Naphthalene Enhances Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Biodegradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Soil and Water: Effect and Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Culture Media
2.2. Enrichment, Isolation, and Identification of PAH-Degrading Bacteria
2.3. Degradation of PAHs in a Single, Binary, and Mixture Systems
2.4. Determination of PAH Concentration and Calculation of the Degradation Rate
2.5. Determination of Dehydrogenase Activity
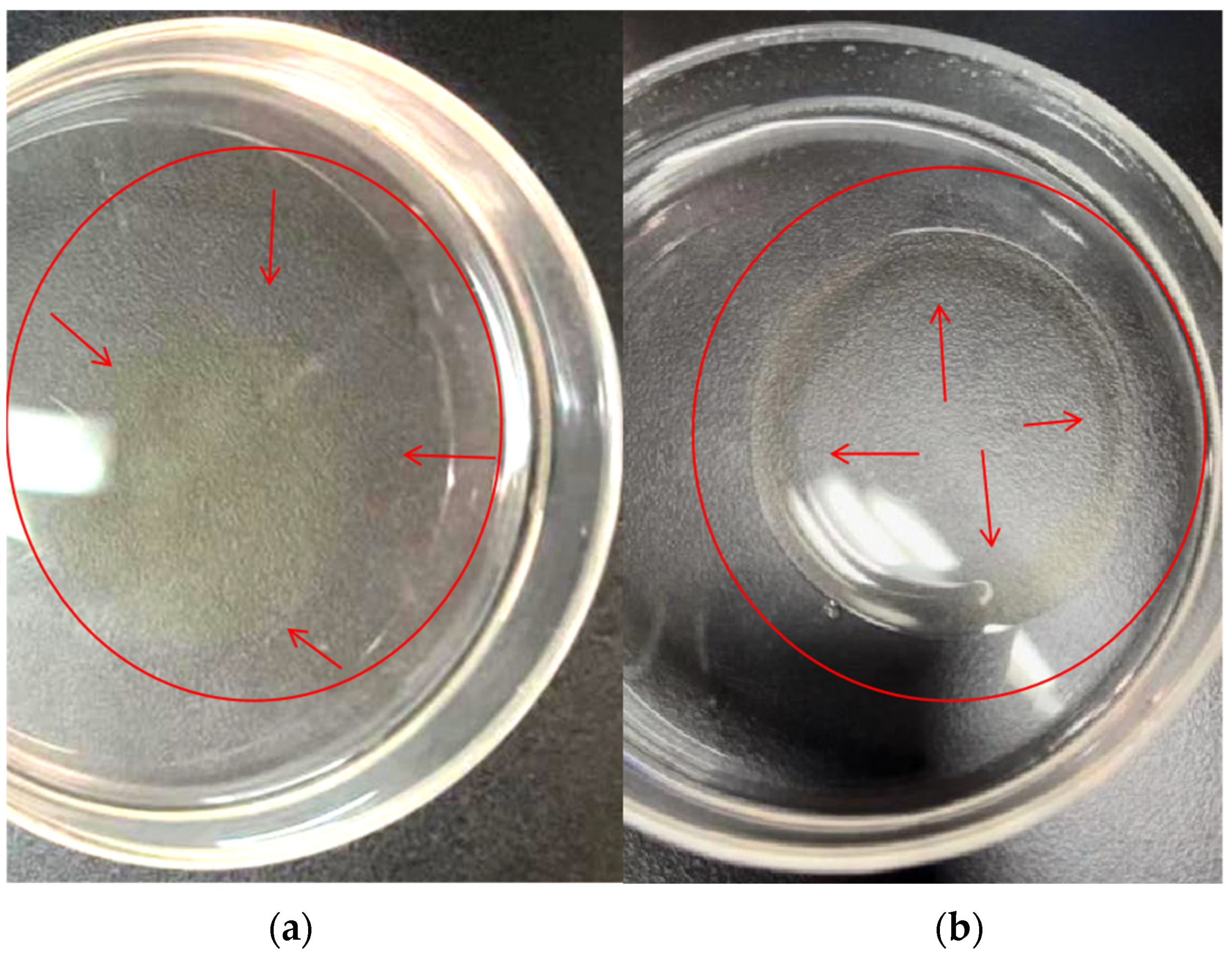
2.6. Oil Spreading Test
2.7. Transcriptome Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
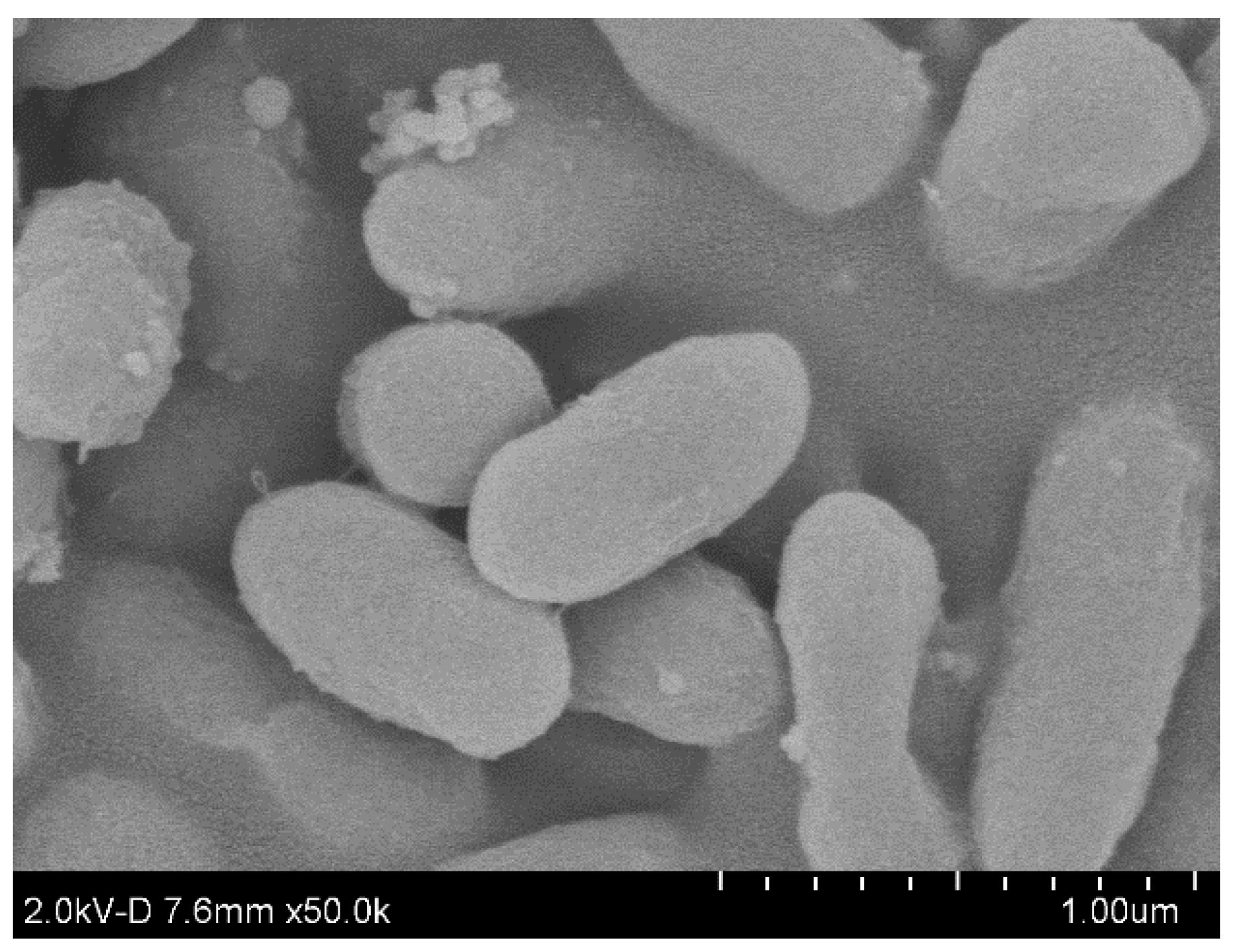
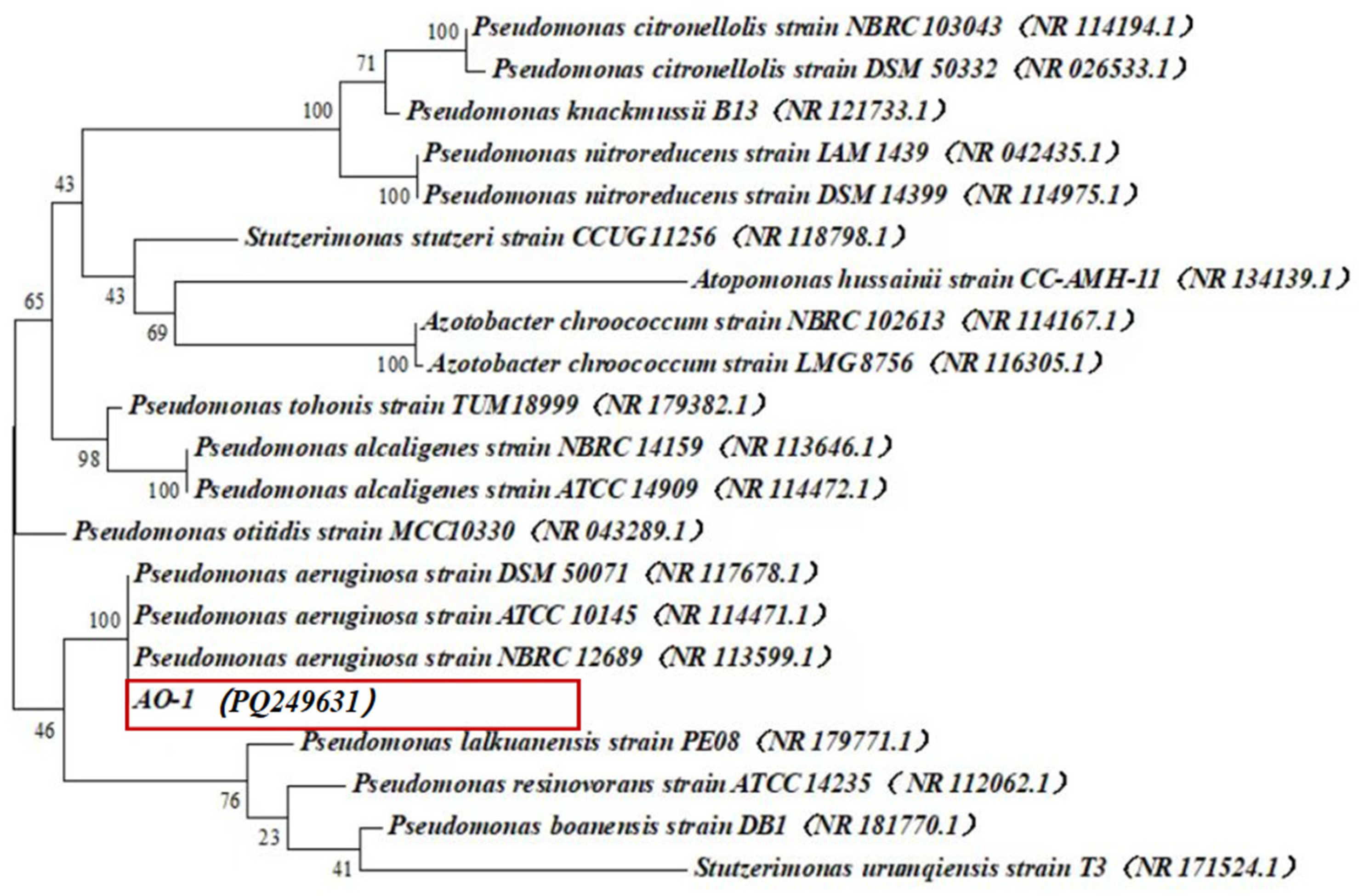
3.1. Isolation and Identification of the PAH-Degrading Strain AO-1
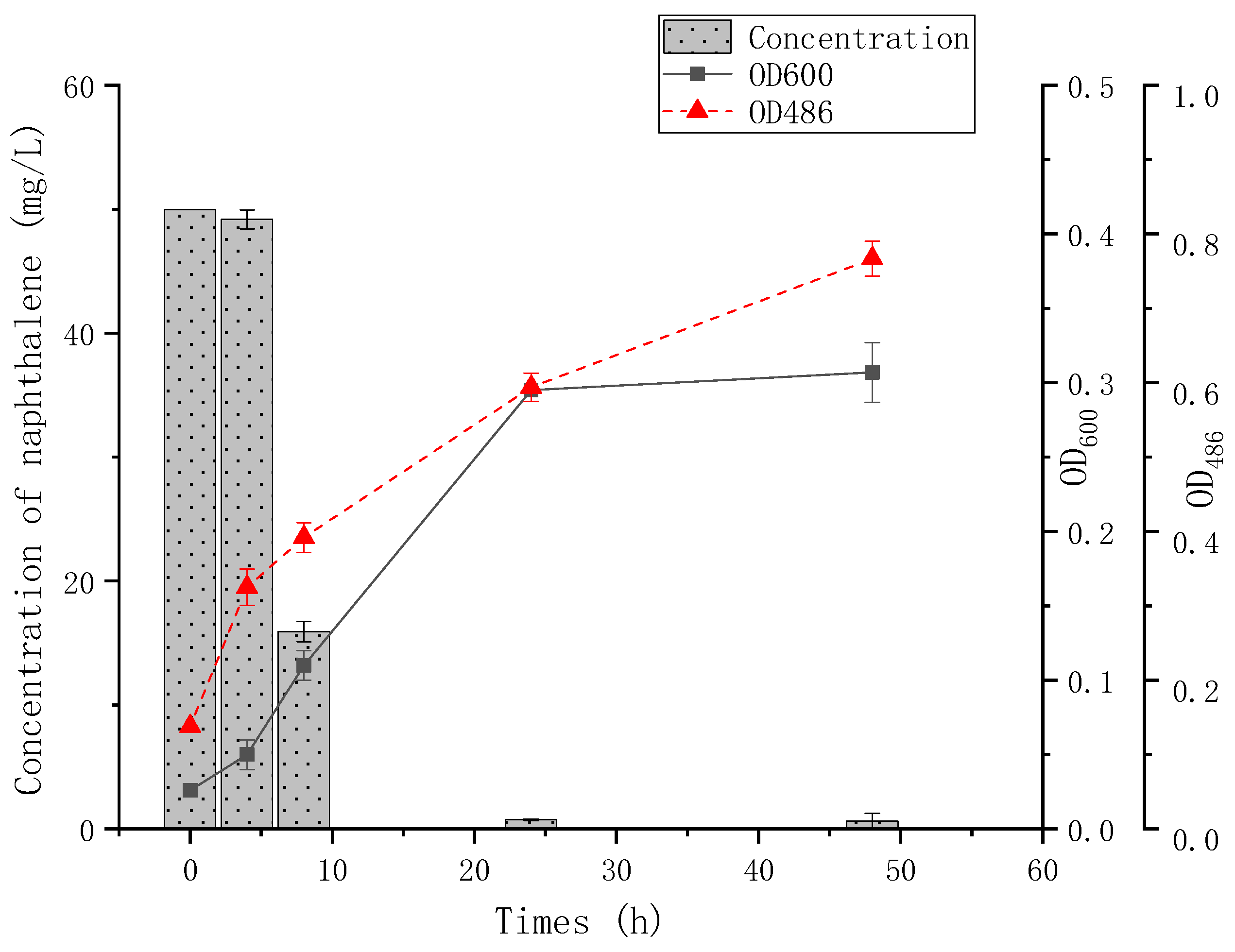
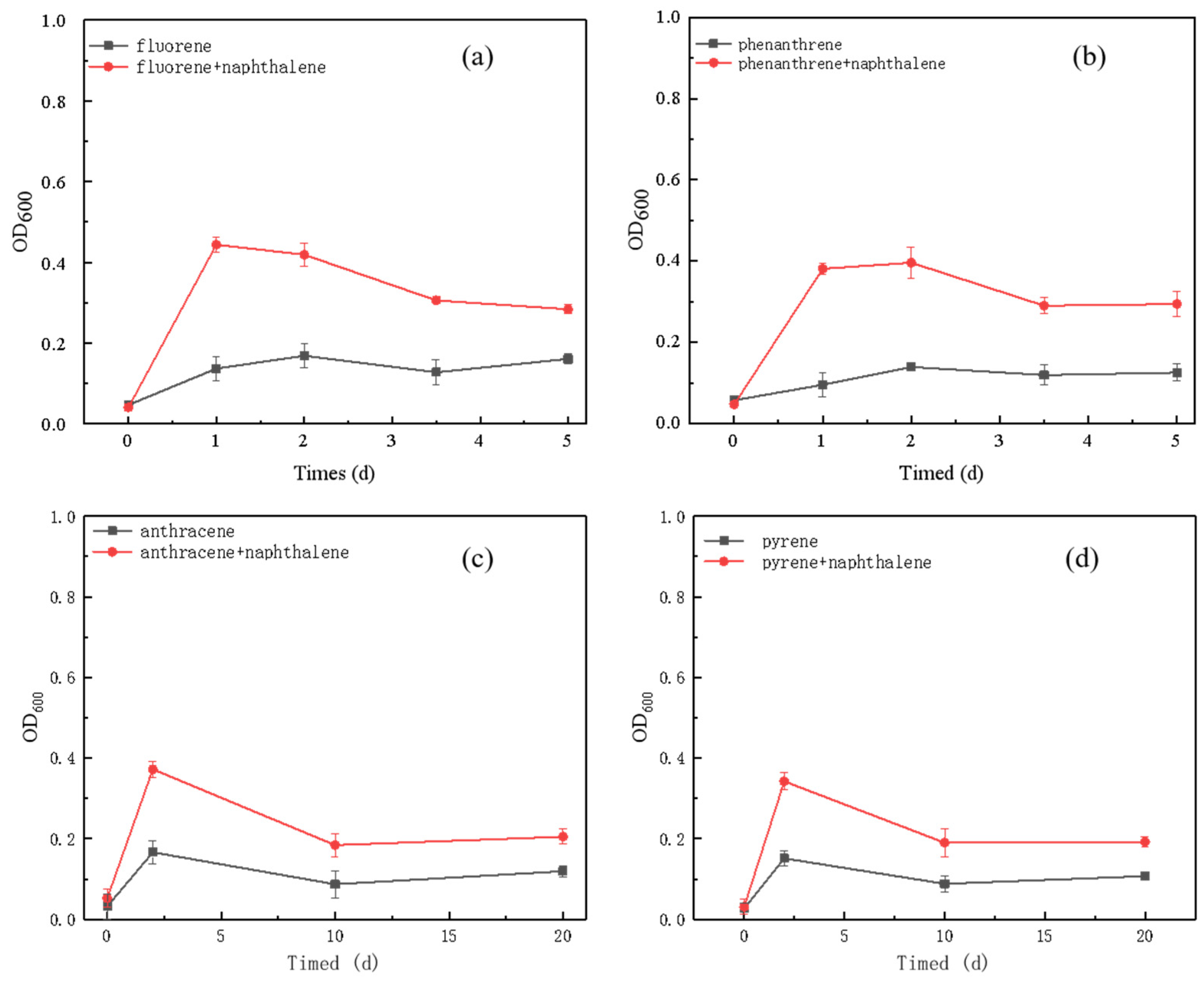
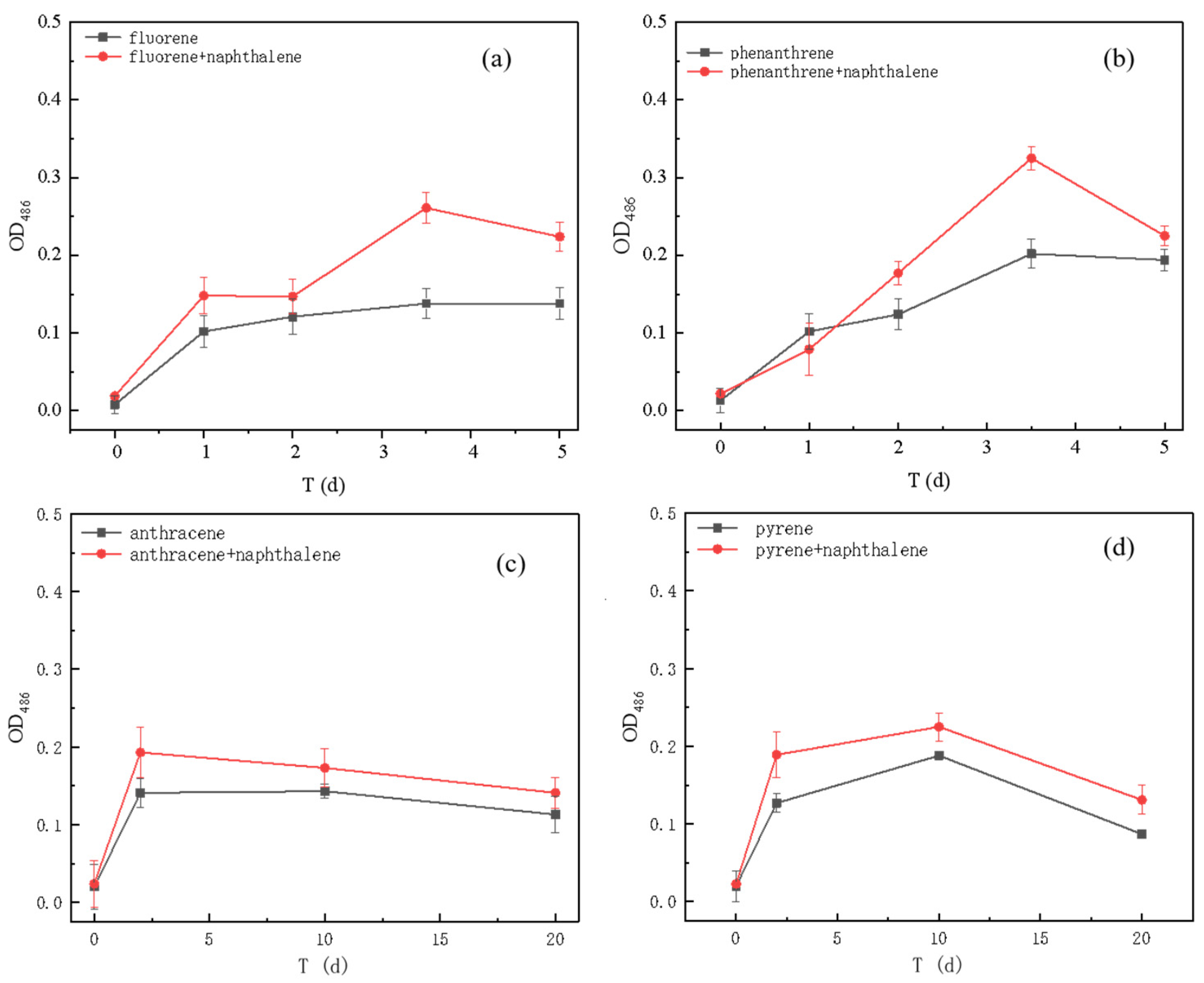
3.2. Degradation of PAHs by Strain AO-1 in Single and Binary Systems
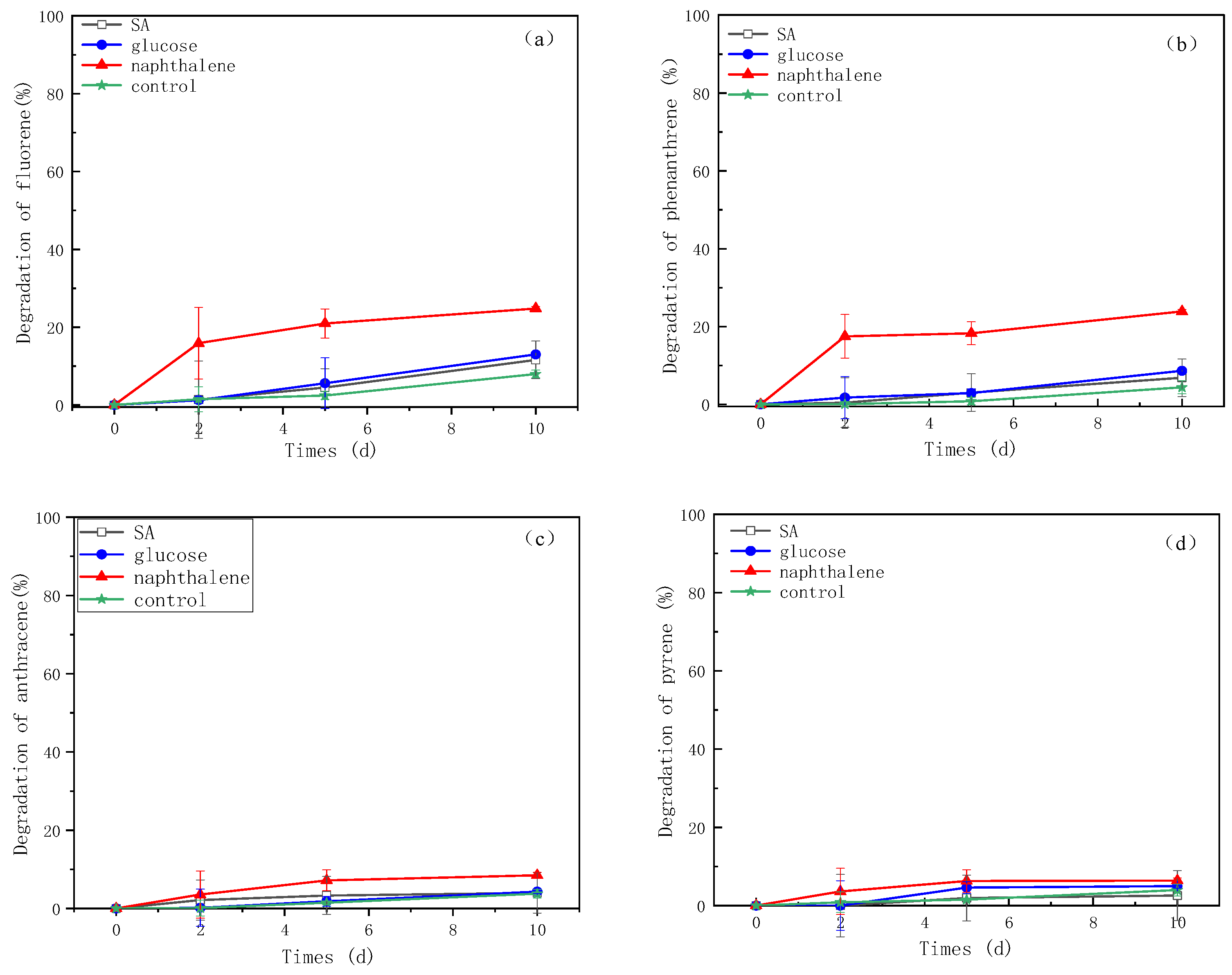
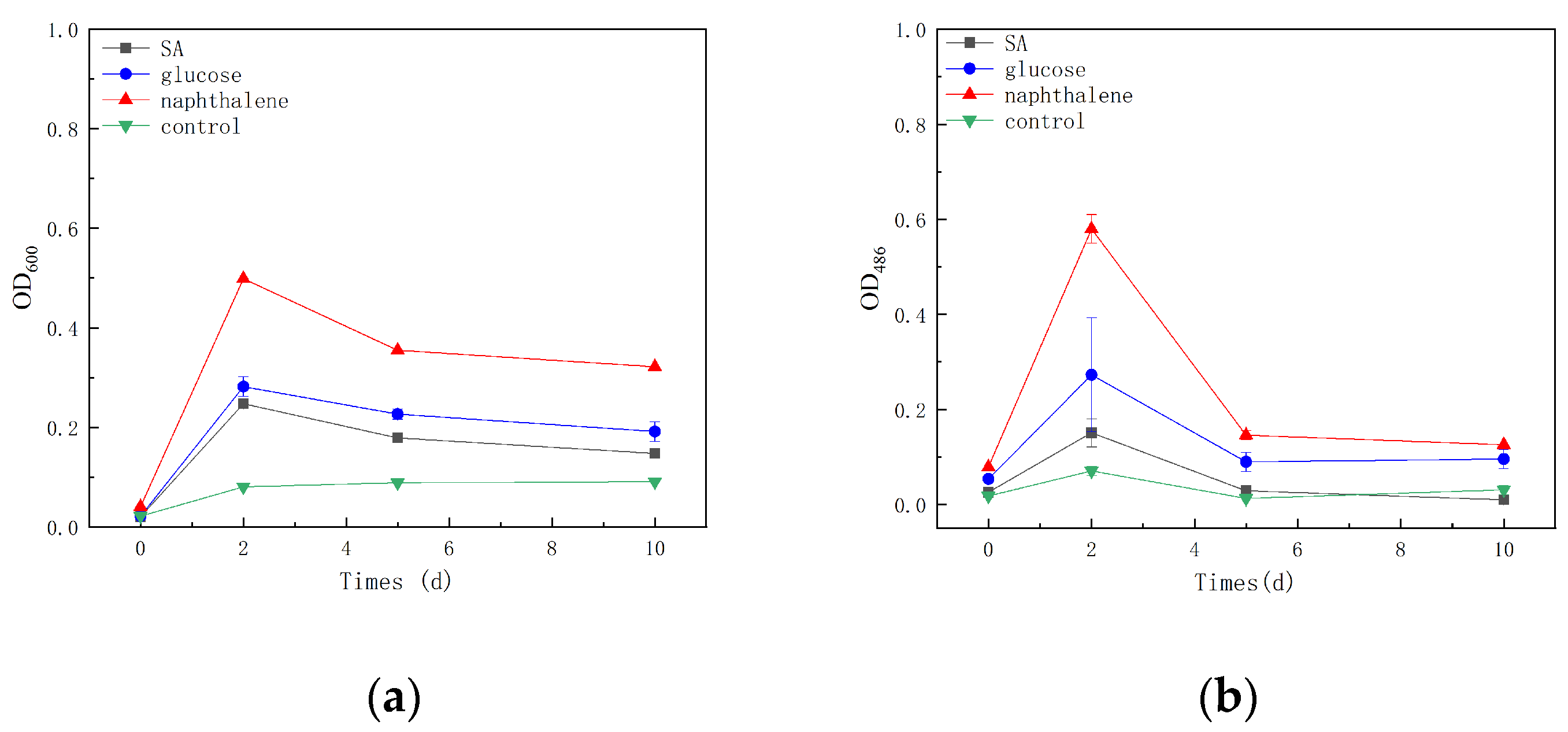
3.3. Degradation of PAHs by Strain AO-1 Using Different Carbon Sources
3.4. Comparative Transcriptional Analysis of Strain AO-1 Using Naphthalene/Glucose as a Carbon Source
3.4.1. Analysis of DEGs
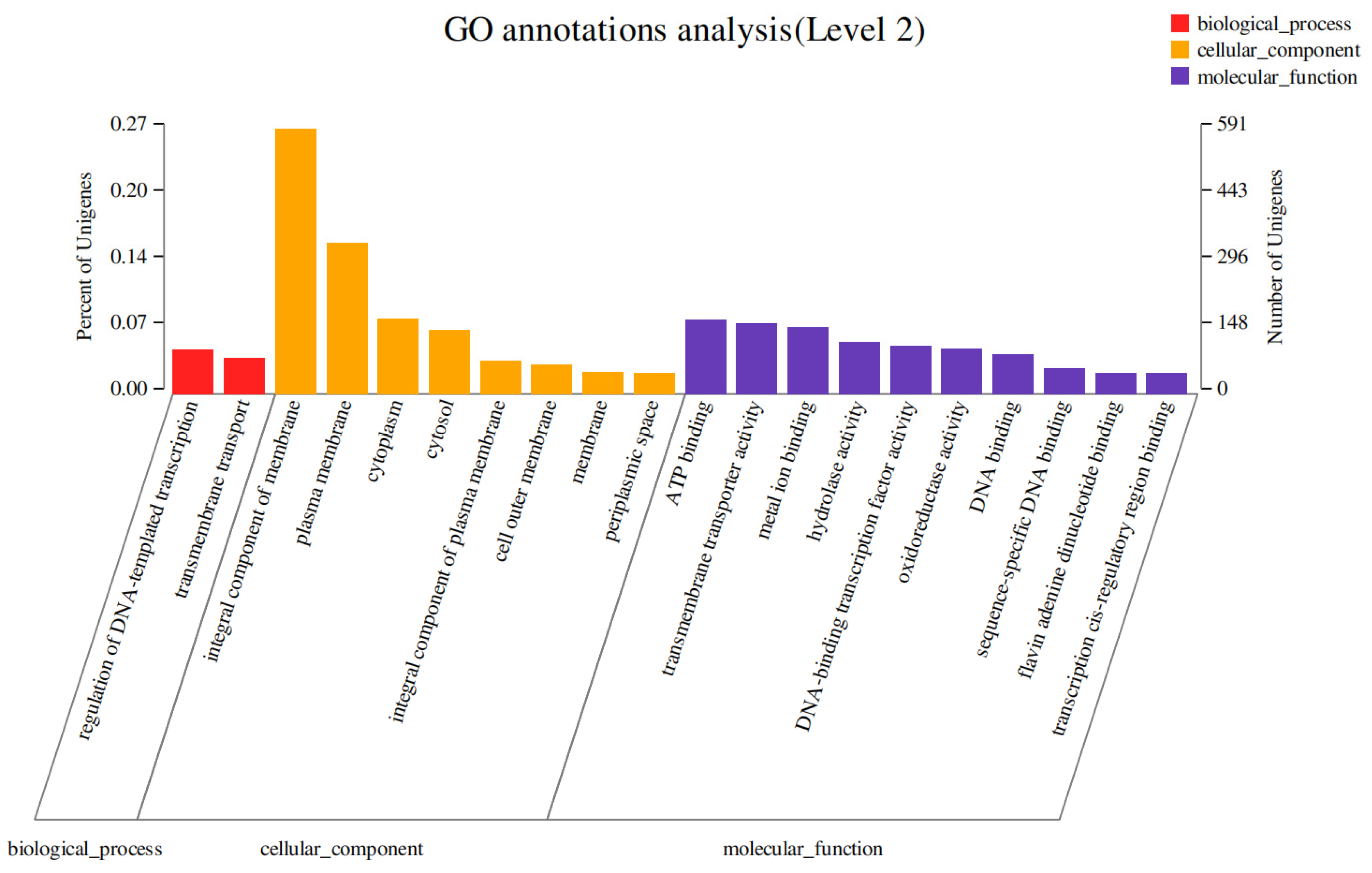
3.4.2. GO Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
3.4.3. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vijayanand, M.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Subramanian, R.; Issac, P.K.; Nasr, M.; Khoo, K.S.; Rajagopal, R.; Greff, B.; Azelee, N.I.W.; Jeon, B.-H.; et al. Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the water environment: A review on toxicity, microbial biodegradation, systematic biological advancements, and environmental fate. Environ. Res 2023, 227, 115716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.Y.; Wu, S.M. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in oil deodorizer distillates: Kinetics, degradation product identification and toxicity. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 187, 105718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.S.; Haritash, A.K. Bacterial degradation of mixed-PAHs and expression of PAH-catabolic genes. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 39, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Song, Y.; He, F.; Jing, M.; Tang, J.; Liu, R. A review of human and animals exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Health risk and adverse effects, photo-induced toxicity and regulating effect of microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Teng, Y.; Ren, W.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Y. A highly effective polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium, Paracoccus sp. HPD-2, shows opposite remediation potential in two soil types. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, W.; Ma, Y.; Gao, X.; Ming, H.; Jia, J. Effects of bioaugmentation by isolated Achromobacter xylosoxidans BP1 on PAHs degradation and microbial community in contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 334, 117491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartell, B.; Boufadel, M.; Rodriguez-Freire, L. An effort to understand and improve the anaerobic biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: A literature review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 157, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaren, K.C.F.; Lopes, E.S.; Rocha, H.G.V.; Domingos, A.C.A.; Jurelevicius, D.A.; Seldin, L. Naphthalene-Degrading Bacteria with Potential for Remediating Marine Environments. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Liu, J.; Yu, B.; Zhou, Q. Phytoremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated saline-alkali soil by wild ornamental Iridaceae species. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2017, 19, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, R.S.; Vermelho, A.B.; Rosado, A.S. Petroleum-degrading enzymes: Bioremediation and new prospects. Enzym. Res. 2011, 2011, 475193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, B. Bioresources for control of environmental pollution. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 147, 137–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hu, H.; Xu, P.; Tang, H. Soil bioremediation by Pseudomonas brassicacearum MPDS and its enzyme involved in degrading PAHs. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Huang, H.J.; Tu, Z.H. Phenanthrene Degradation by Sphingobium sp. PM1B in Soil Containing Polyethylene Microplastics: Effects and Mechanisms. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.Q.; Jia, T.; Liu, J.X.; Chai, B.F. Relationships among protozoa, bacteria and fungi in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, F.; Ahmad, A.; Rafatullah, M. Review on bioremediation technologies of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from soil: Mechanisms and future perspective. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2023, 179, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, L.; Yang, L.; Luan, T.; Chen, B. Transcriptional response of Mycobacterium sp. strain A1-PYR to multiple polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminations. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Biodegradation of high-molecular weight PAHs by Rhodococcus wratislaviensis strain 9: Overexpression of amidohydrolase induced by pyrene and BaP. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651 Pt 1, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yessentayeva, K.; Reinhard, A.; Berzhanova, R.; Mukasheva, T.; Urich, T.; Mikolasch, A. Bacterial crude oil and polyaromatic hydrocarbon degraders from Kazakh oil fields as barley growth support. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Thavamani, P.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Lee, Y.B.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Remediation approaches for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminated soils: Technological constraints, emerging trends and future directions. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 944–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, B.; Zhou, S. Fulvic acid enhancing pyrene biodegradation by immobilized Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Effect and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 403, 130857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Su, Q.; Yi, Q.; Guo, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Determining the degradation mechanism and application potential of benzopyrene-degrading bacterium Acinetobacter XS-4 by screening. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 456, 131666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Qian, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yu, F.; Huang, T.; Zhang, B.; Peng, T.; Hu, Z. Comparative genomics reveals evidence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in the moderately halophilic genus Pontibacillus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, K.; Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Krishnan, K.; Megharaj, M. Anaerobic Microbial Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A Comprehensive Review. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 251, 25–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, A.; Suman, S.K.; Vasavdutta, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Vempatapu, B.P.; Ray, A.; Kanaujia, P.K. Degradation of multiple PAHs and co-contaminants by microbial consortia and their toxicity assessment. Biodegradation 2024, 35, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, N.; Irazusta, V.; Isaac, P.; Estévez, C.; Maizel, D.; Ferrero, M.A. Identification of proteins induced by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and proposal of the phenanthrene catabolic pathway in Amycolatopsis tucumanensis DSM 45259. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 175, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.; Nain, L.; Singh, S.B.; Varghese, E.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, S.; Singh, N. Bacteria and fungi mediated degradation of poly aromatic hydrocarbons and effect of surfactant Tween-80. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehetre, G.T.; Dastager, S.G.; Dharne, M.S. Biodegradation of mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by pure and mixed cultures of biosurfactant producing thermophilic and thermo-tolerant bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Kang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, T.; Qian, T.; Li, B. Biodegradation of phenanthrene-Cr (VI) co-contamination by Pseudomonas aeruginosa AO-4 and characterization of enhanced degradation of phenanthrene. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ling, J.; Yin, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Khan, I.; Dong, J. Evaluation of the Different Nutritional and Environmental Parameters on Microbial Pyrene Degradation by Mangrove Culturable Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Park, J.-W.; Ahn, I.-S. Effect of additional carbon source on naphthalene biodegradation by Pseudomonas putida G7. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 105, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritash, A.K.; Kaushik, C.P. Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 169, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringfellow, W.T.; Aitken, M.D. Competitive metabolism of naphthalene, methylnaphthalenes, and fluorene by phenanthrene-degrading pseudomonads. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanella, P.; Taketani, R.G.; Gil-Solsona, R.; Saldanha, L.L.; Naranjo, S.B.E.; Sancho, J.V.; Portolés, T.; Andreote, F.D.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Barceló, D.; et al. A comprehensive study on diesel oil bioremediation under microcosm conditions using a combined microbiological, enzymatic, mass spectrometry, and metabarcoding approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 101250–101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean-Ross, D.; Moody, J.; Cerniglia, C.E. Utilization of mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria isolated from contaminated sediment. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.C.; Kumar, M.; Lin, J.G. Anaerobic biotransformation of fluorene and phenanthrene by sulfate-reducing bacteria and identification of biotransformation pathway. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 164, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, G.S.; Hema, T.; Gandhimathi, R.; Selvin, J.; Thomas, T.A.; Ravji, T.R.; Natarajaseenivasan, K. Optimization and production of a biosurfactant from the sponge-associated marine fungus Aspergillus ustus MSF3. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavania, M.; Cheema, S.; Sarma, P.M.; Mandal, A.K.; Lal, B. Biodegradation of asphalt by Garciaella petrolearia TERIG02 for viscosity reduction of heavy oil. Biodegradation 2012, 23, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young Kevin, D. The Selective Value of Bacterial Shape. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 660–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Zang, T.; Wei, J.; Wu, H.; Wei, C.; Qiu, G.; Li, F. A biosurfactant-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa S5 isolated from coking wastewater and its application for bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patowary, R.; Patowary, K.; Kalita, M.C.; Deka, S.; Borah, J.M.; Joshi, S.J.; Zhang, M.; Peng, W.; Sharma, G.; Rinklebe, J.; et al. Biodegradation of hazardous naphthalene and cleaner production of rhamnolipids—Green approaches of pollution mitigation. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, M.; Hirata, Y.; Imanaka, T. A study on the structure–function relationship of lipopeptide biosurfactants. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2000, 1488, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, J.M.; Li, M.S.; Zhu, S.T.; Pan, T. From Antagonism to Enhancement: Triton X-100 Surfactant Affects Phenanthrene Interfacial Biodegradation by Mycobacteria through a Shift in Uptake Mechanisms. Langmuir 2024, 40, 11106–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Xu, G.; Deng, K. Synergic degradation of diesel by Scirpus triqueter and its endophytic bacteria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8198–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.S.; Haritash, A.K. Haritash, Catabolic enzyme activity and kinetics of pyrene degradation by novel bacterial strains isolated from contaminated soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guo, C.; Wei, Y.; Lin, W.; Yi, X.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z. Cosolubilization synergism occurrence in codesorption of PAH mixtures during surfactant-enhanced remediation of contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hou, Z.; Yang, C.; Ma, C.; Tao, F.; Xu, P. Degradation of n-alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in petroleum by a newly isolated Pseudomonas aeruginosa DQ8. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4111–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentz, J.A.; Alvarez, P.J.; Schnoor, J.L. Repression of Pseudomonas putida phenanthrene-degrading activity by plant root extracts and exudates. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Co-biodegradation of pyrene and other PAHs by the bacterium Acinetobacter johnsonii. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Pathak, B.; Fulekar, M.H. Molecular approaches for biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compounds: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2015, 14, 241–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, S.B.; Sharma, R.; Chaudhary, P.; Pandey, A.K.; Ansari, R.; Vasudevan, V.; Arora, A.; Singh, S.; Saha, S.; et al. Enhanced biodegradation of PAHs by microbial consortium with different amendment and their fate in in-situ condition. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Fu, D.; Chakraborty, R.; Singh, R.P.; Terry, N. Enhanced crude oil depletion by constructed bacterial consortium comprising bioemulsifier producer and petroleum hydrocarbon degraders. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Apte, S.K.; Phale, P.S. Preferential utilization of aromatic compounds over glucose by Pseudomonas putida CSV86. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.S.; Haritash, A.K. Catabolic enzyme activities during biodegradation of three-ring PAHs by novel DTU-1Y and DTU-7P strains isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3101–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-P.; Tian, Y.-X.; Hao, Z.-D.; Ma, Y.-L. Transcriptomic analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa DN1 upon degradation of fluoranthene. Microbiol. China 2020, 47, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra, G.; Taylor, T.D.; Absalón, A.E.; Cortés-Espinosa, D.V. Comparative metagenomic analysis of PAH degradation in soil by a mixed microbial consortium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Feng, Q.; Li, K.; Lin, J.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y.; Gai, H.; Song, H.; Huang, T.; Zhu, Q.; et al. The metabolism of pyrene by a novel Altererythrobacter sp. with in-situ co-substrates: A mechanistic analysis based on pathway, genomics, and enzyme activity. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, D.; Richez, M.; Bergonzi, C.; Chabriere, E.; Elias, M. Crystal structure of the phosphate-binding protein (PBP-1) of an ABC-type phosphate transporter from Clostridium perfringens. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Hu, B.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, X.; Liu, Y. Assembly of fungal mycelium-carbon nanotube composites and their application in pyrene removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



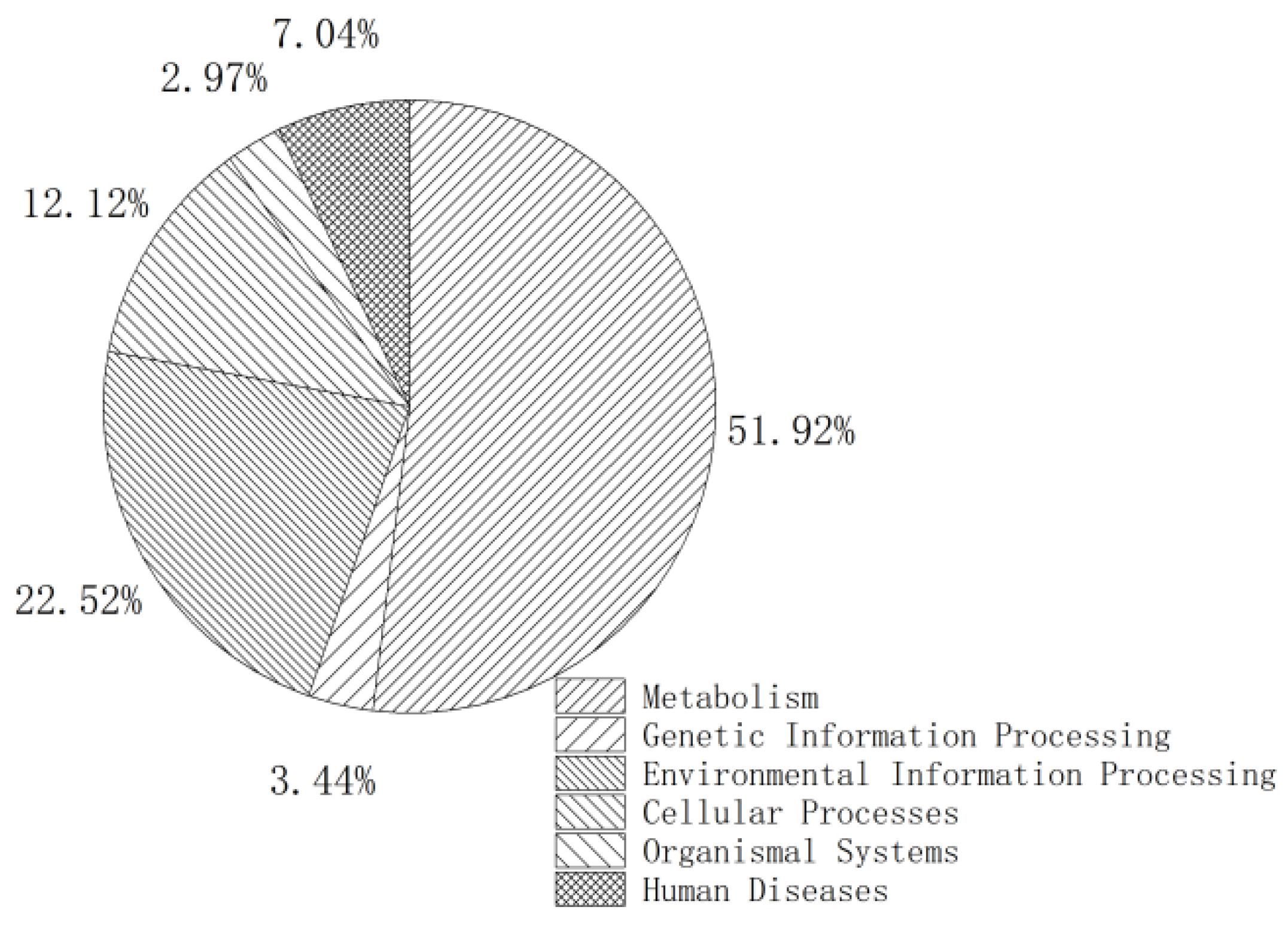
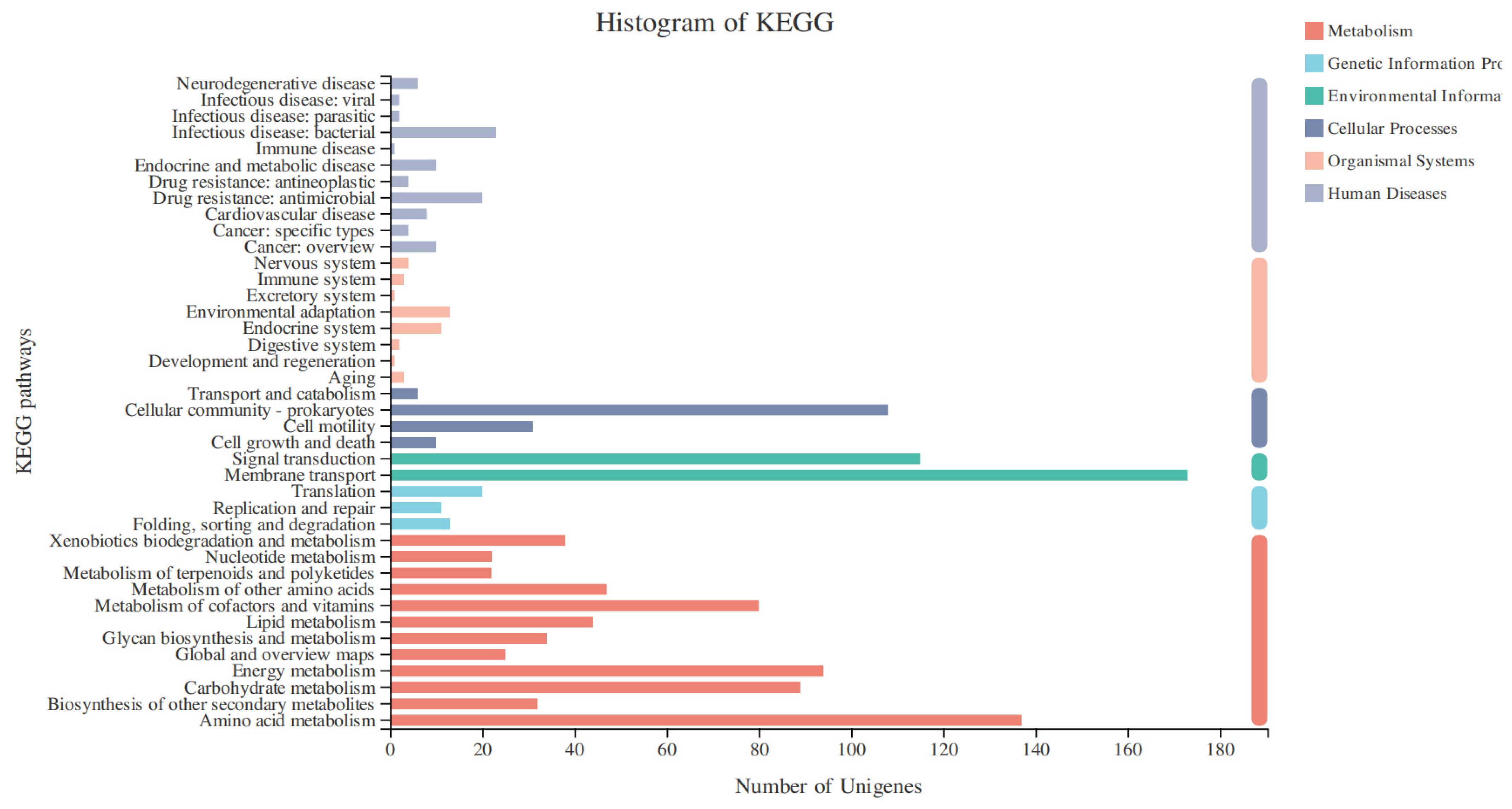
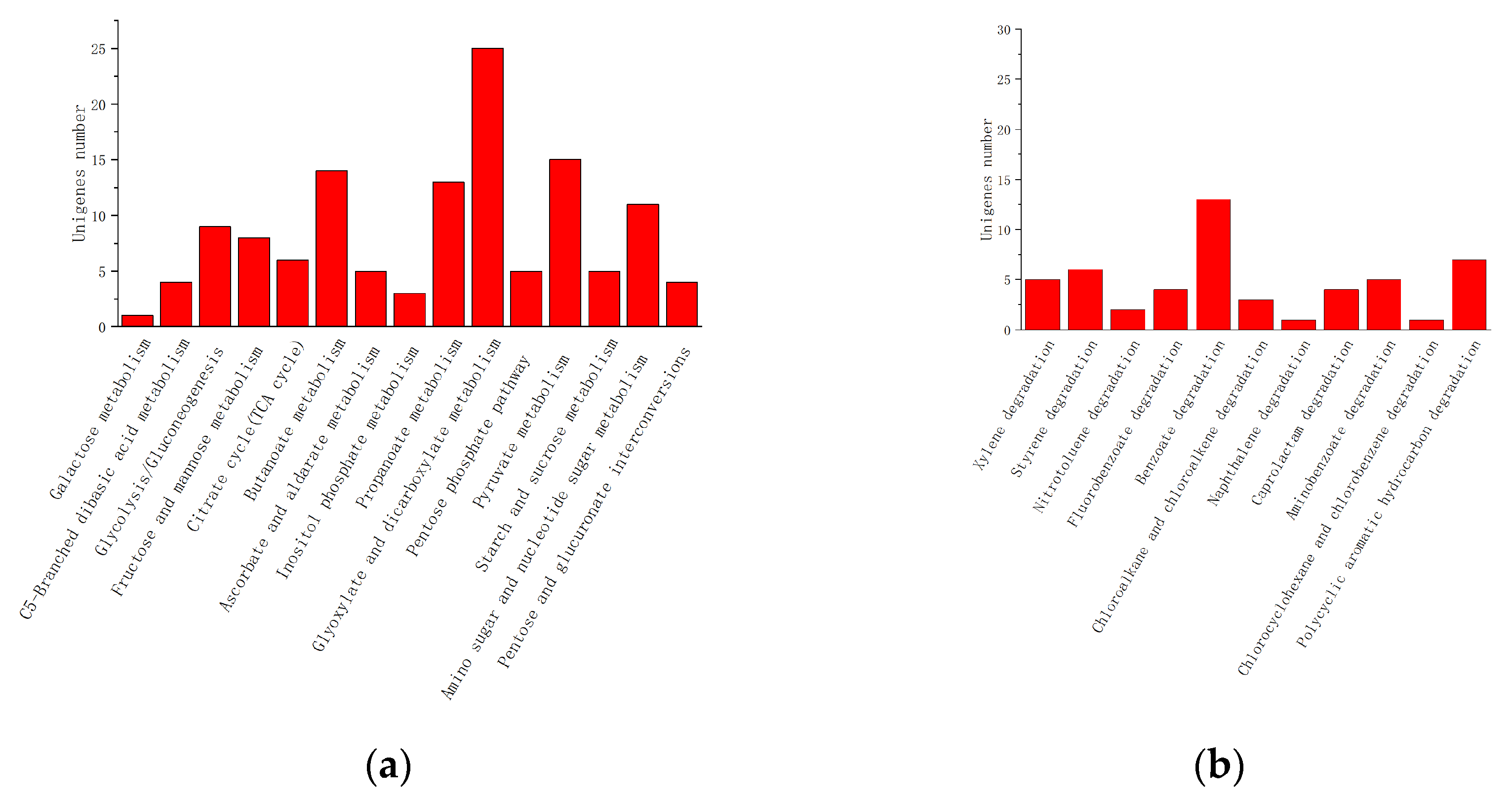
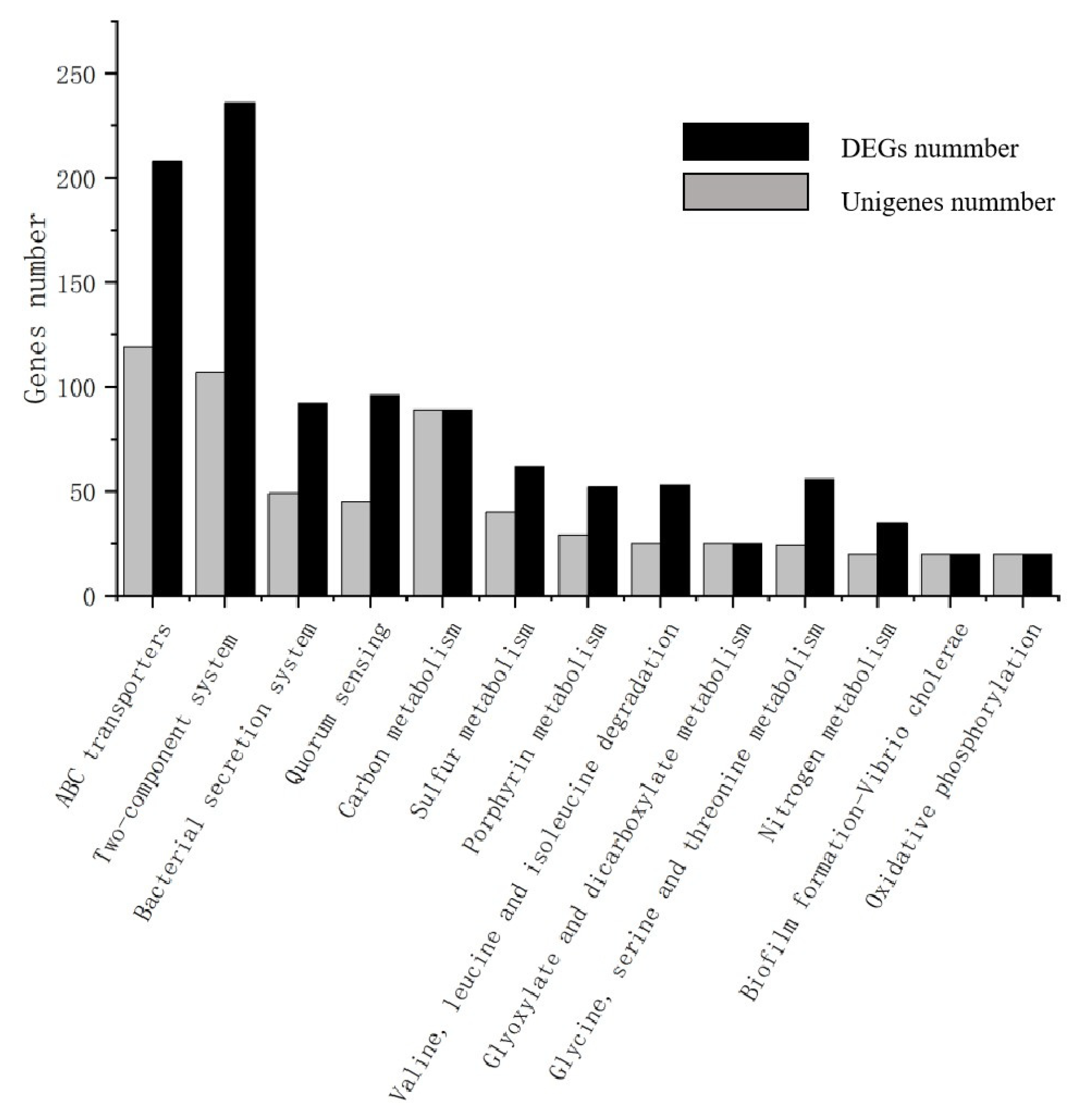
| Glucose | Naphthalene | |
|---|---|---|
| Total reads | 8,905,770 | 11,130,466 |
| Genome mapped reads | 8,458,394 | 10,604,094 |
| Genome mapped ratio (%) | 94.98% | 95.27% |
| Unique mapped reads | 8,146,305 | 10,339,297 |
| Unique mapped reads ratio (%) | 91.47% | 92.89% |
| Function | Gene Name/ID | Description | log2FC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dehydrogenase | PA5020 | acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.438767457 |
| PA3427 | short-chain dehydrogenase | 2.794084994 | |
| PA3277 | short-chain dehydrogenase | 2.954645971 | |
| PA2550 | acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 2.830526555 | |
| PA1828 | short-chain dehydrogenase | 1.811890265 | |
| PA1649 | short-chain dehydrogenase | 1.480148338 | |
| PA0507 | acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.248184246 | |
| ABC transporter | PA4502 | ABC transporter | 1.012813583 |
| PA4505 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 1.243181403 | |
| PA4506 | peptide ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 1.522150457 | |
| PA1809 | ABC transporter permease | 1.19286622 | |
| Oxygenase | PA2418 | quercetin 2,3-dioxygenase | 1.721872237 |
| hemO | heme oxygenase | 0.201583681 | |
| PA0817 | ring-cleaving dioxygenase | 1.119065597 | |
| tauD | taurine dioxygenase | 0.21071465 | |
| PA2024 | ring-cleaving dioxygenase | 0.664658298 | |
| pobA | 4-hydroxybenzoate 3-monooxygenase | 1.474047973 | |
| hpaA | 4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase large subunit | 1.402494712 | |
| Transferase | PA1185 | glutathione S-transferase | 1.448512881 |
| accD | acetyl-CoA carboxylase carboxyltransferase subunit beta | 0.670339435 | |
| PA4351 | acyltransferase | 1.769503856 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Han, L.; Yang, J.; Kang, L.; Tang, L.; Qian, T. Naphthalene Enhances Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Biodegradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Soil and Water: Effect and Mechanism. Water 2024, 16, 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172537
Li B, Liu H, Liu X, Han L, Yang J, Kang L, Tang L, Qian T. Naphthalene Enhances Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Biodegradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Soil and Water: Effect and Mechanism. Water. 2024; 16(17):2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172537
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bo, Hulong Liu, Xiaona Liu, Li Han, Jing Yang, Lingke Kang, Liuyuan Tang, and Tianwei Qian. 2024. "Naphthalene Enhances Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Biodegradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Soil and Water: Effect and Mechanism" Water 16, no. 17: 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172537
APA StyleLi, B., Liu, H., Liu, X., Han, L., Yang, J., Kang, L., Tang, L., & Qian, T. (2024). Naphthalene Enhances Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Biodegradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Soil and Water: Effect and Mechanism. Water, 16(17), 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172537





