Green Analytical Method for Perfluorocarboxylic Acids (PFCAs) in Water of Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Coupled with Thermal Desorption–Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standards and Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation, Derivatization, and Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction (SBSE)
2.4. Analysis Using Thermal Desorption–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (TD-GC-MS)
2.5. Optimization of Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Parameters
2.6. Quality Control and Quality Assurance
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Method Detection Limit (MDL)
2.9. Analysis of PFCAs in Real Water Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction
- (1)
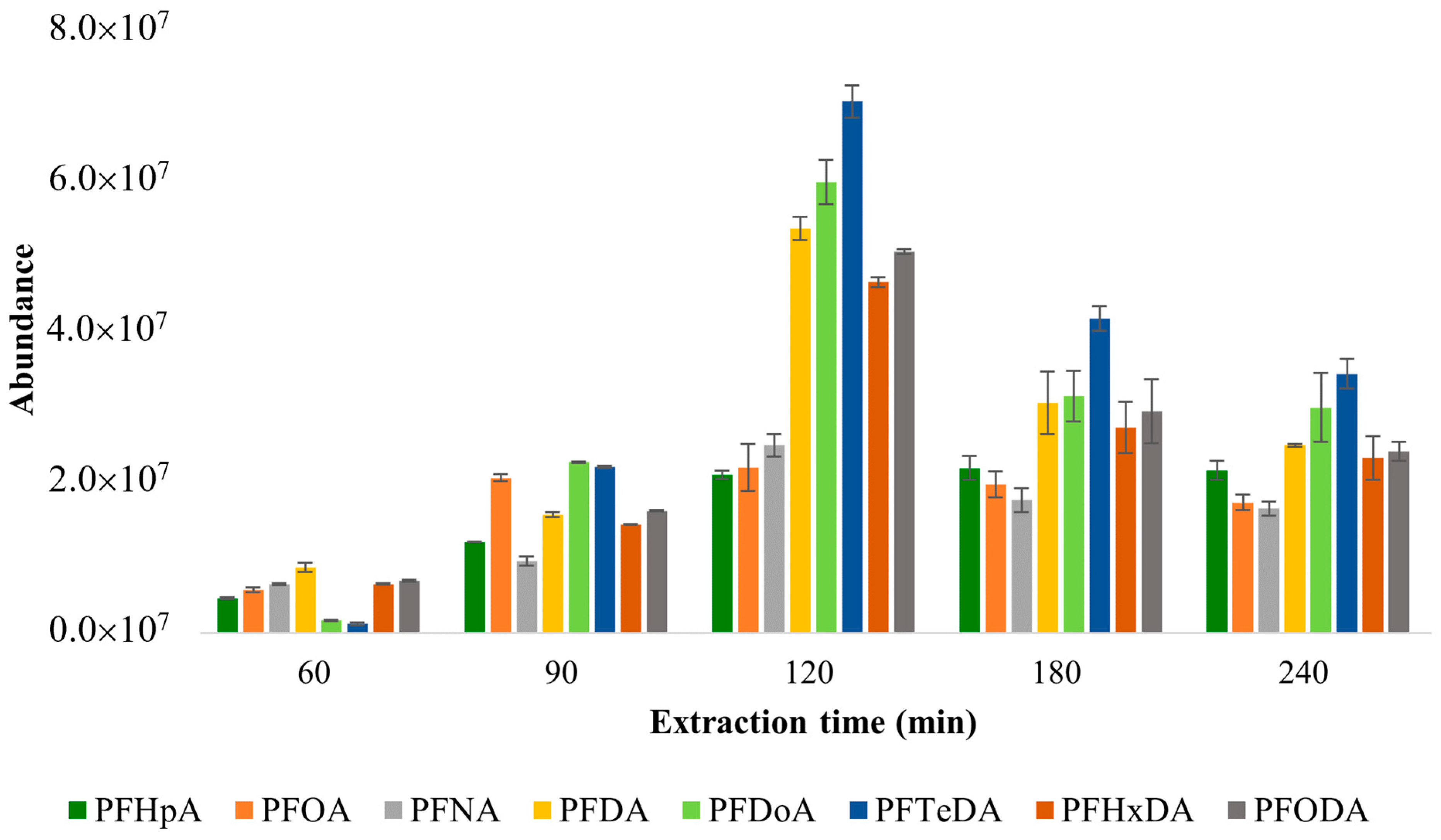
- Five different extraction times (60 min, 90 min, 120 min, 180 min, and 240 min) were tested for the extraction time optimization;
- (2)
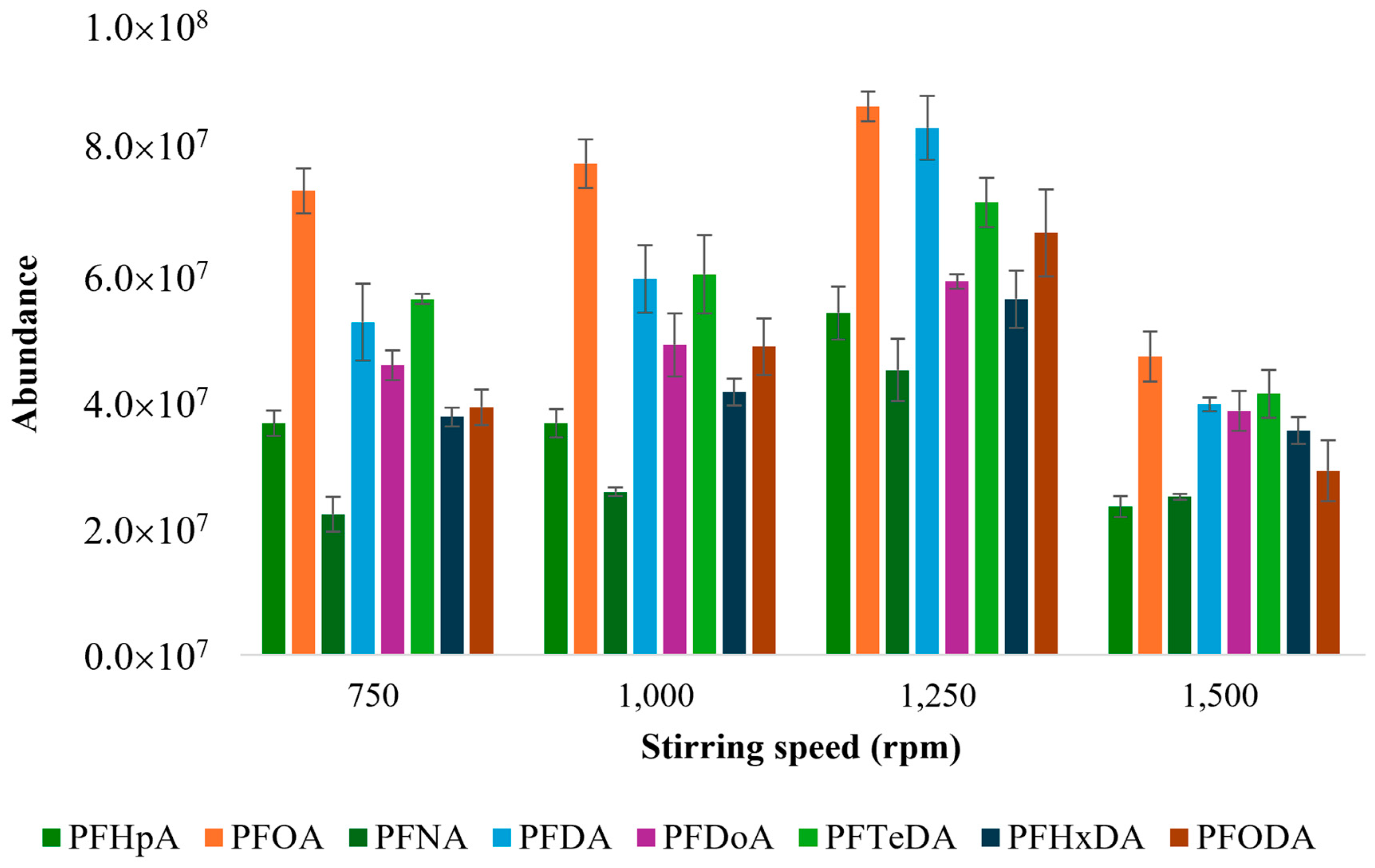
- Four stir bar stirring speeds were investigated (750 rpm, 1000 rpm, 1250 rpm, and 1500 rpm);
- (3)
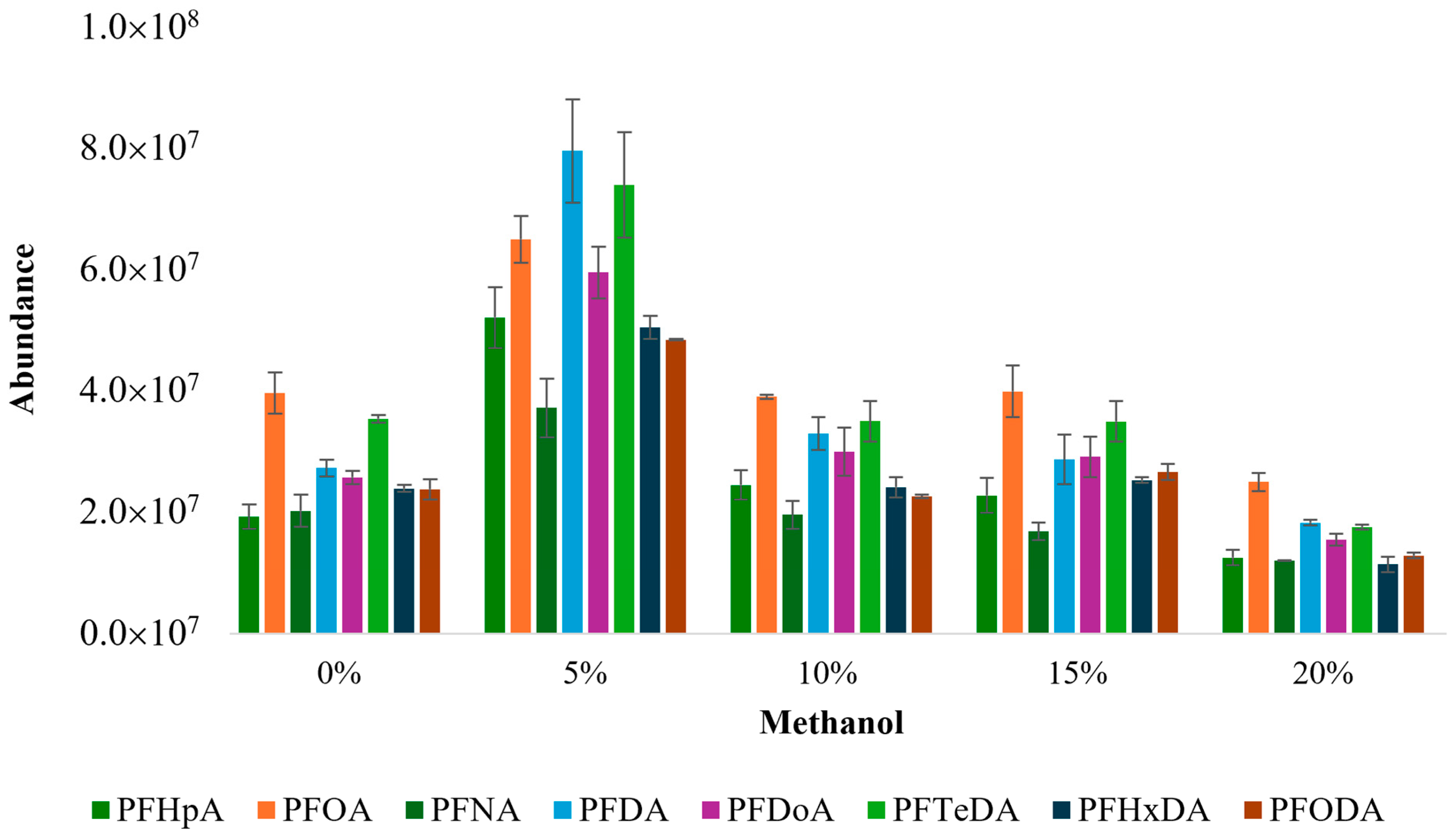
- Five methanol concentrations (0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20%) were tested for the solvent composition optimization during SBSE;
- (4)
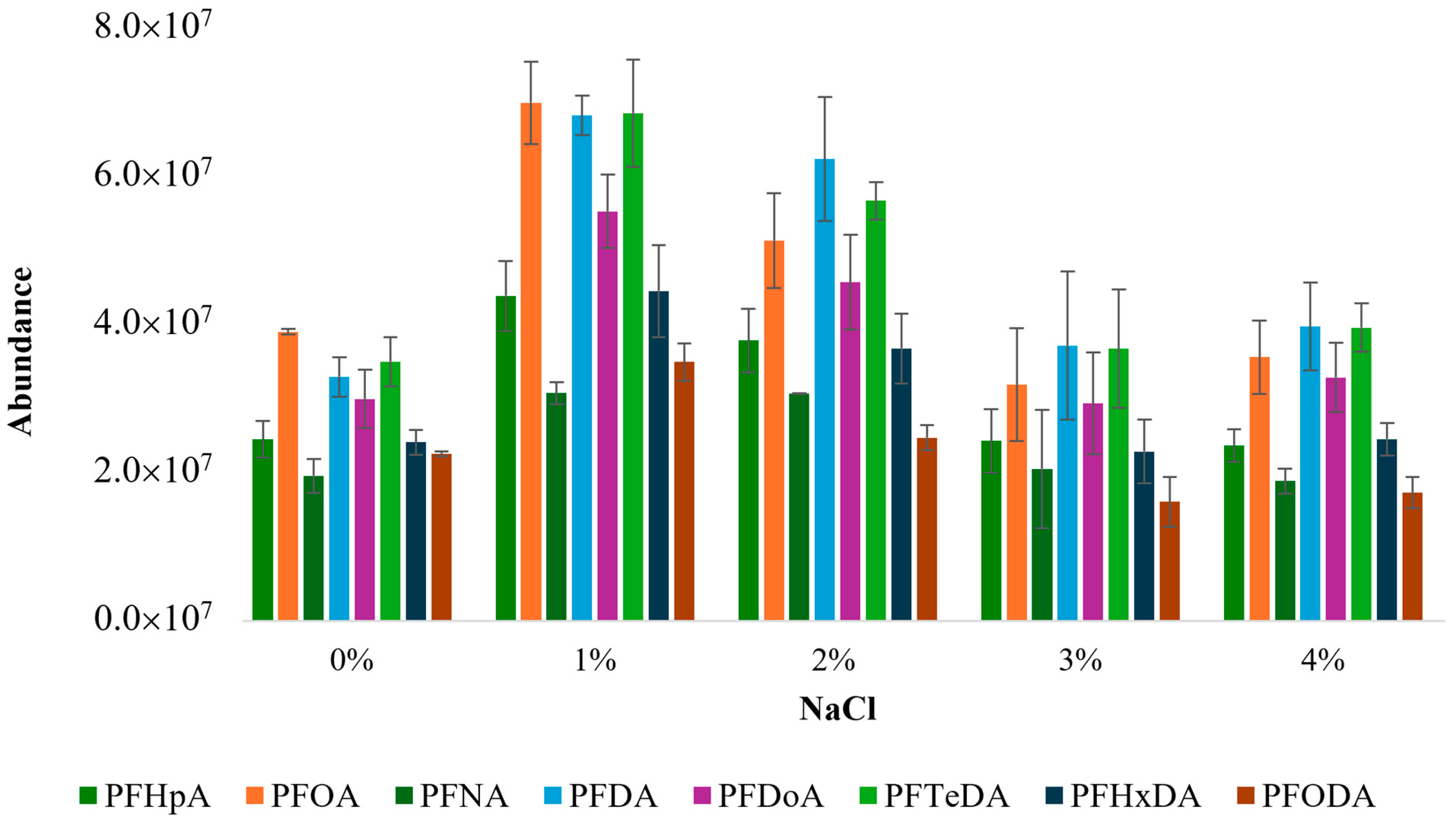
- Five salt (NaCl) weight (w/v) percentages (0%, 1%, 2%, 3%, and 4%) were tested upon obtaining the optimized conditions in (1) to (3);
- (5)
- Three different pH conditions (pH 4, no pH adjustment, and pH 10) were tested.
3.1.1. Optimization of Extraction Time
3.1.2. Optimization of Stirring Speed
3.1.3. Optimization of Solvent Composition
3.1.4. Optimization of Ionic Strength
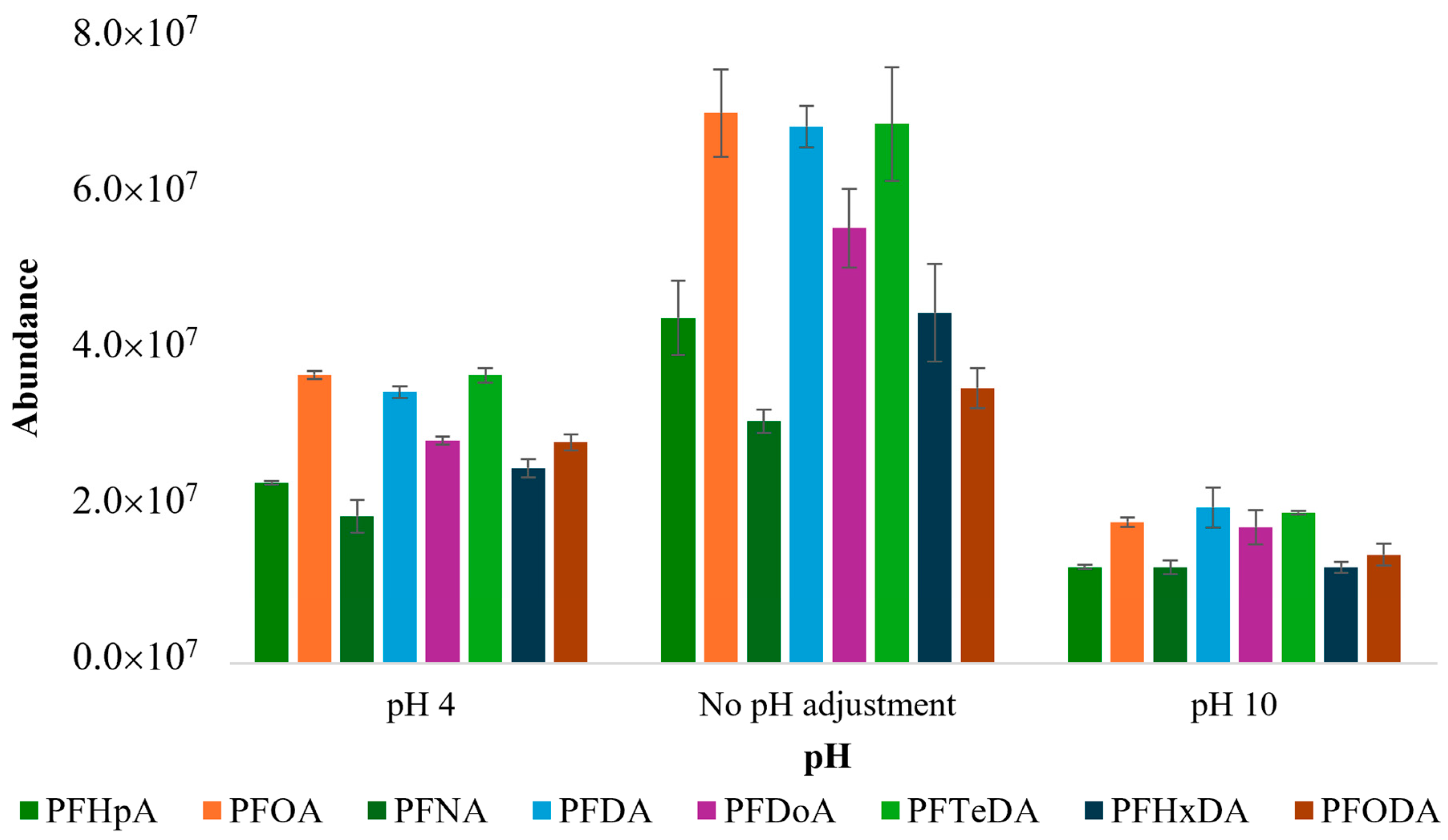
3.1.5. Optimization of pH
3.2. Evaluating SBSE-TD-GC-MS Performance: Linearity, Recovery, and Sensitivity Metrics
3.3. Method Repeatability
3.4. Spiked Recovery Experiment
3.5. Determination of PFCAs in Real Water Samples
3.6. Method Strengths and Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OECD. Toward a New Comprehensive Global Database of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): Summary Report on Updating the OECD 2007 List of per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs); Series on Risk Management, No. 39; OECD: Paris, France, 2018; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, Z.; Song, M.; Ikram, S.; Zahra, Z. Overview of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Their Applications, Sources, and Potential Impacts on Human Health. Pollutants 2024, 4, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.L.; Ko, Y.C.; Hwang, B.H.; Li, Z.G.; Yang, T.C.C.; Lee, M.R. Determination of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids in Water by Ion-Pair Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction and Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Injection Port Derivatization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 726, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; De Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Environment: Terminology, Classification, and Origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz-Narbonne, H.; Xia, C.; Shalin, A.; Whitehead, H.D.; Yang, D.; Peaslee, G.F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Peng, H.; Blum, A.; et al. Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Canadian Fast Food Packaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dewitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-Ending Story of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthoff, M.; Müller, J.; Jürling, H.; Schlummer, M.; Fiedler, D. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Consumer Products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14546–14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abunada, Z.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Bashir, M.J.K. An Overview of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Environment: Source, Fate, Risk and Regulations. Water 2020, 12, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, H.; Mæhlum, T.; Haarstad, K.; Slinde, G.A.; Arp, H.P.H. Leachate Emissions of Short-And Long-Chain per-And Polyfluoralkyl Substances (PFASs) from Various Norwegian Landfills. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Sobhani, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dharmaraja, R. Environmental Technology & Innovation Recent Advances in the Analysis of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)—A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.H.; Gai, N.; Zhang, P.; Piao, H.T.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.C.; Jiao, X.C.; Yin, X.C.; Tan, K.Y.; Yang, Y.L. Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Surface Waters and Tapwater in the Qiantang River Watershed—Influences from Paper, Textile, and Leather Industries. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zango, Z.U.; Ethiraj, B.; Al-Mubaddel, F.S.; Alam, M.M.; Lawal, M.A.; Kadir, H.A.; Khoo, K.S.; Garba, Z.N.; Usman, F.; Zango, M.U.; et al. An Overview on Human Exposure, Toxicity, Solid-Phase Microextraction and Adsorptive Removal of Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids (PFCAs) from Water Matrices. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.X.; Di Lorenzo, R.A.; Clouthier, J.T.; Young, C.J.; VandenBoer, T.C. A Rapid Derivatization for Quantitation of Perfluorinated Carboxylic Acids from Aqueous Matrices by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 7648–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, N.; Müller, L.; Enge, S.; Ungethüm, T.; Simat, T.J. Thermal Desorption—Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry (TD-GC-MS) Analysis of PFAS Used in Food Contact Materials. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2024, 41, 1099–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giorgi, A.; Basile, G.; Bertola, F.; Tavoletta, F.; Busardò, F.P.; Tini, A. A Green Analytical Method for the Simultaneous Determination of 17 Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Human Serum and Semen by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 246, 116203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, J.; Ducatman, A.; Elliott, M.; Wen, S.; Wahlang, B.; Barnett, J.; Cave, M.C. Environmental Perfluoroalkyl Acid Exposures Are Associated with Liver Disease Characterized by Apoptosis and Altered Serum Adipocytokines. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Xu, X. Exposure to Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Mortality in US Adults: A population-based cohort study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 067007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Winquist, A. PFAS and Cancer, a Scoping Review of the Epidemiologic Evidence. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Qiao, B.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Sun, H. Target and Nontarget Analysis of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Surface Water, Groundwater and Sediments of Three Typical Fluorochemical Industrial Parks in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltenberg, E.M.; Dasu, K.; Lefkovitz, L.F.; Thorn, J.; Schumitz, D. Sampling of Freely Dissolved Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Surface Water and Groundwater Using a Newly Developed Passive Sampler. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A.L.B.; Zhang, Y.; Westerman, D.C.; Richardson, S.D. Improved Total Organic Fluorine Methods for More Comprehensive Measurement of PFAS in Industrial Wastewater, River Water, and Air. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Tokranov, A.K.; Bexfield, L.M.; Lindsey, B.D.; Johnson, T.D.; Lombard, M.A.; Watson, E. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Groundwater Used as a Source of Drinking Water in the Eastern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Kwon, J.B.; Choi, H.; Shin, S.K.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.K. Study on Pollution Characteristics of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Shallow Groundwater. Water 2023, 15, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Wang, X.; Yamashita, N. Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Surface Water, Gas and Particle in Open Ocean and Coastal Environment. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junttila, V.; Vähä, E.; Perkola, N.; Räike, A.; Siimes, K.; Mehtonen, J.; Kankaanpää, H.; Mannio, J. PFASs in Finnish Rivers and Fish and the Loading of PFASs to the Baltic Sea. Water 2019, 11, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Dong, B.; Wu, J. Review on Per-and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances’ (PFASs’) Pollution Characteristics and Possible Sources in Surface Water and Precipitation of China. Water 2022, 14, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Hu, L.X.; Liu, T.; Zhao, J.H.; Yang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Ying, G.G. Per-and Polyfluoralkyl Substances (PFAS) in Drinking Water System: Target and Non-Target Screening and Removal Assessment. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.J.; Okvitasari, A.R.; Huang, F.Y.; Tsai, C.S. Characteristics, Pollution Patterns and Risks of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Drinking Water Sources of Taiwan. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussabek, D.; Söderman, A.; Imura, T.; Persson, K.M.; Nakagawa, K.; Ahrens, L.; Berndtsson, R. PFAS in the Drinking Water Source: Analysis of the Contamination Levels, Origin and Emission Rates. Water 2023, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardian, M.G.E.; Boongaling, E.G.; Bernardo-Boongaling, V.R.R.; Gamonchuang, J.; Boontongto, T.; Burakham, R.; Arnnok, P.; Aga, D.S. Prevalence of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Drinking and Source Water from Two Asian Countries. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallen, C.; Eaglesham, G.; Drage, D.; Nguyen, T.H.; Mueller, J.F. A Mass Estimate of Perfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Release from Australian Wastewater Treatment Plants. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.; Thompson, K.; Quiñones, O.; Dickenson, E.; Bott, C. Assessment of PFAS Fate, Transport, and Treatment Inhibition Associated with a Simulated AFFF Release within a WASTEWATER Treatment Plant. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, O.P.; Bhardwaj, M.K.; Gupta, V. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Environment: A Review. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2022, 375, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Drinking Water Health Advisories for PFAS Fact Sheet for Public Water Systems (PFOA, PFOS, GenX Chemicals and PFBS); US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nahar, K.; Zulkarnain, N.A.; Niven, R.K. A Review of Analytical Methods and Technologies for Monitoring Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Water. Water 2023, 15, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Yan, H. Advancements in Detection Techniques for Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Comprehensive Review. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 176, 117754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, U.; Schulze, S.; Slawik, C.; Kunz, S.; Paschke, A.; Schüürmann, G. Gas Chromatographic Determination of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids in Aqueous Samples—A Tutorial Review. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2017, 949, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Wu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.; Yang, L.; Peng, L. Trace Analysis Method Based on UPLC-MS/MS for the Determination of (C2-C18) Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Its Application to Tap Water and Bottled Water. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarębska, M.; Bajkacz, S. Poly-and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)—Recent Advances in the Aquatic Environment Analysis. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 163, 117062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbiyi, O.D.; Ajiboye, T.O.; Omotola, E.O.; Oladoye, P.O.; Olanrewaju, C.A.; Quinete, N. Analytical Approaches for Screening of Per-and Poly Fluoroalkyl Substances in Food Items: A Review of Recent Advances and Improvements. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aßhoff, N.; Bernsmann, T.; Esselen, M.; Stahl, T. A Sensitive Method for the Determination of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Food and Food Contact Material Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1730, 465041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, S.; Chawengkijwanich, C.; Gopalakrishnan, M. Detection Methods for Sub-Nanogram Level of Emerging Pollutants—Per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 168, 113377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, K.L.; Hwang, J.H.; Esfahani, A.R.; Sadmani, A.H.M.A.; Lee, W.H. Recent Developments of PFAS-Detecting Sensors and Future Direction: A Review. Micromachines 2020, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.U.; Crimi, M.; Andreescu, S. Current and Emerging Analytical Techniques for the Determination of PFAS in Environmental Samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 37, e00198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanim-Al Hassan, M.; Chen, X.; Fnu, P.I.J.; Osonga, F.J.; Sadik, O.A.; Li, M.; Chen, H. Rapid Detection of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Using Paper Spray-Based Mass Spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, S.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.; Jeon, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Moon, H. Target and Non-Target Analyses of Neutral per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Fluorochemical Industries Using GC-MS/MS and GC-TOF: Insights on Their Environmental Fate. Environ. Int. 2023, 182, 108311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, M.; Müller, V.; Feldmann, J.; Leitner, E. Analysis of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Raw Materials Intended for the Production of Paper-Based Food Contact Materials–Evaluating LC-MS/MS versus Total Fluorine and Extractable Organic Fluorine. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A 2024, 41, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brase, R.A.; Mullin, E.J.; Spink, D.C. Legacy and Emerging Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Analytical Techniques, Environmental Fate, and Health Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, N.; Kannan, K.; Taniyasu, S.; Horii, Y.; Okazawa, T.; Petrick, G.; Gamo, T. Analysis of Perfluorinated Acids at Parts-per-Quadrillion Levels in Seawater Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5522–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stróżyńska, M.; Schuhen, K. Extraction and Derivatization for Perfluorocarboxylic Acids in Liquid and Solid Matrices: A Review. Anal. Sci. Adv. 2020, 2, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Landa, E.N.; Holbrook, K.L.; Walker, W.S.; Lee, W.-Y. Rapid, Efficient, and Green Analytical Technique for Determination of Fluorotelomer Alcohol in Water by Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, Z.G.; Liu, X.; Schumacher, B.A.; Smeltz, M.G.; Liberatore, H.K. Method Development for Thermal Desorption-Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (TD-GC–MS/MS) Analysis of Trace Level Fluorotelomer Alcohols Emitted from Consumer Products. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1705, 464204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufková, V.; Čabala, R.; Maradová, D.; Štícha, M. A Fast Derivatization Procedure for Gas Chromatographic Analysis of Perfluorinated Organic Acids. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8659–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Determination of Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids in Environmental Water Samples by Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction with GC-MS Analysis. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2020, 43, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; López, J.F.; Sandoval-Pauker, C.; Calvillo Solís, J.J.; Glass, S.; Habib, A.; Lee, W.Y.; Wong, M.S.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Villagrán, D. Trap-n-Zap: Electrocatalytic Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) with UiO-66 Modified Boron Nitride Electrodes at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. Appl. Catal. B 2024, 355, 124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołebiowski, M.; Siedlecka, E.; Paszkiewicz, M.; Brzozowski, K.; Stepnowski, P. Perfluorocarboxylic Acids in Cell Growth Media and Technologically Treated Waters: Determination with GC and GC-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stróżyńska, M.; Schuhen, K. Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction Followed by Triethylsilyl Derivatization and Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry for Perfluorocarboxylic Acids Determination in Water Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1597, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Lin, H.; Yamazaki, E.; Eun, H.; Lam, P.K.S.; Yamashita, N. Quality Assurance and Quality Control of Solid Phase Extraction for PFAS in Water and Novel Analytical Techniques for PFAS Analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, A.; Basauri, O.; Rodil, R.; Usobiaga, A.; Fernández, L.A.; Etxebarria, N.; Zuloaga, O. Stir-Bar Sorptive Extraction: A View on Method Optimisation, Novel Applications, Limitations and Potential Solutions. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2642–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, A.; Carriera, F.; Di Fiore, C.; Avino, P. Poly-and Perfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Analysis in Environmental Matrices: An Overview of the Extraction and Chromatographic Detection Methods. Analytica 2024, 5, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaga, R.; Bayona, J.M. Determination of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids in Aqueous Matrices by Ion-Pair Solid-Phase Microextraction-in-Port Derivatization-Gas Chromatography-Negative Ion Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1042, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, M.; Naccarato, A.; Sindona, G.; Tagarelli, A. A Rapid and Sensitive Assay of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids in Aqueous Matrices by Headspace Solid Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography-Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1251, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltussen, E.; Sandra, P.; David, F.; Cramers, C. Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction (SBSE), a Novel Extraction Technique for Aqueous Samples: Theory and Principles. J. Microcolumn Sep. 1999, 11, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, K.L.; Badmos, S.; Habib, A.; Landa, E.N.; Quaye, G.E.; Su, X.; Lee, W. Investigating the Effects of Storage Conditions on Urinary Volatilomes for Their Reliability in Disease Diagnosis. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2023, 11, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noriega Landa, E.; Quaye, G.E.; Su, X.; Badmos, S.; Holbrook, K.L.; Polascik, T.J.; Adams, E.S.; Deivasigamani, S.; Gao, Q.; Annabi, M.H.; et al. Urinary Fatty Acid Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Detection. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0297615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, F.; Ochiai, N.; Sandra, P. Two Decades of Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction: A Retrospective and Future Outlook. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, C.S.; Logue, B.A. Ultratrace Analysis of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Drinking Water Using Ice Concentration Linked with Extractive Stirrer and High Performance Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1659, 462493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, I.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Malvar, J.L.; Alonso, E. Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Determination of Polar and Non-Polar Emerging and Priority Pollutants in Environmental Waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1500, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaverde-de-Sáa, E.; Racamonde, I.; Quintana, J.B.; Rodil, R.; Cela, R. Ion-Pair Sorptive Extraction of Perfluorinated Compounds from Water with Low-Cost Polymeric Materials: Polyethersulfone vs Polydimethylsiloxane. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 740, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhou, Z.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Liang, Y.; Hu, B. One-Pot Polymerization of Monolith Coated Stir Bar for High Efficient Sorptive Extraction of Perfluoroalkyl Acids from Environmental Water Samples Followed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry Detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1553, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Definition and Procedure for the Determination of the Method Detection Limit—Revision 1.11; EPA 821-R-16-006; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, J.M.F. Stir-Bar Sorptive Extraction: 15 Years Making Sample Preparation More Environment-Friendly. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, C.A.; Field, J.A. Determination of Perfluorocarboxylates in Groundwater Impacted by Fire-Fighting Activity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2800–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.F.; Moody, C.A.; Spencer, C.; Small, J.M.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.A. Analysis for Perfluorocarboxylic Acids/Anions in Surface Waters and Precipitation Using GC-MS and Analysis of PFOA from Large-Volume Samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6405–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, A.O.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.A. Distribution of Perfluorocarboxylate Isomers in Select Samples from the North American Environment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 1801–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufková, V.; Čabala, R.; Ševčík, V. Determination of C 5-C 12 Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids in River Water Samples in the Czech Republic by GC-MS after SPE Preconcentration. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Ballesteros, E.; Gallego, M. Semiautomated Solid-Phase Extraction Followed by Derivatisation and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry for Determination of Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Water. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1318, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Sun, H. Cost-Effective Detection of Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids with Gas Chromatography: Optimization of Derivatization Approaches and Method Validation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, A. Simultaneous Determination of Nine Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids by a Series of Amide Acetals Derivatization and Gas Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1622, 461132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound Name | Acronym | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | CAS No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Perfluoroheptanoic acid | PFHpA | C7HF13O2 | 364.06 | 375-85-9 |
| 2 | Perfluorooctanoic acid | PFOA | C8HF15O2 | 414.07 | 335-67-1 |
| 3 | Perfluorononanoic acid | PFNA | C9HF17O2 | 464.08 | 375-95-1 |
| 4 | Perfluorodecanoic acid | PFDA | C10HF19O2 | 514.08 | 335-76-2 |
| 5 | Perfluoroundecanoic acid | PFUnA | C11HF21O2 | 564.09 | 2058-94-8 |
| 6 | Perfluorododecanoic acid | PFDoA | C12HF23O2 | 614.1 | 307-55-1 |
| 7 | Perfluorotetradecanoic acid | PFTeDA | C14HF27O2 | 714.11 | 376-06-7 |
| 8 | Perfluorohexadecanoic acid | PFHxDA | C16HF31O2 | 814.13 | 67905-19-5 |
| 9 | Perfluorooctadecanoic acid | PFODA | C18HF35O2 | 914.1 | 16517-11-6 |
| Analyte | Retention Time (min) | Parent Ion (m/z) | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | % Recovery (±SD) | LOD (ng/L) | LOQ (ng/L) | MDL (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFHpA | 5.884 | 405 | 0.9984 | 97 (±11) | 21.17 | 138.27 | 293.96 |
| PFOA | 6.640 | 455 | 0.9948 | 94 (±11) | 21.20 | 103.13 | 495.37 |
| PFNA | 7.614 | 505 | 0.9956 | 86 (±5) | 30.12 | 90.80 | 980.37 |
| PFDA | 8.448 | 555 | 0.9893 | 91 (±10) | 54.29 | 169.85 | 888.30 |
| PFUnA | 9.416 | 605 | 0.9892 | 88 (±10) | 34.39 | 132.90 | 1227.97 |
| PFDoA | 10.002 | 655 | 0.9925 | 85 (±8) | 73.96 | 192.01 | 1458.84 |
| PFTeDA | 11.422 | 755 | 0.9906 | 85 (±3) | 35.02 | 107.10 | 925.13 |
| PFHxDA | 12.728 | 855 | 0.9988 | 79 (±7) | 51.75 | 128.33 | 955.47 |
| PFODA | 13.943 | 955 | 0.9929 | 77 (±6) | 42.05 | 87.74 | 1148.09 |
| Sl No. | Target PFCAs | Matrix/Sources | Derivatizing Agent | Extraction Method | Sample Volume | Instrumentation | Recovery % | LOD (ng/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFDoA | Groundwater | Methyl iodide, Diazomethane | SPE | 200 mL | GC-ECNI-MS | 35–90 | 18–36 µg/L | [73] |
| 2 | PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA | Wastewater, Seawater | Tetrabutylammonium, Butanol, Thionyl chloride | IP-SPME | 5 mL | GC–NCI-MS | 35–90 | 20–750 | [61] |
| 3 | TFA, PFPrA, PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA | Surface water, Lake water, Sewage WTP, Precipitation | 2,4-difluoroaniline and N, N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide | SPE | 300 mL | GC-EI-MS | 25–137 | 0.01–0.5 | [74] |
| 4 | PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA | River water | Isobutyl chloroformate, Pyridine, Isobutanol | LLE | 500 mL | GC-EI-MS | N/A | 200–2200 µg/L | [53] |
| 5 | PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA | Surface water, Precipitation | 2,4-difluoroaniline and DCC | IP-LLE | 500 mL | GC-NCI-MS | 91–98 | 0.3–5.9 | [75] |
| 6 | PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA | River water | Propyl chloroformate, Propanol | HS-SPME | 10 mL | GC–QqQ–MS/MS | 84.4–116.8 | 0.08–6.6 | [62] |
| 7 | PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA | River Water | Isobutyl chloroformate, Pyridine, Isobutanol | SPE | 250 mL | GC-NCI-MS | 53–111 | 0.1–24 | [76] |
| 8 | PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA | Surface water | Tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate | IP-DLLME | 10 mL | GC-NCI-MS/MS | 95–98 | 37–51 | [3] |
| 9 | PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA | Drinking water/wastewater | Isobutyl chloroformate, DCC in Pyridine, Isobutanol | SPE | 250 mL | GC-DSQ II-MS | 94–98 | 0.1–0.5 | [77] |
| 10 | PFPrA, PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA | Wastewater | Triethylsilanol, H2SO4 | SPE | 250 mL | GC-EI-MS | 93–108 | 4–48 | [57] |
| 11 | PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA, PFTeA | River water, Lake water | Isobutyl chloroformate, Pyridine, Isobutanol | DLLME | 1 mL | GC-EI-MS | 83.7–117 | 0.9–3 | [54] |
| 12 | PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA | Surface water | 2,4-difluoroaniline and DCC | SPE | 500 mL | GC-µECD | 62–118 | 1140–6320 | [78] |
| 13 | PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA | Tap water | 2,3,4,5,6- pentafluorobenzyl bromide | SPE | 500 mL | GC-EI-MS | 40.1–101.8 | 0.1–0.28 | [79] |
| 14 | TFA, PFPrA, PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA | Tap water, Precipitation, Ocean water | Diphenyl diazomethane | SPE | 250 mL | GC-ECNI-MS | 83–130 | 0.06–14.6 | [13] |
| 15 | PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA, PFTeDA, PFHxDA, PFODA | Wastewater, Tap water | Isobutyl chloroformate, Isobutanol, Pyridine | SBSE | 1 mL | GC-EI-MS | 47–97 | 21.17–73.96 | This work |
| Repeatability (RSD %; n = 7) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyte | D.I. Water | Tap Water | ||
| 100 ng/L | 1000 ng/L | 100 ng/L | 1000 ng/L | |
| PFHpA | 8.6% | 6.5% | 13.1% | 9.7% |
| PFOA | 13.3% | 10.3% | 9.4% | 8.6% |
| PFNA | 10.0% | 9.5% | 11.4% | 7.2% |
| PFDA | 6.2% | 8.2% | 12.3% | 6.2% |
| PFUnA | 12.5% | 10.2% | 9.6% | 12.5% |
| PFDoA | 13.4% | 12.1% | 7.8% | 12.0% |
| PFTeDA | 12.9% | 8.3% | 8.9% | 10.2% |
| PFHxDA | 11.6% | 12.7% | 12.0% | 9.0% |
| PFODA | 6.7% | 9.6% | 12.8% | 9.4% |
| Tap Water | Wastewater Influent | Wastewater Effluent | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyte | 10 ng | 20 ng | 10 ng | 20 ng | 10 ng | 20 ng |
| PFHpA | 68 (±8) | 81 (±7) | 29 (±12) | 27 (±9) | 45 (±8) | 64 (±11) |
| PFOA | 74 (±5) | 77 (±13) | 31 (±7) | 26 (±8) | 46 (±7) | 53 (±3) |
| PFNA | 75 (±6) | 73 (±10) | 35 (±4) | 21 (±7) | 59 (±12) | 44 (±11) |
| PFDA | 90 (±10) | 87 (±12) | 31 (±9) | 23 (±6) | 56 (±6) | 49 (±10) |
| PFUnA | 69 (±3) | 61 (±1) | 29 (±9) | 29 (±10) | 43 (±6) | 45 (±11) |
| PFDoA | 82 (±13) | 93 (±7) | 32 (±6) | 27 (±9) | 56 (±11) | 65 (±10) |
| PFTeDA | 85 (±15) | 96 (±6) | 41 (±10) | 30 (±6) | 53 (±4) | 74 (±8) |
| PFHxDA | 84 (±8) | 93 (±1) | 44 (±11) | 31 (±10) | 57 (±11) | 62 (±6) |
| PFODA | 82 (±8) | 92 (±6) | 42(±2) | 24 (±10) | 65 (±14) | 61 (±10) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habib, A.; Noriega Landa, E.; Holbrook, K.L.; Chacon, A.A.; Lee, W.-Y. Green Analytical Method for Perfluorocarboxylic Acids (PFCAs) in Water of Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Coupled with Thermal Desorption–Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectroscopy. Water 2024, 16, 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172543
Habib A, Noriega Landa E, Holbrook KL, Chacon AA, Lee W-Y. Green Analytical Method for Perfluorocarboxylic Acids (PFCAs) in Water of Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Coupled with Thermal Desorption–Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectroscopy. Water. 2024; 16(17):2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172543
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabib, Ahsan, Elizabeth Noriega Landa, Kiana L. Holbrook, Angelica A. Chacon, and Wen-Yee Lee. 2024. "Green Analytical Method for Perfluorocarboxylic Acids (PFCAs) in Water of Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Coupled with Thermal Desorption–Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectroscopy" Water 16, no. 17: 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172543
APA StyleHabib, A., Noriega Landa, E., Holbrook, K. L., Chacon, A. A., & Lee, W.-Y. (2024). Green Analytical Method for Perfluorocarboxylic Acids (PFCAs) in Water of Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Coupled with Thermal Desorption–Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectroscopy. Water, 16(17), 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172543








