A Hydrological and Hydrochemical Study of the Gudiyalchay River: Understanding Groundwater–River Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
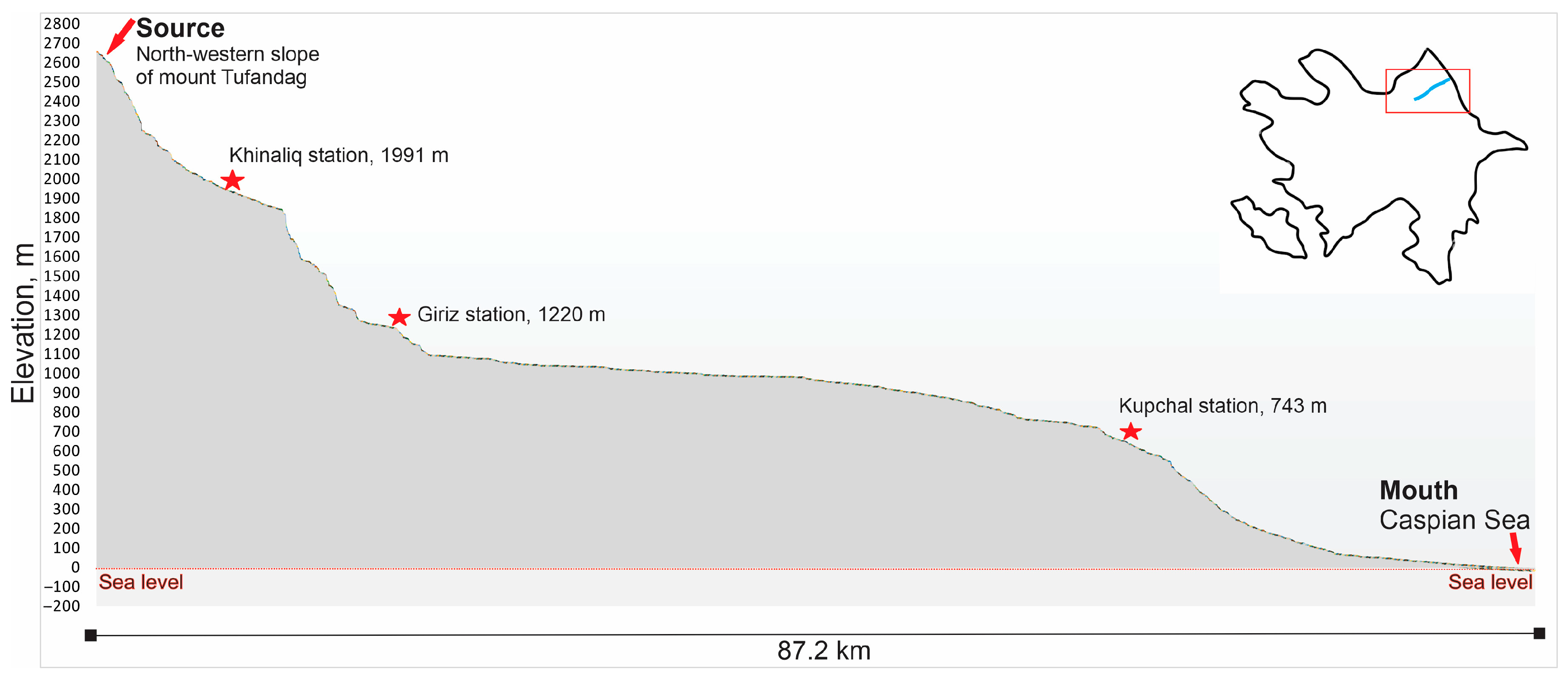
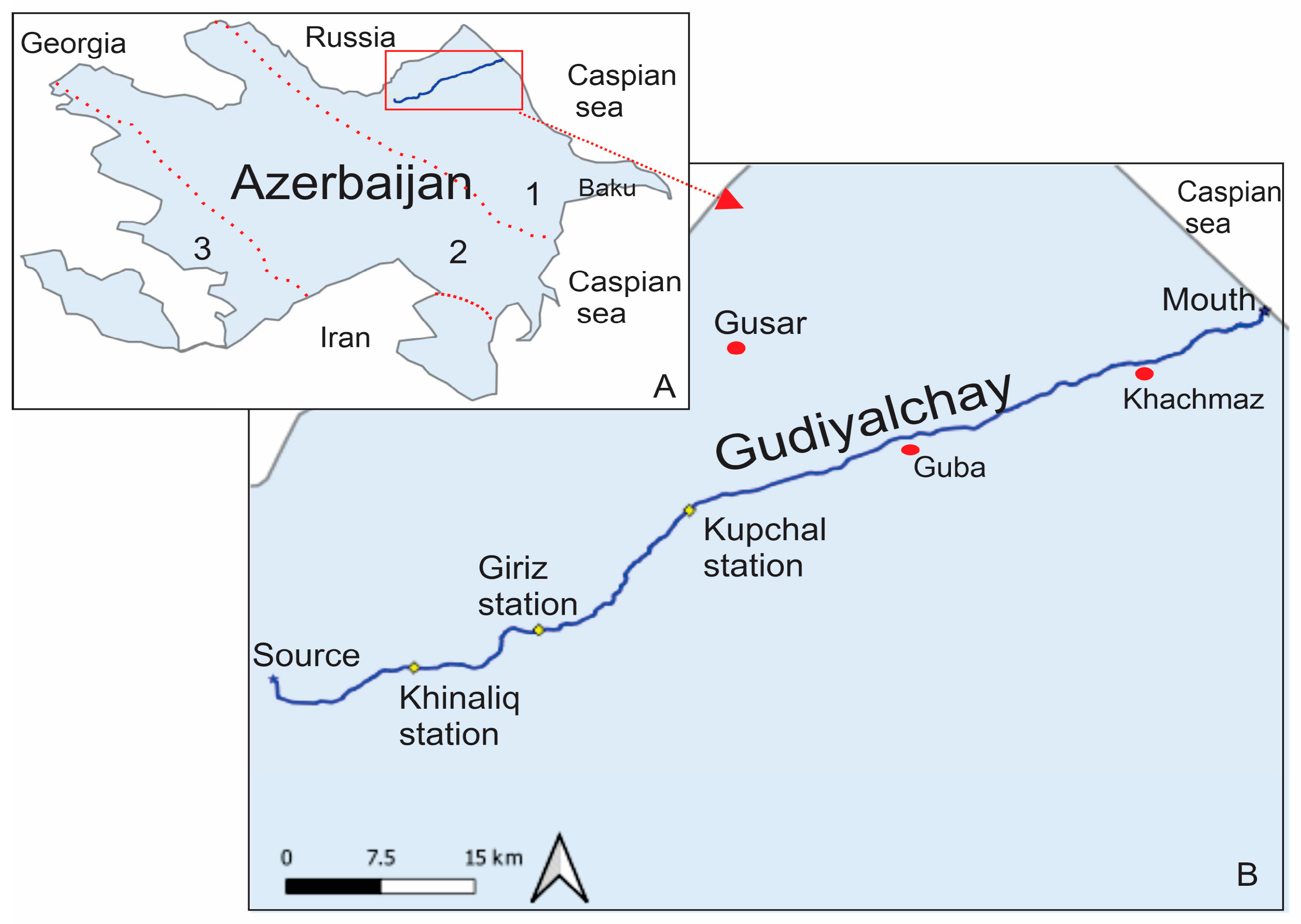
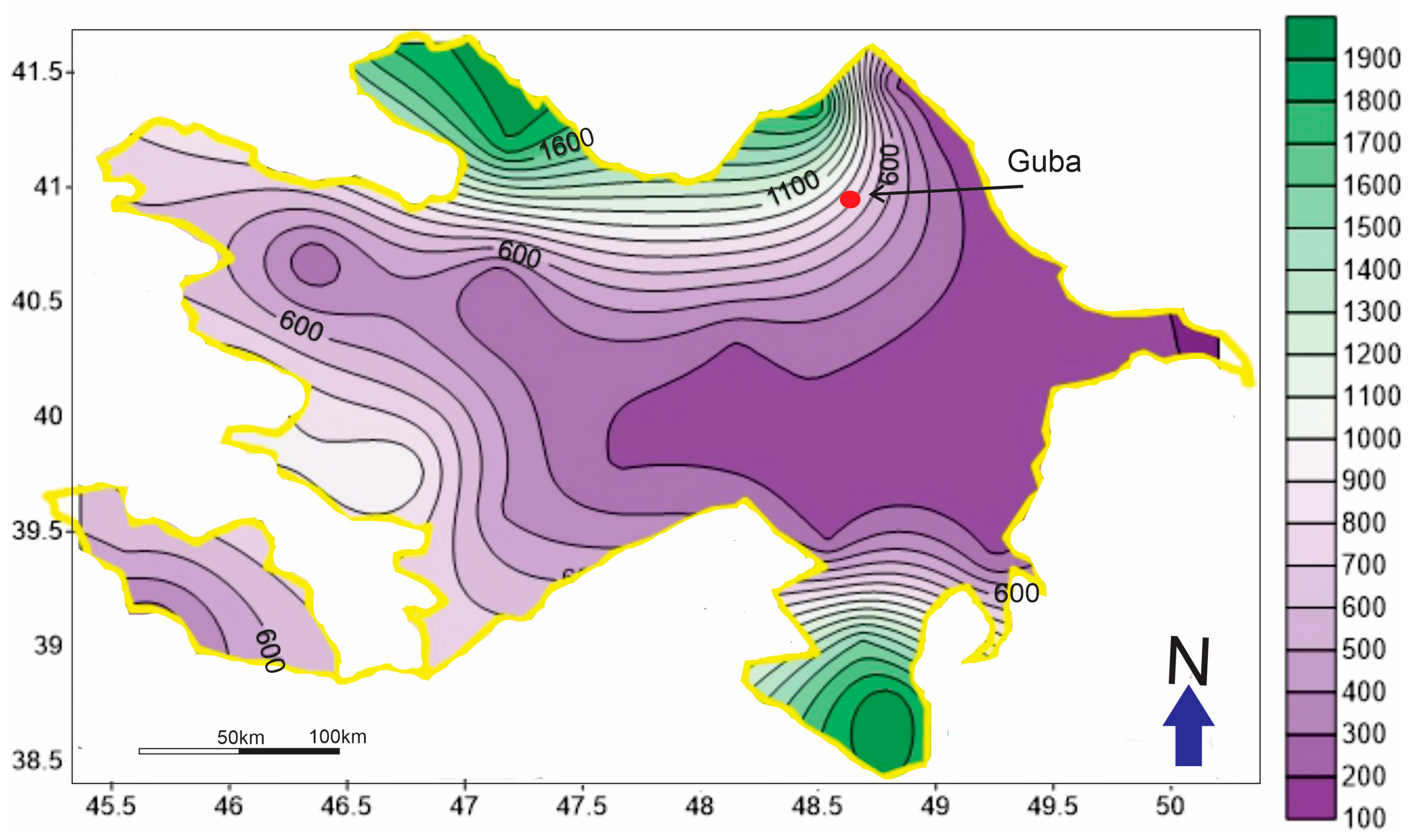
2.1. Gudiyalchay River
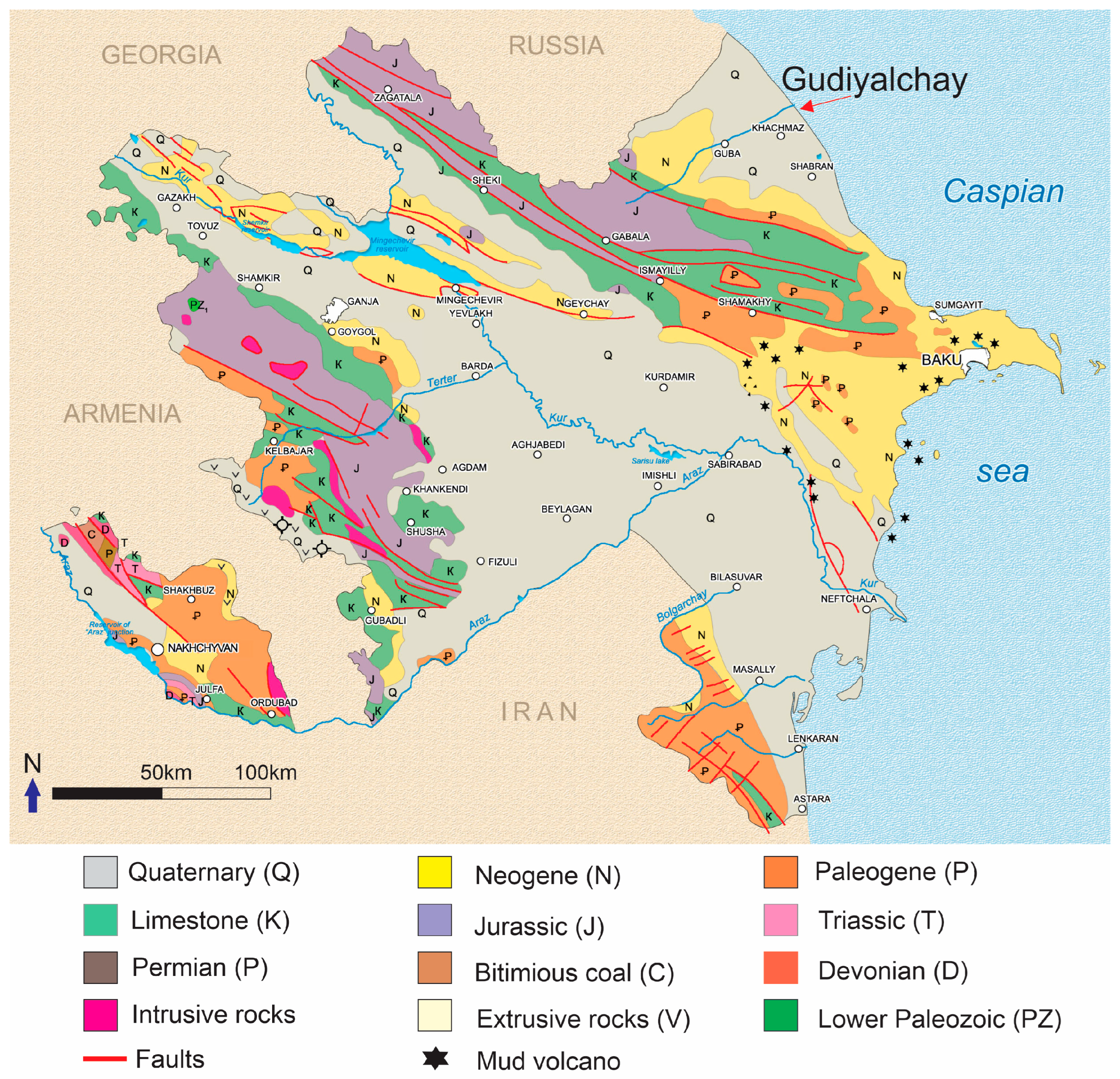
2.2. Geology
- Sedimentary Rocks: These rocks form much of the mountainous terrain. Sandstone, shale, and conglomerates are also present, deposited in environments from deep marine settings to river deltas and floodplains.
- Metamorphic Rocks: Due to intense tectonic activity and the collision between the Arabian and Eurasian plates, original sedimentary and igneous rocks have transformed into metamorphic rocks. In the Azerbaijani part of the Greater Caucasus, schist, slate, and marble are common examples.
- Igneous Rocks: The region contains both intrusive igneous rocks like granite and diorite and extrusive rocks like basalt. These indicate volcanic activity and magma intrusion during mountain-building processes.
- Volcanic Rocks: Evidence of past volcanic activity includes volcanic rocks such as tuffs and volcanic breccias, remnants of eruptions that shaped the landscape.
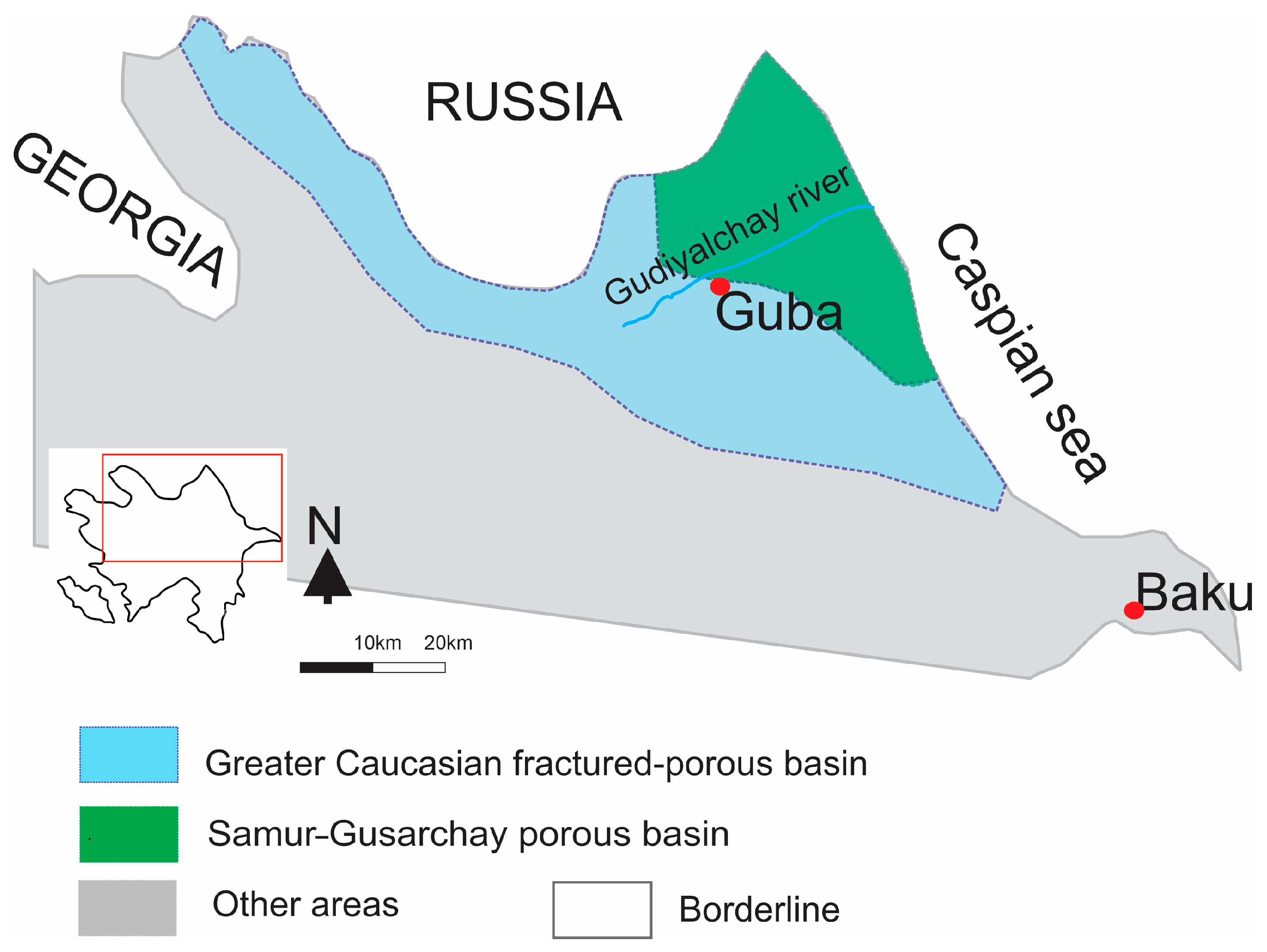
2.3. Hydrogeology
- Greater Caucasian fractured-porous basin;
- Samur–Gusarchay porous water basin.
2.4. Climate
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Methods
4. Results
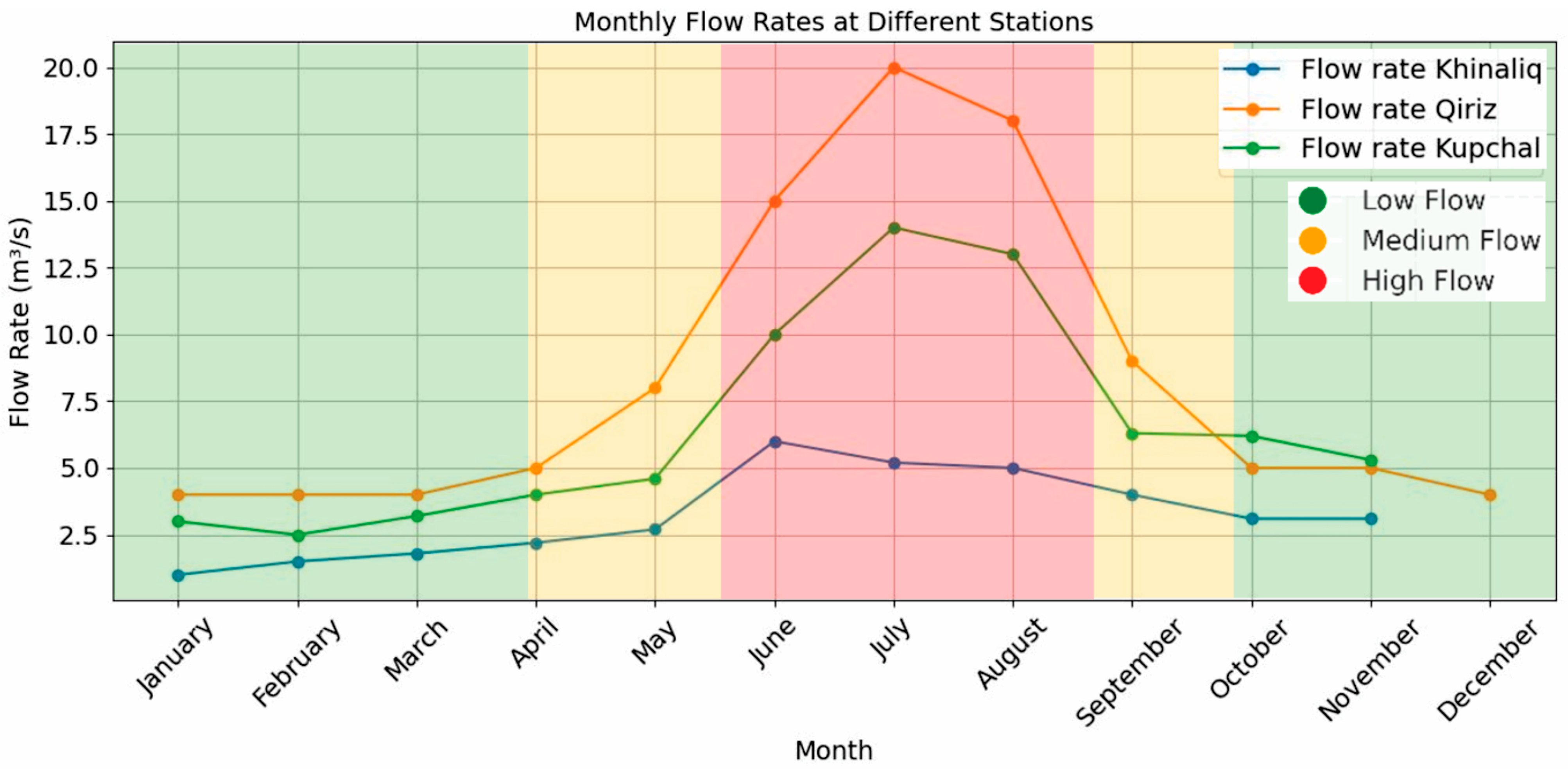
4.1. Flow Rate Analysis
Flow Rate Variations with Elevation Change
- Evaporation: A wider river surface increases exposure to sunlight and wind, potentially leading to higher rates of evaporation.
- Infiltration: A broader riverbed enhances the interaction between surface water and the surrounding groundwater system. The widened channel may also facilitate more groundwater discharge zones, where river water percolates into the groundwater system.
- Water Extraction: The lower parts of the Gudiyalchay River include agricultural areas, leading to substantial water extraction for irrigation, domestic, and industrial uses, which further impacts the flow. İmanov F.A. and Ələkbərov A.B. [13] note that since 1948, a small arch above the Gudiyalchay–Kupchal station has been diverting an average of 0.30 m3/s of water per month from the river. The calculations by İmanov F.A. and Ələkbərov A.B. [13] show that the average flow rate at Kupchal station from 1991 to 2010 decreased by 0.58 m3/s compared to the average flow rate from 1950 to 1990, due to anthropogenic activities.
4.2. Hydrochemical Characteristics
5. Discussion
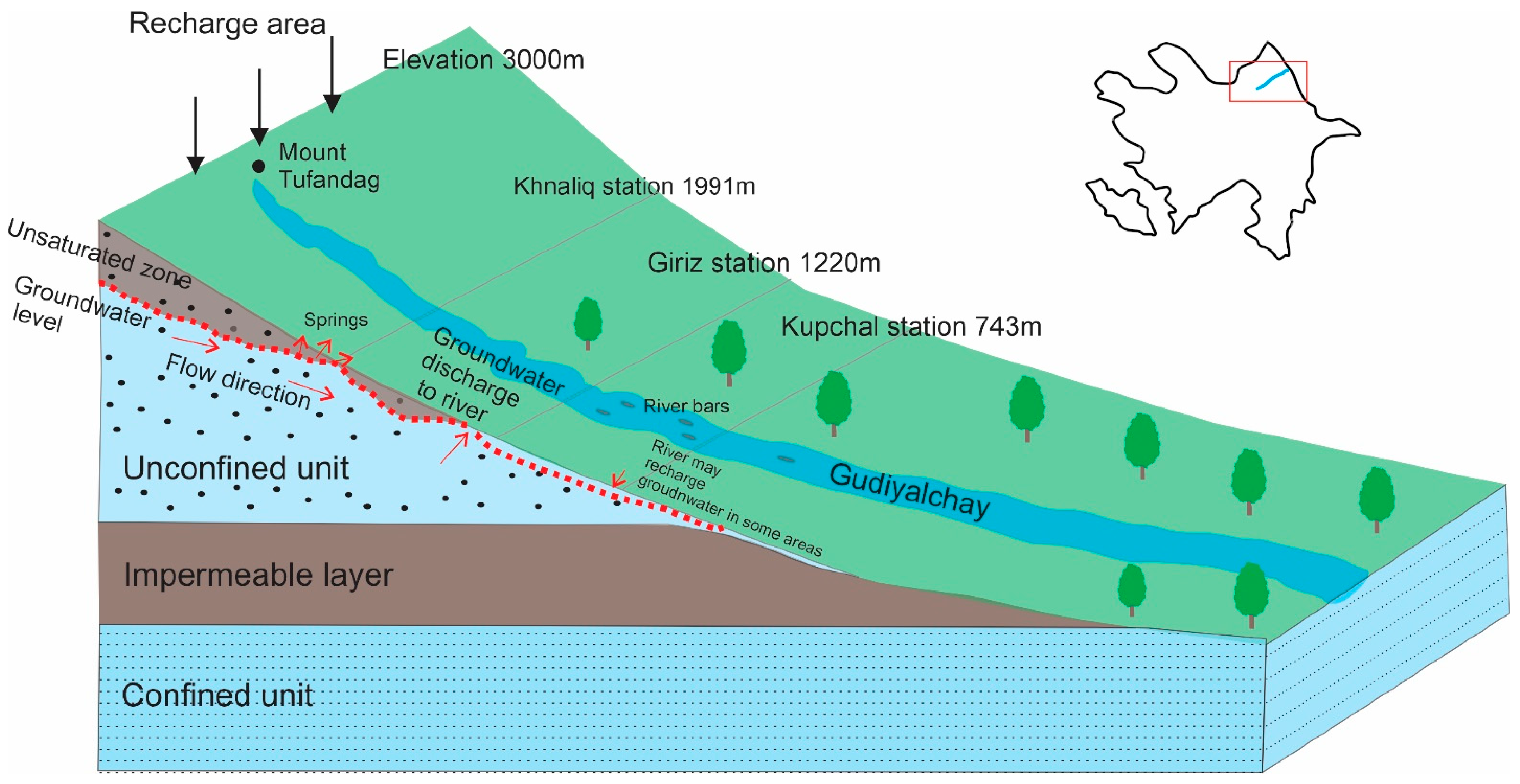
- Flow Formation Zone: This zone is primarily located in the mountainous areas where river catchments originate. Groundwater forms and discharges in this zone, often emerging as springs that feed the rivers. The number and discharge of springs typically increase with elevation up to a certain height.
- High Mountain Areas (>2500 m)—Source of Gudiyalchay River: These areas have rocky, poorly permeable ground and steep valley slopes, promoting surface runoff. Groundwater formation here uses about 15% of atmospheric precipitation. Springs are rare.
- Mid-Mountain Areas (1000–2500 m): These are the areas where the Khinaliq and Giriz stations are located. These areas have gentler slopes and widespread sediments, which favor groundwater formation. Most springs are found here, and their flow patterns follow a delayed response to precipitation.
- Low Mountain and Foothill Areas (500–1000 m)—Areas near the Kupchal Station: These areas transition from denudation to accumulation forms. Rivers flow through wide valleys of alluvial sediments, where collected groundwater feeds the rivers throughout the year. Precipitation is lower, leading to fewer and smaller springs.
- Transit Zone—Elevations after the Kupchal Station: In the central parts of river alluvial fans, groundwater flows between different layers. The unconfined water layers, thickest at their source, thin out as they move downward, while confined layers increase in thickness.
- Discharge Zone: This zone is located in the foothills and plains where the natural flow regime is disrupted. Here, the river’s flow decreases as water is absorbed into the ground, forming springs at the edges of alluvial fans. In the summer, groundwater levels drop, causing many springs to dry up.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mammadova, L.; Negri, S. Understanding the impacts of overexploitation on the Salento aquifer: A comprehensive review through well data analysis. Sustain. Futures 2024, 7, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ələkbərov, A.B.; Imanov, F.A. Azərbaycanın su ehtiyyatları: Problemlər, Yanaşmalar, Realliqlar. Water Probl. Sci. Technol. 2016, UOT551.493, 15–25. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Tahirov, R.; Zeynalova, M. Azərbaycanın su resurlarının mühafizəsi. J. Metaphys. 2021, 4, 101–109. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Humbatova, S.I.; Hajiyev, N.G.O. Ecological agriculture and land resources in Azerbaijan. Econ. Soc. Dev. Book Proc. 2020, 2, 242–256. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Azerbaijan. Su Resursları. Available online: https://eco.gov.az/az/melumat-merkezi/kitabxana (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Alakbarov, A.B.; Groundwater of Azerbaijan. Dutch Portal to International Hydrology. Available online: https://www.hydrology.nl/images/docs/ihp/groundwater_governance/Groundwater_of_Azerbaijan.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Рустамoв, С.Г.; Кашкай, П.М. Вoдные Ресурсы Азербайджанскoй CCP. Academy of Sciences of the AzSSR, Institute of Geography; Baku, Azerbaijan, 1989; 184p. [Google Scholar]
- Məmmədov, M. Azərbaycanın Hidroqrafiyası, 2nd ed.; Təhsil NPM: Bakı, Azərbaycan, 2012; 254p. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Abduyev, M. Azərbaycanın dağ Çaylarının Hidrokimyəvi Xarakteristikası Coğrafi Qanunauyğunluqları; ADPU: Bakı, Azərbaycan, 2021; 363p. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Azerbaijan Coğrafiya Cəmiyyəti. Azərbaycan Çayları. Available online: https://gsaz.az/articles/view/108/ (accessed on 10 July 2024). (In Azerbaijani).
- Kazimova, S. Azərbaycanda müasir iqlim dəyişmələrinin su ehtiyatlarına təsiri. Lənkəran Dövlət Univ. Nəşrləri. 2018, 1, 137. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Azersu. Bülleten. Available online: https://azersu.az/img/staticPageFile/1583323317iyul-2013az.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- İmanov, F.A.; Ələkbərov, A.B. Azərbaycanın su Ehtiyyatlarının Müasir Dəyişmələri və Inteqrasiyalı Idarə Edilməsi; Mütərcim: Bakı, Azerbaijan, 2017; ISBN 978-9952-283327. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.; Song, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, S. River–Spring Connectivity and Hydrogeochemical Processes in a Karst Water System of Northern China: A Case Study of Jinan Spring Catchment. Water 2024, 16, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yapiyev, V.; Rossi, P.M.; Ala-Aho, P.; Marttila, H. Stable Water Isotopes as an Indicator of Surface Water Intrusion in Shallow Aquifer Wells: A Cold Climate Perspective. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broecker, T.; Teuber, K.; Gollo, V.S.; Nützmann, G.; Lewandowski, J.; Hinkelmann, R. Integral flow modelling approach for surface water-groundwater interactions along a rippled streambed. Water 2019, 11, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petpongpan, C.; Ekkawatpanit, C.; Bailey, R.T.; Kositgittiwong, D. Improving integrated surface water–groundwater modelling with groundwater extraction for water management. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2021, 66, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Ganguly, S. A Review on the Research Advances in Groundwater–Surface Water Interaction with an Overview of the Phenomenon. Water 2023, 15, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, G.; Foglia, L.; Giudici, M.; Mehl, S.; Margiotta, S.; Negri, S.L. Effects of different boundary conditions on the simulation of groundwater flow in a multi-layered coastal aquifer system (Taranto Gulf, southern Italy). Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 2123–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, G.; Giudici, M.; Margiotta, S.; Mazzone, F.; Negri, S. Numerical modeling of the groundwater flow in the fractured and karst aquifer of the Salento peninsula (Southern Italy). Acque Sotter. 2013, 2, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, G.; Giudici, M.; Margiotta, S.; Negri, S. Conceptualization and characterization of a coastal multi-layered aquifer system in the Taranto Gulf (southern Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurrəhmanova, G.C. Qusarçay-Qudiyalçay hövzələrində Landşaft Diferensiasiyasının Çay axınına Təsiri. Coğrafiya Və Təbii Resur. 2018, 1, 42–48. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Geological Survey (USGS). Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS Collection 2 Level-1. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- Həbibov, T. Azərbaycan Geologiyası; Azərbaycan Dövlət Pedaqoji Universiteti, Azərbaycan Respublikası Təhsil Nazirliyi: Bakı, Azərbaycan, 2011; 317p. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Азизбекoв, Х., Ш. Геoлoгия СССР; «Недра» XLVII. Азербайджанская ССР: Мoсква, Russia, 1972; pp. 1–520. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Alizade, A.A. Geology of Azerbaijan II; Institute of Geology and Geophysics: Baku, Azerbaijan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- АлиЗаде, А. Геoлoгия в Азербайджане; Хoзяйственные Минералы; Nafta-Press: Baku, Azerbaijan, 2003; pp. 1–577. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Adamia, S.; Zakariadze, G.; Chkhotua, T.; Sadratze, N.; Tsereteli, N.; Chabukiani, A.; Gventsadze, A. Geology of the Caucasus: A Review. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 20, 489–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azərbaycanın Geoloji Xəritəsi. Available online: https://azerbaijan.az/geological (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Howard, K.; Israfilov, R.; Israfilov, Y.; Griffith, A.; Ismailova, M.; Rashidov, T. Use of groundwater models for managing serious urban water issues in Baku, the capital city of Azerbaijan. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on New Directions in Urban Water Management, Paris, France, 12–14 September 2007; UNESCO: Paris, France. [Google Scholar]
- Eyvazova, Y.M. Böyük Qafqazın Şimal-Şərq Yamacı və Şirvan Çaylarının Ekoloji Axımı; Namizədlik Dissertasiyasının Avtoreferatı: Bakı, Azerbaijan, 2005; 29p. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Alakbarov, A.B. Groundwater quality status and problems of sustainability in Azerbaijan. In XXXVIII IAH Congress: Groundwater Quality Sustainability; University of Silesia Press: Krakow, Poland, 2010; pp. 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Aliyev, F.S.; Askerov, F.S. Sources of groundwater supply to urbanized areas in Azerbaijan: National development of groundwater resources. NATO Sci. Ser. V Earth Environ. Sci. 2006, 74, 59–77. [Google Scholar]
- Alakbarov, A.; Agamirzayev, R.; Alakbarov, P. Geoenvironmental problems in Azerbaijan. Urban groundwater management and sustainability, NATO Sci. Ser. V Earth Environ. Sci. 2006, 74, 39–58. [Google Scholar]
- İmanov, F.; Aliyeva, I.; Nagiyev, S.; Leummens, H. Changes in the annual flow of the Kura River. Geogr. J. Pol. Geogr. Soc. 2023, 94, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudov, R.N. Azərbaycanın su Resurslar; Bakı, Azərbaycan, 2003; 24p. Available online: https://www.azadliq.org/a/su-resurs-quraqliq/31686642.html (accessed on 24 August 2024). (In Azerbaijani).
- İsmayılov, V.M. Böyük Qafqaz Çaylarının Rejim Xüsusiyyətlərinin Coğrafi Qanunauyğunluqları. In Coğrafiya Elmlər Namizədliyi və Alimlik Dərəcəsi Almaq Üçün Təqdim Edilmiş Dissertasiya iş; AMEA: Baku, Azerbaijan, 2009; 167p. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- National Hydrometeorological Service. Yağıntının Miqdarı. Available online: https://meteo.az/index.php?ln=az&pg=226 (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rüstəmov, S.H. Azərbaycan SSR-Nin Çayları və Onların Hidroloji Xüsusiyyətləri; SSR EA Nəşriyyatı: Bakı, Azərbaycan, 1960. (In Azerbaijani) [Google Scholar]
- Huntington, J.L.; Niswonger, R.G. Role of surface-water and groundwater interactions on projected summertime streamflow in snow dominated regions: An integrated modeling approach. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazvimavi, D.; Clarke, S.; Day, J.; Dube, T.; Kanyerere, T.; Machingura, J.; Malijani, E.; Mkunyana, Y.P.; Swartbooi, E. Understanding of Surface Water-Groundwater Interactions from Headwaters to Lowlands for Catchment Scale Sustainable Water Resources Management. Water Res. Comm. 2022, 22, 61. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Part 1: Major Concepts of Ground-Water Hydrology. In Ground Water and Surface Water: A Single Resource; USGS: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski, J.; Meinikmann, K.; Krause, S. Advances in groundwater-surface water interactions: Recent advances and interdisciplinary challenges. Water 2020, 12, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.; Therrien, R.; Renard, P.; Simmons, C.T.; Franssen, H.-J.H. Advances in understanding river-groundwater interactions. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 818–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, L.; Kalin, R.M.; Bertram, D.; Kanjaye, M.; Nkhata, M.; Sibande, H. Quantification of temporal variations in Base Flow Index using sporadic river data: Application to the Bua Catchment, Malawi. Water 2019, 11, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Guo, S.; Tan, L.; Li, T.; Burrows, R.M.; Cai, Q. Temporal effects of groundwater on physical and biotic components of a karst stream. Water 2019, 11, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwegian Water Resources and Energy Directorate (NVE). River Basin Management Plan 2011—River Basin District Vestlandet. Available online: https://publikasjoner.nve.no/report/2011/report2011_05.pdf. (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Engeland, K.; Aano, A.; Steffensen, I.; Støren, E.; Paasche, Ø. New flood frequency estimates for the largest river in Norway based on the combination of short and long time series. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 5595–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aano, A.; Engeland, K. Integrated GIS Analysis for Flood Risk Assessment in Norwegian Rivers: A Case Study of Sokna River 2024. Available online: https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EGU24/EGU24-19378.html (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Alfredsen, K.; Tekle, M.G. Effect of flow ramping on stranding potential related to river morphology—Developing hydraulic indices for peaking severity. River Res. Appl. 2023, 40, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrede, T.I.; Tørudstad, V.; Pons, V.; Alfredsen, K.; Muthanna, T.M. From flood paths to floodways, an efficient method to map, identify and evaluate suitable floodways: A case study from Trondheim, Norway. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 346, 118672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Station | Ca (Cation) mg/L | Mg (Cation) mg/L | Na+K (Cation) mg/L | HCO3 (Anion) mg/L | SO4 (Anion) mg/L | Cl (Anion) mg/L | TDS mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khinaliq | 38.2 | 13.9 | 15.2 | 130.2 | 68.5 | 3.7 | 271 |
| Giriz | 48.7 | 13.6 | 16.5 | 154.3 | 74.8 | 4.2 | 312 |
| Kupchal | 49.7 | 18.3 | 19.2 | 164.4 | 76.6 | 4.3 | 328 |
| Maximum acceptable limit | 150 | 50 | 200 | 400 | 250 | 250 | 1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mammadova, L.; Negri, S.; Tahmazova, M.-K.; Mammadov, V. A Hydrological and Hydrochemical Study of the Gudiyalchay River: Understanding Groundwater–River Interactions. Water 2024, 16, 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172480
Mammadova L, Negri S, Tahmazova M-K, Mammadov V. A Hydrological and Hydrochemical Study of the Gudiyalchay River: Understanding Groundwater–River Interactions. Water. 2024; 16(17):2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172480
Chicago/Turabian StyleMammadova, Lala, Sergio Negri, Malak-Khanim Tahmazova, and Vagif Mammadov. 2024. "A Hydrological and Hydrochemical Study of the Gudiyalchay River: Understanding Groundwater–River Interactions" Water 16, no. 17: 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172480
APA StyleMammadova, L., Negri, S., Tahmazova, M.-K., & Mammadov, V. (2024). A Hydrological and Hydrochemical Study of the Gudiyalchay River: Understanding Groundwater–River Interactions. Water, 16(17), 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172480





