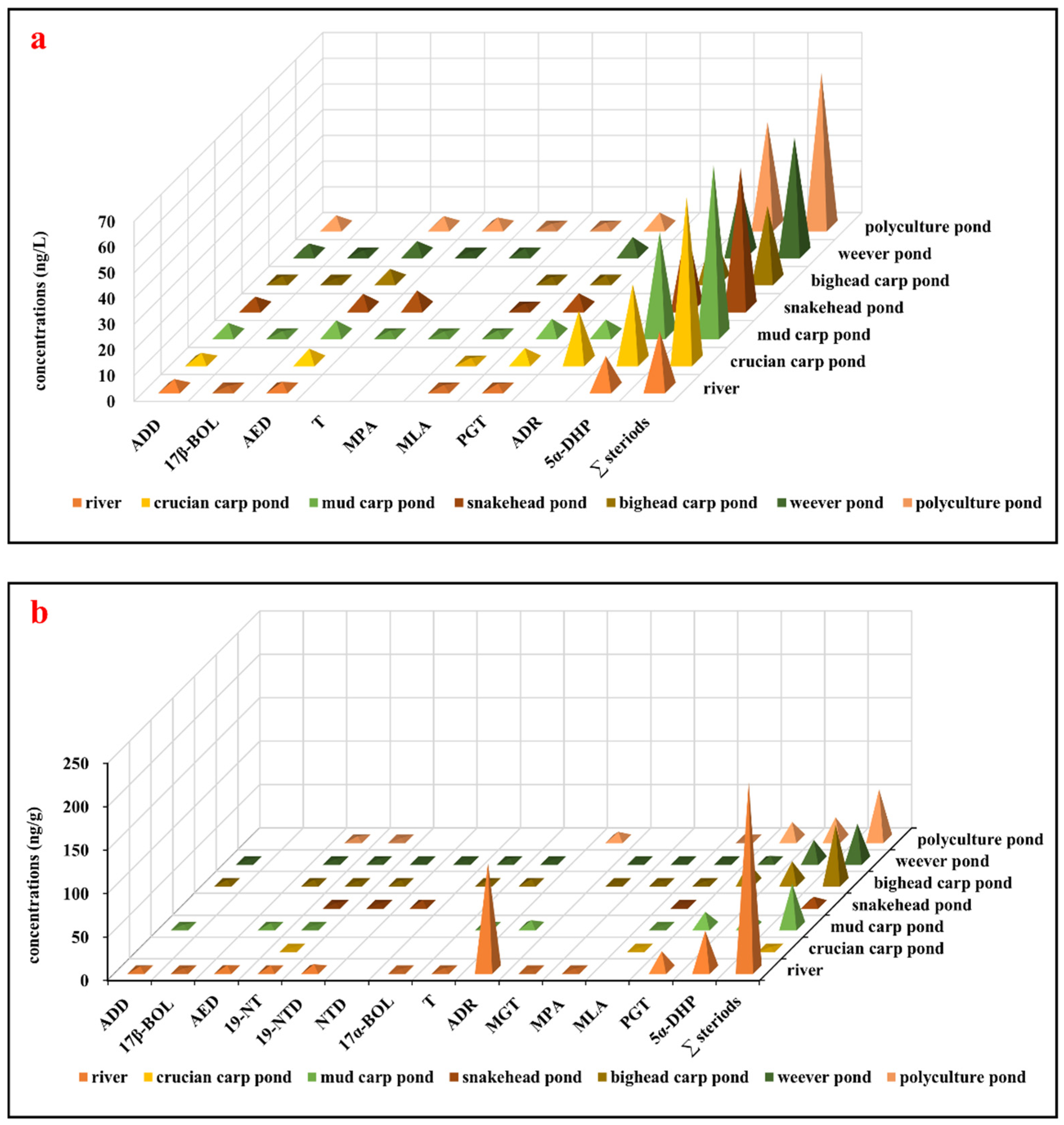
The concentrations of steroid hormones detected in water samples from the river and targeted freshwater aquaculture ponds are summarized in Figure 2a and SI Table S3. In general, nine steroid hormones were detected in water samples, with concentrations ranging from 0.88 ± 0.17 ng/L (17β-BOL) to 12.4 ± 2.30 ng/L (5α-DHP) in river water and from 0.66 ± 0.17 ng/L (T, weever pond) to 40.5 ± 5.08 ng/L (5α-DHP, polyculture pond) in pond water. These concentrations are comparable to those reported in other typical freshwater and marine aquaculture farms [25], as well as effluents from WWTPs [29] and surface water [14]. ADD, AED, PGT, and 5α-DHP were detected in all water samples, with total detected compound concentrations of 22.1 ± 2.45 ng/L in river water and ranging from 28.8 ± 3.22 ng/L (bighead carp pond) to 65.8 ± 4.30 ng/L (mud carp pond) in pond water. Given that all fish ponds receive water from the same river, there were minimal variations in the types and concentrations of steroid hormones across the aquatic environments. Notably, 5α-DHP emerged as the predominant steroid hormone in the aquatic environment, with the highest concentrations observed (12.4 ± 2.30 ng/L in river water and from 19.2 ± 2.32 ng/L in bighead carp pond water to 40.5 ± 5.08 ng/L in polyculture pond water). The concentrations of 5α-DHP in the waters of all fish ponds exceeded those found in river water, indicating the potential presence of alternative sources, such as feed, within the pond ecosystems.
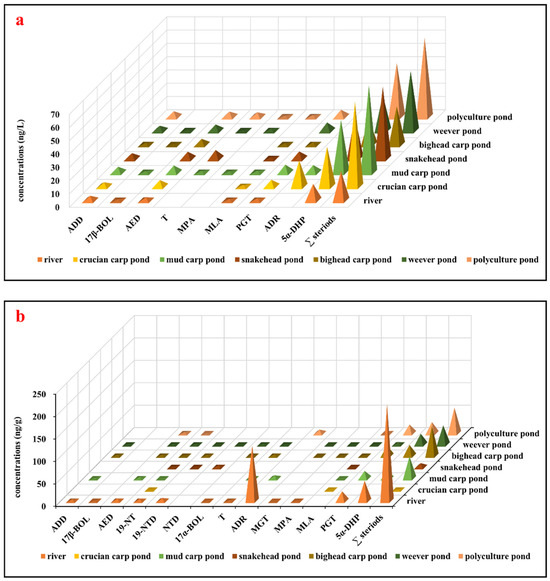
Figure 2.
Concentrations of detected steroid hormones from the river and targeted freshwater aquaculture ponds: (a) Concentrations of detected steroid hormones in water samples (ng/L). (b) Concentrations of detected steroid hormones in sediments (ng/g). Abbreviations: ADD, androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione; 17β-BOL, 17β-boldenone; AED, 4-androstene-3,17-dione; 19-NT, 19-nortestosterone; 19-NTD, 19-norethindrone; NTD, norethynodrel; 17α-BOL, 17α-boldenone; T, testosterone; ADR, androsterone; MGT, megestrol; MPA, medroxyprogesterone acetate; MLA, melengestrol acetate; PGT, progesterone; 5α-DHP, 5α-dihydroprogesterone; ∑ steroids, the sum of all detected steroid hormones.
The occurrences of steroid hormones in sediment samples from the river and targeted freshwater aquaculture ponds are summarized in Figure 2b and SI Table S4. Fourteen steroid hormones were detected in sediments, with concentrations ranging from 0.59 ± 0.11 ng/g (MGT) to 123 ± 19.9 ng/g (ADR) in river sediments and from 0.36 ± 0.08 ng/g (19-NTD, weever pond) to 24.9 ± 3.64 ng/g (5α-DHP, polyculture pond) in pond sediments. Total detected compounds amounted to 216 ± 17.7 ng/g in river sediment and varied from 1.16 ± 0.14 ng/g (crucian carp pond) to 66.3 ± 5.86 ng/g (bighead carp pond) in pond sediments. The compound 19-NT was consistently detected in all sediment samples, with AED, PGT, 5α-DHP, and MLA prevalent in aquaculture pond sediments. Previous investigations on steroid hormones in sediments are limited. As shown in SI Table S4, the concentrations of AED (1.54–5.24 ng/g) in this study were higher than those reported in aquaculture farms (0.10–1.3 ng/g) [11,25], and Hailing Bay (0.10–0.80 ng/g) [10] but much lower than levels found in fishing ports (<0.28–11 ng/g) [30] and receiving rivers from WWTPs in China (1.4–34 ng/g) [31]. The levels of PGT in this study, ranging from 5.50 ng/g to 22.3 ng/g, resembled those reported in most sediment samples in Spain (ND–6.8 ng/g) [32], Malaysia (0.33–5.3 ng/g) [33], the United States (2.9–22 ng/g) [34], and our previous investigation in fishing ports (<0.24–17 ng/g) [31] but significantly lower compared to those detected in the river sediment in Canada (<13.5–1213 ng/g) [35]. Synthetic steroid hormone 5α-DHP concentrations (15.0–45.1 ng/g) exceeded those in river sediments (5.9 ng/g) [36] but closely resembled those of fishing port sediments (ND–43 ng/g) [30]. These findings indicated that steroid hormones are prevalent in water and sediments, with detected levels akin to those reported in other studies.
3.2. Occurrence of Steroid Hormones in Feed Samples
In the studied freshwater aquaculture ponds, fish were provided commercial feed, in which eight steroid hormones were identified. These included four synthetic steroid hormones (5α-DHP, 17α-BOL, 17β-BOL, and MPA) and four nature steroid hormones (ADD, AED, T, and PGT). The concentrations of synthetic steroid hormones ranged from <LOQ (AED) to 3.43 ± 0.17 ng/g (ADD) (SI Table S4), which were comparatively lower than those previously reported in both freshwater and marine aquaculture contexts [11,25]. Due to ethical and health concerns associated with farm animal husbandry, numerous countries, including China, have outlawed the illegal use of steroid hormones as growth promoters. The present findings indicate that steroid hormones banned in China [37] were not detected in the feeds of this study. In addition, the lower concentrations of steroid hormones in the feed may imply a trend towards a more judicious and regulated administration of steroid hormone dosages.
3.3. Occurrence of Steroid Hormones in Fish Samples
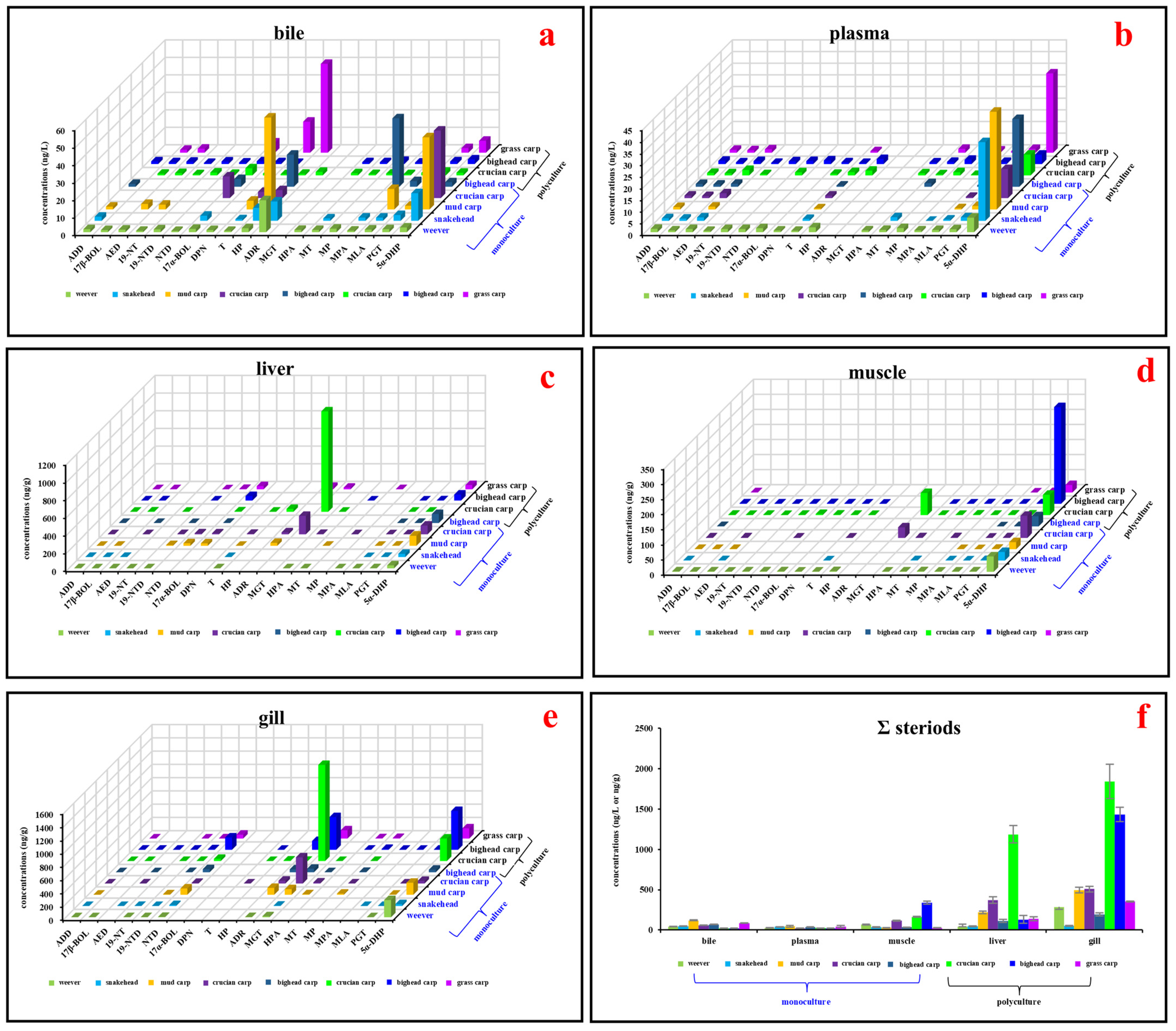
Nineteen steroid hormones were detected in at least one type of tissue (Figure 3 and SI Tables S5 and S6). The aggregate concentrations of these steroid hormones varied across bile, plasma, muscle, liver, and gill, ranging from 20.2 ± 1.80 ng/L (bighead carp with polyculture mode) to 120 ± 6.65 ng/L (mud carp with monoculture mode), from 19.7 ± 3.53 ng/L (crucian carp with monoculture mode) to 46.7 ± 5.12 ng/L (mud carp with monoculture mode), from 27.8 ± 1.21 ng/g (grass carp with polyculture mode) to 339 ± 18.1 ng/g (bighead carp with polyculture mode), from 44.1 ± 2.31 ng/g (weever with monoculture mode) to 1190 ± 108 ng/g (crucian carp with polyculture mode), and from 51.8 ± 3.89 ng/g (snakehead with monoculture mode) to 1480 ± 223 ng/g (crucian carp with polyculture mode), respectively. While no distinct pattern of steroid hormone distribution across tissues was evident, 5α-DHP consistently displayed higher concentrations (Figure 3 and SI Tables S5 and S6). As an artificially synthesized steroid hormone, 5α-DHP in organisms should be enriched from the environment. According to the physical and chemical parameters of 5α-DHP, its relatively high logKow value (3.46) makes it easier to accumulate from water bodies to sediments and organisms [38].
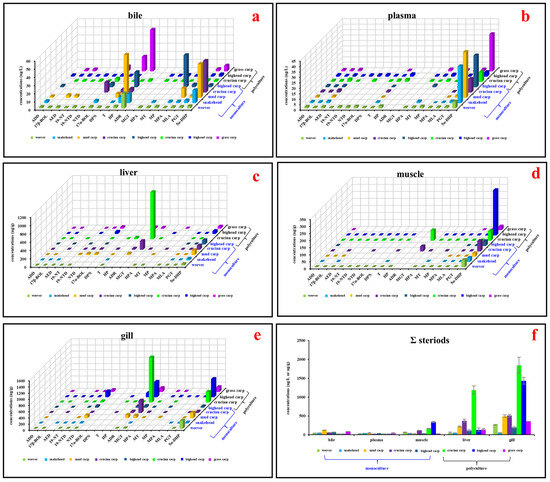
Figure 3.
Concentrations of detected steroid hormones in various fish tissues: (a) Steroid hormone concentrations in bile samples (ng/L). (b) Steroid hormone concentrations in plasma samples (ng/L). (c) Steroid hormone concentrations in liver samples (ng/g). (d) Steroid hormone concentrations in muscle samples (ng/g). (e) Steroid hormone concentrations in gill samples (ng/g). (f) Aggregate concentrations of all detected steroid hormones across different fish tissues (ng/L or ng/g). Abbreviations: ADD, androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione; 17β-BOL, 17β-boldenone; AED, 4-androstene-3,17-dione; 19-NT, 19-nortestosterone; 19-NTD, 19-norethindrone; NTD, norethynodrel; 17α-BOL, 17α-boldenone; DPN, drospirenone; T, testosterone; HP, hydroxy progesterone; ADR, androsterone; MGT, megestrol; 17α-DHP, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone acetate; MT, methyl testosterone; MP, medroxy progesterone; MPA, medroxyprogesterone acetate; MLA, melengestrol acetate; PGT, progesterone; 5α-DHP, 5α-dihydroprogesterone; ∑ steroids, the sum of all detected steroid hormones.
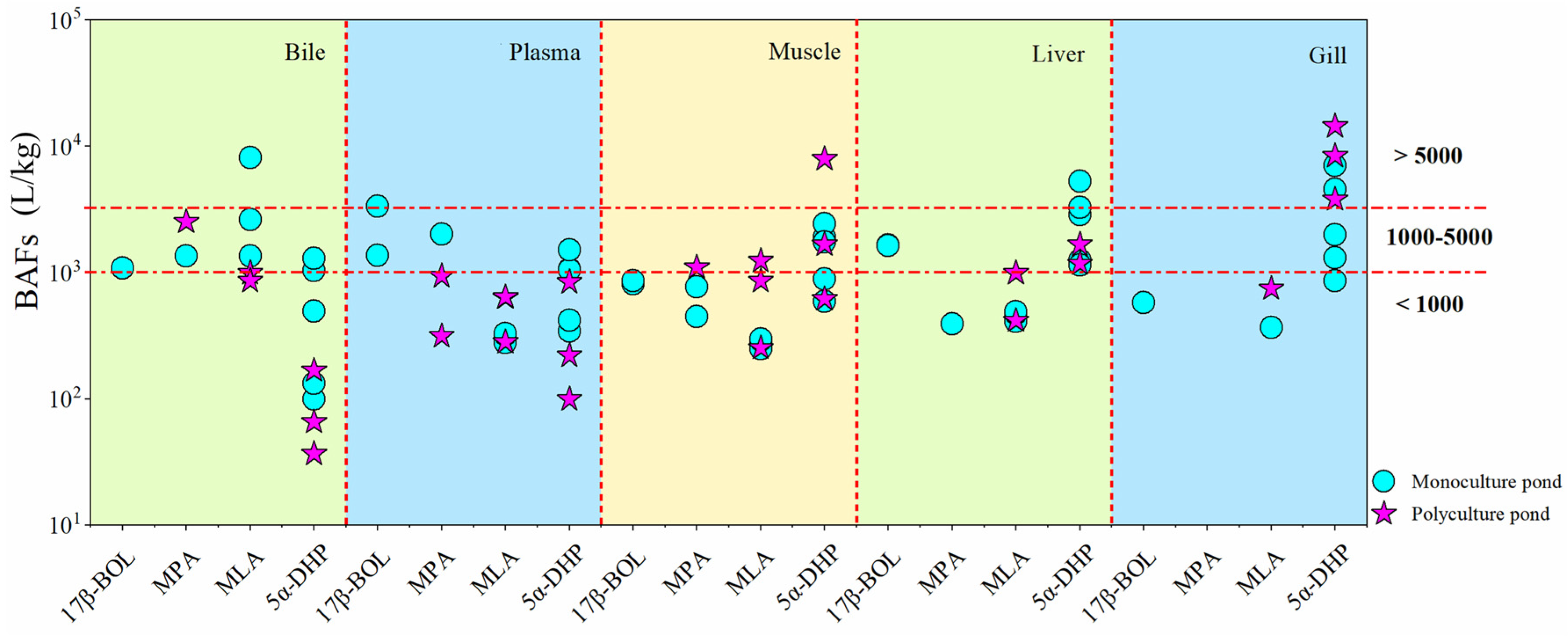
The BAFs for four synthetic steroid hormones (17β-BOL, MPA, MLA, and 5α-DHP) across different tissues and fish species are shown in Figure 4 and SI Table S7. BAF thresholds of 1000 and 5000 L/kg distinguished bioaccumulation potential, where values exceeding 5000 L/kg indicated bioaccumulation, and those between 1000 and 5000 L/kg suggested potential bioaccumulation [39]. Results showed that the highest BAFs for 17β-BOL, MPA, MLA, and 5α-DHP were observed as follows: 1081 L/kg, 2530 L/kg, 8125 L/kg, and 1291 L/kg in bile; 3369 L/kg, 2022 L/kg, 640 L/kg, and 1516 L/kg in plasma; 858 L/kg, 1101 L/kg, 1239 L/kg, and 7926 L/kg in muscle; 1658 L/kg, 395 L/kg, 993 L/kg, and 5312 L/kg in liver; and 577 L/kg, 0 L/kg, 747 L/kg, and 14,444 L/kg in gill, respectively (SI Table S7). These results demonstrate variable bioaccumulations across tissues (Figure 4), with 5α-DHP being particularly prominent, indicating its propensity for bioaccumulation from aquatic environments. It is worth mentioning that 5α-DHP showed significant bioaccumulation potential in muscle tissue, especially in bighead carp under polyculture conditions, highlighting the potential risks associated with its presence in the consumable parts of fish.
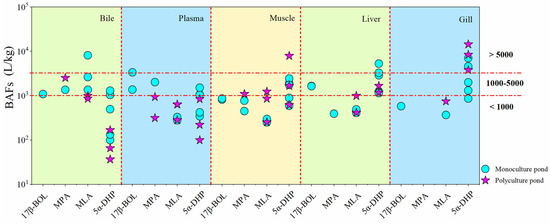
Figure 4.
Bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) of synthetic steroid hormones in various fish tissues. BAF thresholds of 1000 and 5000 L/kg were employed to evaluate bioaccumulation potential, where values exceeding 5000 L/kg indicated bioaccumulation and those ranging from 1000 to 5000 L/kg suggested potential bioaccumulation. Abbreviations: 17β-BOL, 17β-boldenone; MPA, medroxyprogesterone acetate; MLA, melengestrol acetate; 5α-DHP, 5α-dihydroprogesterone.
3.4. Ecological Risk Assessment
Steroid hormone residues in the environment can pose ecological risks and adverse effects on aquatic organisms. This study utilized the RQ approach to assess the potential ecological risks of these steroid hormones. However, due to limited aquatic toxicity data, a comprehensive risk assessment was challenging. Consequently, RQ values were calculated for seven steroid hormones in the aquatic environment and nine in sediment.
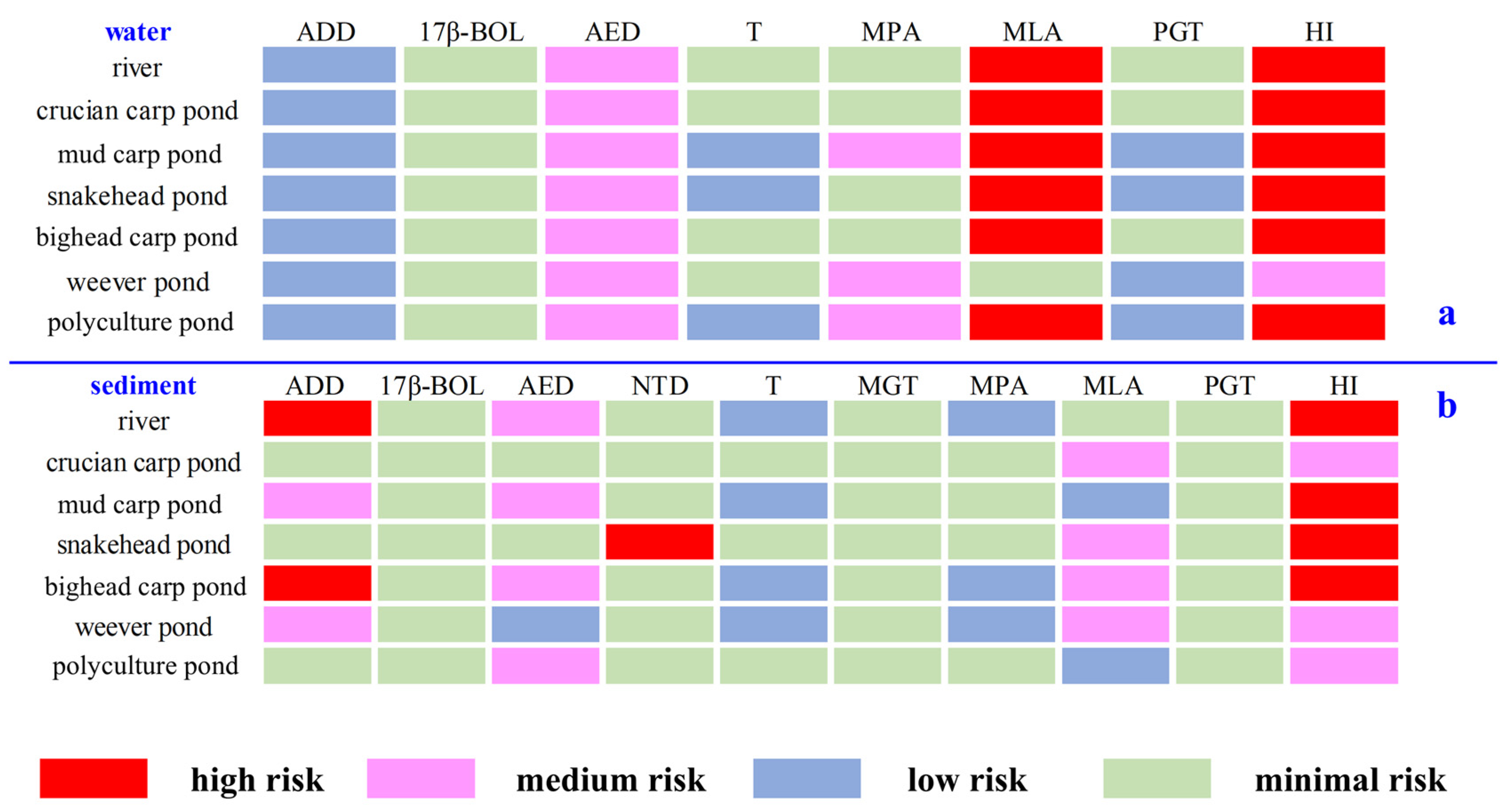
In the aquatic environment, ADD, 17β-BOL, T, and PGT posed low or negligible risks, while AED and most MPAs were at medium risk, and MLA exhibited high risk at all sites except the weever pond (Figure 5 and SI Table S8). The HI indicated high risk at all sampling sites (ranging from 2.02 ± 0.29 in the river to 2.65 ± 0.47 in the polyculture pond), primarily due to AED and MLA, except for the weever pond, which showed medium risk (0.66 ± 0.08). AED, commonly found in aquatic environments, has been associated with medium to high risk in other settings, such as aquaculture farms or domestic sewage [25,40]. Short-term exposure to environmental concentrations of AED may alter fish morphology or stimulate aromatase activity in fish brains [41], suggesting that steroid hormone pollution in aquaculture ponds poses serious risks to aquatic organisms and may escalate through the food chain, endangering human health. Furthermore, the untreated discharge of aquaculture wastewater could exert eco-toxic effects on the receiving ecosystems.
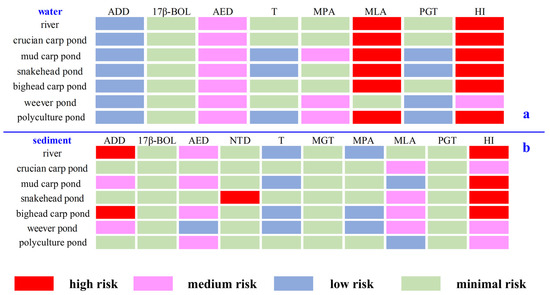
Figure 5.
Risk quotients of detected steroid hormones: (a) Risk quotients of detected steroids in water samples. (b) Risk quotients of detected steroids in sediments. Abbreviations: ADD, androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione; 17β-BOL, 17β-boldenone; AED, 4-androstene-3,17-dione; NTD, norethynodrel; T, testosterone; MGT, megestrol; MPA, medroxyprogesterone acetate; MLA, melengestrol acetate; PGT, progesterone; HI, hazard index.
Studies have shown that sediment is the primary reservoir for steroid hormones in the environment, and 73% of total steroid hormones accumulate in sediment [42]. However, the ecological risks associated with various steroid hormones in fish pond sediments remain underexplored, highlighting the need for quantitative risk assessments. This study showed that 17β-BOL, T, MGT, MPA, and PGT posed low or negligible risks, while AED and MLA posed medium risks at most sampling sites. ADD exhibited medium risk in mud carp and snakehead ponds and high risk in river and crucian carp pond. NTD was generally risk-free, except in the snakehead pond, where it displayed high risk (Figure 5 and SI Table S9). HI results indicated medium risks in the crucian carp pond (0.12 ± 0.03), weever pond (0.95 ± 0.12), and polyculture pond (0.25 ± 0.04), whereas risks were high in the river (3.28 ± 0.47), mud carp pond (1.03 ± 0.10), snakehead pond (98.5 ± 35.0), and bighead carp pond (2.41 ± 0.10). It is worth noting that this is consistent with the conclusion of the previous study on steroid hormone risks of 15 typical fishing ports in Southeast China. That is, the ecological risk of steroid hormones in the sediment environment of fishing ports needs to attract more attention [30]. High risks of steroid hormones in both aquatic and sediment environments imply the necessity for further research and proper management of aquaculture ecosystems.
3.5. Human Health Risk Assessment
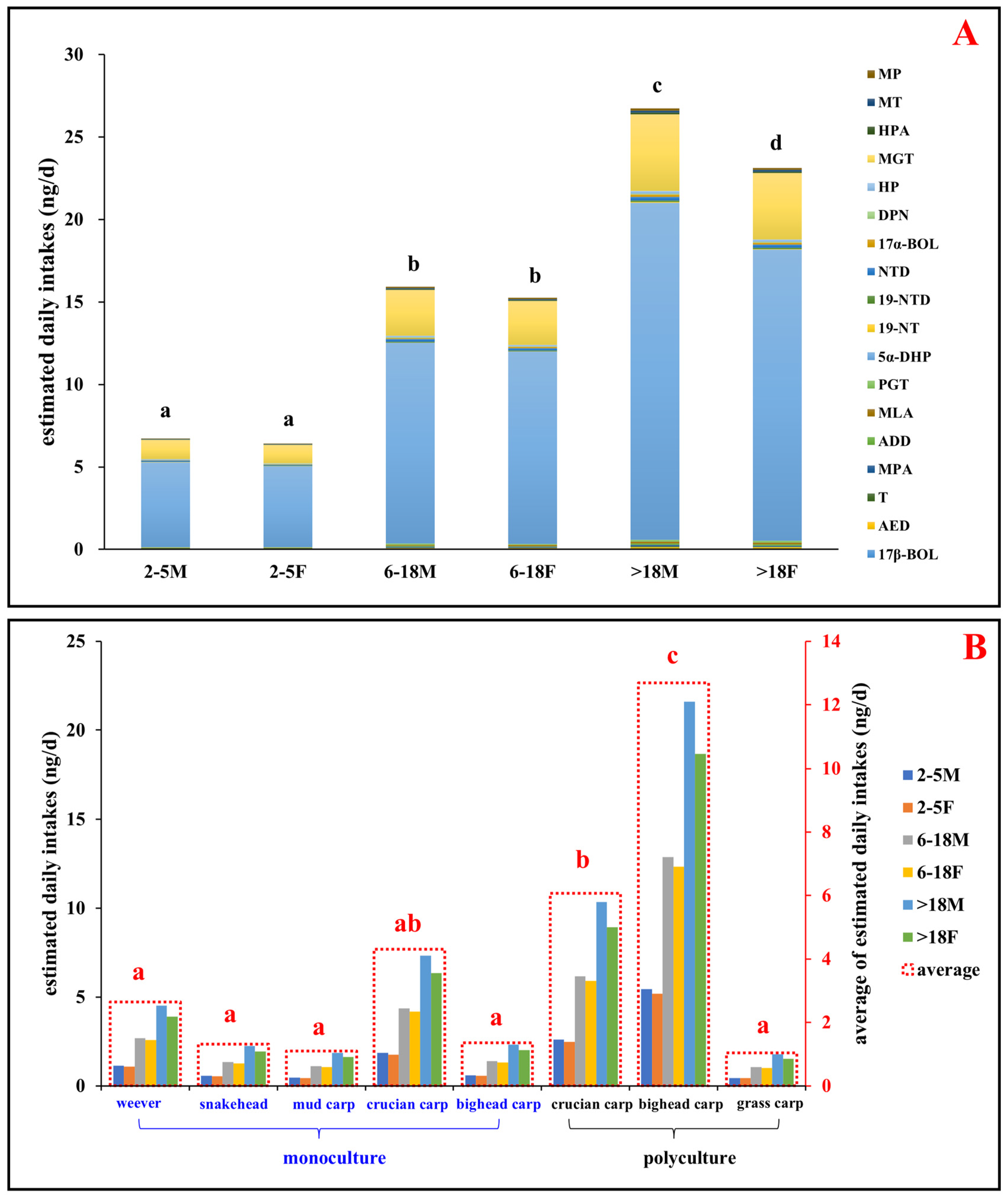
The estimated daily intake (EDIs) values were calculated to evaluate potential human health risks from the consumption of aquatic products. The dietary exposure for local consumers was categorized into six demographic groups: children (2–5 years, male and female), adolescents (6–18 years, male and female) and adults (>18 years, male and female). Results showed that the EDIs of total steroid hormones from aquatic products by male and female children, adolescents, and adults were 0.45–5.43 ng/day/person and 0.43–6.43 ng/day/person, 1.06–12.9 ng/day/person and 1.01–12.3 ng/day/person, and 1.77–21.6 ng/day/person and 1.53–18.7 ng/day/person, respectively (Figure 6 and SI Tables S10 and S11). These EDI estimates are comparable to those reported for marine fish consumption in the Pearl River Delta in 2022 [13] yet significantly lower than those reported for freshwater and marine fish consumption in South China in 2017 [11,25]. The lower EDI values in the present study may result from effective local government measures, such as regulating land-based wastewater discharges and restricting steroid hormone use in aquaculture [13].
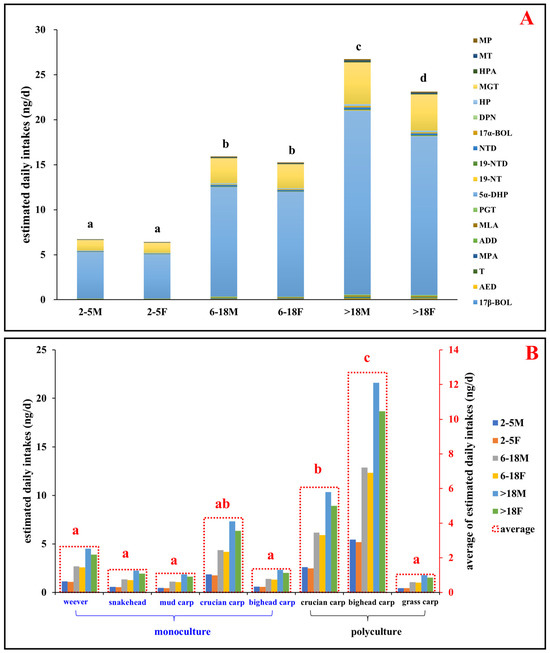
Figure 6.
Estimated daily intakes (EDIs, ng/d) of steroid hormones via fish consumption: (A) EDIs of individual detected steroid hormones in aquatic products across different age and sex groups, calculated based on the maximum concentration of each steroid hormone in fish muscle. (B) EDIs of the total detected steroid hormones from various fish species across different age and sex groups. Age and sex categories: 2–5 M and 2–5 F, children (2–5 years, male and female); 6–18 M and 6–18 F, adolescents (6–18 years, male and female); >18 M and >18 F, adults (>18 years, male and female). Letters (a, b, c, d) denote statistically significant differences between groups. Abbreviations: MP, medroxy progesterone; MT, methyl testosterone; HPA, hydroxyprogesterone acetate; MGT, megestrol; HP, hydroxy progesterone; DPN, drospirenone; 17α-BOL, 17α-boldenone; NTD norethynodrel; 19-NTD, 19-norethindrone; 19-NT, 19-nortestosterone; 5α-DHP, 5α-dihydroprogesterone; PGT, progesterone; MLA, melengestrol acetate; ADD, androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione; MPA, medroxyprogesterone acetate; T, testosterone; AED, 4-androstene-3,17-dione; 17β-BOL, 17β-boldenone.
Furthermore, the health risk assessment revealed higher risks for males than females across all age groups and fish species, which is consistent with the findings of Liu [25]. The differences in EDI values among groups mainly reflect variations in fish consumption. Notably, there were no significant EDI differences between genders in childhood or adolescence, but significant variations were observed in adulthood (Figure 6, p < 0.01). In addition, the EDIs from consuming weever, snakehead, mud carp, crucian carp, and bighead carp in monoculture were 1.03–4.51 ng/day/person, 0.54–2.24 ng/day/person, 0.45–1.87 ng/day/person, 1.76–7.34 ng/day/person, and 0.56–2.32 ng/day/person, respectively (Figure 6). Conversely, EDIs from consuming crucian carp, bighead carp, and grass carp in polyculture were 2.49–10.3 ng/day/person, 5.19–21.6 ng/day/person, and 0.43–1.77 ng/day/person, respectively (Figure 6). The significantly higher EDI values for bighead carp in polyculture compared to monoculture and other species (p < 0.01) suggest a link between health risks and both fish species and aquaculture types. The health risks were notably higher for polyculture consumption, especially of bighead and crucian carp, while grass carp in polyculture and other species in monoculture posed lower risks. Considering that the water source and feed are identical for both polyculture and monoculture fish ponds, the observed differences in risks between these aquaculture modes might stem from two primary factors. First, the variance in the release of steroid hormones from sediments could be attributed to differences in pond drying durations prior to the current cultivation cycle, leading to varied steroid hormone reserves in the sediment. This underscores the importance of pond drying before the start of a cultivation cycle. Second, the interspecies competition for food and habitat in polyculture environments could induce physiological stress, potentially enhancing the synthesis and accumulation of steroid hormones in fish. Additionally, this competition may cause disturbances in the sediment by the fish in polyculture ponds, further promoting the release of steroid hormones from the sediment.
According to the guidelines of the International Joint Food and Agricultural Organization’s World Health Organization Expert Committee on Food Additives, only T and PGT have ADIs of 120 μg/d and 1800 μg/d for a 60 kg adult. Based on the available EDIs and corresponding ADIs, the risks of T and PGT to the health of local consumers via the consumption of aquatic products were calculated. The calculated HQs of T and PGT ranged from 0 to 4.188 × 10−7 and 3.903 × 10−8 to 6.848 × 10−8 (Table 1). Such low HQs suggested that the health risks associated with these two steroids for adults consuming aquatic products are minimal, regardless of whether they originate from polyculture mode or monoculture systems. This finding is consistent with previous reports on marine aquaculture [13,25]. However, these findings are based only on theoretical calculations for an individual substance. Future studies should address the potential adverse effects from combined steroid hormone exposure.

Table 1.
The hazard quotients (HQs) of testosterone and progesterone for local adult consumers.
4. Conclusions
This study comprehensively examined the distribution of steroid hormones in the environment, their bioaccumulation in aquatic products, and associated environmental and health risks within commercial freshwater aquaculture farms employing different aquaculture modes (monoculture and polyculture). Totals of 9, 14, and 19 steroid hormones were detected in water, sediment, and biotic samples, respectively. Steroid hormones are ubiquitous in the aquatic environment and sediments of target fish ponds at concentrations of ng/L and ng/g. HI calculation results revealed medium to high risk across all sampling sites, indicating the necessity for further research and effective management of aquaculture environments.
Despite low EDI and HQ values, the high BAFs highlighted the importance of stringent regulatory measures by local authorities, such as controlling steroid use in aquaculture and addressing pollution from human activities. Additionally, steroid hormone-related health risk is linked not only to the fish species but also closely to the mode of aquaculture practice. Findings suggest that the health risks of steroid hormones exposure from consuming fish reared in polyculture systems (e.g., bighead carp) are higher, compared to monoculture systems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16202872/s1, Table S1: Detailed characterization of Androgens, Glucocorticoids, and Progestagens along with their multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) parameters in rapid resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (RRLC-MS/MS); Table S2: Recoveries of steroids in water, sediment, and biota samples; Table S3: Concentrations of detected steroid hormones in water samples; Table S4: Concentrations of detected steroid hormones in sediment samples; Table S5: Concentrations of detected steroid hormones in fish tissues under monoculture rearing conditions; Table S6: Concentrations of detected steroid hormones in fish tissues under polyculture rearing conditions; Table S7: Bio-concentration factor (BAF) values of four synthetic steroid hormones across various tissues in multiple fish species; Table S8: Calculated risk quotient (RQ) and hazard index (HI) for seven steroid hormones in aqueous environments; Table S9: Calculated risk quotient (RQ) and hazard index (HI) for nine steroid hormones in sediments; Table S10: Estimated daily intake (EDIs) values of detected steroid hormones from aquatic product consumption in monoculture system among male and female children, adolescents and adults; Table S11: Estimated daily intake (EDIs) values of detected steroid hormones from aquatic product consumption in polyculture system among male and female children, adolescents and adults.
Author Contributions
S.-S.L.: methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. Y.-F.L.: visualization and investigation. J.-J.N.: methodology and formal analysis. L.X.: methodology. L.-G.W.: data curation. D.-L.H.: investigation. X.-H.W.: methodology. Q.-H.T.: investigation. F.-Y.D.: conceptualization and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS (NO. 2020TS01), Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Pollution and Environmental Safety (2019B030301008), and Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai) (SML2023SP237).
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the findings of this study are provided in the Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Cho, S.H.; Pyo, H.; Lee, J.J.; Zee, S.; Kim, E.; Park, J.W.; Park, C.B. Reproductive disorders linked to the interaction between sex steroid and thyroid hormonal activities, oxidative stress responses, and the rate of metabolism of tris (1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCPP) in zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 265, 115535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.Q.; Jing, Z.X.; Pan, C.G.; Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Hou, L.P.; Dong, Z.D. The progestin norethindrone alters growth, reproductive histology and gene expression in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzegorzek, M.; Wartalska, K.; Kowalik, R. Occurrence and sources of hormones in water resources—Environmental and health impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 37907–37922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, D.Y.; Kacew, S.; Dekant, W. Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA): Possible modes of action of toxicity and carcinogenicity in rodents. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Kumar, V.; Vimal, S.; Umesh, M.; Sharma, P.; Thazeem, B.; Kaur, K.; Thomas, J.; Pasrija, R.; Utreja, D. Hazard identification of endocrine-disrupting carcinogens (EDCs) in relation to cancers in humans. Environ. Toxicol. Phar. 2024, 109, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, S.; Willi, R.A.; Salgueiro-González, N.; Fent, K. Effects of new generation progestins, including as mixtures and in combination with other classes of steroid hormones, on zebrafish early life stages. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazrouei, B.; Islayem, D.; Alskafi, F.; Catacutan, M.K.; Amna, R.; Nasrat, S.; Sizirici, B.; Yildiz, I. Steroid hormones in wastewater: Sources, treatments, environmental risks, and regulations. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishan, A.; Khalid, N.K.; Rayaroth, M.P.; Thomas, S.; Nazim, A.; Aravindakumar, C.T.; Aravind, U.K. Occurrence and distribution of steroid hormones (estrogen) and other contaminants of emerging concern in a south indian water body. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.; Yavari, Z.; Nikoo, M.R.; Al-Nuaimi, A.; Karimi, H. Machine learning model optimization for removal of steroid hormones from wastewater. Chemosphere 2023, 343, 140209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Ying, G.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, Y.Y.; He, L.Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.R.; Zhao, J.L. Occurrence and removal of progestagens in two representative swine farms: Effectiveness of lagoon and digester treatment. Water Res. 2015, 77, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Qi, Z.H.; Chen, H.; Hao, Q.W.; Hu, Y.X.; Zhao, J.L.; Ying, G.G. Steroid bioaccumulation profiles in typical freshwater aquaculture environments of South China and their human health risks via fish consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toso, A.; Garoche, C.; Balaguer, P. Human and fish differences in steroid receptors activation: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.P.; Xie, H.W.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Zhu, Y.C.; Tao, H.C.; Wong, M.H. Spatiotemporal distribution, source apportionment and risk assessment of typical hormones and phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in environmental and biological samples from the mariculture areas in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojoghoro, J.O.; Scrimshaw, M.D.; Sumpter, J.P. Steroid hormones in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, Z.G.; Cui, H.W.; Bai, Y.; Yin, Z.D.; Qu, K.M. Hazardous substances and their removal in recirculating aquaculture systems: A review. Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.A.d.S.; Starling, M.C.V.; de Barros, A.L.C.; Santos, M.C.; da Silva, E.S.; Viana, G.C.C.; Ribeiro, L.F.d.S.; Simcik, M.F.; Amorim, C.C. Occurrence of antibiotics, hormones and PFAs in surface water from a Nile tilapia aquaculture facility in a Brazilian hydroelectric reservoir. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi-Lalabadi, M.; Pirsaheb, M. Investigation of steroid hormone residues in fish: A systematic review. Process Saf. Environ. 2021, 152, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Liu, S.; Pan, Y.F.; Wu, N.N.; Huang, Q.Y.; Li, H.X.; Lin, L.; Hou, R.; Xu, X.R.; Cheng, Y.Y. Steroid metabolites as overlooked emerging contaminants: Insights from multimedia partitioning and source–sink simulation in an estuarine environment. J. Hazard Mater. 2024, 461, 132673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnalls, T.J.; Beresford, N.; Kugathas, S.; Margiotta-Casaluci, L.; Scholze, M.; Scott, A.P.; Sumpter, J.P. From single chemicals to mixtures—Reproductive effects of levonorgestrel and ethinylestradiol on the fathead minnow. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 169, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Lam, T.-T.; Quan, T.C.; Bui, M.Q.; Dao, Y.H.; Le, G.T. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals in Vietnamese marine fish: Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.D.; Shearer, G.; Farrington, W.H. The effect of cooking on veterinary drug residues in food: 1. Clenbuterol. Food Addit. Contam. 1995, 12, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleadin, J.; Samardžija, M. Hormonally active substances in the food chain from farm animals to consumers. Vet. Stanica 2019, 50, 501–512. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Yang, Z.G.; Luo, Z.F.; Li, H.P.; Chen, G.Y. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in wild freshwater fishes: Species, tissues, sizes and human health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Tan, X.; Huang, C.; Zhao, H.; Lan, W. Sources, pollution characteristics, and ecological risk assessment of steroids in Beihai bay, Guangxi. Water 2022, 14, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.R.; Hao, Q.W.; Zhao, J.L.; Ying, G.G. Three classes of steroids in typical freshwater aquaculture farms: Comparison to marine aquaculture farms. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E.C. (European Commission) (Ed.) European Commission Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances and Commission Regulation No 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substances, Part II; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.Y.; Wu, F.C.; Shen, R.L.; Zeng, E.Y. Dietary intake and potential health risk of DDTs and PBDEs via seafood consumption in South China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2010, 73, 1812–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food Supply-Livestock and Fish Primary Equivalent. 2011. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/CL/ (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Yu, Q.M.; Yang, X.D.; Zhao, F.Z.; Hu, X.D.; Ren, H.Q.; Geng, J.J. Occurrence and removal of progestogens from wastewater treatment plants in China: Spatiotemporal variation and process comparison. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tian, F.; Pan, Y.F.; Li, H.X.; Lin, L.; Hou, R.; Zhang, L.B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.S.; Xu, X.R. Contamination and ecological risks of steroid metabolites require more attention in the environment: Evidence from the fishing ports. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.L.; Pei, J.Y.; Zhang, R.J.; Wang, S.P.; Zeng, W.B.; Huang, D.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Yu, K.F. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in mariculture farms, estuaries and the coast of the Beibu Gulf, China: Bioconcentration and diet safety of seafood. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2018, 154, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alda, M.J.L.; Gil, A.; Paz, E.; Barceló, D. Occurrence and analysis of estrogens and progestogens in river sediments by liquid chromatography-electrospray-mass spectrometry. Analyst 2002, 127, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, T.F.T.; Aris, A.Z.; Yusoff, F.M.; Mustafa, S. Occurrence, distribution, and sources of emerging organic contaminants in tropical coastal sediments of anthropogenically impacted Klang River estuary, Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulabagal, V.; Wilson, C.; Hayworth, J.S. An ultrahigh-performance chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry quantitative method for trace analysis of potential endocrine disrupting steroid hormones in estuarine sediments. Rapid Commun. Mass Sp. 2017, 31, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarahmadi, H.; Duy, S.V.; Hachad, M.; Dorner, S.; Sauvé, S.; Prévost, M. Seasonal variations of steroid hormones released by wastewater treatment plants to river water and sediments: Distribution between particulate and dissolved phases. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.S.; Ying, G.G.; Liu, S.; Lai, H.J.; Chen, Z.F.; Pan, C.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Chen, J. Analysis of 21 progestagens in various matrices by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) with diverse sample pretreatment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7299–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, Aquaculture Medication Understanding Sheet No. 1 and 2. 2022. Available online: http://www.yyj.moa.gov.cn/gzdt/202211/t20221115_6415528.htm (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Fent, K. Progestins as endocrine disrupters in aquatic ecosystems: Concentrations, effects and risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioaccumulation Criteria. 2012. Available online: http://www.pbtprofiler.net/criteria.asp/ (accessed on 2 March 2024).
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.S.; Deng, W.J.; Ying, G.G. Removal of steroid hormones and biocides from rural wastewater by an integrated constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallgren, S.; Olsén, K.H. Effects on guppy brain aromatase activity following short-term steroid and 4-nonylphenol exposures. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhao, J.L.; Ying, G.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Pan, C.G. Emission estimation and multimedia fate modeling of seven steroids at the river basin scale in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7982–7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).