Abstract
In this study, a comparison of the concentrations of eight heavy metals (including Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cr, As, Cd, and Hg) was conducted between wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus. Significant differences in the concentrations of Zn, Cd, As, and Hg were observed between wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus. The results showed that the mean Zn concentration was significantly higher in cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus (3.051 ± 0.738 mg/kg) when compared to its wild counterpart (2.512 ± 0.407 mg/kg). In contrast, the mean Cd concentration was found to be lower in the cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus (0.001 ± 0.0007 mg/kg) than in the wild ones (0.003 ± 0.003 mg/kg). Likewise, the wild samples demonstrated a higher mean As concentration (1.494 ± 0.659 mg/kg) than the cultured samples (0.594 ± 0.215 mg/kg). Lastly, it was noted that the mean Hg concentration was considerably higher in the cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus (0.042 ± 0.016 mg/kg) than in the wild specimens (0.014 ± 0.011 mg/kg). Pollution levels and health risks were evaluated using the single-factor pollution index (SFI), metal pollution index (MPI), and health risk assessment methods. The results showed that, for Cu, Zn, Cr, and Cd, both wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus had SFI values below 1 compared to the marine organism quality standards. The MPI values for wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus were 0.188 ± 0.051 and 0.172 ± 0.054, respectively, both far below the safety limit of 2 for pollution-free aquatic products. The Hazard Index (HI) for wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus were below 1, indicating no health risks from long-term consumption. A discriminant analysis, based on Zn, Cd, As, and Hg concentrations, distinguished wild from cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus with a 96.0% accuracy, remaining stable at over 94.9% upon cross-validation. These findings accurately evaluate that there is no risk to human health from consuming Oplegnathus fasciatus, which is significant in safeguarding public health.
1. Introduction
Due to the discharge of heavy-metal-laden wastewater from human industrial and agricultural activities, the level of heavy metals in marine waters is increasing [1,2]. The occurrence and dispersal of these heavy metals within marine ecosystems are shaped by both natural processes and human interventions. In wild habitats, these heavy metals can enter water bodies through natural processes like volcanic activity, the weathering of rocks, and soil erosion. Moreover, human activities have significantly increased their concentrations. Industrial discharges, mining operations, agricultural runoff, and wastewater treatment plants are major contributors to heavy metal pollution in rivers, lakes, and oceans [3]. In aquaculture, sources of heavy metals include contaminated feed, water used for fish culturing, and the use of metal-containing antifouling paints on fish-culturing structures [4]. These heavy metals accumulate in the tissues of cultured fish, posing health risks to both the fish and humans who consume them. The primary mechanism of heavy metal accumulation in fish involves the direct absorption of heavy metals from water through the gills and indirect absorption through the food chain. Within the fish body, heavy metals accumulate mainly in organs such as the gills, liver, kidneys, and muscle tissues, thereby affecting the fish’s physiological functions [5].
The accumulation of heavy metals in fish is significantly influenced by their concentration in the surrounding water and food sources [6]. Fish species residing in different habitats and possessing diverse feeding habits exhibit distinct characteristics in the accumulation and distribution of metal elements within their bodies. Considerable differences in heavy metal compositions have been observed between wild and cultured populations of Scophthalmus maximus and Oncorhynchus mykiss [7,8]. Numerous studies indicate that cultured fish tend to have lower levels of heavy metals [9], owing to the control over feed contamination and water quality management in aquaculture, which leads to safer products [10]. Nevertheless, there are also findings suggesting higher concentrations of heavy metals and pollutants in cultured fish [11], indicating the need for continued research and improvement in aquaculture practices. As predators in the aquatic ecosystem, fish not only bear the brunt of heavy metals’ toxicity but also serve as vectors for contaminant propagation to higher trophic levels, potentially posing health risks to both the fish and humans who consume them. The National Food Safety Standards GB 2762-2022 stipulate that the maximum permissible limits for Pb, Cu, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg in edible fish are set at 0.5, 50, 50, 2, 0.1, 0.5, and 0.05 mg/kg [12], respectively. In light of the persistence, prolonged biological half-life, and inherent toxicity of heavy metals, undertaking a thorough health risk assessment of heavy metal ingestion is paramount [13].
The reef-associated fish Oplegnathus fasciatus, belonging to the Perciformes family of Oplegnathidae, primarily distributes along the coastlines of the Pacific and Indian oceans [14]. In recent years, due to the impact of high-intensity fishing activities, seawater pollution, and habitat destruction, the resource population of Oplegnathus fasciatus has experienced significant declines [15]. This species boasts rapid growth, nutritionally rich muscle, and high economic and edible values [16]. As a native natural fish species with no distinct peak fishing season, Oplegnathus fasciatus holds promising prospects for aquaculture. With the advancement in seedling-breeding technology, industrialized aquaculture schemes have also been proposed. However, the current research lacks attention to the differences in heavy metal accumulation and health risks in Oplegnathus fasciatus. Using Oplegnathus fasciatus as a case study, this research aims to analyze the heavy metal differences between wild and cultured individuals, reveal the distinct characteristics of metal accumulation in both groups, and conduct a discriminant analysis based on these differences. The findings aim to assess the potential risks to human health from consuming Oplegnathus fasciatus, offering scientific evidence for an aquatic product quality safety evaluation, thereby promoting its sustainable utilization and management strategy formulation. Concurrently, the surveillance of heavy metals in fish yields invaluable intelligence on the contamination status of fish, laying a scientific groundwork for effective preventative and remedial actions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
This study encompassed the use of a total of 88 specimens of the species Oplegnathus fasciatus, including 44 from a wild population and 44 from a cultured population (Table 1). The wild samples were collected in winter 2022 from the interconnected waters between the Yangtze River estuary and the northern Zhejiang coastal areas in China using the gillnet fishing vessel “Zhepuyu 32128” with a hull length of 44 m and a mesh size of 40 mm (Figure 1). The water depths at the wild sampling localities ranged from 11.9 to 48.36 m, with a bottom sea temperature range of 12.3 to 16.2 °C, a bottom sea salinity range of 24.81 to 30.19, and a chlorophyll-a concentration range of 0.61–0.84 mg/L. The cultured samples were obtained in winter 2022 from a farming facility on Xixuan Island (Figure 1). The aquaculture farm conducted daily monitoring of water quality, primarily focusing on water temperature, salinity, and pH levels. These specimens were reared in concrete tanks measuring 5.0 m × 5.0 m × 1.5 m, illuminated by fluorescent lamps with an intensity of 116 lx, and maintained under conditions of 200% to 300% daily water exchange, water temperature ranging from 20 to 22 °C, salinity from 22 to 26, and pH levels between 7.6 and 8.0. The fish were fed with “Yubao” feed at a daily ration of 3% of their body weight. All samples were preserved in ice upon collection and transported to the laboratory for analysis after being individually frozen. Prior to dissection, the samples were thawed, rinsed with deionized water, and dissected using stainless steel knives to separate the muscle tissues. The deionized water was Milli-Q water with a resistivity of 18.2 MΩ·cm at 25 °C, sourced from the ultra-pure water purifier (Synergy, Millipore, Alsace, France). The mass of each tissue was recorded, and all tissue samples were immediately freeze-dried for storage after processing.

Table 1.
Sample composition of wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus.
Figure 1.
Map of the sampling areas for wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus.
2.2. Determination of Metal Content
The muscle samples were packed in plastic bottles and underwent a 72 h freeze-drying process. Following this, the freeze-dried tissues were placed into 10 mL centrifuge tubes containing grinding beads. Then, using a grinder, the samples were pulverized into a fine powder. For the measurement of Hg in the Oplegnathus fasciatus samples, 0.03 g of the sample (dry weight) was taken and analyzed using a direct mercury analyzer (DMA-80, Milestone, Sorisole, Italy). To determine the concentrations of Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cr, Cd, and As in the samples, 0.10 g of the tissue was placed in a polytetrafluoroethylene digestion tube. A 6 mL mixture of HNO3 (Trace Metal, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA.) and H2O2 (superior purity, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) in a ratio of 4:2 (v/v) was added to the tube. The mixture was shaken thoroughly, tightened, and then digested in a fully automated microwave digestion system (ETHOSUP, LabTech, Beijing, China). After the digestion solution cooled, it was transferred to a 50 mL centrifuge tube and brought to a final volume of 50 mL with ultrapure water. The metal concentrations were determined using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (7900a ICP-MS, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The digestion cans and glassware used in the experiment were soaked in HNO3 prior to use and thoroughly rinsed with deionized water to minimize potential contamination from the external environment and interference with analytical detection. The quality control of the testing method was verified by simultaneously analyzing the standard reference material for component analysis of salmon freeze-dried powder (GBW 10210). The recovery rates of Hg, Cr, Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, As, and Cd were 85.9%, 99.9%, 115%, 110.2%, 92.3%, 86.4%, 85%, and 86.6%, respectively. The recovery rates of the eight heavy metal elements ranged from 85% to 115%, thus meeting the quality control requirements. Additionally, the sample exhibited an RSD of less than 10%, indicating a high level of reliability.
2.3. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution Levels in Samples
The evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the muscle samples of Oplegnathus fasciatus was conducted according to the standards outlined in the Marine Biological Quality (GB 18421-2001). Both the single factor index (SFI) and metal pollution index (MPI) methods were utilized to assess the pollution levels and differences in heavy metal accumulation capabilities across the samples. Specifically, the single factor index (SFI) method evaluates the pollution level of each heavy metal individually. However, the specific calculation method and details of SFI are beyond the scope of this study and will be addressed in future research.
In the equation, SFI denotes the pollution index for heavy metal i, Ci represents the measured content of heavy metal i in the biological sample (mg/kg, wet weight), and Si refers to the evaluation standard value for heavy metal i (mg/kg, wet weight).
In the equation, Cn represents the concentration of the nth heavy metal in the sample (measured in mg/kg, based on wet weight), where n denotes the number of evaluated elements. According to the National Food Safety Standards (GB 2762-2022), the maximum values in edible fish for Cu, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg are 50, 50, 2, 0.1, 0.5, and 0.05 mg/kg, respectively. The evaluation criteria for SFI and MPI are outlined in the following table (Table 2 and Table 3).

Table 2.
The single factor index (SFI) value with the corresponding pollution criteria [17].

Table 3.
The metal pollution index (MPI) value with the corresponding pollution criteria [18].
2.4. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Exposure
2.4.1. Estimated Daily Intake (EDI)
In the absence of specific daily average intake data for the studied samples, this research employs the daily average intake of bottom-dwelling fish as an approximate substitute for the daily average intake of the samples. Based on the heavy metal concentrations in the Oplegnathus fasciatus and the average daily consumption of bottom-dwelling fish, the estimated daily intake (EDI) of these six heavy metals is calculated using the following formula:
where FIR represents the fish ingestion rate per day (g·d−1), Ci denotes the heavy metal concentration (mg/kg), and BW stands for the average body weight of an adult (60 kg). According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) survey data, the average ingestion rate of bottom-dwelling fish in China is 8.96 g·d−1.
2.4.2. Non-Carcinogenic Risk Evaluation
The target hazard quotient (THQ) is a comprehensive risk index that compares pollutant intake with standard reference doses and is often used for non-carcinogenic risk assessment of heavy metals. A THQ value below 1 suggests no significant health risk to the exposed population, whereas a THQ value greater than or equal to 1 indicates a health risk. The calculation formula is as follows:
where EF represents the exposure frequency (365 d∙a−1), ED represents the exposure duration (70 a), Ci is the heavy metal mass fraction in fish (mg∙kg−1), RFD is the reference dose (mg∙kg−1∙d−1), BW is the average body weight of an adult (60 kg), and AT stands for the average exposure time (25,550 d). The RFDs for Mn, Cu, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg are 0.14, 0.04, 0.3, 0.003, 0.001, 0.0003, and 0.0003 mg/kg·d−1, respectively. Given the combined and cumulative effects of heavy metals in the body, the hazard index (HI) is often used to comprehensively evaluate the risks posed by various heavy metals to human health. Similarly, an HI value greater than or equal to 1 indicates potential harm to humans, while a lower value suggests negligible risk. The HI is calculated using the following formula:
2.5. The Stepwise Discriminant Analysis
Utilizing the stepwise discriminant analysis (SDA) method in IBM SPSS V27.0.1 Statistics software, we have established a discriminant formula to distinguish between wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus.
The calculation formula for discriminant accuracy (Pa) is:
where A represents the number of correctly classified individuals, and B represents the total number of samples in that particular group.
For the comprehensive discriminant rate (Da), the calculation formula is:
where Ai is the number of correctly classified individuals in the i group, Bi is the total number of samples in the i group, and n represents the total number of groups.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis in this study was performed using an independent-sample t-test (α = 0.05) implemented via IBM SPSS V27.0.1 Statistics software. The t-test was considered the most suitable method for analyzing our dataset, as it ensured the clarity and accuracy of our findings. Specifically, we employed the t-test to investigate variations in metal concentrations between wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus, with a p-value < 0.01 indicating a highly significant difference and a p-value < 0.05 representing a significant difference.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Heavy Metal Concentrations in Wild and Cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus
The concentrations of eight heavy metal elements (Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg) in Oplegnathus fasciatus ranged from 2.676 to 65.721, 0.093 to 0.376, 0.107 to 1.01, 1.737 to 3.358, 0.004 to 0.146, 0.0005 to 0.018, 0.596 to 3.57, and 0.0007 to 0.058 mg/kg, respectively (Table 4). Notably, the concentrations of Fe and Zn were significantly higher than those of the other heavy metals. A comparative analysis revealed that, among these metals, only the concentrations of Cu, Zn, and Hg were lower in wild Oplegnathus fasciatus compared to the cultured counterparts, whereas the concentrations of the remaining heavy metals were higher in wild individuals. Upon performing a statistical analysis to test the differences in heavy metal concentrations between wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus, the results indicated highly significant differences in Zn, Cd, As, and Hg concentrations, while no significant differences were observed in Fe, Mn, Cu, and Cr concentrations.

Table 4.
Concentrations and differences in heavy metal elements (mg/kg, wet weight) between 44 wild and 44 cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus (independent-sample t-test, α = 0.05).
3.2. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution Levels in Oplegnathus fasciatus
To evaluate the pollution levels of heavy metals in the muscle tissue of wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus, the Single Factor Index (SFI) and Multi-Pollution Index (MPI) were employed, referencing the national standards for marine organism quality. Based on the analysis of three categories of pollution indices, it was observed that, for Cu, Zn, Cr, and Cd, the SFI values for both wild and cultured specimens were less than 1 when compared to the first-class marine organism quality standards (Table 5). For As, 79% of the SFI values in wild Oplegnathus fasciatus exceeded 1, with the highest reaching 3.57, while only 4% of the SFI values in cultured individuals surpassed 1, with the peak reaching 1.14. Similarly, for Hg, 2% of the SFI values in wild specimens exceeded 1, peaking at 1.16, while 24% of the SFI values in cultured specimens exceeded 1, with the highest value being 2.14. When compared to the second-class marine organism quality standards, the SFI values for Cu, Zn, Cr, Cd, and As in both wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus were less than 1. Moreover, 100% of the Hg SFI values in wild specimens were below 1, whereas 2% of the SFI values in cultured specimens exceeded 1.

Table 5.
Heavy metal pollution indices of Oplegnathus fasciatus.
The MPI for wild Oplegnathus fasciatus was 0.188 ± 0.051, while, for cultured individuals, it was 0.172 ± 0.054. The MPI values for both wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus were far below 2, satisfying the safety requirements for pollution-free aquatic products.
3.3. Evaluation of Health Risks
The accumulation of toxic elements in Oplegnathus fasciatus poses potential harm to consumer health, given that muscle tissue is the primary edible portion of this fish species. Therefore, conducting a health risk assessment on the muscle tissue of Oplegnathus fasciatus is crucial. The Estimated Daily Intake (EDI) of the eight toxic elements was calculated based on the concentration of these elements in the muscle and the daily average consumption of the fish in China as suggested by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
The average EDIs for the toxic elements Mn, Cu, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg were significantly lower than the Provisional Tolerable Daily Intakes (PTDIs) established by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Furthermore, the average Target Hazard Quotients (THQs) for these six heavy metals were all below 1. Specifically, among the wild specimens, the highest THQ value was recorded for As (0.80497), and the lowest was for Mn (0.00019). Conversely, for the cultured individuals, As exhibited the highest THQ (0.32049), while Cd had the lowest (0.00018). The Hazard Index (HI) for wild Oplegnathus fasciatus was 0.81861, which was higher than the HI of 0.34930 recorded for the cultured variety. Nevertheless, both values were less than 1, indicating that there is no potential health risk associated with the long-term consumption of Oplegnathus fasciatus by local residents due to heavy metal exposure (Table 6).

Table 6.
Evaluation of health risks associated with heavy metals in the muscle tissue of Oplegnathus fasciatus.
3.4. Discriminant Analysis of Wild and Cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus
After screening the metal concentrations in Oplegnathus fasciatus, four significant variables were identified: X1: Zn, X2: Cd, X3: As, and X4: Hg. The discriminant function equations established for wild and cultured specimens are as follows:
For wild Oplegnathus fasciatus (FC1): Y1 = 5.892X1 + 136.157X2 + 4.796X3 + 50.176X4 − 12.305;
For cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus (FC2): Y2 = 8.197X1 − 376.372X2 +1.084X3 + 161.404X4 − 16.761.
Based on the discriminant equations FC1 and FC2, scatter plots for both wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus were calculated and plotted (Figure 2).
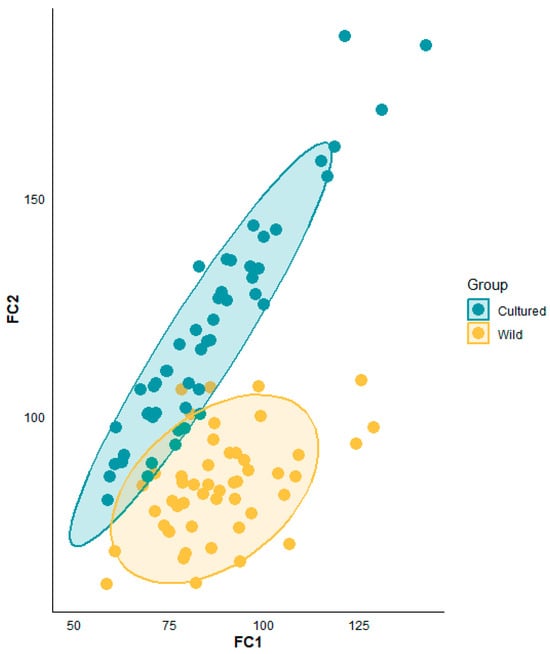
Figure 2.
The scatter diagram representing discriminant function equations for heavy metals in the muscle tissue of wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus.
The discriminant results reveal that, in the initial discrimination, the accuracy for wild Oplegnathus fasciatus was 91.8%, while, for cultured individuals, it was 100%, resulting in an overall accuracy of 96.0%. Following cross-validation, the accuracy for wild specimens decreased to 89.8%, but the accuracy for cultured specimens remained at 100%, yielding an overall accuracy of 94.9%. Although the cross-validation results exhibited a slight decrease compared to the initial discrimination, the accuracy rates remained above 94% (Table 7).

Table 7.
Stepwise discriminant analysis results based on metal concentrations in Oplegnathus fasciatus.
4. Discussion
4.1. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Wild and Cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus
In this study, a comprehensive comparative analysis of heavy metal concentrations in wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus revealed significant differences in heavy metal accumulation between these two groups. Among the eight heavy metals tested, comprehensive comparisons revealed significant differences in the accumulation of Zn, Cd, As, and Hg between cultured and wild Oplegnathus fasciatus. However, no significant differences were observed in the concentrations of Fe, Mn, Cu, and Cr. We observed that both wild and cultured specimens contained relatively high concentrations of Fe and Zn, and further noted a wide range in Fe content. Fe and Zn are essential trace elements for the growth and overall health of fish. Specifically, Fe plays a key role in biochemical processes such as oxygen transport, electron transfer, and energy metabolism, while Zn is vital for enzymatic reactions, metabolic functions, immune response, reproduction, and maintaining cell membrane integrity [19]. Similar findings have been observed in studies regarding Channa punctatus, where the content of Fe and Zn in its muscle tissue is significantly higher than other heavy metal elements [20]. The Fe content in the muscle tissues of both cultured and wild Oplegnathus fasciatus showed a wide range, which may be attributed to factors such as age, size, metabolic rate, health status, diet, and feeding habits [21].
A statistical analysis showed that cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus had higher Zn and Hg concentrations than wild ones. The elevated Zn, crucial for fish growth, may stem from feed additives as fish efficiently absorb Zn from feed. Previous studies noted Zn content differences in cultured and wild Psetta maxima [7]. The higher Hg in cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus contradicts findings in other fish, possibly due to higher water temperatures and varied food composition in cultured environments. Methylmercury accumulates in organisms through the food chain [22]. Despite Oplegnathus fasciatus’s low trophic position [23], their increased Hg levels in captivity may relate to a richer feed and higher consumption. Higher water temperatures in cultured environments boost fish activity, raising energy demands and potentially increasing food intake. The consistent food supply in captivity may also elevate Hg accumulation [24].
Wild Oplegnathus fasciatus show high Cd and As levels, likely due to heavy metal pollution in their habitats. The latest research found that, in the surface sediments of the south area of the Yangtze River Estuary, although the ecological risk levels of As and Cd are low, the content of As in 2021 was 9.583 ± 1.713, which was significantly higher than that in previous years [25]. There is no significant correlation between total As concentration and trophic level [26], representing a stark contrast to the biomagnification of mercury, particularly methylmercury, which is a quintessential example of heavy metal biomagnification in organisms [27]. Aquaculture ponds have better water quality as a result of rigorous treatment, unlike natural sea areas where purification relies on less efficient natural processes, making them more vulnerable to pollution [28]. Additionally, salinity is a critical factor influencing heavy metal accumulation in marine organisms. Research has revealed that arsenic concentrations in marine organisms increase with rising salinity. Nearshore-cultured spotted knifejaw breams often exhibit lower salinity levels due to factors such as surface runoff and precipitation, compared to those in natural sea areas [29,30,31]. It is noteworthy that As exhibits the potential for biomagnification in benthic food chains. Studies have shown that inorganic As can be efficiently transformed in benthic food chains, primarily occurring at the level of primary consumers [32]. Given that wild spotted knifejaw breams predominantly feed on invertebrates, the accumulation of As in their food sources may contribute to the high As concentrations observed in their bodies.
4.2. Heavy Metal Concentrations and Safety Evaluation of Wild and Cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus
Upon a thorough computation and comparison of indices such as SFI, MPI, EDI, THQ, and HI with the threshold values stipulated in the “Marine Organism Quality” standard (GB 18421-2001), it is evident that wild Oplegnathus fasciatus exhibit relatively high concentrations of Cd and As, with As concentrations specifically surpassing the first-class limit set by the standard. In contrast, cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus demonstrate elevated concentrations of Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cr, and Hg, particularly Hg concentrations exceeding both first- and second-class limits. Nevertheless, rigorous non-carcinogenic risk assessments indicate that the ingestion of both wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus does not pose a significant risk to human health in terms of heavy metal exposure. This finding underscores that, although cultured specimens exhibit higher concentrations of certain heavy metals compared to their wild counterparts, it does not necessarily imply a reduced level of food safety. Provided that these heavy metal concentrations remain within the nationally mandated safety thresholds, both wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus can be consumed safely. Overall, the levels of heavy metal pollution in both wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus are relatively low, fulfilling the safety requirements for pollution-free aquatic products. However, given the cumulative effects of heavy metals and the potential risks associated with long-term exposure, the continuous monitoring and management of heavy metal content in marine fish species like Oplegnathus fasciatus remain paramount. Moreover, studies that correlate elevated mercury levels in human blood with fish consumption [33,34] further underscore the crucial importance of heavy metal monitoring.
4.3. Heavy Metals for Distinguishing Wild and Cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus
In our discriminant analysis, we successfully identified Zn, Cd, As, and Hg as four crucial variables and constructed corresponding discriminant functions. This achievement not only validated the conclusions of the differential test but also emphasized the pivotal role of these four heavy metal elements in distinguishing between wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus. The accurate discrimination of Oplegnathus fasciatus between wild and cultured origin, through the measurement of these element concentrations, holds significant implications for strengthening market surveillance and assisting consumer choices. In studies utilizing heavy metal elements for the population classification of various species, notable discriminatory results have been achieved. For instance, the discrimination accuracy for different populations of Eriocheir sinensi was 98.3% [35], while, for trout, the accuracy reached 100% between wild and cultured groups [36]. Similarly, the discrimination accuracy for Anguilla japonica populations stood at 72.7% [37], and, for salmon, it ranged from 87% to 94% between wild and cultured groups [38]. Furthermore, the discrimination accuracy for Apostichopus japonicu populations from different sea areas was 100% [39], as well as for wild and cultured Micropterus salmoides populations [40], reaching a perfect score. Moreover, the discrimination accuracy for wild and cultured Lates calcarifer populations was 88% [41]. Although the discrimination accuracy achieved in this study for wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus shows a good performance when compared to other heavy-metal-based species discrimination analyses, there is still room for improvement. In future research, we plan to introduce additional heavy metal elements, and consider the measurement of isotopes, aiming to further enhance the accuracy of discrimination.
5. Conclusions
Through a comparative analysis of heavy metal concentrations in wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus, this study revealed distinct patterns of heavy metal accumulation between the two sources. Notably, Zn, Cd, As, and Hg were successfully identified as key variables for distinguishing wild from cultured specimens, leading to the development of an efficient discriminant function. While the discrimination accuracy achieved in this study is commendable compared to other species-specific discriminant analyses, there remains potential for further improvement. Health risk assessment results indicate that both wild and cultured Oplegnathus fasciatus are safe for consumption, fulfilling the requirements for pollution-free aquatic products. However, given the cumulative effects of heavy metals, the continued monitoring and management of heavy metals in marine fish remain crucial. In future research, we aim to introduce the measurement of additional heavy metal elements and isotopes to enhance the accuracy of discrimination. Furthermore, we plan to delve deeper into the mechanisms of heavy metal accumulation in different environments and the factors influencing them, providing a more scientific basis for the development of policies regarding marine food safety and the prevention and control of heavy metal pollution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.L. and K.Z.; methodology, K.L. and W.Q.; software, K.L.; validation, W.Q., K.Z. and K.X.; formal analysis, K.L.; investigation, K.Z.; resources, W.Q. and K.X.; data curation, K.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, K.L. and K.Z.; writing—review and editing, W.Q. and K.X.; visualization, K.L.; supervision, K.X.; project administration, K.Z.; funding acquisition, K.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant [Grant number: LGN21C190005], the Key Technology and System Exploration of Quota Fishing, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs Agricultural Finance of China [Grant number: 36, 2017], and the National Key R&D Program of China [Grant number: 2019YFD0901204].
Institutional Review Board Statement
The studies in Oplegnathus fasciatus received approval from Zhejiang Ocean University’s committee on the ethics of animal experiments (Approval numbers: ZJOU-AQU-2022-090, approved on 15 April 2022).
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff members of the Scientific Observing and Experimental Station of Fishery Resources for Key Fishing Grounds, Ministry of Agriculture, and Marine Fisheries Research Institute of Zhejiang for providing assistance at laboratory. We are also grateful to all the reviewers for their valuable comments and advices.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Li, L.; Wang, S.; Shen, X.; Jiang, M. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in the water of China’s coastal shellfish culture areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18392–18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Bao, K.; Wang, H.; Dai, Y.; Wu, S.; Yan, K.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Q.; Lu, J. Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Nutrients and Heavy Metals in the Coastal Zone of Yantai, China. Water 2024, 16, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, W.A.; Zaghloul, K.H.; Abdel-Khalek, A.A.; Abo-Hegab, S. Risk assessment and toxic effects of metal pollution in two cultured and wild fish species from highly degraded aquatic habitats. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 65, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emenike, E.C.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Anidiobi, S.U. Heavy metal pollution in aquaculture: Sources, impacts and mitigation techniques. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4476–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauliutė, G.; Svecevičius, G. Heavy metal interactions during accumulation via direct route in fish: A review. Zool. Ecol. 2015, 25, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceda-Veiga, A.; Monroy, M.; de Sostoa, A. Metal bioaccumulation in the Mediterranean barbel (Barbus meridionalis) in a Mediterranean River receiving effluents from urban and industrial wastewater treatment plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 76, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubourg, S.P.; Losada, V.; Prego, R. Distribution of lipids and trace minerals in different muscle sites of farmed and wild turbot (Psetta maxima). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FLallah, A.A.; Siavash Saei-Dehkordi, S.; Nematollahi, A. Comparative assessment of proximate composition, physicochemical parameters, fatty acid profile and mineral content in farmed and wild rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mas, L.; Claret, A.; Reinders, M.J.; Banovic, M.; Krystallis, A.; Guerrero, L. Farmed or wild fish? Segmenting European consumers based on their beliefs. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 735992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanpiwat, P.; Sthiannopkao, S.; Widmer, K.; Himeno, S.; Miyataka, H.; Vu, N.U.; Tran, V.V. Assessment of metal and bacterial contamination in cultivated fish and impact on human health for residents living in the Mekong Delta. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, T.; Viscardi, V.; Fasano, E.; Farina, A.; Amodio-Cocchieri, R. Polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine pesticides, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in wild, farmed, and frozen marine seafood marketed in Campania, Italy. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods. State Administration for Market Regulation, National Health Commission: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Bortey-Sam, N.; Nakayama, S.M.M.; Ikenaka, Y.; Akoto, O.; Baidoo, E.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Mizukawa, H.; Ishizuka, M. Human health risks from metals and metalloid via consumption of food animals near gold mines in Tarkwa, Ghana: Estimation of the daily intakes and target hazard quotients (THQs). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 111, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Su, J.; Miao, X. Fish Taxonomy; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1996. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, K.; Lv, Z.; Huang, B.; Li, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, L. Analysis of Current Situation of Proliferation and Release of Island and Reef Fishes in the Coastal Waters of Zhejiang. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 41, 459–465+472. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Li, J.; Qu, Y.; Cai, C. Analysis of Nutrient Components and Evaluation of Nutritive Quality in the Muscle of Oplegnathus fasciatus. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2010, 31, 71–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.; Wu, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q. Heavy metal enrichment characteristics and risk assessment of typical fishes in tropical seagrass beds. South China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 48–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, H.; Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Lin, C.; Feng, J. Heavy metals concentrations of marine commercial species and health risk estimation in Huizhou. Ecol. Sci. 2020, 39, 95–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, S.P.; Kaushik, S.J. Nutrition and metabolism of minerals in fish. Animals 2021, 11, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.; Usmani, N. Assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Ni, Fe, Co, Mn, Cr, Zn) in rivulet water, their accumulations and alterations in hematology of fish Channa punctatus. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, N.; Weber, M.J.; Pierce, C.L.; Cashatt, D. Factors influencing fish mercury concentrations in Iowa rivers. Ecotoxicology 2019, 28, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammilleri, G.; Galluzzo, F.G.; Fazio, F.; Pulvirenti, A.; Vella, A.; Lo Dico, G.M.; Macaluso, A.; Ciaccio, G.; Ferrantelli, V. Mercury detection in benthic and pelagic fish collected from western Sicily (Southern Italy). Animals 2019, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F. Feeding Ecology of Three Enhancement and Releasing Species in Zhoushan Islands; Zhejiang Ocean University: Zhoushan, China, 2023; (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartup, A.T.; Thackray, C.P.; Qureshi, A.; Dassuncao, C.; Gillespie, K.; Hanke, A.; Sunderland, E.M. Climate change and overfishing increase neurotoxicant in marine predators. Nature 2019, 572, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Yuan, Q.; Ping, X.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Chao, M. Time series analysis and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from the Yangtze Estuary and Hangzhou Bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2023, 50, 252–258. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, N.P.C.; Agusa, T.; Ha, N.N.; Tuyen, B.C.; Tanabe, S.; Takeuchi, I. Stable isotope-guided analysis of biomagnication profiles of arsenic species in a tropical mangrove ecosystem. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, R.A.; Jardine, T.D.; Chumchal, M.M.; Kidd, K.A.; Campbell, L.M. Biomagnification of mercury in aquatic food webs: A worldwide meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13385–13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Du, Z.; Zhang, F. A GIS-based health assessment of the offshore marine ecosystem in north Zhejiang Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 8183–8193. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Popowich, A.; Zhang, Q.; Le, X. Arsenobetaine: The ongoing mystery. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 3, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Song, D.; Du, S.; Zhang, L. Arsenic speciation in wild marine organisms and a health risk assessment in a subtropical bay of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clowes, L.A.; Francesconi, K.A. Uptake and elimination of arsenobetaine by the mussel Mytilus edulis is related to salinity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 137, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Prey-specific determination of arsenic bioaccumulation and transformation in a marine benthic fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hightower, J.M.; Moore, D. Mercury levels in high-end consumers of fish. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaffey, K.R.; Clickner, R.P.; Bodurow, C.C. Blood organic mercury and dietary mercury intake: National health and nutrition examination survey, 1999 and 2000. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Huang, D.M.; Cai, Y.Q.; Meng, X.J.; Shi, Y.F.; Kong, C.; Huang, X.Y.; Tang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.X. Geographical Origin Traceability of Chinese Mitten Crabs Based on Mineral Elements and Stable Isotopes. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 125–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zitek, A.; Sturm, M.; Waidbacher, H.; Prohaska, T. Discrimination of wild and hatchery trout by natural chronological patters of elements and isotopes in otoliths using LA-ICP-MS. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2010, 17, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Omura, Y.; Okazaki, E. Distinct regional profiles of trace element content in muscle of Japanese eel Anguilla japonica from Japan, Taiwan, and China. Fish. Sci. 2006, 72, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.A.; Hobbie, K.A.; Smith, B.W. Chemical profiling with modeling differentiates wild and farm-raised salmon. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11768–11774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y.; Xu, J. The classification of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) according to region of origin using multi-element analysis and pattern recognition techniques. Food Control 2012, 23, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrà, M.O.; Ghidini, S.; Zanardi, E.; Badiani, A.; Ianieri, A. Authentication of European sea bass according to production method and geographical origin by light stable isotope ratio and rare earth elements analyses combined with chemometrics. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2019, 8, 7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, K.; Mazumder, D.; Sammut, J.; Saintilan, N.; Crawford, J.; Gadd, P. Isotopic and elemental profiling to trace the geographic origins of farmed and wild-caught Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Aquaculture 2019, 502, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).