Quantifying the Influence of Climatic and Anthropogenic Factors on Multi-Scalar Streamflow Variation of Jialing River, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
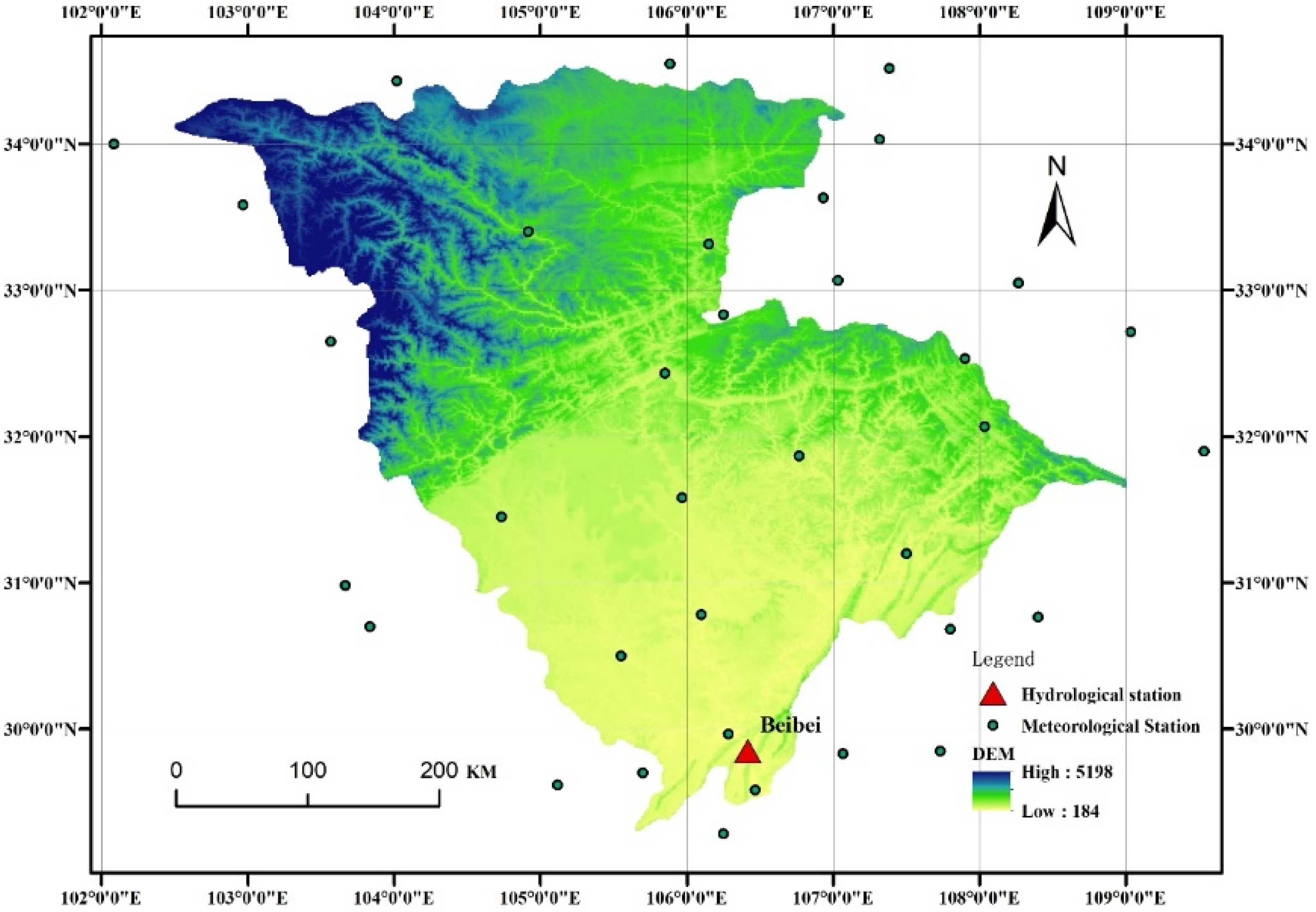
2. Study Region and Data
3. Approaches
3.1. Trend and Mutation Testing Approaches
3.2. Concentration Degree (CD) and Concentration Period (CP)
3.3. ABCD Hydrological Model
3.4. Multi-Scalar Budyko Model
3.5. Vertical Decomposition Method Based on Multi-Scalar Budyko Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Trend Analysis
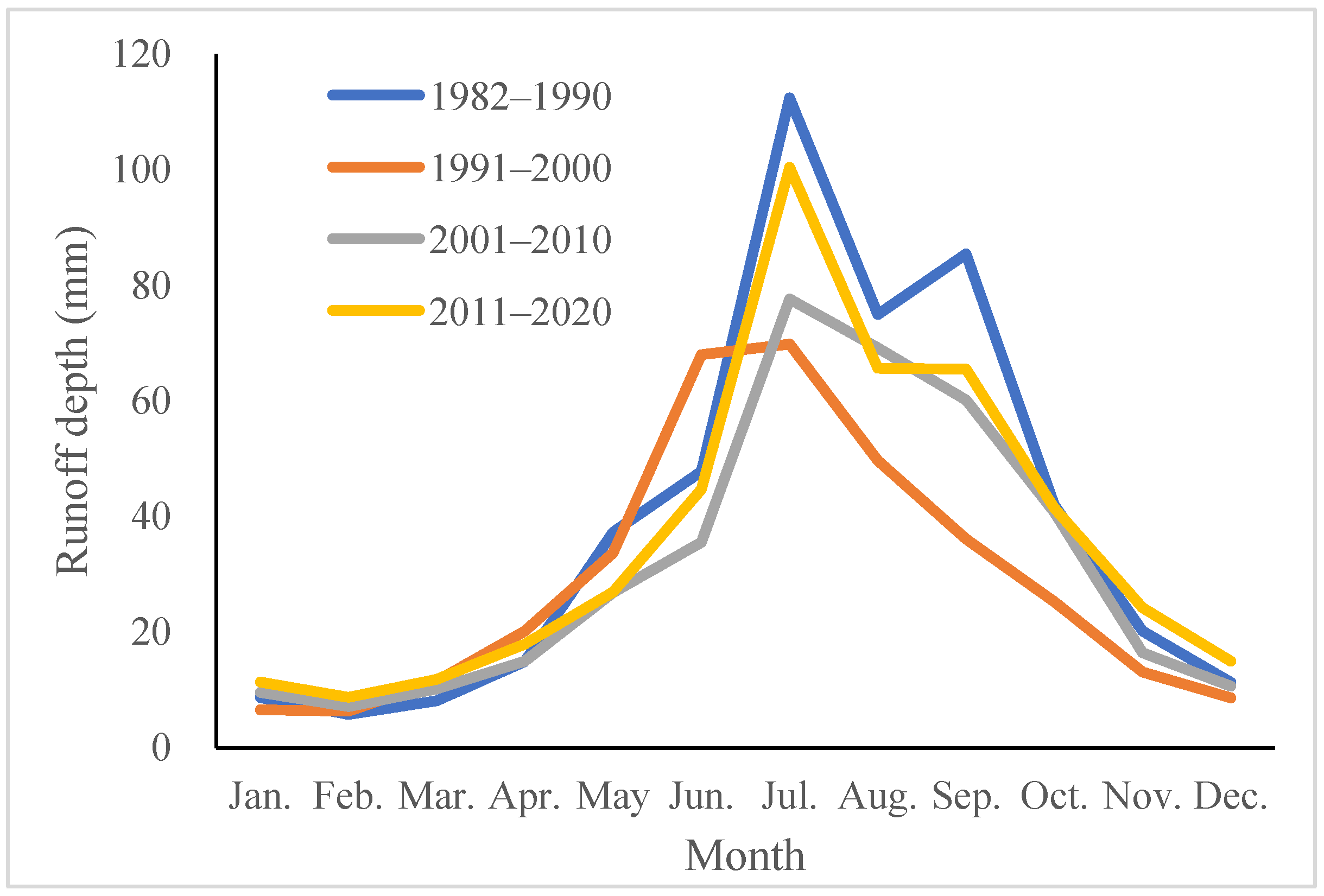
4.2. Intra-Annual Variation Characteristics Analysis
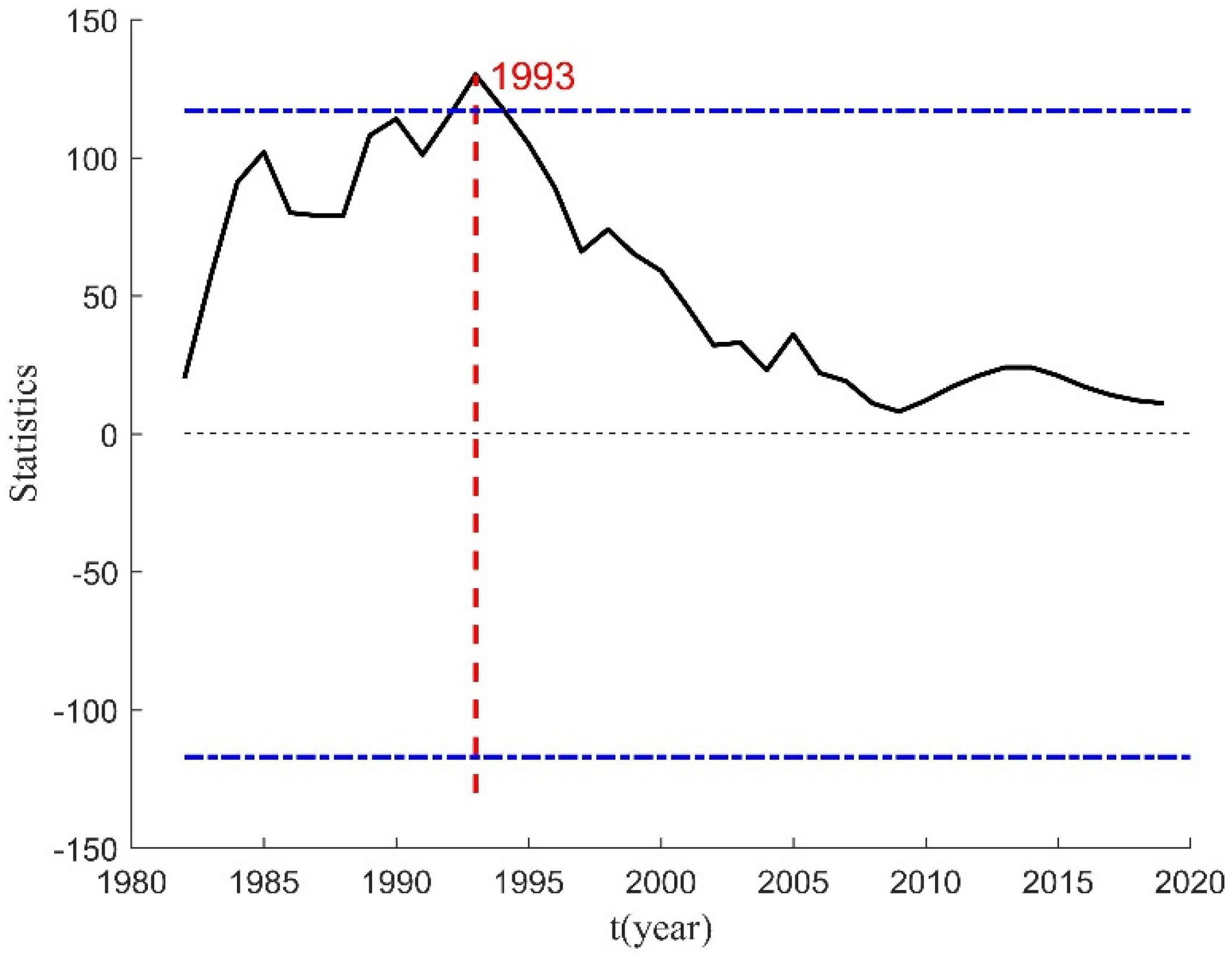
4.3. Mutation Analysis
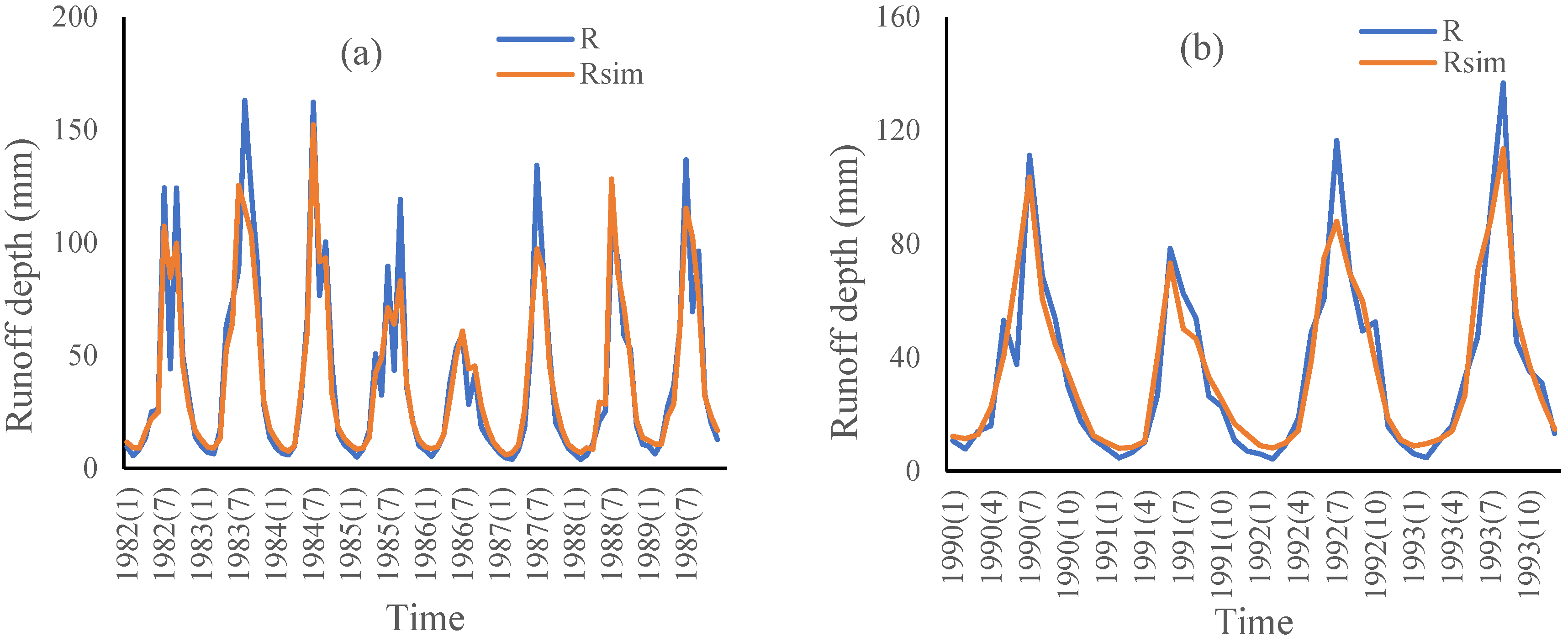
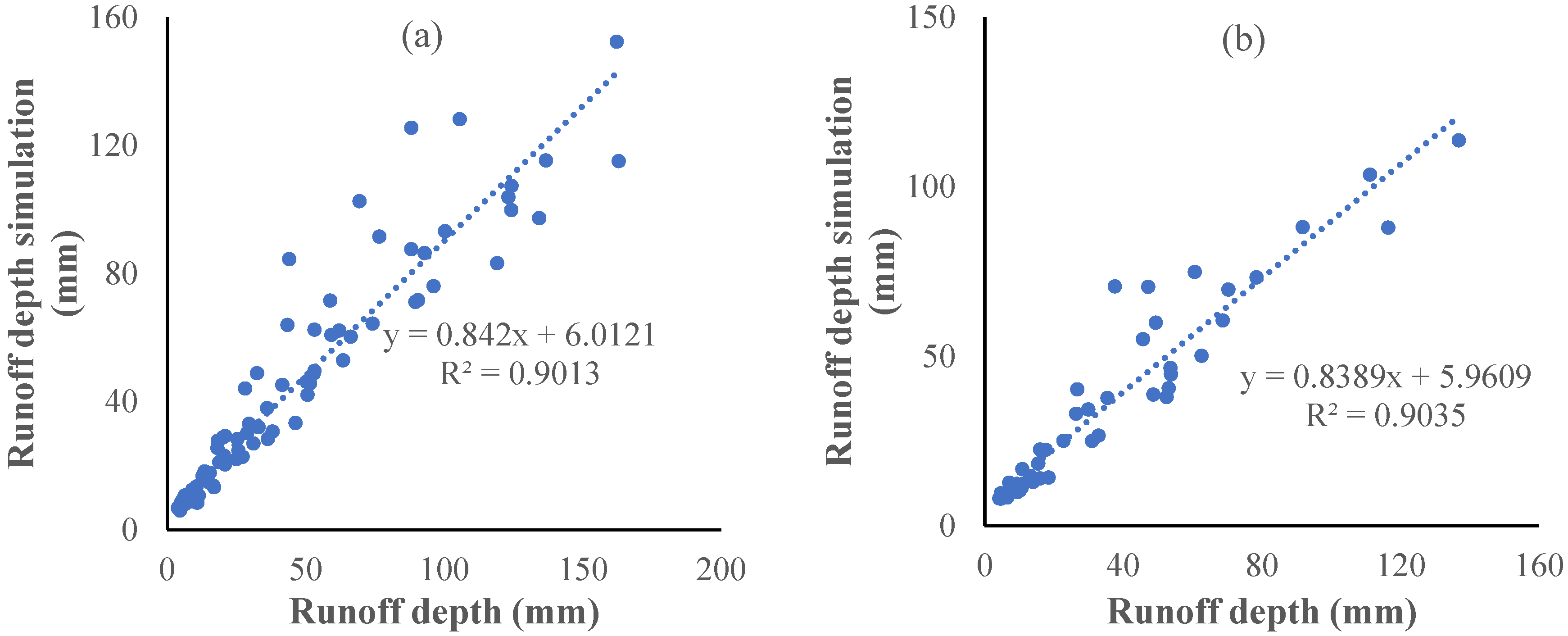
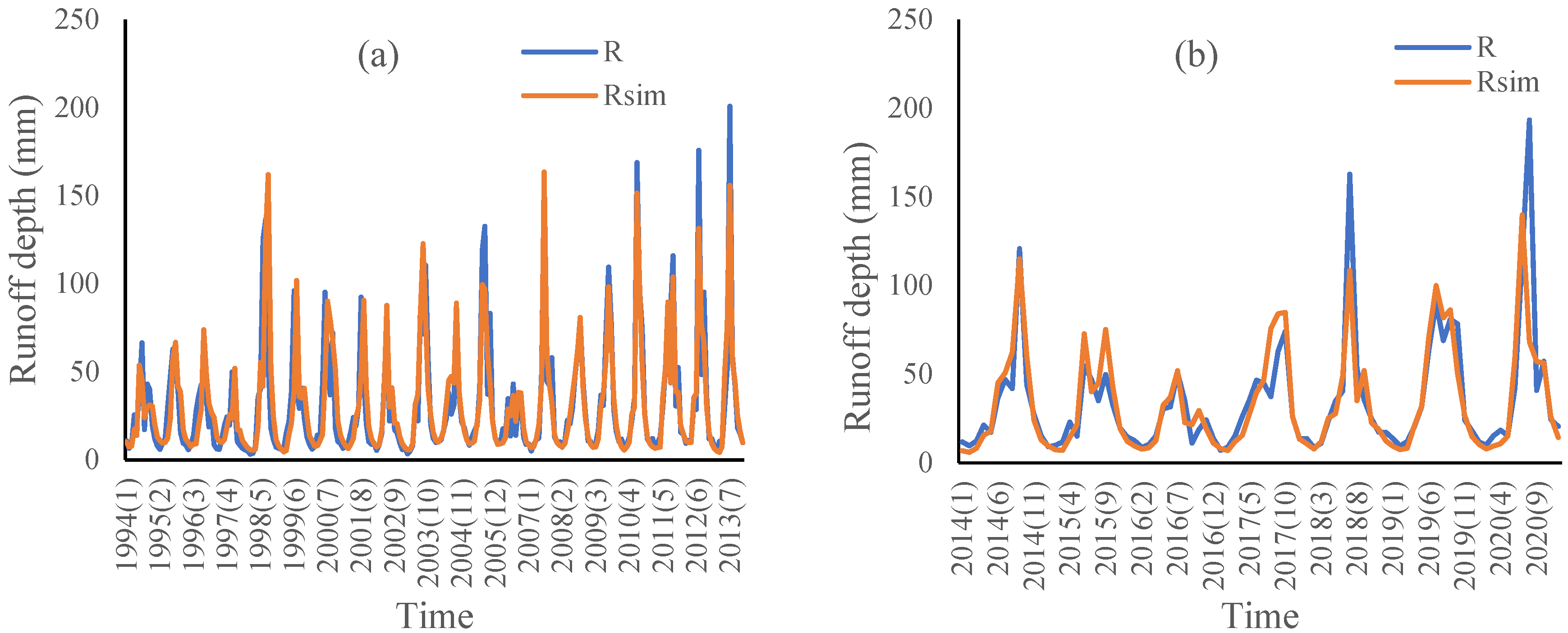
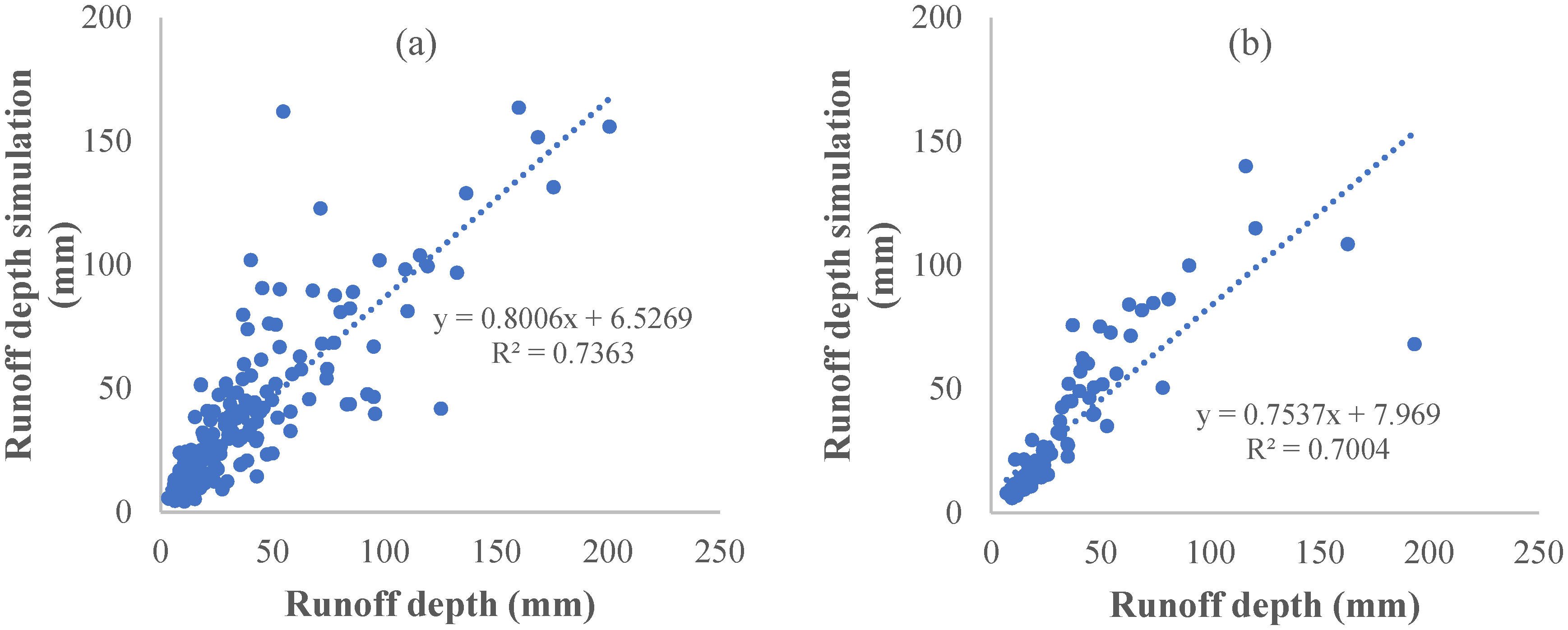
4.4. ABCD Model Simulation
4.5. Attribution Analysis of Multi-Timescale Runoff
4.6. Discussion
4.7. Limitations and Future Research
- (1)
- This study did not analyze the impact of vegetation changes on runoff. Subsequent research will quantitatively analyze the impact of vegetation changes on multi-scale (seasonal, monthly) runoff changes.
- (2)
- This study did not analyze the combined effect of climatic factors and human factors on runoff changes. Subsequent research will quantitatively analyze the impact of the interaction between climatic factors and human activities on multi-scale (seasonal, monthly) runoff changes.
- (3)
- This research did not analyze the impact of reservoir on runoff, so quantitative analysis of the impact of reservoir scheduling on multi-scale (quarterly and monthly) runoff changes will be the next research focus.
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The monthly runoff in the JLR presented a “single peak” distribution, and the concentration degree and concentration period of runoff in the JLR both showed an insignificant reduction trend.
- (2)
- The mutation year of discharge was 1993.
- (3)
- Climate change played a dominant role on annual runoff variation, with a contribution of 73.51%.
- (4)
- Climatic factors were the dominant factor on annual, summer, fall and winter runoff variations.
- (5)
- Except for November, climatic factors were a leading factor causing runoff changes in the other 11 months.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, T.-N.-D.; Lakshmi, V. Enhancing human resilience against climate change: Assessment of hydroclimatic extremes and sea level rise impacts on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Qin, D.; Jiang, N.; Wang, G. Rainfall-runoff evolution of Sanchuan River and its cause analysis. J. Yellow River 2007, 59, 42–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Milly, P.C.; Dunne, K.A.; Vecchia, A.V. Global pattern of trends in streamflow and water availability in a changing climate. Nature 2005, 438, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.; Bishop, K.; Zarnetske, J.; Minaudo, C.; Chapin, F.; Krause, S.; Hannah, D.M.; Conner, L.; Ellison, D.; Godsey, S.E.; et al. Human domination of the global water cycle absent from depictions and perceptions. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Song, H.; Wei, H.; Wu, L. Attribution Analysis of Climate and Anthropic Factors on Runoff and Vegetation Changes in the Source Area of the Yangtze River from 1982 to 2016. Land 2021, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Lai, Z.; Xia, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. Future Runoff Variation and Flood Disaster Prediction of the Yellow River Basin Based on CA-Markov and SWAT. Land 2021, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, R.; Ji, G. Attribution of the Runoff Changes in Jialing River Based on Budyko Complementary relationship method. J. N. China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 44, 49–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Xiao, W.; Lu, F.; Wang, Y.; Hou, B.; Zhang, X. Analysis of multi-time scale runoff evolution law of Huayuankou hydrological station. J. Yellow River 2022, 44, 25–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F. Study on runoff characteristics and evolution law of Qinghai Lake Basin in recent 60 years. J. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2020, 62, 1–7+13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nie, N.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, D. Separating the impacts of climate variability, land-use change and large reservoir operations on streamflow in the Yangtze River basin, China, using a hydrological modeling approach. Int. J. Dig. Earth 2021, 14, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, Y.; Yan, M.; Zhao, X. Quantitative estimation of the impact of precipitation and human activities on runoff change of the Huangfuchuan River basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, D.; Pumo, D.; Viola, F. Budyko’s based method for annual runoff characterization across different climatic areas: An application to United States. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 3189–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, Q.; Cheng, L.; Xia, J. A Budyko-based framework for quantifying the impacts of aridity index and other factors on annual runoff. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-N.-D.; Tapas, M.R.; Do, S.K.; Etheridge, R.; Lakshmi, V. Investigating the impacts of climate change on hydroclimatic extremes in the Tar-Pamlico River basin, North Carolina. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 363, 121375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.-N.-D.; Nguyen, B.Q.; Grodzka-Łukaszewska, M.; Sinicyn, G.; Lakshmi, V. The role of reservoirs under the impacts of climate change on the Srepok River basin, Central Highlands of Vietnam. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1304845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devia, G.K.; Ganasri, B.P.; Dwarakish, G.S. A review on hydrological models. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Yue, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, W. Assessing the Impact of Vegetation Variation, Climate and Human Factors on the Streamflow Variation of Yarlung Zangbo River with the Corrected Budyko Equation. Forests 2023, 14, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Yan, D.; Lai, Z. Attribution Analysis of Seasonal Runoff in the Source Region of the Yellow River Using Seasonal Budyko Hypothesis. Land 2021, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Ji, G. Assessing the contribution of vegetation variation to streamflow variation in the Lancang River Basin, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 10, 1058055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Ji, G. Attribution analysis of multi-temporal scale changes of streamflow in the source area of Lancang River with seasonal scale Budyko model. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1229198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sun, J. Effects of precipitation changes and human activities on the runoff flux of the Yellow River into the sea in the last 50 years. J. Adv. Water Sci. 2003, 14, 690–695. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Niu, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, Z. Analysis of runoff evolution law in Yarlung Zangbo River Basin from 1961 to 2015. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 110–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Han, L.; Tang, X.; Jin, Z. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of vegetation coverage in jinsha river basin. J. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 1191–1196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.Q.; Van Binh, D.; Tran, T.-N.-D.; Kantoush, S.A.; Sumi, T. Response of streamflow and sediment variability to cascade dam development and climate change in the Sai Gon Dong Nai River basin. Clim. Dyn. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; He, Y.; Mu, X. Contributions of climate change and human activities to runoff and sediment discharge reductions in the Jialing River, a main tributary of the upper Yangtze River, China. J. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 145, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, F. Analysis of precipitation and runoff evolution in Jialing River Basin. J. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 19, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Mu, X.; Zhao, G. Runoff Variation Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Jialing River Basin in Recent 50a. J. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 33, 12–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, M. Contribution Analysis of the Spatial-Temporal Changes in Streamflow in a Typical Elevation Transitional Watershed of Southwest China over the Past Six Decades. Forests 2019, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Mu, X.; He, Y.; Chen, K. Variations in runoff, sediment load, and their relationship for a major sediment source area of the Jialing River basin, southern China. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Jiao, X.; Zhou, H. Hydrologic regime alteration and influence factors in the Jialing River of the Yangtze River, China. J. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gao, H.; Chai, S.; He, Z.; Ji, G. Attribution analysis of different driving forces on vegetation and streamflowvariation in the Jialing River Basin, China. Open Geosci. 2022, 14, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, S.; Ruan, Q.; Tang, C. Synergetic impact of climate and vegetation cover on runoff, sediment, and nitrogen and phosphorus losses in the Jialing River Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 361, 132141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, hare soil and grass. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A J. Math. Phys. Sci. 1948, 193, 120–145. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.Q.; Tran, T.-N.-D.; Grodzka-Łukaszewska, M.; Sinicyn, G.; Lakshmi, V. Assessment of Urbanization-Induced Land-Use Change and Its Impact on Temperature, Evaporation, and Humidity in Central Vietnam. Water 2022, 14, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A Non-Parametric Approach to the Change-Point Problem. J. R. Stat. Soc. J. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Shi, N.; Zhou, W.; Qiu, Y. Concentration of Precipitation in Flood Season and Its Relationship with Drought and Flood in Guilin. J. Meteorol. Res. Appl. 2007, 52, 23–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.A. Improved Methods for National Water Assessment; Water Resources Council: Olympia, WA, USA, 1981; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Alimohammadi, N.; Wang, D. Modeling interannual variability of seasonal evaporation and storage change based on the extended Budyko framework. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6067–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hejazi, M. Quantifying the relative contribution of the climate and direct human impacts on mean annual streamflow in the contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, W.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J. Attribution analysis of seasonal runoff changes based on the extended Budyko hypothesis. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2017, 36, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; He, Y.; Shao, Y. Attribution Analysis of Runoff Change and Its Influencing Factors in the Upper Reaches of Jialing River. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 124–131. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Z Statistic | β (mm/a) | Trends | Significance Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | −1.01 | −0.18 | Decrease | Insignificant |
| Spr. | −1.01 | −0.18 | Decrease | Insignificant |
| Sum. | −0.75 | −0.79 | Decrease | Insignificant |
| Aut. | −0.40 | −0.01 | Decrease | Insignificant |
| Win. | 3.99 | 0.34 | Increase | 0.01 |
| Jan. | 2.85 | 0.12 | Increase | 0.01 |
| Feb. | 3.63 | 0.12 | Increase | 0.01 |
| Mar. | 2.95 | 0.14 | Increase | 0.01 |
| Apr. | 0.82 | 0.11 | Increase | Insignificant |
| May | −1.74 | −0.22 | Decrease | Insignificant |
| Jun. | −0.89 | −0.12 | Decrease | Insignificant |
| Jul. | −0.51 | −0.03 | Decrease | Insignificant |
| Aug. | −0.31 | −0.05 | Decrease | Insignificant |
| Sep. | −1.04 | −0.25 | Decrease | Insignificant |
| Oct. | 0.27 | 0.24 | Increase | Insignificant |
| Nov. | 0.92 | 0.14 | Increase | Insignificant |
| Dec. | 2.93 | 0.11 | Increase | 0.01 |
| Period | RCD | RCP (°) | Maximum Runoff |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1982–1990 | 0.56 | 250.06 | Sep. |
| 1991–2000 | 0.51 | 272.63 | Oct. |
| 2001–2010 | 0.50 | 247.35 | Sep. |
| 2011–2020 | 0.48 | 247.53 | Sep. |
| Period | a | b | c | d | NSE | RE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base period | 0.88 | 282.36 | 0.05 | 0.17 | calibration period (1982–1989) | 0.90 | −0.57% |
| verification period (1990–1993) | 0.90 | 0.88% | |||||
| Variation period | 0.91 | 278.80 | 0.02 | 0.10 | calibration period (1994–2013) | 0.73 | 1.04% |
| verification period (2014–2020) | 0.70 | −1.60% |
| Time Scale | Parameter | R2 | RE (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω | φ | |||
| Year | 1.28 | 0.18 | 0.99 | 0.003 |
| Spr. | 1.50 | 0.39 | 0.99 | 0.03 |
| Sum. | 1.33 | 0.10 | 0.99 | 0.001 |
| Aut. | 1.23 | 0.11 | 0.99 | 0.03 |
| Win. | 1.08 | 0.21 | 0.99 | −0.03 |
| Jan. | 1.07 | 0.23 | 0.99 | −0.02 |
| Feb. | 1.31 | 0.40 | 0.92 | −0.06 |
| Mar. | 1.48 | 0.58 | 0.98 | 0.12 |
| Apr. | 1.25 | 0.13 | 0.95 | −0.24 |
| May | 1.52 | 0.24 | 0.98 | −0.01 |
| Jun. | 1.48 | 0.14 | 0.98 | 0.05 |
| Jul. | 1.24 | 0.06 | 0.99 | −0.06 |
| Aug. | 1.50 | 0.12 | 0.99 | 0.02 |
| Sep. | 1.28 | 0.07 | 0.99 | −0.01 |
| Oct. | 1.26 | 0.12 | 0.99 | 0.17 |
| Nov. | 1.17 | 0.17 | 0.99 | −0.001 |
| Dec. | 1.02 | 0.16 | 0.97 | −0.04 |
| Time Scale | Base Period P-ΔS/mm | Variation Period P-ΔS/mm | Base Period Ep/mm | Variation Period Ep/mm | Base Period ΔS/mm | Variation Period ΔS/mm | Base Period E/mm | Variation Period E/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 898.81 | 862.94 | 829.24 | 881.54 | 10.82 | 4.48 | 442.67 | 478.70 |
| Spr. | 168.96 | 178.98 | 246.35 | 265.35 | 22.12 | 7.04 | 108.69 | 121.04 |
| Sum. | 441.32 | 402.98 | 333.78 | 353.89 | 32.32 | 22.21 | 205.08 | 214.50 |
| Aut. | 228.54 | 211.02 | 159.82 | 165.70 | −14.41 | 16.66 | 93.66 | 102.06 |
| Win. | 59.97 | 69.95 | 89.29 | 96.60 | −29.20 | −41.43 | 35.24 | 41.10 |
| Jan. | 19.14 | 22.12 | 27.69 | 29.69 | −9.93 | −13.26 | 10.93 | 12.65 |
| Feb. | 18.53 | 22.99 | 35.79 | 39.07 | −6.17 | −11.67 | 13.04 | 15.22 |
| Mar. | 28.87 | 37.05 | 56.47 | 66.15 | −2.84 | −8.70 | 20.53 | 25.57 |
| Apr. | 48.66 | 57.24 | 84.10 | 89.70 | 4.44 | 2.74 | 33.72 | 39.21 |
| May | 91.44 | 84.69 | 105.78 | 109.50 | 20.51 | 13.00 | 54.44 | 56.26 |
| Jun. | 113.58 | 112.71 | 106.93 | 110.87 | 23.79 | 12.24 | 62.20 | 64.69 |
| Jul. | 180.25 | 160.03 | 114.40 | 124.43 | 8.01 | 9.08 | 73.36 | 78.25 |
| Aug. | 147.5 | 130.23 | 112.46 | 118.59 | 0.52 | 0.90 | 69.53 | 71.56 |
| Sep. | 120.64 | 105.21 | 73.41 | 76.92 | 9.87 | 25.59 | 46.43 | 49.77 |
| Oct. | 70.4 | 68.48 | 51.45 | 53.05 | −10.29 | 1.84 | 29.67 | 32.76 |
| Nov. | 37.5 | 37.32 | 34.97 | 35.74 | −13.99 | −10.76 | 17.56 | 19.53 |
| Dec. | 22.3 | 24.84 | 25.81 | 27.84 | −13.10 | −16.50 | 11.27 | 13.22 |
| Time Scale | ΔRc (mm) | ΔRH (mm) | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | −52.86 | −19.04 | 73.51 | 26.49 |
| Spr. | 0.88 | −3.21 | −37.62 | 137.62 |
| Sum. | −42.90 | −4.87 | 89.81 | 10.19 |
| Aut. | −20.52 | −5.41 | 79.15 | 20.85 |
| Win. | 5.53 | −1.41 | 134.22 | −34.22 |
| Jan. | 1.72 | −0.46 | 136.34 | −36.34 |
| Feb. | 2.23 | 0.05 | 97.81 | 2.19 |
| Mar. | 3.43 | −0.30 | 109.53 | −9.53 |
| Apr. | 3.78 | −0.68 | 122.03 | −22.03 |
| May | −7.30 | −1.25 | 85.38 | 14.62 |
| Jun. | −3.33 | −0.03 | 99.11 | 0.89 |
| Jul. | −23.01 | −2.10 | 91.62 | 8.38 |
| Aug. | −20.05 | 0.76 | 103.92 | −3.92 |
| Sep. | −17.23 | −1.55 | 91.76 | 8.24 |
| Oct. | −3.35 | −1.65 | 66.99 | 33.01 |
| Nov. | −0.71 | −1.44 | 32.91 | 67.09 |
| Dec. | 1.43 | −0.85 | 246.23 | −146.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, M.; Hu, S.; Hu, X.; Long, Y. Quantifying the Influence of Climatic and Anthropogenic Factors on Multi-Scalar Streamflow Variation of Jialing River, China. Water 2024, 16, 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182702
Jia M, Hu S, Hu X, Long Y. Quantifying the Influence of Climatic and Anthropogenic Factors on Multi-Scalar Streamflow Variation of Jialing River, China. Water. 2024; 16(18):2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182702
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Mengya, Shixiong Hu, Xuyue Hu, and Yuannan Long. 2024. "Quantifying the Influence of Climatic and Anthropogenic Factors on Multi-Scalar Streamflow Variation of Jialing River, China" Water 16, no. 18: 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182702
APA StyleJia, M., Hu, S., Hu, X., & Long, Y. (2024). Quantifying the Influence of Climatic and Anthropogenic Factors on Multi-Scalar Streamflow Variation of Jialing River, China. Water, 16(18), 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182702






