The Economic Impact of Water Vulnerability on Corporate Sustainability: A Perspective of Corporate Capital Cost
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Socio-Economic Impact of Water Vulnerability
2.2. Environmental Factors Affecting Corporate Capital Costs
2.3. Government Water Governance
2.4. Review
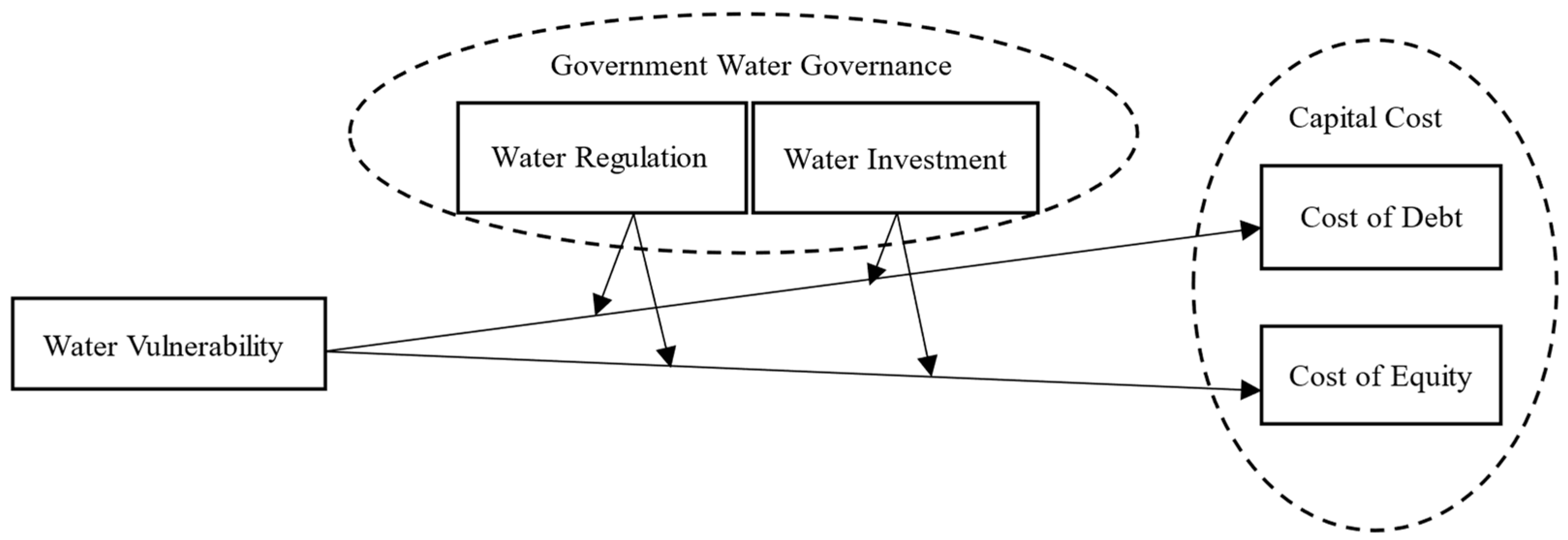
3. Hypothesis
3.1. The Impact of Water Vulnerability on Corporate Capital Cost
3.2. The Moderating Effect of Government Water Governance
4. Study Design and Data Description
4.1. Sampling
4.2. Construction of Variables
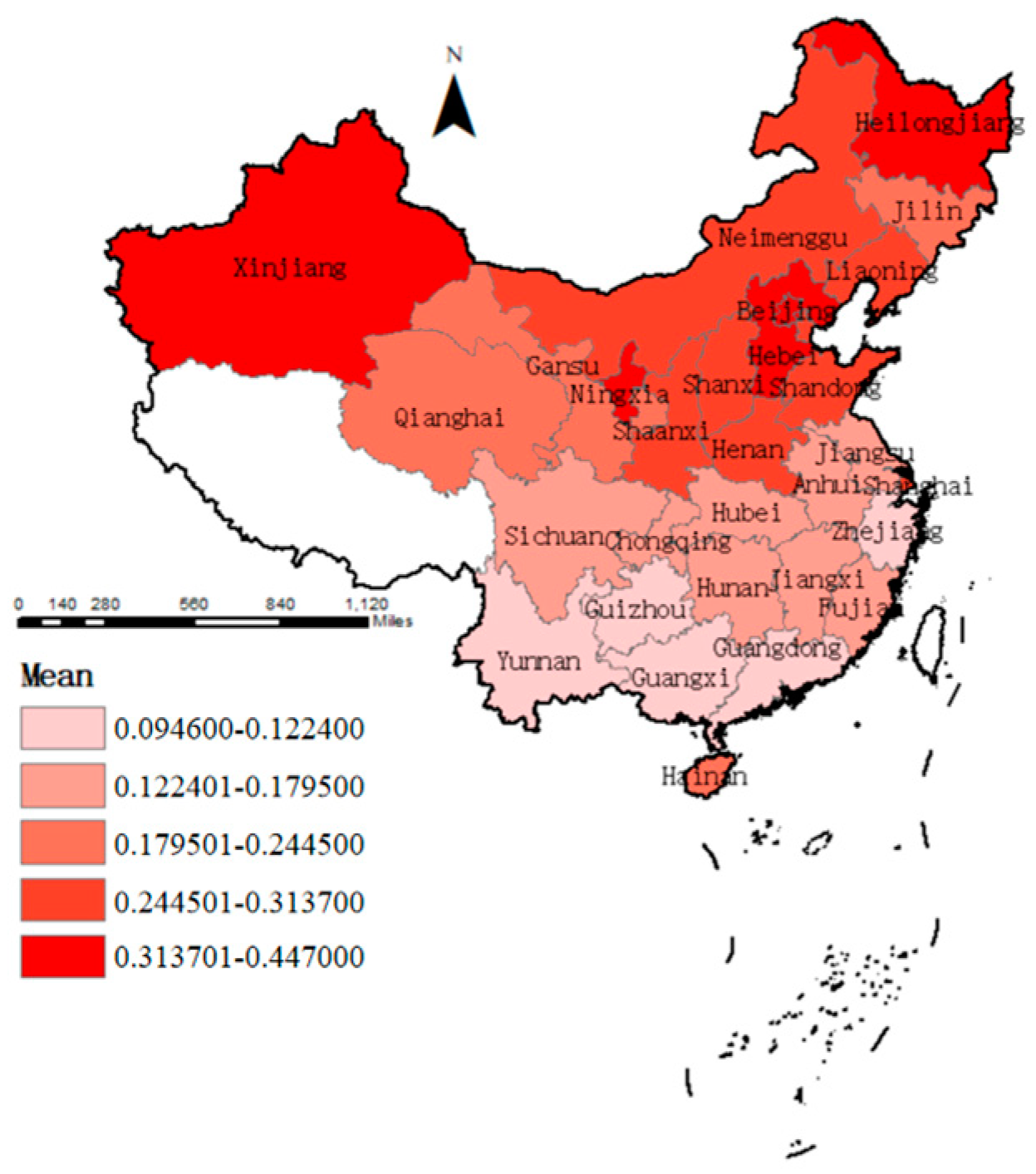
4.2.1. Water Vulnerability
4.2.2. Capital Cost
4.2.3. Water Governance
4.2.4. Control Variables
4.3. Model and Estimate Method
5. Empirical Analysis
5.1. Descriptive Analysis
5.2. Results of Main Regression
5.3. Robustness
5.4. Endogeneity Tests
5.5. Channel Analysis
5.6. Moderating Effect
5.7. Heterogeneity
5.7.1. Industrial Heterogeneity
5.7.2. Firm Heterogeneity
6. Discussion and Conclusions
7. Limitation and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Meteorological Organization. State of Global Water Resources 2021; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- World Economic Forum. The Global Risks Report 2016; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P.; Hillier, D.; Comfort, D. Corporate water stewardship. J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 2015, 5, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, E. From Risks to Shared Value? Corporate Strategies in Building a Global Water. Accounting and Disclosure Regime. Water Altern. 2013, 5, 636–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.Z.; Wang, T.; Miao, Y.J. Corporate water risk: A new research hotspot under climate change. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 2623–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, R.; Peng, N.; Bowen, F. The Wealth Effect of Corporate Water Actions: How Past Corporate Responsibility and Irresponsibility Influence Stock Market Reactions. J. Bus. Ethics 2022, 180, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Zhou, Z.T.; Su, K.; Liu, K.; An, H. Water risk and financial analysts’ information environment: Empirical evidence from China. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2024, 33, 1265–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, C.; Rodrigues, R.G.; Ferreira, J.J. Linking natural resources and performance of. small agricultural businesses: Do entrepreneurial orientation and environmental sustainability orientation matter? Sustain. Dev. 2022, 30, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Schillebeeckx, S.J.D.; Lit Liak, T. The management of natural resources: An overview and research agenda. Acad. Manag. J. 2015, 58, 1595–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashman, P. A Natural Resource Dependence Perspective of the Firm: How and Why Firms. Manage Natural Resource Scarcity. Bus. Soc. 2021, 60, 1279–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashman, P.; Rivera, J. Ecological uncertainty, adaptation, and mitigation in the U.S. ski. resort industry: Managing resource dependence and institutional pressures: Ecological Uncertainty, Adaptation, and Mitigation. Strateg. Manag. J. 2016, 37, 1507–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Weng, J.; Chen, J.; Qiu, B. Multi-scale Water Vulnerability Assessment Research. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2014, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Ye, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H. Does Water Matter? the Impact of Water Vulnerability on Corporate Financial Performance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Z.; Chen, X.; He, Y. Spatiotemporal analysis of water resources system vulnerability in the Lancang River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burritt, R.L.; Christ, K.L.; Omori, A. Drivers of corporate water-related disclosure: Evidence from Japan. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 129, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortas, E.; Burritt, R.L.; Christ, K.L. The influence of macro factors on corporate water. management: A multi-country quantile regression approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojamo, S.; Rudebeck, T. Corporate Engagement in Water Policy and Governance: A Literature Review on Water Stewardship and Water Security. Water Altern. Interdiscip. J. Water Politics Dev. 2024, 17, 292–324. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Yuan, B.B. Environmental policy mechanism of local governments in the treatment of haze pollution: Policy tools, spatial correlations and threshold effects. Resour. Sci. 2021, 43, 40–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, L.; Liu, X.H. The Study of Emission Reduction Effects of Different. Environmental Regulations on the Different Environmental Pollution Types. Ningxia Soc. Sci. 2021, 5, 140–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Hou, G.S. Smog Pollution, Local Government Behavior and Enterprise. Innovation Intention—Based on the Empirical Data of Listed Manufacturing Companies. Soft Sci. 2020, 34, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.; Jiang, Y.B. The Influence of Environmental Regulation on the. Behavior of Enterprise Environmental Governance: Based on a Quasi-Natural Experiment of New Environmental Protection Law. Bus. Manag. J. 2019, 41, 54–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Zheng, Y. Progress and future prospects of water resources vulnerability at home and abroad. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2022, 36, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, K.; Dobson, B.; Decker, C.; Hall, J.W. An Integrated Framework for Risk-Based Analysis of Economic Impacts of Drought and Water Scarcity in England and Wales. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR027715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kaluarachchi, J.J. A risk-based hydro-economic analysis for land and water management in water deficit and salinity affected farming regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 166, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chun, W.; Cui, Y. Urban water resources allocation and low-carbon economic development based on soft computing. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, B. Water-energy scarcity nexus risk in the national trade system based on multiregional input-output and network environ analyses. Appl. Energy 2020, 268, 114974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qu, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhao, H.; Chiu, A.C.F.; Liang, S.; Zou, J.; Xu, M. Virtual water scarcity risk in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 160, 104886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugochukwu, U.C.; Chukwuone, N.; Jidere, C.; Ezeudu, B.; Ikpo, C.; Ozor, J. Heavy metal contamination of soil, sediment and water due to galena mining in Ebonyi State Nigeria: Economic costs of pollution based on exposure health risks. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 32, 1115864. [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, A.; Evans, S.; Manidis, T.; Campbell, C.; Naidenko, O.V. Exposure-based assessment and economic valuation of adverse birth outcomes and cancer risk due to nitrate in United States drinking water. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleick, P.H. Water, Drought, Climate Change, and Conflict in Syria. Weather Clim. Soc. 2014, 6, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, J.; Hertig, E.; Tramblay, Y.; Scheffran, J. Climate change vulnerability, water resources and social implications in North Africa. Reginal Environ. Chang. 2020, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnafous, L.; Lall, U.; Siegel, J. A water risk index for portfolio exposure to climatic. extremes: Conceptualization and an application to the mining industry. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2075–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthulingam, S.; Dhanorkar, S.; Corbett, C.J. Does Water Scarcity Affect Environmental Performance? Evidence from Manufacturing Facilities in Texas. Manag. Sci. 2022, 68, 2785–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northey, S.A.; Mudd, G.M.; Werner, T.T.; Haque, N.; Yellishetty, M. Sustainable water. management and improved corporate reporting in mining. Water Resour. Ind. 2019, 21, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, R.; Liberti, J.; Liu, B.Y.; Meier, I. A Firm’s Cost of Capital. Annu. Rev. Financ. Econ. 2017, 9, 259–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhan, Z. Can Fintech Alleviate the Financing Constraints of Enterprises?—Evidence from the Chinese Securities Market. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlemlih, M. Corporate social responsibility and firm financing decisions: A literature review. J. Multinatl. Financ. Manag. 2017, 42–43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, S.; Saadi, S.; Boubaker, S.; Chourou, L. External Governance and the Cost of Equity Financing. J. Financ. Res. 2019, 42, 817–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.S.; Liu, C.; Ni, X.; Pang, J.R. Stock market liberalization and corporate investment revisited: Evidence from China. J. Bank. Financ. 2024, 158, 107053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daouk, H.; Lee, C.M.C.; Ng, D. Capital market governance: How do security laws affect market performance? J. Corp. Financ. 2006, 12, 560–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amairi, H.; Gallali, M.I.; Sassi, S. Market pressure and cost of equity: Revisited. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 47 Pt B, 102749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, D.; Loncan, T. Stock market integration, cost of equity capital, and corporate investment: Evidence from Brazil. Eur. Financ. Manag. 2019, 25, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Gutierrez, P.L.; López-Iturriaga, F.J.; Rodriguez-Sanz, J.A. Labour market conditions and the corporate financing decision: A European analysis. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2021, 58, 101431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.B.; Lin, C. Economic policy uncertainty and directors and officers liability insurance: A perspective on capital market pressures. Geneva Pap. Risk Insur. Issues Pract. 2024, 49, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.H. Monetary Policy, Interest Rate Transmission and the Financing Cost of Small and Medium Enterprises: An Empirical Analysis Based on Actual Financing Costs. Econ. Rev. 2017, 5, 28–39+90. [Google Scholar]
- Lendvai, J.; Raciborski, R.; Vogel, L. Macroeconomic effects of an equity transaction tax in a general-equilibrium model. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2013, 37, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, C.; Nguyen, T.H.; Huynh, T. Customer satisfaction and the cost of capital. Rev. Account. Stud. 2021, 26, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, G.; Volz, U.; Murinde, V.; Ayas, S. The impact of climate vulnerability on firms’ cost of capital and access to finance. World Dev. 2021, 137, 105131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.H.; Kerstein, J.; Wang, C. The impact of climate risk on firm performance and. financing choices: An international comparison. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2018, 49, 633–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, Y.; Temiz, H. Climate change exposure, environmental performance, and the cost of capital in the energy sector: Fossil fuel versus renewable energy firms. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Xu, X.Y.; Yang, Y. Does Corporate Climate Risk Affect the Cost of Equity—Evidence from Textual Analysis with Machine Learning. Chin. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2023, 15, 19–46+125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.H. Public Pressure, Property Rights Nature, and Corporate Financing Behavior: A Study Based on the “PM2.5 Burst” Event. Econ. Sci. 2016, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Chan, K.C.; Chen, Y. The impact of air pollution on the cost of debt financing: Evidence from the bond market. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 31, 464–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Bai, M.; Hou, G.; Truong, C. Drought risk and capital structure dynamics. Account. Financ. 2022, 62, 3397–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkila, T. Evidence for Tackling the Complexities of Water Governance. Public Adm. Rev. 2017, 77, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, C.; Metcalf, L.; Irwin, J. An Exploratory Study in Community Perspectives of Sustainability Leadership in the Murray Darling Basin. J. Bus. Ethics 2014, 124, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.N.; Zeng, X.T.; Chen, C.; Kong, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Dong, H. Scenario Analysis of Initial Water-Rights Allocation to Improve Regional Water Productivities. Water 2019, 11, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Zhou, N.X.; Zhou, Z.F.; Zeng, H.X. Effect and mechanism of ‘the Ten-point Water Plan’ on the intensity of industrial water pollution. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.C.; Chen, G.F.; Ni, H.Z.; Wang, Y.; Rao, P. Impact of Water Saving Policy on Water Resource and Economy for Hebei, China Based on an Improved Computable General Equilibrium Model. Water 2022, 14, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckmann, J.; Flaig, D.; Grethe, H.; Siddig, K. Modelling Sectorally Differentiated Water Prices—Water Preservation and Welfare Gains Through Price Reform? Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2327–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zeng, M.; Jin, Y.; Zeng, H. Does China’s river chief policy improve corporate water disclosure? A quasi-natural experimental. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Uyttenhove, P.; Vaneetvelde, V. Planning green infrastructure to mitigate urban surface water flooding risk—A methodology to identify priority areas applied in the city of Ghent. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 194, 103703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniran, A.; Daniell, K.A.; Pittock, J. Water Infrastructure Development in Nigeria: Trend, Size, and Purpose. Water 2021, 13, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Yang, W.T.; Scanlon, B.R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D.; Burek, P.; Pan, Y.; You, L.; Wada, Y. South-to-North Water Diversion stabilizing Beijing’s groundwater levels. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, K.M. Tool-power: Water infrastructure as wellsprings of state power. Geoforum 2014, 57, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudoin, L.; Arenas, D. From Raindrops to a Common Stream: Using the Social-Ecological Systems Framework for Research on Sustainable Water Management. Organ. Environ. 2020, 33, 126–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Qin, C.H.; Zhu, Y.N.; Zhao, Y.; He, G.; Wang, L. Assessment of Multi-Regional Comprehensive Benefits of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project in China. Water 2024, 16, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Kato, T. Spatial-temporal analysis of urban water resource vulnerability in China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, D.O.; Abass, K. Water supply and mining: The policy paradox in Ghana. Water Policy 2014, 16, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelton, J. Accounting as a human right: The case of water information. Account. Audit. Account. J. 2013, 26, 267–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, J.; Hinojosa, L. Virtual water trade and the contestation of hydrosocial territories. Water Int. 2016, 41, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of the Relationship between Economic Development and Water Resources–Ecological Management Capacity in China Based on Nighttime Lighting Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F. A Three-Dimensional Conceptual Framework of Corporate Water. Responsibility. Organ. Environ. 2015, 28, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, D.; Elizabeth Palmer, J. Water as a corporate resource. J. Global. Responsib. 2014, 5, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, K.L. Water management accounting and the wine supply chain: Empirical evidence from Australia. Br. Account. Rev. 2014, 46, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Li, W.; Wen, J. Spatiotemporal changes of manufacturing firms in the flood prone Yangtze Delta. Environ. Hazards 2022, 21, 334–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Ma, L.L.; Yang, L.J.; Jiang, X.Y. Business interruption risk analysis based on fuzzy BN: A case study of flood disaster. China Saf. Sci. J. 2019, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Harrison, J.; Chen, L. A framework for the practice of corporate environmental responsibility in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 426–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H. The Impact of Public Participation on Local Government’s Environmental Governance—An Analysis of Provincial Data 2003–2013. Chin. Public Adm. 2017, 33, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Greenstone, M.; List, J.A.; Syverson, C. The Effects of Environmental Regulation on the Competitiveness of U.S. Manufacturing; MIT Department of Economics Working Paper No. 12–24; NBER: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Available online: http://www.ssrn.com/abstract=2145006 (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Long, X.N.; Wan, W. Environmental Regulation, Corporate Profit Margins and Compliance Cost Heterogeneity of Different Scale Enterprises. China Ind. Econ. 2017, 6, 155–174. [Google Scholar]
- Egan, M. Driving Water Management Change Where Economic Incentive is Limited. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 132, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambooy, T. Corporate social responsibility: Sustainable water use. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 852–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, L.L. The impact of risk-taking level on green technology. innovation: Evidence from energy-intensive listed companies in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 124685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petts, G.; Gurnell, A. Hydrogeomorphic Effects of Reservoirs, Dams, and Diversions. Treatise Geomorphol. 2022, 9, 144–166. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Guo, H.; Huang, N.; Ye, J. Health risks of exposure to waste pollution: Evidence from Beijing. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 63, 101540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Deng, Y.; Wang, P.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, S. Does air pollution suppress firm’s total factor productivity? Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2023, 43, 2906–2927. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Chen, Y. Assessing the Vulnerability of Basin Water Resources Based on Entropy Weight Method: A Case Study of the Huaihe River basin. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. 2016, 33, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.B.; Li, X.G.; Liu, J.F.; Fu, Z. Vulnerability assessment of water resources in the northwest typical area based on comprehensive weighting method. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2018, 32, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Adams, M.B.; Buckle, M.J. Corporate risk and property insurance: Evidence. from the People’s Republic of China. J. Risk Insur. 2003, 70, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.S.; Ye, K.T.; Zhang, D. Measuring and Evaluating Cost of Equity Capital: Evidence from Chinese Stock Markets. Account. Res. 2012, 11, 12–22+94. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.G.; Zheng, J.; Bo, S.J. Environmental uncertainty, diversification and the cost of capital. Account. Res. 2015, 2, 36–43+93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, H.; Chen, X. The impact of water information disclosure on the cost of capital: An empirical study of China’s capital market. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2018, 25, 1332–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, H. Water Information Disclosure, Political Connections and Cost of Capital: Evidence from High Water Sensitivity Industry of 2010 to 2015. J. Cent. South Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2018, 24, 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, D.K. Air Pollution, Government Regulations and High-quality Economic Development. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 20–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Kahn, M.E.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. The consequences of spatially differentiated. water pollution regulation in China. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 88, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Qiao, M.; Zhao, X. Evaluation of human-environment. system vulnerability for sustainable development in the Liupan mountainous region of Ningxia, China. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Zhao, Q.L.; Li, S.; Chang, C.-C. Ecological Security Evaluation of Heilongjiang. Province with Pressure-State-Response Model. Environ. Sci. 2008, 4, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.F.; Hu, C.Z.; Qi, X.W.; Zheng, H.; Shan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, J. Strategies for Water Resources Regulation. and Water Environment Protection in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Strateg. Study CAE 2019, 21, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, J.M. Econometric Analysis of Cross Section and Panel Data; MIT Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, S.N.; Zingales, L. Do investment-cash flow sensitivities provide useful measures of financing constraints? Q. J. Econ. 1997, 112, 169–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Ye, B. Analyses of Mediating Effects: The Development of Methods and Models. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 22, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulcke, P.; Vionnet, S.; Vousvouras, C.; Weder, G. Nestlé’s corporate water strategy over time: A backward- and forward-looking view. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2020, 36, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, P.; Adapa, L.M.; Buisman, C. How can innovation theories be applied to. water technology innovation? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 122910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.Y.; Morris, D. Thresholds in natural resource rents and state-owned enterprise. profitability: Cross country evidence. Energy Econ. 2022, 106, 105779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, S.; Han, Y.; Peng, K. The nature of state-owned enterprises and collection. of pollutant discharge fees: A study based on Chinese industrial enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarini, B.; Hinojales, M. State-Owned Enterprises and Debt Sustainability Analysis: The Case of the People’s Republic of China. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2019, 6, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, J.Z.; Lobo, G.J.; Wang, Y. Effects of Audit Quality on Earnings. Management and Cost of Equity Capital: Evidence from China. Contemp. Account. Res. 2011, 28, 892–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yang, X. Probability of Default, Financing Costs, and Third-Party Credit Enhancement Effect: An Analysis of Private Corporate Bonds. Financ. Econ. Res. 2021, 36, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Pan, X.F.; Qu, Y.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, W.X. Air pollution, human capital and corporate social responsibility performance: Evidence from China. Appl. Econ. 2022, 54, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, F.E.; Bansal, P.; Slawinski, N. Scale matters: The scale of environmental issues in corporate collective actions. Strateg. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 1411–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dimensions | Items | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Absolute value of annual precipitation variation | China Water Resources Statistical Yearbook |
| Absolute value of annual total water resources variation | China Water Resources Statistical Yearbook | |
| Exposure | GDP per capita | China Statistical Yearbook |
| Share of GDP in primary production | China Statistical Yearbook | |
| Water resources per capita | China Statistical Yearbook | |
| Total water resources/total area of the region | China Water Resources Statistical Yearbook, China Urban and Rural Construction Statistical Yearbook | |
| Total water resources/total annual rainfall | China Water Resources Statistical Yearbook | |
| Proportion of high-quality surface water | China Water Resources Statistical Yearbook, China Environmental Statistical Yearbook | |
| Ratio of water resources supply to demand | China Urban and Rural Construction Statistical Yearbook | |
| Proportion of groundwater supply | China Water Resources Statistical Yearbook | |
| Water consumption of CNY 10,000 of GDP | China Water Resources Bulletin | |
| Water consumption of CNY 10,000 of industrial value added | China Water Resources Bulletin | |
| Water consumption by urban residents for domestic use | China Water Resources Bulletin | |
| Water consumption for agricultural irrigation | China Water Resources Bulletin | |
| Hazard | Regional population affected/National population affected in the year | Bulletin of flood and drought disasters in China |
| Regional direct economic losses/National losses in the year | Bulletin of flood and drought disasters in China | |
| Area of crops affected in the region/National damage in the year | Bulletin of flood and drought disasters in China | |
| Population with drinking water difficulties in the region/National population affected in the year | Bulletin of flood and drought disasters in China | |
| Adaptivity | Wastewater treatment rate | China Urban and Rural Construction Statistical Yearbook |
| Water reuse rate | China Urban and Rural Construction Statistical Yearbook | |
| Ratio of protected arable land | China Water Resources Statistical Yearbook | |
| Protection of population ratio | China Water Resources Statistical Yearbook | |
| Effective utilization rate of irrigation water | China Water Resources Bulletin |
| Region | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North China | 0.343 | 0.338 | 0.293 | 0.331 | 0.278 | 0.317 |
| Northeast China | 0.319 | 0.320 | 0.312 | 0.275 | 0.273 | 0.300 |
| Northwest China | 0.332 | 0.312 | 0.310 | 0.295 | 0.274 | 0.305 |
| Eastern China | 0.232 | 0.195 | 0.189 | 0.186 | 0.179 | 0.196 |
| South-Central-China | 0.192 | 0.183 | 0.177 | 0.162 | 0.159 | 0.175 |
| Southwest China | 0.143 | 0.140 | 0.131 | 0.130 | 0.119 | 0.133 |
| Variables | Mean | S.D. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r_debt | 0.009 | 0.025 | −0.097 | 0.063 |
| r_equity | 0.038 | 0.035 | 0.001 | 0.207 |
| Water_Vul | 0.193 | 0.091 | 0.065 | 0.392 |
| Water_Ins | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.005 |
| Water_Inv | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.026 |
| ROA | 0.056 | 0.045 | 0.002 | 0.228 |
| BM | 0.629 | 0.247 | 0.122 | 1.189 |
| SIZE | 22.343 | 1.246 | 20.114 | 26.140 |
| LEV | 0.401 | 0.183 | 0.064 | 0.837 |
| TOVER | 5.666 | 0.738 | 3.674 | 7.196 |
| SHR | 0.155 | 0.107 | 0.017 | 0.521 |
| LGDP | 10.718 | 0.679 | 8.499 | 11.615 |
| GGROWTH | 5.986 | 2.017 | 0.500 | 9.300 |
| Water_Vul | r_equity | r_debt | Water_Ins | Water_Inv | ROA | BM | SIZE | LEV | TOVER | SHR | LGDP | GGROWTH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water_Vul | 0.045 | 0.043 *** | −0.164 ** | −0.1034 *** | −0.124 *** | 0.055 *** | 0.099 *** | 0.049 *** | −0.032 *** | 0.027 *** | −0.472 *** | −0.079 *** | |
| r_equity | 0.013 | 0.020 ** | −0.022 ** | 0.0083 | 0.561 *** | 0.437 *** | 0.425 *** | 0.113 *** | −0.308 *** | 0.157 *** | 0.028 *** | −0.069 *** | |
| r_debt | 0.038 *** | 0.049 *** | −0.004 | 0.0048 | −0.054 *** | 0.062 *** | 0.082 *** | 0.050 *** | −0.032 *** | −0.014 | −0.039 *** | 0.001 | |
| Water_Ins | −0.205 *** | −0.024 ** | −0.003 | 0.1284 *** | 0.024 ** | −0.047 *** | −0.055 *** | −0.021 ** | 0.075 *** | −0.021 ** | 0.228 *** | 0.060 *** | |
| Water_Inv | 0.055 *** | 0.001 | 0.018 * | 0.171 *** | 0.000 | −0.004 | 0.036 *** | 0.012 | 0.039 *** | 0.013 | −0.468 *** | 0.129 *** | |
| ROA | −0.108 *** | 0.368 *** | −0.044 *** | 0.016 | −0.028 *** | −0.338 *** | −0.091 *** | −0.382 *** | −0.105 *** | 0.130 *** | 0.123 *** | 0.015 | |
| BM | 0.078 *** | 0.434 *** | 0.072 *** | −0.052 *** | 0.017 *** | −0.372 *** | 0.518 *** | 0.396 *** | −0.273 *** | 0.087 *** | −0.067 *** | −0.079 *** | |
| SIZE | 0.133 *** | 0.455 *** | 0.083 *** | −0.052 *** | 0.040 *** | −0.077 *** | 0.532 *** | 0.525 *** | −0.352 *** | 0.124 *** | −0.132 *** | −0.037 *** | |
| LEV | 0.057 *** | 0.167 ** | 0.046 *** | −0.015 | 0.035 *** | −0.366 *** | 0.394 *** | 0.532 *** | −0.051 *** | 0.026 *** | −0.070 *** | −0.027 *** | |
| TOVER | −0.046 *** | −0.254 *** | −0.043 *** | 0.073 *** | 0.041 *** | −0.010 *** | −0.281 *** | −0.386 *** | −0.060 *** | −0.310 *** | 0.076 *** | −0.151 *** | |
| SHR | 0.048 *** | 0.164 *** | −0.005 | −0.028 *** | 0.010 | 0.105 *** | 0.115 *** | 0.207 *** | 0.052 *** | −0.357 *** | −0.032 *** | 0.004 | |
| LGDP | −0.450 *** | 0.005 *** | −0.033 *** | 0.130 *** | −0.544 *** | 0.108 *** | −0.073 *** | −0.128 *** | −0.077 *** | 0.053 *** | −0.040 *** | −0.109 *** | |
| GGROWTH | −0.042 *** | −0.037 *** | −0.008 | 0.089 *** | 0.081 *** | 0.009 | −0.032 *** | −0.052 *** | −0.024 ** | −0.180 *** | 0.005 | −0.017 * |
| Cost of Debt | Cost of Equity | |
|---|---|---|
| Water_Vul | 0.018 *** | 0.015 *** |
| (3.12) | (2.92) | |
| ROA | −0.017 ** | 0.459 *** |
| (−1.88) | (3.56) | |
| BM | 0.003 * | 0.065 *** |
| (1.74) | (3.07) | |
| SIZE | 0.001 *** | 0.005 *** |
| (4.41) | (2.83) | |
| LEV | −0.002 | 0.011 ** |
| (−0.35) | (2.49) | |
| TOVER | −0.001 * | 0.002 *** |
| (−1.98) | (3.42) | |
| SHR | −0.007 *** | −0.006 ** |
| (−2.97) | (−2.12) | |
| LGDP | 0.001 | 0.001 *** |
| (1.03) | (2.79) | |
| GGROWTH | 0.001 | 0.001 ** |
| (0.01) | (2.23) | |
| Constant | −0.013 | −0.185 *** |
| (−0.35) | (−3.04) | |
| Fixed Effects | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 12,363 | 12,363 |
| Sample Change | PSM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost of Debt | Cost of Equity | Cost of Debt | Cost of Equity | |
| Water_Vul | 0.021 *** (2.56) | 0.011 ** (2.49) | 0.032 ** (2.48) | 0.021 * (1.78) |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Fixed Effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | 2.413 * (1.75) | 1.460 ** (2.41) | 0.090 *** (2.81) | 0.011 (1.34) |
| Obs | 8736 | 8736 | 11,476 | 11,476 |
| Water_Vul | r_equity | r_debt | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water_Vul | 0.010 ** (2.68) | 0.013 ** (1.88) | |
| VUL_hat | −0.006 (−0.37) | −0.012 (−0.17) | |
| SUN | 0.213 *** (4.59) | ||
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | −1.175 *** (−3.46) | −0.179 *** (−5.68) | −0.016 * (−1.73) |
| Obs | 12,361 | 12,361 | 12,361 |
| r_debt | r_equity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | |
| r_debt | KZ | r_debt | r_equity | KZ | r_equity | |
| Water_Vul | 0.018 *** (3.12) | 0.035 ** (2.17) | 0.018 *** (3.35) | 0.015 *** (2.92) | 0.001 ** (2.03) | 0.011 *** (3.06) |
| KZ | 0.030 ** (2.84) | 0.332 *** (2.98) | ||||
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Fixed Effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | −0.013 (−0.35) | −0.043 (−0.68) | −0.012 (−0.93) | −0.185 *** (−3.04) | −0.614 (−0.54) | −0.172 ** (−2.16) |
| Obs | 12,361 | 12,361 | 12,361 | 12,361 | 12,361 | 12,361 |
| r_debt | r_equity | |
|---|---|---|
| Water_Vul | 0.019 *** | 0.065 *** |
| (2.61) | (3.88) | |
| Water_Ins | 0.097 | 0.179 |
| (1.03) | (1.24) | |
| Water_Vul × Water_Ins | 3.268 * | −1.854 |
| (1.68) | (−0.98) | |
| Water_Vul | 0.018 *** | 0.015 *** |
| (2.75) | (2.94) | |
| Water_Inv | 0.232 * | 0.087 |
| (1.71) | (1.08) | |
| Water_Vul × Water_Inv | −1.397 * | −0.166 |
| (−1.67) | (−0.83) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes |
| Fix Effects | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 12,363 | 12,363 |
| r_debt | r_equity | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Heterogeneity | Firm Heterogeneity | Industrial Heterogeneity | Firm Heterogeneity | |||||
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | |
| Water_Vul | 0.004 (0.36) | 0.022 *** (2.67) | 0.020 ** (2.45) | 0.016 ** (2.02) | 0.010 (1.10) | 0.013 ** (1.88) | 0.002 (0.19) | 0.024 *** (2.86) |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Fix Effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 3246 | 9015 | 4001 | 8360 | 3246 | 9015 | 4001 | 8360 |
| Chow Test | 3.01 ** | 2.75 * | 3.72 ** | 4.72 *** | ||||
| Panel A—Water Regulation | ||||||||
| r_debt | r_equity | |||||||
| Industrial Heterogeneity | Firm Heterogeneity | Industrial Heterogeneity | Firm Heterogeneity | |||||
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | |
| Water_Vul | 0.004 (0.34) | 0.023 *** (3.57) | 0.024 ** (1.98) | 0.017 ** (2.21) | 0.014 (0.17) | 0.013 ** (2.11) | 0.002 (1.09) | 0.026 *** (2.67) |
| Water_Ins | 0.174 (0.39) | 0.076 (0.73) | 0.341 (0.12) | 0.036 (0.24) | 0.321 (0.81) | 0.055 (0.52) | −0.041 (0.18) | 0.220 (1.25) |
| Water_Vul × Water_Ins | 1.752 (1.08) | 4.018 * (1.82) | 3.675 (1.59) | 3.481 * (1.92) | −2.404 (−1.69) | −2.410 (−1.42) | −4.966 (−1.59) | 3.147 (1.44) |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Fix Effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 3246 | 9015 | 4001 | 8360 | 3246 | 9015 | 4001 | 8360 |
| Chow Test | 4.44 ** | 4.15 ** | 3.96 ** | 4.88 *** | ||||
| Panel B—Water Investment | ||||||||
| r_debt | r_equity | |||||||
| Industrial Heterogeneity | Firm Heterogeneity | Industrial Heterogeneity | Firm Heterogeneity | |||||
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | |
| Water_Vul | 0.004 (0.34) | 0.022 *** (3.56) | 0.0210** (1.88) | 0.016 ** (2.08) | 0.112 (0.16) | 0.012 ** (2.09) | 0.001 (1.03) | 0.024 *** (2.64) |
| Water_Inv | 0.090 (0.22) | 0.276 * (1.85) | 0.111 (0.37) | 0.302 * (1.94) | 0.346 (0.84) | −0.069 (−1.06) | −0.1131 (−0.17) | 0.220* (1.77) |
| Water_Vul × Water_Inv | −0.184 * (−1.69) | 1.733 * (1.79) | −0.404 (−1.15) | −2.652 ** (−2.24) | −2.868 ** (−2.53) | 1.780 ** (1.98) | 0.256 (0.86) | 0.160 (0.44) |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Fix Effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Obs | 3246 | 9015 | 4001 | 8360 | 3246 | 9015 | 4001 | 8360 |
| Chow Test | 4.72 ** | 3.98 ** | 4.01 ** | 4.90 *** | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.; Gao, P.; Wang, M. The Economic Impact of Water Vulnerability on Corporate Sustainability: A Perspective of Corporate Capital Cost. Water 2024, 16, 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182560
Zheng L, Gao P, Wang M. The Economic Impact of Water Vulnerability on Corporate Sustainability: A Perspective of Corporate Capital Cost. Water. 2024; 16(18):2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182560
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Liyuan, Pengqun Gao, and Mengjiao Wang. 2024. "The Economic Impact of Water Vulnerability on Corporate Sustainability: A Perspective of Corporate Capital Cost" Water 16, no. 18: 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182560
APA StyleZheng, L., Gao, P., & Wang, M. (2024). The Economic Impact of Water Vulnerability on Corporate Sustainability: A Perspective of Corporate Capital Cost. Water, 16(18), 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182560






