Detection and Measurement of Bacterial Contaminants in Stored River Water Consumed in Ekpoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
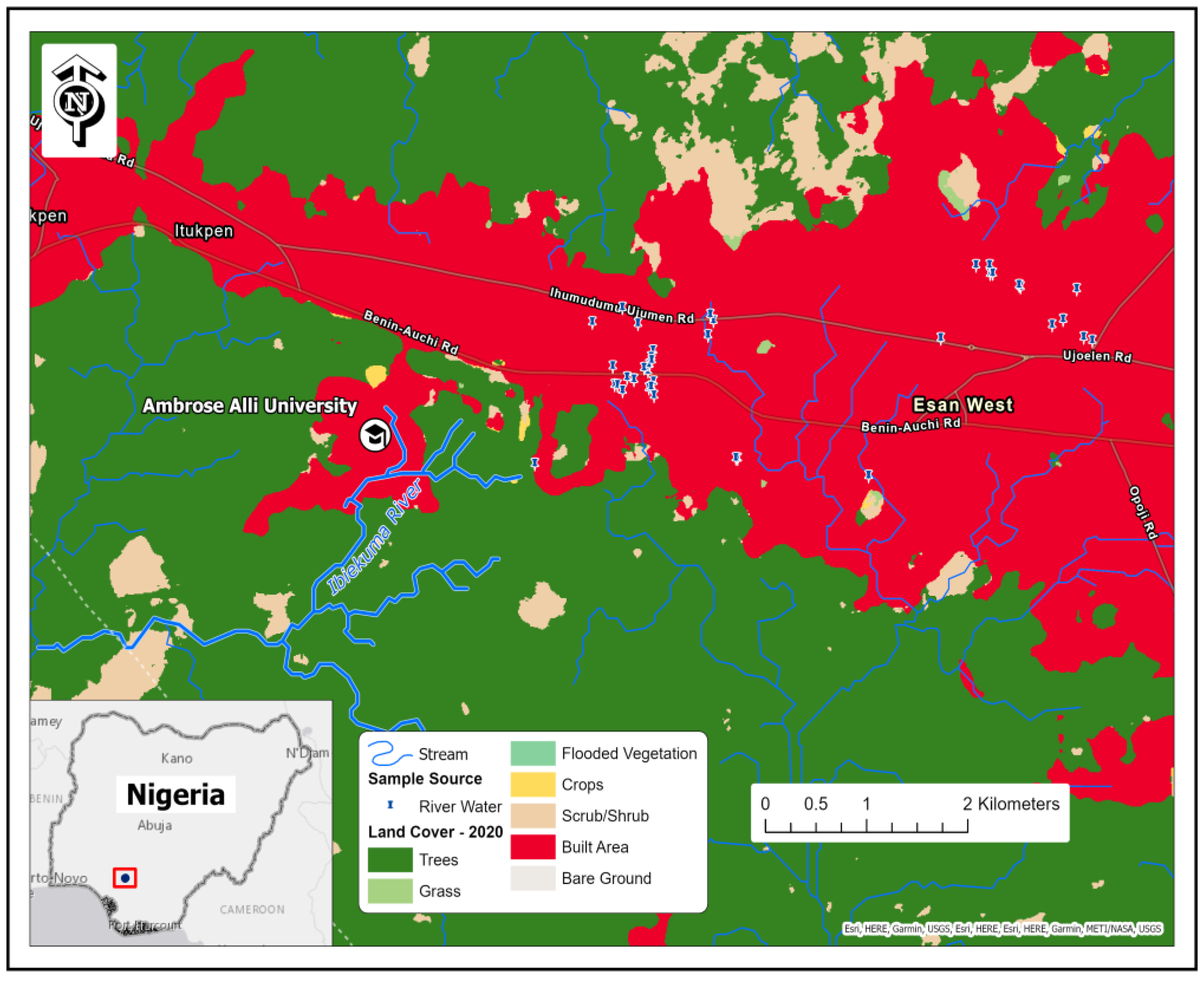
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Sampling Procedure
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. Bacteriological Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical and Chemical Water Quality
3.2. Bacterial Count and Occurrence
3.2.1. Heterotrophic Bacterial Counts
3.2.2. Total Coliform and Fecal Coliform Counts
3.3. Trend of Water Quality Studies in Ekpoma, Nigeria
3.4. Recommended Approach for Water Quality Improvement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emenike, P.C.; Nnaji, C.C.; Tenebe, I.T. Assessment of Geospatial and Hydrochemical Interactions of Groundwater Quality, Southwestern Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noemdoe, S.; Jonker, L.; Swatuk, L.A. Perceptions of Water Scarcity: The Case of Genadendal and Outstations. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2006, 31, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO; UNICEF; World Bank. State of the World’s Drinking Water: An Urgent Call to Action to Accelerate Progress on Ensuring Safe Drinking Water for All; WHO; UNICEF; World Bank. 2022, p. 114. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240060807 (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- World Health Organization Drinking-Water. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Blake, S.; Henry, T.; Murray, J.; Flood, R.; Muller, M.R.; Jones, A.G.; Rath, V. Compositional Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Thermal Groundwater Provenance: A Hydrogeochemical Case Study from Ireland. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 75, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Enyoh, E.C.; Ohiagu, F.O. Evaluation of Some Groundwater Sources in Ota, Ogun State, Southwestern Nigeria. Nat. Sci. 2021, 36, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Alens, O.P. Assessment of the Use of Surface Water and Its Environmental Health Effects in Ekpoma, Nigeria. Nternational J. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 6, 2147–2161. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, R.L.; Kase, J.A.; Harrison, L.M.; Balan, K.V.; Babu, U.; Chen, Y.; Macarisin, D.; Kwon, H.J.; Zheng, J.; Stevens, E.L.; et al. The Persistence of Bacterial Pathogens in Surface Water and Its Impact on Global Food Safety. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Zakwan, M.; Pulikkal, A.K.; Lalthazula, R. Impact of Unplanned Urbanization on Surface Water Quality of the Twin Cities of Telangana State, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCDC Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://ncdc.gov.ng/diseases/sitreps/?cat=7&name=An%20update%20of%20Cholera%20outbreak%20in%20Nigeria (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- Babatimehin, O.I.; Uyeh, J.O.; Onukogu, A.U. Analysis of the Re-Emergence and Occurrence of Cholera in Lagos State, Nigeria. Bull. Geography. Socio-Econ. Ser. 2017, 36, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, A.U.; Haruna, U.A.; Amos, O.A.; Olajide, E.O.; Amene, T.; Odususi, O.D.; Adewusi, B.A.; Abia, C.; Safari, J.; Sorinola, F.W.; et al. Tackling Cholera Outbreak Amidst COVID-19 Pandemic in Nigeria: Challenges and Recommendations. Public Health Rev. 2022, 43, 1604776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malu, C. Brazil Floods: Waterborne Disease Outbreak Kills Four People. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cq559gexxy5o (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- CDC Waterborne Outbreaks Summary Reports. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/healthy-water-data/study-results/index.html (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- Horton, H. Hospital Admissions for Waterborne Diseases in England up 60%, Report Shows. Guardian. 2024. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2024/mar/29/hospital-admissions-for-waterborne-diseases-in-england-up-60-report-shows (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- WHO Millions at Risk from Cholera Due to Lack of Clean Water, Soap and Toilets, and Shortage of Cholera Vaccine. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/20-03-2024-millions-at-risk-from-cholera-due-to-lack-of-clean-water-soap-and-toilets-and-shortage-of-cholera-vaccine (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- Addo, B.E.; Amankwaa, G.; Gyasi, R.M. Physicochemical and Bacteriological Quality of Sachet Water Used by Ghanaian University Students: Implications for Public Health. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2019, 9, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntunen, J.; Meriläinen, P.; Simola, A. Public Health and Economic Risk Assessment of Waterborne Contaminants and Pathogens in Finland. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omole, D.O.; Emenike, C.P.; Tenebe, I.T.; Akinde, A.O.; Badejo, A.A. An Assessment of Water Related Diseases in a Nigerian Community. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 10, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osarenmwinda, O.; Idaehor, A.G. Bacteriological and Physicochemical Analyses of Well Water Used for Drinking in Ekpoma-Edo State, Nigeria. J. Microbiol. Exp. 2019, 7, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVilbiss, S.E.; Steele, M.K.; Krometis, L.-A.H.; Badgley, B.D. Freshwater Salinization Increases Survival of Escherichia Coli and Risk of Bacterial Impairment. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Table 8.3, WHO Guideline Values for Drinking-Water Quality: Bacteria; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Omoni, V.T.; Bankole, P.O.; Omoche, O.; Obida, C.; Igben, C.; Stephen, O.E.; Ogwo, E.I.; Torjir, D.N. Evaluation of the Effects of Abattoir Effluent on the Physicochemical and Bacteriological Quality of River Benue, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 195, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unuigboje, A.; Oriakhi, H. An Assessment of Resident’s Coping Mechanisms Towards Meeting Their Water Needs in Ekpoma, Edo State. Niger. J. Educ. Health Technol. Res. 2015, 7, 288–298. [Google Scholar]
- Jemikalajah, D.J. Analysis of Bacterial Load in Domestic Water Sources in Ekpoma, Edo State, Nigeria. Borno Med. J. 2018, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olonaiye, E.G.; Ra, N.; Garba, N.N.; Ejimah, A.A. Determination of Radioactivity Concentration In Harvested Water Within Ekpoma, Edo State. Fudma J. Sci. 2019, 3, 456–461. [Google Scholar]
- Tenebe, I.T.; Babatunde, E.O.; Neris, J.B.; Mikano, C.; Ezeudu, O.B.; Edo, O.C.; Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Chukwuka, C.D.; Benson, N.U. Reliability of Stored River Water as an Alternative for Consumption in Ekpoma, Nigeria: A Human Health Risk Assessment. J. Water Health 2023, 21, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turay, A.A.; Ejovwoke, I.; Okodua, M.A.; Okwori, A.E.J.; Anyanwu, R.A. Assessment of Bacteriologic Profile of Reservoir Water in Ekpoma, Edo, Nigeria. Int. J. Community Res. 2014, 3, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzma, S.; Saccoccia, L.; Chertock, M. 25 Countries, Housing One-Quarter of the Population, Face Extremely High Water Stress. 2023. Available online: https://www.wri.org/insights/highest-water-stressed-countries (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Ajibade, F.O.; Olajire, O.O.; Ajibade, T.F.; Fadugba, O.G.; Idowu, T.E.; Adelodun, B.; Opafola, O.T.; Lasisi, K.H.; Adewumi, J.R.; Pham, Q.B. Groundwater Potential Assessment as a Preliminary Step to Solving Water Scarcity Challenges in Ekpoma, Edo State, Nigeria. Acta Geophys. 2021, 69, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edokpayi, C.; Osimen, E. Hydrobiological Studies on Ibiekuma River at Ekpoma, Southern Nigeria, after Impoundment: The Faunal Characteristics. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. 2009, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenebe, I.; Emenike, P.C.; Babatunde, E.O.; Neris, J.B.; Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Dede-Bamfo, N.; Etu, E.E.; Ogarekpe, N.M.; Emakhu, J.; Nsikak, B.U. Assessing the State of Rainwater for Consumption in a Community in Dire Need of Clean Water: Human and Health Risk Using HERisk. Water Pract. Technol. 2022, 17, 2005–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapter 5 Water Quality Conditions|Monitoring & Assessment|US EPA. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/water/archive/web/html/vms50.html (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- National Research Council (US). Safe Drinking Water Microbiology of Drinking Water. In Drinking Water and Health: Volume 1; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Tenebe, I.T.; Emenike, P.C.; Nnaji, C.C.; Babatunde, E.O.; Ogarekpe, N.M.; Dede-Bamfo, N.; Omole, D.O. Bacterial Characterization and Quantification of Rainwater Harvested in a Rural Community in Nigeria. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of a Most Probable Number Method for Detection and Quantification of Legionella Pneumophila. Pathogens 2022, 11, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutrition Center for Food Safety and Applied. BAM Appendix 2: Most Probable Number from Serial Dilutions; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/laboratory-methods-food/bam-appendix-2-most-probable-number-serial-dilutions (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Akinduti, P.A.; Olasehinde, G.I.; Ejilude, O.; Taiwo, O.S.; Obafemi, Y.D. Fecal Carriage and Phylo-Diversity of Community-Acquired bla TEM Enteric Bacilli in Southwest Nigeria. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Fatima, R.; Soomro, Z.A.; Hussain, M.; Ahmad, S.R.; Ramzan, H.S. Bacteriological Quality Assessment of Water Supply Schemes (WSS) of Mianwali, Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasana, J.; Morin, J.; Ndikuyeze, A.; Kamoso, P. Impact of Water Supply and Sanitation on Diarrheal Morbidity among Young Children in the Socioeconomic and Cultural Context of Rwanda (Africa). Environ. Res. 2002, 90, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, C.A.; Mihelcic, J.R. Effect of Storage Tank Material and Maintenance on Household Water Quality. J.-Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2012, 104, E521–E529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, C.I.; Dal Bello, M.; Bunse, C.; Pinhassi, J.; Gore, J. Warmer Temperatures Favor Slower-Growing Bacteria in Natural Marine Communities. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitter, C.; Petzoldt, H.; Korth, A.; Schwab, F.; Stange, C.; Hambsch, B.; Tiehm, A.; Lagkouvardos, I.; Gescher, J.; Hügler, M. Seasonal Dynamics in the Number and Composition of Coliform Bacteria in Drinking Water Reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakyi, P.A.; Asare, R. Impact of Temperature on Bacterial Growth and Survival in Drinking-Water Pipes. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 4, 807–817. [Google Scholar]
- Tokajian, S.; Hashwa, F. Water Quality Problems Associated with Intermittent Water Supply. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalchisa, D.; Megersa, M.; Beyene, A. Assessment of the Quality of Drinking Water in Storage Tanks and Its Implication on the Safety of Urban Water Supply in Developing Countries. Environ. Syst. Res. 2017, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Utz, R.M.; Pace, M.L.; Grese, M.; Yepsen, M. Increased River Alkalinization in the Eastern U.S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10302–10311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Testa, J.M.; Herrmann, M.; Najjar, R.G. Decoupling of Estuarine Hypoxia and Acidification as Revealed by Historical Water Quality Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber-Scannell, P.K.; Duffy, L.K. Effects of Total Dissolved Solids on Aquatic Organisms: A Review of Literature and Recommendation for Salmonid Species. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedadi, M.; Amakdouf, H.; Barnossi, A.E.; Moussaoui, A.E.; Kara, M.; Asmi, H.E.; Merzouki, M.; Bari, A. Impact of Anthropogenic Activities on the Physicochemical and Bacteriological Quality of Water along Oued Fez River (Morocco). Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talepour, N.; Hadi, M.; Nasseri, S.; Jaafarzadeh Haghighi Fard, N.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Borji, S.H. Isolation, Identification and Reviewing the Health Effect of HPC Bacteria in Household Point-of-Use (PoU) Water Treatment Devices: A Case Study, Ahvaz, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, L.H.; Ercumen, A.; Pickering, A.J.; Arsenault, J.E.; Islam, M.; Parvez, S.M.; Unicomb, L.; Rahman, M.; Davis, J.; Luby, S.P. Ingestion of Fecal Bacteria along Multiple Pathways by Young Children in Rural Bangladesh Participating in a Cluster-Randomized Trial of Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Interventions (WASH Benefits). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13828–13838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irobehian, Y.G.; Moses, U.A.; Olufemi, A.O.; Odiamehi, O.D. Physicochemical and Bacteriological Assessment of Groundwater Quality in Etsako East Local Government Area of Edo State, Nigeria. Ethiop. J. Sci. Technol. 2023, 16, 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, J.M. Surveillance of Waterborne Disease Outbreaks Associated with Drinking Water—United States, 2015–2020. MMWR. Surveill. Summ. 2024, 73, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeChevallier, M.W.; Prosser, T.; Stevens, M. Opportunistic Pathogens in Drinking Water Distribution Systems—A Review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health and Disease Heterogeneity: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.K.; Kass, P.H.; Soupir, M.L.; Biswas, S.; Singh, V.P. Contamination of Water Resources by Pathogenic Bacteria. AMB Express 2014, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubeh, B.; Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Resistance of Gram-Positive Bacteria to Current Antibacterial Agents and Overcoming Approaches. Molecules 2020, 25, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo Higuita, N.I.; Huycke, M.M. Enterococcal Disease, Epidemiology, and Implications for Treatment. In Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection; Gilmore, M.S., Clewell, D.B., Ike, Y., Shankar, N., Eds.; Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Hidalgo, L.; de Alarcón, A.; López-Cortes, L.E.; Luque-Márquez, R.; López-Cortes, L.F.; Gutiérrez-Valencia, A.; Gil-Navarro, M.V. Enterococcus Faecalis Endocarditis and Outpatient Treatment: A Systematic Review of Current Alternatives. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errington, J.; van der Aart, L.T. Microbe Profile: Bacillus Subtilis: Model Organism for Cellular Development, and Industrial Workhorse. Microbiology 2020, 166, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flindt, M.L.H. Pulmonary disease due to inhalation of derivatives of Bacillus subtilis containing proteolytic enzyme. Lancet 1969, 293, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, I.; Kutsuna, S.; Ohkusu, M.; Kato, T.; Miyashita, M.; Moriya, A.; Ohkusu, K. Bacillus Subtilis Variant Natto Bacteremia of Gastrointestinal Origin, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2022, 28, 1718–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsonis, I.; Karamani, L.; Xaplanteri, P.; Kolonitsiou, F.; Zampakis, P.; Gatzounis, G.; Marangos, M.; Assimakopoulos, S.F. Spontaneous Cerebral Abscess Due to Bacillus Subtilis in an Immunocompetent Male Patient: A Case Report and Review of Literature. World J. Clin. Cases 2018, 6, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Mendis, N.; Trigui, H.; Oliver, J.D.; Faucher, S.P. The Importance of the Viable but Non-Culturable State in Human Bacterial Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newby, P. The Significance and Detection of VBNC Microorganisms. Available online: https://www.americanpharmaceuticalreview.com/Featured-Articles/113051-The-Significance-and-Detection-of-VBNC-Microorganisms/ (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Pawlowski, D.R.; Metzger, D.J.; Raslawsky, A.; Howlett, A.; Siebert, G.; Karalus, R.J.; Garrett, S.; Whitehouse, C.A. Entry of Yersinia Pestis into the Viable but Nonculturable State in a Low-Temperature Tap Water Microcosm. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beshiru, A.; Okareh, O.T.; Chigor, V.N.; Igbinosa, E.O. Assessment of Water Quality of Rivers That Serve as Water Sources for Drinking and Domestic Functions in Rural and Pre-Urban Communities in Edo North, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| District ID | Parameters | Mean | Standard Deviation | Min. | Max. | WHO Guidelines |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EK 1 | pH | 8.7 | 0.4 | 8.0 | 9.2 | 6.5–8.5 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 70.5 | 58.6 | 0.1 | 195.3 | ≤400 μS/cm | |
| TEMP (°C) | 27.8 | 1.4 | 25.5 | 30.3 | 10–22 °C | |
| TDS (mg/L) | 35.2 | 29.4 | 0.1 | 97.9 | ≤500 mg/L | |
| EK 2 | pH | 8.9 | 0.2 | 8.7 | 9.1 | 6.5–8.5 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 77.5 | 58.0 | 28.6 | 161.7 | ≤400 μS/cm | |
| TEMP (°C) | 28.1 | 1.5 | 26.4 | 30.0 | 10–22 °C | |
| TDS (mg/L) | 38.8 | 29.0 | 14.3 | 80.9 | ≤500 mg/L | |
| EK 3 | pH | 8.4 | 0.5 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 6.5–8.5 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 82.3 | 125.9 | 0.4 | 227.3 | ≤400 μS/cm | |
| TEMP (°C) | 29.1 | 0.8 | 28.2 | 29.5 | 10–22 °C | |
| TDS (mg/L) | 41.2 | 63.1 | 0.2 | 113.8 | ≤500 mg/L | |
| EK 4 | pH | 8.8 | 0.3 | 8.1 | 9.2 | 6.5–8.5 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 41.3 | 47.3 | 0.1 | 179.3 | ≤400 μS/cm | |
| TEMP (°C) | 28.6 | 1.2 | 26.2 | 30.2 | 10–22 °C | |
| TDS (mg/L) | 20.6 | 23.7 | 0.1 | 89.4 | ≤500 mg/L | |
| EK 5 | pH | 9.1 | 0.0 | 9.1 | 9.1 | 6.5–8.5 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 27.7 | 0.0 | 27.7 | 27.7 | ≤400 μS/cm | |
| TEMP (°C) | 27.7 | 0.0 | 27.7 | 27.7 | 10–22 °C | |
| TDS (mg/L) | 13.9 | 0.0 | 13.9 | 13.9 | ≤500 mg/L |
| Regulatory Guidelines | HPC (CFU/100 mL) | TCC (CFU/100 mL) | FCC (CFU/100 mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USEPA | 500.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| WHO | No limit set | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| District | Total Samples Collected | |||
| EK1 | 54 | 451.1 × 104 | 1049.4 × 104 | 130.0 × 104 |
| EK2 | 12 | 2505.0 × 104 | 3670.0 × 104 | 330.0 × 104 |
| EK3 | 9 | 380.0 × 104 | 1660.0 × 104 | - |
| EK4 | 45 | 367.1 × 104 | 2268.6 × 104 | 800.0 × 104 |
| EK5 | 3 | 1320.0 × 104 | 4400.0 × 104 | - |
| District ID | EK 1 | EK 2 | EK 3 | EK 4 | EK 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Samples | 54 | 12 | 9 | 45 | 3 | ||
| Fit for Drinking | 21 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | ||
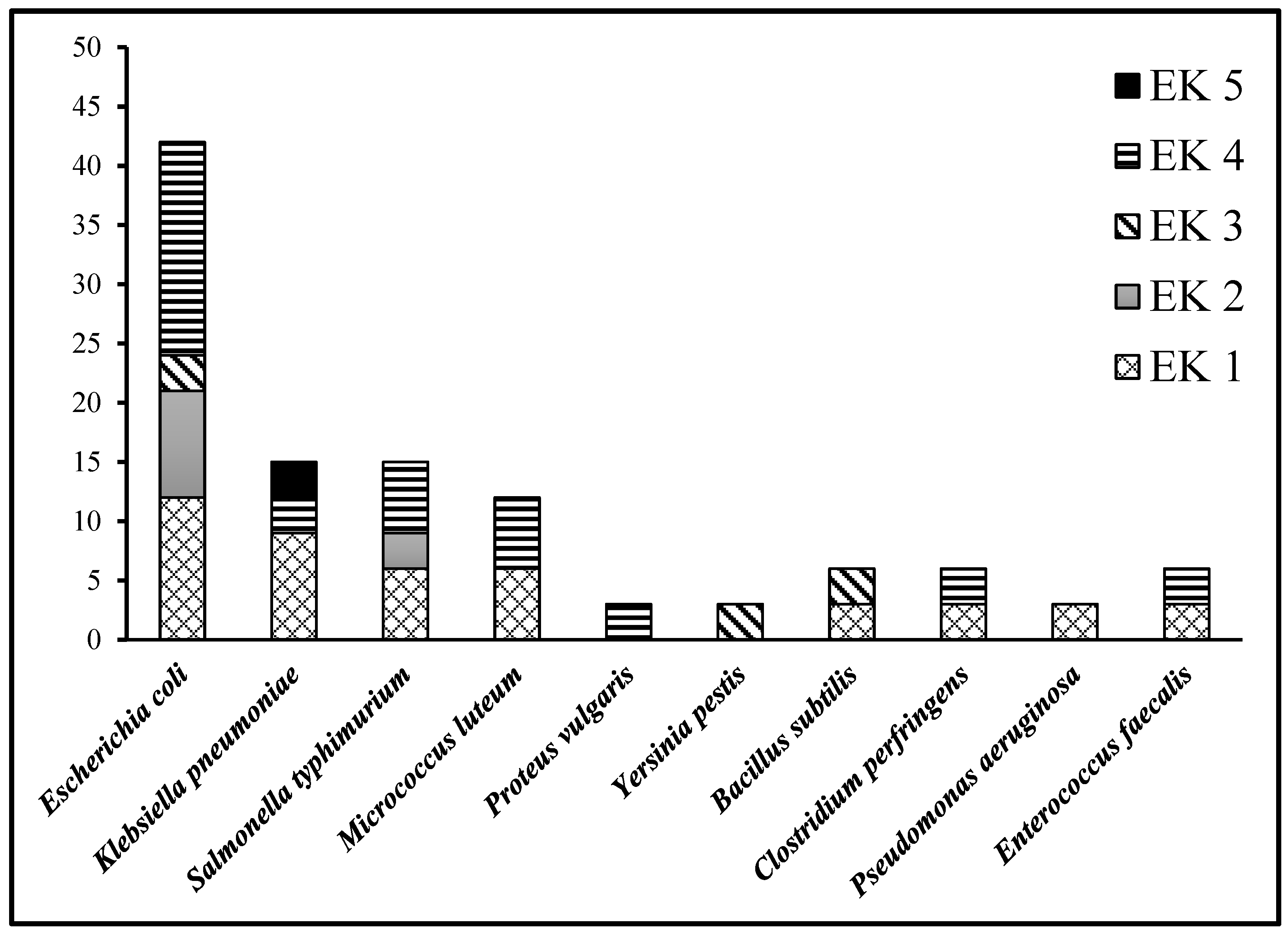
| Bacteria Species | Colonial Appearance | Unfit for Drinking | 33 | 12 | 9 | 39 | 3 |
| Escherichia coli | Gram −ve short rods | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Gram −ve short rods | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | |
| Salmonella typhimurium | Gram −ve short rods | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| Micrococcus luteum | Gram +ve long cocci | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | |
| Proteus vulgaris | Gram −ve short rods | No | No | No | Yes | No | |
| Yersinia pestis | Gram −ve short rods | No | No | Yes | No | No | |
| Bacillus subtilis | Gram +ve long rods | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | |
| Clostridium perfringens | Gram +ve long rods | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Gram −ve short rods | Yes | No | No | No | No | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | Gram +ve long cocci | Yes | No | No | No | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tenebe, I.T.; Babatunde, E.O.; Ogarekpe, N.M.; Emakhu, J.; Etu, E.-E.; Edo, O.C.; Omeje, M.; Benson, N.U. Detection and Measurement of Bacterial Contaminants in Stored River Water Consumed in Ekpoma. Water 2024, 16, 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182696
Tenebe IT, Babatunde EO, Ogarekpe NM, Emakhu J, Etu E-E, Edo OC, Omeje M, Benson NU. Detection and Measurement of Bacterial Contaminants in Stored River Water Consumed in Ekpoma. Water. 2024; 16(18):2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182696
Chicago/Turabian StyleTenebe, Imokhai T., Eunice O. Babatunde, Nkpa M. Ogarekpe, Joshua Emakhu, Egbe-Etu Etu, Onome C. Edo, Maxwell Omeje, and Nsikak U. Benson. 2024. "Detection and Measurement of Bacterial Contaminants in Stored River Water Consumed in Ekpoma" Water 16, no. 18: 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182696
APA StyleTenebe, I. T., Babatunde, E. O., Ogarekpe, N. M., Emakhu, J., Etu, E.-E., Edo, O. C., Omeje, M., & Benson, N. U. (2024). Detection and Measurement of Bacterial Contaminants in Stored River Water Consumed in Ekpoma. Water, 16(18), 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182696






