Spatial Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Saline Water Intrusion and Potentially Hazardous Pollutants in a Coastal Groundwater Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
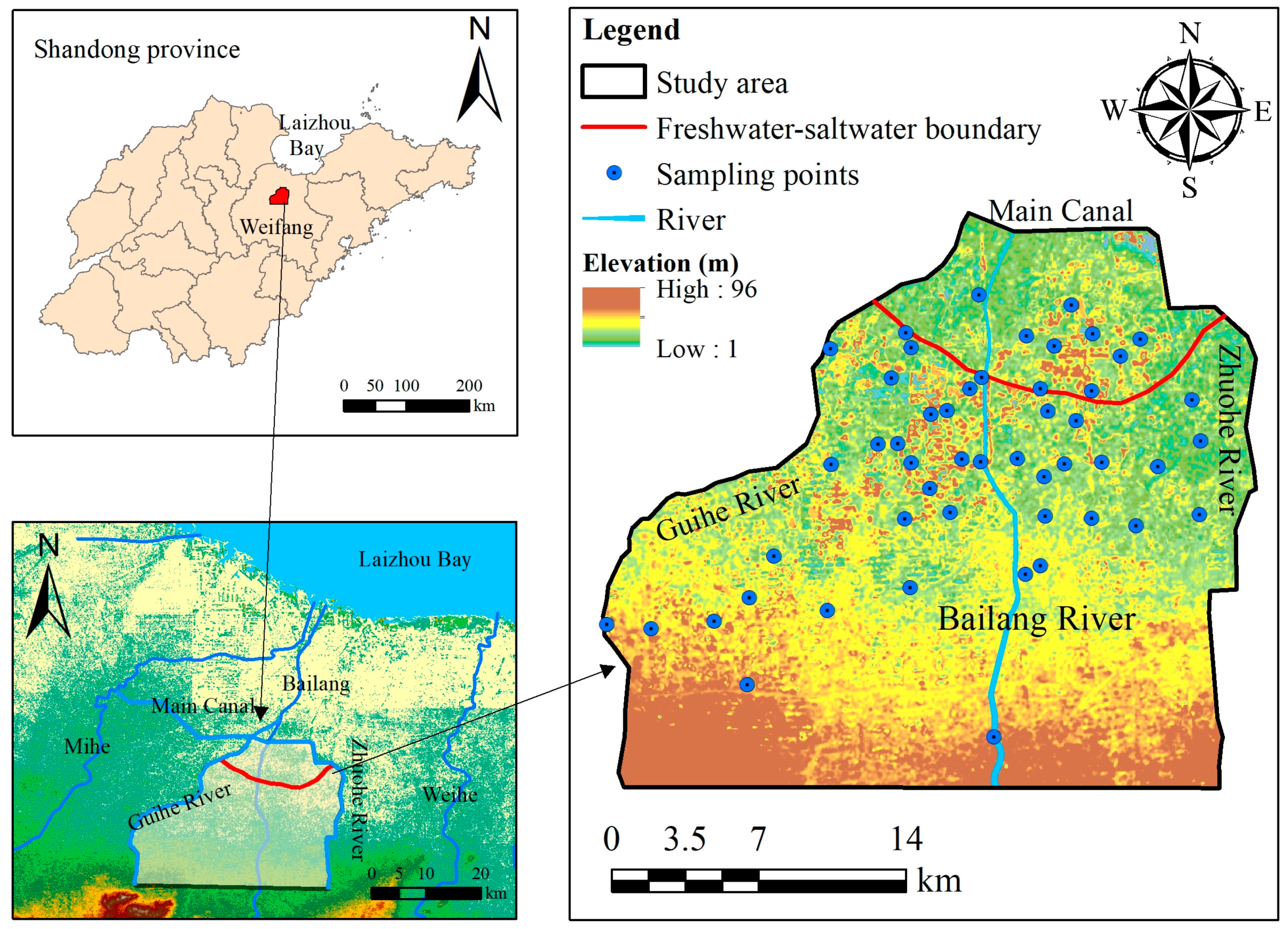
2.1. Location and Climatic Conditions of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Groundwater Quality Index (WQI)
2.4. Health Risk Assessment
2.5. Spatial Interpolation
3. Results
3.1. Groundwater Quality Types and Hydrochemical Types
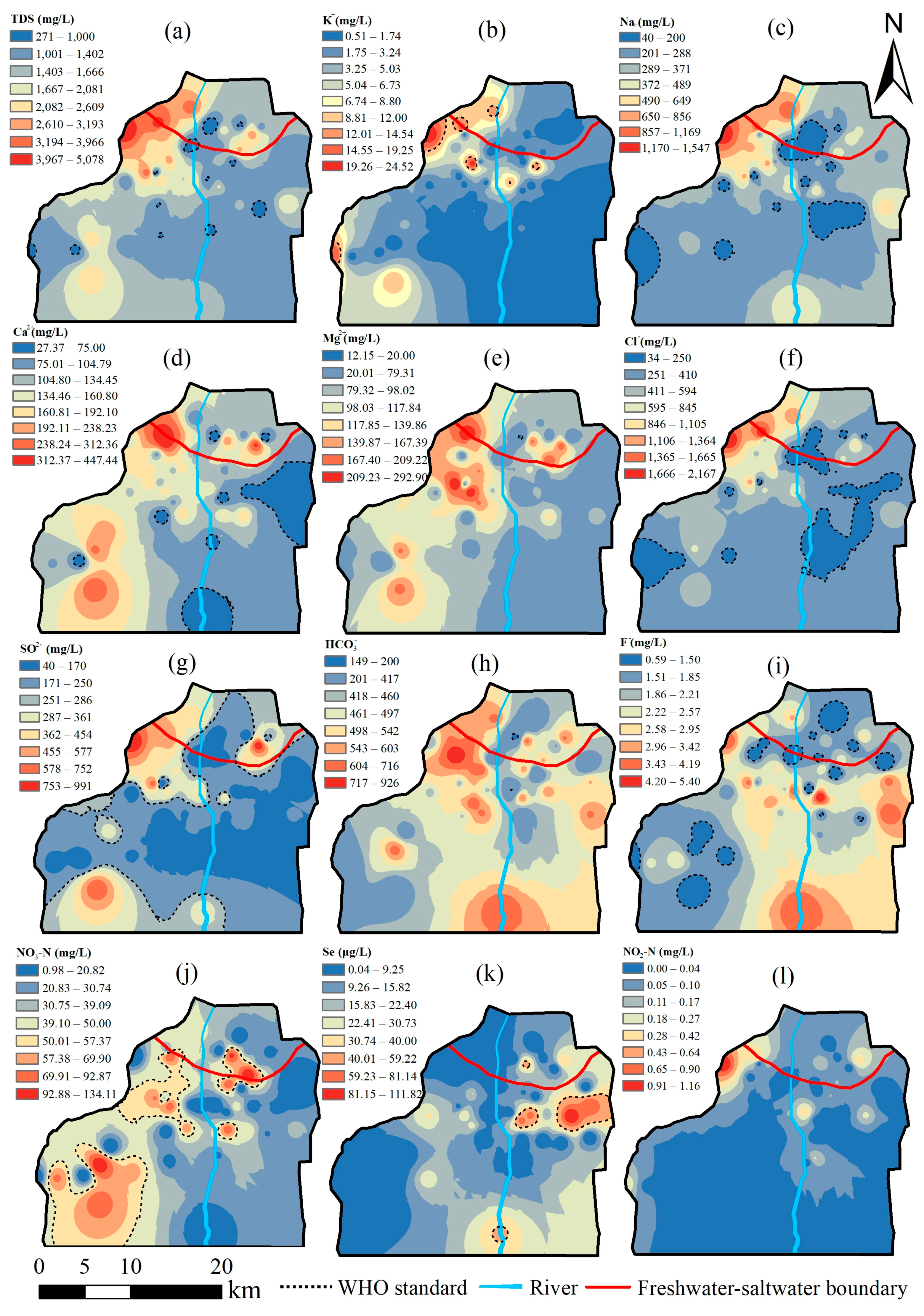
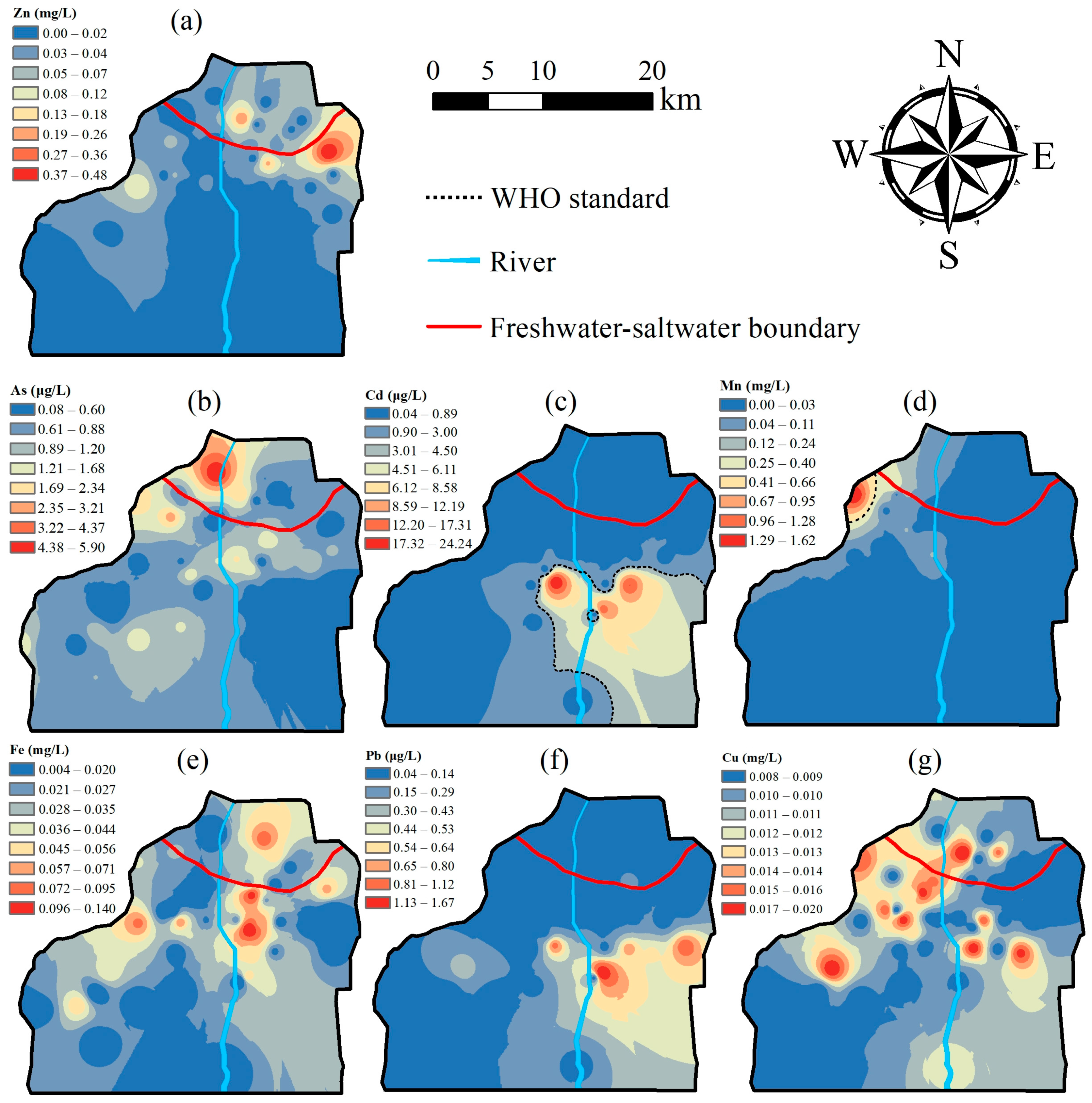
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Groundwater Quality
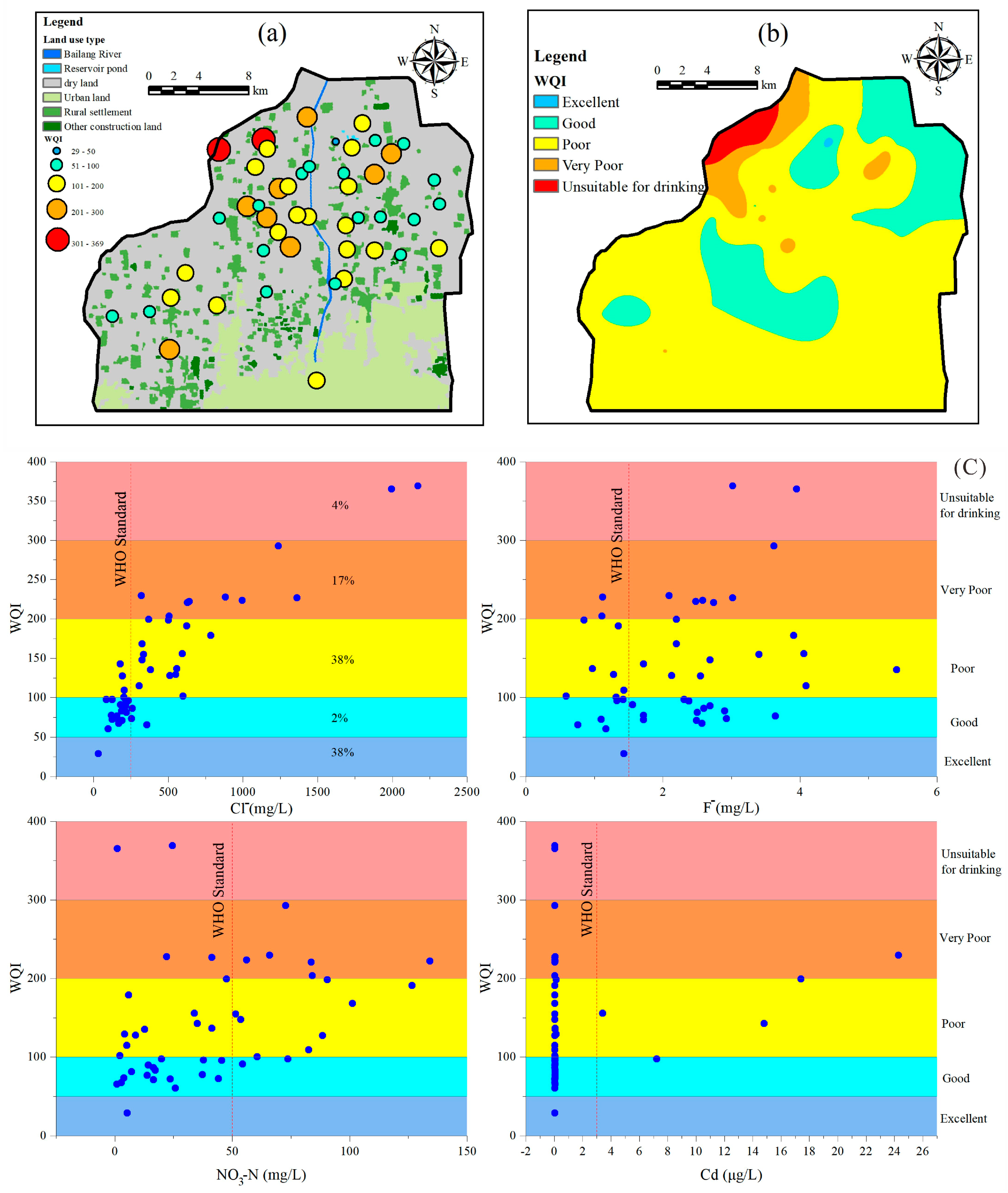
3.3. Groundwater Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
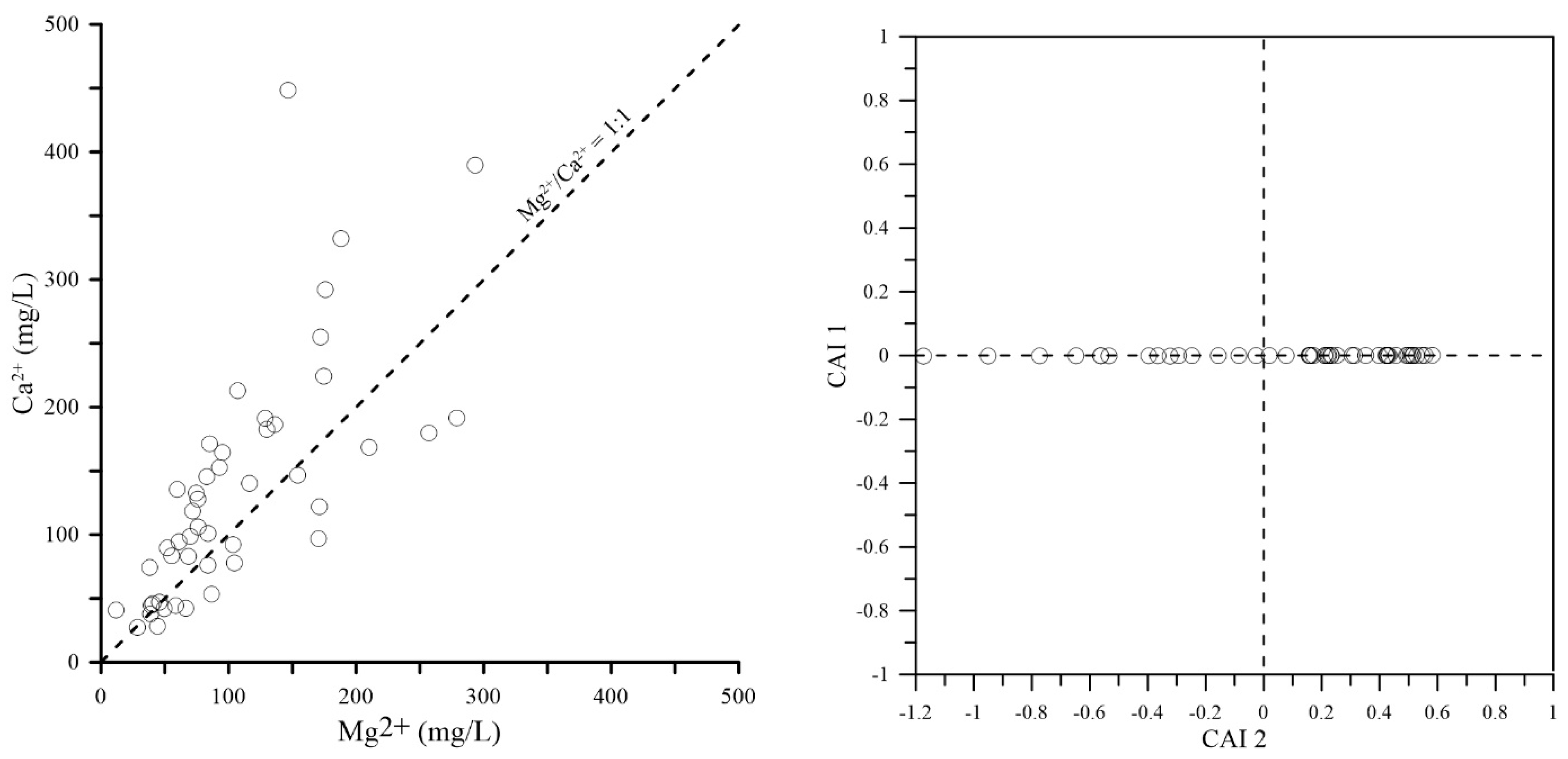
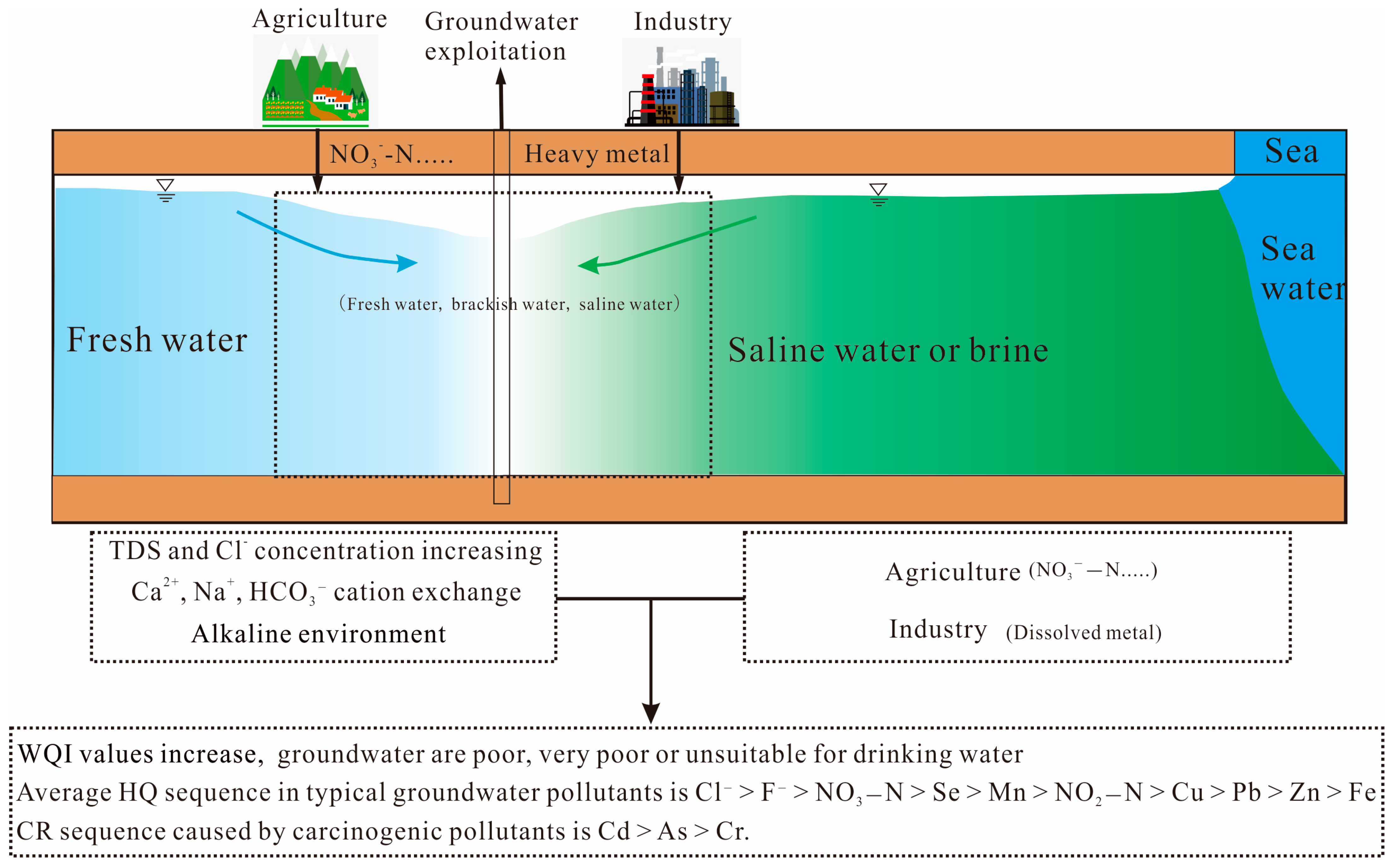
4.1. Direct Effects of Saline Water Intrusion
4.2. Health Risk Assessment and Main Factors
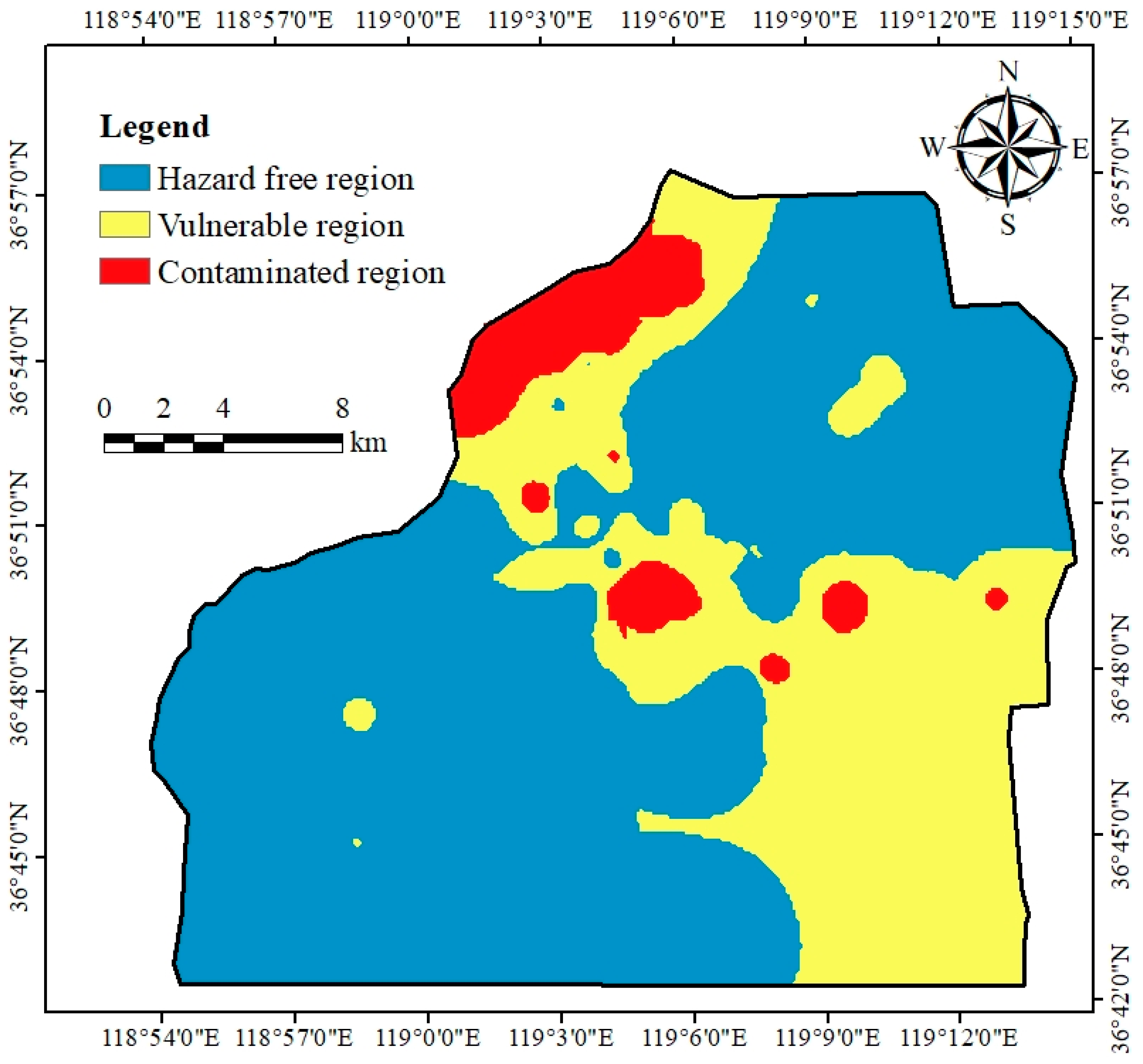
4.3. Spatial Distribution of HQ and CR
4.4. Adaptability of the Research Framework
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Post, V.E.A. Fresh and saline groundwater interaction in coastal aquifers: Is our technology ready for the problems ahead? Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansari, N. Management of water resources in Iraq: Perspectives and prognoses. Engineering 2013, 5, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H. Groundwater chemistry, distribution and potential health risk appraisal of nitrate enriched groundwater: A case study from the semi-urban region of South India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Su, Q.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.J.; Liu, J.T. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of dissolved heavy metals in groundwater of eastern China coastal zone. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.H.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Lin, Y.C.; Luo, Y.M. Influence of coastal groundwater salinization on the distribution and risks of heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Possible effect of submarine groundwater discharge on the pollution of coastal water: Occurrence, source, and risks of endocrine disrupting chemicals in coastal groundwater and adjacent seawater influenced by reclaimed water irrigation. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.H. Spatio-temporal analysis of groundwater chemistry, quality and potential human health risks in the Pinggu basin of North China Plain: Evidence from high-resolution monitoring dataset of 2015–2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Gao, Z.J.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.T.; Li, W.; Deng, Q.J.; Lv, L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Su, Q. Hydrochemistry characters and hydrochemical processes under the impact of anthropogenic activity in the Yiyuan city, Northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solgi, E.; Jalili, M. Zoning and human health risk assessment of arsenic and nitrate contamination in groundwater of agricultural areas of the twenty-two village with geostatistics (Case study: Chahardoli Plain of Qorveh, Kurdistan Province, Iran). Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, W.E.; Pope, J.P. Current challenges using models to forecast seawater intrusion: Lessons from the Eastern Shore of Virginia, U.S.A. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, R.; Xue, C.; Wu, J. Progress, opportunities and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13224–13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Tian, R.; He, S.; He, X.; Xue, C.; Zhang, K. Geochemistry, hydraulic connectivity and quality appraisal of multilayered groundwater in the Hongdunzi Coal Mine, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ. 2018, 37, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.F.; Xiao, Y.; Hao, Q.C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.B.; Dong, G.F. Groundwater geochemical signatures and implication for sustainable development in a typical endorheic watershed on Tibetan plateau. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48312–48329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.; Hou, G. Evolutionary process of saline-water intrusion in Holocene and Late Pleistocene groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naujokas, M.; Anderson, B.; Ahsan, H.; Aposhian, H.V.; Suk, W. The broad scope of health effects from chronic arsenic exposure: Update on a worldwide public health problem. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilzadeh, M.; Jaafari, J.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Panahandeh, M.; Javid, A.; Javan, S. Investigation of the extent of contamination of heavy metals in agricultural soil using statistical analyses and contamination indices. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess 2019, 25, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Nagpal, A.K.; Kaur, I. Appraisal of heavy metal contents in groundwater and associated health hazards posed to human population of Ropar wetland, Punjab, India and its environs. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, S.; RamyaPriya, R.; Elango, L. Long-term exposure to chromium contaminated waters and the associated human health risk in a highly contaminated industrialised region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 4276–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, I.; Singh, U.K.; Singh, R.P. An Overview on Heavy Metal Contamination of Water System and Sustainable Approach for Remediation, Water Pollution and Management Practices; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 255–277. [Google Scholar]
- Azhdarpoor, A.; Radfard, M.; Pakdel, M.; Abbasnia, A.; Badeenezhad, A.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Yousefi, M. Assessing fluoride and nitrate contaminants in drinking water resource and their health risk assessment in a semiarid region of southwest Iran. Desalin. Water Treat 2019, 149, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, H.; Jafari, A.; Kamarehie, B.; Fakhri, Y.; Ghaderpoury, A.; Karami, M.A.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Shams, M.; Bidarpoor, F.; Salimi, M. Health risk assessment related to the fluoride, nitrate, and nitrite in the drinking water in the Sanandaj, Kurdistan county, Iran. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, G.T.; Yun, S.T.; Mayer, B.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, J.S.; Kim, K.; Koh, Y.K. Fluorine geochemistry in bedrock groundwater of South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 385, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.S. Co-contamination of Arsenic and Fluoride in the Groundwater of Unconsolidated Aquifers Under Reducing Environments. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, R.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, A. Geochemical and geostatistical appraisal of fluoride contamination: An insight into the quaternary aquifer. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.P.; Chen, Q.; Wei, J.C.; Wang, H.M.; Shi, L.Q.; Ning, F.Z.; Liu, S.L.; Yang, M.Y.; Xue, X.; Dong, F.Y. The study on the mechanism of fluorine transformation between water and rock (soil) in seawater intrusion areas based on FTIR spectrum. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, M.A.; Fakhri, Y.; Rezania, S.; Alinejad, A.A.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Yousefi, M.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Saghi, M.H.; Ahmadpour, M. Non-Carcinogenic Health Risk Assessment due to Fluoride Exposure from Tea Consumption in Iran Using Monte Carlo Simulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. He 2019, 16, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Pham, Q.B.; Gupta, N.; Rezania, S.; Kamyab, H.; Yadav, S.; Vymazal, J.; Kumar, V.; Tri, D.Q.; et al. Fluoride Contamination, Health Problems and Remediation Methods in Asian Groundwater: A Comprehensive Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmahon, P.B.; Brown, C.J.; Johnson, T.D.; Belitz, K.; Lindsey, B.D. Fluoride Occurrence in United States Groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Jia, C.; Gao, M.S.; Chang, W.B.; Wang, Y.J. Hydrochemical characteristics and functions of groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay based on the multivariate statistical analysis approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 250, 107153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, M.; Tang, Z.; Hou, G.; Guo, F. Responses of submarine groundwater to silty-sand coast reclamation: A case study in south of Laizhou Bay, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 181, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasnia, A.; Yousefi, N.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Radfard, M.; Yousefi, M.; Alimohammadi, M. Evaluation of groundwater quality using water quality index and its suitability for assess ing water for drinking and irrigation purposes: Case study of Sistan and Baluchistan province (Iran). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 988–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.Z.; Shao, D.G.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J.K. Evaluation of water quality in the Southto-North Water Diversion Project of China using the water quality index (WQI) method. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Patel, N.; Jindal, T.; Srivastava, P.; Bhowmik, A. Assessment of spatial and temporal variations in water quality by the application of multivariate statistical methods in the Kali River, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, F.; Almadani, S.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Alwaqdani, E.; Alfaifi, H.; Alharbi, T. Influence of seawater intrusion and heavy metals contamination on groundwater quality, Red Sea coast, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 165, 112094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njuguna, S.M.; Onyango, J.A.; Githaiga, K.B.; Gituru, R.W.; Yan, X. Application of multivariate statistical analysis and water quality index in health risk assessment by domestic use of river water. Case study of Tana River in Kenya. Process Safety and Environmental. Protection 2020, 133, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githaiga, K.B.; Njuguna, S.M.; Gituru, R.W.; Yan, X. Water quality assessment multivariate analysis human health risks of heavy metals in eight major lakes in Kenya. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Hou, H.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. An integrated geospatial correlation analysis human health risk assessment approach for investigating abandoned industrial sites. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghfam, S.; Abdi, M.; Khatibi, R.; Nadiri, A.A. An investigation into uncertainties within Human Health Risk Assessment to gain an insight into plans to mitigate impacts of arsenic contamination. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 211, 127667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Rana, A.; Mian, H.R.; Saleem, S.; Mohseni, M.; Jasim, S.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. Human health risk-based life cycle assessment of drinking water treatment for heavy metal(loids) removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrocks, T.; Holden, E.; Wedge, D.; Wijns, C. 3-D geochemical interpolation guided by geophysical inversion models. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Yin, S.; Wang, W. Spatial interpolation of the extreme hourly precipitation at different return levels in the Haihe River basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Lei, M.; Yang, S.; Yang, J.; Guo, G.; Zhou, X. Comparing ordinary kriging and inverse distance weighting for soil as pollution in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15597–15608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Mattevada, S.; O Bryant, S.E. Comparison of the accuracy of kriging and IDW interpolations in estimating groundwater arsenic concentrations in Texas. Environ. Res. 2014, 130, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khouni, I.; Louhichi, G.; Ghrabi, A. Use of GIS based Inverse Distance Weighted interpolation to assess surface water quality: Case of Wadi El Bey, Tunisia. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, C. Estimation of the spatial rainfall distribution using inverse distance weighting (IDW) in the middle of Taiwan. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 10, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, M.M.; Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A.; Hao, K.Z.; Xiaosheng, Q.; Sham, A.W.L. Investigation of groundwater table distribution using borehole piezometer data interpolation: Case study of Singapore. Eng. Geol. 2020, 271, 105590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charizopoulos, N.; Zagana, E.; Psilovikos, A. Assessment of natural and anthropogenic impacts in groundwater, utilizing multivariate statistical analysis and inverse distance weighted interpolation modeling: The case of a Scopia basin (Central Greece). Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Kumar Jha, S.; Sivakumar, B. Reconstruction of daily rainfall data using the concepts of networks: Accounting for spatial connections in neighborhood selection. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Song, X.F.; Currell, M.J.; Yang, J.L.; Xiao, G.Q. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Sun, T.; Fan, H.; Wu, B.; Li, M.; Qian, L. Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater quality and human health risk assessment of nitrate in the largest peninsula of China based on high-density sampling: A case study of Weifang. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 322, 129164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Guan, D.X.; Farooqi, A.; Khan, S.; Zahir, S.; Jehan, S.; Khattak, S.A.; Khan, M.S.; Khan, R. Fluoride prevalence in groundwater around a fluorite mining area in the flood plain of the River Swat. Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeller, H. Qualitative Evaluation of Groundwater Resources. In: Methods and Techniques of Groundwater investigations and Development UNESCO. Water Resour. Ser. 1967, 33, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.M.; Puls, R.W. Arsenate and Arsenite Removal by Zerovalent Iron: Effects of Phosphate, Silicate, Carbonate, Borate, Sulfate, Chromate, Molybdate, and Nitrate, Relative to Chloride. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4522–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Jia, C.P.; Wei, J.C.; Dong, F.Y.; Yang, W.G.; Hao, D.C.; Jia, Z.W.; Ji, Y.H. Geochemical process of groundwater fluoride evolution along global coastal plains: Evidence from the comparison in seawater intrusion area and soil salinization area. Chem. Geol. 2020, 552, 119779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Kazemi Moghaddam, V.; Maghsoudi Nasab, S.; Nabizadeh, R.; Hadei, M.; Zarei, A.; Baghal Asghari, F.; Mohammadi, A.A. Northwest of Iran as an endemic area in terms of fluoride contamination: A case study on the correlation of fluoride concentration with physicochemical characteristics of groundwater sources in Showt. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 155, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouei, A.I.; Mahvi, A.H.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Asgharnia, H.A.; Fallah, S.H.; Khafajeh, A.A. Fluoride concentration in potable groundwater in rural areas of Khaf city, Razavi Khorasan Province, northeastern Iran. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 3, 201–203. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, M.; Asghari, F.; Zuccarello, P.; Oliveri Conti, G.; Ejlali, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Ferrante, M. Spatial Distribution Variation and Probabilistic Risk Assessment of Exposure to Fluoride in Ground Water Supplies: A Case Study in an Endemic Fluorosis Region of Northwest Iran. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Adult | Child | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingestion rate (IR) | 2.5 | 0.78 | L/d |
| Exposure frequency (EF) | 350 | 350 | d/a |
| Exposure duration (ED) | 26 | 6 | a |
| Average body weight (BW) | 80 | 15 | kg |
| Average time (AT) | 8760 | 2190 | d |
| Elements | RfDi | SFi | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 0.003 | 0.5 | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| As | 0.0003 | 1.5 | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| Cd | 0.0005 | 6.1 | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| Mn | 0.02 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| Fe | 0.3 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| Pb | 0.0014 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| Cu | 0.04 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| Zn | 0.3 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| F- | 0.04 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| NO3-N | 1.6 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| Cl- | 0.1 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| NO2-N | 0.1 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| Se | 0.005 | - | (mg·kg−1·d−1) |
| Chemical Indicators | Unit | Max | Min | Average | Median | WHO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | mg/L | 24.55 | 0.51 | 3.22 | 1 | 12 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 1548.41 | 39.37 | 350.16 | 268.35 | 200 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 448.45 | 27.33 | 134.88 | 118.5 | 75 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 293.3 | 11.78 | 105.4 | 83.81 | 20 |
| Fe | mg/L | 0.14 | 0.004 | 0.03 | 0.021 | 0.3 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 2171.16 | 32.29 | 461.85 | 322.24 | 250 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 992.15 | 39.13 | 261.31 | 178.71 | 250 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 927.22 | 148.01 | 499.07 | 477.4 | 200 |
| F− | mg/L | 5.41 | 0.59 | 2.28 | 2.31 | 1.5 |
| NO2-N | mg/L | 1.16 | 0.003 | 0.09 | 0.007 | 3 |
| NO3-N | mg/L | 134.25 | 0.96 | 40.39 | 35.17 | 50 |
| TDS | mg/L | 5082 | 266 | 1749.85 | 1489 | 1000 |
| Cu | mg/L | 0.02 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 2 |
| Zn | mg/L | 0.482 | 0.001 | 0.037 | 0.006 | 4 |
| Mn | mg/L | 1.62 | 0.0005 | 0.086 | 0.003 | 0.4 |
| Pb | μg/L | 1.68 | 0.09 | 0.221 | 0.09 | 0.01 |
| Cd | μg/L | 24.3 | 0.05 | 1.912 | 0.05 | 0.003 |
| As | μg/L | 5.9 | 0.09 | 0.984 | 0.71 | 0.01 |
| Se | μg/L | 112 | 0.05 | 18.354 | 5.94 | 0.04 |
| pH | 8.72 | 6.94 | 7.68 | 7.63 | 6.5–8.5 |
| Parameter | Weight (wi) | Wi |
|---|---|---|
| K+ | 2 | 0.0444 |
| Na+ | 2 | 0.0444 |
| Ca2+ | 3 | 0.0667 |
| Mg2+ | 3 | 0.0667 |
| Cl− | 5 | 0.1111 |
| SO42− | 5 | 0.1111 |
| HCO3− | 1 | 0.0222 |
| F− | 5 | 0.1111 |
| NO3-N | 5 | 0.1111 |
| TDS | 4 | 0.0889 |
| Mn | 5 | 0.1111 |
| Pb | 5 | 0.1111 |
| Total | 45 | 1 |
| Indicator | Regressive Coefficient | Standard Error |
|---|---|---|
| Mn | 0.00238 | 0.00007 |
| Fe | 0.00002 | 0.00286 |
| Pb | 0.00006 | 0.00114 |
| Cu | 0.00002 | 0.00319 |
| Zn | 0.00006 | 0.00108 |
| F− | 0.00633 | 0.00001 |
| NO3-N | 0.00461 | 0.00001 |
| Cl− | 0.99800 | 0.00000 |
| NO2-N | 0.00036 | 0.00043 |
| Se | 0.00107 | 0.00007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, M. Spatial Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Saline Water Intrusion and Potentially Hazardous Pollutants in a Coastal Groundwater Environment. Water 2024, 16, 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182573
Sun Z, Yang X, Liu S, Wang J, Li M. Spatial Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Saline Water Intrusion and Potentially Hazardous Pollutants in a Coastal Groundwater Environment. Water. 2024; 16(18):2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182573
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zengbing, Xiao Yang, Sen Liu, Jiangbo Wang, and Mingbo Li. 2024. "Spatial Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Saline Water Intrusion and Potentially Hazardous Pollutants in a Coastal Groundwater Environment" Water 16, no. 18: 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182573
APA StyleSun, Z., Yang, X., Liu, S., Wang, J., & Li, M. (2024). Spatial Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Saline Water Intrusion and Potentially Hazardous Pollutants in a Coastal Groundwater Environment. Water, 16(18), 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182573






