Abstract
The aim of the article is to assess the level of aliphatic hydrocarbon (AHC) contamination in bottom sediments of the Azov–Black Sea coast of the Crimea, as well as to identify potential sources of its formation. Bottom sediment samples obtained from 19 stations during the research cruise of the R/V “Professor Vodyanitsky” (June 2020) were used as the material for this investigation. Sampling stations were located along the coast of the Crimean Peninsula and the Caucasus coastlines (the Black and Azov Seas). N-hexane extracts of sediments were studied by gas chromatography to determine the AHC amount and composition. It was established that AHC concentrations in the study area varied from 1.30 to 127.8 mg/100 g. Generally, bottom sediments of the Black and Azov Seas were characterized by low AHC contents, while increased AHC contents were found in the outer harbor of Sevastopol and Yalta regions. To identify potential hydrocarbon sources, various hydrocarbon markers were used. In most of the study areas, n-alkane composition was determined by similar sources of inputs and organic compound transformation. At the same time, oil pollution linked with use of fuel was recorded almost everywhere.
1. Introduction
Most coastal areas of economically developed regions are characterized by high population densities, growing urbanization, and an increasing diversity of human activities both in the mainland and offshore. Since economic interests often prevail over environmental concerns, the state of coastal ecosystems is defined not so much by the scale of activities as by the ever-increasing intensity of anthropogenic impacts on marine areas. Sources of pollutants entering the coastal waters are numerous and different, but taking into account that oil and oil products are nowadays in widespread use, the problem of oil contamination remains a serious and global issue, requiring regular environmental monitoring. While many hydrocarbons are synthesized by organisms and are commonly present in the biosphere, a significant proportion of them originate from sources associated with human activities as well as natural petroleum seepage [1,2,3].
Ongoing studies on the qualitative and quantitative composition of hydrocarbons (HCs) in bottom sediments are a prerequisite for controlling marine environment quality and organizing protection of coastal water areas, as bottom sediments are the ultimate reservoir for natural and anthropogenic organic compounds coming from the water column and various coastal pollution sources [4,5,6].
Hydrophobic properties of HCs facilitate their adsorption by solid particles and accumulation in different fractions of bottom sediments. Aliphatic hydrocarbons (AHCs) that are the components of crude oil [7,8,9,10] are widely used to calculate geochemical markers, and may indicate oil contamination [5,11]. Numerous studies [1,5,6,7,11,12,13] provide information on AHC genesis from a variety of allochthonous and autochthonous sources (biogenic genesis) due to the biosynthesis of higher plants, some algae and bacteria. Also, there is a number of AHCs entering the hydrosphere as a result of anthropogenic impacts involving offshore oil and gas exploration, emergency spills, river runoffs and waste incineration, municipal and industrial discharges, offshore petroleum exploration and production activities [1,3,12,13,14,15]. It has been shown that the analysis of individual n-alkanes allows for an explanation of the sources of their inputs in bottom sediments, and is considered an active tool for estimating the biogenic as well as anthropogenic origin of organic substances or natural petroleum seepage [3,16,17].
Bottom sediments with high concentrations of AHCs may serve as a source of secondary pollution having an adverse impact on the marine environment [18,19]. Owing to the diversity of AHC sources entering the sea, researchers use various indices and ratios that allow them to differentiate between the sources of hydrocarbon inputs and evaluate their environmental effects [18,20,21]. These indices (markers) are based on the distribution of n-alkanes in hydrocarbon mixtures from various sources. For example, the prevalence of odd-numbered compounds over even-numbered ones shows the increased role of plants in the formation of hydrocarbons. Contrastingly, the predominance of even-numbered compounds over odd-numbered ones demonstrates transformed organic matter and the presence of oil hydrocarbons (OHs) [20].
Among the tools often used to assess the hydrocarbon sources is the Carbon Preference Index (CPI). It is a numerical representation of the predominance of odd-numbered over even-numbered n-alkanes in aliphatic hydrocarbons over a specified range of carbon numbers [22]. The amount of chromatographically unresolved complex mixture (UCM) is of importance to determine the source of the HCs. The UCM is a complex mixture commonly associated with the OH distribution that is not distinguished by gas chromatographic analysis, and is described as a “hump” on the chromatogram [23]. The ratio of terrigenous and aquatic hydrocarbons (TARs) [24] contributes to determining the major source of the hydrocarbons, namely allochthonous or autochthonous.
Thus, the aim of the article is to assess the level of AHC contamination in the bottom sediments of the Azov–Black Sea coast of the Crimea, as well as to identify potential sources of its formation.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sampling
Samples of bottom sediments obtained by a box corer during the 113th cruise of the R/V “Professor Vodyanitsky” (June 2020) along a given grid of stations were used as the material for this study (Figure 1). Sampling stations were located along the coast of the Crimean Peninsula and the Caucasus coastlines (the Black and Azov Seas). Their numbering was retained in accordance with the cruise report.
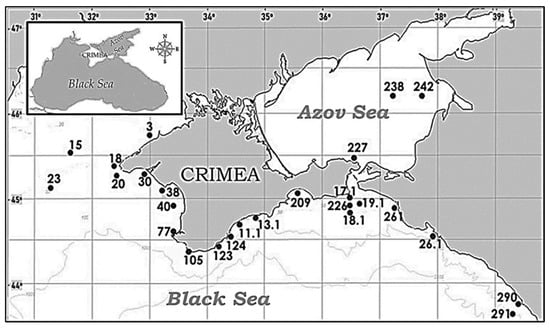
Figure 1.
Map of sea bottom sediment sampling (113th cruise of the R/V “Professor Vodyanitsky”, June 2020).
The depth at the bottom sediments’ sampling stations off the Crimean coast in the Black Sea was 15–82 m, that of the Caucasian coast was 115–1300 m and that of the Azov Sea was 5–12 m. All samples were packed in special containers and labeled. The total number of operated stations (st.) was as follows (Figure 1): in the Black Sea Crimean area—19 st. (st. 3, 15, 23, 18, 20, 30, 38, 40, 77 at western Crimean coast and st. 105, 123, 124, 11.1, 13.1, 209, 226, 17.1, 18.1, 19.1 at eastern Crimean coast); the Black Sea Caucasian zone—4 st. (st. 261, 26.1, 290, 291); and the Azov Sea waters—3 st. (st. 227, 238, 242). Samples of bottom sediment were lifted on the vessel board using a dredger. On the deck, without removing the whole sample from the dredger, three samples of bottom sediment (layer 0–5 cm) were collected in different surface areas of the total sample using a 5 cm diameter tube for chemical analysis. The tube collection was carried out under visual control in order to avoid large bottom-dwelling organisms, shells and other objects entering the sample. In the laboratory, bottom sediments were dried to an air-dry condition, ground in an inert mortar and sifted through sieves with a cell diameter of 0.25 mm for further determination of hydrocarbon concentrations.
2.2. Chemical Analysis
Sample preparation and analyses were carried out according to [25]. Bottom sediment samples used for analyses were air-dried to an air-dry condition at room temperature (in the absence of sunlight); following this, the fraction with a particle diameter of 1 mm was sieved off.
To calculate the hydrocarbon content per 1 g of dry bottom sediment, it was important to determine the mass fraction of the dry residue. Simultaneously, as the sample was taken, the same sample of bottom sediments in the amount of 1–2 g was dried to a constant weight in a heating oven at a temperature 110 °C and afterwards held in a desiccator. The moisture of bottom sediments was determined using the formula Kmois. = Pdry/Pmois., where Pmois. is the wet weight of the test sample in grams and Pdry is the weight of the test sample dried to a constant weight in grams.
The sample for analyses (5–7 g) was extracted with 150 mL of n-hexane in a Soxhlet apparatus for 1 h. The extract was sedimented for 10 min and poured through a funnel with a paper filter into a clean conical flask. The resulting extract was purified in a glass column for liquid chromatography (15 cm × 1 cm) with the bottom end pulled back and filled with aluminum oxide (to remove polar compounds). Aluminum oxide (the second degree of activity for “chromatography”) was calcined in a muffle furnace at a temperature of 600 °C for 3 h, and after adsorbent cooling, it was placed in a glass flask with a lapped rim, with 4% of the adsorbent weight in distilled water added; the flask was shaken for 1–2 min. Aluminum oxide treated in this way was used in a day.
After passing the extract through the aluminum oxide column, it was dried with anhydrous sodium sulphate. The hexane extract was concentrated to a volume of 1 mL using a vertical rotary evaporator. An aliquot part of the concentrated extract (1 µL) was injected with a microsyringe into the “Cristall 5000.2” gas chromatograph evaporator (“Chromatek”, Yoshkar-Ola, Russia) heated to 250 °C with a flame ionization detector (FID).
The hydrocarbons were separated in a TR-1MS 30 × 0.32 mm capillary column with a fixed stationary phase thickness of 0.25 µm (“Thermo Fisher Scientific”, Waltham, MA, USA). The column temperature was programmed from 70 °C to 280 °C (rate of temperature rise 8 °C /min). Carrier gas flow (nitrogen) in the column was 2.5 mL/min without flow division. Detector temperature was 320 °C. Standard samples of a mixture of paraffinic hydrocarbons (C8–C40) and pristane plus phytane in hexane were used to identify n-alkanes (“Supelco”, Bellefonte, PA, USA). The gas chromatographic study was conducted on the base of the scientific and educational center for collective use “Spectrometry and chromatography” of IBSS.
2.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Quantitative determination of the total content of oil hydrocarbons (oil products) was carried out by absolute calibration of FID with a hydrocarbon mixture that was prepared gravimetrically with a content in the range of 0.1–5.0 mg/mL. A standard sample ASTM D2887 Reference Gas Oil Sample 1, Lot 2, analytical standard, pkg of 6 × 1 mL SUPELCO 48873 was used as a hydrocarbon mixture.
Quantitative calculation of the chromatograms was performed using ChromatecAnalyst 3.0 software. The total area of peaks relative to the baseline in the range of retention from C17 to C40 was determined on the chromatograms. Based on the processed data, the calibration dependence of the peak areas of the calibration solutions on the concentration of oil products in these solutions was determined. The linear correlation coefficient (R2) was not less than 0.97.
Stability control of the chromatograph calibration was performed before each series of sample measurements using control solutions of the standard sample. If the series contained more than ten test samples, the stability was checked after every ten samples.
A method blanks analysis (n = 5) was conducted, and AHC concentrations were found to be below the respective limits of quantification (LOQ). The limits of detection (LOD) were calculated as the quotient of three times the standard deviation of the linear coefficient of the calibration line and the slope of the curve, while the LOQ values were estimated as 3 × LOD. For AHCs, the LOD and LOQ values were 0.09–0.27 μg/g and 0.27–0.81 μg/g, respectively.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The standard error of the mean was determined using Excel’s parquet analysis at a reliability level of 0.95. Pearson correlation coefficients (pv < 0.05) between the variables (AHC, OH, CES, n-alkanes) were calculated.
A scope diagram was used to identify outliers from the statistical sampling. Two ends of the box represent the first and the third quartiles of all data points. Two ends of each panel represent the minimum and the maximum values ignoring outliers.
The sampling stations were grouped according to the content and composition of n-alkanes using tree clustering and the Euclidean distance as a measure.
The method of principal components, allowing the most efficient analysis of multivariate systems, was used to analyze multivariate data. During the principal component analysis (PCA), the data were pre-standardized using a Z-transformation procedure. The PCA model was tested for suitability using the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) criterion, a value that characterizes the degree of applicability of factor analysis to a given sample. The KMO test was conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics. This method was applied to determine (relatively quantitatively) the main sources of AHCs in water at various sampling stations. The analysis was performed using the Varimax rotation method. The number of principal components was determined using Scree test [26].
The data were processed using the Microsoft Excel and Statistica 12 software packages.
2.5. Identification of Potential Sources of AHCs
Hydrocarbon markers are used to identify the potential sources of aliphatic hydrocarbons. In particular, the following were used to differentiate the oil and biogenic genesis of the detected AHCs:
- -
- UCM/R is the ratio of the unresolved complex mixture to the aliphatic fraction of hydrocarbons [27,28];
- -
- Average chain length (ACL) [29,30] ACL = (27·C27 + 29·C29 + 31·C31 + 33·C33 + 35·C35 + 37·C37)/C27 + C29 + C31 + C33 + C35 + C37);
- -
- Ratio between low-molecular-weight and high-molecular-weight homologues (low molecular weight to high molecular weight, LWH/HWH) [31,32] LWH/HWH = ∑C21−/∑C22+;
- -
- Carbon Preference Index (CPI), in particular CPI2, calculated for the high molecular weight part of the spectrum [33,34] CPI2 = (1/2){(C25 + C27 + C29 + C31 + C33 + C35)/(C24 + C26 + C28 + C30 + C32 + C34) + (C25 + C27 + C29 + C31 + C33 + C35)/(C26 + C28 + C30 + C32 + C34 + C36)}.
Individual biomarkers allow for clarification of the biogenic component of compounds, in particular, evaluating the contribution of autochthonous and allochthonous substances and herbaceous and woody vegetation to the formation of the allochthonous component of AHCs entering bottom sediments.
- -
- TAR index (terrigenous/aquatic ratio), that is, the ratio of terrigenous and autochthonous compounds, serves to differentiate the allochthonous and autochthonous origin of hydrocarbons [24] TAR = ∑C27+29+31/∑C15+17+19;
- -
- C31/C19—reflects the ratio of terrigenous and marine n-alkanes [35];
- -
- C31/C29—reflects the ratio of the contribution of herbaceous and woody vegetation to the formation of the terrigenous part of organic matter [12,36,37].
3. Results
Bottom sediments were represented mainly by dark gray silty sediment with an admixture of shell rock and sand. A faint smelt of hydrogen sulfide was registered in the bottom sediments of some stations. These are the silts that largely accumulate both natural organic matter and compounds of anthropogenic origin.
In the research areas, AHC concentrations varied from 1.30 to 127.8 mg/100 g with an average value of 38.9 ± 5.1 mg/100 g (Figure 2). In the western part of the Black Sea Crimean coast, the frequency of cases of concentrations exceeding the average values (63%) was higher compared to the eastern part of the Black Sea Crimean coast (27%). In the Sea of Azov, the excess of the average values was 33%, which corresponded to the western part of the Black Sea Crimean coast.
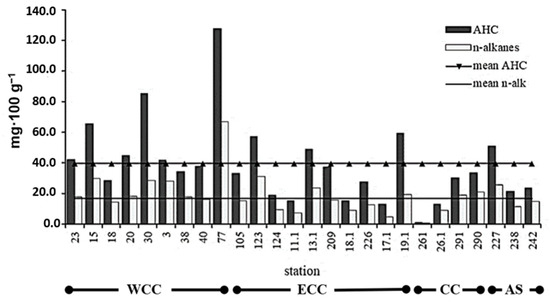
Figure 2.
The concentrations of aliphatic hydrocarbons (AHCs) and n-alkanes in bottom sediments of the Black and Azov Seas (113th cruise of the R/V “Professor Vodyanitsky”, June 2020). WCC—Black Sea western Crimean coast, ECC—Black Sea eastern Crimean coast, CC—Black Sea Caucasian coast, AS—the Azov Sea.
The contents of n-alkanes in bottom sediments of the Crimean coast varied from 0.9 to 67.0 mg/100 g with an average value 18.9 ± 2.5 mg/100 g.
More reliable information regarding AHC origin found in bottom sediments was provided by their composition, as well as the presence of the UCM (Table 1). At most stations in the western waters, n-alkane distribution was bimodal, indicating the presence of different sources of AHC influx into the bottom sediments. Data on the dominant n-alkanes are given in Table 1. The maximum in the low-molecular region predominantly accounted for the autochthonous homologue C17. In the high-molecular field of the spectrum, the maximum of C28 as well as neighboring even homologues (C26, C30) were found almost everywhere. Near the eastern coast, the distribution of n-alkanes was predominantly unimodal with a maximum in the field of high temperature. The dominant peaks were shown at C26, C28 and C30. N-alkanes with a hydrocarbon chain length of more than 30 were recorded in significant quantities (>10%) at stations located along the eastern Crimean shoreline. In other zones, they were sporadic. Distribution of n-alkanes in the Azov Sea at two stations (stations 227 and 238), along with the predominance of high-molecular even compounds, was also characterized by a high content of homologues C22 and C24. Station 242 was the exception, with a pronounced peak of C17. In 4 of 26 sampling stations, the presence of UCM was detected (Table 1).

Table 1.
Contents and characteristics of n-alkane composition in bottom sediments of the Black Sea and the Azov Sea (the results of the 113th cruise of the R/V “Professor Vodyanitsky”, June 2020).
Bottom sediments of the investigated areas of the Black and Azov Seas were characterized by low AHC contents that did not reach the generally accepted norms (50 mg/100 g) [38] at 77% of the sampling stations. At the same time, bottom sediments with AHC content not exceeding 1 mg/100 g would be considered absolutely unpolluted [5]. AHC concentrations in bottom sediments reached these values only at station 261, adjacent to the Caucasus coastline. The literature contains data [39] on the chloroform-extractable substances (CESs) and oil hydrocarbons (OHs) content at the same grid of stations. OH content did not exceed the conditional norms [38] for bottom sediments, and amounted to 21.8 ± 2.6 mg/100 g on average. Thus, as can be seen, the study area was not significantly oil polluted.
The analysis of the mean values of CESs, OHs (calculated on the basis of data from [39]), AHCs and n-alkanes (Figure 3) demonstrated that at station 77 (outer harbor of Sevastopol city) all the above-mentioned indicators increased, which is not typical for the coastal waters of the Black and Azov Seas. However, there were the stations that were distinguished by AHC concentrations exceeding the average: st. 23, st. 15, st. 20, st. 30, st. 3, st. 77, st. 123, st. 13.1, st. 19.1 and st. 227. They were often associated with increased levels of CES and OH [39]. The correlation coefficient between CES and AHC contents was equal to 0.92, and made up 0.51 between OHs and AHCs, which indicated a close relationship between the former components and practically no relationship between the latter components of organic matter. Based on the values of the correlation coefficients, the concentration of AHCs and n-alkanes was determined by the content of CESs rather than by the presence of oil products (pollution that is largely due to anthropogenic factors, such as fuel use) in bottom sediments.
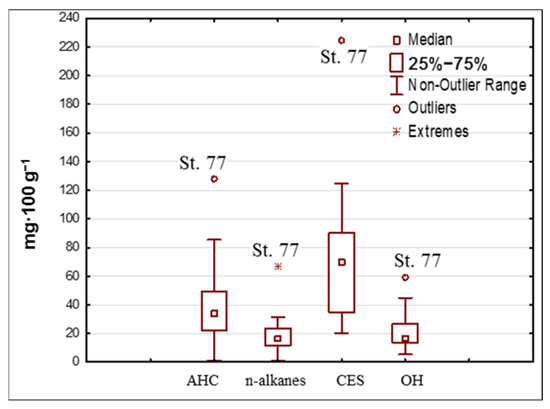
Figure 3.
Analysis of aliphatic hydrocarbons (AHCs), n-alkanes, chloroform-extractable substances (CES) (calculated based on data from [39]) and oil hydrocarbons (OHs) (calculated based on data from [39]) mean concentrations values in bottom sediments of the Black Sea and the Azov Sea (113th cruise of the R/V “Professor Vodyanitsky”, June 2020).
Slightly higher AHC concentrations were registered in the western part (with the exception of st. 77) of the Black Sea compared to the eastern: 46.1 ± 6.0 mg/100 g (comparable to the content in contaminated bottom sediments—50 mg/100 g) versus 28.7 ± 5.1 mg/100 g (Figure 4).
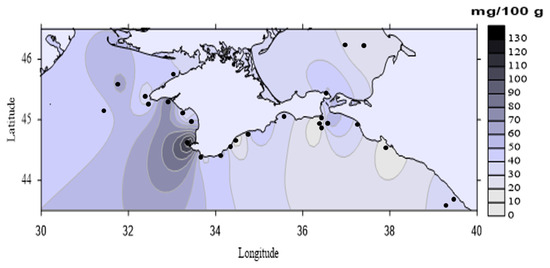
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of aliphatic hydrocarbons in bottom sediments in the coastal waters of the Crimea (the results of the 113th cruise of the R/V “Professor Vodyanitsky”, June 2020).
At stations 77 and 123, the “hump” of the uniform background had smooth outlines, and was shifted to the high-temperature field (Figure 5), which demonstrated its nature as oil [34]. The specificity of the curve with the uniform background at stations 3 and 18.1 (Figure 5) likely indicated the presence of both petrogenic compounds and degradation products of natural organic compounds, in particular plant detritus [28].
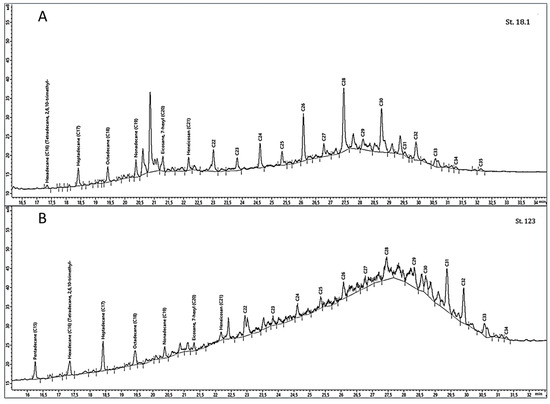
Figure 5.
Typical chromatograms of n-hexane extracts of n-alkanes with the presence of the unresolved complex mixture ((A)—shift of the “hump” to the high-temperature field; (B)—even distribution of the “hump”) in the bottom sediments of the Black Sea and the Azov Sea (the results of the 113th cruise of the R/V “Professor Vodyanitsky”, June 2020).
Before PCA, model adequacy testing was performed using the KMO criterion. It showed acceptable model adequacy (KMO = 0.795 > 0.5), which allows for further discussion. The spatial distribution of stations, the characteristics of which included n-alkane composition, was examined by the principal component method, allowing us to analyze more efficiently the multidimensional systems (Figure 6). As a result, we managed to distinguish two key factors: PC1 (50.53% of variability) and PC2 (18.81%). The first one was closely related (connection with a factor of 0.70 and higher) to almost all n-alkanes. The factor PC2 had a fairly close relationship with compounds C20 and C24, which were often associated with microbial processes.
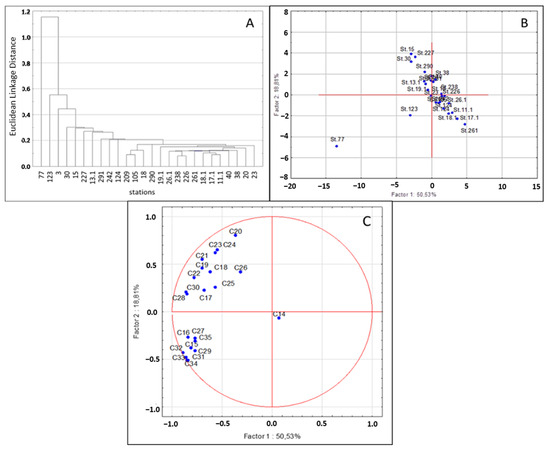
Figure 6.
Results of statistical analysis of the composition of n-alkanes in bottom sediments of the Black and Azov seas (the results of the 113th cruise of the R/V “Professor Vodyanitsky”, June 2020): (A) tree dendrogram of sampling stations; (B) location of sampling stations in factor axes (PCA); (C) factor loadings scheme (PCA).
Sampling locations plotted in axes PC1/PC2 formed a single circle. Only st. 77 and st. 123 exhibited anomalous values. A typical pattern was confirmed by the results of the cluster analysis (Figure 6) showing that station 123 and particularly station 77 had a significant distance from the other grouped stations. Thus, the results of the analysis indicated relatively similar conditions for the accumulation and transformation of n-alkanes in bottom sediments of the coastal waters of the Azov and Black Seas. The exceptions were the sites in the cities of Sevastopol (station 77) and Yalta (station 123).
4. Discussion
Detailed studies of AHC concentrations in the Kerch Strait water areas, which was the part of the study sea area during 2019–2021, showed a range of AHC contents constituting 2.1–23.3 mg/100 g [40], slightly higher compared to the coastal average values. These concentrations were low and comparable with the AHC contents in relatively safe areas of the world’s oceans [6,15,41,42].
Increased pollution levels registered in the western waters were usually attributed to the runoff of European rivers, particularly the Danube [43], carried by the Black Sea currents over the long distances. Likewise, the concentrations of pollutants in this area were linked to the hydrological regime of the rivers [44]. Elevated levels of contamination might also be related to gas and oil production on the Black Sea shelf (area of st. 15). The concentrations of AHCs in the Black Sea (35.8 ± 4.2 mg/100 g) and the Azov Sea (32.2 ± 9.5 mg/100 g) were similar, indicating the approximately identical level of pollution in the study areas. The zone adjacent to the Kerch Strait, especially on the Azov Sea side, was characterized by elevated AHC levels. The increased AHC contents in bottom sediments in the Kerch Strait zone had been evidenced earlier as well [40]. High AHC contents were also registered in the outer harbors of the cities of Sevastopol and Yalta. All of these mentioned areas were found under high anthropogenic load, associated with both growing urbanization and intensive shipping.
Along with a high concentration of autochthonous C17 found at many stations [34], an increased content of even high-molecular homologues in the n-alkane composition was recorded: C28 and its neighboring even homologues (C26, C30) were registered as the maximum values almost everywhere. A similar distribution of n-alkanes in bottom sediments with a predominance of even high-molecular homologues (C28, C30, C32) was described for the estuarine zone of the Yellow River [45]. The predominance of even high-molecular homologues in combination with CPI < 1 was associated with anthropogenic impacts, particularly the intensive burning of fossil fuels [17,46]. With regard to other sources, the presence of C26 and C28 was linked to the probable input of fossil fuels into bottom sediments [17,19,28]. Thus, we can assume the presence of oil contamination of the surface layer of bottom sediments in the study area due to the use of mineral fuels in ships and in coastal areas. The content of C16 reduced relative to that of C17, which confirmed negligible involvement of microbial processes in the formation of composition of bottom sediments [40].
The range of identified n-alkanes had specific spatial features. In the eastern parts of the water area, proportion of high-molecular compounds (hydrocarbon chains longer than 30) exceeded 10% almost everywhere. In other regions, they were in the single digits. It is known that an increased content of these homologues was recorded in the humus of coniferous and deciduous forests, and was virtually not found in bottom sediments [34,47,48]. The presence of these n-alkanes, especially odd-numbered, might evidence a significant contribution of terrestrial higher vegetation to the formation of the n-alkane composition in bottom sediments in the eastern water areas as compared to the western zones. In the Sea of Azov, a high contribution of C22 and C24 compounds that were predominantly bacterial in nature [49] was also observed and might illustrate the active development of the microbial community in the bottom sediments.
Study of the UCM/AHC ratio showed that at st. 77 and st. 123, it exceeded a value of 4. This was the evidence of accumulation of transformed petrogenic hydrocarbons [28,50,51], and it demonstrated the chronic inflow of oil to the bottom sediments. Thus, relatively high concentrations of AHCs and n-alkanes at stations 77 and 123 might be a consequence of oil pollution. The ratio of UCM to the amount of AHCs at st. 3 and st. 18.1 also showed the presence of fresh oil and autochthonous compounds (UCM/AHC < 4) [52].
In 12 of 26 sampling stations, n-alkanes of allochthonous origin (C31/C19 > 0.4) predominated [53]. The average value of this marker for the water area was 0.84 ± 0.27. At all stations where a predominance of allochthonous components was observed, they were mainly identified as originating from terrestrial herbaceous vegetation (C31/C29 > 0.4) [37].
The TAR index (Table 1), also allowing us to differentiate autochthonous and allochthonous matter [24], had an average value of 0.84 ± 0.14, which generally corresponded to the predominance of autochthonous matter. The values typical for the prevalence of allochthonous sources of n-alkanes were found at stations 77, 105, 123, 124, 18.1 and 17.1. All of them were located in the area of the southern and the eastern coastline of the Crimea.
The CPI2 index had an average value of 0.49 ± 0.13 that, in general, indicated the absence of oil pollution and confirmed the biogenic background of the AHCs. However, at stations 123, 261 and 77, the values of this marker indicated the presence of oil products and may probably be related to fuel use.
The ratio between high-molecular n-alkanes and low-molecular ones (LWH/HWH) averaged 2.24 ± 0.2. In total, this indicated the predominance of autochthonous compounds [31], although the presence of petrogenic n-alkanes was not excluded [32]. At nine stations (Table 1), its value exceeded 2, which suggested the presence of fresh oil in the bottom sediments. At seven stations, this ratio was about 1, which showed the approximately equal proportion of terrigenous and autochthonous matter.
The average hydrocarbon chain length of n-alkanes (ACL) was 28 ± 0.2, which illustrated the relative stability of this indicator. The permanence of the ACL showed the absence of significant changes in the ecosystem [29]. Thus, we can assume the persistent accumulation conditions for AHCs in the bottom sediments. Its maximum values were at st. 77 and st. 123, where ACL = 30, which apparently might be a consequence of accumulation of heavy hydrocarbon fractions resulting from destruction of oil products.
Application of the principal component method showed that the major factor determining the composition of n-alkanes in bottom sediments of the coastal areas of the Black and Azov Seas was mixed sources biogenic and anthropogenic in nature. A secondary factor represented microbial destruction and transformation of compounds. These were supported by our conclusions regarding negligible involvement of microbial destructive activity relative to autochthonous products and produced on the basis of a reduced ratio of C16 relative to C17.
As a result, at the majority of stations the composition of n-alkanes was determined by similar sources of inflow and transformation of organic compounds. AHC contents and their composition were more consistent with the areas with natural sources of AHCs. Moreover, the distribution of n-alkanes indicates the presence of contamination of bottom sediments by oil refining products and is most likely associated with the use of fuel in ships and in coastal economic zones. Significant oil pollution was detected in the outer harbors of the cities of Sevastopol (station 77) and Yalta (station 123). In the other study areas, the content of AHCs, including oil, was found to be insignificant.
Markers of oil pollution as well as elevated AHC levels were revealed at stations located in the vicinity of large urban territories: Yalta and Sevastopol. One of the reasons for the increased AHC contents in these areas may be the coastal discharges of oil products [43], as well as oil spills on the surface water layers [54]. Thus, the distribution and composition of AHCs in the coastal zone of the Crimea is determined by both large-scale (on the scale of the Rim Current) and local-scale processes, such as flushing of compounds from the coastal areas and fuel spills during the operation of ships.
5. Conclusions
Bottom sediments of the investigated areas of the Black and Azov Seas were characterized by low AHC contents (1.30–127.8 mg/100 g, on average 38.9 ± 5.1 mg/100 g) that did not reach the generally accepted norms (50 mg/100 g). In the western part of the water area, increased AHC concentrations (46.1 ± 6.0 mg/100 g) relative to the eastern part (28.7 ± 5.1 mg/100 g) were registered. Elevated AHC contents were detected in the outer harbors of Sevastopol and Yalta. In the Azov Sea, AHC contents did not differ on average from the adjacent eastern area of the Black Sea. Slightly increased AHC concentrations were registered in the Kerch region of the Azov Sea. These are the ecological risk zones that require further detailed research, and may be recommended as testing sites for carrying out monitoring of contamination by the investigated toxicants.
The levels of AHCs and composition of their n-alkanes were more in line with areas with natural sources of hydrocarbons inputs. In most of the investigated areas, n-alkane composition was determined by similar sources of inputs and transformation of organic compounds. In the western part of the water area, the influence of allochthonous matter was less pronounced. At the same time, oil pollution linked with use of fuel was recorded almost everywhere. Significant oil pollution of bottom sediments was also registered in the outer harbors of Sevastopol and Yalta.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.S. and E.T.; methodology and validation, O.S. and E.T.; investigation, O.S. and E.T.; formal analysis and writing—original draft preparation, O.S., E.T. and S.A.; writing—review and editing, O.S., E.T., N.M. and E.S.; visualization, S.A.; supervision, E.T., S.A. and V.E.; project administration, G.M. and V.E.; funding acquisition, G.M. and V.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The publication was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (Agreement No. 075-15-2024-528 of 24 April 2024 on the implementation of a large-scale research project within the priority areas of scientific and technological development).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are sincerely grateful to the crew of the R/V “Vodyanitsky” for their help with the fieldwork. Special thanks to the head of the expedition senior researcher of the Laboratory of Chemoecology of IBSS, N.V. Burdiyan for organizing and sampling bottom sediments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abrams, M.A.; Narimanov, A.A. Geochemical evaluation of hydrocarbons and their potential sources in the western South Caspian depression, Republic of Azerbaijan. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 1997, 14, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.A.; Apanel, A.M.; Timoshenko, O.M.; Kosenkova, N.N. Oil families and their potential sources in the Northeastern Timan Pechora Basin, Russia. AAPG Bull. 1999, 83, 553–577. [Google Scholar]
- Lavrenova, E.; Kruglyakova, M. Specific features of temporal and spatial distributions of light hydrocarbons in the Sea of Azov. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2010, 30, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Bauer, J.E. Use of C-14 and C-13 natural abundances for evaluating riverine, estuarine, and coastal DOC and POC sources and cycling: A review and synthesis. Org. Geochem. 2001, 32, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkman, J.K.; Holdsworth, D.G.; Neill, G.P.; Bavor, H.J., Jr. Identification of natural, anthropogenic and petroleum hydrocarbons in aquatic sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 112, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Han, Y.; Xia, J.; Tan, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, S. Composition and distribution of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds and biomarkers in seafloor sediments from offshore of the Leizhou Peninsula (South China). ACS Omega 2021, 6, 34286–34293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, J.C.; Pelletier, E.; Brochu, C.; Khalil, M.; Catoggio, J.A. Determination of hydrocarbons sources using n-alkane and polyaromatica hydrocarbon distribution indexes. Case study: Rio de la Pata Estuary, Argentina. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.C.; Bícego, M.C.; Taniguchi, S.; Montone, R.C. Aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments in Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctica. Antarctic. Sci. 2004, 16, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.J.; Chefetz, B.; Deshmukh, A.P.; Hatcher, P.G. Comparison of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon distributions and sedimentary organic matter characteristics in contaminated, coastal sediments from Pensacola Bay, Florida. Mar. Environ. Res. 2005, 59, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches Filho, P.J.; Sousa, E.E.H.; Luz, L.P.; Betemps, G.R.; Kerstner, T.; Caramão, E.B. Environmental assessment and qualitative study of polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the region of colony Z-3—Laguna dos Patos, Pelotas. RS. Rev. Thema. 2010, 7, 1–9. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Maciel, D.C.; Souza, J.R.B.; Taniguchi, S.; Bicego, M.C.; Schettini, C.A.F.; Zanardi-Lamardo, E. Hydro-carbons in sediments along a tropical estuary-shelftransition area: Sources and spatial distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficken, K.J.; Li, B.; Swain, D.L.; Eglinton, G. An n-alkane proxy for the sedimentary input of submerged/floating freshwater aquatic macrophytes. Org. Geochem. 2000, 31, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commendatore, M.G.; Esteves, J.L.; Colombo, J.C. Hydrocarbons in coastal sediments of Patagonia, Argentina: Levels and probable sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moeinpour, A. Aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons risk assessment in coastal water and sediments of Khark Island, SW Iran. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 108, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarabadi, A.R.; Bakhtiari, A.R.; Aliabadian, M.; Toosi, A.S. Spatial distribution and composition of aliphatic hydrocarbons, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and hopanes in superficial sediments of the coral reefs of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 195–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches Filho, P.J.; Luz, L.P.; Betemps, G.R.; Silva, M.D.R.G.; Caramão, E.B. Studies of n-alkanes in the sediments of Colony Z3 (Pelotas–RS–Brazil). Braz. J. Aquat. Sci. Technol. 2013, 17, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Wu, F.; Xiong, Y.; Li, F.; Du, X.; An, D.; Wang, L. Source characterization of sedimentary organic matter using molecular and stable carbon isotopic composition of n-alkanes and fatty acids in sediment core from Lake Dianchi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Zamora, J.V. Distribution of hydrocarbons in recent marine sediments off the coast of Baja California. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 92, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, P.M.; Márcia, C.B. Investigation of natural and anthropogenic hydrocarbon inputs in sediments using geochemical markers. I. Santos, SP––Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, T.K.; Krull, E.S.; Bowater, A.; Grice, K.; Gleixner, G. The occurrence of short chain n-alkanes with an even over odd predominance in higher plants and soils. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maioli, O.L.G.; Rodrigues, K.C.; Knoppers, B.A.; Azevedo, D.A. Pollution source evaluation using petroleum and aliphatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from two Brazilian estuarine systems. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commendatore, M.G.; Esteves, J.L. Natural and anthropogenic hydrocarbons in sediments from the Chubut River (Patagonia, Argentina). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrington, J.W.; Quinn, J.G. “Unresolved Complex Mixture” (UCM): A brief history of the term and moving beyond it. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silliman, J.E.; Schelske, C.L. Saturated hydrocarbons in the sediments of Lake Apopka, Florida. Org. Geochem. 2003, 34, 253–260. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/organic-geochemistry/vol/34/issue/2 (accessed on 11 July 2024). [CrossRef]
- Drugov, Y.S.; Rodin, A.A. Environmental Analyses in Oil and Petroleum Product Spills: A Practical Guide; BINOM. Laboratory of Knowledge: Moscow, Russia, 2007; 270p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Cattell, R.B. The scree plot test for the number of factors. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1966, 1, 140–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larin, A.A.; Pavlenko, L.F.; Skrypnik, G.V.; Korpakova, I.G. Oil pollution of the Black sea coastal environment. Mar. Ecol. J. 2011, 2, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Zhai, S. The distribution and environmental significance of n-alkanes in the Changjiang River estuary sediments. Acta Sientiae Circumstantiae 2008, 28, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Sakari, M.; Zakaria, M.P.; Lajis, N.; Mohamed, C.A.R.; Shahpoury, P.; Anita, S.; Chandru, K. Characterization, distribution, sources and origins of aliphatic hydrocarbons from surface sediment of Prai strait, Penang, Malaysia: A widespread anthropogenic input. Environ. Asia. 2008, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Meyers, P.A.; Wu, W.; Jia, C.; Xie, S. Significance of long chain iso and anteiso monomethyl alkanes in the Lamiaceae (mint family). Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, M.; Guillard, R.R.L.; Chase, T. Hydrocarbons of marine phytoplankton. Mar. Biol. 1971, 8, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-C.; Sun, S.; Ma, H.-Q.; Liu, Y. Sources and distribution of aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Calvin, M. Hydrocarbon distribution of algae and bacteria, and microbiological activity in sediments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1969, 64, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemirovskaya, I.A. Oil in the Ocean (Pollution and Natural Flow); Scientific World: Moscow, Russia, 2013; 432p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yusoff, A.; Mohamad, S.; Assim, Z. Aliphatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from south China sea off kuching division, sarawak. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2012, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, R.; Xu, Y.; Chong, J.; Jaffe, R. Sediment and soil organic matter source assessment as revealed by the molecular distribution and carbon isotopic composition of n–alkanes. Org. Geochem. 2005, 36, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkman, J.K.; Johns, R.B.; Gillan, F.T.; Perry, G.J.; Bavor, H.J. Microbial lipids of an intertidal sediment—I. Fatty acids and hydrocarbons. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta. 1980, 44, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutch Target and Intervention Values (2000) (the New Dutch List). Annexes. Circular on Target Values and Intervention Values for Soil Remediation. Available online: https://support.esdat.net/Environmental%20Standards/dutch/annexs_i2000dutch%20environmental%20standards.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Tikhonova, E.A. Organic matter of bottom sediments of the Crimean and Caucasian coasts (Azov and Black Seas). Ecol. Saf. Coast. Shelf Zones Sea 2021, 3, 52–67. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemirovskaya, I.A.; Zavialov, P.O.; Khramtsova, A.V. Hydrocarbon pollution in the waters and sediments of the Kerch Strait. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stakėnienė, R.; Jokšas, K.; Galkus, A.; Raudonytė-Svirbutavičienė, E. Aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the bottom sediments from Klaipėda Harbour, Lithuania (Baltic Sea). Chem. Ecol. 2016, 32, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloveva, O.V.; Tikhonova, E.A.; Gurov, K.I.; Kotelyanets, E.A. Hydrocarbons composition of sea bottom sediments (Balaklava Bay, Black Sea). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 2405–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, S.A. Assessment of background pollution by petroleum products of the Black and Caspian seas using remote sensing data and model calculations. In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference “Environmental problems of our time”, Maykop, Russia, 12–15 May 2009; pp. 25–44. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Dyatlov, S.E.; Podpletnaya, N.F.; Zaporozhets, S.A. Variability of the content of petroleum products in water and bottom sediments of the Odessa region of the northwestern part of the Black Sea. Bull. ONU. Ser. Geogr. Geol. Sci. 2015, 20, 159–169. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Z.; Da, C. n-Alkanes in sediments from the Yellow River Estuary, China: Occurrence, sources and historical sedimentary record. Ecotoxicol. Envir. Saf. 2018, 150, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Z.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Chen, T.-H. Source apportionment of sediment-associated aliphatic hydrocarbon in a eutrophicated shallow lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 4006–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W.; Huang, C.; Xie, B. Characterization of n-alkanes and their carbon isotopic composition in sediments from a small catchment of the Dianchi watershed. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diefendorf, A.F.; Leslie, A.B.; Wing, S.L. Leaf wax composition and carbon isotopes vary among major conifer 620 groups. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 170, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordadze, G.N.; Poshibaeva, A.R.; Giruts, M.V.; Gayanova, A.A.; Semenova, E.M.; Koshelev, V.N. Formation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons from Prokaryote Biomass: 2. Formation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Biomarkers from Biomass of Geobacillus jurassicus Bacteria Isolated from Crude Oil. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, M.A.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Characterization of biogenic and petroleum derived organic matter in aerosols over remote, rural and urban areas. In Identification and Analysis of Organic Pollutants in Air; Keith, L.H., Ed.; Ann Arbor Science/Butterworth Publishers: Woburn, MA, USA, 1984; pp. 353–370. [Google Scholar]
- Simoneit, B.R.T. Characterization of organic constituents in aerosols in relation to their origin and transport: A review. Int. J. Environ. Analyt. Chem. 1986, 23, 207–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouloubassi, I.; Saliot, A. Investigation of anthropogenic and natural organic inputs in estuarine sediments using hydrocarbon markers (NAN, LAB, PAH). Oceanol. Acta. 1993, 16, 145–161. [Google Scholar]
- Fagbote, E.O.; Olanipekun, E.O. Characterization, distribution, sources and origins of aliphatic hydrocarbons of soils of Agbabu bitumen deposit area, western Nigeria. Afr. J. Sci. Res. 2012, 10, 563–585. [Google Scholar]
- Zagranichny, K.A. On the issue of sources and volumes of oil components entering the Black Sea. Eng. Bull. Don. 2014, 28, 80–92. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).