Surface Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Analysis at the Confluence of the Wei River and Yellow River, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Entropy-Weighted Water Quality Index (EWQI)
2.3.2. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics
3.2. Evaluation of Surface Water Quality and Health Risk Assessment
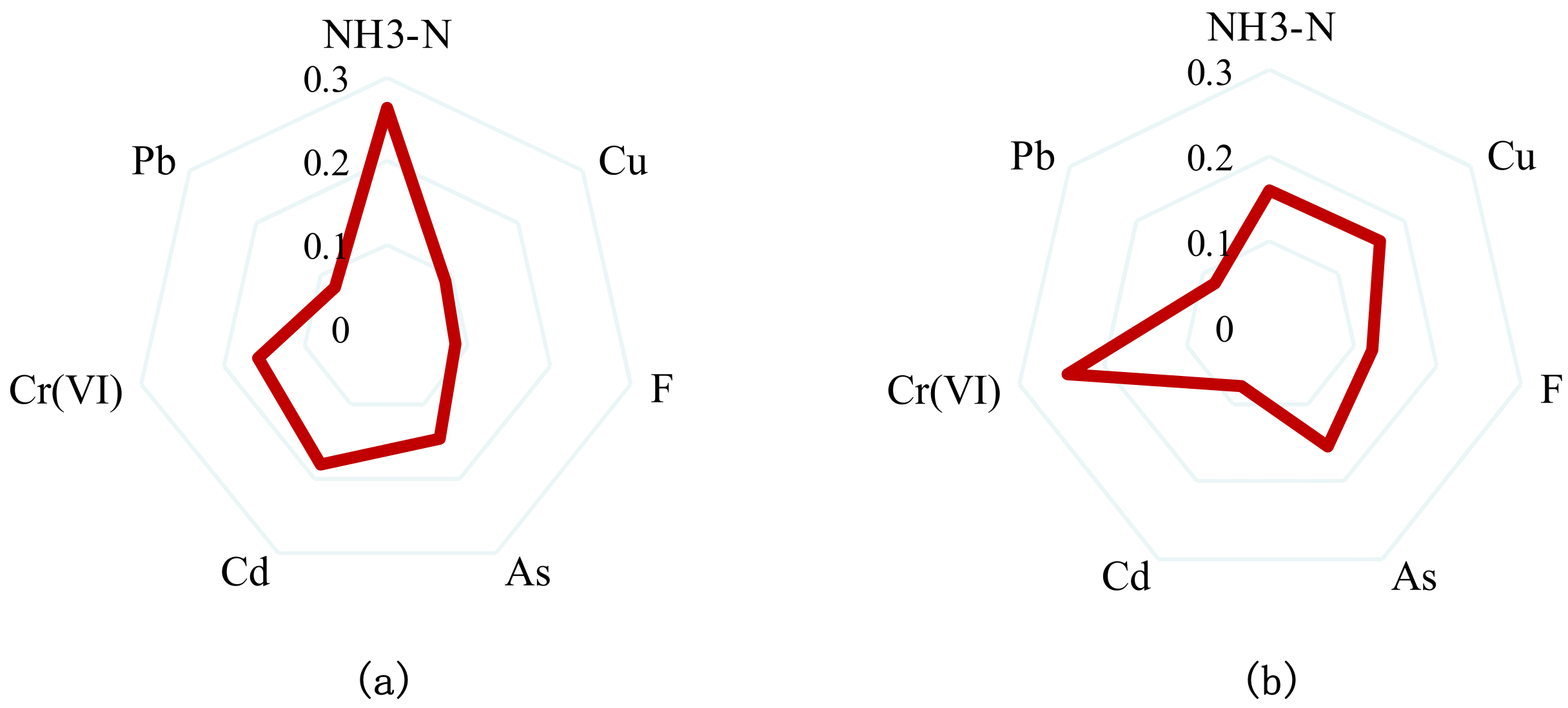
3.3. The Analysis of the Pollution Source
- (1)
- Correlation Analysis
- (2)
- The result of PCA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T. Water quality and interaction between groundwater and surface water impacted by agricultural activities in an oasis-desert region. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, in [Electronic Resource], 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.B.; Patra, K.C. Integrated PCA–RNN approach for surface water quality assessment in the Mahanadi river system. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 7701–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.Y.; Elshewey, A.M.; El-kenawy, E.S.M.; Ibrahim, A.; Talaat, F.M.; Tarek, Z. Water quality prediction using machine learning models based on grid search method. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 8, 35307–35334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Lin, Z.; Zheng, N.; Chen, Y. Identification of water pollution sources and analysis of pollution trigger conditions in Jiuqu River, Luxian County, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 19815–19830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, S.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Soil heavy metal contamination and health risks associated with artisanal gold mining in Tongguan, Shaanxi, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 141, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Lu, N.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, D. Research of Heavy Metals Pollution Soil Risk Evaluation by Means of Engineering in Gold Mining Area, Tongguan, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 170, 032100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liang, W.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, L.; Fan, Y.; Tian, T.; Liu, X. Ecolcgical and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil around the gold mining area in Tongguan of Shaanxi Province. Geol. China 2021, 48, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Shi, C.; Wang, J. A study of the differences in heavy metal distributions in different types of farmland in a mining area. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, A.; Zhang, Z.; Mamat, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y. Pollution assessment and health risk evaluation of eight (metalloid) heavy metals in farmland soil of 146 cities in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3949–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, L.; Xie, D.; Hu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in farmland soils around mining areas and pollution assessment. Huanjing Kexue 2022, 43, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, A.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, G.; Xiao, X.; Cao, J. Source analysis and risk evaluation of heavy metal in the river sediment of polymetallic mining area: Taking the Tonglüshan skarn type Cu-Fe-Au deposit as an example, Hubei section of the Yangtze River Basin, China. China Geol. 2022, 5, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J. Contents of heavy metals in bottom sediments of the Taiyu River in the Tongguan gold mining area, Xiao Qinling Mountains, and contamination assessments. Geol. Bull. China 2008, 27, 1263–1671. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Fang, H.; Li, X.; Ke, H.; Qiao, G. Accumulation and environmental risk on heavy metal pollution in bottom sediments of surface waters in Xiao Qinling gold mine Belt, China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 773, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhao, W. Runoff sensitivity increases with land use/cover change contributing to runoff decline across the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Song, M.; Huang, Y.; Jing, W. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use Changes with Ecosystem Service Value in the Yellow River Basin. Land 2022, 11, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenaya, A.; Berger, M.; Brinkhoff, T.; Ribas-Ribas, M.; Wurl, O. Usage of antibiotics in aquaculture and the impact on coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejazy, M.; Norouzi, R.; Abdi, F.; Javid, F. The impact of aquaculture activities on nitrogenous and phosphorous pollution of water resources in northern Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Feng, S.; Hao, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, B. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of organophosphate esters in aquaculture farms and natural water bodies adjacent to the Huanghe River delta. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 41, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. China Environment Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/shjzlbz/200206/W020061027509896672057.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Hui, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, C.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of water-deficient rivers in China: A case study of the Ciyao River Basin in Shanxi Province. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2023, 15, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Yin, D.; Wu, X.; Cui, H.; An, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Quality Evaluation of Groundwater in Jinta Basin, Northwest China. Water 2023, 15, 4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unigwe, C.; Egbueri, J. Drinking water quality assessment based on statistical analysis and three water quality indices (MWQI, IWQI and EWQI): A case study. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Lv, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, F.; Wang, Q. Spatial–Temporal Changes in Shallow Groundwater Quality with Human Health Risk Assessment in the Luxi Plain (China). Water 2023, 15, 4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinkaralar, O.; Isinkaralar, K.; Bayraktar, E. Monitoring the spatial distribution pattern according to urban land use and health risk assessment on potential toxic metal contamination via street dust in Ankara, Türkiye. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Gao, Z.; Wang, M.; Feng, J.; Xia, L.; Liu, J. Health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in a typical mining town in north China based on Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoumi, D.; Al-Aizari, H.S.; Alaraidh, I.A.; Okla, M.K.; Assal, M.E.; Aizari, A.R.; Moshab, M.S.; Chakiri, S.; Bejjaji, Z. Seasonal Variations and Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Water Quality Index (WQI) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA): A Case Study. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishan, G.; Bhagwat, A.; Sejwal, P.; Yadav, B.K.; Kansal, M.L.; Bradley, A.; Singh, S.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, L.M.; Muste, M. Assessment of groundwater salinity using principal component analysis (PCA): A case study from Mewat (Nuh), Haryana, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Wang, P.; Tansey, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, H. An LSTM neural network for improving wheat yield estimates by integrating remote sensing data and meteorological data in the Guanzhong Plain, PR China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 310, 108629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, S.; Shi, P. Topography and Landforms. In The Geography of Contemporary China; World Regional Geography Book Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 29, pp. 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Shi, X.; Sun, S.; Sun, J.; Hui, B.; He, D.; Chong, F.; Yang, Z. Co-evolution of the Cenozoic tectonics, geomorphology, environment and ecosystem in the Qinling Mountains and adjacent areas, Central China. Geosyst. Geoenviron. 2022, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Hu, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, H. Isotope and fluid inclusion geochemistry and genesis of the Qiangma gold deposit, Xiaoqinling gold field, Qinling Orogen, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 66, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ding, Z.; Qin, W.; Cao, W.; Lu, W.; Xu, X.; Yin, Z. Changes in sediment load in a typical watershed in the tableland and gully region of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2019, 182, 104132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, P.; Du, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Z. Hydrogeochemical processes regulating the groundwater geochemistry and human health risk of groundwater in the rural areas of the Wei River Basin, China. Expo. Health 2024, 16, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L. The pattern, change and driven factors of vegetation cover in the Qin Mountains region. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Pan, L.; Qi, Y.; Guan, X.; Li, J. Land use and land cover change in the Yellow River Basin from 1980 to 2015 and its impact on the ecosystem services. Land 2021, 10, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 494-2009; Water Quality-Guidance on Sampling Techniques. China Environment Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/200910/W020111114543133505806.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- HJ 493-2009; Water Quality Sampling—Technical Regulation of the Preservation and Handling of Samples. China Environment Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/200910/W020111114540735543139.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Amiri, V.; Rezaei, M.; Sohrabi, N. Groundwater quality assessment using entropy weighted water quality index (EWQI) in Lenjanat, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3479–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A. Anthropogenic Effects on Surface Water Quality Assessment in Baitarani River Basin, Odisha Using GIS and MCDM Techniques. Eng. Res. Transcr. 2023, 5, 37–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2015 Update to the 1998 U.S. EPA Supplemental Environmental Projects Policy. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-04/documents/sepupdatedpolicy15.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Varol, M.; Tokatlı, C. Evaluation of the water quality of a highly polluted stream with water quality indices and health risk assessment methods. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbasi, J.C.; Chukwu, C.N.; Nweke, N.D.; Uwajingba, H.C.; Khan, M.Y.A.; Egbueri, J.C. Water pollution indexing and health risk assessment due to PTE ingestion and dermal absorption for nine human populations in Southeast Nigeria. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 21, 100921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 25.3-2014; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Technical Guidelines for RISK Assessment of Contaminated Sites. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. Available online: https://english.mee.gov.cn/Resources/standards/Soil/Method_Standard4/201605/W020160506416578822108.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Exposure Factors Handbook, 2011st ed.; EPA/600/R-09/052F; Office of Research and Development, United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/exposure-factors-handbook (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Guidelines for Exposure Assessment; EPA/600/Z-92/001; Office of Research and Development, United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/guidelines-exposure-assessment (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment; EPA/630/P-03/001F; Office of Research and Development, Risk Assessment Forum: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2013-09/documents/cancer_guidelines_final_3-25-05.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Daffertshofer, A.; Lamoth, C.; Meijer, O.; Beek, P.J. PCA in studying coordination and variability: A tutorial. Clin. Biomech. 2004, 19, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maćkiewicz, A.; Ratajczak, W. Principal components analysis (PCA). Comput. Geosci. 1993, 19, 303–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.; Sun, J.; Dai, J.; Rao, F. Research on Development of Health Tourism Products in Qinling Mountains; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 2352–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, Y.; Kuang, J. Historical earthquake records in the Weihe Basin, central China and new insights for geothermal genesis. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1287450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, P.; Cui, X.; He, S. Groundwater quality, health risk, and major influencing factors in the lower Beiluo River watershed of northwest China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2021, 27, 1987–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Risk Type | Risk Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Carcinogenic Risk | High Risk | |
| Moderate Risk | ||
| Low Risk | ||
| Negligible Risk | ||
| Non-Carcinogenic Risk | High Risk | |
| Moderate Risk | ||
| Low Risk | ||
| No Significant Risk |
| Parameters | The Dry Season | The Wet Season | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | STD | CV (%) | ES (%) | Min | Max | Mean | STD | CV (%) | ES (%) | |
| (mg/L) | 3.22 | 527 | 118.66 | 111.5 | 93.97 | 4.08 | 956 | 163.6 | 212 | 129.59 | ||
| 1.6 | 20.6 | 6.88 | 4.14 | 60.14 | 2.04 | 23.3 | 8.41 | 5.08 | 60.42 | |||
| 26.7 | 139 | 70.89 | 24.62 | 34.73 | 17.1 | 382 | 100.47 | 66.6 | 66.29 | |||
| 3.87 | 77.9 | 33.79 | 19.18 | 56.75 | 3.84 | 62.4 | 31.21 | 17.44 | 55.89 | |||
| (mg/L) | 3.51 | 366 | 137.34 | 103.3 | 75.22 | 2.07 | 1776 | 139.26 | 275.86 | 198.09 | ||
| (mg/L) | 40.3 | 973 | 251.96 | 181.2 | 71.92 | 32.8 | 1968 | 238.2 | 338.87 | 142.26 | ||
| (mg/L) | 28.43 | 525.09 | 164.91 | 107.8 | 65.37 | 11.1 | 108 | 45.45 | 19.67 | 43.29 | ||
| (mg/L) | 0 | 16.43 | 5.53 | 5 | 90.35 | 0 | 1.52 | 0.08 | 0.34 | 441.44 | ||
| (mg/L) | 0 | 0.3 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 119.24 | 0 | 1.43 | 0.17 | 0.28 | 166.48 | ||
| (mg/L) | 0.27 | 2.26 | 0.72 | 0.36 | 49.49 | 15 | 0.15 | 2.23 | 0.63 | 0.36 | 57.51 | 5 |
| 0.16 | 0.92 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 62.11 | 0.04 | 0.72 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 81.54 | 7.5 | ||
| Mn (µg/L) | 0.52 | 773 | 123.23 | 145.81 | 115.79 | 31 | 800 | 241.12 | 91.48 | |||
| Ni (µg/L) | 1.17 | 12.5 | 5.47 | 2.7 | 49.81 | 2.21 | 18.3 | 7.83 | 56.74 | |||
| (µg/L) | 1.58 | 19.3 | 5.9 | 3.64 | 61.63 | 8.17 | 54.5 | 15.94 | 55.17 | |||
| (µg/L) | <0.2 | 0.33 | / | 0.05 | 15.81 | 0.2 | 0.44 | 0.31 | 49.59 | |||
| (µg/L) | 0.38 | 25.1 | 2.74 | 3.93 | 143.64 | 2.5 | 0.38 | 29.1 | 3.41 | 156.44 | 5 | |
| Hg (µg/L) | <0.16 | <0.16 | / | / | / | <0.16 | <0.16 | / | / | / | ||
| As (µg/L) | <1.20 | 16.92 | / | 3.82 | 86.8 | 1.13 | 81.1 | 18.53 | 110.02 | 10 | ||
| Ag (µg/L) | <0.16 | <0.16 | / | / | / | <0.16 | 0.9 | / | / | 15.81 | ||
| Fe (mg/L) | <0.07 | 0.85 | / | 0.2 | 73.15 | <0.07 | 1.49 | / | / | 95.52 | ||
| (mg/L) | <0.004 | 0.03 | / | 0.01 | 65.28 | 0.14 | 54.8 | 19.4 | 60.95 | 95 | ||
| The Location of the Sample | Name | The Dry Season | The Wet Season | The Location of the Sample | Name | The Dry Season | The Wet Season | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huanghe | upstream | W-35 | I | V | Liuyehe | upstream | W-12 | I | V |
| midstream | W-36 | I | V | midstream | W-13 | I | V | ||
| downstream | W-37 | I | II | downstream | W-14 | I | V | ||
| Beiluohe | upstream | W-40 | I | V | Luofuhe | upstream | W-15 | I | V |
| midstream | W-39 | I | V | midstream | W-16 | I | V | ||
| downstream | W-38 | I | V | downstream | W-17 | I | V | ||
| Weihe | upstream | W-18 | I | V | Jingouhe | upstream | W-01 | I | II |
| W-19 | I | V | W-05 | I | V | ||||
| midstream | W-20 | I | V | midstream | W-02 | I | V | ||
| downstream | W-21 | I | V | downstream | W-03 | I | V | ||
| W-22 | I | V | Changjianhe | upstream | W-07 | I | V | ||
| The southern part of the river wetland | W-23 | II | V | W-09 | I | V | |||
| W-24 | I | V | midstream | W-08 | I | V | |||
| W-25 | I | V | W-10 | I | V | ||||
| W-26 | I | V | downstream | W-11 | I | V | |||
| W-27 | II | V | The northern part of the river wetland | W-31 | I | V | |||
| W-28 | II | V | W-32 | II | V | ||||
| W-29 | I | V | W-33 | I | V | ||||
| W-30 | II | V | W-34 | I | V | ||||
| Xiaopuyu Reservoir | W-06 | I | V | Tiegou Reservoir | W-04 | I | V | ||
| Risk Pathway | The Wet Season | The Dry Season | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | Children | Adults | Children | ||
| Carcinogenic risk | The oral ingestion | ||||
| The dermal contact | |||||
| Non-carcinogenic risk | The oral ingestion | ||||
| The dermal contact | |||||
| Parameters | The Dry Season | The Wet Season | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPC1 | DPC2 | DPC3 | WPC1 | WPC2 | WPC3 | |
| −0.083 | 0.032 | −0.707 | 0.160 | 0.012 | 0.739 | |
| 0.062 | −0.630 | 0.413 | 0.843 | 0.211 | 0.197 | |
| −0.032 | 0.473 | 0.634 | −0.632 | 0.191 | 0.518 | |
| 0.984 | −0.043 | −0.018 | 0.037 | 0.879 | 0.078 | |
| 0.970 | 0.106 | 0.122 | −0.028 | 0.782 | −0.141 | |
| −0.193 | −0.605 | −0.060 | 0.816 | −0.153 | 0.299 | |
| −0.100 | 0.713 | 0.255 | 0.230 | −0.459 | 0.619 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Guo, W.; Yan, J. Surface Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Analysis at the Confluence of the Wei River and Yellow River, China. Water 2024, 16, 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16142035
Zhang J, Hao Z, Liu X, Wang B, Guo W, Yan J. Surface Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Analysis at the Confluence of the Wei River and Yellow River, China. Water. 2024; 16(14):2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16142035
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingru, Ziqiong Hao, Xiaohuang Liu, Bo Wang, Wei Guo, and Jingjing Yan. 2024. "Surface Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Analysis at the Confluence of the Wei River and Yellow River, China" Water 16, no. 14: 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16142035
APA StyleZhang, J., Hao, Z., Liu, X., Wang, B., Guo, W., & Yan, J. (2024). Surface Water Quality Evaluation and Pollution Source Analysis at the Confluence of the Wei River and Yellow River, China. Water, 16(14), 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16142035






