Occurrence and Formation Mechanisms of High-Fluoride Groundwater in Xiong’an New Area, Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
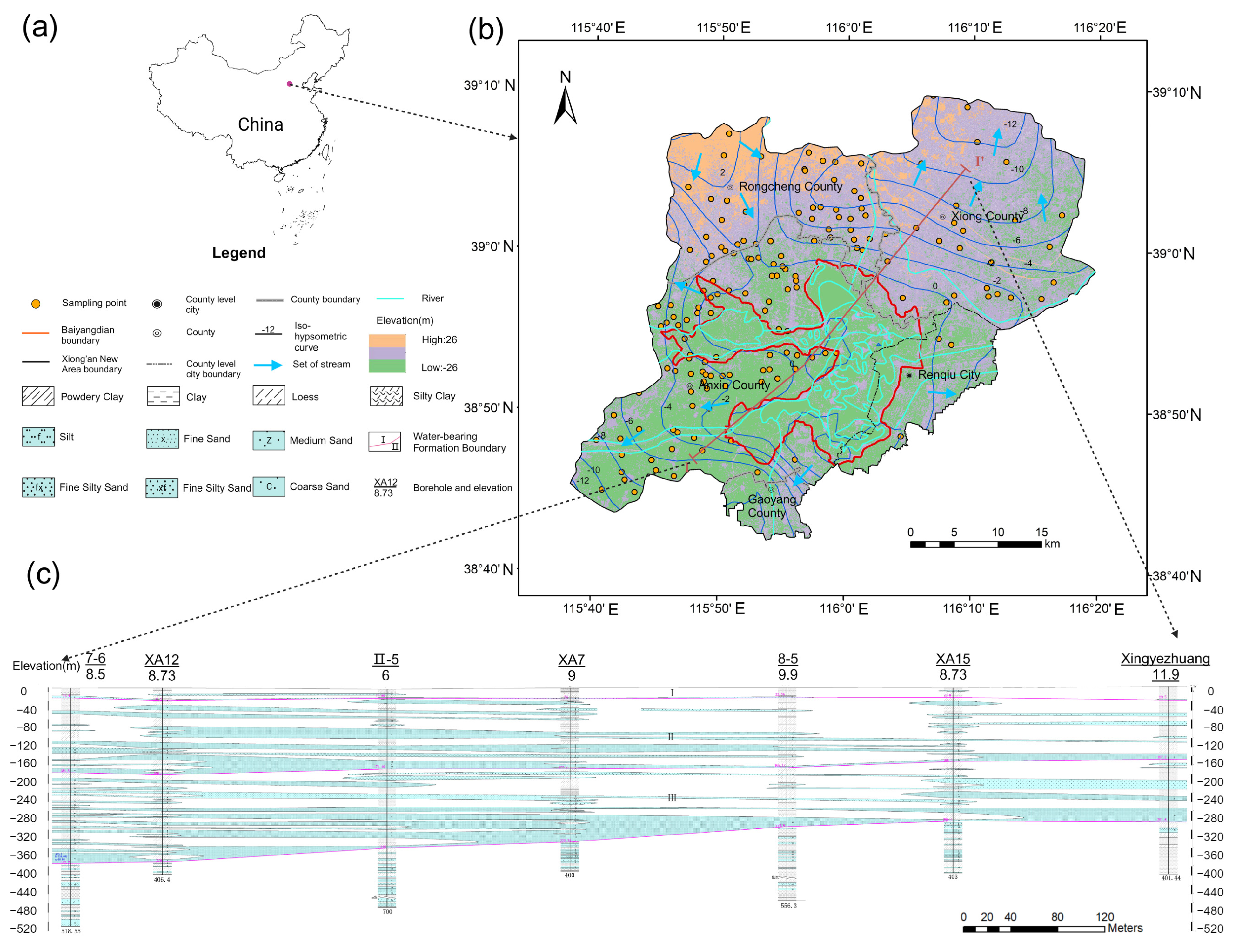
2. Research Area
2.1. Overview of the Research Area
2.2. Stratum Lithologic and Main Mineral Composition
2.3. Hydrogeology
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Water Sampling and Detection
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. General Hydrochemistry of Groundwater
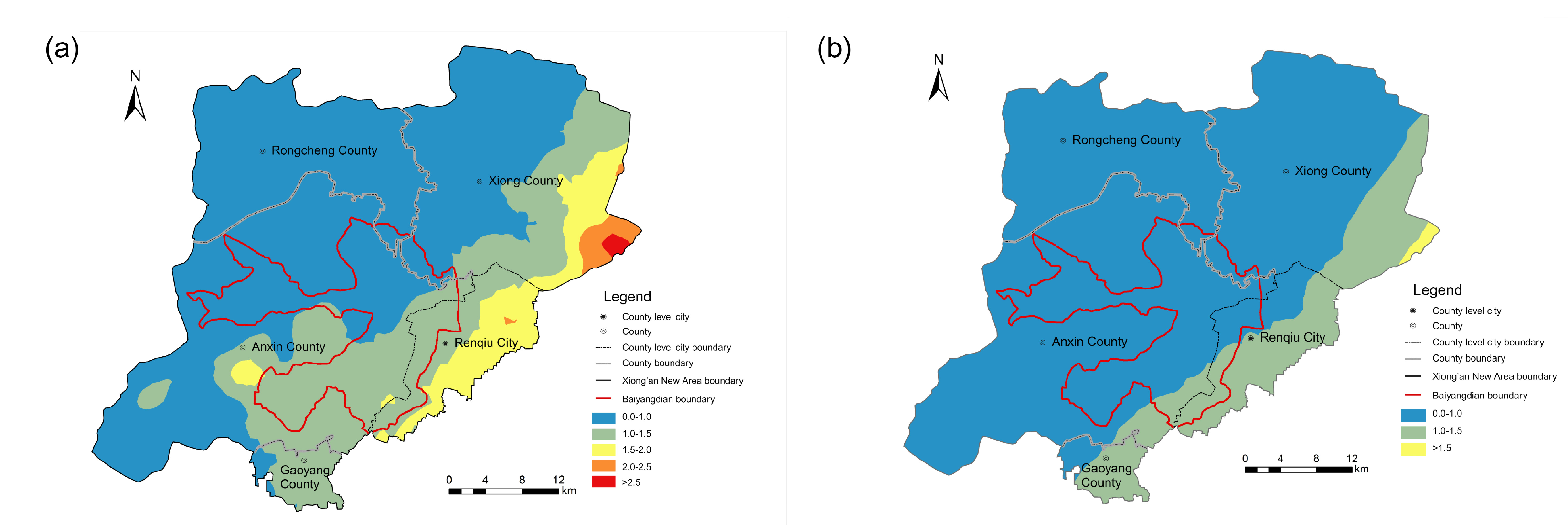
4.2. Distribution of Fluoride-Bearing Groundwater
4.3. Hydrochemical Processes for Fluoride Enrichment
5. Discussion
5.1. Genesis Analysis of Groundwater Hydrochemistry
5.2. Formation Mechanisms of High Fluoride Groundwater
5.2.1. Alkaline Environment
5.2.2. Competitive Adsorption
5.2.3. Evaporation
5.2.4. Evaporite Dissolution and Salt Effect
5.2.5. Ion Exchange
5.2.6. Dissolution Equilibrium of the Typical Minerals
- (1)
- F-bearing minerals dissolution equilibrium
- (2)
- Calcium and magnesium dissolution equilibrium
5.3. Practical Implication
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Global analysis and prediction of fluoride in groundwater. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Howard, K. Groundwater fluoride and arsenic mobilization in a typical deep aquifer system within a semi-arid basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Ayub, M.; Bundschuh, J.; Gao, X.; Ullah, Z.; Ali, L.; Li, C.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, S.; Rinklebe, J. Geochemical control, water quality indexing, source distribution, and potential health risk of fluoride and arsenic in groundwater: Occurrence, sources apportionment, and positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Goswami, R.; Patel, A.K.; Srivastava, M.; Das, N. Scenario, perspectives and mechanism of arsenic and fluoride co-occurrence in the groundwater: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, I.; Singh, U.K. Exploring a variance decomposition approach integrated with the Monte Carlo method to evaluate groundwater fluoride exposure on the residents of a typical fluorosis endemic semi-arid tract of India. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunkari, E.D.; Abu, M.; Zango, M.S. Geochemical evolution and tracing of groundwater salinization using different ionic ratios, multivariate statistical and geochemical modeling approaches in a typical semi-arid basin. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 236, 103742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwiathi, N.F.; Gao, X.; Li, C.; Rashid, A. The occurrence of geogenic fluoride in shallow aquifers of Kenya Rift Valley and its implications in groundwater management. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2022, 229, 113046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Patra, P.K. Hydrogeochemical characterisation and health hazards of fluoride enriched groundwater in diverse aquifer types. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Brown, C.J.; Johnson, T.D.; Belitz, K.; Lindsey, B.D. Fluoride occurrence in United States groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaiz, A.; Khattak, J.A.; Hussain, I.; Masood, N.; Javed, T.; Farooqi, A. Salinity enrichment, sources and its contribution to elevated groundwater arsenic and fluoride levels in Rachna Doab, Punjab Pakistan: Stable isotope (δ2H and δ18O) approach as an evidence. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Najafi Saleh, H.; Yaseri, M.; Jalilzadeh, M.; Mohammadi, A.A. Association of consumption of excess hard water, body mass index and waist circumference with risk of hypertension in individuals living in hard and soft water areas. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakate, R.; More, S.; Duvva, L.K.; Enjamuri, S. Groundwater chemistry and health hazard risk valuation of fluoride and nitrate enhanced groundwater from a semi-urban region of South India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2023, 30, 43554–43572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, V.; Nwabisa, D.P.; Rajmohan, N. Evaluation of high fluoride contaminated fractured rock aquifer in South Africa–Geochemical and chemometric approaches. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, S.; Qin, L.; Li, X. Investigating sources, driving forces and potential health risks of nitrate and fluoride in groundwater of a typical alluvial fan plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health of China. China Health Statistical Yearbook; Peking Union Medical College Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. World Health Organ. 2011, 216, 303–304. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5749-2022[S/OL]; Sanitary Standard for Drinking Water; State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- GB/T 14848-2017[S/OL]; Groundwater Quality Standard; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Gao, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Feng, J.; Fang, S.; Cui, Y. Formation and in situ treatment of high fluoride concentrations in SG of a semi-arid region: Jiaolai Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xiao, Y.; Han, P.; Hao, Q.; Gu, X.; Men, B.; Huang, L. Investigation of groundwater contamination and health implications in a typical semiarid basin of North China. Water 2020, 12, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, A.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Source and enrichment mechanism of fluoride in groundwater of the Hotan Oasis within the Tarim Basin, Northwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, T.; Mathurin, F.A.; Drake, H.; Åström, M.E. Fluoride abundance and controls in fresh groundwater in Quaternary deposits and bedrock fractures in an area with fluorine-rich granitoid rocks. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zango, M.S.; Sunkari, E.D.; Abu, M.; Lermi, A. Hydrogeochemical controls and human health risk assessment of groundwater fluoride and boron in the semi-arid North East region of Ghana. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 207, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Farooqi, A.; Gao, X.; Zahir, S.; Noor, S.; Khattak, J.A. Geochemical modeling, source apportionment, health risk exposure and control of higher fluoride in groundwater of sub-district Dargai, Pakistan. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Ni, P.; Liang, X. Occurrence and formation of high fluoride groundwater in the Hengshui area of the North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, H.; Fu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Nan, T.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z. Spatial distribution and controlling mechanisms of high fluoride groundwater in the coastal plain of Bohai Rim, North China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Fang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zou, Z.; Gao, Y.; Xu, P.; Jiao, X.; Ren, M. Assessing the Hydrochemistry, Groundwater Drinking Quality, and Possible Hazard to Human Health in Shizuishan Area, Northwest China. Water 2023, 15, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Qian, C.; Zhu, G. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region, northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhu, Y. An isotope hydrochemical approach to understand fluoride release into groundwaters of the Datong Basin, Northern China. Environ. Sci.-Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xue, X.; Qian, K.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y. Hydrogeochemical processes controlling the mobilization and enrichment of fluoride in groundwater of the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhu, C. Water quality responses to the interaction between surface water and groundwater along the Songhua River, NE China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1591–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; Mi, W.; Xie, S.; Ji, L. Land-use change caused by anthropogenic activities increase fluoride and arsenic pollution in groundwater and human health risk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ke, L.; Pan, H.; Zhan, S.; Liu, K.; Ma, R. Long-Term Surface Water Changes and Driving Cause in Xiong’an, China: From Dense Landsat Time Series Images and Synthetic Analysis. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, S.; Kong, X.; Zheng, W.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, R.; Song, X.; Sprenger, M. Interaction of Surface Water and Groundwater Influenced by Groundwater Over-Extraction, Waste Water Discharge and Water Transfer in Xiong’an New Area, China. Water 2019, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Qi, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, B.; Yi, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Hebei Key Laboratory of Geological Resources and Environment Monitoring and Protection; et al. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater and Pore-Water and the Paleoenvironmental Evolution in the Past 3.10 Ma in the Xiong’an New Area, North China. China Geol. 2021, 4, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, J. Shallow Groundwater Dynamics in North China Plain. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Guo, H.; Zhan, Y. Groundwater Hydrochemical Characteristics and Processes along Flow Paths in the North China Plain. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 70–71, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Xing, L.; Zhan, Y.; Li, F.; Shao, J.; Niu, H.; Liang, X.; Li, C. Geochemical Behaviors of Rare Earth Elements in Groundwater along a Flow Path in the North China Plain. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 117, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, H.; Huo, S. Organochlorine Pesticides in Aquatic Hydrophyte Tissues and Surrounding Sediments in Baiyangdian Wetland, China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 67, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, B.; Yang, Q.; Lan, Y. Impacts of Water Level Fluctuations on Detritus Accumulation in Lake Baiyangdian, China. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Jin, M.; Liang, X.; Zhan, H. Estimating groundwater recharge beneath irrigated farmland using environmental tracers fluoride, chloride and sulfate. Hydrogeolo. J. 2013, 21, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, Z.; Song, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, S. Groundwater quality assessment and hydrogeochemical processes in typical watersheds in Zhangjiakou region, northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2022, 29, 3521–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xie, X. Evolution of groundwater salinity and fluoride in the deep confined aquifers of Cangzhou in the North China plain after the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 147, 105485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Currell, M.J.; Guo, H. Controls on distributions of sulphate, fluoride, and salinity in aquitard porewater from the North China Plain: Long-term implications for groundwater quality. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Qian, K.; Xie, X.; Xue, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Fluoride and iodine enrichment in groundwater of North China Plain: Evidences from speciation analysis and geochemical modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Song, X.; Lu, Y.; Liang, S.; Liu, G. Fluoride enrichment mechanisms and related health risks of groundwater in the transition zone of geomorphic units, northern China. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, H.; Ma, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Study on Hydrochemical Origins and Health Geology Regionalization of Shallow Groundwater in Xiong’an New Area. Geol. China 2022, 1–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Ma, F. Groundwater Resources and Environment in China; Earthquake Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K. Research on Commonjunctive Sustainability of Groundwater Resources and Wetlands in Xiong’an New Area. Ph.D. Dissertation, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. Study on sustainable utilization of groundwater resources in North China Plain. Resour. Sci. 2009, 31, 355–360. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB 5749-2006[S/OL]; Hygienic Standard of Drinking, Water; Ministry of Health of People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S. A characterization of groundwater fluoride, influencing factors and risk to human health in the southwest plain of Shandong Province, North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Dalkilic, M.; Zhu, C. SUPCRTBL: A revised and extended thermodynamic dataset and software package of SUPCRT92. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 90, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C. Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3—A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. U. S. Geol. Surv. Tech. Methods 2013, 6, 497. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Teng, Y.; Tu, K.; Zhu, C. A library of BASIC scripts of reaction rates for geochemical modeling using phreeqc. Comput. Geosci.-UK 2019, 133, 104316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Geochemical factors controlling the occurrence of high-fluoride groundwater in the western region of the Ordos basin, northwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeller, H. Geochemistry of groundwater. In Groundwater Studies-an International Guide for Research and Practice; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1977; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Guo, H.; Xi, B.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, R.; Yi, W.; Xue, X. Sources of groundwater salinity and potential impact on arsenic mobility in the western Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, C.K.; Kumari, R.; Singh, N.; Mallick, J.; Mukherjee, S. Fluoride enrichment in aquifers of the Thar Desert: Controlling factors and its geochemical modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2462–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Bootharaju, M.; Pradeep, T. Surface complexation of fluoride at the activated nano-gibbsite water interface. Colloid. Surface. A 2014, 462, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, F. Geochemical controls on fluoride concentrations in natural waters from the middle Loess Plateau, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currell, M.; Cartwright, I.; Raveggi, M.; Han, D. Controls on elevated fluoride and arsenic concentrations in groundwater from the Yuncheng Basin, China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacks, G.; Bhattacharya, P.; Chaudhary, V.; Singh, K. Controls on the genesis of some high-fluoride groundwaters in India. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, M.E.; Manzano, M.; Vives, L. Assessment of processes controlling the regional distribution of fluoride and arsenic in groundwater of the Pampeano Aquifer in the Del Azul Creek basin (Argentina). J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1067–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W. Diverse mechanisms drive fluoride enrichment in groundwater in two neighboring sites in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaka, L.A.; Wilke, F.D.; Olago, D.O.; Odada, E.O.; Mulch, A.; Musolff, A. Groundwater fluoride enrichment in an active rift setting: Central Kenya Rift case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q. Enrichment of fluoride in groundwater under the impact of saline water intrusion at the salt lake area of Yuncheng basin, northern China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, J. Aqueous geochemistry of high-fluoride groundwater in Datong Basin, Northern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palandri, J.L.; Kharaka, Y.K. A Compilation of Rate Param of Water-Mineral Interaction Kinetics for Application to Geochemical Modeling; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2004.
- Daniele, L.; Vallejos, Á.; Corbella, M.; Molina, L.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Hydrogeochemistry and geochemical simulations to assess water–rock interactions in complex carbonate aquifers: The case of Aguadulce (SE Spain). Appl. Geochem. 2013, 29, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, D.; Sun, J.; Jamieson, J.; Siade, A.; Atteia, O.; Seibert, S.; Higginson, S.; Prommer, H. Fluoride release from carbonate-rich fluorapatite during managed aquifer recharge: Model-based development of mitigation strategies. Water Res. 2021, 193, 116880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.D.; Binning, P.; Stipp, S. Fluoride removal by calcite: Evidence for fluorite precipitation and surface adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9561–9568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Kumar, E.; Sillanpää, M. Fluoride removal from water by adsorption—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 811–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palahouane, B.; Drouiche, N.; Aoudj, S.; Bensadok, K. Cost-effective electrocoagulation process for the remediation of fluoride from pretreated photovoltaic wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 22, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Teng, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zuo, R.; Li, J.; Chen, H. Riverbank filtration in China: A review and perspective. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpana, L.; Brindha, K.; Elango, L. FIMAR: A new Fluoride Index to mitigate geogenic contamination by Managed Aquifer Recharge. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Knibbe, W.-J.; Feng, C.; Liu, W.; Medema, G.; van der Meer, W. Potential impacts of changing supply-water quality on drinking water distribution: A review. Water Res. 2017, 116, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 164-2020; The Technical Specification for Environmental Monitoring of Groundwater. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Matthess, G. The Properties of Groundwater; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, B.B.S.; Gupta, R.P. Applied Hydrogeology of Fractured Rocks; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2010. [Google Scholar]



| Param | Unit | SG * (n = 172) | DG ** (n = 193) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Avg | SD *** | Min | Max | Avg | SD | ||
| pH | - | 6.88 | 8.60 | 7.58 | 0.33 | 6.79 | 8.90 | 7.91 | 0.48 |
| TDS | mg/L | 7.06 | 3913.60 | 920.27 | 627.77 | 35.70 | 3836.43 | 397.63 | 300.33 |
| K+ | mg/L | 0.07 | 2.99 | 0.75 | 0.48 | 0.19 | 2.64 | 0.91 | 0.44 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 6.40 | 203.00 | 63.21 | 35.56 | 1.60 | 128.10 | 23.56 | 18.25 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 12.54 | 818.32 | 152.31 | 140.82 | 18.25 | 1085.89 | 92.06 | 82.66 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 0.01 | 225.90 | 53.78 | 38.21 | 0.01 | 269.20 | 13.69 | 22.93 |
| SiO2 | mg/L | 2.38 | 37.26 | 24.96 | 4.81 | 14.23 | 36.94 | 21.85 | 4.57 |
| F− | mg/L | 0.17 | 3.22 | 0.70 | 0.53 | 0.11 | 1.79 | 0.46 | 0.40 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 115.00 | 827.60 | 418.01 | 141.78 | 154.30 | 446.30 | 238.56 | 60.45 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 7.20 | 1864.50 | 218.84 | 339.24 | 4.10 | 2328.70 | 54.54 | 170.20 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 0.72 | 448.20 | 92.74 | 83.25 | 2.80 | 812.40 | 38.94 | 63.96 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 0.01 | 188.17 | 12.30 | 21.60 | 0.01 | 49.15 | 7.58 | 8.05 |
| CO32− | mg/L | 0.01 | 11.90 | 1.34 | 2.14 | 0.01 | 29.80 | 4.42 | 4.36 |
| SIfluorite | - | −6.80 | −0.99 | −2.50 | 1.21 | −7.37 | −1.35 | −3.41 | 1.44 |
| SIcalcite | - | −1.37 | 0.85 | 0.34 | 0.26 | −1.87 | 1.12 | 0.07 | 0.59 |
| SIgypsum | - | −3.19 | −0.54 | −1.94 | 0.57 | −3.64 | −0.71 | −2.68 | 0.41 |
| SIdolomite | - | −3.17 | 2.42 | 1.25 | 0.63 | −3.66 | 2.92 | 0.40 | 1.33 |
| SIhalite | - | −8.39 | −5.19 | −6.78 | 0.74 | −8.70 | −4.75 | −7.24 | 0.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhao, K.; Hu, B. Occurrence and Formation Mechanisms of High-Fluoride Groundwater in Xiong’an New Area, Northern China. Water 2024, 16, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020358
Dong Y, Wang Z, Wang D, Zhao K, Hu B. Occurrence and Formation Mechanisms of High-Fluoride Groundwater in Xiong’an New Area, Northern China. Water. 2024; 16(2):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020358
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yihan, Ziqian Wang, Dong Wang, Kai Zhao, and Bin Hu. 2024. "Occurrence and Formation Mechanisms of High-Fluoride Groundwater in Xiong’an New Area, Northern China" Water 16, no. 2: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020358
APA StyleDong, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, D., Zhao, K., & Hu, B. (2024). Occurrence and Formation Mechanisms of High-Fluoride Groundwater in Xiong’an New Area, Northern China. Water, 16(2), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020358







