Scenario-Based Modeling on Chlorophyll-a in Uiam Reservoir of Korea According to Variation of Dam Discharge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
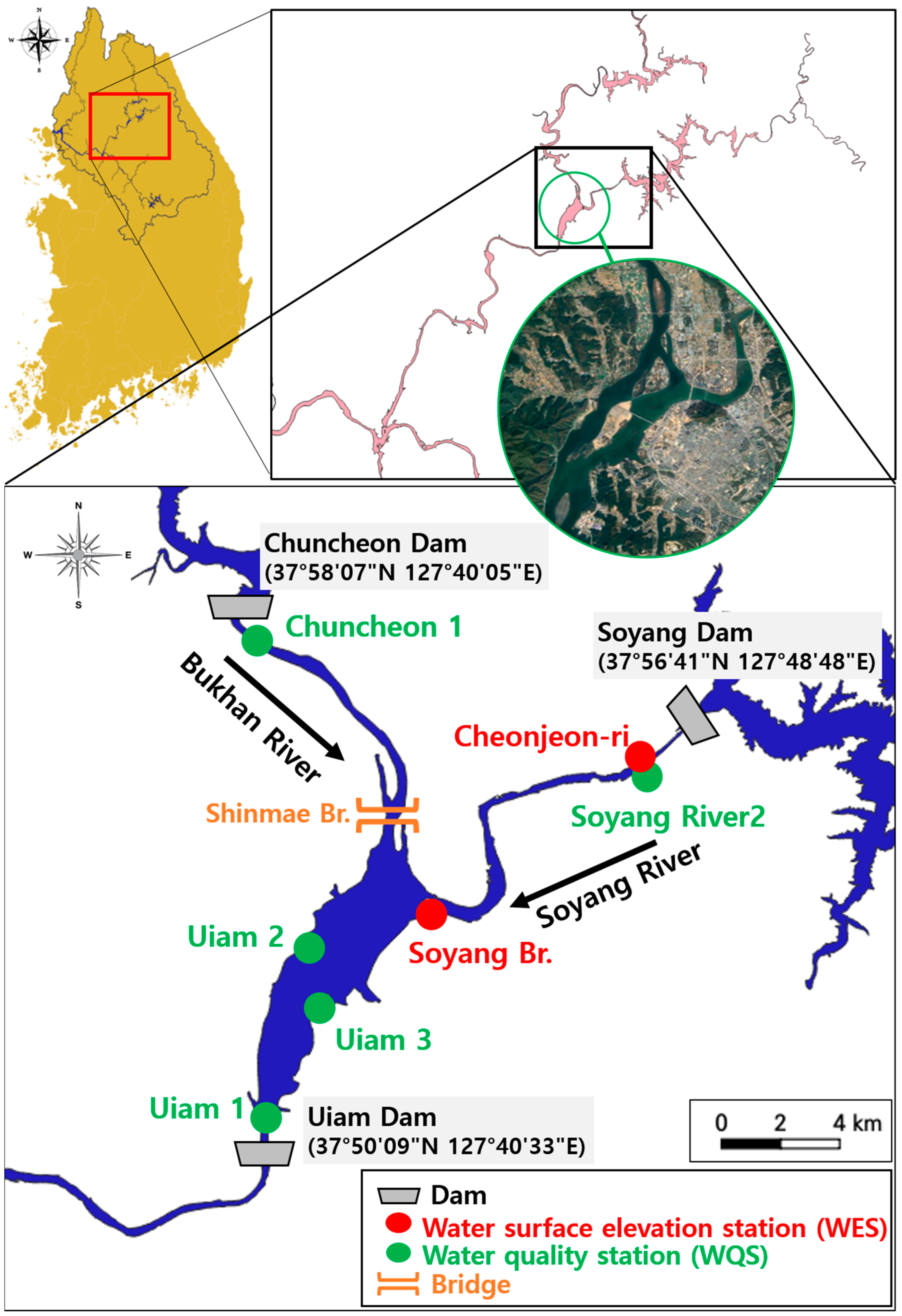
2.1. Feature of Study Area
2.2. Construction of Numerical Model
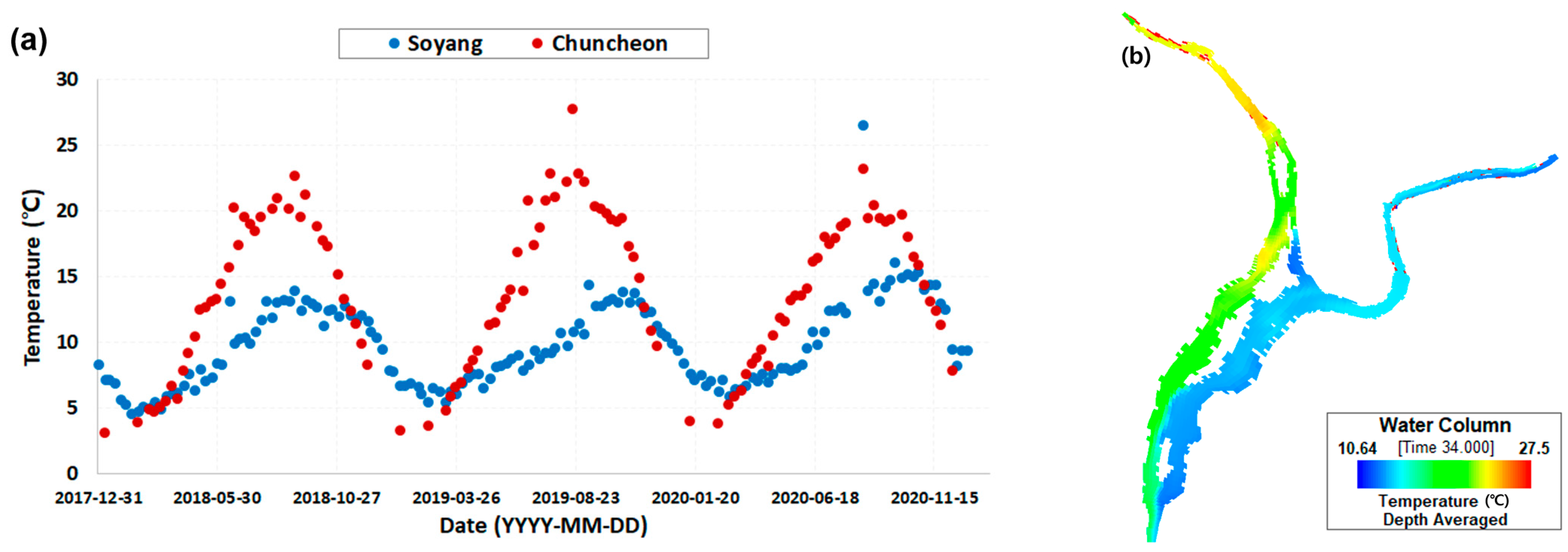
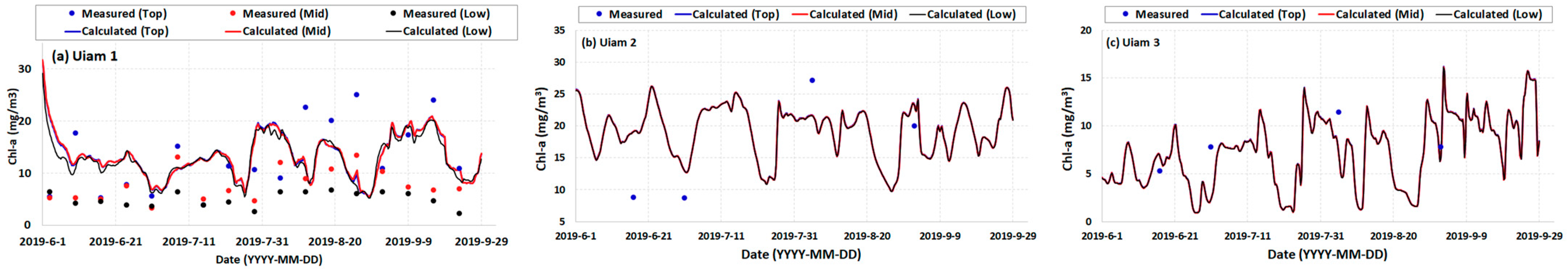
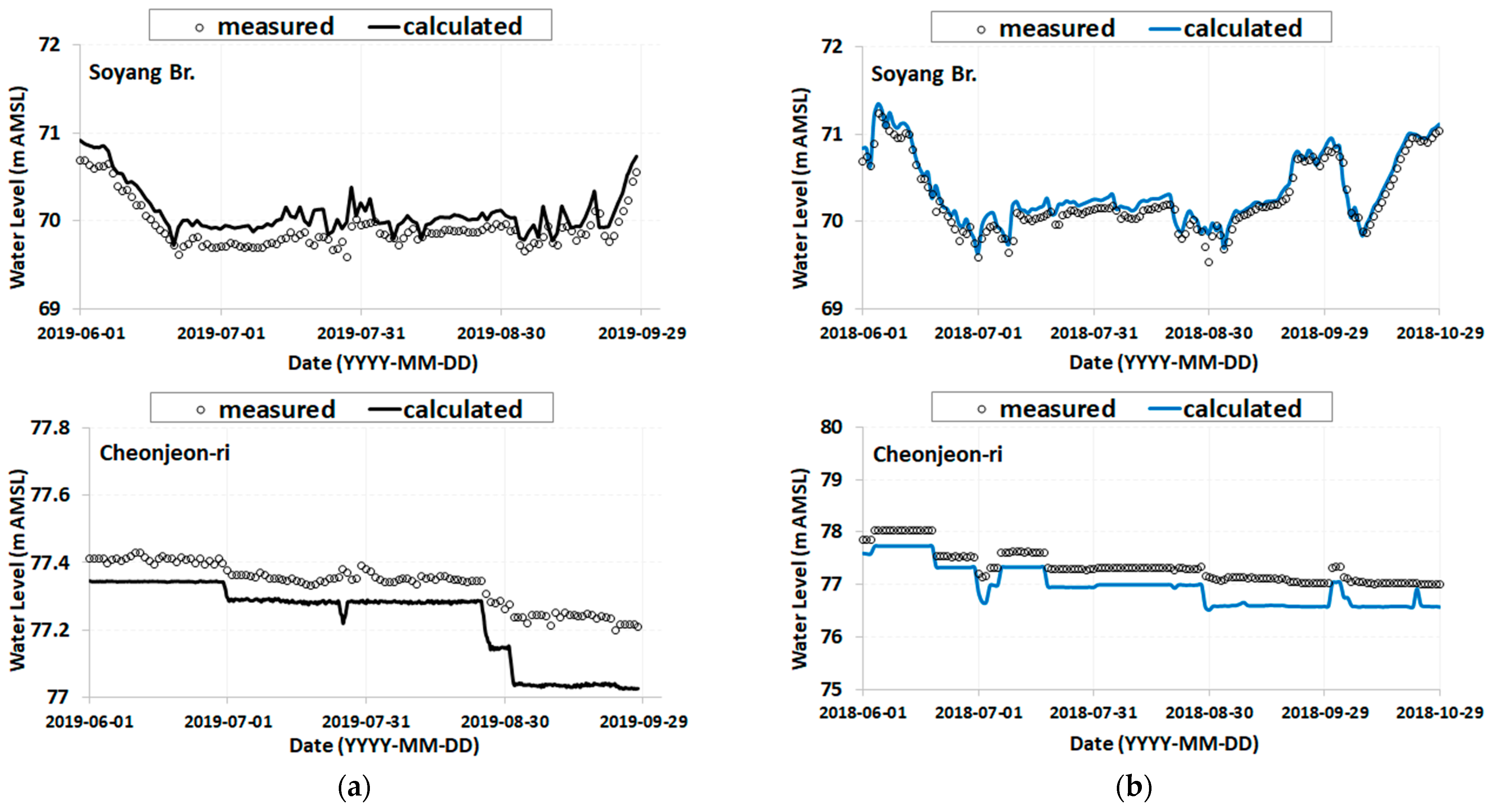
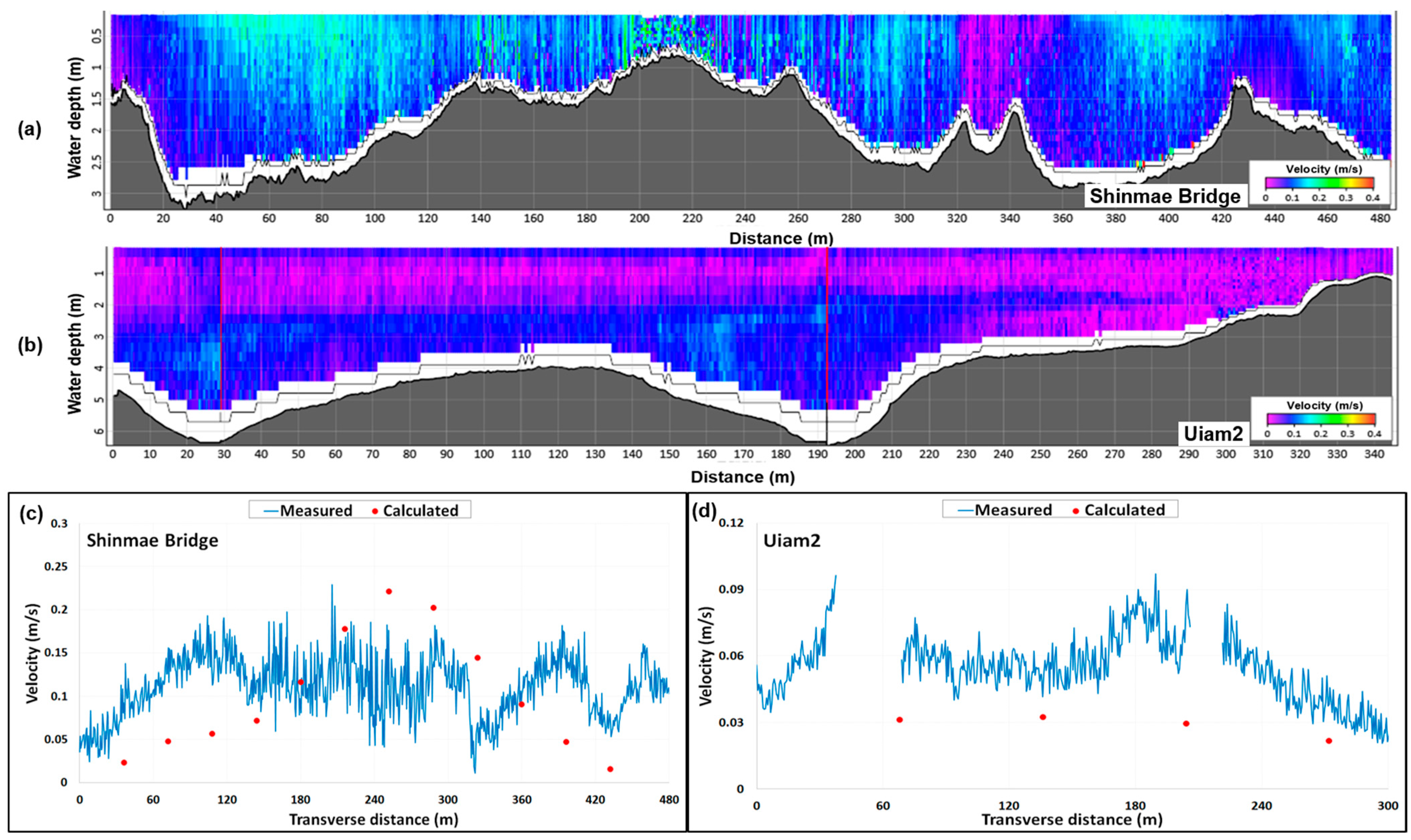
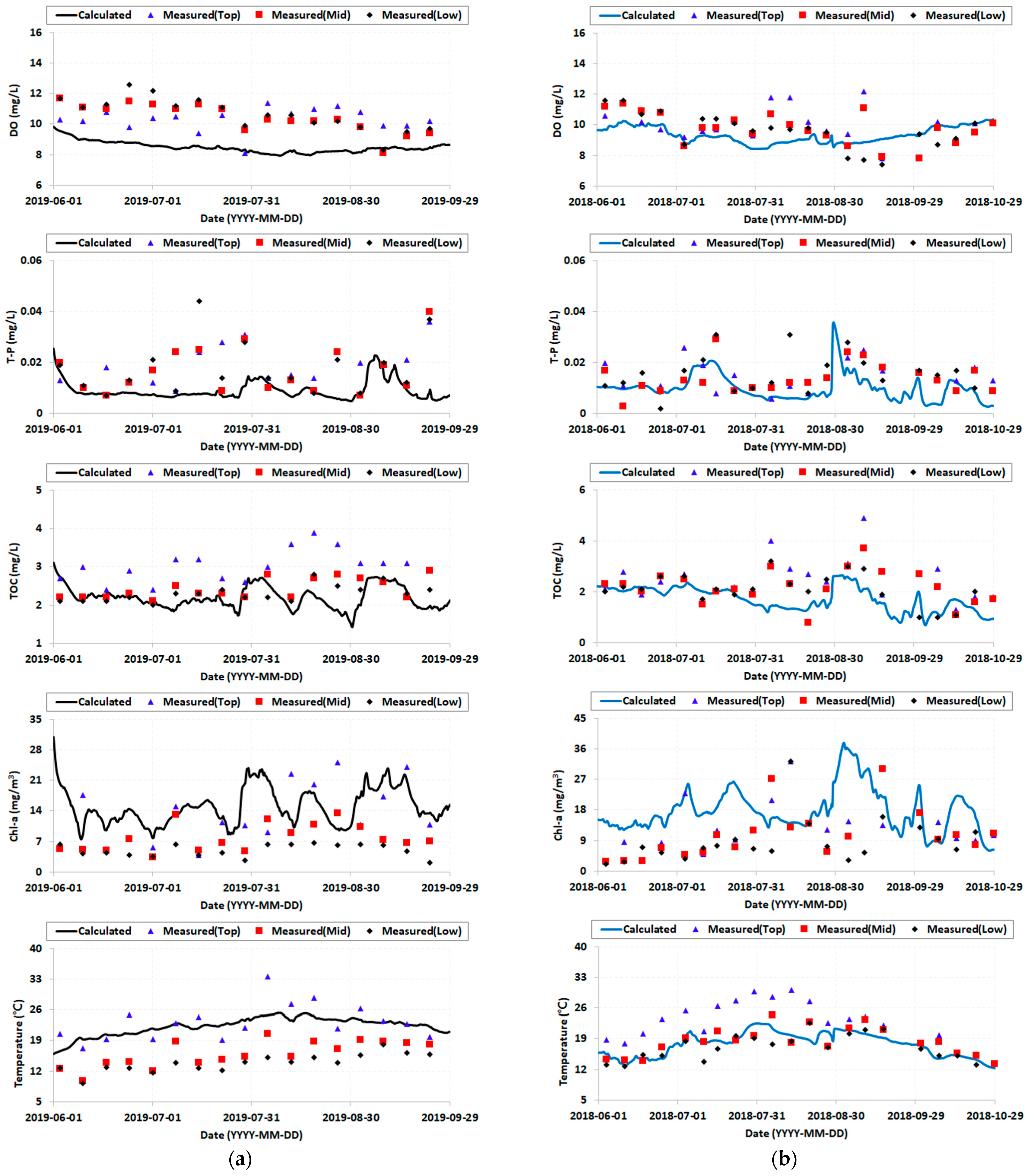
2.3. Model Calibration and Verification
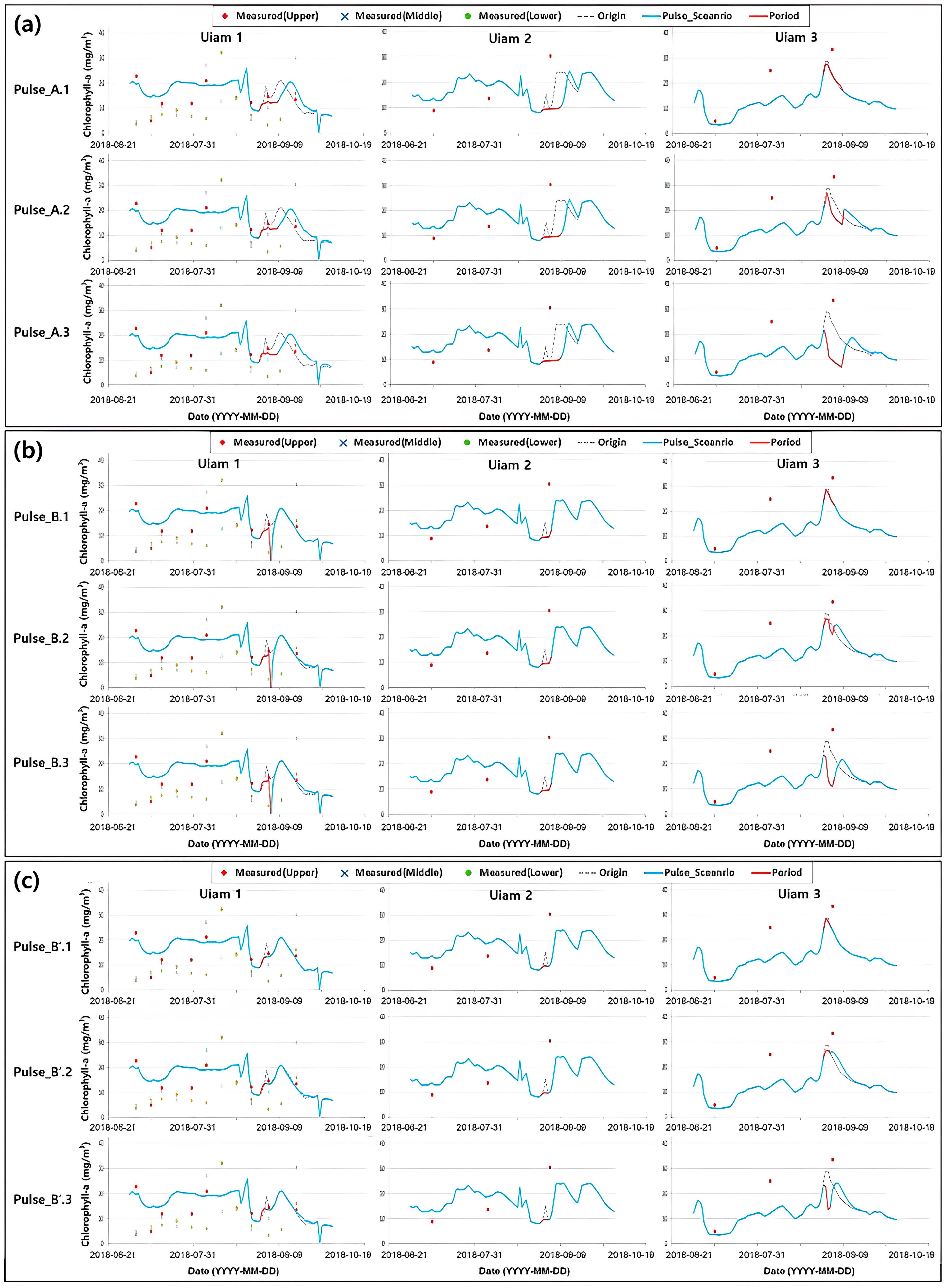
2.4. Scenarios of Dam Operation
3. Results and Discussion
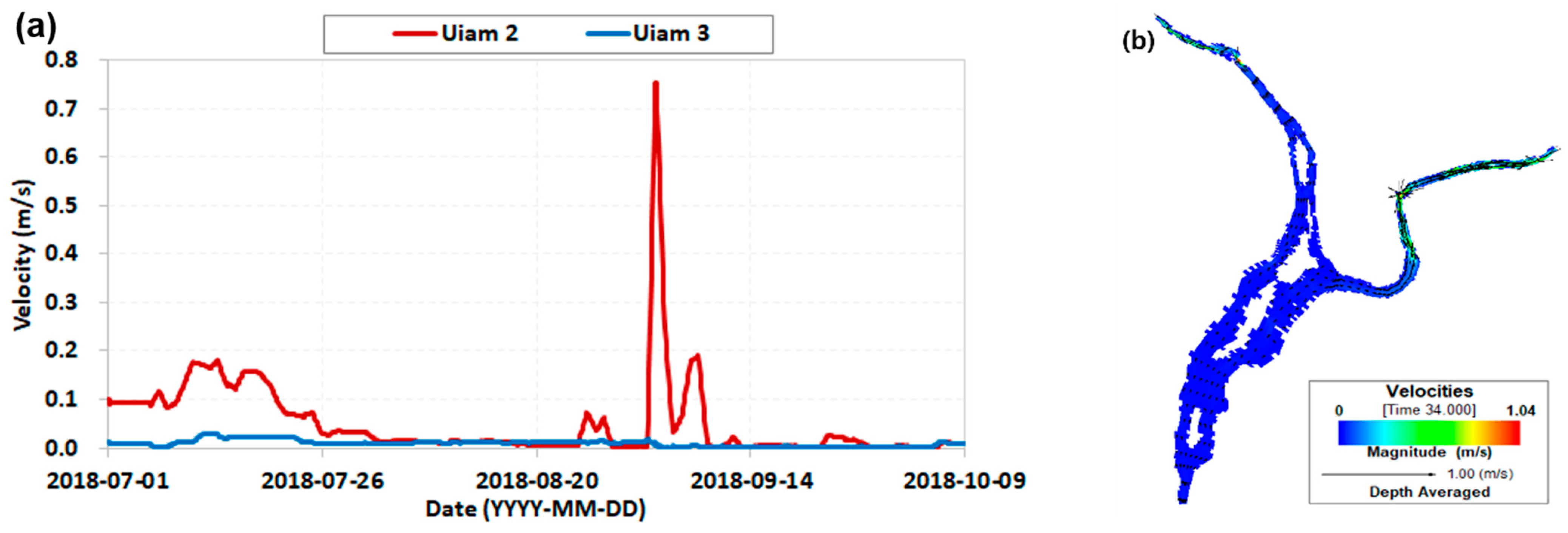
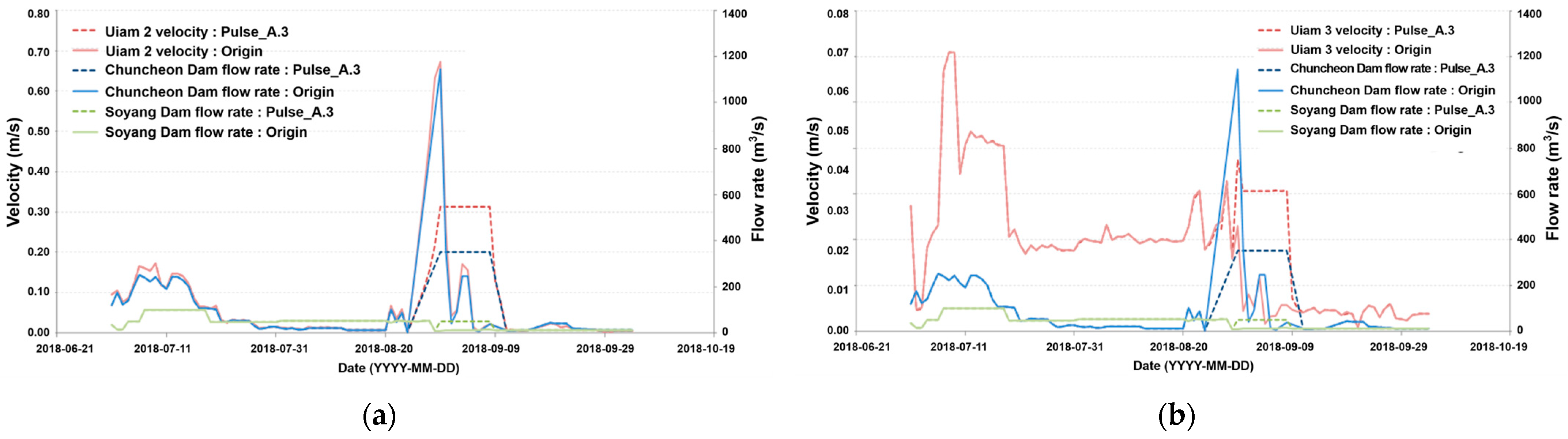
3.1. Results of Dam Operation
3.2. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, P.C.; Gammie, A.J.; Hollinrake, K.; Codd, G.A. Pneumonia associated with contact with cyanobacteria. BMJ Br. Med. J. 1990, 300, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderian, D.; Noori, R.; Heggy, E.; Bateni, S.M.; Bhattarai, R.; Nohegar, A.; Sharma, S. A water quality database for global lakes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 202, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texeira, M.D.G.L.C.; Costa, M.D.C.N.; Carvalho, V.L.P.D.; Pereira, M.D.S.; Hage, E. Gastroenteritis epidemic in the area of the Itaparica Dam, Bahia, Brazil. Bull. Pan Am. Health Organ. 1993, 27, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, P.R.; Griffiths, D.J. Artificial destratification of a small tropical reservoir: Effects upon the phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 1993, 254, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Azevedo, S.M.; An, J.S.; Molica, R.J.; Jochimsen, E.M.; Lau, S.; Rinehart, K.L.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.K. Human fatalities from cyanobacteria: Chemical and biological evidence for cyanotoxins. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconer, I.R.; Humpage, A.R. Health risk assessment of cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in drinking water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funari, E.; Testai, E. Human health risk assessment related to cyanotoxins exposure. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 38, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanchett, G.; Oliveira-Filho, E.C. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins: From impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human health to anticarcinogenic effects. Toxins 2013, 5, 1896–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, J.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Freitas, M. Effects of microcystin-LR and cylindrospermopsin on plant-soil systems: A review of their relevance for agricultural plant quality and public health. Environ. Res. 2017, 153, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Han, X. Decline of sperm quality and testicular function in male mice during chronic low-dose exposure to microcystin-LR. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.P.; Kumar, H.D.; Smith, R.C.; Worrest, R. Effects of solar UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with climate change. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2007, 6, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, S. The dead zones: Oxygen-starved coastal waters. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, A120–A125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codd, G.A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacterial toxins: Risk management for health protection. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, P.W.; Boyer, G.; Hall, C.; Waller, S.; Gehrts, K. Distribution and toxicity of a new colonial Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in the San Francisco Bay Estuary, California. Hydrobiologia 2005, 541, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, G.; Lee, J. Cyanobacterial biofilms on sedimentation basins in a water treatment plant in South Korea. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dencheva, K. State of macrophytobenthic communities and ecological status of the Varna Bay, Varna lakes and Burgas Bay. Phytol. Balc. 2010, 16, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, I.R.; Lee, G.H.; Ham, K.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Jeong, U.H. The study on decline plan of primary production organic matter of Uiam lake basin. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Health 2004, 30, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.M.; Heo, S.N.; Noh, H.R.; Yang, H.J.; Han, M.S. Relationship between limnological characteristics and algal bloom in lake-type and river-type reservoirs, Korea. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 36, 124–138. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.G. Causes of algal bloom and reduction measures. Bull. Korea Environ. Preserv. Assoc. 2014, 412, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Management of Cyanobacteria in Drinking-Water Supplies: Information for Regulators and Water Suppliers; WHO/FWC/WSH/15.03; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Fu, M.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, P.; Pan, L.; Chen, X. Reducing the water residence time is inadequate to limit the algal proliferation in eutrophic lakes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, A.M.; Anderson, E.J.; Beletsky, D.; Boland, S.; Bosch, N.S.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Zagorski, M.A. Record-setting algal bloom in Lake Erie caused by agricultural and meteorological trends consistent with expected future conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6448–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhu, J.; Lu, S. Numerical simulation of an algal bloom in Dianshan Lake. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, B.D.; Eberly, J.O.; Jung, C.M.; Medina, V.F. Review and Evaluation of Reservoir Management Strategies for Harmful Algal Blooms; U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Summers, E.J.; Ryder, J.L. A critical review of operational strategies for the management of harmful algal blooms (HABs) in inland reservoirs. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kwak, J.; Ahn, J.M.; Kim, H.; Jeon, J.; Kim, K. Oscillation flow dam operation method for algal bloom mitigation. Water 2022, 14, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, J.M. A Three-Dimensional Environmental Fluid Dynamics Computer Code: Theoretical and Computational Aspects; Virginia Institute of Marine Science, Gloucester Point: Virginia, MS, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.; Jong, J.; Mun, H.; Kim, K.; Seo, I. Mixing analysis of oil spilled into the river by GPS-equipped drifter experiment and numerical modeling. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2016, 32, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cunanan, A.M.; Salvacion, J.W. Analysis of water temperature of Laguna Lake using EFDC model. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 3, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.A. Influence of pumped-storage hydroelectric plant operation on a shallow polymictic lake: Predictions from 3-D hydrodynamic modeling. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2010, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lai, G.; Li, L. Predicting the hydrological impacts of the Poyang Lake project using an EFDC model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 05015009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Kim, S.E.; Baek, K.O. Modeling of algal fluctuations in the reservoir according to the opening of Yeongju Dam. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2023, 56, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.Y.; Baek, K.O. Study of the Mitigation of Algae in Lake Uiam according to the Operation of the Chuncheon Dam and the Soyang Dam. KSCE J. Civ. Environ. Eng. Res. 2022, 42, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.; Seo, I.W.; Kim, D. Effects of hydropeaking by an upstream dam on thermal mixing in a riverine lake. J. Hydrol. 2024, 633, 130992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Xu, Z. Prediction of algal blooming using EFDC model: Case study in the Daoxiang Lake. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, S.; Tsai, C.W. Assessment of uncertainty sources in water quality modeling in the Niagara River. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Acharya, K.; Yu, Z. Modeling impacts of Yangtze River water transfer on water ages in Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, Y.; Kim, B. Simulation of eutrophication in a reservoir by CE-QUAL-W2 for the evaluation of the importance of point sources and summer monsoon. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2019, 35, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, B. Application of a 2-dimensional water quality model (CE-QUAL-W2) to the turbidity interflow in a deep reservoir (Lake Soyang, Korea). Lake Reserv. Manag. 2006, 22, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.K.; Lee, Y. Numerical simulations on the application of a closed-loop lake water heat pump system in the Lake Soyang, Korea. Energies 2020, 13, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Resource Management Information System. Available online: http://wamis.go.kr (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Water Environment Information System. Available online: http://water.nier.go (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Tetra Tech, Inc. The Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code Theory and Computation Volume 3: Water Quality Module; Technical report; Tetra Tech Inc.: Virginia, MS, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulation. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Very Good | Good | Satisfactory | Unsatisfactory | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBIAS (%) | <25 | 25–40 | 40–70 | ≥70 |
| RMSE | The closer to 0, the higher the reliability. | |||
| DO | T-P | TOC | Chl-a | Temp. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uiam 1 | Calibration | PBIAS | 17.70 | 47.39 | 12.55 | 52.70 | 11.52 |
| RMSE | 2.00 | 0.01 | 0.34 | 8.24 | 3.34 | ||
| Validation | PBIAS | 9.32 | 38.63 | 27.97 | 61.74 | 9.15 | |
| RMSE | 1.06 | 0.01 | 0.69 | 13.22 | 2.12 | ||
| Period | Additional Opening at Uiam Dam (m) | Pulse Discharge at Chuncheon Dam (M3/s) | Pulse Discharge at Soyang Dam (m3/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulse_A.1 | 31 August~8 September | 1 | 250 | - |
| Pulse_A.2 | 31 August~8 September | 1 | 250 | 30 |
| Pulse_A.3 | 31 August~8 September | 1 | 250 | 50 |
| Pulse_B.1 | 31 August~4 September | 0.5 | 250 | - |
| Pulse_B.2 | 31 August~4 September | 0.5 | 250 | 30 |
| Pulse_B.3 | 31 August~4 September | 0.5 | 250 | 50 |
| Pulse_B’.1 | 31 August~2 September | 0.5 | 212 | - |
| Pulse_ B’.2 | 31 August~2 September | 0.5 | 212 | 30 |
| Pulse_ B’.3 | 31 August~2 September | 0.5 | 212 | 50 |
| Scenario Name | Uiam 1 | Uiam 2 | Uiam 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difference (mg/m3) | Reduction Rate (%) | Difference (mg/m3) | Reduction Rate (%) | Difference (mg/m3) | Reduction Rate (%) | |
| Pulse_A.1 | −7.595 | 38.8 | −15.067 | 61.0 | −1.611 | 6.2 |
| Pulse_A.2 | −7.300 | 37.2 | −15.067 | 61.0 | −6.355 | 26.8 |
| Pulse_A.3 | −7.466 | 37.1 | −15.067 | 61.0 | −17.433 | 60.6 |
| Pulse_B.1 | −7.310 | 37.3 | −5.836 | 38.3 | −1.887 | 4.5 |
| Pulse_B.2 | −6.937 | 35.4 | −5.834 | 38.3 | −3.482 | 14.2 |
| Pulse_B.3 | −6.673 | 34.0 | −5.834 | 38.3 | −15.250 | 53.0 |
| Pulse_B′.1 | −5.701 | 30.3 | −5.541 | 36.3 | −1.296 | 4.5 |
| Pulse_B′.2 | −5.270 | 28.0 | −5.541 | 36.3 | −2.241 | 8.0 |
| Pulse_B′.3 | −4.997 | 26.6 | −5.541 | 36.3 | −15.263 | 53.1 |
| Before Revision (to 2015) | After Revision (from 2016) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference item | Number of cyanobacteria, Chl-a | Number of cyanobacteria | ||
| Alert step | Caution | 500 cells/mL, 15 mg/m3 | Attention | 1000 cells/mL |
| Warning | 5000 cells/mL, 25 mg/m3 | Warning | 10,000 cells/mL | |
| Emergency | 1,000,000 cells/mL, 100 mg/m3 | Emergency | 1,000,000 cells/mL | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.Y.; Baek, K.O. Scenario-Based Modeling on Chlorophyll-a in Uiam Reservoir of Korea According to Variation of Dam Discharge. Water 2024, 16, 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152120
Lee DY, Baek KO. Scenario-Based Modeling on Chlorophyll-a in Uiam Reservoir of Korea According to Variation of Dam Discharge. Water. 2024; 16(15):2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dong Yeol, and Kyong Oh Baek. 2024. "Scenario-Based Modeling on Chlorophyll-a in Uiam Reservoir of Korea According to Variation of Dam Discharge" Water 16, no. 15: 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152120
APA StyleLee, D. Y., & Baek, K. O. (2024). Scenario-Based Modeling on Chlorophyll-a in Uiam Reservoir of Korea According to Variation of Dam Discharge. Water, 16(15), 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152120







