Decontamination Potential of Ultraviolet Type C Radiation in Water Treatment Systems: Targeting Microbial Inactivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Global Importance of Water and Sanitation Hygiene
1.2. Overview of Waterborne Diseases and Their Impact
- Improved sanitation infrastructure: Investing in and ensuring the functionality of toilets, sewage systems, and wastewater treatment facilities is crucial to breaking the cycle of contamination.
- Hygiene education: Promoting handwashing with soap, safe water-handling practices, and proper food hygiene are essential for preventing the spread of pathogens.
- Access to safe and reliable water sources: This includes implementing and maintaining water treatment systems, protecting water sources from contamination, and ensuring equitable access to safe water for all.
1.3. UV Disinfection as a Water Treatment Method
2. Understanding UV Disinfection
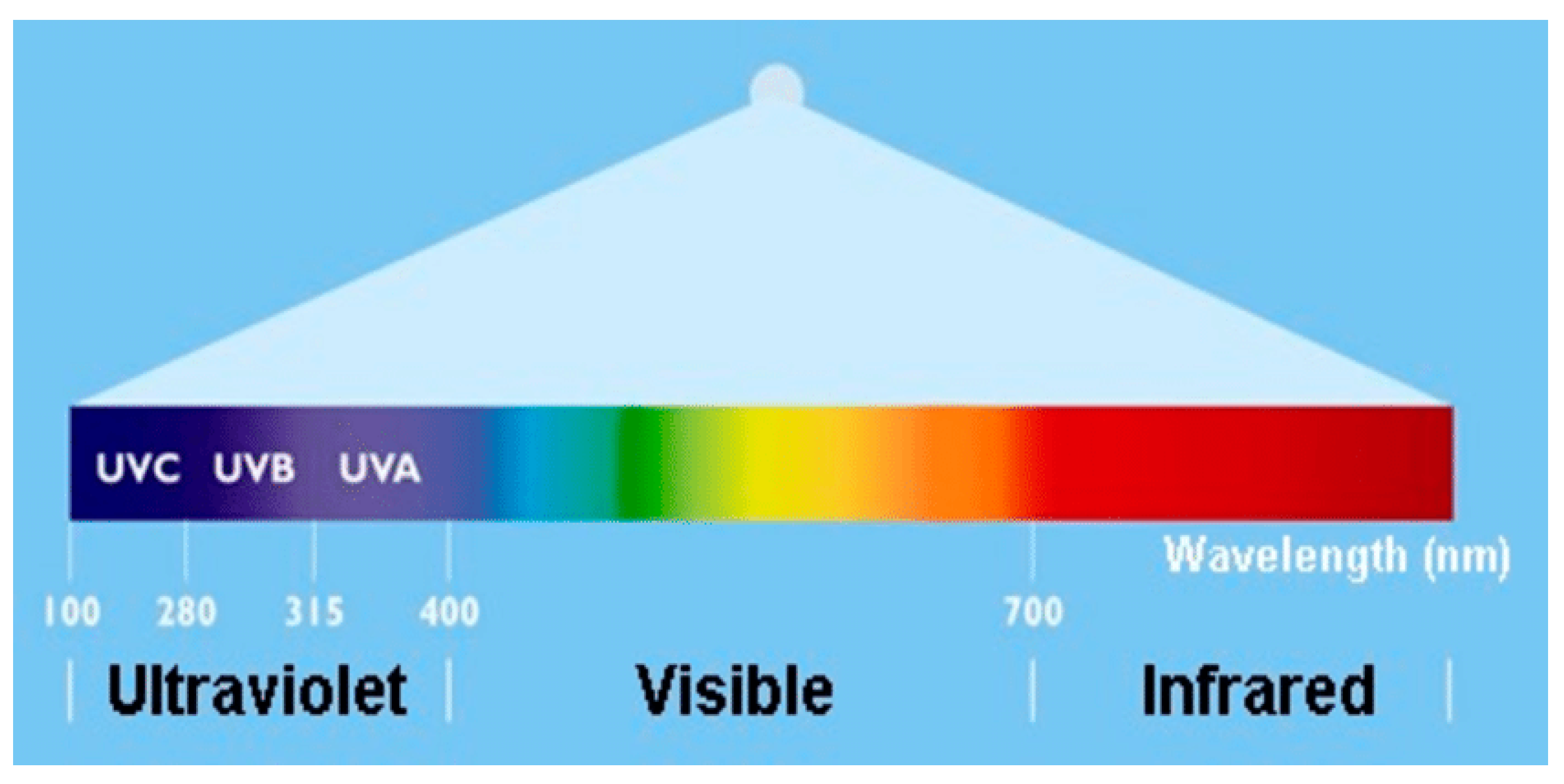
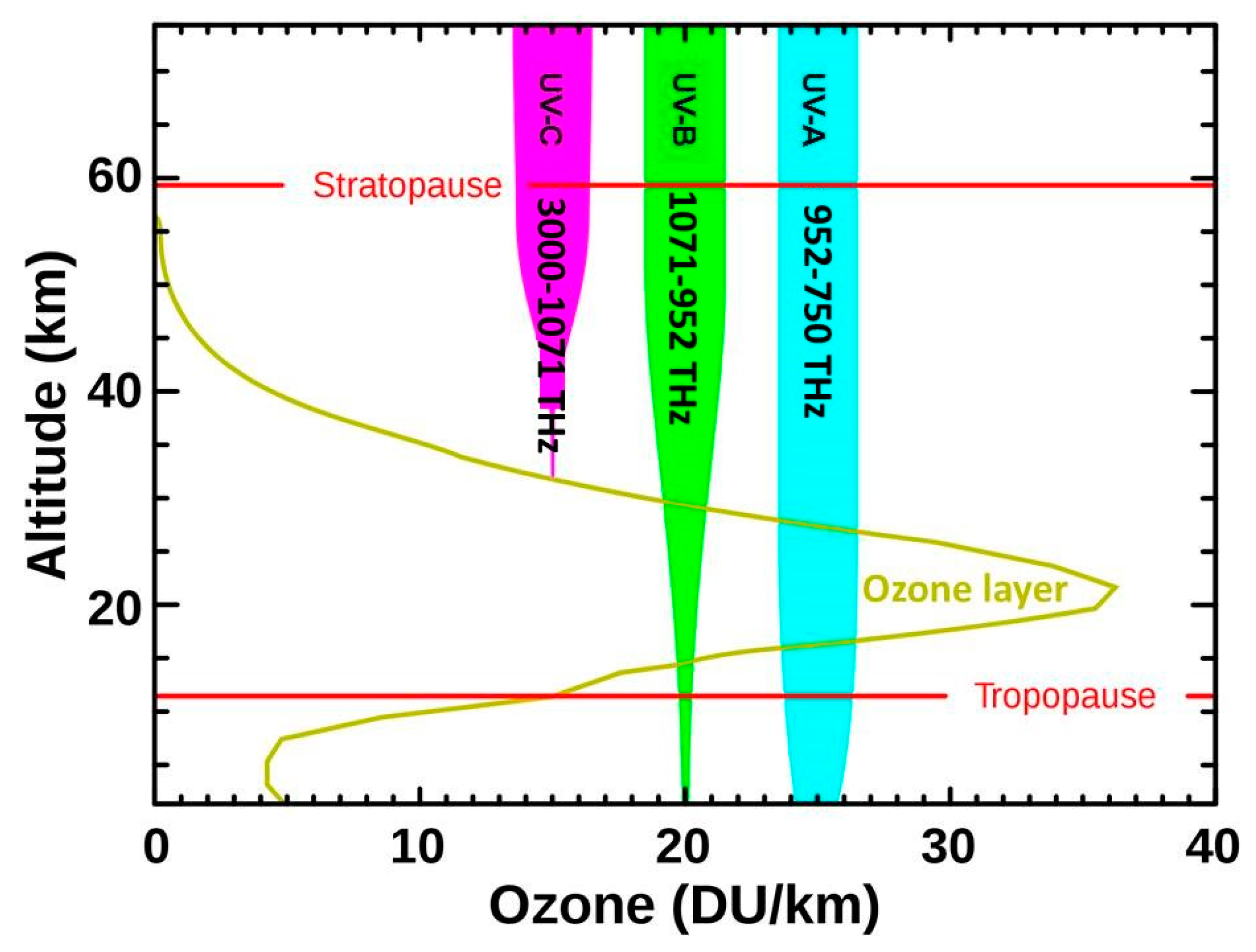
2.1. The Electromagnetic Spectrum and UV Radiation
2.2. Mechanisms of UV Disinfection at the Cellular Level
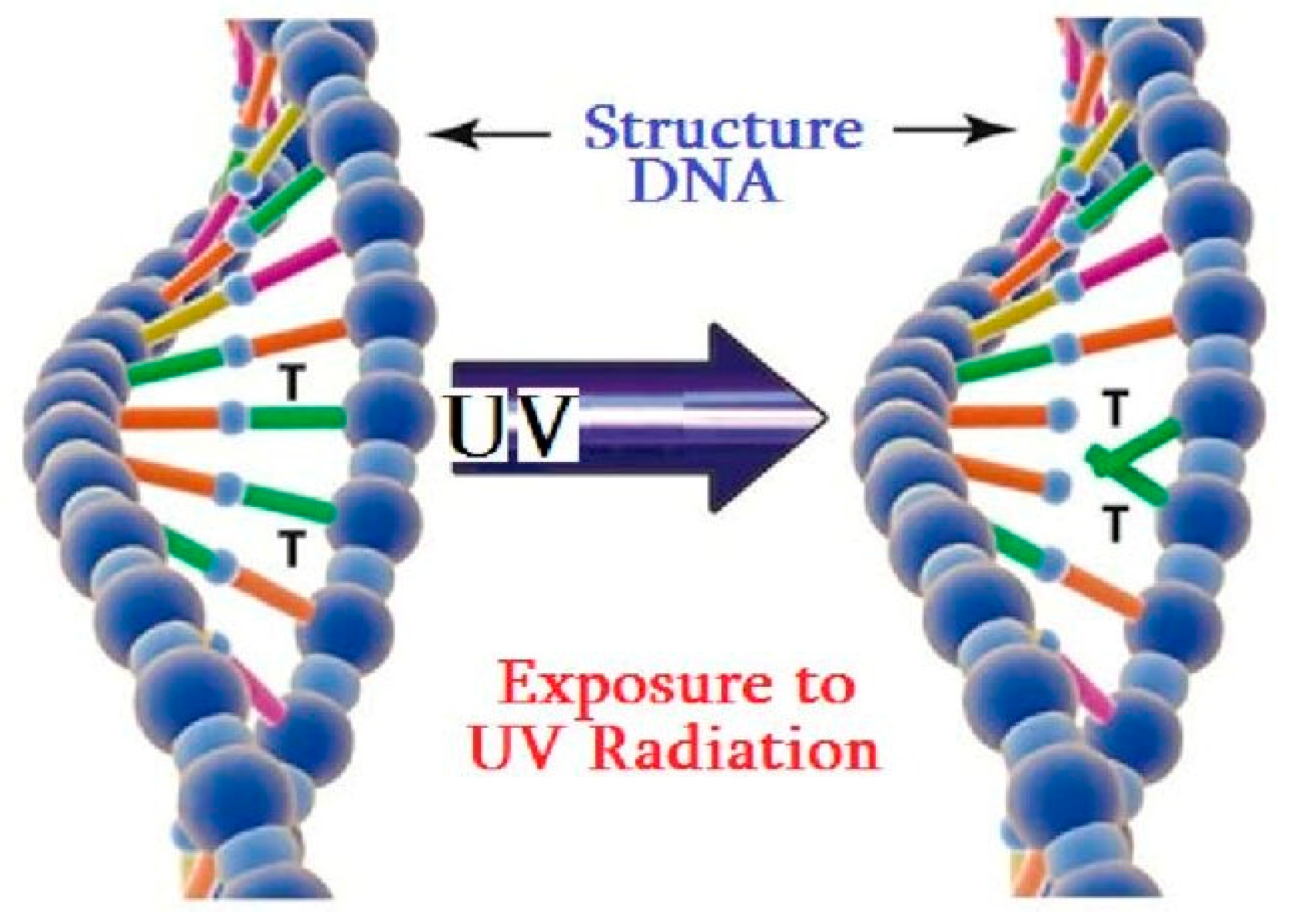
2.3. Factors Affecting UV Disinfection Efficacy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area and Sample Site

3.2. Materials
3.2.1. Sample Collection
3.2.2. Laboratory Experiments Procedure
3.2.3. Determination of Coliforms in Water
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Results of the Physicochemical Properties of Water Samples
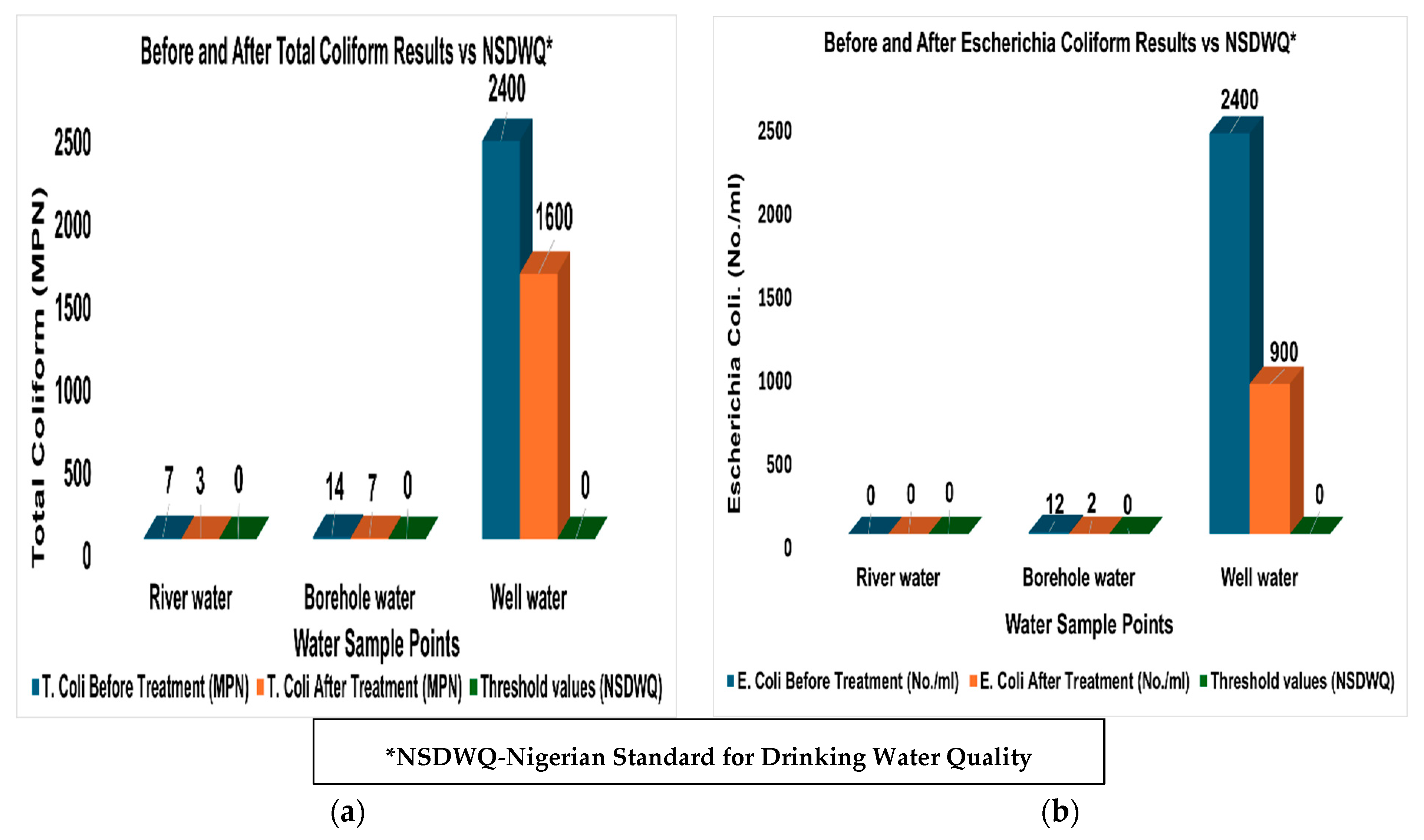
4.2. Results of the Water Quality Tests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bazaanah, P.; Mothapo, R.A. Sustainability of drinking water and sanitation delivery systems in rural communities of the Lepelle Nkumpi Local Municipality, South Africa. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 14223–14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Johnston, R.B.; Ambelu, A.; Arnold, B.F.; Bain, R.; Brauer, M.; Brown, J.; Caruso, B.A.; Clasen, T.; Colford, J.M.; et al. Burden of disease attributable to unsafe drinking water, sanitation, and hygiene in domestic settings: A global analysis for selected adverse health outcomes. Lancet 2023, 401, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegoke, H.A.; Solihu, H.; Bilewu, S.O. Analysis of sanitation and waterborne disease occurrence in Ondo State, Nigeria. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 11885–11903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Sanitation. 22 March 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sanitation (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- WHO. Progress on Household Drinking-Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2022: Special Focus on Gender. 6 July 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/progress-on-household-drinking-water--sanitation-and-hygiene-2000-2022---special-focus-on-gender (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Matta, G.; Kumar, P.; Uniyal, D.P.; Joshi, D.U. Communicating Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene under Sustainable Development Goals 3, 4, and 6 as the Panacea for Epidemics and Pandemics Referencing the Succession of COVID-19 Surges. ACS ES&T Water 2022, 2, 667–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.; Zweben, C. Comprehensive Composite Materials, Composite Materials; Elsevier Science; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zakiyyah, S.N.; Ibrahim, A.U.; Babiker, M.S.; Gaffar, S.; Ozsoz, M.; Zein, M.I.H.L.; Hartati, Y.W. Detection of Tropical Diseases Caused by Mosquitoes Using CRISPR-Based Biosensors. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siramaneerat, I.; Agushybana, F. Clean Water, Housing Condition, and Diarrhea among Children under Five Years Old in Indonesia: Partial Least Square-Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). Open Public Health J. 2023, 16, e187494452303274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.-E.; Fu, Y.-Z.; Yao, W. Knowledge, Practice of Personal Hygiene, School Sanitation, and Risk Factors of Contracting Diarrhea among Rural Students from Five Western Provinces in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyapillai, T.; Kulothungan, K.; Vignesh, N.J.; Dharmaraj, R.B.; George, N. Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) Practices among Households in Perambalur District: A Cross-Sectional Study. Cureus 2022, 14, e30115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, U.; Sarkar, S.; Duttagupta, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Das, K.; Saha, S.; Mukherjee, A. Influence of Hydrology and Sanitation on Groundwater Coliform Contamination in Some Parts of Western Bengal Basin: Implication to Safe Drinking Water. Front. Water 2022, 4, 875624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdon, R.S.M.A.; Salem, A.; Ahmed, H.G.I.; ElZahar, M.M.H. Use of Chitosan for Enhancing the Process of Surface Water Purification in Egypt. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2022, 13, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nounkeu, C.D.; Teta, I.; Dharod, J.M.; Saha Foudjo, B.U.; Ntentie, F.R.; Boris, A.K.; Georges, N.T.; Oben, J. Limited water access is associated with food insecurity and diarrheal episodes among children suffering from moderate acute malnutrition in Far-North Cameroon. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2022, 12, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO; UNICEF; JMP. Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene in Schools. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/wash-documents/progress-of-drinking-water-sanitation-and-hygiene-in-schools---special-focus-on-covid-19.pdf (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Lopes, R.H.; Silva, C.R.D.V.; Salvador, P.T.C.D.O.; Silva, I.D.S.; Heller, L.; Uchôa, S.A.D.C. Surveillance of Drinking Water Quality Worldwide: Scoping Review Protocol. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffoor, H.; Farooq, M.; Mahmood, S. Socio-Cultural Barriers of Safe Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Practices in South Punjab Pakistan. Glob. Soc. Sci. Rev. 2020, 5, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Yoon, H.-W.; Lee, M.-A.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, C.J. Impact of UV-C Irradiation on Bacterial Disinfection in a Drinking Water Purification System. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duering, H.; Westerhoff, T.; Kipp, F.; Stein, C. Short-Wave Ultraviolet-Light-Based Disinfection of Surface Environment Using Light-Emitting Diodes: A New Approach to Prevent Health-Care-Associated Infections. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, U.; Faizan, M.; Sajid, M. Effective removal of hazardous pollutants from water and deactivation of water-borne pathogens using multifunctional synthetic adsorbent materials: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellal, M.S.; Hemdan, B.A.; Youssef, M.; El-Taweel, G.E.; Taleb, E.M.A. Novel electro-oxidation unit for electro-disinfection of E. coli and some waterborne pathogens during wastewater treatment: Batch and continuous experiments. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Boyd, J.M.; Woodbeck, M.; Andrews, R.C.; Qin, F.; Hrudey, S.E.; Li, X.F. Formation of N-Nitrosamines from Eleven Disinfection Treatments of Seven Different Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4857–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Z.-Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.-H.; Hu, H.-Y. Evaluation and prospects of nanomaterial-enabled innovative processes and devices for water disinfection: A state-of-the-art review. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Miino, M.C.; Caccamo, F.M.; Torretta, V.; Rada, E.C.; Sorlini, S. Disinfection of Wastewater by UV-Based Treatment for Reuse in a Circular Economy Perspective. Where Are We at? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.; Joshi, L.T.; McGinn, C. Hospital surface disinfection using ultraviolet germicidal irradiation technology: A review. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, B.A.; Mahoney, L.E.; Yao, S. Field evaluation of a novel UV water disinfection system for use in underserved rural communities. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliki, A.; El Moustaine, R.; Chahlaoui, A.; Boudellah, A.; Sadki, M.; Belkhiri, A.; Taouraout, A. Seasonal Bacterial Contamination of Groundwater in the Zagora Area, Morocco. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2023, 24, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, J.; Hammond, B. Photobiomodulation of the Visual System and Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, E.R.; Vendrami, J.A.; Duarte, A.C.; Júnior, E.C.B.; Onmori, R.K.; Hui, W.S. Assembly of UV-Ozone Reactor to Combat of Coronavirus and Other Pathogenic Microorganisms. Rev. Bras. Apl. Vácuo 2021, 40, e1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottman, G.; Floyd, L.; Viereck, R. Measurements of the solar ultraviolet irradiance. Sol. Var. Eff. Clim. 2023, 141, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darré, M.; Vicente, A.R.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Artés-Hernández, F. Postharvest Ultraviolet Radiation in Fruit and Vegetables: Applications and Factors Modulating Its Efficacy on Bioactive Compounds and Microbial Growth. Foods 2022, 11, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackey, S.S.; Vowotor, M.K.; Owusu, A.; Mensah-Amoah, P.; Tatchie, E.T.; Sefa-Ntiri, B.; Hood, C.O.; Atiemo, S.M. Spectroscopic Study of UV Transparency of Some Materials. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, I. Ozone Depletion Theory. 2024. Available online: https://ozonedepletiontheory.info/ (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Berens, P.J.T.; Molinier, J. Formation and Recognition of UV-Induced DNA Damage within Genome Complexity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaelewyn, L.; Van Der Straeten, D.; De Coninck, B.; Vandenbussche, F. Ultraviolet Radiation From a Plant Perspective: The Plant-Microorganism Context. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 597642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslowska, K.H.; Makiela-Dzbenska, K.; Fijalkowska, I.J. The SOS system: A complex and tightly regulated response to DNA damage. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2019, 60, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Handa, N.; Kusano, K. DNA Double-Strand Breaks and Their Consequences in Bacterial Genomes. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushitashvili, Z.; Bibilashvili, A. Mechanism of Processes Stimulated by Ultraviolet Radiation. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 609, 012051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcaid, A.-E.; Faycal, T.; Tounssi, T. Chlorine Decay Modeling in a Water Distribution Network in Mohammedia City, Morocco. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2023, 24, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ray, M.B.; Mao, T.; Sun, W. Impact of UV irradiation on disinfection by-product formation and speciation from post-chlorination of dissolved organic matter. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-AQUA 2021, 70, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeiszadeh, M.; Adeli, B. A Critical Review on Ultraviolet Disinfection Systems against COVID-19 Outbreak: Applicability, Validation, and Safety Considerations. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguntoke, O.; Komolafe, O.A.; Annegarn, H.J. Statistical analysis of shallow well characteristics as indicators of water quality in parts of Ibadan City, Nigeria. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2013, 3, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, A.M.; Towolawi, A.T.; Olanigan, A.A.; Olujimi, O.O.; Arowolo, T.A. Comparative Assessment of Groundwater Quality in Rural and Urban Areas of Nigeria. In Research and Practices in Water Quality; InTech: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbiye, A.; Fagbenle, E.; Busari, A.; Onakunle, O.; Omole, D. Rain water harvesting: A sustainable alternative for domestic water supply in South–Western Nigeria: In the case study of Ado-Odo/Ota LGA Ogun State. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1036, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.; Amadu, L. Urbanization, cities, and health: The challenges to Nigeria—A review. Ann. Afr. Med. 2017, 16, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isukuru, E.J.; Opha, J.O.; Isaiah, O.W.; Orovwighose, B.; Emmanuel, S.S. Nigeria’s water crisis: Abundant water, polluted reality. Clean. Water 2024, 2, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugonma, D.-A.; Olajuyigbe, S. Post-Harvest Storage Handling of Parkia Biglobosa Benth. Sold in Ibadan North Local Government Area, Oyo State, Nigeria. In Harnessing the Uniqueness of Forests for Sustainable Development in a Diversifying Economy, Proceedings of the 39th Annual Conference of the Forestry Association of Nigeria, Forestry Research Institute of Nigeria, Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria; ResearchGate: Ibadan, Nigeria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Adutwum, F.N.; Alhassan, E.H.; Abobi, S.M. Effects of water quality on rural livelihoods: A case of Tamale Metropolis. Ghana J. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2022, 8, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazoe, H. Water quality monitoring. Anal. Sci. 2023, 39, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masindi, V.; Foteinis, S. Groundwater contamination in sub-Saharan Africa: Implications for groundwater protection in developing countries. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 2, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osiemo, M.M.; Ogendi, G.M.; M’Erimba, C. Microbial Quality of Drinking Water and Prevalence of Water-Related Diseases in Marigat Urban Centre, Kenya. Environ. Health Insights 2019, 13, 117863021983698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, J. What Is a UV Water Purifier and How Does It Work? 2023. Available online: https://thietbinganhnuoc.com/en/technical-blog/what-is-a-uv-water-purifier-and-how-does-it-work/?srsltid=AfmBOoo6Fm-gJFb6pHU3B1jhg1rAs-2P_zObEImqeYo22zkutuCF1fzx (accessed on 9 August 2024).


| Parameters | Well Water | Borehole Water | River Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.2 | 6.8 | 8.3 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 20 | 8 | 45 |
| Hardness (CaCO3/L) | 32 | 22 | 80 |
| Temperature | 32 | 35 | 33 |
| Total dissolved solid (mg/L) | 85 | 75 | 124 |
| Total suspended solid (mg/L) | 10 | 5 | 20 |
| Parameters | Before Treatment | After Treatment | % Reduction | Threshold Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River Water Sample | ||||
| Total coliforms (MPN) | 7 | 3 | 57.143 | 0 |
| Escherichia coli. (No./mL) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Borehole Water Sample | ||||
| Total coliforms (MPN) | 14 | 7 | 50 | 0 |
| Escherichia coli. (No./mL) | 12 | 2 | 83.333 | 0 |
| Well Water Sample | ||||
| Total coliforms (MPN) | 2400 | 1600 | 33.333 | 0 |
| Escherichia coli. (No./mL) | 2400 | 900 | 62.5 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adeniyi, A.O.; Jimoh, M.O. Decontamination Potential of Ultraviolet Type C Radiation in Water Treatment Systems: Targeting Microbial Inactivation. Water 2024, 16, 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192725
Adeniyi AO, Jimoh MO. Decontamination Potential of Ultraviolet Type C Radiation in Water Treatment Systems: Targeting Microbial Inactivation. Water. 2024; 16(19):2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192725
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdeniyi, Abayomi Olusegun, and Modupe Olufunmilayo Jimoh. 2024. "Decontamination Potential of Ultraviolet Type C Radiation in Water Treatment Systems: Targeting Microbial Inactivation" Water 16, no. 19: 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192725
APA StyleAdeniyi, A. O., & Jimoh, M. O. (2024). Decontamination Potential of Ultraviolet Type C Radiation in Water Treatment Systems: Targeting Microbial Inactivation. Water, 16(19), 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192725






