A Spectral Precursor Indicative of Artificial Water Reservoir-Induced Seismicity: Observations from the Xiangjiaba Reservoir, Southwestern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
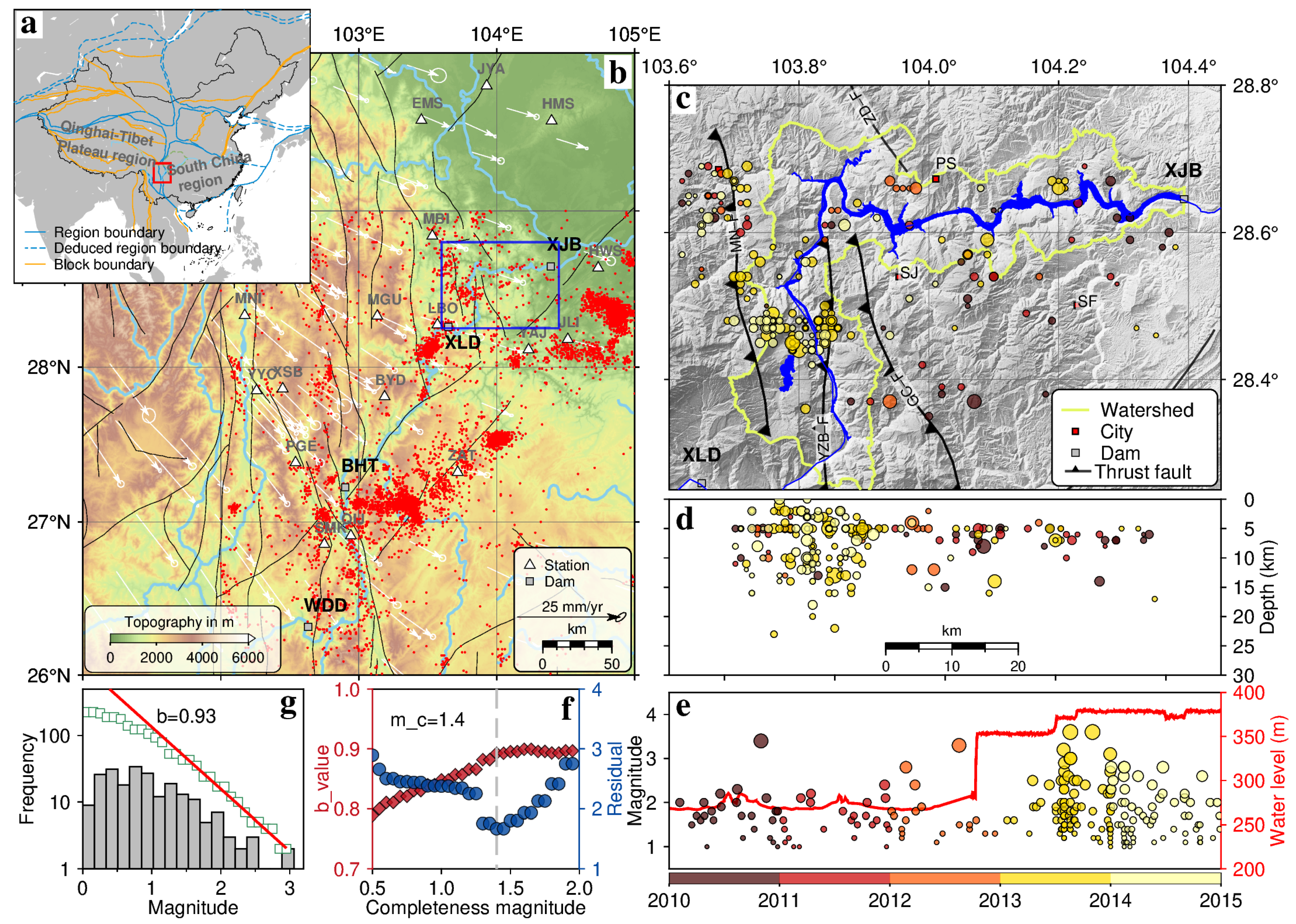
2. Background of the XJB Reservoir
2.1. Geological Settings
2.2. Seismicity and Water Levels
3. Methodology
3.1. Seismic Data
3.2. Data Processing
3.2.1. Power Spectra of Earthquakes
3.2.2. Spectral Parameters
3.2.3. Data Processing Workflow
4. Results
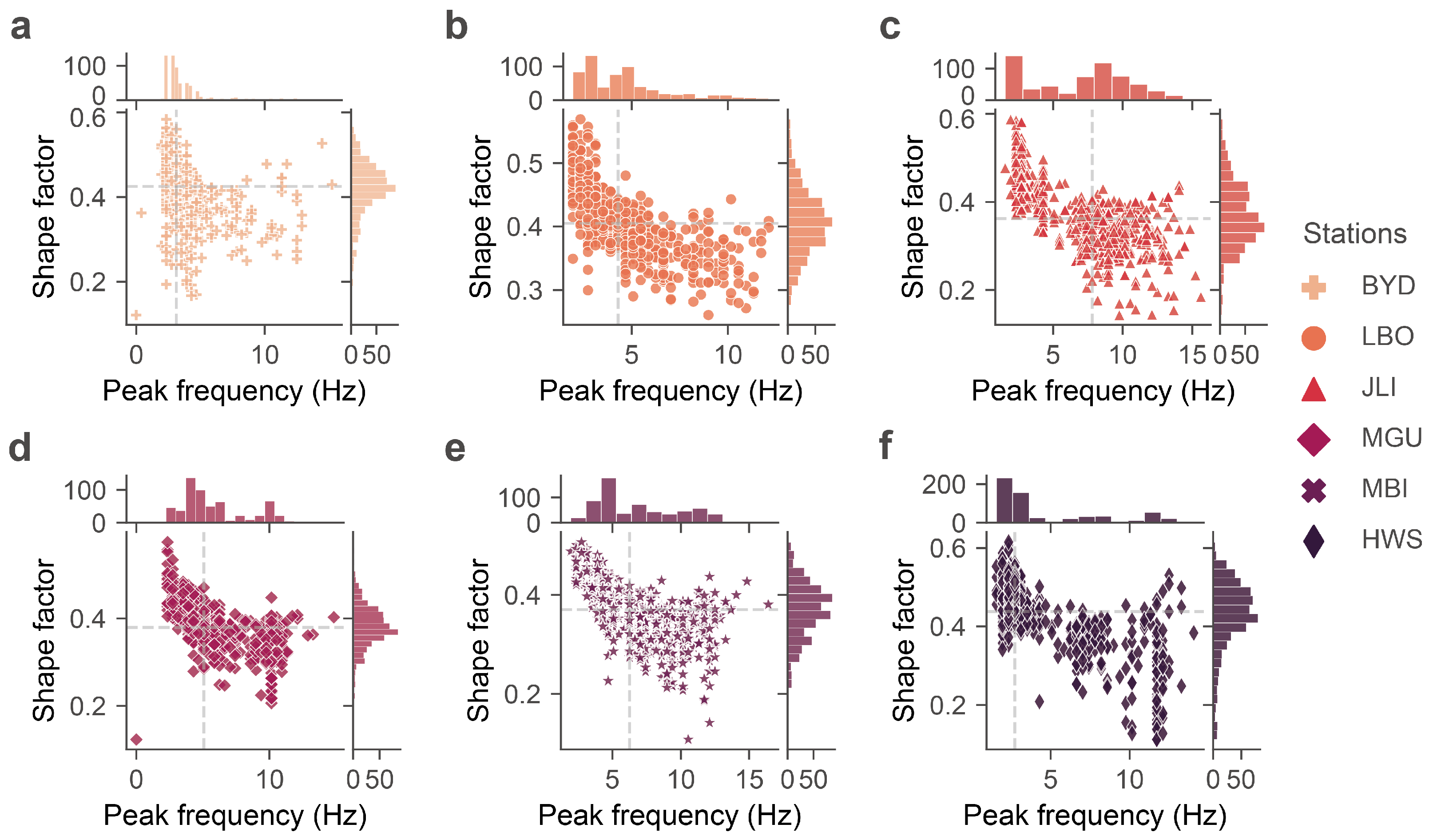
4.1. Joint Distribution of Spectral Parameters and Site Effects
4.2. Temporal Process of Spectral Parameters and the New Indicator
4.3. Spatial Variation in Spectral Parameters
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The power spectral characteristics of earthquakes in the XJB reservoir area can be effectively captured using two spectral parameters, the peak frequency and shape factor. The shape factor follows a normal distribution within the 0.2–0.6 range, while the peak frequency spans 2–14 Hz, with the highest proportion observed in the lower frequency band of 2–6 Hz.
- (2)
- The estimation of spectral parameters is influenced by site-specific factors. The peak frequency is particularly sensitive to azimuthal angles, whereas the shape factor is more responsive to epicentral distances.
- (3)
- There are minimal discrepancies in the distribution of spectral parameters before and after reservoir impoundment. Post-impoundment, there is a slight increase in the proportion of high peak frequencies, correlating with a higher occurrence of microseismic events. Temporal analysis shows no significant shifts in individual parameters in response to water level changes. However, a notable increase in the ratio (k) of the shape factor to the peak frequency after reservoir impoundment suggests its potential as a precursor indicator for RIS.
- (4)
- Spatial variations in spectral parameters reflect differences in the seismogenic structure within the reservoir area and the effects of reservoir water on seismic sources. Particularly, several regions between the two faults in the tail section of the XJB reservoir exhibit an increase ratio (k) of the shape factor to the peak frequency after impoundment, indicating that these areas require close monitoring for future RIS study.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sayão, E.; França, G.S.; Holanda, M.; Gonçalves, A. Spatial database and website for reservoir-triggered seismicity in Brazil. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2001–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, D.; Jiang, L.; Nielsen, K.; Yin, J.; Liu, J.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. High-resolution water level and storage variation datasets for 338 reservoirs in China during 2010–2021. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 5671–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Năstase, G.; Şerban, A.; Năstase, A.F.; Dragomir, G.; Brezeanu, A.I.; Iordan, N.F. Hydropower development in Romania. A review from its beginnings to the present. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Liu, M.; Lu, N.; Godt, J.W.; Luo, G. Did the Zipingpu Reservoir trigger the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L20315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.K. Artificial water reservoir-triggered seismicity (RTS): Most prominent anthropogenic seismicity. Surv. Geophys. 2022, 43, 619–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahalaut, K. On the Common Features of Reservoir Water-Level Variations and Their Influence on Earthquake Triggering: An Inherency of Physical Mechanism of Reservoir-Triggered Seismicity. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2021, 111, 2720–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carder, D.S. Seismic investigations in the Boulder Dam area, 1940-1944, and the influence of reservoir loading on local earthquake activity. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1945, 35, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; Foulger, G.; Gluyas, J.; Davies, R.; Julian, B. HiQuake: The human-induced earthquake database. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2017, 88, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.K. Reservoir triggered seismicity (RTS) at Koyna, India, over the past 50 yrs. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2018, 108, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michas, G.; Pavlou, K.; Vallianatos, F.; Drakatos, G. Correlation between seismicity and water level fluctuations in the Polyphyto Dam, North Greece. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2020, 177, 3851–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Shen, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Peng, B.; Xu, X.; Gao, R. Seismic evidence for fluid-driven pore pressure increase and its links with induced seismicity in the Xinfengjiang Reservoir, South China. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2021JB023548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.L.; Qin, L.L.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Wang, X.M.; Tang, X.L.; An, R.D. The application of a multi-beam echo-sounder in the analysis of the sedimentation situation of a large reservoir after an earthquake. Water 2018, 10, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Nakatsugawa, M.; Ohashi, H. Research of impacts of the 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake on sediment transport in the Atsuma River basin using the SWAT model. Water 2021, 13, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ge, S.; Yang, Q.; Ma, X. Impoundment-associated hydro-mechanical changes and regional seismicity near the Xiluodu reservoir, Southwestern China. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB021590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, A.F.; Cowie, P.; Lunn, R.; Pearce, R. spatio-temporal evolution of induced seismicity at Açu reservoir, NE Brazil. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 158, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lei, X.; Liao, W.; Li, J.; Yao, Y. Statistical parameters of seismicity induced by the impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir, Central China. Tectonophysics 2019, 751, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, G. What causes the spatiotemporal patterns of seismicity in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, central China? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 592, 117618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, F.; Deng, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Dai, S.; Shao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, W. Statistical investigation of induced seismicity associated with the impoundment of the Xiangjiaba Reservoir, Southwestern China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2024, 83, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L. Analysis of the cross-correlation between seismicity and water level in the Koyna area of India. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2010, 100, 2317–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Deng, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, F. Failure analysis of water-bearing rock under direct tension using acoustic emission. Eng. Geol. 2022, 299, 106541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Zheng, S.; Yan, C.; Chen, Z. Attenuation, site effects, and source parameters in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2013, 103, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, C.; Shashidhar, D. Stress drop variations of triggered earthquakes at Koyna–Warna, western India: A case study. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 131, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L. Study on Seismic Source Parameter Characteristics of Baihetan Reservoir Area in the Lower Reaches of the Jinsha River. Water 2024, 16, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yue, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Diao, G.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, W.; Li, Y.; Feng, Z. Discussion on genesis of induced earthquake based on focal mechanism in Xiangjiaba reservoir region. Seismol. Geol. 2015, 37, 565–575. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Cheng, W.; Diao, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, W. Seismicity of the Xiangjiaba reservoir after impoundment. Earthq. Res. China 2015, 31, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, C.; Lei, H.; Yao, M. Seismic activities before and after the impoundment of the Xiangjiaba and Xiluodu reservoirs in the lower Jinsha River. Earthq. Sci. 2022, 35, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, B.; Chang, T. Seismicity characteristics of Xiangjiaba Reservoir region before and after the impoundment. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2019, 39, 919–923. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Li, L.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Yu, J. Twin-peak frequencies of acoustic emission due to the fracture of marble and their possible mechanism. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2018, 50, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Deng, J.; Zheng, L.; Liu, J. Dominant frequency characteristics of acoustic emissions in white marble during direct tensile tests. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Deng, J.; Pak, R.Y.; Liu, J.; Lyu, C. Experimental study on the failure process of water-bearing rock under uniaxial tension based on dominant frequency analysis of acoustic emission. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.; Adam, L.; Sarout, J.; van Wijk, K.; Kennedy, B.; Dautriat, J. The relation between viscosity and acoustic emissions as a laboratory analogue for volcano seismicity. Geology 2019, 47, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Boundaries between active-tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the China mainland. Chin. J. Geophys. 2005, 48, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shen, Z.K. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q. Active tectonics and earthquake activities in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2003, 10, 66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Ren, Z.; Xu, C.; Wei, Z.; Lu, R.; Tan, X.; Dong, S.; et al. Discussion on seismogenic structure of Jiuzhaigou earthquake and its implication for current strain state in the southeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin. J. Geophys. 2017, 60, 4018–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Royden, L.H.; Burchfiel, B.C.; King, R.W.; Wang, E.; Chen, Z.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet. Science 1997, 276, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Nie, G.; Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Su, G. Kinematical and structural patterns of Yingjing-Mabian-Yanjin fault zone, southeast of Tibetan Plateau, and its segmentation from earthquakes. Seismol. Geol. 2005, 27, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Deng, J.; Hu, W.; Xu, C.; Ge, H.; Zheng, J. 36Cl exposure dating of the Mahu Giant landslide (Sichuan Province, China). Eng. Geol. 2021, 285, 106039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liao, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, Y. Influences of the Three Gorges Project on seismic activities in the reservoir area. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldhauser, F.; Ellsworth, W. A double-difference earthquake location algorithm: Method and application to the Northern Hayward Fault, California. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2000, 90, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.E.; Ringler, A.T.; Wilson, D.C.; Bahavar, M.; Koper, K.D. How processing methodologies can distort and bias power spectral density estimates of seismic background noise. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2020, 91, 1694–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, P. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: A method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 1967, 15, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, D.E.; Buland, R.P. Ambient noise levels in the continental United States. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2004, 94, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.R. Observations and Modeling of Seismic Background Noise; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1993; Volume 93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, J. A new method for determining the crack classification criterion in acoustic emission parameter analysis. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 130, 104323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Ohtsu, M. Crack classification in concrete based on acoustic emission. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzo, D.; Nardone, L.; La Rocca, M.; Esposito, A.M.; Manzo, R.; Di Maio, R. Statistical moments of power spectrum: A fast tool for the classification of seismic events recorded on volcanoes. Adv. Geosci. 2020, 52, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.V. Automatic earthquake recognition and timing from single traces. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1978, 68, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Hirasawa, T. Body wave spectra from propagating shear cracks. J. Phys. Earth 1973, 21, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, K.; Kitamura, M.; Lei, X.; Katayama, I. Identification of fracturing behavior in thermally cracked granite using the frequency spectral characteristics of acoustic emission. J. Mineral. Petrol. Sci. 2023, 118, 221014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y. Cascade effects of triggered earthquakes of cascade dams: Taking Xiluodu and Xiangjiaba reservoirs as examples. Chin. J. Geophys. 2023, 66, 2470–2488. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Z.; Chen, F.; Deng, J.; Zhao, S.; Dai, S.; Zhu, J. A Spectral Precursor Indicative of Artificial Water Reservoir-Induced Seismicity: Observations from the Xiangjiaba Reservoir, Southwestern China. Water 2024, 16, 2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162217
Fu Z, Chen F, Deng J, Zhao S, Dai S, Zhu J. A Spectral Precursor Indicative of Artificial Water Reservoir-Induced Seismicity: Observations from the Xiangjiaba Reservoir, Southwestern China. Water. 2024; 16(16):2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162217
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Ziguo, Fei Chen, Jianhui Deng, Siyuan Zhao, Shigui Dai, and Jun Zhu. 2024. "A Spectral Precursor Indicative of Artificial Water Reservoir-Induced Seismicity: Observations from the Xiangjiaba Reservoir, Southwestern China" Water 16, no. 16: 2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162217
APA StyleFu, Z., Chen, F., Deng, J., Zhao, S., Dai, S., & Zhu, J. (2024). A Spectral Precursor Indicative of Artificial Water Reservoir-Induced Seismicity: Observations from the Xiangjiaba Reservoir, Southwestern China. Water, 16(16), 2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162217







